|
|
Research and Development of Continuous SiC Fibers and SiCf/SiC Composities
YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1157–1165
 Abstract
Abstract(
1610 )
 HTML
HTML(
42)
 PDF
PDF(401KB)(
2448
)
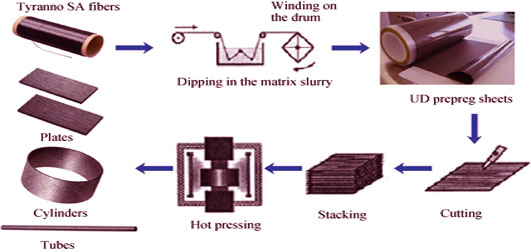
Polymer-derived method is the main preparation method for continuous SiC fiber. So far, three generations of SiC-based fibers have been developed. SiC fiber is mainly used as reinforcement for SiC matrix to prepare SiCf/SiC composite, which exhibits excellent properties such as high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, high-temperature creep resistance, and neutron radiation stability. Therefore, it is considered as a promising preferred alternative material for structural components which works under harsh environments. In this review, the domestic and oversea development of the polymer-derived SiC fibers are introduced, in particular the different approaches for preparation and the characteristics of the 3rd generation fibers. Then, the development of SiCf/SiC preparation technology and properties are reviewed and the relationship between the innovation in fabrication of SiCf/SiC composite and the development of SiC fiber is hightlighted. Finally, the application progress of SiCf/SiC composite in high performance aero-engines and fusion power cores is summerized. Meanwhile, some perspectives on the development of domestic SiC fibers and SiCf/SiC are also discussed.
|
|
|
Defects in Ge Doped SiC Crystals
ZHANG Fu-Sheng, CHEN Xiu-Fang, CUI Ying-Xin, XIAO Long-Fei, XIE Xue-Jian, XU Xian-Gang, HU Xiao-Bo
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1166–1170
 Abstract
Abstract(
967 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(396KB)(
1292
)
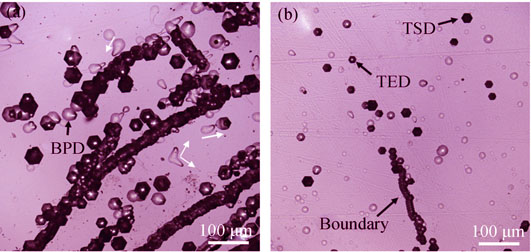
2-inch Ge doped and undoped SiC crystals were grown by physical vapor transport (PVT) method and characterized by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), Raman spectroscopy, stereomicroscope, laser scanning confocal microscope (LEXT), high resolution X-ray diffractometry (HRXRD). The experimental results showed that the element Ge was effectively doped into 6H-SiC crystal with doping level reaching up to 2.52×1018/cm3. Following crystal growth, the Ge concentration in crystal gradually dropped due to impurity source depletion and leakage. Raman mapping clearly shows that the excessive Ge doping can cause SiC polytype structure transformation from 6H-SiC into 15R-SiC at the initial crystal growth stage and then rapidly transform from 15R-SiC back into 6H-SiC following the Ge concentration reduction in the growth process. Microscopic observation indicates that the excessive Ge doping at initial growth stage results in the increase of hollow density and the multiply of dislocation. And the dislocation density in doped crystal is almost two-fold of that in undoped crystal. HRXRD pattern demonstrates that the lattice parameters in Ge doped SiC crystal are enlarged because of a longer atomic bonds caused by Ge doping. Therefore, the Ge doped SiC substrates have smaller lattice mismatch with III-nitride materials, which is beneficial to the reduction of dislocations density and the improvement of device performance.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Rare Earth Nitride ScN and YN Microcrystalline
CONG Ri-Dong, CUI Hang, ZHANG Jian, CUI Qi-Liang
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1171–1176
 Abstract
Abstract(
745 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(375KB)(
1048
)
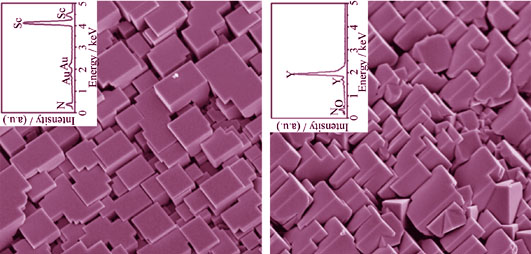
Rare earth nitride ScN and YN crystals were synthesized through direct nitridation of Sc and Y metals with nitrogen using plasma assisted direct current arc discharge method. This new method is fast, low cost and high yield for preparing rare earth metal nitrides. Structural and elemental characterization indicate that the as-synthesized ScN crystals are stoichiometric single crystalline and YN crystals are nonstoichiometric polycrystalline with random orientation single crystal particles. Considering XRD, EDS, HRTEM, and PL results of YN crystals, non-crystalline phase of metal Y is deduced to be formed in YN which contributes to the high contents of Y in EDS results. PL spectrum shows that the presence of large amounts of N vacancy in YN crystals. In addition, the microstructure formation mechanism of YN and ScN samples is analyzed. The difference between them is attributed to the high dissociation pressure of yttrium-group metal nitrides of limiting compositions as well as the high quench rate (103 K/s) that would result in the disordered arrangements of the clusters of Y atoms and then forming non-crystalline structure upon quenching.
|
|
|
Effect of Edge Angles on Growth of Thin Surface Layer of Z-cut NH4H2PO4 Crystal
CHENG Gao, LI Ming-Wei, YIN Hua-Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1177–1183
 Abstract
Abstract(
572 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(539KB)(
1033
)
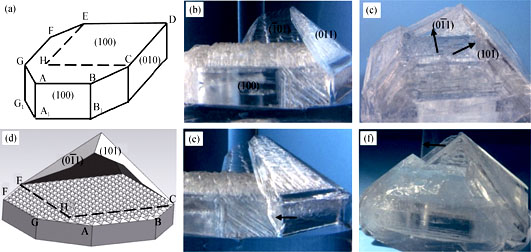
The Z-cut NH4H2PO4 (ADP) crystal plate samples with different types of edge angle were prepared. During crystal growth experiments, formation and growth characteristics of thin surface layers of different Z-cut plate samples were observed. Meanwhile, the tangential growth rate V and the corresponding kinetics coefficients β of thin surface layers were calculated in the present study. The results show that destruction of the normal angles has significantly influences on “judgment” of the original morphology of Z-cut plate, and further influence formation and growth of thin surface layers. When the thin surface layers meet with each other at normal edge angles, where the intersecting angles form, the thin surface layers generate mainly at intersecting angles and spread out along the edges. This phenomenon suggests that edge angles may be the main origin of thin surface layers. In addition, the average growth kinetics coefficient βn at normal angle is calculated to be 131.8 μm/s, much higher than 11.6 μm/s of βa at destroyed angle. These experimental and calculated results suggest that lack of normal angles remarkably decreases the tangential growth rate of thin surface layers.
|
|
|
Mechanism of Faces Growth in Preparing Calcium Sulphate Whiskers Using Sodium Oleate
HAO Hai-Qing, YUAN Zhi-Tao, LI Li-Xia, ZHANG Chen
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1184–1190
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(542KB)(
971
)
The crystal structure of calcium sulphate whiskers and adsorption of sodium oleate on crystal faces were investigated through methods of solution chemistry calculation, X-ray diffraction analysis and molecular dynamics simulation. Furthermore, the growth of crystal faces was explored in presence of sodium oleate. Results showed that calcium, oxygen and hydrogen atoms were primarily distributed on crystal faces of (200) and (400). Interaction energies between sodium oleate and faces of (200) and (400) were much smaller than those of other faces. Distances between oleic acid and calcium on crystal faces of (200) and (400) were 0.269 nm and 0.237 nm, respectively, which were smaller than those between oleic acid and sodium. It could reasonably deduce that calcium was the active site of crystal faces. The selective adsorption of sodium oleate prevented growths of (200) face and (400) face. Differences in growth rate of crystal faces made whiskers grow along c-axis.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Fabrication and Catalytic Performance of Chromium Oxide for Low-concentration NO Oxidation at Ambient Temperature
WU Mei-Jian, GAO Zhen-Yuan, YUAN Jing, ZHAO Kun-Feng, CAI Ting, YANG Ling, ZHANG Tao, HE Dan-Nong
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1191–1197
 Abstract
Abstract(
786 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(579KB)(
1297
)
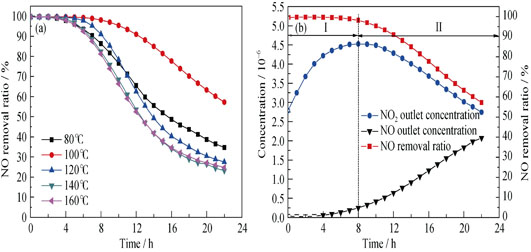
The chromic oxide catalysts were synthesized by hydrothermal method using CTAB as surfactant and NH3·H2O as precipitant. Physiochemical properties of these catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform lufrared specfroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The catalytic NO removal performances for different NO concentrations at room temperature was also investigated. It was shown that under the conditions of space velocity of 60, 000 mL/(g·h) and NO concentration of 1×10-6, sample of Cr-100 exhibited the best catalytic performance, which maintained 120 h as removal ratio of NO more than 90%. This excellent catalytic performance could be attributed to the surface ions ratio of Cr6+/Cr3+. The FT-IR analysis indicated that catalyst deactivation was due to the active sites of chromic oxide occupied by nitrates, consistent with the results of XPS. Furthermore, the activity tests in different conditions demonstrated that low NO concentration could slow down the rate of nitrate accumulation and prolong the catalyst lifetime.
|
|
|
Self Supported Synthesis of Porous Molybdenum-titanium Oxide and the Resulting Structural Transformation
LI Li-Cheng, HE Tian-Tian, ZHAO Xue-Juan, QIAN Qi, WANG Lei, LI Xiao-Bao
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1198–1204
 Abstract
Abstract(
716 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(436KB)(
805
)
A series of porous molybdenum-titanium oxide (Mo-TiO2) were prepared by mutual support of MoO3 and TiO2, and the resulting structural transformation with calcination temperature was also studied in the present study. The as-prepared samples were characterized mainly by XRD, BET, FESEM, and TG/DSC. When the calcination temperature was lower than 600℃, MoO3 can maintain solid state. Mesoporous Mo-TiO2 with surface area of 182 m2/g was obtained via mutual support of MoO3 and TiO2. The oxide loaded by more well-dispersed MoO3 possessed significantly better hydrodesulfurization performance than that prepared by impregnation did. As MoO3 was fused at above 600℃, “self supported effect” was disappeared and the porous structure of Mo-TiO2 collapsed finally.
|
|
|
Low-temperature Removal of NO by Spherical Activated Carbon Loaded with MnOx-CeO2 and Melamine
LI Jun, PAN Lei, WANG Ji-Tong, LONG Dong-Hui, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1205–1211
 Abstract
Abstract(
723 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(528KB)(
1083
)
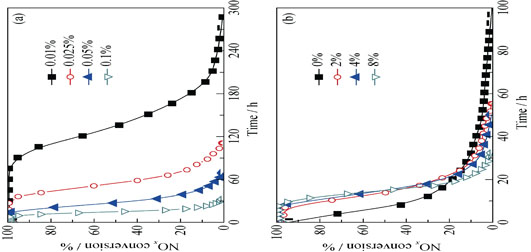
A spherical activated carbon (SAC) loaded with MnOx-CeO2 and melamine was prepared as the catalyst for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO at low temperature (120-180℃). Physical and chemical properties of the catalysts were characterized by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and N2 adsorption-desorption technologies, respectively. The results show that about 99% NOx conversion for 8.8 h at 180℃ is achieved over the catalyst with 10% melamine and 8% Mn loading (the mole ratio of Mn:Ce was fixed at 1:1) under the condition of 0.1% NO, 8% O2 and a space velocity of 6000 h-1. When the calcination temperature is higher than 400℃, the melamine-SCR activity is decreased obviously due to the crystallinity of the metal oxides increasing. When melamine loading is more than 15%, the specific surface area and pore volume of the catalysts decrease significantly, leading to a decline in the stationary-state NOx conversion. However, the increase of metal oxides loading and reaction temperature is found to be beneficial to melamine-SCR reactivity, and the stationary-state NOx conversion is always maintained at about 99% over a wide concentration range of NO and O2.
|
|
|
Highly Efficient Synthesis of LTA-type Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieve by Improved Ionothermal Method with Low Dosage of Structure-directing Agent
ZHAO Xin-Hong, GAO Xiang-Ping, ZHAO Jiang-Bo, ZHANG Xiao-Xiao, HAO Zhi-Xin
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1212–1218
 Abstract
Abstract(
829 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(546KB)(
1074
)
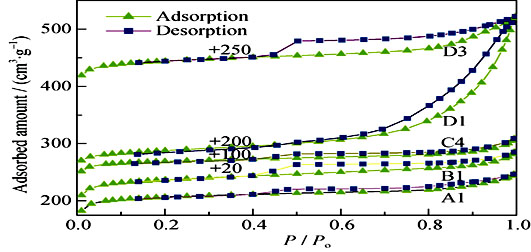
Aluminophosphate molecular sieve with LTA topology was efficiently synthesized by seed-assisted and improved ionothermal method with low dosages of organic amines and ionic liquids (ILs). The influences of organic amine type, crystallization temperature, amount of organic species, and seed crystals on the synthesis of LTA-type material were investigated, to refine the synthetic conditions. The results indicate that LTA-type molecular sieve is synthesized even by adding small amount of seed crystal into initial gels, of which both molar ratios of ILs/Al2O3 and Amine/Al2O3 are decreased to 0.67. Utilization rate of inorganic raw materials during as-synthesis is up to 86% under optimal conditions. Structure and morphology of the products, together with organic species occluded in cavities were fully analyzed by XRD, SEM, N2 physisorption, TG-DTA, CHN elemental analysis, and liquid 13C NMR. The results show that the resultant LTA molecular sieve is a hierarchically porous material with both micropores and mesopores inside. It is the cooperative structure-directing effect between morpholine and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium cations that guides the formation of LTA molecular sieve.
|
|
|
Dieletric and Ferroelctric Properties of Ba(Zr0.15Ti0.85)O3 Thick Film
ZHANG Ying –Tang, YAN Qian
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1219–1222
 Abstract
Abstract(
606 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(337KB)(
992
)
Ba(Zr0.15Ti0.85)O3 (BZT) thick film was prepared by a tape-casting technique and its morphology was characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Its dielectric and ferroelectric properies were investigated using LCR meter and Sawyer-Tower circuit. The results indicate that there is obvious dielectric relaxation behavior in BZT thick film. Its breakdown field strength, saturated polarization and remnant polarization are 60 kV/cm, 58.1 μC/ cm2 and 20.9 μC/cm2, respectively.
|
|
|
Effect of Nickel Nitrate Concentration on Microstructure and Microwave Absorbing Property of Ni/RGO Nanocomposite Material
ZHU Hai, YANG Li, LIU Hong-Bo, CHEN Hui, XIA Xiao-Hong
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1223–1229
 Abstract
Abstract(
587 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(607KB)(
936
)
A technique for obtaining reduced graphite oxide (RGO) with Ni nanoparticle dispersed on the surface via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method was reported. XRD and SEM observations were carried out to confirm the microstructure of Ni/RGO composite. Magnetic property of Ni/RGO was characterized by vector network analyzer. The influence of Ni(NO3)2 concentration on micromorphology and microwave absorbing property were also discussed. As the concentration of Ni(NO3)2 is 1.5 mol/L, the range of the reflection loss (RL) less than -5 dB is 9 GHz, of which the max value reaches -40 dB.
|
|
|
Comparison on Structure and Electrochemical Performances of NiAl-LDH, CoAl-LDH and NiCoAl-LDH
KANG Gui-Ying, CHEN Yong, LI Juan-Juan
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1230–1236
 Abstract
Abstract(
1201 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(572KB)(
1308
)
NiAl, CoAl and NiCoAl hydroxides were fabricated via urea decomposition method. The structure and morphology of samples were characterized by X-Ray diffraction, FTIR, scanning electron microscope, X-ray photoelectron spectroscope, and nitrogen adsorption desorption. The results indicate that three samples exhibit hydrotalcite structure and different morphology. Specific surface area of NiCoAl is the smallest among the three samples. Ni and Co elements coexist in the form of bivalent in NiCoAl-LDH. Cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) and AC impedance tests demonstrate that, at the current density of 0.6 A/g, specific capacitance of NiAl, CoAl and NiCoAl electrodes is 468, 507 and 929 F/g, respectively. The capacitance retention of their electrodes is 30%, 36% and 40%, respectively, after 3000 cycles at the current density of 6 A/g. Based on these properties, NiCoAl is superior in electrochemical performance to the others.
|
|
|
Photoelectrochemical Properties of MoS2 Modified TiO2 Nanotube Arrays
YU Lian-Qing, HUANG Cheng-Xing, ZHANG Ya-Ping, DONG Kai-Tuo, HAO Lan-Zhong
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1237–1241
 Abstract
Abstract(
1031 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(468KB)(
1248
)
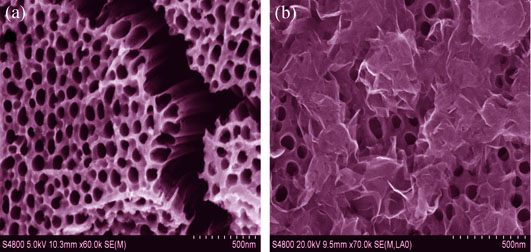
Well aligned TiO2 nanotube arrays were grown by anodization method on Ti foils in ethylene glycol electrolyte. Flowers-like molybdenum disulfide composed with nanoflakes was synthesized by hydrothermal process on TiO2 nanotube arrays, using sodium molybdate, thiourea and L-Cysteine as reactants. The obtained samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray detector. Linear sweeps voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and Mott-Schottky plots of samples were analyzed by electrochemical workstation. The results showed that a flowers-like MoS2 with diameter of c.a. 200 nm was synthesized, forming a heterojunction between TiO2 nanotube arrays and MoS2, which can effectively promote the separation of photogenerated charges, reduce the electron-hole recombination. Optimum concentration of sodium molybdate was obtained at 0.8 mmol/L, its corresponding photoconversion efficiency reached 1.65%, which was 2.89 times as high as that of pure TiO2, and the charge transfer resistance decreased approximately 50%. The MoS2/TiO2 composite exhibited high carrier density of 3.38×1023 cm-3, which was about 24 times higher than that of pure TiO2 nanotube arrays.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Spherical Li4Ti5O12 as Anode Material for Lithium-ion Secondary Battery
YAN Hui, Qi Lu, ZHANG Ding, WANG Zheng-De, LIU Yun-Ying, WANG Xiao-Xia, ZHU Tie-Yong
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1242–1248
 Abstract
Abstract(
727 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(517KB)(
959
)
Self-made TiO2 with different particle sizes was adopted to react in LiOH solution via a fast hydrothermal process, from which spherical spinel lithium titanium oxide Li4Ti5O12 was efficiently prepared. In detail, precursor was obtained from hydrothermal reaction between TiO2 with 5 mol/L LiOH solution at 100℃ for 20 h, and Li4Ti5O12 was synthesized by calcining the precursor at 800℃ for 2 h. The mechanism of the hydrothermal process discussed show that an even Li-Ti-O mixture is formed during Li cation diffusing into the TiO2, resulting in the structure conversion to pure Li4Ti5O12 fast at high temperature. While all the obtained Li4Ti5O12 with different particle sizes show stable electrochemical cycling ability, the 0.5 µm Li4Ti5O12 exhibits optimal electrochemical performance. Its initial discharge capacity reaches 158 mAh/g at 0.2 C and more than 99% of capacity is retained after 70 cycles, while the reversible capability readily exceeds 125 mAh/g after 50 cycles at 0.2 C at 50℃.
|
|
|
PPP Addition to Improve Thermoelectric Properties of ZnO-based Thermoelectric Composites
WU Zi-Hua, XIE Hua-Qing, WANG Yuan-Yuan, MAO Jian-Hui, XING Jiao-Jiao, LI Yi-Huai
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1249–1254
 Abstract
Abstract(
535 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(445KB)(
948
)
PPP@Zn1-xCoxO (x=0, 0.025) nanocomposites were prepared by Sol-Gel method, then bulk samples were prepared by spark plasma sintering. And thermoelectric properties of the samples were studied. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations indicate that PPP nanoparticles are smaller than 200 nm. With the increase of PPP content, Seebeck coefficient gradually increases at first and then decreases, while electric conductivity increases quickly. Compared with ZnO bulk samples, the thermal conductivity of PPP@Zn1-xCoxO nanocomposite is decreased. The thermal conductivity of 9wt% PPP@Zn0.975Co0.025O is decreased to 5.4 W/(m·K) at 640 K. The increase of electrical conductivity and the decrease of thermal conductivity resulted in a great increase in the value of thermoelectric properties. 9wt% PPP@Zn0.975Co0.025O has a maximal ZT value of 0.16 at 870 K, which is 8 times of that of Zn0.975Co0.025O bulk material.
|
|
|
Electroresistance in Phase Separated La0.4Ca0.6Mn0.98Ru0.02O3
BIE Ye-Guang, HU Ni, LIU Feng-Ming, DUAN Tian-Ci, PEI Ling, Deng Gang
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1255–1257
 Abstract
Abstract(
545 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(250KB)(
918
)
Single-phase manganite La0.4Ca0.6Mn0.98Ru0.02O3 shows a typical electronic phase separated state, i.e. the ferromagnetic metal and charge-ordered insulating phase. This provides an ideal platform for investigating electroresistance effect. The sample was synthesized by using standard solid state reaction method, and the pure phase was demonstrated using X-ray diffraction. The colossal electroresistance were measured at various input current intensities. The experiments reveal remarkable electroresistance effect (~80%) which can be triggered by increasing the current intensity. In addition, the resistance state of the sample can be switched immediately and repeatedly by switching the current intensity. The current stabilized ferromagnetic phase would be responsible for these phenomena.
|
|
|
Wide Bandgap Engineering of β-(Al, Ga)2O3 Mixed Crystals
XIAO Hai-Lin, SHAO Gang-Qin, SAI Qing-Lin, XIA Chang-Tai, ZHOU Sheng-Ming, YI Xue-Zhuan
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1258–1262
 Abstract
Abstract(
705 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(414KB)(
1386
)
Bandgap tunable β-(Al, Ga)2O3 mixed crystals with different Al3+ concentration were grown by the optical floating zone (OFZ) method. When the nominal Al3+ doping concentration was close to 0.26, cracking appeared. The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed that β-(Al, Ga)2O3 mixed crystals kept the crystal structure of β-Ga2O3 without foreign phases and the lattice parameters decreased with the increasing Al3+ concentration. 27Al magic angle spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy showed that Al3+ occupied Ga3+ positions and the ratio of Al3+(IV)/ Al3+(VI) was about 1:3.The transmittance spectra were measured to investigate the bandgap of β-(Al, Ga)2O3 mixed crystals. Results showed that the bandgap increased continuously with the Al3+ concentration increasing from 4.72 eV to 5.32 eV, which may extend the application of β-Ga2O3 crystal in optoelectronic devices operating at shorter wavelength.
|
|
|
Four-step Method for Growing High-quality GaAs Films on Si Substrate by Molecular Beam Epitaxy
LIU Guang-Zheng, XU Bo, YE Xiao-Ling, LIU Feng-Qi, WANG Zhan-Guo
2016 Vol. 31 (11): 1263–1268
 Abstract
Abstract(
716 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(401KB)(
765
)
To improve quality and repeatability of GaAs growth on Si substrate, a new method named as four-step growth was proposed by successively inserting a low temperature (LT) and a high temperature (HT) GaAs buffer layer between the GaAs nucleation layer and the normal GaAs epilayer. The grown layers through four-step method showed high quality, i.e. single domain structure, mirror-like surface even under strong white light, reduced surface roughness and less surface defects, as well as high repeatability. Even without any post-growth annealing process, a 1 μm thick GaAs epilayer with root mean square (RMS) roughness of only 2.1 nm in 5 μm× 5 μm scanning areas was obtained while the full width at half maximum (FWHM) value of the GaAs (004) peak from double crystal X-ray diffraction ω-scan was just 210.6 arcsec.
|
|