|
|
Research Progress on Silicon-based Luminescent Glass and Its Preparation Techniques
WANG Lian-Jun, ZHOU Bei-Ying, GU Shi-Jia, JIANG Wan
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1013–1022
 Abstract
Abstract(
1106 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(549KB)(
1190
)
Due to high transmittance, excellent chemical stability, ease of machining, and other advantages, silicon-based oxide glass is considered to be an ideal matrix material. By introducing different lighting dopants, the optical glass with different properties has been widely used in many fields. However, the preparation technologies of the optical glass are facing new challenges because of these volatile and unstable lighting dopants which easy to be decomposed. This review introduces the development status and the preparation techniques of the silicon-based light-emitting glass containing bismuth ions, quantum dots and phosphors. By comparing the melting method, Sol-Gel, solid-state sintering and spark plasma sintering (SPS), the research progress and superiority of SPS technology applied in optical glass preparation are focused on and the developments of this new preparation technology are also reviewed.
|
|
|
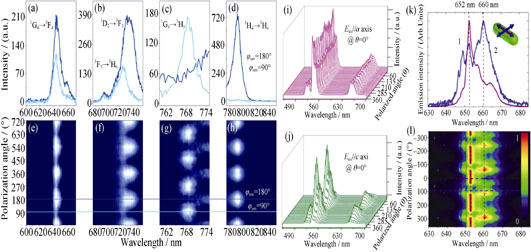
Upconversion Spectroscopic Investigation of Single Nanoparticles
ZHOU Jia-Jia, QIU Jian-Rong
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1023–1030
 Abstract
Abstract(
957 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(573KB)(
1262
)
Upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) have made a significant and valuable contribution to photophysics and biomedicine, due to their specific spectroscopic characteristics. However, the ensemble spectroscopy of UCNPs is limited for the electronic behavior in average effect, which ignores the fact that the nanoparticles are heterogeneous. Towards the research focus on heterogeneous intrinsic structure, unique photophysical phenomena, and advanced applications, the optical characterization of single UCNPs are promoted to a frontier breakthrough of UCNPs community. Electronic behavior detection aimed at a single nanoparticle displays signals from the micro-structure of nanoparticles, while single nanoparticle spectroscopy offers clear insight into the interplay between intrinsic and extrinsic influences without noise, and subsequently gives instructions for the high quality preparation of UCNPs. Single nanoparticle optical characterization possesses a powerful capacity to explore the crystalline structure anisotropy related optical differences, or some unexpected unique optical phenomena at sub-micron and even nano-scale. In this review, the importance of single UCNPs characterization and single particle detection methods are overviewed, in which the considerable emphasis is placed on the specific spectroscopic study of single UCNPs Showing fantastic photophysical phenomena beyond ensemble measurement. Finally, this review identifies promising opportunities in which single UCNPs characterization technique can accelerate on-going research with a remarkable depth and breadth, facilitate discovery of upconversion nanoparticles that overcome fundamental limitations of current ensemble level.
|
|
|
Application of Magnetic Materials in Synchrotron Radiation and Free Electron Laser
HE Yong-Zhou, ZHOU Qiao-Gen
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1031–1038
 Abstract
Abstract(
770 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(527KB)(
1359
)
The synchrotron radiation and free electron laser are electromagnetic radiation light sources which are both generated by the relativistic electron beam. Both sources have been widely used in the national economic, scientific and technical researches, national defense and military fields. The insert device made of permanent magnet is one of the key equipments of the synchrotron radiation light source and the free electron laser facility. Magnetic properties and quality of magnetic materials especially have significant influence on magnetic field quality, magnetic field peak value, magnetic field stability and operation scheme of insert devices. This paper reviewed characteristics of synchrotron radiation and free electron laser, and their conceptual application.
|
|
|
Influences of Ion Exchange and Thermal Treatment on Photoluminescence of Noble Metal Doped Silicate Glasses
YANG Xiu-Chun
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1039–1045
 Abstract
Abstract(
779 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(442KB)(
965
)
Noble metallic nanoparticles-glass composites have attracted much interest because of their technical potential as nonlinear media. In present work, the influences of ion-exchange and thermal treatment on the photoluminescence of noble metal doped silicate glasses were discussed based on photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy and ligand field theory. The results indicate that metallic ion concentration in silicate glass increases with extending ion-exchanged period. There exist isolated Ag+ ions and Ag2+ clusters in Ag-doped silicate glass. Concentration of the isolated Ag+ ions decreases quickly and Ag32+ clusters appear after annealing the Ag-doped silicate glass in H2. While there exist only isolated Cu+ and Cu2+ ions in the Cu-doped silicate glass, no photoluminescence of Cu+ clusters are found in the glass. The existence of Cu2+ ions makes the luminescence of Cu+ quenching. It is very difficult to introduce Cu+ ions into the annealed Ag-doped glass in H2 via Cu+ for Na+ ion-exchange.
|
|
|
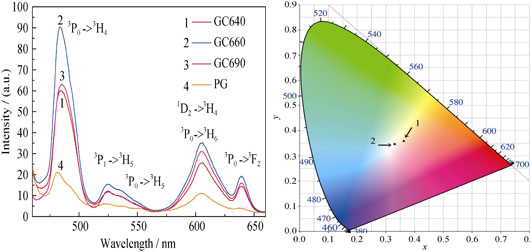
Enhanced Luminescent Properties of Pr3+ Doped Ba2LaF7 Glass Ceramics for White Light-emitting Diodes
ZHANG Zhi-Xiong, OUYANG Shao-Ye, ZHANG Yue-Pin, XIA Hai-Ping
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1046–1050
 Abstract
Abstract(
667 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(337KB)(
986
)
Pr3+-activated 50SiO2 -10AlF3-5TiO2-30BaF2-4LaF3 glass were synthesized by a conventional melting technique, and then annealed at 640℃, 660℃ and 690℃, respectively. Transparent Ba2LaF7: Pr3+ glass ceramics were successfully prepared and the transparency still remained at a high level. X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscope were used to monitor the evolution and microstructural changes after the glass specimens were annealed at temperature increasing from 640℃ to 690℃. The spectral properties of glass and glass ceramics were also investigated. Results show that Ba2LaF7 nanocrystals were precipitated in the teat-treated glasses and the measured luminescent properties indicate that Pr3+ ions are gradually incorporated into the precipitated Ba2LaF7 crystalline phase. Under 443 nm excitation, the Commission Internationale de L’Eclairage (CIE) chromaticity coordinates for the glass ceramics heated at 660 ℃, were estimated to be (0.323, 0.343) and exactly located in the region of white light. Current findings reveal a fact that the prepared materials have potential as replacements of commonly employed phosphors applicating in white light-emitting diodes.
|
|
|
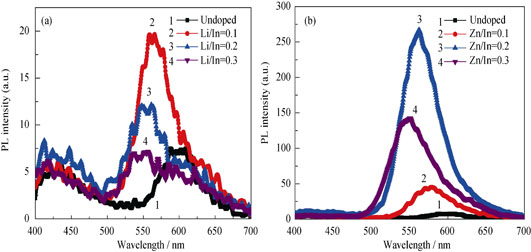
Doping of InP Quantum Dots and Its Optical Properties
YANG Suo-Long, WANG Xiao-Fang, JIANG Chun-Li, ZHAO Ya-Wen, ZENG Rong-Guang, WANG Huai-Sheng, LAI Xin-Chun
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1051–1057
 Abstract
Abstract(
1426 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(652KB)(
1511
)
The Li+ and Zn2+ doped InP quantum dots (denoted as Li: InP QDs and Zn: InP QDs) were synthesized via an in-situ nucleation doping approach. Effects of dopant on the structure, size and optical property of QDs were investigated in detail. The results showed that Li: InP and Zn: InP QDs were well crystallized with uniform size. In the case of Li+ dopant, Li+ did not enter the InP lattice, but inhibited the nucleation and growth of InP QDs. Blue shifts were observed in UV-Vis absorption spectra and fluorescence spectra due to the quantum size effect of Li: InP QDs. Compared with Li+, Zn2+ dopant also inhibited nucleation and growth of InP QDs, but InP/Zn3P2/ZnO composite was produced with a core-shell structure, resulted in a great improvement of photoluminescence (PL) intensity. Especially when the doping concentration of Zn/In atomic ratio was 0.2, the PL intensity was increased more than 100 times as compared with that of undoped InP QDs. This work may provide a considerable approach to the synthesis of short-wavelength InP QDs.
|
|
|
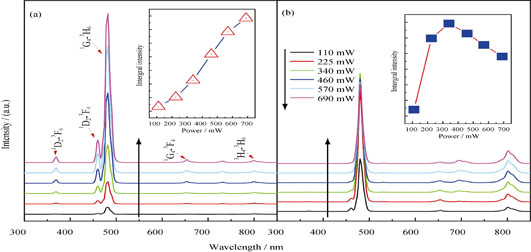
Preparation and Modified Upconversion Luminescence In NaGd(WO4)2:Yb3+/Tm3+ Inverse Opal Photonic Crystals
WANG Yun-Feng, SONG Jin-Fan, TANG Xiao-Yan, HU Dong-Mei
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1058–1062
 Abstract
Abstract(
701 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(353KB)(
1051
)
Photonic crystal (PC) possesses long-scale periodicity and has been widely applied in modifying visible and near-infrared photonic band gap. One of the extraordinary properties of the PCs is the modulation on spontaneous emission of embedded luminescence centers. In this study, three-dimensional NaGd (WO4)2:Yb3+/Tm3+ inverse opal photonic crystals (IOPC) with highly oridered periodic structure were prepared by self-assembly method using PMMA as template. The modulation effect of PC on emission spectra and dynamics of Tm3+ ions were systemically studied. In NaGd (WO4)2:Yb3+/Tm3+ inverse opal photonic crystals, due to unique cavity structure and photonic band gap effect, the emission line of 1G4-3H6 transition decreases by ~45% and the spontaneous radiation rate is suppressed by ~30%. Meanwhile, the up-conversion local thermal effect is largely suppressed. This experimental analysis indicates that the IOPC structure is an effective device for improving efficiency of up-conversion luminescence.
|
|
|
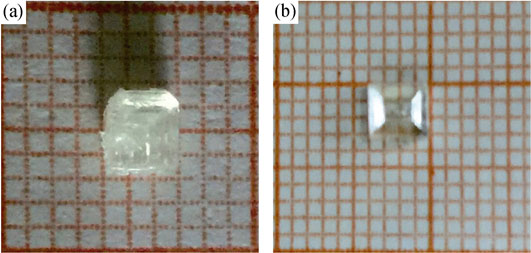
Solution Growth and Performance of CH3NH3PbCl3 Single Crystal
WANG Wan-Fu, SU Jing, LEI Yong, ZHONG Kun, WANG Di
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1063–1067
 Abstract
Abstract(
1071 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(438KB)(
1269
)
Perovskite-type organic-inorganic hybrids CH3NH3PbX3(X= halogen) are good application materials for solid-state solar cell devices. To study the basic performances of these perovskite compounds, growth and optical-electrical properties of the large single crystals with high quality are of great necessity. In present study, CH3NH3PbCl3 single crystals with dimension of about 4 mm×3 mm×3 mm were grown by evaporation and inversion crystallization method. Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) of the obtained crystals powder showed that the crystals were of cubic structure, and their lattice constants were 0.56833 nm and 0.56891 nm, respectively. Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) and Raman spectra of the crystals were measured and the peaks were assigned. The optical properties were characterized by UV-VIS-NIR and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The results showed that the absorption edge of CH3NH3PbCl3 crystal was about 423 nm, with the photoluminescence peak at 433 nm, the band gap at 2.97 eV. As compared with the optical properties of CH3NH3PbCl3 thin films, CH3NH3PbCl3 single crystal has application advantages in solar cell. Finally, the band structure of CH3NH3PbCl3 crystal was studied by the first principle, and the band gap value was calculated to be 2.428 eV, which was in good agreement with the present experimental result.
|
|
|
Growth and Thermo-luminescence Properties of Dy: Bi4Si3O12 Crystals
WANG Mei-Ling, XU Jia-Yue, ZHANG Yan, CHU Yao-Qing, YANG Bo-Bo, SHEN Hui, TIAN Tian
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1068–1072
 Abstract
Abstract(
618 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(460KB)(
890
)
Dy3+ doped Bi4Si3O12 (BSO) crystals were grown by the vertical Bridgman method with doping contents of 0.1mol%, 0.2mol%, 0.3mol%, 2mol%, 3mol% and 4 mol%. It was found that the crystallization behavior was modified by heavy doping and the surface precipitated phase disappeared gradually with the dopant content increase. The maximum light yield of the BSO crystals doped with 0.1mol% Dy3+ was up to 145% of that of pure BSO. The thermo-luminescence (TL) spectra showed that the intensity of TL peaks increased slightly and Dy3+ doping is helpful to light yield when doping content is less than 0.3mol%. However, it induced more defects when the dopant content was larger than 2mol%. High doping may lead to competitive luminescence between Dy3+ ions and Bi3+ ions, resulting in decrease of light yield.
|
|
|
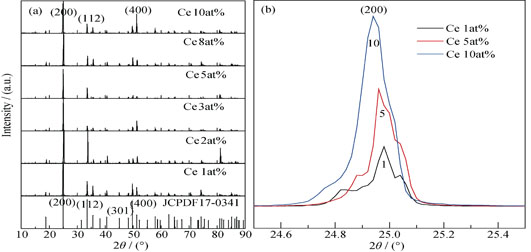
Ce Doping Concentration on Luminescence Property of YVO4:Ce3+ Crystals
YANG Guang-Wu, YANG Rui-Xia, ZHANG Shou-Chao, ZHU Fei
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1073–1080
 Abstract
Abstract(
808 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(595KB)(
1269
)
Pure YVO4 crystal and YVO4 crystal doped with different Ce concentrations were grown by Czochralski method. XRD pattern shows Ce3+ ion enters the YVO4 lattice by occupying the Y3+ site and the crystal structure was not significantly changed. The detection of UV excitation spectrum and emission spectrum of YVO4: Ce3+ at room temperature showed that excited at 325 nm the YVO4: Ce3+ emits two spectra. The main emission spectrum at 445 nm is a broadband peak, caused by transition of 2D3/2→2F5/2 of Ce3+. The other one is a weak peak emission centered around 620 nm, which presents the emission of V4+. With increase of Ce mole fraction from 1at% to 8at%, the blue emission intensity gradually increases to a maximum value. As Ce fraction increases to 10.0at%, the emission intensity decreases gradually, indicating an obvious concentration quenching. The red emission intensity gradually increases to a maximum value when Ce fraction increases to 10.0at%. Detection by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) shows that Ce4+ and V4+ ions coexist in YVO4:Ce3+, which may result from some of the Ce3+ losing electrons to be oxidized into Ce4+, and most of them being captured by the V5+ ions and, therefore, resulting in V5+→V4+ transformation. Based on V4+ d orbital splitting into 2A1, 2B1, 2B2, and 2E, the 620 nm red emission under 325 nm and 450 nm excitation probably originated from electronic transitions between the V4+splitted d orbits. In conclusion, present analytical data of the luminescence spectra of YVO4: Ce3+ provide a theoretical support for YVO4:Ce3+ emitting red light and blue light simultaneously under UV excitation.
|
|
|
Preparation and Down-conversion Luminescent Properties of Tb3+, Yb3+ Co-doped Sr2B2O5
DAI Zhi-Gang, LI You-Fen, LI Gang, YANG Ru
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1081–1086
 Abstract
Abstract(
693 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(478KB)(
1107
)
Tb3+ and Yb3+ co-doped Sr2B2O5 phosphors were synthesized by conventional solid-state reactions. The obtained Sr2B2O5: Tb3+, Yb3+ phosphors were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and photoluminescence (PL) spectra. XRD results show that all prepared phosphors can be readily indexed to pure monoclinic phase of Sr2B2O5. The dominant excitation at 374 nm was observed among three strong excitation peaks located at 354, 374 and 487 nm monitored at 543 nm and 980 nm, by which Sr2B2O5 phosphors could be considered as having a strong absorption in the near ultraviolet region of sunlight. Under the ultraviolet light excitation at 374 nm, the strong intensity of visible emission from Tb3+: 5D4→7FJ ( J = 6, 5, 4, 3), and near-infrared (NIR) emission from Yb3+ (2F5/2→2F7/2) were detected. The relationship between the luminescence spectra and Yb3+ doping content demonstrated the monoclinic Sr2B2O5 exhibited the excellent quenching concentration.
|
|
|
Eu3+ Activated Y2O3 Red Phosphor Monospheres: Size-controlled Processing and Luminescence Property
QU Jiao, ZHU Qi, Li Ji-Guang, SUN Xu-Dong
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1087–1093
 Abstract
Abstract(
700 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(648KB)(
1052
)
Monodispersed (Y, Eu)2O3 spheres (110-550 nm in diameter) were calcined from precursors synthesized via homogeneous precipitation. Systematic characterizations of the products were carried out by XRD, FE-SEM, TEM, and PLE/PL analyses. Large spherical particles were resulted via seeded growth and NH4NO3 addition. Calcining the basic carbonate precursor at 600℃ yielded cubic (Y, Eu)2O3. The spherical shape and excellent dispersion of the precursor particles were largely retained to the oxides after annealing up to 1000℃. The polycrystalline (Y, Eu)2O3 spheres exhibited typical red emission at 615 nm (the 5D0→7F2 transition of Eu3+) under UV excitation at 242 nm. The phosphors showed a substantially size-dependent luminescent behavior. Shorter fluorescence lifetime (1.15-1.57 ms), decreased asymmetry factor (I(5D0→7F2)/I(5D0→7F1)) of luminescence, and enhanced luminescent intensity were observed along with increasing particle size.
|
|
|
Infrared Emission Property of (Ca, Cr) Co-doped YAG Ceramics
BU Cong-Hao, HE Gang, LI Jiang-Tao
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1094–1098
 Abstract
Abstract(
735 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(470KB)(
14175
)
(Ca, Cr) co-doped YAG ceramics were synthesized by high temperature solid state reaction. The effects of Ca2+ and Cr3+ ions doping on the infrared emission properties of YAG ceramics were investigated. X-ray diffraction results showed that the phase composition of the prepared samples were yttrium aluminum garnet, which indicated that the Ca2+ and Cr3+ irons were incorporated into the crystal lattice of yttrium-aluminate garnet structure. Infrared absorption results showed that the infrared absorptivity of the (Ca, Cr) co-doped samples was 0.90, which was 29 times higher than that of the pure YAG sample (0.03). The band gap of YAG ceramics were decreased 1.77 eV by Ca2+ and Cr3+ co-doping based on calculation of the absorbance test results. Therefore, the absorption of the free carrier was improved, which is the main reason why the (Ca, Cr) co-doping YAG ceramics have a high emissivity in near infrared wavelength.
|
|
|
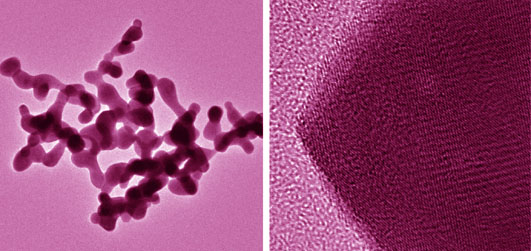
Fabrication and Optical Properties of Ce, Pr Co-doped LuAG Transparent Ceramics
ZHOU Ding, SHI Ying, FAN Ling-Cong, LIN De-Bao, SUN Ze-Qing, XU Jia-Yue
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1099–1102
 Abstract
Abstract(
754 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(339KB)(
1069
)
Cerium and Praseodymium co-doped Lu3Al5O12 nanocrystalline powders were synthesized by reverse titration, using ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) and ammonium hydrogen carbonate (NH4HCO3) mixed precipitator. The optical properties of 0.25at%Pr: LuAG ceramics doped with 0, 0.1at%, 0.2at% and 0.3at% Ce3+ ions were measured. The Ce, Pr: LuAG powders showed a weak agglomeration with a primary particle size of about 60 nm after calcining at 1200℃ for 2 h. Ce, Pr co-doped LuAG transparent ceramics were obtained after green compacts were cold isostatic pressed and sintered in flowing H2 atmosphere at 1800℃ for 6 h. The in-line transmittance of the double face polished Ce, Pr co-doped LuAG ceramic at 800 nm wavelength was 82%. The X-ray excited emission spectrum showed that the emission intensity at 550 nm wavelength was enhanced in Ce, Pr co-doped LuAG transparent ceramics by energy transfer from 5d-4f of Pr3+ ions to Ce3+ ions, and the emission intensity reached maximum value when the dopant contents were 0.2at%Ce and 0.25at%Pr.
|
|
|
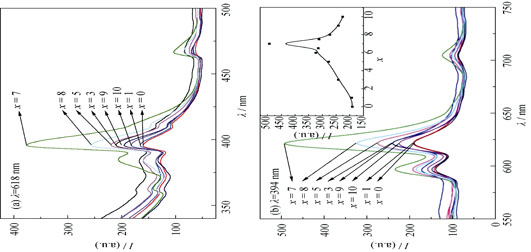
Effect of Strontium on Luminescence Properties and Substitution Site of Eu Doped Sr-Ca-Hydroxyapatite
YIN Hai-Rong, LIU Jing, QIAO Yin-Po, LI Yan-Xiao, ZHANG Pan, ZHOU Qin, YANG Chen
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1103–1109
 Abstract
Abstract(
718 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
1030
)
A series of Europium (Eu) and Strontium (Sr) codoped hydroxyapatite samples (Ca10-x-Srx-HAp: Eu) were designed and prepared using the chemical co-precipitation method. The crystalline structure, chemical composition and luminescent property of samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and photoluminescent spectrum (PL). XRD patterns showed that Eu doping had little effect on the structure of the samples, while with the increase of Sr content, crystallinity and interplanar crystal spacing were increased. PL spectra indicate that the fluorescence intensity at 596 nm and 618 nm of Ca-Sr-HAp: Eu samples increased firstly and then decreased with increase of Sr content at 394 nm excitation, and the strongest peak appeared in the Ca3-Sr7-HAp: Eu samples. At the same time, the fluorescence lifetime of the samples showed the same tendency with the increase of Sr content. In addition, the ratio of magnitude between electric dipole and magnetic dipole transition (IR/IO) also increased firstly and decreased subsequently along with the increase of Sr content in the matrix. Furthermore, the energy transfer parameters (f) calculated from luminescent dynamic of Eu3+ correlating to different sites and transitions present the reverse change. It is concluded that the doped sites of Eu3+ ions in the host lattice are affected by the content and location of Sr2+ ions in the matrix. Thereby a tunable luminescent property of Ca10-x-Srx-HAp: Eu samples can be obtained by changing the site of Eu ions in the matrix through adjusting the value of Sr/Ca.
|
|
|
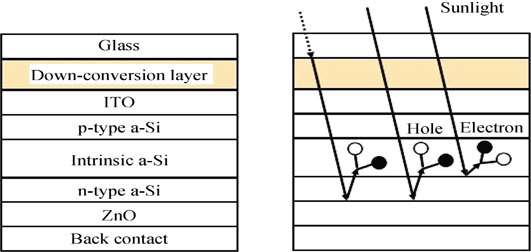
Down-conversion Photoluminescence Properties of YVO4: Eu3+@SiO2 Core-shell Structures for Solar Cell Applications
TAN Man-Lin, SHANG Xu-Ran, MA Qing, WANG Xiao-Wei, FU Dong-Ju, LI Dong-Shuang, ZHANG Wei-Li, CHEN Jian-Jun, ZHANG Hua-Yu
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1110–1116
 Abstract
Abstract(
685 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(461KB)(
1062
)
Europium ions doped yttrium vanadate (YVO4: Eu3+) has excellent emission properties for down-conversion applications. However, the serious surface defects of YVO4: Eu3+ hinder the improvement of luminescent efficiency. In order to improve the particle size distribution and morphology of YVO4: Eu3+ nano-powders, mono-dispersed spherical YVO4: Eu3+@SiO2 core-shell structure materials were prepared by coating a layer of YVO4: Eu3+ onto the surface of SiO2 microspheres. With the shell-core ratio setting as 0.6, the luminescence intensity of YVO4: Eu3+@SiO2 core-shell structure composite could reach up to more than 90% of pure YVO4: Eu3+ nano-powder. Furthermore, the prepared YVO4: Eu3+@SiO2 core-shell structure films were used as down-conversion materials for amorphous silicon thin film solar cells. The cell parameters such as short current density and photoelectric conversion efficiency increased from original 6.694 mA/cm2 and 9.40% to 8.417 mA/cm2 and 10.15%, respectively. Thus YVO4: Eu3+@SiO2 core-shell configuration can be fabricated from YVO4: Eu3+ and SiO2 microsphere to avoid agglomeration. The prepared YVO4: Eu3+@SiO2 core-shell structures have regular morphology and uniform particle sizes, which are suitable to be used as down-conversion light emitting layer in amorphous silicon solar cells.
|
|
|
Lycium ruthenicum Murray and Graphene Nanoplates for Dye Sensitized Solar Cell
XIE Shou-Dong, WANG Gang, CHEN Hui-Yuan, LIN Hong, YAN Zhi-Nan, ZHANG Hui
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1117–1122
 Abstract
Abstract(
720 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
996
)
The natural dye was extracted from Lycium ruthenicum Murray which was cultivated in Tibetan Plateau. The UV-Vis absorption spectra and cyclic voltammetry were used to characterize the dyes and confirm the optimal pH of the dye solutions. The influence of different contents of ethyl cellulose(EC) on the performance of electric catalytic of graphene nanoplates(GNs) counter electrode were investigated through electrochemical impedance spectra, cyclic voltammetry and Tafel polarization curve. DSCs were assembled by using the natural pigments with optimal pH as sensitizers and the GNs counter electrode with different contents of EC as counter electrode. It was found that the GNs counter electrode with 10wt% EC achieved the best performance of electric catalytic. The highest power conversion efficiency of the GNs counter electrode with 10wt% EC was 0.92%, close to that of Pt counter electrode (0.99%).
|
|
|
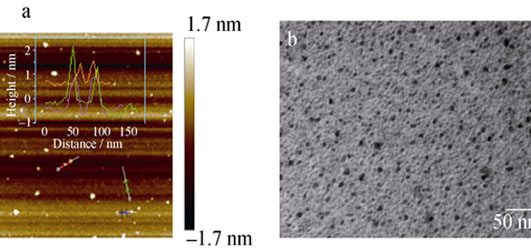
Preparation and Optical Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots Containing Nitrogen
ZHANG Dong-Mei, TIAN Lei, GUO Hui-Lin
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1123–1128
 Abstract
Abstract(
833 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1175
)
Graphene quantum dots containing nitrogen (NGQDs) were synthesized by the hydrothermal method. AFM, TEM and XPS were employed to investigate the morphology and composition of NGQDs, and their optical properties were studied by UV-Vis and photoluminescent (PL) spectroscopy. AFM and TEM images showed that NGQDs were about 8.9 nm in size and 0.6-2.0 nm in thickness (1-3 layers graphene). The result of XPS showed that nitrogen content in NGQDs was ~17% and nitrogen existed mainly in the form of "pyrrolic N". Spectroscopy experiments indicated that excitation spectra of NGQDs were similar to their absorption spectra, and their emission spectra were excitation-independent. In addition, quantum yield of NGQDs was calculated to be ~18%, increasing with the content of nitrogen in NGQDs increase. Furthermore, the lifetime decay curve was well fitted to a double exponential decay curve (τ1=2.93 ns, τ2=9.00 ns), which indicates that there are two feature chromophores in NGQDs. The chromophores are sp2 clusters with oxygen groups and pyrrolic ring.
|
|
|
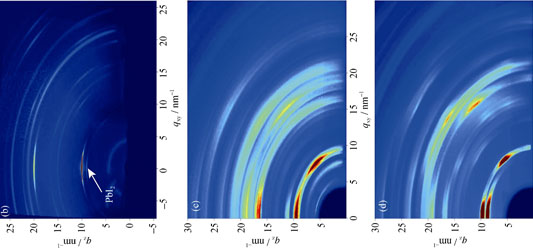
Fabrication and Characterization of High Stability (EDA)(FA)2[Pb3I10] Layered Perovskite Film
GAO Yan-Min, JIANG Wen-Long, YANG Tie-Ying, ZUO Yin-Ze
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1129–1134
 Abstract
Abstract(
980 )
 HTML
HTML(
19)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1253
)
A new two-dimensional layered hybrid perovskite solar-cell absorber was synthesized by one-step method, using (EDA)I2, (FA)I, and PbI2 with a 1:2:3 stoichiometric ratio in a solvent mixture of N, N-dimethylformamide(DMF). Ethylenediamine(EDA) cation was introduced into the perovskite lattice to synthesize a layered structure with improved resistance to the degradation by humidity in air. The effects of humidity and time on crystal structure, composition, morphology, and absorption spectra of (EDA)(FA)2[Pb3I10] and CH3NH3PbI3 were analyzed by in situ grazing incidence X-ray diffraction(GIXRD), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), atomic force microscope(AFM), and UV-Vis spectroscope. The results reveal that the prepared (EDA)(FA)2[Pb3I10] film is more moisture resistant than the CH3NH3PbI3 film which is widely used in the perovskite solar cell. SEM analysis reveals that the (EDA)(FA)2[Pb3I10] film has a layered structure, which can reduce the degradation caused by moisture. What’s more, UV-Vis light absorption spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy(AFM) results show that the layered structure film is also a suitable absorber for perovskite solar cells. Photoluminescence spectrum(PL) reveals that bandgap of the (EDA)(FA)2[Pb3I10] film is 1.67 eV, which is close to the optimum value for solar photoelectric conversion. As compared to CH3NH3PbI3 film, the low-cost perovskite structure offers greater tunability on a molecular level for further material optimization and possibility for widely used in the future.
|
|
|
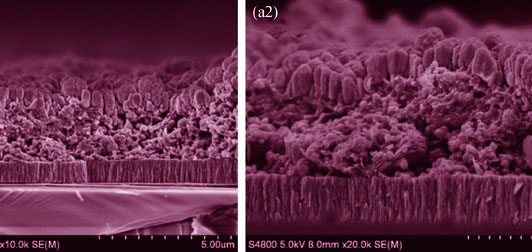
Synthesis of Core-shell Structure In2Se3/Cuse Micro/Nano-powders Followed by Coated-rapid Heating Treatment Method for Preparing CuInSe2 Thin Films
LI Bin, LI Ying-Lian, MO Shu-Yi, CHEN Ming-Guang, WANG Dong-Sheng, LONG Fei
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1135–1140
 Abstract
Abstract(
748 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
1112
)
Different In2Se3/CuSe nano-powders were successfully fabricated by ultrasound and microwave solvothermal, atmospheric pressure, or high pressure solvothermal methods. Then the thin film solar cell absorbent layer was prepared through coated-rapid heating treatment system using above nano-powders. The phase, morphology and composition of the powders and CIS film were characterized by XRD, Raman, FESEM, and TEM. The results showed that the ultrasonic microwave solvothermal and atmospheric pressure solvothermal methods produced a mixture of In2Se3/CuSe. However, high pressure solvothermal method obtained core-shell structure In2Se3/CuSe powders (In2Se3-core, CuSe-shell). In addition, FESEM analysis revealed that the In2Se3/CuSe powders prepared by high pressure solvothermal method were easier to produce smooth and dense CIS film. The fabricated CIS thin-film solar cell was demonstrated its photoelectric conversion property with open-circuit voltage of 50 mV and short-circuit current density of 8 mA/cm2.
|
|
|
Liquid-assisted Hot-pressed Sintering of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 Targets
HUANG Yao-Qin, ZHENG Guo-Yuan, MO Shu-Yi, HE Li-Qiu, WANG Dong-Sheng, LONG Fei
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1141–1146
 Abstract
Abstract(
680 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1010
)
CIGS target was prepared by one step hot-pressing sintering using CuIn0.7Ga0.3Se2, In0.7Ga0.3Se and CuSe as precursor powder. Archimedes method, XRD, Raman, SEM, and EDS were carried out to investigate the effects of liquid-assisted sintering on the relative density, phase, structure, morphology, and composition of CIGS target. The results showed that CuSe would turn into liquid phase when temperature was increased to the liquid phase points. The liquid phase can significantly reduce sintering temperature (about 50℃ dropping) and accelerate the sintering process. When sintered at 575℃, the target can obtain the relative density of 96.18%, single phase, dense microstructure with good grain growth. In addition, using the target with molar ratio of Cu : In : Ga : Se =23.0 : 18.2 : 6.5 : 52.3, CIGS thin films were also prepared by sputtering-heat treatment, followed assembled into AZO/ZnO/CdS/CIGS/Mo solar cell. The fabricated CIGS solar cells presented a photoelectric conversion efficiency of 9.6%.
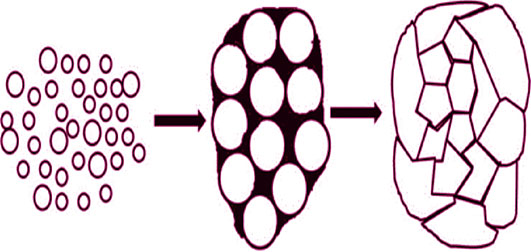
|
|
|
Synthesis, Growth and Scintillation Properties of Large Size Bi4Si3O12 Crystals
XU Jia-Yue, WANG Jie, CHEN Wei, XIAO Xue-Feng, YANG Bo-Bo, WANG Zhan-Yong, LI Fei, XIE Hui-Dong
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1147–1150
 Abstract
Abstract(
978 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(307KB)(
840
)
Using stoichiometric Si(OC2H5)4 and Bi(NO3)3·5H2O as precursors and citric acid as solvent, polycrystalline Bi4Si3O12 (BSO) powders were synthesized by Sol-Gel method and sintered at high temperature. Batch production of 250 g powders was realized. Using as-synthesized BSO powders and <001>-oriented BSO seeds, BSO crystals were grown in the vertical Bridgman furnace. The crystallization behavior was discussed and high quality BSO crystal up to 30 mm × 30 mm × 210 mm was obtained. The scintillation characteristics of BSO single crystals were investigated. The energy resolution of the BSO crystal was 18.9% and the relative light yield of the crystal was 7.2% compared with CsI(Tl) at the same conditions.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Ce-doped Gd3(Al, Ga)5O12 Powders Using Co-precipitation Method
ZHANG Ye, CHEN Xian-Qiang, QIN Hai-Ming, LUO Zhao-Hua, JIANG Jun, JIANG Hao-Chuan
2016 Vol. 31 (10): 1151–1156
 Abstract
Abstract(
916 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(383KB)(
1135
)
Ce-doped Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12 (GAGG) precursors were co-precipitated from a mixed solution of gadolinium, aluminum and gallium nitrates using ammonium hydroxide as precipitant. and then characterized by TG/DTA analysis. GAGG powders were obtained by calcining the precursors at 800℃, 850℃, 900℃, 1000℃, 1100℃ and 1200℃. Phase evolution of GAGG powders were investigated by XRD analysis which showed that a pure GAGG phase was obtained. SEM observation demonstrated that the obtaimed poovders were mainly amorphous with size mainly about 100-150 nm in diameter. PL spectra of GAGG powders showed strong emission around 560 nm. The highest transparency of as prepared ceramic was obtained when GAGG powders were calcined at 900℃.
|
|