|
|
Recent Progress on Preparation of Transition Metal Compounds as Counter Electrodes for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
ZHANG Chen-Le, ZHANG Pei-Xin, YUN Si-Ning, LI Yong-Liang, HE Ting-Shu
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 113–122
 Abstract
Abstract(
1385 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(706KB)(
1332
)
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have attracted extensive attention in recent years due to their simple fabrication, low cost and environmental friendliness. The production process for counter electrode (CE) as one of the key components of DSSC, will significantly affect the DSSCs development and application. Therefore, it is important to develop low cost and high performance catalytic materials instead of noble metal Pt to reduce the production cost of DSSC. Transition metal compounds with Pt-like catalytic activity have become a hot research area for CEs of DSSC in recent years, due to their wide variety and simple preparation. This review briefly addresses recent progresses of transition metal compound CEs of DSSC, focusing on their preparation methods and performance. In addition, the development trends and application prospects of CEs were also discussed.
|
|
|
Research Progress of Graphene and Its Composites as Electrodes for Capacitive Deionization
FENG Ai-Hu, YU Yun, SONG Li-Xin
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 123–134
 Abstract
Abstract(
1320 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(704KB)(
1824
)
Capacitive deionization is an energy-efficient and environment-friendly desalination method, which forces ionic species toward oppositely charged high-surface-area electrodes under an electric field to achieve the purpose of desalination. The key technology is to prepare electrode materials, which require high specific surface area, reasonable pore size distribution and excellent electrical conductivity. Graphene is a desired kind of electrode material used in capacitive deionization for its high specific surface area and wonderful conductivity. However, the actual specific surface area is far below the theoretical value due to the effect of aggregation of graphene. The three-dimensional graphene or the composite materials can overcome aggregation effect to improve the performance of electrode. The research progress of the capacitive deionization technology based on graphene and its composite electrode are reviewed in detail. The existing problems and application prospect are also objectively pointed out in this review.

|
|
|
Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon/Sulfur Composite Based on Lotus-leaves and Its Property for Li-S Batteries
YANG Shu-Ting, YAN Chong, CAO Zhao-Xia, SHI Meng-Jiao, LI Yan-Lei, YIN Yan-Hong
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 135–140
 Abstract
Abstract(
951 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(522KB)(
950
)
The carbon skeleton with high specific surface (572.1 m2/g) and large number of hierarchical pores especially micro-pores (average pore size at 3.2 nm) was obtained from common lotus-leaves by using multistage carbonization method. Ball milling and melting method were used to synthesize different S contents (48wt%/ 62wt%/71wt%) carbon/sulfur composite materials. XRD, FESEM, EDS, and TG were employed to analyze structure and morphology of the samples. The result indicated that element sulfur was uniformly accommodated in the skeletons which were composed by graphene-like layered structure and micrometer sticks. Charge/discharge tests at current density of 0.1C in the voltage range of 1.2-2.8 V showed that the initial discharge specific capacity of the carbon/sulfur composite (62wt%) reached 1246 mAh/g, and its capacity still remained 600 mAh/g even after 100 charge/discharge cycles. The results prove that the obtain composites can suppress the “shuttle effect” of polysulfide species effectively.

|
|
|
Effect of Substrate Temperature on CdTe Thin Film Property and Solar Cell Performance
CAO Sheng, WU Li-Li, FENG Liang-Huan, WANG Wen-Wu, ZHANG Jing-Quan, YU Xiao-Qi, LI Xin-Xin, LI Wei, LI Bing
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 141–147
 Abstract
Abstract(
700 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(550KB)(
1011
)
Vapor transport deposition is an excellent method for preparing large area CdTe thin films with high quality and uniformity. Polycrystalline CdTe thin films were deposited by home-made vapor transport deposition system (VTD). The effects of substrate temperature on the property of CdTe film and the performance of CdTe solar cell were investigated. CdTe thin films were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-Vis spectrometer, and Hall Effect system. The results show that the CdTe thin films deposited by vapor transport deposition are cubic phase with a preferred orientation in (111) direction. The average grain size increases from 2 μm to 6 μm and the carrier concentration increases from 1.93×1010 cm-3 to 2.36×1013 cm-3 when the substrate temperature increases from 520 ℃ to 620 ℃. This suggests that high substrate temperature can increase the carrier density significantly due to the suppressed defect recombination. The performance of CdTe thin film solar cells deposited at different substrate temperatures demonstrates that high substrate temperature (610℃) can greatly improve the efficiency, open circuit voltage and fill factor of the solar cells. But the substrate temperature higher than 610℃ will reduce the spectral response of the cells in long wavelength region, which results in the degradation of solar cell performance. The small-area CdTe thin film solar cell without back contact layer deposited at substrate temperature of 610℃ obtains the best conversion efficiency of 11.2%.

|
|
|
Structures and Electrochemical Properties of V2Ti0.5Cr0.5Ni1-xMox(x=0.02-0.08) Ni/MH Battery Anode Materials
TONG Yan-Wei, ZHANG Xue-Feng, FANG Min-Xian
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 148–152
 Abstract
Abstract(
617 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(403KB)(
881
)
In order to improve the cycle stability of Ni/MH battery, the V2Ti0.5Cr0.5Ni1-xMox(x=0.02-0.08) electrode alloys were prepared by arc-melting, and the effects of Mo content on microstructure and electrochemical properties were investigated systematically. The results show that all of the electrode materials mainly consist of a V-based solid solution phase with BCC structure and TiNi-based secondary phase which precipitates along the grain boundary of the BCC main phase. The electrochemical measurements indicate that the maximum discharge capacity of the alloy electrode increases firstly and then decreases with increasing x from 0.02 to 0.08. The cycle stability and electrochemical kinetic response of the alloy electrodes are strengthened firstly and then weakened, and reach the best performance at x=0.04.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Glucose Biosensor Based on Flower-like MoS2 Micrometer Material
ZHAO De-Rui, ZHAI Ying-Jiao, LI Jin-Hua, CHU Xue-Ying, XU Ming-Ze, LI Xue, FANG Xuan, WEI Zhi-Peng, WANG Xiao-Hua
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 153–158
 Abstract
Abstract(
1033 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(458KB)(
1188
)
Flower-like MoS2 micrometer material was successfully synthesized by hydrothermal reaction, which was then used to prepare the glucose biosensor. The performance of the prepared glucose biosensor was examined. Results indicated that as-synthesized MoS2 is flower-like structure in good crystallinity at ~3.6 μm in length with specific surface area 9.646 m2/g. The biosensor with MoS2 electrode has a high responsivity of glucose, due to good electrocatalytic activity and small electrical impedance of MoS2. Glucose detection revealed that oxidation peak current showed a good linear relationship with glucose concentration in the range of 0~20 mmol/L with a correlation coefficient (R) 0.9653. The sensitivity is 262 μA•L/mmol.
|
|
|
Adsorption of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide on Different-sized Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals
GAN Qiong-Zhi, WEN Xiao-Ling, DING Yi-Ming, OUYANG Jian-Ming
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 159–164
 Abstract
Abstract(
741 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
948
)
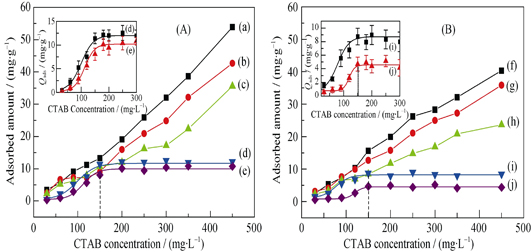
The aim of this study was to compare the adsorption difference of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) on nano/micron calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) and dihydrate (COD) crystals, so as to explore the stone formation mechanism. The crystal phase transformation before and after adsorption was analyzed by XRD and FT-IR. Adsorbed amount of nano/micron COM and COD to CTAB was detected by colorimetry. Zeta potentials of crystals were measured by Zeta potential analyzer. The adsorption curves of large-sized COM and COD (3 μm and 10 μm) formed a platform with increase of c (CTAB), while the small-sized COM and COD (50 nm, 100 nm and 1 μm) showed linear-type. The adsorbed amounts of COM and COD crystals were reduced with increase of crystal size. Adsorbed amounts of CTAB on COM were more than COD with the same size, because CTAB is more likely to adsorb to the negative charges on the COM surface. In conclusion, adsorption of crystals is related to the specific surface area and crystal structure. The adsorption quantity, absolute values of zeta potential of crystals and electrostatic repulsive-force are increased with the decrease of crystal size because of the increased specific surface area and exposed oxalate ions. The adsorption could inhibit the aggregation of urine crystals thus reduce the risk of calcium oxalate stone formation.
|
|
|
Thermal Expansion Behaviors of CdGeAs2 Crystal
ZHEN Zhen, ZHAO Bei-Jun, ZHU Shi-Fu, HE Zhi-Yu, CHEN Bao-Jun, HUANG Wei, PU Yun-Xiao, ZHONG Yi-Kai
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 165–170
 Abstract
Abstract(
820 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(746KB)(
1084
)
Thermal expansion measurements by WinTA 100 on tetragonal chalcopyrite cadmium germanium arsenide (CdGeAs2) crystal were carried out in the temperature range between 320 K and 620 K. Based on these measurements, the mechanisms of thermal expansion anisotropy is proposed. It is found that the axial thermal expansion coefficients (αa and αc) are both positive, and αa>>αc, which exhibits anisotropic thermal behavior intensively. By the least squares method, the functional relationship between structural parameters (a, c) and temperature (T) is set up, which are coincident with published literature. Furthermore, the tetragonal distortion δ=2-c/a, the interatomic distances (lCd-As and lGe-As) and the bond expansion coefficients (αCd-As and αGe-As) are calculated at different temperatures, respectively. Simultaneously, it is also found that a, c, δ, lCd-As,lGe-As, and αGe-As increase with temperature increase, while c/a and αGe-As are just the opposite. When T=360 K, αCd-As is 6.36 times of αGe-As. Hence, the difference between αCd-As and αGe-As is the main reason for the significant anisotropy of thermal expansion.

|
|
|
Electronic Structure, Plane Acoustic Velocity and Refractive Property of LiNbO3 and LiTaO3
SHAO Dong-Yuan, CHENG Nan-Pu, CHEN Jing-Jing, LI Xiao, CHEN Zhi-Qian, LI Chun-Mei, HUI Qun
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 171–179
 Abstract
Abstract(
904 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(746KB)(
1475
)
Lattice parameters, electronic structures and elastic constants of lithium niobate and lithium tantalate were calculated with the plane wave pseudopotential method based on the first-principles density functional theory. The results show that calculated lattice parameters and elastic constants are in consistent with the corresponding experimental values. It was found that the bottom of the valence band and the top of the conductive band are mainly determined by electron orbits of O-2p and Nb-4d (Ta-5d). The chemical bonds theory indicate that Li, Nb (Ta) and O atoms have two types of bonds, and the Mulliken population analysis exhibits that there are two corresponding bond populations. The Nb-O (Ta-O) covalence is stronger than that of Li-O, and band length shorter than that of Li-O. Moreover, the planar acoustic velocities, studied by Christoffel equation, shows that the three-dimensional images of the planar acoustic wave consisting of a longitudinal wave and two transverse waves, indicating the anisotropic feature. The velocity of the longitudinal wave is larger than those of the two transverse waves. In xz and yz planes, not only the plane projections of the planar acoustic waves show the stronger anisotropy than those in xy plane which have a six-fold symmetry, but also the velocities of the two transverse waves are equal in [001] and  directions. The calculated static dielectric constants and optical permittivity indicate the refractive index of LiNbO3 is stronger than that of LiTaO3. directions. The calculated static dielectric constants and optical permittivity indicate the refractive index of LiNbO3 is stronger than that of LiTaO3.

|
|
|
Fabrication and Application of Small Core Chalcogenide Glass Fibers in Nonlinear Optics
GUO Wei, ZHANG Bin, ZHAI Cheng-Cheng, QI Si-Sheng, YU Yi, YANG An-Ping, LI Lei, YANG Zhi-Yong, WANG Rong-Ping, TANG Ding-Yuan, TAO Guang-Ming, LUTHER-DAVIES Barry
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 180–184
 Abstract
Abstract(
844 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(372KB)(
888
)
High purity Ge-As-Se and Ge-As-S chalcogenide glasses were synthesized by a dynamic distillation technique. Small-core step-index fibers with Ge-As-Se glass core and Ge-As-S glass cladding were fabricated through a two-step rod-in-tube approach. Supercontinuum generation was measured using a femtosecond laser as the pump. The impurities associated with C, H and O could be efficiently eliminated when Al and GaCl3 were used as the oxygen getter and C/H scavenging agent, respectively. The as-fabricated GeAsSe/GeAsS fibers have a numerical aperture of ~1.3, and show good transmitting property in the 2-9 μm spectral range. When a 22 cm long fiber with a core diameter of 6 µm is pumped with 4.6 kW peak power and 320 fs pulses at a repetition rate of 10.5 MHz at 4.0 μm, supercontinuum spanning from ~1.9 to ~8.2 µm is generated with a dynamic range of ±10 dB and an average power of ~4.5 mW.
|
|
|
Preparation and Infrared Radiation Property of Lanthanum-cerium Oxide Ceramics by (Ca,Fe) Co-doping
WANG Feng, BU Cong-Hao, YE Jian-Ke, LI Jiang-Tao, HE Zhi-Yong, ZHANG Qi-Fu
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 185–189
 Abstract
Abstract(
884 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(351KB)(
882
)
(Ca,Fe) co-doped lanthanum-cerium oxide (La1.9Ca0.1Ce1.9Fe0.1O7) infrared radiation ceramics were prepared via solid state reaction by using La2O3, CeO2, CaO and Fe2O3 as starting materials. The phase, micro-structure, chemical composition, UV-Vis-NIR reflectivity spectrum, and UV-Vis absorption spectrum of the samples were characterized by X-ray diffractometer, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer. The infrared emissivity of the samples in 3-5 μm waveband was also measured by an infrared emissometer. The phase and EDS analysis showed the co-doped sample also had fluorite structure, indicating that Ca and Fe irons entered the crystal lattice of lanthanum-cerium oxide. An impurity energy level was introduced into lanthanum-cerium oxide by co-doping of Ca and Fe irons, which enhanced the free-carrier absorption and impurity energy level absorption of the sample. This led to a significant increase of absorption and emission in the region of 0.75-5 μm, transforming lanthanum-cerium oxide ceramic from high reflection to high absorption (radiation) ceramic after (Ca,Fe) co-doping. The (Ca,Fe) co-doped sample exhibited an absorptivity of 0.88 in 0.75-2.5 μm waveband and an infrared emissivity of 0.752 in 3-5 μm waveband, increasing by 1660% and 60%, respectively, as compared with that of pure La2Ce2O7 ceramic sample.

|
|
|
Toughness and Thermal Shock of SiC Fiber/Yttria-stabilized-zirconia Composite Thick Thermal Barrier Coatings
MA Rong-Bin, CHENG Xu-Dong, ZOU Jun, LI Qing-Yu, HUANG Xia
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 190–194
 Abstract
Abstract(
852 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(425KB)(
1093
)
Using ZrO2-8wt%Y2O3 (8YSZ) and agglomerated P7216 (8YSZ and Perlite powder ) powders as raw materials, SiC fiber/YSZ (SFY) composite thick thermal barrier coatings (TBCs, >4 mm in thick) were prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spray (APS) on substrate. The microstructures of columnar coating were analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). It showed that SFY coatings had a reinforced concrete frame structure, which protected the coatings from failure caused by thickened coatings. Based on the technique of computed tomography, the porosity of TBCs were investigated. And the thermal shock, fracture toughness and thermal conductivity (TC) of both SFY and YSZ coatings were examined and discussed for the SiC fiber toughening mechanism. Test results showed that the SFY coatings had higher fracture toughness and better thermal shock resistance than the YSZ TBCs. At 25℃, the TC of SFY coatings was 0.632 W/(m·K), about 50% reduction of typical APS YSZ TBCs. Data from this study showed that the SiC fiber effectively hindered crack growth and diffusion by crack deflection and crack termination of SFY coating, which was beneficial for growing of the reticular microcrack and improving thermal shock resistance and fracture toughness.

|
|
|
Friction and Wear Behavior of Ni-SiC Composite Coating Prepared on TA15 Alloy
GUO Wen, MI Guo-Ji, ZHANG Jin-Long, WANG Zhen-Ya
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 195–200
 Abstract
Abstract(
730 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(601KB)(
911
)
Ni-SiC composite coatings were prepared on TA15 alloy by composite electroplating technology. The effects of the coating on friction and wear behavior of the substrate were investigated. The results show that the obtained coating is dense and compact, and possesses higher micro-hardness than the substrate. The coatings have superior friction and wear resistance than the substrate, as the mass losses of the coatings are much lower than those of the substrate under the same sliding conditions. The main wear mechanisms of the substrate sliding against both GCr15 and Al2O3 balls can be concluded as plough wear, adhesive wear accompanied by minor oxidation and abrasive wear. The main wear mechanisms of the Ni-SiC composite coating sliding against GCr15 ball can be set as extractions of the coating tissues and swear of the GCr15 ball on the coating surface, while the predoninate wear mechanisms of the coating sliding against Al2O3 ball could be fatigue wear and delamination abrasion.
|
|
|
Microstructures and Flexural Properties of C/C Composites Doped with CNTs by Electrophoretic Deposition
QI Le-Hua, SHU Yang, LI He-Jun, LI Yun-Yu, MA Hai-Li, SONG Qiang
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 201–206
 Abstract
Abstract(
789 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(486KB)(
1252
)
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were deposited uniformly on 1 k carbon cloth by electrophoretic deposition (EPD). After that, CNT-doped clothes were stacked and densified by pyrocarbon via chemical vapor depositon (CVD) to prepare two dimensional (2D) carbon/carbon (C/C) composites. Effects of EPD CNTs on CVD process, microstructure and flexural property of 2D C/C composites were investigated. Results show that EPD CNTs are dispersed in the plane parallel to carbon fiber surface with random orientations and a high distribution density, leading to the decrease of densification rate of EPD CNT-doped C/C composites and the formation of pyrocarbon with high Lc and small La values. EPD CNTs increase the flexural strength and modulus of C/C composites and the improvements can reach 31.4% and 13.9% when the loading of EPD CNTs is 0.74wt%, with corresponding flexural strength and modulus being 150.83 MPa and 23.44 GPa, respectively. Further increasing the dope of EPD CNTs can decrease the flexural property of C/C composites, resulting in their bulk density decrease. The introduction of EPD CNTs changes the fracture mode of C/C composites from brittle fracture to pesudo-plastic fracture, which is related to the change of pyrocarbon in microstructures and the resulted carbon fiber pullout.

|
|
|
Preparation of Zirconia Ceramics with High Density and Fine Grains by Oscillatory Pressure Sintering
LI Shuang, XIE Zhi-Peng
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 207–212
 Abstract
Abstract(
910 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(390KB)(
1081
)
To fulfill the demands of ceramic components with high strength, high toughness and high reliability in key projects, a novel oscillatory pressure sintering (OPS) method was proposed in this study. With this new method, zirconia ceramics with high relative density, fine grains, high fracture strength, and excellent reliability, were prepared. As a comparison, zirconia ceramics were sintered by pressure-less sintering (PS) method and hot pressing (HP) method at same temperature. SEM analysis shows that the oscillatory pressure inhibits the rapid grain growth of zirconia at high temperature. Statistic results indicate that the OPS zirconia presents fine grain size at 251 nm, while the average sizes of PS and HP zirconia are 451 and 298 nm, respectively. In addition, the oscillatory pressure induces plastic deformation of grains and sliding of grain boundaries, facilitating elimination of closed pores at grain boundaries. As a result, the relative density of OPS zirconia reaches approximately 99.7%. Due to the refinement of grains and the increase in relative density, the OPS zirconia presents an increase from 1003 MPa to 1572 MPa in flexural strength, and an increase from 13 to 32 in Weibull modulus. Furthermore, its resistance to low temperature degradation is also improved because of the microstructure evolution.

|
|
|
Investigation on Two Methods for Evaluating Mechanical Properties of Tube Materials
LIU Zhao, BAO Yi-Wang, WAN De-Tian, HU Chun-Lin, MA De-Long, TIAN Yuan
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 213–219
 Abstract
Abstract(
1094 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(434KB)(
962
)
Elastic modulus and bending strength of tube materials were evaluated via compressing a split ring sample or a closed ring sample for different materials. Elastic modulus was estimated from the load-displacement relationship and sample dimensions in the range of elasticity, while bending strength was derived through the critical load at fracture. In this work, four tube materials were divided in two groups to research the applicable scopes of two methods. The results indicate that the split ring is suitable for materials with high brittleness and low limit strain, while the closed ring is available for low-stiffness materials. Comparison with the three-point bending data demonstrated the validity and convenience of two methods with the respective applicable range.
|
|
|
Superior Electrochemical Performance of Graphene via Carboxyl Functionalization and Surfactant Intercalation
YU Jian-Hua, XU Li-Li, ZHU Qian-Qian, WANG Xiao-Xia, YUN Mao-Jin, DONG Li-Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (2): 220–224
 Abstract
Abstract(
1412 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(314KB)(
898
)
Superior capacitance of carboxyl functionalized and surfactant-intercalated graphene were prepared by a relatively simple with two-step solution-based processing technique. In comparison to pristine graphene, surface carboxyl functionalization and surfactant intercalation can tailor its specific capacitance from 50 F/g to 230 F/g. Meanwhile, the modified materials retain more than 95% of their capacitance after 800 charge-discharge cycles, demonstrating good cyclic stability. Surfactant itself cannot improve the performance of pristine graphene as graphene intercalated with surfactant has a specific capacitance of 45 F/g, however, carboxyl groups can dramatically enhance specific capacitance to 130 F/g. The excellent performance of functionalized graphene emphasizes the importance of controlling its surface chemistry.
|
|