|
|
Research Progresses of New Type Alkali-activated Cementitious Material Catalyst
ZHANG Yao-Jun, YANG Meng-Yang, KANG Le, ZHANG Li, ZHANG Ke
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 225–233
 Abstract
Abstract(
1296 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(501KB)(
1221
)
Alkali-activated solid aluminosilicate-based cementitious material is one of prospective research fields of advanced inorganic non-metallic materials. Its classification, preparation process, formation mechanism, and potential applications are reviewed in this paper. It is considered that its microstructure and chemical characteristics intensively depend on the raw materials and synthesis conditions. Geopolymers derive from alkali-activated metakaolin or fly ash with low calcium content, while the amorphous calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gels root in the chemical-activated solid wastes of granular blast furnace slag, steel slag and other solid aluminosilicate wastes with high calcium contents. Even though durability of alkali-activated cementitious materials as the building structure materials has been widely studied in the past decades, the intrinsic brittleness still restricts their applications in the field of civil and building engineering. Therefore, exploration of a new applied approach is by far the best option. In recent years, many researches report that the alkali-activated cementitious materials are used as novel precursors and catalysts for some kinds of heterogeneous reactions. The latest research progresses on alkali-activated cementitious material-based catalysts are discussed.
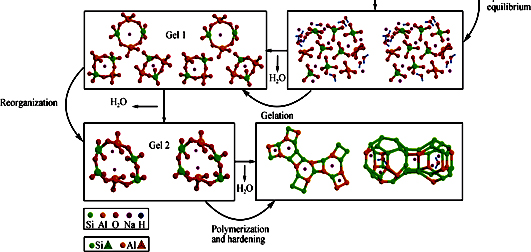
|
|
|
Influence of Calcination Temperature on Performance of NiO/γ-Al2O3 Catalyst for CO2-CH4 Reforming to Produce Syngas
MO Wen-Long, MA Feng-Yun, LIU Yue-E, LIU Jing-Mei, ZHONG Mei, Aisha· Nulahong
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 234–240
 Abstract
Abstract(
775 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(529KB)(
920
)
A series of NiO/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for CH4/CO2 reforming were prepared by altering calcination temperature using hydrolysis-deposition method, and recorded as cat-500, cat-600, cat-700, and cat-800 according to the calcination temperature. XRD and H2-TPR results showed that there was a strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) in the form of NiAl2O4 spinel in the prepared catalyst when the calcination temperature was as high as 700 ℃. Results of XRD, TG-DTG and TPH for the spent catalysts showed that the Ni grain size of cat-700 and cat-800 catalysts was 9.8 nm and 8.7 nm, respectively, lower than that of cat-500 and cat-600 catalysts (15.7 nm and 13.6 nm, respectively), indicating well dispersion of Ni grain. The deposited carbon during reaction was assigned to filamentous one, massive accumulation of which would increase bed pressure drop and decrease catalyst performance. Long term stability test demonstrated that the conversion of CO2 over cat-800 catalyst was up to 95% and kept stable in 110 h.
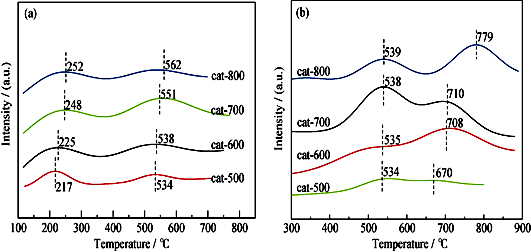
|
|
|
Fabrication of Au Nanoparticles / Bilayer TiO2 Nanotube Periodical Structure and Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Ethanol
JIN Zhao, CHEN Qi-Han, ZHENG Meng-Jia, ZHAO Peng, LI Qian, CUI Xiao-Qiang
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 241–247
 Abstract
Abstract(
903 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(562KB)(
862
)
The bilayer TiO2 nanotube periodical structure was fabricated by a two-step anodization method. The morphology of this bilayer TiO2 nanotube could be controlled by adjusting the tube diameter under different anodizing voltages. The optimized bilayer periodical nanostructure was obtained under a first voltage of 60 V and second voltage of 40 V. Au nanoparticles were then decorated onto the periodical TiO2 nanotube surface by using in-situ photoreduction. The influences of precursor concentration and irradiation time were investigated. The best morphology and distribution of Au NPs on TiO2 were obtained in 0.05 mmol/L HAuCl4 solution accompanied by irradiation for 90 min. This green method of in-situ photoreduction greatly enhanced the catalytic activity of Au nanoparticles due to the fact of avoiding reducing and protective agents. As-prepared Au/TiO2 periodical hetero-nanostructures could be directly used as working electrode and showed good catalytic activity and stability for electrocatalytic oxidation of ethanol. Except for Au nanoparticles, other metal nanoparticles such as Ag, Pd, and Cu could also be decorated onto the bilayer TiO2 nanotube periodical structure by using this method. This novel hetero-nanostructure shows great potential in application for preparing high efficient anode materials for fuel cell.
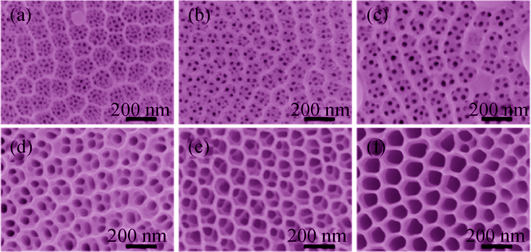
|
|
|
Rapid Synthesis and Catalytic Application of B-EU-1/ZSM-5 Composite Zeolite Based on Dual Template
YANG Dong-Hua, LI Jian-Hua, WANG Xin-Bo, GUO Chao, LV Ai-Ning, DONG Mei, Li Xiao-Feng, DOU Tao
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 248–256
 Abstract
Abstract(
733 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(592KB)(
712
)
B-ZSM-5/EU-1 composite zeolite was synthesized with different hydroxides as alkaline materials. It was found that guiding role of sodium was the strongest by comparing structure-directing effect and appearance characteristics. The surface of B-ZSM-5/EU-1 composite zeolite was smooth without obvious crystal limits. The synthetic samples were investigated by TG-DTG, N2 adsorption-desorption and NH3-TPD. The results show that the template weight loss rate of dual-mode-one-step composite zeolite is 5.67% , which is lower than that of mechanical composite zeolite (7.31%). The specific surface area, pore volume and microporous average pore size have significantly enlarged, meanwhile the amount and strength of acid have also increased, which will be favorable for the aromatization trend of methanol and the priority diffusion of xylene from the composite zeolite. The performance of the composite zeolite catalyst was evaluated in conversion of methanol to xylene. The results show that the selectivity of aromatics in the oil phase reaches 66.72% by using a dual-mode composite zeolite as a catalyst, of xylene in the aromatics reaches 46.15%, and of p-xylene in the xylene reaches 30.75%. The above results can be attributed to special pore structure for the catalytic reaction, which benefits for the priority diffusion of xylene with a smaller particle size from the B-EU-1/ZSM-5 zeolite.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Zeolite Hybrid Supported Carbon Membranes with High Hydrogen Permselective Performance
ZHANG Bing, JIANG Yuan, WU Yong-Hong, LU Yun-Hua, ZHAO Dan-Dan, WANG Tong-Hua
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 257–262
 Abstract
Abstract(
883 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
935
)
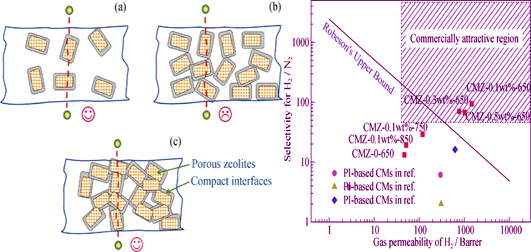
Plate supported carbon membranes were prepared by precursor of 1, 4-bis(4-amino-2-trifluoromethylphenoxy) benzene-1, 2, 3, 4-cyclobutanetetracar-boxylic dianhydride type polyimide modified with zeolite ZSM-5, through the processes of spin-coating and pyrolysis. Thermal stability of precursor, surface functional groups, microstructure, morphology, and separation performance of membranes were characterized by the techniques of thermogravimetric analysis, infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, and gas permeation, respectively. Effects of incorporating amount of ZSM-5 and pyrolysis temperature on structure and gas separation performance of carbon membranes were investigated. Results show that thermal stability and carbon residue of precursor are reduced by ZSM-5 modification. Simultaneously, the microstructure of carbon membranes becomes more compact. Incorporation of zeolite remarkably increases the gas permeability of carbon membranes. In addition, the gas permeability first decreases then increases with increased incorporation of ZSM-5. As the pyrolysis temperature elevating, both permeability and selectivity of as-obtained carbon membranes decrease. The separation performance of hybrid carbon membranes prepared at pyrolysis temperature of 650℃ is by far the Robeson's upper bound for H2/N2 system.
|
|
|
Effects of SnS Doping on Photovoltaic Performance of P3HT:PCBM Multilayer Heterojunction Solar Cells
LU Guan-Hong, ZHAO Xin-Luo, WANG Yan, ZHU Shu-Ying, SUN Jing, XIE Xiao-Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 263–268
 Abstract
Abstract(
814 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(597KB)(
768
)
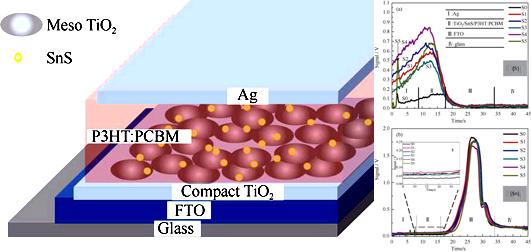
SnS was deposited on the surface of FTO/TiO2 electrodes with different molar concentration ratio of Sn2+ and S2- using successive ionic layer absorption and reaction (SILAR) method. Afterwards, the as-prepared TiO2/SnS composite electrode was assembled into a multilayer heterojunction solar cell with an architecture of FTO/TiO2/SnS/ P3HT:PCBM/Ag. The TiO2/SnS composite films were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectra analysis and Glow discharge optical emission spectrometer (GD-OES). The photovoltaic performance of solar cells were determined using UV-Vis spectra and I-V curves. Results showed that incorporation of SnS significantly improved the short-circuit current of the multilayer heterojunction solar cells. Meanwhile, the dependence of the photovoltaic performance of solar cells on the molar concentration ratio of Sn2+/S2- was investigated systematically. During the SILAR processes, a series of electrodes were prepared in the precusor solutions with different Sn2+/S2- molar concentration ratios (n(Sn2+):n(S2-)= 1:1, 1:1.25, 1:1.5, 1:1.75 and 1:2). Moreover, GD-OES method distinguished the effects of Sn2+/S2- ratio on the SnSx layer deposition. It was found that the Sn2+/S2- ratio of SILAR precursors, dominated by thickness and chemical composition of SnSx, affected photovoltaic performance of the solar cells significantly. I-V test results testified that the ratio of Sn2+/S2- molar concentration was optimized at 1:1.5, which resulted in the highest photoelectric conversion efficiency. The open-circuit voltage (Voc), short-circuit current density (Jsc), fill factor (FF), and power conversion efficiency (PCE) reached 0.373 V, 1.92 mA/cm2, 51.2%, and 0.369%, respectively.
|
|
|
Photoelectrochemical Properties of AgX(Cl, Br)-TiO2 Heterojunction Nanocomposites
ZHANG Ya-Ping, ZHANG An-Yu, YU Lian-Qing, DONG Kai-Tuo, LI Yan, HAO Lan-Zhong
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 269–273
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
810
)
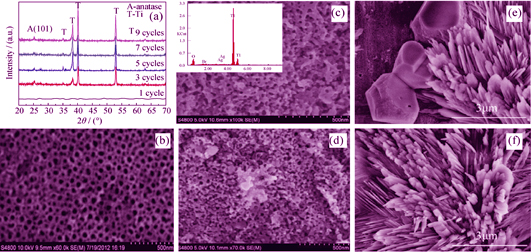
Sunlight-driven photoelectrochemical water splitting into hydrogen and oxygen presents a great way to develop green solar energy. Titanium dioxide is believed to be one of the most stable photoanode materials. Here, ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays were prepared by anodic oxidation method. Then AgCl or AgBr were successfully deposited on TiO2 nanotube arrays by dipping method. The morphology and crystal structures of AgX-TiO2 heterojunctions were tested by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The results showed that AgCl was deposited with 50 nm thickness and 1 μm length structure, while AgBr can be evenly dispersed on surface of TiO2 nanotube arrays. AgX amount increased with extending impregnation recycling time, and formed different surface morphology of nanotube arrays. Electrochemical test indicated that suitable amount of AgBr in the TiO2 nanotube arrays improved the photoelectrochemical properties, an optimum photoconversion efficiency obtained at 2.67%. Excess deposited AgX will lead to incompletely utilizing sunlight due to blocked nanotube arrays, and result in lower photoconversion efficiency.
|
|
|
Electrical Transport Properties in La0.7Ca0.3-xSrxMnO3 Thin Films
ZHANG Yuan-Yuan, TANG Xiao-Dong, CHEN Ying, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 274–278
 Abstract
Abstract(
611 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(412KB)(
982
)
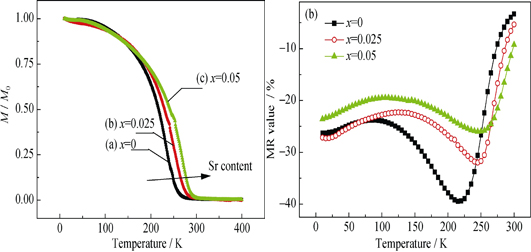
The influence of the chemical composition on the structure, magnetic and electrical transport properties of La0.7Ca0.3-xSrxMnO3 (LCSMO, x≤0.05) thin films was systematically studied. LCSMO thin films were prepared by Sol-Gel method. XRD results show that all the films have typical perovskite structure. With increase of Sr doping concentration, both Curie temperature TC and metal-insulator transition temperature TMI of LCSMO thin films increase monotonously. When Sr doping concentration x≤0.05, with increase of temperature, absolute value of MR decreases first, then increases to a maximum value around TMI, and finally decreases, which indicates that the disorder coming from phase separation around TMI contributes greatly to MR. The field dependence of MR values at certain temperature can be classified into two kinds. When the temperature is much lower than TMI, dual gradient of MR with the magnetic field is shown. The tunneling effect on the grain boundaries plays a dominant part in the low magnetic field, and this effect is particularly sensitive to the magnetic field; the suppression of spin fluctuations by magnetic field is the main reason in the high magnetic field range. When the temperature is higher than TMI, MR of LCSMO thin films changes almost linearly with the magnetic field which is mainly due to suppression of spin fluctuations by magnetic field.
|
|
|
Near-infrared Upconversion Luminescences Properties of Yb3+-Tm3+ Co-doped BiOBr Nanocrystals
LI Yong-Jin, LIU Qun, ZHOU Yu-Ting, QIU Jian-Bei, SONG Zhi-Guo
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 279–284
 Abstract
Abstract(
832 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(376KB)(
875
)
Yb3+-Tm3+ co-doped BiOBr nanocrystals were successfully prepared by hydrothermal method, and its upconversion luminescence properties was investigated. Under excitation at 980 nm light, an intense near-infrared (801 nm) accompanied by weak red (655 nm) and blue emissions (485 nm) were observed, which were attributed to the 3H4→3H6, 1G4→3F4 and 1G4→3H6 transitions of Tm3+ ions, respectively. Power dependence studies revealed that blue and red emission resulted from a three-photon process, while the near-infrared emission resulted from a two-photon process, and a possible upconversion mechanism is discussed. As the Yb3+ ions concentration increasing, the overall emission intensity increases and near infrared emission is much stronger than red and blue ones. Consequently, the ratios of near-infrared to visible (I801 nm/I485 nm) reaches 71.4. These results indicate that the Yb3+-Tm3+ co-doped BiOBr nanocrystals have potential applications in biological field as luminescence labeling probers.
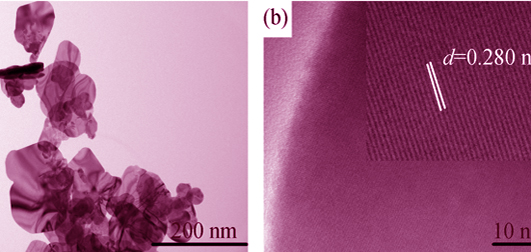
|
|
|
Stress Induced Microstructure Evolution of AlN: Er Film at Different Annealing Temperature
YANG Ming-Ming, MO Ya-Juan, WANG Xiao-Dan, ZENG Xiong-Hui, LIU Xue-Hua, HUANG Jun, ZHANG Ji-Cai, WANG Jian-Feng, XU Ke
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 285–290
 Abstract
Abstract(
726 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(416KB)(
874
)
The microstructure evolution of AlN: Er during thermal treatment was mainly characterized by weak beam diffraction-contrast imaging and high resolution phase-contrast imaging of the transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which was also supported by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy. Three regions could be observed in the TEM for the implanted samples. The region I is about 30 nm in depth below the surface, the region II is about 50 nm in depth under the region I and is the worst damaged area, and the region III is the area below the reigion II. At relatively low annealing temperature, such as 1025℃, the region I disappears. However, this area can be observed again after annealing at 1200℃. Based on the results of XRD, Raman and TEM, the interesting experiment phenomenon are explained on the view of damage recovery and stress releasing. There is a large stress in the region II due to the large radius difference between Er ions and Ga ions. In the annealing process at 1025℃, the region I is affected by the stress from region II, the lattice distortion in region I is produced. Therefore, the region I is observed as region II under TEM observation. In the annealing process at 1200 ℃, the stress in the region I is released from the surface, the lattice distortion is removed and the region I is observed again under TEM.
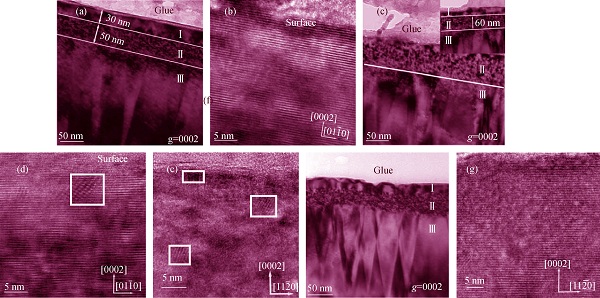
|
|
|
First-principles Calculation on Pt- and Au-modified Anatase TiO2(101) Surface
MA Xin-Guo, YAN Jie, CHEN Zi-Meng, ZHU Lin, XU Guo-Wang, HUANG Chu-Yun, LV Hui
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 291–297
 Abstract
Abstract(
888 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(556KB)(
834
)
Structure stability and electronic structures of anatase TiO2(101) surface modified by noble metal Pt and Au have been investigated using plane-wave ultrasoft pseudopotentials. The results show that the adsorption interaction is weak between noble atoms and anatase TiO2(101) surface, resulting in a slight effect on its electronic structure. However, under O-rich condition, it is found that Pt and Au atoms are favor of the Ti vacancies. Contrary to Au atom, Pt atom tends to diffuse from surface into bulk. Under Ti-rich condition, Pt and Au atoms are favor of the O vacancies. The calculated electronic structures of possible vacancy defects indicate that the appearance of surface vacancies not only avails to wet anatase TiO2(101) surfaces, but also enables their atoms to appear 5d impurity energy levels in band gap.
|
|
|
Modeling of Chemical Vapor Infiltration for Pyrocarbon within Capillaries
TANG Zhe-Peng, ZHANG Zhong-Wei, FANG Jin-Ming, PENG Yu-Qing, LI Ai-Jun, ZHANG Dan
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 298–304
 Abstract
Abstract(
728 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(515KB)(
724
)
Coupling homogeneous gas-phase reaction mechanism with lumped reaction mechanism, the pyrocarbon deposition process of the methane pyrolysis was simulated within the capillaries. The initial concentrations for the involved gas-phase species at the mouth of capillary are obtained firstly by computation of the plug flow using homogeneous gas-phase reaction mechanism during methane pyrolysis. Chemical vapor infiltration of pyrocarbon from methane in the capillary is simulated by deposition model, hydrogen inhibition model and lumped reaction mechanism. Predicted results for the mean deposition rate along the capillary depth are well validated by previously published experimental results, in which, at temperatures of 1373 and 1398 K, methane pressures are ranging from 10 to 20 kPa, and residence times are of 0.08 and 0.2 s. Simulated results show that the gradient of the mean deposition rate profile increases with methane pressure and capillary depth, and the deposition rate for transition capillary is lower than the corresponding closed capillary.
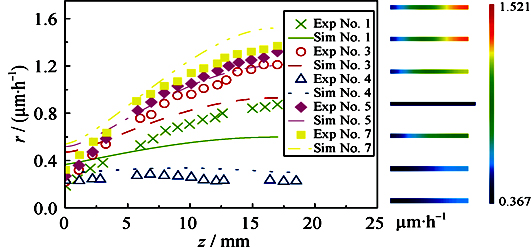
|
|
|
Porous SiC Ceramics with Multiple Pore Structure Fabricated via Gelcasting and Solid State Sintering
WANG Feng, GAO Zhao-Fen, XU Jia-Qiang, ZENG Yu-Ping
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 305–310
 Abstract
Abstract(
958 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(790KB)(
911
)
Porous SiC ceramics with multiple pore structures were fabricated via gelcasting and solid state sintering. A novel gelling agent of Isobam was applied and PMMA was used as both foam stabilizer and pore forming agent. The mechanical properties of porous SiC ceramics were investigated as functions of PMMA content, rotating speed of ball mill, and sintering temperature. With PMMA content increasing from 5wt% to 20wt%, the foaming effect was inhibited while the stability of bubbles increased. When the rotating speed was 220 r/min, the open porosities of the as-prepared SiC ceramics sintered at 2100℃ varied from 51.5% to 72.8%, and compressive strength varied from 7.9 to 48.2 MPa. With the rotating speed increasing from 220 to 280 r/min, the foaming effect was aggravated and the porosities of SiC ceramics sintered at 2100℃ increased. While the sintering temperature increasing from 2050 to 2150℃, the SiC ceramics prepared with PMMA content of 20wt% at rotating speed of 220 r/min decreased in the open porosities while increased in compressive strength.
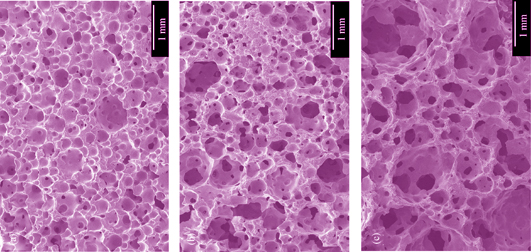
|
|
|
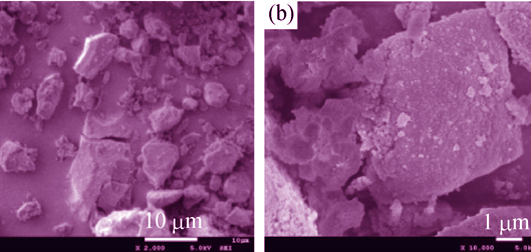
Immobilization of Lipase on KH560 Modified Silica by Sol-Gel Process
SONG Cong, YU Xiao-Wei, QIAN Dan, SUN Zhen-Zhong, JIANG Bo
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 311–316
 Abstract
Abstract(
697 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(423KB)(
802
)
An epoxy-functionalized silica support was prepared through 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxylsilane (KH560) modified silica sol in the presence of triblock copolymer F127 (F-560-S). Surface chemistry, micromorphology and pore structure of the supports were characterized by TG, FTIR, SEM and N2 adsorption-desorption, which showed that the BET surface area and pore volume of epoxy-activated supports increased with the addition of F127. The Candida Antarctica Lipase B (CALB) was immobilized on the resulting carrier by covalent link. The amounts of lipases immobilized were 10 mg/g support and 375 mg/g support on the unmodified silica (U-S) and modified silica (F-560-S), respectively. The immobilized lipases were examined as biocatalysts for transesterification of 1-phenethanol and vinyl acetate in nonaqueous medium. The effects of solvents and temperature on immobilized lipases were systematically investigated. The catalytic activity of the CALB immobilized on F-560-S was improved in various solvents, especially in polar solvents. The immobilized CALBs maintained high activity, while the control experiment using free lipase gave very low ester production in the temperature range of 0-60 ℃. Furthermore, thermal stability of CALB immobilized on F-560-S was improved as compared to the CALB on U-S was observed. The CALB immobilized on F-560-S exhibited high operational stability in organic media which still retained 88.3% of its original activity for 12 h consecutive 7 runs.
|
|
|
Effect of Crystal Size of Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate on Cytotoxicity of African Green Monkey Kidney Epithelial Cells
GAN Qiong-Zhi, ZHANG Chong-Yu, OUYANG Jian-Ming
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 317–323
 Abstract
Abstract(
531 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(518KB)(
682
)
Cytotoxcity differences of submicron (700 nm) and micron (15 μm) calcium oxalate dihydrate (COD) on African green monkey kidney epithelial (Vero) cells were investigated by scanning electron microscope, laser scanning confocal microscope, inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer, flow cytometry, microplate reader, cell proliferation assay kit and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay kit. The results revealed that both submicron and micron COD could decrease cell viability, increase LDH release amount, enhance propidium iodide staining, and up-regulate negatively-charged osteopontin expression, which indicated that both submicron and micron COD crystals could damage Vero cells. Submicron COD exhibited higher cytotoxicity and more adhesion amount than micron COD. The higher cytoxicity of submicron COD was discussed from change of crystal face, surface charge, surface adhesion sites, and hydrogen bonding between cells and crystals.
|
|
|
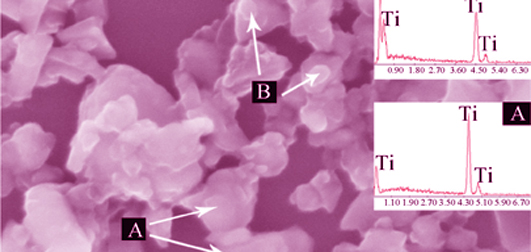
Low-temperature Solid-state Synthesis of Nanometer TiB2-TiC Composite Powder
YU Yin-Hu, WANG Tao, LIAO Qiu-Ping, MIAO Run-Jie, PAN Jian-Feng, ZHANG Du-Bao
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 324–328
 Abstract
Abstract(
1088 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(348KB)(
946
)
TiB2-TiC composite powders were prepared at low temperature in the Ti-B system with the PTFE polytetrafluoroethylene (polytetrafluoroethylene) as a chemical activator. Reaction temperature, phase composition and morphology were measured via differential thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) in order to explore the reaction mechanism, respectively. Actual solid-state reaction synthesis experiments were carried out for the same composition in an argon atmosphere furnace. It was found that TiB2-TiC composite powder could be synthesized successfully at 550℃ by adding 10wt% PTFE into the initial reactant Ti-B mixture. The FESEM image showed that the average size of the product was smaller than 400 nm. According to differential thermal analysis results, the combustion synthesis mainly includes two reaction processes: firstly, the initial reaction between titanium and PTFE particles resulting in great amounts of heat release; subsequently, the released energy triggers the solid-state reaction between titanium and boron particles to form TiB2.
|
|
|
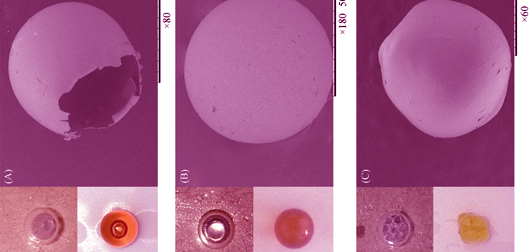
Preparation of Millimeter-scale Alumina Hollow Spheres by Oil1-in-water-in-oil2 Emulsions
LI Hao-Ting, LIAO Qi-Long, WANG Fu
2016 Vol. 31 (3): 329–336
 Abstract
Abstract(
1094 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(418KB)(
960
)
To prepare millimeter-scale alumina hollow spheres by oil1-in-water-in-oil2 emulsions, the influence factors of formation of precursor and curing process were studied. Composite droplets with paraffin liquid as inner core and alumina sol as outer shell were used as precursor. Results showed that the com-droplets had homogeneous and complete core-shell structure when emulsion generator was designed that inner oil could be injected into water phase with the size of millimeters scale. Thickness and diameter of droplets were adjusted by both controlling the injection speed of oil and water phase in the range of 30-80 μm and 800-2200 μm. In the curing process, the semisolid spheres kept hollow structure and spherical when the speed of rotation between 20 r/min to 60 r/min and the flask being put in horizontal. Finally, the prepared hollow ceramic spheres with wall thickness in micrometer-scale and diameter in millimeter-scale formed complete hollow structure and high sphericity after calcining at 1200 ℃ for 4 h. The surface of sphere was relatively smooth with roughness of about 22 nm. The main crystal of the prepared ceramic hollow spheres was alpha alumina.
|
|