|
|
Recent Advances in Fabrication and Sustained/Controlled-release Application of Hollow Silica Microspheres
BAO Yan, WANG Tong
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1269–1278
 Abstract
Abstract(
1440 )
 HTML
HTML(
29)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1467
)
Hollow silica (SiO2) microspheres with special interior spaces, excellent adsorption and permeability, and controllability of material deliveries are suitable for loading and releasing guest molecules of various functionalities such as drug, fragrances, dyes, bacteria, etc. More importantly, hollow silica (SiO2) microspheres have attracted much attention due to their tremendous applications in sustained drug release, medical imaging, environmental protection, and cosmetics industry. In this paper, different preparation methods of hollow silica microspheres are reviewed and compared. Besides, the persistence and efficiency of hollow silica microspheres employed as delivery carriers and superiority of functionalized organic/inorganic hybrid microspheres are emphatically summarized. Meanwhile, the vast potential for future development of hollow silica microspheres as a novel type of sustained/controlled release carriers is prospected.
|
|
|
SOC Stack Impedance Characterization and Identification Based on DRT and ADIS Methods
WANG Xue, ZHANG Wen-Qiang, YU Bo, CHEN Jing
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1279–1288
 Abstract
Abstract(
1298 )
 HTML
HTML(
29)
 PDF
PDF(854KB)(
1701
)
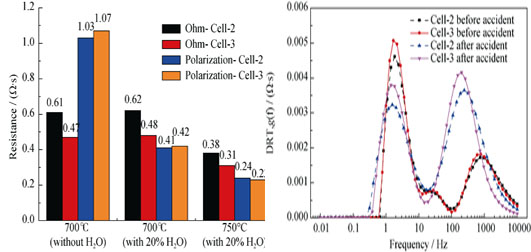
Electrochemical analysis and diagnosis of the SOC stacks, including Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) and Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOEC), are one of the research challenges in world. In order to optimize performance and realize practical SOC application, it is crucial to investigate kinetic mechanisms and reaction principle of the multiple-cells stack. In this paper, the relaxation time distribution method (DRT) combined with the analysis of difference in impedance spectra method (ADIS) were employed to research the complex electrochemical behavior of SOC stacks under different operation modes. The DRT characteristic peaks were identified through the analysis and as-segment of the relaxation time. The changes in the DRT peaks were correlated with the different electrochemical process. The research achievements indicate that the water content should be more than 20% when operated at SOFC mode, while less than 80% when operated at SOEC mode to minimize the gas diffusion resistance. The research achievements can provide theoretical data and establish technical foundation for the further study and application of this novel method, which can reduce the SOC complexity of EIS analysis, apply for the degradation identification and online diagnosis of stacks, and help to improve the SOC performance.
|
|
|
CTAB-assisted Synthesis of MoS2/C Nano-flowers with Improved Electrochemical Performances for Lithium Ion Batteries
CAI Ya-Ling, LI Ya-Fei, WANG Zeng-Mei, ZHANG Yao, CHEN Jian, GUO Xin-Li
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1289–1294
 Abstract
Abstract(
981 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(513KB)(
4308
)
MoS2/C composites were prepared by a simple CTAB assistant thermal reduction method using sodium molybdate, thiourea and CTAB as starting materials. The samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, and TG. It is confirmed that the amorphous carbon is partially inserted into the interlayer spaces of molybdenum disulfide and inhibits the accumulation of (002) plane. Meanwhile, the electrochemical properties were studied in detail. As a consequence, the MoS2/C composites have better electrochemical performance than pure MoS2. The composite synthesized by adding 0.025 g CTAB shows the best electrochemical performance. The initial discharge capacity was 730 mAh/g and a stable capacity above 415 mAh/g was retained for 100 cycles tested at 100 mA/g. At last, the possible growth mechanism of the MoS2/a-C composites and the influence of different micro-morphology are also calculated.
|
|
|
Hydrogen Isotope Effects in Ti1.0Cr1.5V1.7 Alloy
YANG Yong-Bin, LUO De-Li, RAO Yong-Chu, GUO Wen-Sheng
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1295–1300
 Abstract
Abstract(
438 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(429KB)(
846
)
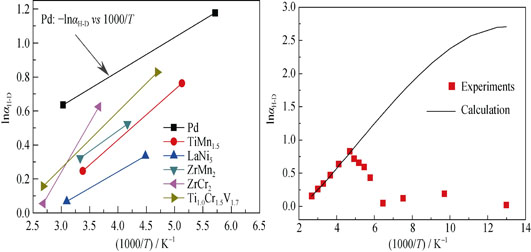
Ti1.0Cr1.5V1.7 alloy was prepared by arc melting and then its morphology and constitution were analyzed by SEM and EDS. The observations showed that the alloy was unhomogeneous with some network-shaped precipitates. The structures of the hydrides of Ti1.0Cr1.5V1.7 were determined by XRD. The structures of the hydrides depended only on the hydrogen content, not on the kind of hydrogen isotopes. The dependences of separation factor (αH-D) on pressure, deuterium concentration and temperature were investigated systematically. Not significantly influenced by pressure, αH-D decreased with the increase of deuterium concentration. However, the dependence of αH-D on temperature was complicated. In 213-373 K, αH-D increased with the decrease of temperature, which agreed with the harmonic oscillator model (HOM). In 77-213 K, the experimental αH-D was different from the calculated value of HOM. According to the results of DSC measurement for the hydrides of Ti1.0Cr1.5V1.7 alloy, the disagreement between the experiments and the HOM in 77-213 K was not induced by phase transitions. Moreover, the maximum αH-D reached 2.29 at 213 K.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Performance of PET-ceramic Separators
XIE Xiao-Hua, LI Xiao-Zhe, LI Wei-Biao, SHAO Guang-Jie, XIA Bao-Jia
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1301–1305
 Abstract
Abstract(
789 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(2183KB)(
1366
)
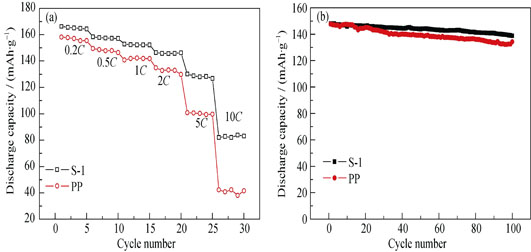
Ceramic-coating separators were prepared with poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) nonwoven membrane as the substrate. Different particle sizes and variable ratios of SiO2 and Al2O3 were coated on the PET surface by dip coating technology, using PVDF-HFP as the binder. The separators took advantage of both kinds of ceramic particles, so that the big pores of PET were filled more effectively. Surface morphology, porosity, electrolyte wettability, thermal stability, ionic conductivity, and electrochemical impedance spectroscope (EIS) of composite separators with different ratios of SiO2 to Al2O3 were systematically investigated, and separators with ratio of SiO2/Al2O3=3/7 showed superior performance. Electrochemical properties of MCMB / LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 2025-type coin cells assembled by the ceramic separators with ratio of SiO2/Al2O3=3/7 were also tested, as compared with commercialized PP separators. The results demonstrated that the ceramic separators performed with 93.9% capacity retention after 100 cycles and capacity of 82.7 mAh/g at 10C rate, better than PP separators.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electro Response of Gelatin/BaTiO3 Core-shell Composite Particles
YANG Xiao-Lei, LU Ya-Ping, GAO Mei-Xiang, XIE Zun-Yuan, GAO Ling-Xiang
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1306–1310
 Abstract
Abstract(
665 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(381KB)(
986
)
The Gelatin/BaTiO3 core-shell composite particles were prepared by directional sedimentary self-assembly on the gelatin microspheres with an average particle size about 0.7-0.9 mm. Morphology, structure, composition, and surface hydrophile of the particle were characterized by TEM, XRD, FT-IR, TG, and optical contact angle measuring instrument. The results show that the composite particles are spherical with hydrophilic surface and good dispersion, of which cubic BaTiO3 shell accounts for about 18.8% of the total weight. After BaTiO3 and Gelatin/BaTiO3 particles being dispersed into gelatin hydrous elastomers cured with/without an electric field, the difference of storage modulus of the elastomers suggests that Gelatin/BaTiO3 composite particles have stronger electro response than pure BaTiO3 particles. These data demonstrate that coating polymer with BaTiO3 significantly can improve BaTiO3 particles electro response.
|
|
|
Effects of Ceramic Precursor Ratio on Antioxidation Properties of Pitch-based Carbon Materials Doped with Si-Zr-B
ZHANG Xu, DONG Zhi-Jun, YUAN Guan-Ming, CONG Ye, LI Xuan-Ke
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1311–1319
 Abstract
Abstract(
584 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(888KB)(
928
)
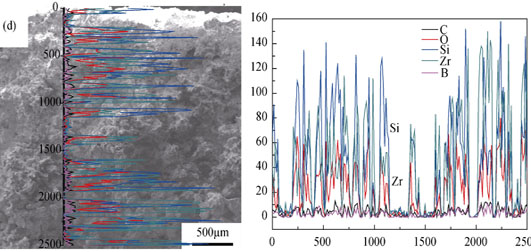
The Si-Zr-B doped coal-tar pitch was synthesized by co-pyrolysis of xylene soluble pitch, silicon carbide precursor, zirconium boride precursor, and zirconium carbide precursor. The pitch-based carbon materials doped with Si-Zr-B were prepared through co-carbonization, cold moulding and followed by high temperature heat treatment from the obtained Si-Zr-B doped coal-tar pitch. The phase composition and microstructure of the carbon materials were characterized by XRD, SEM and EDS. The oxidation behavior of specimens was tested at 1500℃ in static air. The results show that weight loss of the doped carbon materials is increased firstly and then decreased with the decrease of content of silicon carbide precursor in Si-Zr-B doped coal-tar pitch. The doped carbon materials obtained from Si-Zr-B doped coal-tar pitch, with a mass ratio of the polycarbosilane, zirconium carbide precursor and zirconium boride precursor at 1:2:1, shows an excellent oxidant resistance. After oxidation in air at 1500℃ for 4 h, its weight loss and oxidation depth is 27.5wt% and 0.7 mm, respectively. A dense SiO2-ZrO2-B2O3 glassy oxide layer which formed during oxidation in air can effectively reduce the rate of oxygen diffusion and thus improve the oxidation resistance of the carbon materials derived from the doped coal-tar pitch.
|
|
|
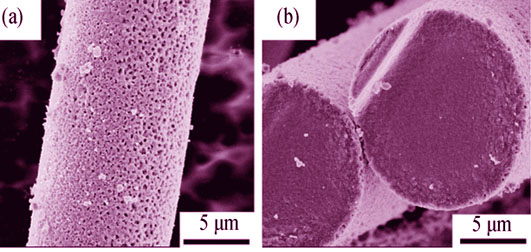
Effect of SiCxOy Decomposition on Densification of SiCO(Al) Fibers during Sintering Process
YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1320–1326
 Abstract
Abstract(
692 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
942
)
The transformation from SiCO(Al) fiber to SiC(Al) fiber by high temperature heat-treatment was studied. The characteristics of SiCxOy decomposition and effects of different heating approaches on microstructure and densification processing of SiCO(Al) fibers were investigated. It was found that SiCxOy phase typically decomposed at temperature ranged from 1430℃ to 1850℃. The SiCxOy phase in the core area of fiber could not be eliminated completely by continuous heat-treatment, even at the temperature as high as 1800℃. Furthermore, large pore faults and grain coarsening tended to generate in the fibers due to over-high decomposition rate, which led to loose structure of fibers. By contrast, static heat-treatment could increase the degree of SiCxOy decomposition. The SiCxOy phase could be completely removed when the fibers were heat-treated at 1650℃ for 1 h, and big pores and heterogenous grains were suppressed. Finally, densified SiC(Al) fibers with large β-SiC grains could be achieved after sintering at 1900℃.
|
|
|
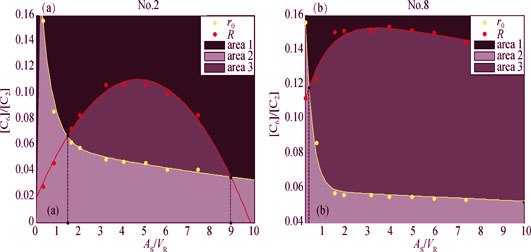
Numerical Simulation for Influence of Surface Area/Volume Ratio and Inlet Gas Pressure on Pyrolytic Carbon Texture
XU Jian, TANG Zhe-Peng, PENG Yu-Qing, GU Chuan-Qing, KOYO Norinaga, LI Ai-Jun
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1327–1334
 Abstract
Abstract(
724 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(512KB)(
897
)
Based on the model of pyrolytic carbon matrix texture formation and transformation in CVI for densification of carbon/carbon composites, a new model was constructed to describe the surface of pyrolytic carbon deposited in a honeycomb structure pores. This new model is related with structure characteristics of graphite microchip. The Monte Carlo method is applied to simulate the pyrocarbon deposition kinetics and to analyze the influence of surface area/volume (AS/VR) and gas pressure on the texture of pyrocarbon in the process of isothermal-isobaric chemical vapor infiltration (ICVI). According to the numerical simulation results, under certain conditions of pressure, various textured carbon were obtained by controlling AS/VR in CVI process. Between two critical values (1.45 mm-1 and 8.9 mm-1 near the inlet, 0.3 mm-1near the outlet) of AS/VR, the high-textured carbon can be obtained. Moreover, if AS/VR is certain value and pressure is less than 30 kPa, pyrolytic medium and high textured carbon texture can be obtained as a result of different pressure in CVI process. There is also a critical pressure value and the high-textured carbon can be obtained if the pressure is greater than the critical value.
|
|
|
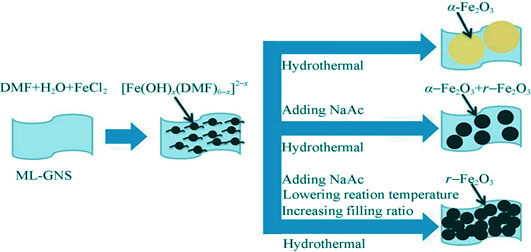
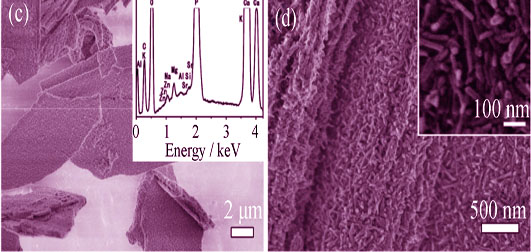
Preparation of Uniform Magnetic Fe2O3 Nanoparticles@multi-layer Graphene Composites with Complexation Method
QIU Xiao-Zhen, XU Jun-Ming, XU Zhen, SONG Kai-Xin, WU Jun, YING Zhi-Hua, HU Wei-Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1335–1340
 Abstract
Abstract(
633 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(1029KB)(
1138
)
One-step hydrothermal reaction and complexation method was used to prepare the extra uniform γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles@multi-layer graphene, which was unnecessary to introduce oxygen function group on graphene. Multi-layer graphene was prepared by simple sonication method that will not introduce rich oxygen functional groups on its surface. Reagent FeCl2, mixture solvent DMF and water were used for hydrothermal reaction, in which DMF could form complexion with metal ion. The effects of sodium acetate, reaction temperature and filling ratio on the prepared product were studied. X-ray diffraction(XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope(XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were used to analyze the microstructures of the composite materials. The magnetic properties of the composites were measured by vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The results show that π-π reaction between carbon ring and complexation of Fe2+ with DMF can be used to prepare iron oxide on the multi-layer graphene. Homogeneous γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with size less than 10 nm can be prepared through the control of oxidation speed of Fe2+ and growth velocity of iron oxide, with good magnetic properties.
|
|
|
Investigation on In Vitro Osteogenic Properties of Multiple-doped Hydroxyapatite with Natural Bone Content
CHENG Yao, WANG Ming, WANG Xing-Xing, XU Zheng-Li, WANG Da-Lin, Zhu Ying-Chun
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1341–1346
 Abstract
Abstract(
709 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(414KB)(
836
)
Hydroxyapatite (HA) has been widely used as artificial bone substitutes because of its good biological activity, but the disadvantages of pure HA have limited its clinical applications. In human natural hard tissues, there are many trace elements doped in hydroxyapatite, which play beneficial roles in biological actions. In this study, multi-doped nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA2) was synthesized by doping trace elements in HA according to the contents in human bones. Alkaline phosphatase activity staining, semi-quantitative PCR measurement (ALP, OCN and OPN) and alizarin red staining were carried out to detect the effect of pure nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA1) and multi-doped nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA2) on proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1cells. Alkaline phosphatase activity experiments prove that the HA2 has a stronger role than HA1 in promoting cell production. Semi quantitative PCR measurement confirms that HA2 is more effective than HA1 in promoting the expression of osteogenic genes. Alizarin red staining results show that HA2 is better than HA1 for MC3T3-E1 cells to produce mineralized nodules. Multiple-doped nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA2) has an obvious promoting effect on the differentiation and osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 comparing with the undoped nanostructured HA1. Multi-doped nanostructured hydroxyapatite (HA2) is more beneficial to bone formation, which has the inorganic composition more close to human bone and is a promising biomaterial for human hard tissue implants.
|
|
|
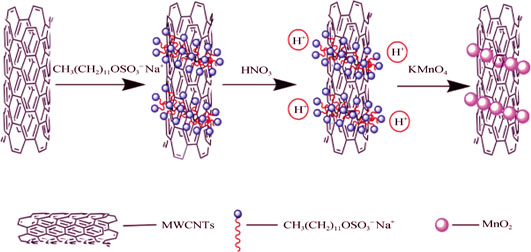
Preparation of MnO2/MWCNTs Catalysts by a Redox Method and Their Activity in Low-temperature SCR
CHEN Jian, ZHENG Yu-Ying, ZHANG Yan-Bing, ZOU Hai-Qiang, LU Xiu-Lian
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1347–1354
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(619KB)(
1041
)
Pristine multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) were modified by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Afterwards, a series of MnO2/MWCNTs were prepared via a redox method and used in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx at 80-180℃. Structural properties and catalytic performance were investigated by specific surface area measurements (BET), X-ray diffraction (XRD), filed emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), and H2 temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR). The characterization results indicate that the nanoflaky MnO2 highly disperse on MWCNTs. The results show that the low-temperature SCR activities of MnO2/MWCNTs catalysts are 85%-100% at 140-180℃ at a weight hourly space velocity of 210 L/(gcat·h), higher than that of catalyst fabricated via the wet impregnation method. The 10% MnO2/MWCNTs catalyst displays first-rate SCR activity, which is attributed to its low crystallinity, high concentrations of Mn4+ and oxygen absorbtion onto the catalyst surface, as well as excellent reducibility. Additionally, compared to the MnOx/MWCNTs catalyst, the 10% MnO2/MWCNTs catalyst exhibits higher resistance to H2O and SO2.
|
|
|
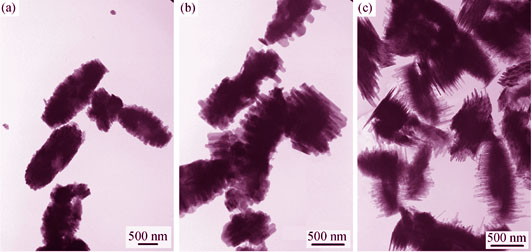
Soft Template-directed Hierarchical Mordenites and Their Performance in Benzylation of Benzene with Benzyl Alcohol
LI Yu-Ping, SUN Cui-Juan, JIA Kun, ZHANG Yi, LI Xiao-Feng, DOU Tao
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1355–1362
 Abstract
Abstract(
668 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(588KB)(
827
)
Mordenite is generally referred to be a one-dimensional micropore zeolite. The major drawback of this pore structure is severe diffusion limitations, especially for the reactions involving bulky molecules. Herein, hierarchical mordenites were successfully prepared through a soft-templating method using a diquaternary ammonium surfactant [C18H37N+(CH3)2C6H12N+(CH3)2C6H13(Br-)2, C18-6-6Br2 for short] as mesoporogen. The obtained samples were characterized by XRD, FT-IR, SEM, TEM, TG-DTG, N2 physical adsorption, and NH3-TPD techniques. The results show that the hierarchical mordenites with nanorods (20-40 nm in width) oriented-assembled structures are synthesized in the presence of the C18-6-6Br2 surfactant. Moreover, the crystal sizes, mesopore surface areas and mesopore volumes of hierarchical mordenites can be systematically tuned by changing the C18-6-6Br2/SiO2 ratios. More importantly, the hierarchical mordenites exhibit much higher catalytic activity and faster reaction rate in the benzylation of benzene with benzyl alcohol than the conventional mordenite. The remarkably enhanced catalytic performance of hierarchical mordenites may be attributable to the more accessible acid sites and much better mass transfer properties with the presence of mesopore. Thus, the special hierarchical mordenites reported here show a great potential for catalytic conversions involving bulky molecules.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Dy,Cr Co-doped ZnGa2O4 Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles
ABDUKAYUM Abdukader, TUERDI Ailijiang, ABDURAHMAN Renagul, TURSUN Mamutjan, NURMAT Nurbiya
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1363–1369
 Abstract
Abstract(
1013 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(537KB)(
1298
)
Dy3+, Cr3+ co-doped ZnGa2O4 persistent luminescence nanoparticles (PLNPs) with long near-infrared afterglow were synthesized by an ethylene glycol assisted hydrothermal method. Persistent luminescence properties of the PLNPs are improved and size of the PLNPs is controlled efficiently via optimization of reaction condition, modification of zinc ratio and co-doping of Dy3+ ion. The results show that the PLNPs have long afterglow time more than 72 h and small grain size of approximately 6 nm, when the pH of the reaction solution, Ga:Zn ratio and doping amount of Dy3+ are 7, 2:1.2 and 1%, respectively. The as-prepared PLNPs exhibit great potential as a molecular probe for biomedical imaging with high signal to noise ratio.
|
|
|
Optical and Structural Properties of Carbon Nanotubes/Black Nickel Composite Coatings by Electrodeposition
ZOU Si-Hao, XIN Shi-Gang, SONG Li-Xin
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1370–1374
 Abstract
Abstract(
637 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
778
)
Carbon nanotubes/black nickel composite coatings with high optical properties on titanium alloy substrate were prepared on the basis of composite electrochemical deposition methods. Micro scale morphology and optical properties of as-prepared materials were analyzed. The effects of carbon nanotubes concentration and electroplating current density on the optical properties were also explored. The results show that grain size of composite coating was small with microporous and increased surface roughness as compared with conventional black nickel coating. The absorptance (αs) over a spectral range of 300-2300 nm was up to 98%, while the emittance (ε) over a 2.5 µm to 20 µm range was 94%, better than those of conventional black nickel coatings. The absorptance of composite coating increased firstly and then decreased with increase of carbon nanotubes concentration and electroplating current density.
|
|
|
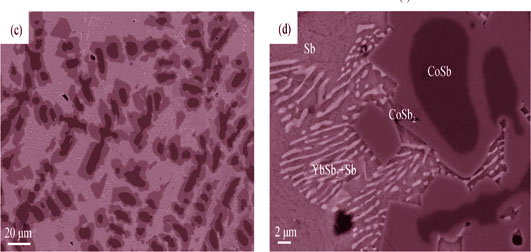
Investigation on Quick Fabrication of n-type Filled Skutterudites
YAO Zheng, QIU Peng-Fei, LI Xiao-Ya, CHEN Li-Dong
2016 Vol. 31 (12): 1375–1382
 Abstract
Abstract(
675 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(609KB)(
1038
)
The cost-effective fabrication of CoSb3-based filled skutterudites (SKD) thermoelectric materials is a bottleneck issue preventing their successful commercial application. In this study, we employed a simple and scalable process to simultaneously produce a rapid formation and consolidation of n-type filled skutterudites. This method, consisting of RF-induction melting, quenching and spark plasma sintering (SPS), required less than a half-hour, significantly shorter than conventional process of furnace melting (over 24 h), annealing (about one week) and SPS. The fabricated bulk SKD materials possessed homogeneous composition and structures with a good thermoelectric performance which are analogous to those materials fabricated according to a conventional process. The homogeneous microstructures and phase composition distribution which was a result of the simultaneously proceeded rapid reaction and densification of the grinding-destructed dendrite networks of the Sb/CoSb/CoSb2 peritectic structure formed in the RF-induction melting and quenching. The good thermoelectric TE performance and the very low consumption of process time and energy would make this simple process a potential and practical method for industrial-level mass production of filled skutterudite thermoelectric materials.
|
|