|
|
Progress on the Fabrication of Ordered Mesoporous Materials with Large Pores by Using Novel Amphiphilic Block Copolymers as Templates
LUO Wei, WEI Jing DENG Yong-Hui, LI Yu-Hui, WANG Lian-Jun, ZHAO Tao, JIANG Wan
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 1–10
 Abstract
Abstract(
1335 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(670KB)(
1387
)
Ever since mesoporous silica M41S were reported in 1992, various mesoporous materials with diverse frameworks, abundant ordered mesostructures and different pore size have been synthesized by using commercial surfactants as template, due to their great potential for applications in energy storage and conversion, environmental remedy, catalysis. However, these mesoporous materials usually have pore sizes of less than 8.0 nm resulting from the low molecule weight of commercial templates, which greatly limit their applications in large guest objects. Moreover, these commercial templates are hard to synthesize ordered mesoporous metal oxides with high crystallinity. Recently, various amphiphilic copolymers with high molecule weight were reported to fabricate novel mesoporous materials, the recent research advances about their templated ordered mesoporous materials with large pore size and highly crystallized framework was reviewd in this paper.
|
|
|
Controlled Synthesis and Electrocatalytic Performance of Porous Nickel Cobaltite Rods
ZHAN Jing, LU Er-Ju, CAI Meng, MA Ya-Lin, ZHANG Chuan-Fu
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 11–17
 Abstract
Abstract(
961 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(907KB)(
1017
)
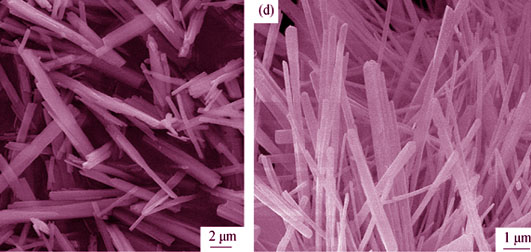
Porous rod-like NiCo2O4 powders were synthesized by coordination precipitation-thermal decomposition using NiCl2·6H2O, CoCl2·6H2O and oxalate as starting materials, and ammonia as coordination agent and pH adjustor. Morphology and structure of the precursor and as-prepared porous NiCo2O4 rods were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, and N2 adsorption/desorption analysis. Influence of solution pH on the morphology of the precurosr was investigated. Cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry were applied to investigate the electrochemical oxidation of ethanol on porous NiCo2O4 rods modified glassy carbon electrode in alkaline medium. The results show that morphology of the precursor depends on pH of the solution. The as-prepared NiCo2O4 rod inherits the morphology of the precursor and shows porous structures consisting of mesopores with a significantly high specific surface area of 89 m2/g and average pore diameter of 12.56 nm. Porous rod-like NiCo2O4 powders exhibit high electrocatalytic activity in cyclic voltammetry measurement. The linear relationships between oxidation peak current and ethanol concentration, and square root of scan rate indicate that ethanol diffusion is a rate-determining step in its oxidation on as-prepared porous NiCo2O4 rods.
|
|
|
Bagasse Activated Carbon Reactivation Promotes Adsorption of CO2
WEI Jian-Wen, LIN Zhi-Feng, HE Ze-Yu, HE Kai-Kai, GENG Lin-Lin, LIAO Lei
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 18–24
 Abstract
Abstract(
1052 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
968
)
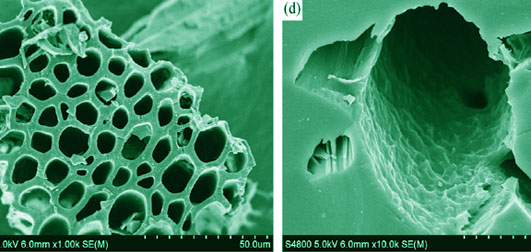
Activated carbon (AC) was prepared from bagasse using ZnCl2 as the activator. The new type of activated carbon (KAC) was prepared from AC using KOH as the second activator. CO2 adsorption/desorption properties were determined by thermal gravimetric analysis method (TGA). The activated carbon materials were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FTIR), N2 adsorption-desorption and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results showed that CO2 adsorption quantities of KAC and AC were 3.45 mmol/g and 1.79 mmol/g, respectively at 60℃. KAC has a better adsorption capacity than AC. The CO2 adsorption capacity after five adsorption/desorption cycles showed no obvious changes, display the materials good regeneration performance. The results of FTIR spectra showed that the characteristic peaks of the two activated carbon materials were almost the same. The polarity of the activated carbon surface increased with the increase of hydroxyl and carboxyl groups on activated carbons. N2 adsorption-desorption spectra and SEM images demonstrated that all the two kinds of materials had abundant pores, and KAC had much more pores which resulted in better adsorption capacity.
|
|
|
Deep Eutectic Solvent Based Polymer Electrolyte for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
YANG Ying, ZHANG Zheng, GAO Jing, LIN Ze-Hua, YAN Jing-Yuan, GUO Xue-Yi
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 25–32
 Abstract
Abstract(
1045 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(796KB)(
1471
)
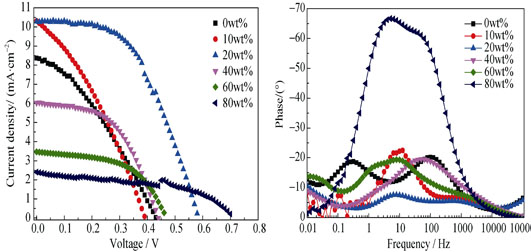
A polymer electrolyte using agarose as polymer matrix, NMP as solvent and deep eutectic solvent (DES) as modifier was investigated and employed in quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) of which the DES was composed by urea and choline chloride. The ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolytes with different urea /choline chloride ratio was studied. It was found that the maximum ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolyte was obtained at urea/choline chloride ratio of 2:1. Under the optimal urea /choline chloride ratio condition, electrochemical properties of the polymer electrolytes and the photovoltaic properties were systematically characterized by photovoltaic tests and electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS). The results showed that both ionic conductivity of electrolyte and photovoltaic performances of the DSSC was optimized with DES content of 20wt%, where the device photovoltaic parameters were as follows, Voc at 0.59 V, Jsc at 10.28 mA/cm2, FF at 0.51, and the cell efficiency at 3.18%.
|
|
|
Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Ce0.85Fe3CoSb12/rGO Thermoelectric Nanocomposite
ZONG Peng-An, CHEN Li-Dong
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 33–38
 Abstract
Abstract(
839 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(471KB)(
864
)
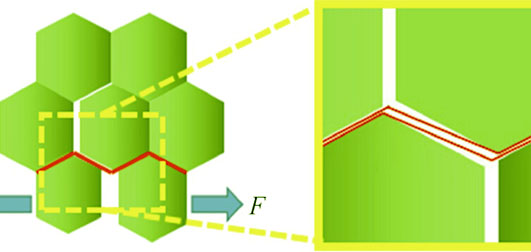
Comparing to n-type filled skutterudite, p-type one owns poorer mechanical propertities, which becomes the weak link of integration and the design of skutterudite based thermoelectric devices. By utilizing outstanding wettability and hydrophily of graphene oxide (GO), network wrapping and homogeneous dispersion of GO were realized in Ce0.85Fe3CoSb12 matrix particles via liquid dispersion. Spark plasma sintering was adopted to realize coherent densification and in-situ reduction of GO to rGO. Thus a 2-5 nm thick three dimensional reduced graphene oxide (rGO) wrapping structure in Ce.85Fe3CoSb12/rGO nanocomposite was obtained, which would enhance the flexural strength and toughness by additional crack-expanding work with bridging effect. Comparing to the pure Ce0.85Fe3CoSb12 material, flexural strength and toughness of Ce.85Fe3CoSb12/rGO nanocomposite with 2.8vol% rGO were enhanced by up to 40% and 33%, respectively. Reinforcing and toughening effects were weakened when rGO content farther increased, due to the thickened rGO layers in the matrix grain boundaries.
|
|
|
Graphene Nanosheets Prepared by Arc Discharge Method and Their Application in Conductive Inkjet
YANG Jie, PAN Zheng-Hui, SHENG Lei-Mei, AN Kang, ZHAO Xin-Luo
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 39–44
 Abstract
Abstract(
794 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(472KB)(
1060
)
Conductive ink is one of the dominant electronic materials for printed electronics technology. As the main component in conductive inks, conductive fillers are required to have favorable electronic properties and good chemical stability. Up to date, graphene-based conductive ink has attracted enormous research interest mainly due to its remarkable electrical properties. In present study, the graphene sheets as the conductive fillers were fabricated via a direct current arc discharge evaporation method. Furthermore, the as-prepared graphene sheets were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and Raman spectra analysis. The results demonstrated that the graphene sheets consisting of 2-10 layers with sheet size ranging from 100 nm to 200 nm had high purity and high crystallinity. Besides, the relationships between conductive properties and coating thicknesses, annealing temperatures and bending angles of conductive ink, were also carried out. It was found that the resistivity of conductive ink was inversely proportional to its thickness and annealing temperature, i.e. with gradual increase in thickness and temperature, the resistivity was decreased. And the resistivity of the conductive ink on the flexible substrate remained stable under different folding angles. Specially, the conductive ink with a thickness of 170 μm achieved the specific resistivity of 0.003 Ω•cm after being annealed at 360℃ for 30 min. The results indicate that arc-discharge graphene sheets are promising alternative for next generation of printed electronics.
|
|
|
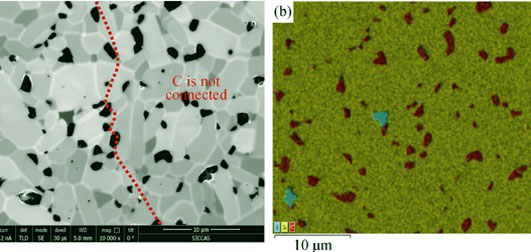
Nonlinear Electrical Behavior of Solid State Sintered SiC Ceramics
CHEN Jian, YIN Jie, ZHU Yun-Zhou, YANG Yong, CHEN Zhong-Ming, ZHANG Jing-Xian, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 45–50
 Abstract
Abstract(
669 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(520KB)(
990
)
The solid state sintered SiC (SSiC) ceramics are mainly used for structural materials, but they are rarely used for electronic devices and resistance components. In this work, the electrical properties of the SSiC ceramics with different carbon additives were investigated, including V-I characteristic, the relationship between current and resistance, as well as the relationship between temperature and resistance. These results show that the SSiC ceramics present obvious nonlinear electrical behavior and their resistance decreases with the current increase. When the electrical field intensity is over 15.8 V/mm for the SSiC ceramics with 3wt% carbon additives, as well as 70.7 V/mm for the SSiC ceramics with 6wt% carbon additives, the boundary barrier is breakdown and the resistance becomes very low, due to the resistance being only controlled by the grain size. The resistance of the SSiC ceramics decreases with the temperature increase at the electrical field intensity of 1 V/mm, indicating thermo-sensitive characteristic of SSiC ceramics of which the resistance is changed from 106 Ω·cm at 25℃ to 5 Ω·cm at 400℃.
|
|
|
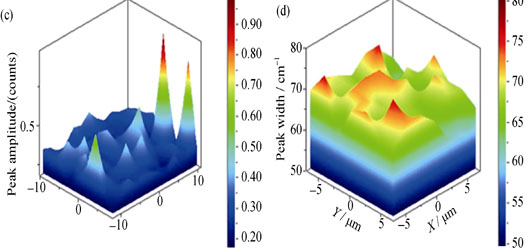
Luminescence of Donor-acceptor-pair in Fluorescent 4H-SiC Doped with Nitrogen, Boron and Aluminum
ZHUO Shi-Yi, LIU Xi, GAO Pan, YAN Cheng-Feng, SHI Er-Wei
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 51–55
 Abstract
Abstract(
871 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(378KB)(
1194
)
Fluorescent 4H-SiC, co-doped with donor and acceptor impurities, can work as phosphor for visible light emission by recombination. Donor concentration and acceptor impurities are two important factors which influence luminescent properties of fluorescent 4H-SiC. In this study, 3 inch N-B-Al co-doped 4H-SiC crystals were prepared by physical vapor transport method. Crystalline type and N-B-Al concentration of the doped 4H-SiC were measured by Raman spectrum and secondary ion mass spectra. Influences of doping concentrations on the photoluminescence were studied by photoluminescence excitation and emission spectra, luminescence decay curves, and internal and external quantum efficiencies. It is found that p-type fluorescent 4H-SiC with low Al doping concentration shows intensive yellow-green fluorescence at room temperature. Heavily doped N and B and lightly doped Al in 4H-SiC produce enough electron hole pairs for the recombination. This sufficient recombination enhances internal quantum efficiency of fluorescent 4H-SiC. Furthermore, the recombination is also helpful to increase their photoluminescence intensity and average fluorescence lifetime.
|
|
|
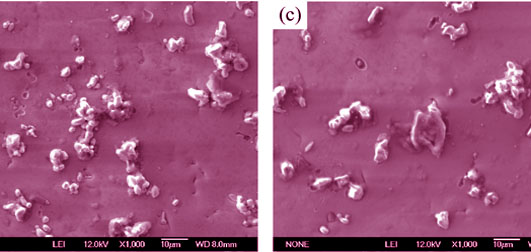
Synthesis and Properties of Self-sensitization Luminescent Composite Coatings
HE Ling, LI Qian-Kun, LI Weng-Sheng, CUI Shuai
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 56–62
 Abstract
Abstract(
591 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(699KB)(
935
)
It is very important for coating to detect integrity and working life in corrosive environment. The self-sensitization luminescent coating were fabricated by electroplating technique from a modified Watts bath combined with blue-emitting (BaMgAl11O17: Eu2+), red-emitting (Y2O3: Eu3+), and green-emtting (CeMgAl11O19: Tb3+) rare-earth fluorescent particles. The surface morphology, microstructure, wettability, deposition rate, hardness, and self-sensitization luminescent property of the obtained composite coatings were characterized by using fluorescence spectrophotometer, surface profile measuring instrument, vickers, scanning electronmicroscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and electrochemical test techniques. The results show that surfactants of non-ionic PEG (polyethylene glycol) and cationic CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) effectively improve the particles deposition rate. The fluorescent particles shows different wettability and matching with nickel, which have different effects on microstructure of the composite coatings. Y2O3: Eu3+ fluorescent particles change the coating crystal orientation and grain refinement, BaMgAl11O17: Eu2+ fluorescent particles make the coating morphology presents knot. The coating hardness is increased obviously in composite coatings containing Y2O3: Eu3+ and CeMgAl11O19: Tb3+ particles. The fluorescent particles show different luminescent characteristics after corrosion, indicating good self-sensitization and effective monitor on the integrity of the composite coatings.
|
|
|
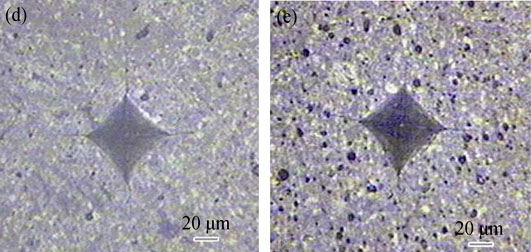
Microstructure and Properties of 3Y-TZP/LZAS Glass-ceramic Functionally Gradient Coatings
GONG Wei, LI Hua, ZHOU Li-Ming, BAI Cao-Zhong, WANG En-Ze
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 63–68
 Abstract
Abstract(
746 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(494KB)(
1002
)
In order to improve toughness of glass-ceramic coatings, 3mol% yattria-tetragonal zirconia polycrystal/Li2O-ZnO-Al2O3-SiO2 (3Y-TZP/LZAS) glass-ceramic functionally gradient coatings on Q235 steel substrate were prepared by slurry method. Phase constitution and microstructure of samples were examined by XRD and SEM, respectively. Their micro-hardness and fracture toughness were measured by indentation method. And their bonding strength of the coatings was also investigated by pulling test. Resulting data indicate that the seamless interfaces among toughening coatings, LZAS transition layer and substrate are obtained. SiO2 in the LZAS glass reacts with iron oxides at interfacial region forming Fe2SiO4 and FeSiO3, which causes tight interface bind between gradient coatings and steel substrate. Micro-hardness and fracture toughness from inner substrate to top surface on the section of the coatings increase gradually. Residual compressive stress toughening, 3Y-TZP particles toughening and 3Y-TZP transformation toughening are the dominant factors for improving fracture toughness of the gradient coatings. Bonding strength of the coatings is up to 16.3 MPa. The gradient coatings withstand more than 30 thermal cycles at 300℃, demonstrating their excellent thermal sock resistance.
|
|
|
APS Bias Voltage on Properties of HfO2 Laser Films Deposited by Reactive Plasma Ion Assisted Electron Evaporation
FU Chao-Li, YANG Yong, MA Yun-Feng, WEI Yu-Quan, JIAO Zheng, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 69–74
 Abstract
Abstract(
709 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(517KB)(
1050
)
The anti laser HfO2 films were deposited by reactive plasma ion assisted electron beam evaporation in low O2-pressure with different Advanced Plasma Source (APS) bias voltages. Properties of HfO2 film sincluding chemical composition, refractive index and residual stress were investigated. Microstructure of HfO2 films was analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Laser induced damage threshold (LIDT) and damage mechanisms of HfO2 films were finally evaluated and discussed. Properties of HfO2 films display sensitive to APS bias voltage. As the APS bias voltage decreases, the O/Hf ratio in the film increases, accompanied by decreasing refractive index and residual stress. The damage morphology of HfO2 films appears in the form of agglomerations of craters with a few hundreds of nanometers, left by evaporation of grains ascribed to strong absorption and accumulation of laser energy at grain-boundaries. HfO2 films with higher LIDT can be grown under lower bias voltage which benefits the achievement of uniform microstructure and the crystallization orientation from () plane to (002) plane with low grain boundary energy and lattice defects.
|
|
|
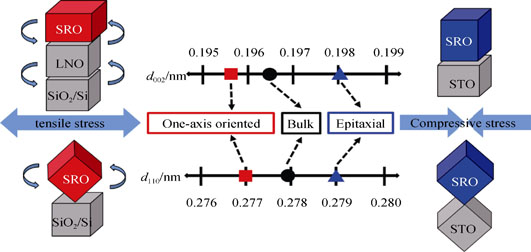
Effect of Residual Stress on Magnetic and Electrical Transport Properties in SrRuO3 Thin Films
ZHU Ming-Kang, DONG Xian-Lin, CHEN Yin, DING Guo-Ji, WANG Gen-Shui
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 75–80
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(434KB)(
1089
)
A series of SrRuO3 (SRO) thin films with preferential orientations were grown on SrTiO3 (STO) and Si substrates respectively by radio frequency (RF) magnetron sputtering technique. XRD results show that STO-based SRO thin films are epitaxial which differ from the one-axis orineted Si-based films. Residual stress type of the deposited films and effect of the stress on magnetic and electrical transport properties were systematically analyzed and summarized. STO-based SRO films suffer from compressive stress due to the lattice and thermal mismatch, while the Si-based films are subjected to tensile stress which is only derived from the thermal mismatch. The compressive stress promotes the Curie temperature (TC) of (001)-oriented SRO films, but reduces the TC of (110)-oriented SRO films, which may be due to the different states of rotation and tilt of RuO6 octahedron. Besides, the (001)-oriented SRO films possess higher TC than the (110)-oriented SRO films all along. The results of temperature versus resistivity measurements reveal that residual resistivity ratio (RRR) of (001)-oriented SRO films is higher than that of (110)-oriented SRO films which deposited on the same substrate. Moreover, the temperature of metal-insulator transition (TMI) increases from 16 K to 32 K while the temperature dependence of resistivity is suppressed by the tensile stress.
|
|
|
Mechanism of Inorganic-organic Surface Modification of Anhydrous Calcium Sulfate Whisker
LV Zhi-Hui, HONG Tian-Zeng, NAI Xue-Ying, DONG Ya-Ping, LI Wu
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 81–85
 Abstract
Abstract(
858 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(611KB)(
938
)
Anhydrous calcium sulfate whisker (ACSw) was modified by dual-surface modification with sodium silicate solution as inorganic modifer and stearic acid as organic modifier. The samples were characterized by water contact angle (WCA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope(FESEM), fourier infrared spectrum (FT-IR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS). The results showed that ACSw surface property changed to Hydrophobic after inorganic-organic modification, while its crystal structure remained unchanged. FT-IR and XPS resutls indicated that -Ca-SiO3 structure was generated firstly on the surface of whiskers after reaction with sodium silicate solution. And then a mixing coating layer containing both -Ca-HSiO3 and -Ca-COOR structures were formed through bonding interaction with stearic acid rather than physical absorption after particle hydrolyzation of -Ca-SiO3 structure.
|
|
|
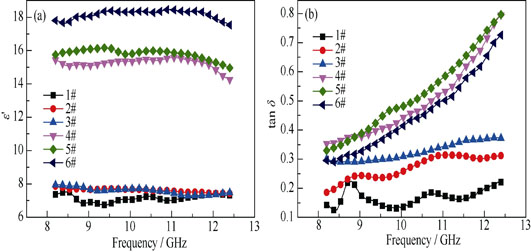
Mechanism of Microwave Dielectric Response in Laminated Cf-Si3N4 Composites
ZHOU Wei, XIAO Peng, LUO Heng
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 86–90
 Abstract
Abstract(
693 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(390KB)(
977
)
Laminated Cf-Si3N4 composites were prepared by gelcasting followed by pressureless sintering at 1600℃ in N2 atmosphere, using short carbon fiber, α-Si3N4 powder as starting materials. Microwave dielectric properties of Cf-Si3N4 composites were investigated in X-band using a network analyzer. Moreover, theoretical model regarding microwave dielectric responses was established by modification of Debye model, and the corresponding mechanism was discussed intensively. Results show that there exists percolation phenomenon in permittivity of laminated Cf-Si3N4 composites with surface density of short carbon fibers increasing due to formation of connected carbon fiber network. Additionally, the relaxation time of Cf-Si3N4 composites converges to multiple values immediately after carbon fibers network being formed, which results from inhomogeneity of microstructure, conductivity and coatings of short carbon fibers. And this dispersity can then weaken as surface density of short carbon fibers increasing. Consequently, the characteristic function of tangent loss evolves from multi-relaxation time model to uni-relaxation time model based on numerical analysis.
|
|
|
Crystal Structure and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8
ZHANG Yao, DING Shi-Hua, LIU Yang-Qiong, DUAN Shao-Ying, XIAO Peng, HAN Lin-Cai
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 91–95
 Abstract
Abstract(
604 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(396KB)(
910
)
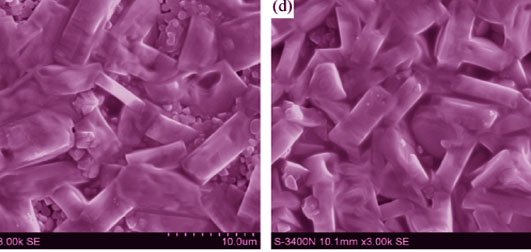
Barium feldspar BaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system materials have been studied extensively for application in microwave devices, microwave substrate and packaging in recent years, due to their remarkable dielectric properties. The hexacelsian-celsian transition, relationship between dielectric properties, and structure of BaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system has attracted widely academic interest. Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8 (x=0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.3, 0.5) ceramics were prepared by solid state sintering processing. The crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of BaO-Al2O3-SiO2 with different MgO contents were studied. The results show that MgO doping reduces sintering temperature and greatly promotes the transition from hexacelisian to celsian at x≥0.15, while the transition reachs 100%. MgO doping effectively increases grain size at x≤0.15. The diffraction peak of celsian is enhanced and the grain size gets larger. Moreover, the density, dielectric constant andτf of Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8 ceramics increases with the increase of MgO content in the range of 0.05≤x≤0.1. In addition, the resonant frequency temperature coefficient is negative. The Ba0.9Mg0.1Al2Si2O8 sintered at 1400℃ exhibits a high Q×f value of 16461 GHz, εr=6.44 and τf= -30.6×10-6 K-1 at x=0.1. The dielectric constant of Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8 ceramics is related with its Mg2+ polarizability and its structure. The effect of electronegativity, the size of ions and the crystal structure on Q×f value of Ba1-xMgxAl2Si2O8 ceramics are also discussed.
|
|
|
Thermal Stable Perovskite Solar Cells Improved by ZnO/Graphene Oxide as Electron Transfer Layers
JIANG Wen-Long, ZHOU Wei, YING Ji-Fei, YANG Tie-Ying, GAO Yan-Min
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 96–100
 Abstract
Abstract(
1212 )
 HTML
HTML(
40)
 PDF
PDF(387KB)(
1268
)
ZnO/graphene oxide (GO) nano-particles (NPs) layer was prepared using a facile solution process and employed as an electron conductor to improve the thermal stability of perovskite solar cells. Structural changes during the degradation process in high temperature environment were characterized via in situ grazing incidence X-ray diffraction. The optical properties and surface morphologies of the films were characterized. It was observed that smooth and compact structure of ZnO/GO layer works as a protection layer to prevent decomposition of perovskite film which is converted into PbI2 during the annealing process reaction. The perovskite film grown on ZnO/GO layer exhibited enhanced crystallization, high surface coverage ratio as well as preferred in-plane orientation of the (110) plane.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Physical Properties of Solar Material Cu1-xLixInSe2
HUANG Rong-Tie, ZHENG Ming, SUI Li-Fang, CAI Chuan-Bing, HUANG Fu-Qiang
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 101–106
 Abstract
Abstract(
755 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(500KB)(
943
)
Bulk materials of Li-doped Cu1-xLixInSe2 (x = 0-0.4) were prepared by solid state reaction in evacuated and sealed quartz tubes at 873 K. To understand the physical properties of the materials, the structural, electrical and optical properties were systematically investigated. After doping with lithium, the samples crystallize in chalcopyrite structure with large grain sizes. Electrical resistivity and optical band gap of Li-doped Cu1-xLixInSe2 are greatly enhanced to 2.73×108 Ω·cm and 1.33 eV from original values of 1.98×102 Ω·cm and 0.9 eV, respectively. The large band gap improves the open circuit voltage, indicating that the Li-doping CuInSe2 could be a promising material to future photovoltaic applications.
|
|
|
Sol-Gel-derived Mesoporous Calcium Aluminum Phosphate Bioactive Glasses with High Surface Area
MA Peng-Fei, LI Ri-Hong, ZHANG Long
2017 Vol. 32 (1): 107–112
 Abstract
Abstract(
687 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(363KB)(
1150
)
High surface area mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBGs) with composition CaO-Al2O3-P2O5 were fabricated using a simple aqueous Sol-Gel method without any template. Structural characterization of the phosphate-based MBGs was performed by BET, DTA, XRD and FTIR, and MBGs’ in vitro bioactivity was evaluated by soaking them in simulate body fluid for up to 15 d at 36.5℃. The highest specific surface area is found to be 461.1 m2/g for the MBG with 5mol% CaO, and it decreased with increasing CaO content. And the glass structure for all the samples was confirmed by XRD and FTIR. However, the MBG with 20mol% CaO exhibits the best in vitro bioactivity using simulated body fluid among all samples. The unique combination of a higher specific surface area and relatively high CaO content enables mesoporous calcium aluminum phosphate bioactive glasses to be promising candidates for biomedical applications.
|
|