|
|
Preparation and Biological Application of Graphene Quantum Dots
SUN Xiao-Dan, LIU Zhong-Qun, YAN Hao
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 337–344
 Abstract
Abstract(
1666 )
 HTML
HTML(
21)
 PDF
PDF(473KB)(
2047
)
As the derivatives of graphene, graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have the excellent properties of graphene, and photoluminescence (PL) properties that ordinary graphene does not possess, which is attributed to quantum confinement effect and boundary effect. Moreover, GQDs perform well in terms of cytotoxicity and biocompatibility. Recently, the synthetic method of GQDs is increasingly diverse, which is usually divided into two main groups: top-down and bottom-up. With increasing application of GQDs in biomedical field, higher requirements on their morphology and size control are put forward. In this paper, we focus on the synthetic methods that are promising to control morphology and size of GQDs. Advantages and disadvantages of these methods are listed and analyzed comparatively. The biological applications of GQDs, including biological imaging, biological sensors, drug delivery and antibacterial agents, etc. are introduced. Suggestions on the choice of synthetic method for preparation of GQDs are given based on the requirements of diverse applications. The remained problems and the development directions in the research of GQDs are put forward.
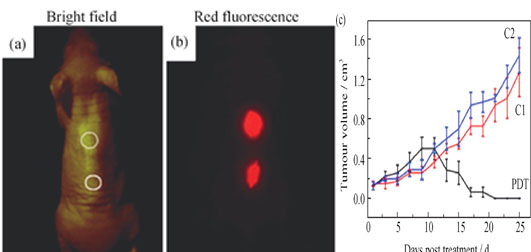
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Graphene-MoS2 Composite Anode Materials
LIU Zhan-Qiang, TANG Yu-Feng, LIN Tian-Quan, BI Hui, YU Liu-Tao, HUANG Fu-Qiang
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 345–350
 Abstract
Abstract(
1024 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(485KB)(
1265
)
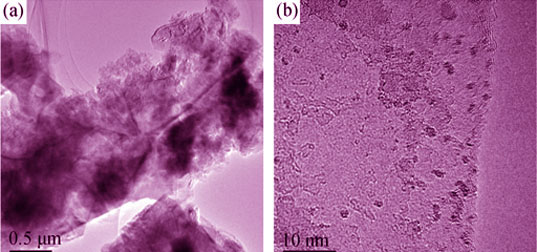
To meet the high performances of lithium ion batteries, it is very important to develop novel anode materials with high electrochemical capacity to replace the current carbon based materials. Molybdenum disulfide is widely known as a potential anode material and graphene is an effective additive for achieving the electrochemical properties of MoS2. In this study, with the aid of mechanical milling, edge-opened graphite was designed to be exfoliated into graphene by layered MoS2 to form composite anode materials, Gr/MoS2. This method was applicable to prepare Gr-MoS2 composites in large scale. The composite anode samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, EDS, HRTEM, Raman spectra, electrochemical testing. The results showed that the graphite with large size disappeared and element carbon was uniformly distributed in the ball-milling treated composite. With increase of the mass ratio of MoS2 to edge-opened graphite, the content of graphene in the obtained composite increased, but with more defects existed in the structure. The optimized Gr-MoS2 composites displayed good charge/discharge character and the capacity still maintained at 450 mAh/g after 55 charge/discharge cycles at a current density of 1 A/g.
|
|
|
In-situ Preparation and Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Performance of N-doped Graphene@CNF
SHI Qi, LEI Yong-Peng, WANG Ying-De, WANG Zhong-Min
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 351–357
 Abstract
Abstract(
1755 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(599KB)(
1027
)
By combining the techniques of electrospinning and heat-treatment, N-doped graphene (NG) were in situ grown on cobalt-containing electronspun carbon nanofibers (CNF) to form three-dimensional (3D) interconnected fiber network structure. The effect of cobalt (Co) content on the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity of the as-prepared samples was studied. It is demonstrated that both the formation of NG and introduction of Co significantly increase the electrocatalytic activity. The hybrid shows optimized ORR performance when the weight ratio of Co(NO3)2·6H2O to PAN in electronspun solution is 1: 10. The as-obtained catalyst exhibits superior ORR catalytic performance with onset potential of 0.84 V (vs RHE), near four electron transfer pathway. In addition, the sample presents better stability and methanol tolerance than Pt/C in alkaline media. As-obtained interconnected fiber networks facilitate electron and mass transfer to provide more active sites, favorable to the enhancement of electrocatalytic activity. This strategy is also available to prepare other 3D interconnected fiber composites for using in energy and environmental fields.
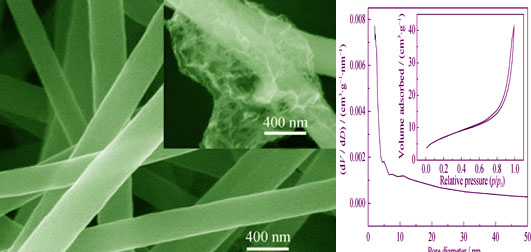
|
|
|
p-type CuI Films Grown by Iodination of Copper and Their Application As Hole Transporting Layers for Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
LIU Chang, YUAN Shuai, ZHANG Hai-Liang, CAO Bing-Qiang, WU Li-Li, YIN Long-Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 358–364
 Abstract
Abstract(
1506 )
 HTML
HTML(
21)
 PDF
PDF(588KB)(
1691
)
γ-phase copper iodide (γ-CuI) is a wide bandgap p-type semiconductor with a band gap of 3.1 eV, which is suitable for optoelectronic devices like light-emitting diodes and solar cells. A simple and convenient method of iodination of copper film to prepare CuI film was reported. The effects of iodination time, reaction temperature, and copper/iodine ratio on the transparent and conductive properties of CuI film were explored. CuI films with high transmittance over 75% in the visible range and low resistivity of 4.4×10-2 Ω·cm were grown under the optimized iodination time (30 min) and iodination temperature (120℃). The CuI films were adopted as hole transporting layers for CuI/CH3NH3PbI3/PCBM inverted planar perovskite solar cell and a maximum photovoltaic efficiency of 8.35% was obtained. The influences of the transparent and conductive properties of CuI films on the solar cell photovoltaic efficiency were also discussed.
|
|
|
Hydrophobic and Environment-resistant Properties of SiO2/TiO2/SiO2-TiO2 Multilayer Antireflective Films in Wide Solar Spectra Range
TAN Man-Lin, ZHANG Li-Jie, WANG Xiao-Wei, MA Qing, FU Dong-Ju, ZHANG Wei-Li, LI Dong-Shuang, CHEN Jian-Jun, ZHANG Hua-Yu
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 365–371
 Abstract
Abstract(
734 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(458KB)(
1106
)
In the help of coatings optimization design using TFCcal program, wide spectrum antireflective SiO2/ TiO2/SiO2-TiO2 multilayer films with thickness precisely controlled were prepared on low iron glass using sol gel process and Czochralski method. The thickness of above layers were separately set as 80.9 nm (SiO2-TiO2, inner layer), 125.0 nm (TiO2, inter-layer) and 95.5 nm (SiO2, outer layer) according to the results of calculation. A high transmission and highly hydrophobic film was prepared by Czochralski method combined with methyl triethoxysilane (MTES) SiO2 modified base-catalyzed sol. The average optical transmittance could reach 97.03% in the wavelength range of 400-700 nm. After annealing treatment, the surface water contact angles were almost around 131.5°. Furthermore, the optical transmittance only reduced 0.143% after aging for two months, showing that the prepared SiO2/TiO2/SiO2-TiO2 multilayer antireflective films had excellent hydrophobic and environment resistant properties.
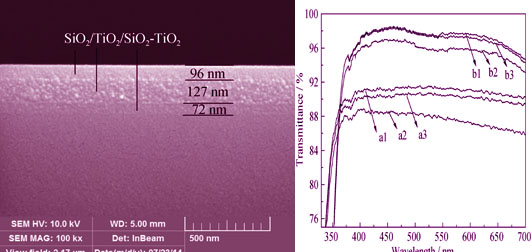
|
|
|
Improved Preparation Method and Luminescence Properties of LuTaO4:Ln3+(Ln=Eu,Tb) Thin Film
WU Shuang, LIU Bo, QIU Zhi-Che, CHEN Shi-Wei, ZHANG Juan-Nan, LIU Xiao-Lin, GU Mu, HUANG Shi-Ming, NI Chen
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 372–376
 Abstract
Abstract(
615 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(426KB)(
658
)
LuTaO4 is a kind of novel material for radiation detectors, but using it to prepare high-quality and transparent thin film is of great challenges. In our previous study, high-quality LuTaO4 thin film was prepared with thickness of single film only about 60 nm, but multilayers film easy to crack. In this study, to ensure no cracking and high transparency of thin film, PVP was chosen as adhesive and single LuTaO4:Ln3+(Ln=Eu,Tb) film of 100 nm was prepared by modulating solid and PVP content through lots of exploration, with improved luminescence properties and high transparency simultaneously. This method lays the foundations for preparation of high-quality applicable LuTaO4:Ln3+(Ln=Eu,Tb) thick film.
|
|
|
Fabrication of b-oriented MFI Film via Langmuir-Blodgett Technique
NIAN Pei, YU Ting, SU Mei-Hui, WANG Zheng, ZHANG Bin-Xing, LI Shan, SONG Zhi, MA Qiang
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 377–382
 Abstract
Abstract(
952 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(454KB)(
1549
)
A compact and highly b-oriented MFI-type zeolite monolayer was fabricated by assembling anisotropic zeolite micro-crystals extending over the centimeter scale by Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) method. The LB monolayer was subsequently employed as a seed layer for the secondary growth of highly b-oriented and defect-free MFI zeolite films. Firstly, LB technique was used to assemble a highly b-oriented MFI type zeolite monolayer on stainless steel substrates and platinum electrodes at an optimum target pressure of 20 mN/m constantly. Secondly, the precursor pretreatment method for preparing highly b-oriented MFI films was proved to be achievable. The crystal intergrowth and orientation of the MFI films were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The experimental results confirmed that the precursor pretreatment method was an effective route to suppress the undesired a-oriented twin growth during the secondary growth step. Finally, the highly b-oriented MFI-type zeolite film modified platinum electrodes were further tested as the working electrodes in an aqueous solution including [Fe(CN)6]3- with a diameter of 0.72 nm. Cyclic voltammetry experimental results demonstrated that the b-oriented MFI films fabricated by the Langmuir-Blodgett method were defect-free.
|
|
|
Preparation of Superhydrophobic Surface Based on SiC Particulate Reinforced Composite
BAO Xiao-Hui, MING Ping-Mei, BI Xiang-Yang
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 383–387
 Abstract
Abstract(
775 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
786
)
Micro- and nano-structures were prepared based on SiC particulate reinforced composite substrate using electrochemical etching process, and effects of current density and etching time on morphology characteristics and superhydrophobicity of the etched surfaces were investigated. The results show that a special hierarchical structure consisting of particle-shaped microstructures and nano-structrues (particle- or squama-shaped) is formed on the etched SiC/Al composite at the current density of 6 A/dm2, which keeps almost unchanged during etching period. Under optimized process conditions, superhydrophobic surface can be obtained, achieving a water contact angle of up to 160.7° and an extremely small tilting angle of 4°. All these data demonstrate that SiC/Al composite has potential to be used as self-cleaning surface.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Magnetoelectric Properties of NiFe2O4-BiFeO3 Nanotubes
HAN Wei, YANG Shu-Min, LI Hai-Tao, QI Yun-Kai, GU Jian-Jun
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 388–392
 Abstract
Abstract(
887 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(430KB)(
885
)
xNFO-(1-x)BFO (NFO-BFO) nanotube arrays were fabricated by means of Sol-Gel method utilizing nanochannel alumina as templates. Scanning electron microscopy study revealed that the outer diameter of nanotube was about 70 nm, and the internal diameter was about 50 nm, the length was about 80 μm. Meanwhile, ferroelectric phase BFO of perovskite structure and ferromagnetic phase NFO of spinel structure were formed through self-assembly growth in X-ray diffraction patterns. Significant ferromagnetic and polarized characteristics of nanotube arrays were demonstrated by means of magnetic and ferroelectric measurement at room temperature, and the direction of easy magnetization was along the long axis. With increasing ratio of NFO, the magnetic and polarized properties of nanotube arrays increased gradually. The calculation results of NFO’s ferromagnetic contribution indicated that magnetoelectric coupling effect existed in the NFO-BFO composite nanotube arrays.
|
|
|
Effects of Al and O Content on Transformation from SiAlCO to Si(Al)C Fibers after High Temperature Treatment
YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 393–400
 Abstract
Abstract(
573 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(553KB)(
756
)
Continuous SiAlCO fibers were prepared by polymer-derived method using polyaluminocarbosilane (PACS) with various Al contents as precursor. The O content of the fibers was controlled by different curing methods. The effects of the Al and O content on SiCxOy decomposition, β-SiC grain growth, and fiber morphological evolution in the heat-treatment process were investigated. The results reveal that SiCxOy decompostion initiates at 1300℃ and completes at 1700℃ for all kinds of fibers, which is irrelevant to Al and O contents. Al in the fibers is beneficial to reduction of both coarse SiC crystallites and interconnected pores on the surface, and increases suppressing effects on the growth of β-SiC under the tempertature above 1700℃, resulting in densification. Excessive carbon is eliminated as CO and CO2 by oxygen from SiAlCO fibers during annealing process. However, excessive oxygen creates big pores in fibers, harmful to densification. A densified Si(Al)C fiber with a decently large crystallite size of β-SiC can be achieved with an optimal Al and O content of 0.6wt% and 9wt%, respectively.

|
|
|
Mechanism and Criterion of Spontaneous Breakage of Tempered Glass
BAO Yi-Wang, LIU Zheng-Quan
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 401–406
 Abstract
Abstract(
1556 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(326KB)(
1914
)
Tempered glass is widely used in building and furniture as a type of safety glass. However, spontaneous breakage of tempered glass is a serious problem known as "glass cancer" characterized by sudden and catastrophic. It is important to reduce, prevent and predict this phenomenon of spontaneous breakage of tempered glass through preparation and application. This study focused on the mechanism of spontaneous breakage of tempered glass and provided the answers on the reasons of spontaneous breakage. The critical conditions including internal and external influence factors on spontaneous breakage were discussed. It is demonstrated that the spontaneous breakage of tempered glass is caused by stress concentration in glass itself while the stress concentration may result from various particles or defects in the glass. Furthermore, local strength is defined for tempered glass which is non-linear distributed along thickness of the glass together with residual stress. The maximum of the local strength occurs at surface of tempered glass, while the lowest value is at neutral layer. The fundamental reason behind spontaneous breakage of tempered glass is that the stress concentration in the glass exceeds local strength, while impurities, such as nickel sulfide or monolithic silicon particles traditionally considered as the breakage causes, are actually indirect causes. A criterion for spontaneous breakage of tempered glass is also revealed which is useful for analysis of breakage of glass.
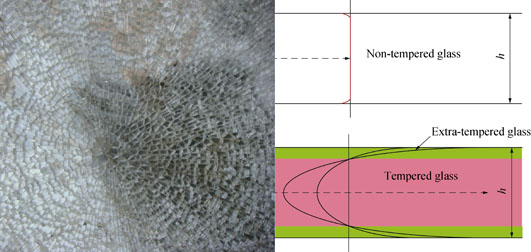
|
|
|
Photocatalytic Performance of Nano-TiO2/Diatomite Composite
ZHANG Guang-Xin, DONG Xiong-Bo, ZHENG Shui-Lin
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 407–412
 Abstract
Abstract(
834 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(628KB)(
938
)
Nano-TiO2/diatomite composite was synthesized by hydrolysis-deposition method using diatomite as supporter and titanium tetrachloride as precursor. The prepared composite was characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and N2 adsorption-desorption. The photocatalytic property of composite was determined by Rhodamine B as a target pollutant. The effects of various parameters that affect the photocatalytic properties of composite were studied. The results show that anatase TiO2 loaded on the surface of diatomite in agglomerate and disperse states. The catalyst dosage, dye solution pH, inorganic ions and illumination intensity could affect the photocatalytic activity of TiO2/diatomite composite in different degrees. The photocatalytic degradation rate of Rhodamine B was up to 99.8% under the conditions as follows: 10 mg/L initial dye concentration, 1.0 g/L catalyst dosage, 300 W UV light intensity, and 60 min illumination time.
|
|
|
Titanium Dioxide Particles Modified by Salicylic Acid and Arginine and Their Photocatalytic Reaction on Oil-Water Interface
LI Lei, ZHANG Qiao-Ling, FAN Hong-Lei, LIU You-Zhi, WEI Bing, FENG Yu-Jie
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 413–420
 Abstract
Abstract(
885 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(637KB)(
956
)
Salicylate acid and arginine-modified TiO2 particles (TiO2-SA/Arg) were successfully fabricated by impregnation approach using salicylate acid and arginine grafted onto the surface of nano-TiO2. The morphology, structure and properties of modified samples were characterized by means of Fourier-transform infrared spectroscope (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), thermogravimetry ansysis (TGA), ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscope (UV-Vis DRS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM), surface contact angle analysis, and particle size distribution analysis. The nitrobenzene adsorption capacity and the ability to be attracted to the oil-water interface of the modified samples were also confirmed. Results revealed that salicylate acid and arginine were modified to TiO2 surface by chelation and bridging structure, respectively. The modified TiO2 had better hydrophobicity, dispersion properties and adsorption capacity of nitrobenzene than the unmodified TiO2. A stable O/W Pickering emulsion was successfully fabricated via the photocatalyst stably adsorbed to oil-water interface. Nitrobenzene in Pickeing emulsion-based photocatalytic reaction system, stabilized by modified photocatalyst, showed a higher removal rate of high concentrations of nitrobenzene than the suspension system.
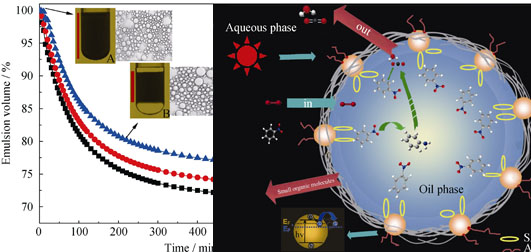
|
|
|
Microwave-assisted Preparation of Copper Hydroxyphosphate and Characterization of Photocatalysis under Visible Light
HU Xiao-Xia, ZHAO Lin, ZHAO Shu-Yu, LI Rong, XING Yan-Jun
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 421–426
 Abstract
Abstract(
987 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(512KB)(
797
)
Copper hydroxyphosphate (Cu2(OH)PO4) was quickly synthesized by microwave-assisted method at low temperature (< 100℃) and normal atmosphere pressure, then characterized by XRD, SEM and Raman spectra. The synthesis parameters were investigated by a series of controled experiments. It is found that molar ratio, initial concentration of CuCl2 and NaH2PO4, and surfactant species were crucial factors determining the formation and morphology of Cu2(OH)PO4. Cu2(OH)PO4 synthesized at different [PO43-] (n(Cu)/n(P)=2) exhibited a various morphologies including grain-like, prism and long-prismatic. Addition of anionic surfactant and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) greatly affects Cu2(OH)PO4 final morphology. The photocatalytic degradation of Cu2(OH)PO4 on methylene blue (MB) was evaluated with addition of H2O2 under visible light irradiation. The results showed that Cu2(OH)PO4 synthesized at conditions when n(Cu)/n(P)=2, [PO43-]=0.0025 mol/L, 6.0 g urea and 0.10 g SDS, microwave heating at 80℃for 30 min exhibited best visible-light photo-degradation activity. The increase in HO· formation in the presence of Cu2(OH)PO4 and the inhibition of HO· generation by adding HO· scavengers (t-butanol) indicated that HO· generated in the reaction system was responsible for the enhanced MB decomposition. Cu2(OH)PO4 exhibited excellent stability and effectiveness after 5 consecutive runs in terms of photodegradation of MB.
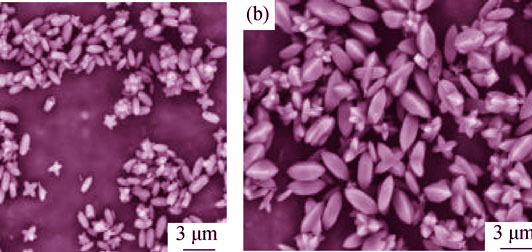
|
|
|
Degradation of Chemical Warfare Agents by Germanium-doped Nanosized TiO2 under Simulated Sunlight Irradiation
SHEN Zhong, ZHONG Jin-Yi, ZHAO Yuan-Zhong, CUI Yan, CHEN Li-Kun, ZHENG He
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 427–433
 Abstract
Abstract(
782 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(919KB)(
913
)
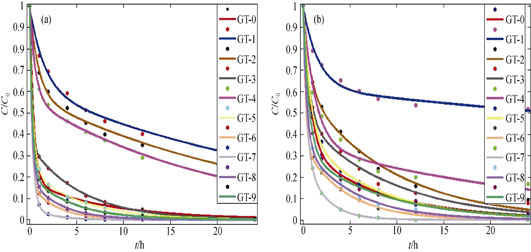
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles doped with varying amounts of germanium were prepared by homogeneous precipitation method. To investigate the relationship between doping content and photocatalytic activity, the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulphide (2-CEES) and dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP) on the prepared samples were examined, and the data were fitted by a kinetic equation. After that, physical properties of the samples were determined by XRD, UV-Vis, BET, BJH, SEM, and TEM. For consideration of toxicity, volatility, flammability, and solubility, hydrofluoroether (HFE) was first used as dispersion solvent. Ge-TiO2 was dispersed in HFE-458 (HCF2CF2CH2OCF2CF2H), and the disinfection efficiency of sulphur mustard (HD), soman (GD) and S-2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl O-ethyl methylphosphonothiolate (VX) were studied under the simulated sunlight irradiation. These results show that Ge (6.24wt%)-TiO2 exhibits the best photocatalytic performance. Appropriate amount of Ge dopant doesn’t change the crystal structure of TiO2, but reduces the grain size, increases the surface area, improves the light utilization, and improves the photocatalytic disinfection activity of TiO2. After reacting with Ge(6.24wt%)-TiO2 and HFE-458 suspension for 60 min, the degradation efficiency of HD, GD and VX is 98.73%, 100% and 100%, respectively.
|
|
|
A Novel Hollow Hydroxyapatite Microspheres/Chitosan Composite Drug Carrier for Controlled Release
ZHU Kai-Ping, SUN Jing, YE Song, ZHOU Jie, WANG Hui, WANG De-Ping
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 434–442
 Abstract
Abstract(
1407 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(855KB)(
1196
)
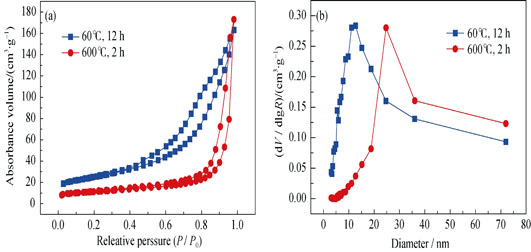
A novel composite drug carrier with excellent sustained and pH-sensitive release performance was prepared by mixing hollow hydroxyapatite (HA) microspheres and chitosan solution with pH-sensitive characteristics. The hollow HA microspheres with mesopores filled on their multilayered spherical shell were obtained by converting borate glass with a novel composition of 19Na2O-17CaO-64B2O3 (wt%). The structure, phase composition and morphology of HA microspheres were characterized by SEM, SEM-EDS, XRD, FTIR and N2 adsorption-desorption measurements. The results indicated that the HA microspheres were B-type carbonated HA with hollow structure, in which the carbonate ions occupied the phosphate sites. The drug release results indicated that the HA microspheres generated burst release at initial stage. Coating the hollow HA microspheres with chitosan (CS) reduced the vancomycin release amount and release rate significantly. Meanwhile, the release profile of vancomycin into PBS with different pH value indicated that the CS-coated composite drug carrier shows pH-sensitive release property. The cumulative percentage of vancomycin released into PBS from the CS (20 g/L)-coated composite drug carrier was 85.63%, 65.85% and 71.85% for pH 6.0, 7.4, 8.5, respectively.
|
|
|
In Situ Analysis of the Liquid Phase Sintering Process of α-SiC Ceramics
LIANG Han-Qin, YAO Xiu-Min, HUANG Zheng-Ren, ZENG Yu-Ping
2016 Vol. 31 (4): 443–448
 Abstract
Abstract(
1560 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(398KB)(
1117
)
The densification process of liquid phase sintered SiC ceramics with Al2O3 and Y2O3 as sintering additives was investigated by in situ measurement apparatus combined with conventional methods. The shrinkage curve, morphology of the sample and liquid phase formation process simulation were observed by high temperature in-situ observation furnace. The relative density, flexural strength and microstructure evolution were characterized by analysis of samples sintered at temperatures ranging from 1640℃ to 1920℃ at 40℃ interval. The obvious temperature that liquid phase began to function was confirmed between 1640℃ to 1680℃. The classical liquid phase sintering theory was testified. Highly-densified SiC ceramics were obtained by being sintered at 1880℃, of which the relative density was (99.46 ± 0.37)%, and the flexural strength was (650 ± 26) MPa.
|
|