|
|
Synthesis and Copper(II) Affinity Performance of Amidoxime Functionalized Mesoporous Silica
WEI Jian-Wen, WANG Ji-Hua, ZHAO Song-Sheng, GENG Lin-Lin
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 449–453
 Abstract
Abstract(
855 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(294KB)(
1040
)
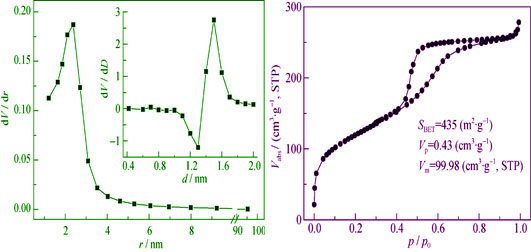
Amidoxime-functionalized mesoporous silica was synthesized with tetraethylorthosilicate and 2-cyanoethyl triethoxysilane as silicon source, potassium chloride as the crystal structure directing agent and poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (propylene glycol)-poly (ethylene glycol) three block copolymers as template. The structure of the samples, pore properties and chelating function groups were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), N2 adsorption desorption isotherms and elemental analysis. XRD spectra and N2 physical adsorption-desorption results indicate that amidoxime functioned mesoporous silica has ordered two-dimensional hexagonal structure with average pore size of 3.96 nm and specific surface area of 435 m2/g. FT-IR spectra shows that cyano is introducted into silica and converted into amidoxime successfully. Amidoxime concentration is about 1.6 mmol/g by elemental analysis and Zeta potential analysis results show that the adsorbent is electronegative. Compared with the Cu2+ adsorption capacities of unmodified silica material (SBA-15) and cyano functionalization of porous silicon oxide (CN-SBA-15), the adsorption capacity of AO-SBA-15 increases by 2 fold and 3.6 fold, respectively. This shows that with the introduction of amidoxime chelating function groups, affinity performance of SBA-15 to the copper ions are markedly improved.
|
|
|
Influence of Preparation Method on Oxidation Degree of Graphene Oxide and Adsorption for Th (IV) and U(VI)
WANG Xiao-Ning, MENG Hu, MA Fu-Yin, LI Zheng, ZHANG Lan
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 454–460
 Abstract
Abstract(
974 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(424KB)(
1107
)
Graphene oxide (GO) was prepared from graphite using Hummers' method, improved Hummers' method and modified Hummers' method. The samples were characterized by FT-IR spectroscope, TGA, XRD, XPS,SEM and element analysis. The results showed that graphene oxide was more oxidized prepared by the improved Hummers' method(IGO). The isothermal adsorption experiments of Th(IV) and U(VI) on graphene oxide showed that the maximum adsorption capacity of Th(IV) on IGO was 192.3 mg/g, increased by 38.5% as compared with that of GO prepared by Hummers’ method. The maximum adsorption capacity of U(VI) was 156.2 mg/g, increased by 28.1%. Both of above values are in accord with Langmuir isotherm model. Furthermore, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of Th (IV) and U(VI) adsorption on IGO were investigated by using batch experiments, confirming that adsorption fits pseudo-second kinetic equations, which are spontaneous and endothermic.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Flower-like Sn3O4 Hollow Microspheres and Their Photocatalytic Activity
CUI Lei, YANG Li-Juan, WANG Fan, XIA Wei-Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 461–465
 Abstract
Abstract(
926 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(530KB)(
1101
)
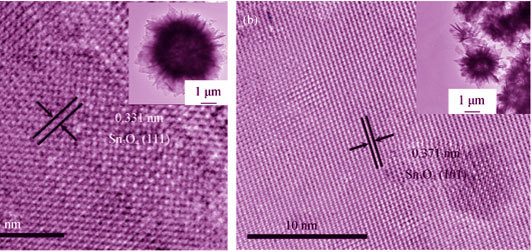
Flower-like Sn3O4 hollow microspheres were synthesized via one-step hydrothermal process with varying reaction temperature (120℃, 135℃ and 150℃). The crystal structure, morphology, composition, specific surface area, and optical property of the obtained products were characterized by X-ray diffraction(XRD), scanning electron microscope(SEM), transmission electron microscope(TEM), high resolution transmission electron microscope(HRTEM), automatic surface area analyzer, UV-Vis absorption spectrum, and photoluminescence spectrum (PL). The photocatalytic experiments of the as-prepared samples were evaluated by decomposing the model pollutants rhodamine B (RhB). Systematical measurements revealed that the morphology of the hollow microsphere structures was faithfully preserved as changing the hydrothermal synthesized temperature. With the increase of the hydrothermal synthesized temperature, the UV-Vis absorption peak of samples shifted from 384 nm to 365 nm and the PL intensity further weakened. Finally, the photocatalytic activity presented that Sn3O4 microspheres hydrothermal synthesized at 120℃ had the best photcatalytic performance.
|
|
|
Preparation, Photocatalytic Property and Antibacterial Property of Ag@TiO2@SiO2 Composite Nanomaterials
SHI Zhen-Wu, GUO Shao-Bo, XUE Qun-Hu
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 466–472
 Abstract
Abstract(
1017 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(525KB)(
1560
)
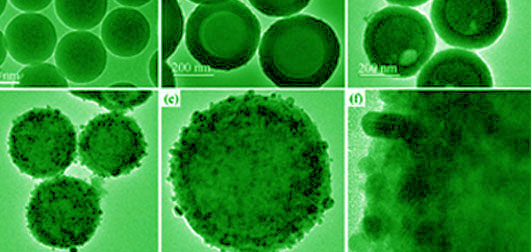
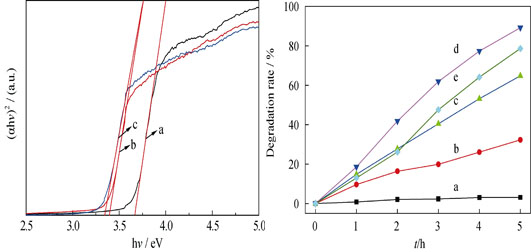
TiO2@SiO2 composites with core-shell structure were successfully synthesized using SiO2 as template by Sol-Gel method. Ag nanoparticles (NPs) were photo-deposited on the surface of TiO2@SiO2 to form core-shell Ag@TiO2@SiO2 composites. The resulting samples were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS). The photocatalytic activity was evaluated by photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine under UV light, and the antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus was also measured. In comparison to TiO2@SiO2, Ag@TiO2@SiO2 exhibited higher photocatalytic activity and antibacterial efficiency after loading uniform Ag NPs on the TiO2. When the concentration of Ag is 0.6 mg/mL, the antibacterial rates against E. coli and S. aureus are 93.41% and 97.37%, respectively. This Ag@TiO2@SiO2 may be used in wastewater treatment, medical equipment and other fields due to its excellent photocatalytic activity and antibacterial property.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal/Solvothermal Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of ZnS Microspheres
WU Xuan-Rong, YANG Qiao-Zhen, ZHAO Yong-Xiang, LU Yan-Luo
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 473–478
 Abstract
Abstract(
901 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(431KB)(
954
)
ZnS microspheres were synthesized via hydrothermal/solvothermal method using Zn(Ac)2·2H2O and CH4N2S as reactants. ZnS was characterized by XRD, SEM and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectrum. The results showed that as-synthesized ZnS microspheres had zinc blende crystalline structure which was self-assembled by small ZnS nanoparticles. As for the photocatalytic degradation of phenol aqueous solution, ZnS microspheres synthesized in (CH2OH)2-H2O system revealed much better photocatalytic activity than that of ZnS synthesized in other solvent systems, and it kept high activity after cycling degradation for 3 times. The enhanced photocatalytic performance of ZnS microspheres could be attributed to the cooperation effect of the following three aspects: the smaller band gap (3.39 eV) being conducive to the absorption of photons, the more complete crystal structure to increase the number of active molecules, and larger specific surface area (19.4 m2/g) being in favor of sufficient contacting between the reaction solution, and the catalyst. The intermediate products were oxalic acid, maleic acid and very little hydroquinone in photocatalytic degradation of phenol by ZnS microspheres.
|
|
|
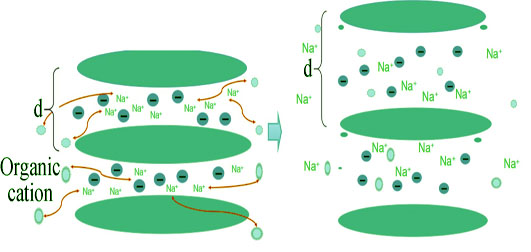
Preparation and Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan/Organic Laponite Nanocomposites
FU Hai-Li, ZHANG Wen, ZHANG Hua, SONG Shao-Bo, LI Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 479–484
 Abstract
Abstract(
933 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(446KB)(
1208
)
Laponite-based secondary intercalation compound was prepared by ion exchange method through intercalating quaternary ammonium salts and chitosan into the layers of hectorite. The layer spacing of the two kinds of secondary intercalation compounds were increased 0.276 nm and 0.262 nm, respectively, compared to the pure laponite. The antibacterial of secondary intercalation compound was tested by Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. cereus). Antibacterial ability of the two kinds of secondary intercalation compounds were determined by using bacteriostatic ring and plate count methods. The results showed that, after being contacted with the two compounds for 24 h, the bacteriostatic rate of the laponite/myristyl trimethyl ammonium bromide/chitosan on E. coli reached up to 100% and 85% on S.cereus. Meanwhile, the laponite/cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide/chitosan was up to 99% on E. coli and S. cereus. The antibacterial process and mechanism on E. coli and S. cereus of the two kinds of compounds were investigated by scanning electron microscope and β-galactosidase activity. The results showed that the compound adsorbed bacterial through the role of mutual attraction between positive and negative charges at first, then the compound penetrated the bacterial cell membrane with the help of hydrophobic interaction of organic cation, and finally exerted the sterilization effect.
|
|
|
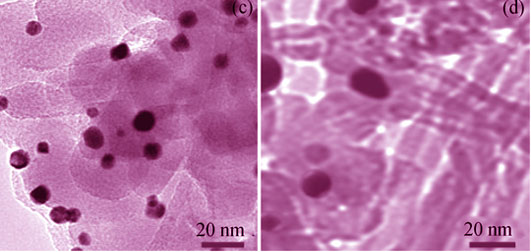
Preparation of Ni-Al2O3 Catalysts by Solution Combustion Method for CO2 Reforming of CH4
MO Wen-Long, MA Feng-Yun, LIU Yue-E, LIU Jing-Mei, ZHONG Mei, Aisha·Nulahong
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 485–491
 Abstract
Abstract(
612 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(563KB)(
846
)
Ni-Al2O3 catalysts with Ni loading of 2wt%, 4wt%, 6wt%, 8wt%, and 10wt% were prepared by solution combustion method for carbon dioxide reforming of methane to produce syngas, and characterized by N2 adsorption-desorption method, XRD, H2-TPR, TPH, Raman, TEM, and TG-DTG techniques. Results showed that all the catalysts preserved large specific surface areas and hierarchical pore size distributions (2-4.5 nm as one part and 4.5-10 nm as another part) as compared to 8IMNi-Al catalyst prepared by impregnation method (Al2O3 as support prepared by solution combustion method). NiO was highly dispersed in the Ni-Al2O3 catalysts, which combined with support with strong metal-support interaction (SMSI), improving the stability performance. The 210 h stability test of 8Ni-Al catalyst showed that conversion rate of CH4 was around 90% with the deactivation rate of only 0.035%/h, lower than that of 8IMNi-Al catalyst within the 182 h endurance test. TG-DTG result demonstrated that carbon deposition rate of 8Ni-Al catalyst was only 0.34 mg/(h·gcat), which was lower than that of 8IMNi-Al catalyst (0.80 mg/(h·gcat)). Therefore, the Ni-Al2O3 catalyst prepared by solution combustion method presented well stability.
|
|
|
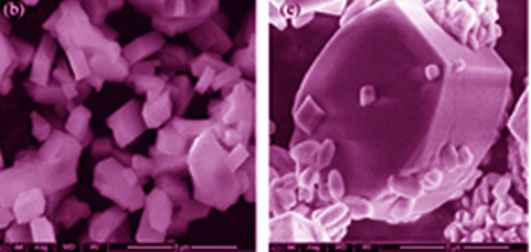
Synthesis and Characterization of ZSM-5/EU-1 Composite Zeolite with ore-shell Structure by One Step
LI Jian-Hua, YANG Dong-Hua, LV Ai-Ning, MA Cun-Cun, Li Xiao-Feng, DOU Tao
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 492–498
 Abstract
Abstract(
947 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(560KB)(
1207
)
ZSM-5/EU-1 core-shell intergrowth composite zeolite was synthesized by one-step crystallization method based on dual-template and appropriate citric acid addition. The properties of core-shell zeolite were characterized by XRD, TEM, FT-IR, NH3-TPD, etc. The results showed that there were ZSM-5 and EU-1 zeolite crystalline phases formed in the core-shell zeolite, as EU-1 overgrowing around ZSM-5 surface defects. The synthetic sample composed of microporous and mesoporous multiple porous composite zeolite, with micropore diameter of 0.94 nm. The core-shell structure increased strong acid content and improved its acidity as compared with the single zeolite. Based on the investigation of citric acid addition and crystallization time influence on the structure and Zeta potential of core-shell zeolite, the optimum condition of core-shell intergrowth was as follows, i.e. n(citrate)/n(Al2O3)=0.8-1.2 and crystallization time of 72-96 h. And the possible growth process of core-shell zeolite was proposed.
|
|
|
Preparation of Octyltrimethoxysilane Modified SiO2 Hydrophobic Antireflective Coating
NIU Yan-Yan, WANG Xiao-Dong, YAO Lan-Fang, TIAN Bing-Tao, FENG Jian-Bin, CAO Yuan-Yuan, ZHANG Qing-Hua, SHEN Jun
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 499–504
 Abstract
Abstract(
949 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(411KB)(
1350
)
The standard SiO2 sol was prepared by sol-gel process using tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) as precursor and ammonia as catalyst. Octyltrimethoxysilane (OTMS) was added into the standard SiO2 sols before and after refluxing to obtain different organosilane modified silica sols, respectively. Silica antireflective (AR) coatings were then prepared from different SiO2 sols by dip-coating method. The optical and structural properties of the AR coatings were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, liquid-state 29Si NMR, UV-Vis-NIR spectrometer, atomic force microscope and water contact angle measurement. The results show that the AR coating prepared from OTMS modified before refluxing has the best moisture-resistant performance. The coated glass substrate obtains a high peak transmittance of 99.7%, with water contact angle of 120°. After been placed in a humid environment for 4 w, the transmittance of SiO2 coatings modified before refluxing is decreased only by 0.23%.
|
|
|
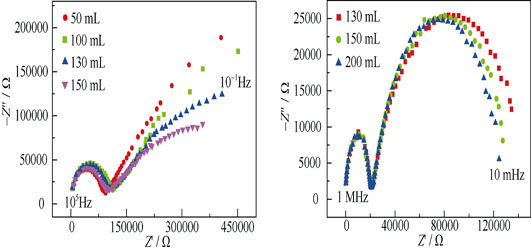
Determination of Hydrogen Content and Dehydrogenation in Molten Aluminum by Concentration Cell Method
WANG Dong, LIU Chun-Ming, LI Sheng-Li, LI Wei-Juan, CHEN Shu-Jiang, YANG Bo-Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 505–509
 Abstract
Abstract(
649 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(436KB)(
923
)
The CaZr0.9In0.1O3-α proton conductor was prepared by solid reaction method with high purity and small particle size. Two types hydrogen sensors and pump based on the proton conductor were fabricated for monitoring the hydrogen content and dehydrogenation in molten aluminum at 760℃. The electromotive force (EMF) and time of hydrogen sensor with the inverted-U electrolyte tube followed a smooth curve in which the EMF tended to be stable after about 13 min whose sensing performance was superior to that with the upright-U electrolyte tube. The sensor EMF increased with the pressure or flow rate of referent gas according to Nernst equation. The equilibrium time of EMF increased and the transferring resistance between the Pt electrode and proton conductor’s transfer resistance decreased with the flow rate of reference gas. Therefore, inverted-U type tube and flow rate value of reference gas were very important to acquire the sensitive and accurate hydrogen content values in molten aluminum. In addition, hydrogen pump based on concentration cell had feasibility and actual using value for the dehydrogenation of molten aluminum.
|
|
|
Preparation of Pt/Ti Electrodes Preferred Growth along the [111] Direction and Its Electrocatalytic Activity for Chlorine Evolution
ZHU Yu-Chan, YUAN Min, ZHANG Huan, WANG Le, QUAN Shan-Shan, CHAI Bo, REN Zhan-Dong
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 510–516
 Abstract
Abstract(
785 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(423KB)(
1022
)
To solve the short service life of dimensionally stable anode (DSA) and the high dosage of Pt electrode in the process of low concentration sodium chloride electrolysis, the Pt/Ti electrode preferred growth along the [111] direction was prepared by magnetron sputtering. The electrode surface of the magnetron sputtering Pt was uniform with particle size of 10 nm. The characteristic peaks of Ti were not found in the XPS spectrum, which showed that the Ti matrix was completely covered by Pt. Electrochemical cyclic voltammetry (CV) results showed that the electrochemical area of the magnetron sputtering Pt was the smallest (1.08 cm2), which was close to the apparent surface area of the electrode. In addition, the electrical amperage ratio of the oxygen adsorption area to the hydrogen adsorption area was only 0.83 calculated from the CV diagram. So it can be predicted that the oxygen adsorption capacity on the magnetron sputtering Pt is very poor and not prone to the oxygen evolution reaction. When the electrode potential was 1.6 V, the chlorine evolution reaction current of the magnetron sputtering Pt was 0.085 A/cm2 in the unit electrochemical area, which was 3.27 and 49.0 times that of the electro-deposition Pt and thermal decomposition Pt, respectively. It showed that the magnetron sputtering Pt had a high activity of chlorine evolution in the unite active site. It may be related to the special morphology of its surface (111) crystal surface. On the basis of the above, the Tafel slope of the magnetron sputtering Pt was 44.3 mV/dec. The mechanism of chlorine evolution reaction was in accordance with the mechanism of Volmer-Heyrovsky, and the rate controlling step was the electrochemical desorption step.
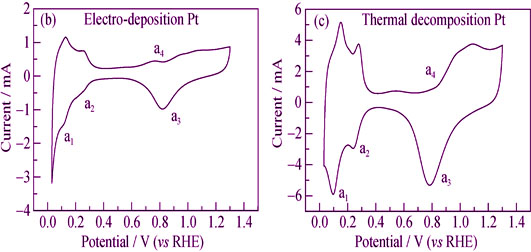
|
|
|
LiFePO4/C Cathode Material Modified by Polyacrylamide
QIN Xian-Zhong, YANG Gai, GAO Jian, CAI Fei-Peng, TAN Chu-Hui
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 517–522
 Abstract
Abstract(
668 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1077
)
LiFePO4/C composite cathode materials containing different amounts of PAM as dispersing agent were synthesized by controlled crystallization-carbon thermal reduction process, to investigate the effect of polyacrylamide (PAM) on the performance of LiFePO4/C. Crystal structure, surface morphology and electrochemical properties of the obtained composites dispersed by PAM were studied by the techniques including thermal chemical analysis, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, carbon content test, constant current charge and discharge testing. The results showed that LiFePO4 material fabricated with 1.5wt%PAM dissolved in acid dispersed more evenly with good flow ability with average particle size of about 100 nm. The first discharge capacities of 1.5wt%PAM-LFP composites were 153.8, 142.5, 138.4, 128.7 and 124.3 mAh/g at 0.1C, 1C, 2C, 5C and 10C ratios, respectively, which capacity retention can keep above 99% at 1C rate after 100 charge/discharge cycles. According to AC impedance spectra measurements, the impedances of 1.5wt%PAM-LiFePO4 decreased evidently and the diffusion coefficient of Li ions increased by 28 times, indicating that Li ion and electric conductivity, discharge capacity and cycling performance were greatly improved. The above results show that LiFePO4/C composite cathode materials dispersed by PAM is suitable for industrial applications.
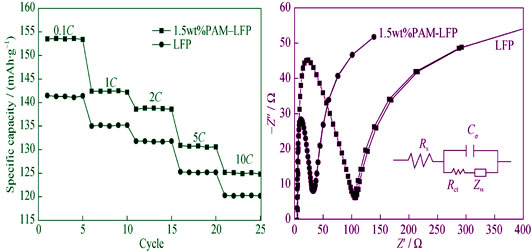
|
|
|
Synthesis and Analysis of a New Silica Nanowire Periodically Wrapped by Nano-spheres
MA Hong-Bing, BAI Hua, XUE Chen, TAO Peng-Fei, XU Qun-Feng, JIANG Nan
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 523–528
 Abstract
Abstract(
699 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(513KB)(
907
)
Lawn-like nanowire arrays silica nanowires were grown on graphite substrate by thermal evaporation of silicon powders using vapor from melted CaCl2 as carrier at 1300℃. A series of analysis technique were employed to investigate the as-grown nanowires. The results show that the as-grown silica nanowires are in length of several micron-meters with the diameter ranging from 50-400 nm, which is identified to be face-centered cubic structure. Systematic analyses reveal that the growth models such as classic vapor-liquid-solid(VLS) model are not applicable to explain the growth of silica nanowire periodically wrapped by nano-spheres. Hereby, an extended VLS model is proposed which can perfectly interpret the silica nanowires’ growth on graphite surface.
|
|
|
Influence of Free Carbon Elimination on Microstructure and Property of SiC Fibers
CAO Shi-Yi, WANG Jun, WANG Hao, WANG Xiao-Zhou
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 529–534
 Abstract
Abstract(
665 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(392KB)(
1057
)
To prepare SiC fibers with different free carbon contents, polycarbosilane (PCS) fibers cured with unsaturated hydrocarbons were pyrolyzed at 1000℃ under controlled hydrogen/nitrogen atmosphere and subsequently heat treated at 1500℃ under nitrogen atmosphere. The process of carbon removal during pyrolysis was investigated using chemical elemental analysis, FTIR, and AES analysis. The microstructure and properties were examined by SEM, TEM, XRD, density measurements, tensile tests and resistivity measurements. The results show that the carbon content in SiC fibers decreases with H2 concentration increasing. The hydrogen atmosphere suppresses H2 evolution and helps to remove excess carbon as CH4 during pyrolysis. Although thin carbon-enriched films are present on the fiber surfaces, the distribution of silicon and carbon is uniform in the fiber cores. The microstructure and properties of the resulting SiC fibers are very dependent on their C/Si chemical compositions. The β-SiC grain size increases with a decrease in the carbon content because the excess carbon aggregates at the grain boundary and impedes the grain growth. Moreover, the removal of free carbon also results in fiber densification, decrease of porosity and improvement of fiber specific resistivity, tensile strength and tensile modulus. Therefore, the nearly stoichiometric SiC fiber has good comprehensive performance.
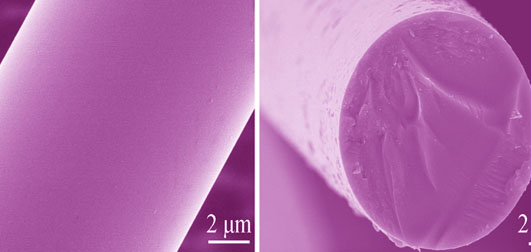
|
|
|
Fabrication and Property of AlN-BN Composites by Hot Isostatic Pressing
PENG Xu, ZHU De-Gui, LI Yang-Xu, ZHOU Jia-Min, LV Zhen, GUO Peng-Chao
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 535–541
 Abstract
Abstract(
932 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
1061
)
AlN-BN composites were fabricated by hot isostatic pressing (HIP) without sintering aid, using aluminum nitride (AlN) and boron nitride (BN) powders as raw materials. The effects of HIP temperature and pressure on microstructure and properties of composites with two different raw material ratios (molar ratio) were investigated. The results show that increasing amount of BN has little impact on densification, but decreases the hardness and thermal conductivity while increases the volume resistivity. The higher the density of the composite is, the higher thermal conductivity, volume resistivity and hardness are. The thermal conductivity and volume resistivity values conform the formula: ![]() . AlN-BN composites with the ratio of nAlN:nBN = 75:25 were prepared at 1600 ℃, 90 MPa and a dwell time of 3 h by HIP, achieving density of 98.03%, thermal conductivity of 77.29 W/(m·K) and a volume resistivity of 1.35 × 1015 Ω·cm. . AlN-BN composites with the ratio of nAlN:nBN = 75:25 were prepared at 1600 ℃, 90 MPa and a dwell time of 3 h by HIP, achieving density of 98.03%, thermal conductivity of 77.29 W/(m·K) and a volume resistivity of 1.35 × 1015 Ω·cm.
|
|
|
Influence Factors of Preparing Carbon-encapsulated Iron Nanoparticles by Gaseous Detonation Method
YAN Hong-Hao, ZHAO Tie-Jun, SUN Gui-Lei, LI Xiao-Jie, HUN Chang-Hong
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 542–546
 Abstract
Abstract(
555 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
860
)
Effects of molar ratio of hydrogen to oxygen and ferrocene mass on synthesis of carbon-encapsulated iron nanoparticles (Fe@C) were studied. Fe@C were prepared by using ferrocene as material resource, which decomposed by high temperature and high speed caused by hydrogen and oxygen detonation in homemade detonation tube. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscope and high resolution transmission electron microscope and it can be found that the molar ratio of hydrogen to oxygen, and ferrocene mass interact each other in the preparation of Fe@C. The molar ratio of hydrogen to oxygen mainly influences the morphology, particle size and dispersion of Fe@C, while ferrocene mass has a great affect on the synthesis of Fe@C. Part of iron element will be oxidized at small dosage of ferrocene, on the contrary, ferrocene couldn’t be decomposed completely. When the molar ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1, ferrocene mass ranges in 2.5-3.5 g, spherical or ellipsoidal like Fe@C is prepared with a clear core-shell structure, and thickness of carbon shell at about 10 nm. In consideration of particle size uniformity, morphology structure and dispersion, the best condition for preparing Fe@C is, the molar ratio of hydrogen to oxygen at 2:1, ferrocene mass at 3.5 g.
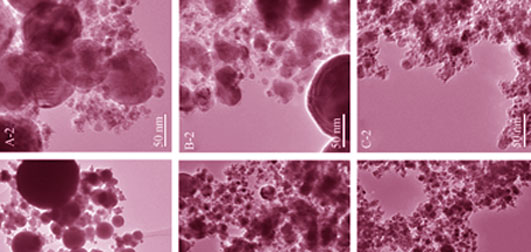
|
|
|
Isothermal Crystal Growth Behavior of CaSiO3 in Ternary Oxide Melts
LIU Jing-Jing, HEULENS Jeroen, GUO Mu-Xing, MOELANS Nele
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 547–554
 Abstract
Abstract(
1332 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(384KB)(
984
)
The process of isothermal wollastonite (CaSiO3) crystallization in the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system was simulated using a phase field model coupled with the FACTSage Toxide thermodynamic database. The effects of composition and temperature on the crystallization behaviour were studied. The simulations show that for the considered cases, the wollastonite morphology is mainly determined by anisotropy in the interface energy and hardly affected by anisotropy in the interface kinetics. In agreement with the observations from in-situ experiments, the simulations show a transition from planar to dendritic growth with decreasing temperature and the dendritic structure becomes finer when the temperature is decreased in further. The growth rates and dendrite tip radii obtained in the simulations agree well with Ivanstov’s theory and are of the same orders of magnitude as those measured experimentally.
|
|
|
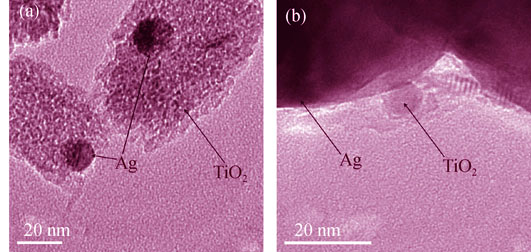
Preparation of Silver Nanoparticle Loaded Mesoporous TiO2 and Its Photocatalytic Property
WANG Hui-Lei1,2, LIU Xiao-Heng 1
2016 Vol. 31 (5): 555–560
 Abstract
Abstract(
2606 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(419KB)(
977
)
A series of Ag-modified mesoporous titania (TiO2) particles with various silver contents were prepared by photoreduction. The prepared Ag-TiO2 samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX) and UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopic (DRS) techniques. The visible light photocatalytic property was demonstrated for photodegradation of methylene blue (MB) solution. The results showed that Ag nanoparticles were firmly immobilized on the TiO2 surface, which improved electron-hole separation by forming the Schottky barrier at the Ag-TiO2 interface. The diffusion of reflectance UV-Vis spectra were also served as an indication that the Ag-TiO2 samples displayed higher red shifts in comparison with un-modified TiO2 sample. Under visible light, the optimal photoactivity was obtained for the sample m-TiO2-Ag- 2.0wt%. The TiO2-Ag catalyst is likely to be used again for a number of times without any additional treatment.
|
|