|
|
Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of Rutile TiO2 Nanosheets
ZHAO Dan-Dan, YU Yan-Long, GAO Dong-Zi, CAO Ya-An
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 1–6
 Abstract
Abstract(
989 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(447KB)(
1660
)
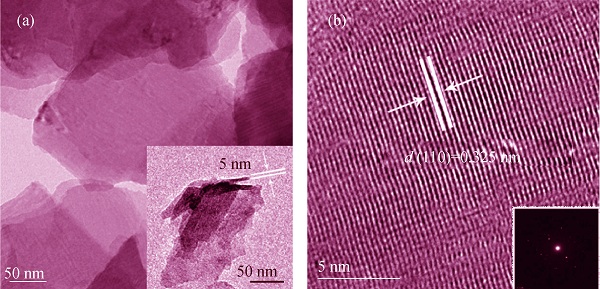
Rutile TiO2 nanosheets were prepared by Sol-Gel method, proton exchange and delamination method. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscope, X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) and photoluminescence (PL). The transference of photogenerated charge carriers was studied. It is revealed that the rutile TiO2 nanosheets (thickness 5 nm) exhibit increased specific surface area (185.7 m2/g) and enlarged energy band gap, resulting in enhanced redox ability, when compared with rutile TiO2 samples. In addition, the photogenerated charge carriers are able to transfer to the surface of nanosheets, due to their unique structure enabling photogenerated charge carriers to be effective separation during photocatalytic reactions. Therefore, the rutile TiO2 nanosheets can enhance photocatalytic activity. Forthermore, the rutile TiO2 nanosheets exhibite higher photocatalytic activity than rutile and anatase TiO2 samples on the photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol under ultraviolet irradiation.
|
|
|
Visible-light Photocatalytic Degradation Effect of Sn-Contained Layered Double Hydroxides on 4-Chlorophenol
SHAO Meng-Meng, JIANG Jun-Hui, XIA Sheng-Jie, NI Zhe-Ming, LIU Feng-Xian
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 7–7
 Abstract
Abstract(
910 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(511KB)(
1434
)
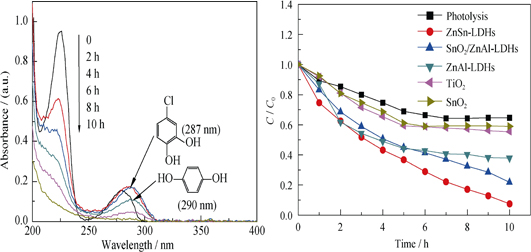
With excellent structural characteristics of layered double hydroxides (LDHs), the high photocatalytic properties of Sn-contained LDHs were synthesized by introducing Sn with photocatalytic activity into the brucite type layers. The obtained LDHs solids were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR), ultraviolet visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-Vis DRS) and Brunauer Emmett Teller (BET) surface area analysis, confirming the crystalline phase, molecular structure, photoresponsive properties and specific surface area. Their photocatalytic activities were evaluated by degradation of 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) under visible light. The results showed that ZnSn-LDHs with skeleton structure containing Sn displayed the best decomposition efficiency of 4-CP (about 92.4% removal efficiency, 34.6 mg/g removal amount) under visible light irradiation. In addition, based on the results from gas chromatography (GC) and periodic density functional theory (DFT) analysis, the photocatalytic degradation mechanism and reaction pathway of 4-CP were investigated in detail. The data presented in this study implied that the main decomposition intermediates of 4-CP were hydrochinone and 4-chloropyrocatechol.
|
|
|
Chemical Kinetics of Disproportionation Decomposition of tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Buserite-type Manganese Oxides
LU Shu-Pei, FENG Li-Li, QI Lin, WANG Li-Li, QI Xing-Yi
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 14–20
 Abstract
Abstract(
793 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(423KB)(
1278
)
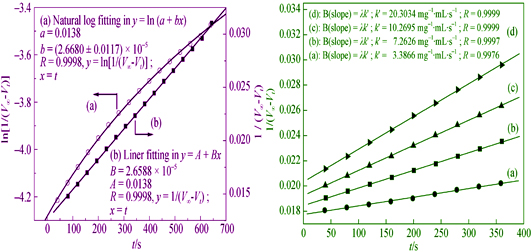
The series of four buserite-type layered manganese oxides (Me-buserites) with different interlayer cations (Me, Me = Mg2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+) were synthesized by using both MnSO4·H2O as Mn source and K2S2O8 as oxidant. The as-synthesized Me-buserites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) and N2 adsorption-desorption (BET), in order to determine their crystal phases, elemental compositions and specific surface areas, respectively. In a 25 mL batch glass reactor, the disproportionation decomposition of tert-butyl hydroperoxide was kinetically investigated with the above Me-buserites as catalysts. The kinetic analyses show that the rate law established herein is second order in tert-butyl hydroperoxide, first order in Me-buserites and then third order overall, and that the apparent activation energy ranges from 56 kJ/mol to 125 kJ/mol. In accordance with the kinetic fittings, the proposed mechanism comprises two elementary reaction steps: pre-equilibrium step and rate-determining step. In terms of the pseudo-second-order rate constant and the half an hour-accumulated O2 volume (both obtained at 338 K), the activity follows the order of Cu-buserite > Mg-buserite > Ni-buserite > Co-buserite. And a 100% selectivity towards tert-butyl alcohol is achieved over all the Me-buserites under selected reaction conditions.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Properties of Nanobelt CaSi2O2N2: Eu0.052+ Fluorescence Fibers
ZHAO Hai-Lei, CUI Bo, WANG Hong-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, ZHANG Qing-Hong
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 21–26
 Abstract
Abstract(
542 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(569KB)(
1345
)
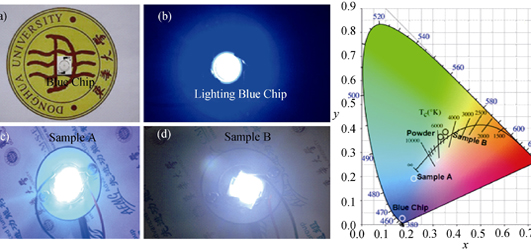
Ca0.95Si2O2N2: Eu0.052+ fluorescent nanobelt fibers for the far field encapsulation of white LEDs were prepared through electrospinning combined with gas-reduction method. By adjusting the ratio of spinning solution, the Ca-Si-O-Eu precursor nanofibers and Ca0.95Si2O2N2: Eu0.052+ luminescence nanofibers with belt structure were obtained. The obtained samples were characterized by FE-SEM, XRD, PL and HSP-3000 LED test system. The obtained sample not only keeps the morphology of nanobelt fiber but also assembles as film with a certain mechanical strength. XRD patterns of sample nitridized at 1250℃ for 4 h demonstrated that it crystallized well which was assigned to JCPDF card of the CaSi2O2N2 crystal, and it maintained CaSi2O2N2 phase after doping Eu2+ ions. Under ultraviolet excitation (400 nm), the emission spectra of Eu2+-doped Ca0.95Si2O2N2 sample contains a board peak near 550 nm, which results from Eu2+ 4f65d→4f7 transition. Based on the far field encapsulation, white LEDs with low correlated color temperature (4832 K), high-color-rendering index (86) and luminous efficacy of 125 lm/W, were fabricated using the Ca0.95Si2O2N2: Eu0.052+ nanobelt fiber mat and blue chip.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Tb3+ Doped BaZrO3 Powders
YANG Yu-Jia, WANG Jing, HE Hui-Fen
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 27–33
 Abstract
Abstract(
703 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(553KB)(
1326
)
Tb3+doped BaZrO3 powders at different Tb3+ concentrations were synthesized by hydrothermal method. The structure, morphology and luminescence properties of the synthesized materials were examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectrum (FTIR) and fluorescence spectrometer, respectively. Parts of hydrothermal products were calcinated to study the effect of temperature on luminescence properties. Analysis results showed that Tb was successfully introduced into the lattice and replaced Zr at B site of perovskite. It was remarkable that all the samples had similar morphology, which was composed of evenly distributed spheres. The broadband emission peaks of the host and the typical emission peaks of Tb3+ were observed in the BaZrO3 doped with Tb3+ under 244 nm excitation, and these peaks reach the maximum at Tb3+ ion content of 5mol%. Temperature had significant influence on their photoluminescence properties. With the calcination temperature increase, the luminescent intensity of Tb3+ doped samples was decreased.
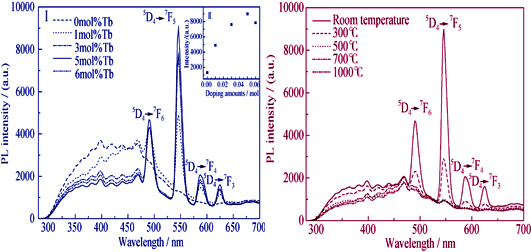
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of ZnFe2O4 Anode for Lithium Ion Battery
LIAO Li-Xia, WANG Ming, FANG Tao, YIN Ge-Ping, ZHOU Xiao-Guang, LOU Shuai-Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 34–38
 Abstract
Abstract(
861 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(402KB)(
1520
)
ZnFe2O4 materials with spinel structure were synthesized from ZnCl2 and FeCl3.6H2O by solvothermal method. Crystal structure and surface morphology were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and fourier transform infrared spectrum (FT-IR). Electrochemical performance was analyzed by constant current charging-discharging technique and cyclic voltammetry. The results showed that the particle size was about 250 nm. As an active material for lithium-ion batteries, the nano ZnFe2O4 material delivered a reversible capacity of 933.1 mAh/g at a current density of 50 mA/g. The specific charge capacity slightly decreased to 813.5 mAh/g, with a retention of 87.2% after 100 cycles. Furthermore, the material was able to release a capacity of 355 mAh/g at a current density as high as 400 mA/g, which demonstrated reasonable rate performance and moderately fast charge/discharge capabilities. Data from this study indicated that ZnFe2O4 nano-material prepared by solvothermal method is a promising anode material for lithium-ion battery with high capacity and superior cycling stability.
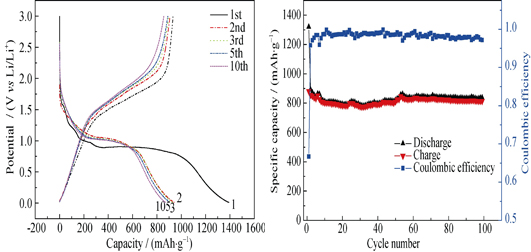
|
|
|
Preparation and Capacitive Properties of Graphite-like Porous Carbon Based on Coal Extracts
LI Jin-Hong, ZHOU Qi-Xiong, MI Hong-Yu, LI Xian, LI Hui-Ping
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 39–46
 Abstract
Abstract(
648 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(615KB)(
1435
)
By using extracts of lignites as carbon precursors, MgO as isolation agent, and KOH as activator, porous graphene-like carbon materials were prepared at 800℃ under an inert atmosphere. Porous carbon materials were characterized by FTIR, XRD, TEM and Raman. Further, electrochemical capacitive properties of porous carbons before and after activation as the electrodes were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge-discharge and impedance spectroscopic techniques. Results indicate that carbon materials after activation exhibit porous film-like shape. The specific surface areas of carbon materials before and after activation are 138.4 m2/g and 1396 m2/g, respectively. Specific capacitances of carbon materials after activation reach 533 F/g and 390 F/g at 1 A/g and 4 A/g, respectively, while those of carbon materials before activation at same conditions are 366 F/g and 198 F/g. After 8000 cycles at a current density of 5 A/g, the capacitance retentions of carbon materials before and after activation are 72.5% and 89.6%, respectively. Accordingly, after KOH activation, the specific capacitance and electrochemical stability of carbon materials are significantly improved. This study verifies that the use of the isolation agent and the activator can obtain highly flexible graphene-like porous carbon with high capacitance performance.
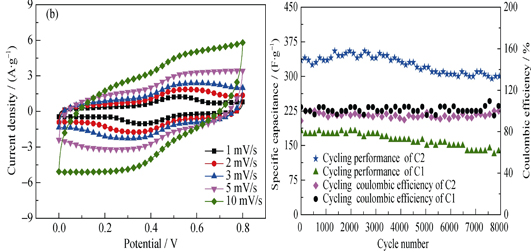
|
|
|
Effect of La, Y Additions on ZrO2-mullite Nano-composite Ceramics by In-situ Controlled Crystallizing from Si-Al-Zr-O Amorphous Bulk
TAN Xiao-Ping, QI Li-Ping, LIANG Shu-Quan
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 47–52
 Abstract
Abstract(
684 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(479KB)(
1108
)
Effects of Y2O3 and La2O3 doping on ZrO2-mullite nano-composite ceramics, prepared by in-situ controlled crystallizing from the Si-Al-Zr-O amorphous bulk, were revealed by means of DSC, XRD, SEM and TEM technologies. The results indicate that the addition of Y2O3 and La2O3 (Y2O3 <1.8wt% and La2O3 <4wt%) can effectively reduce the melting temperatures of Si-Al-Zr-O based amorphous, limit the devitrification phenomenon and is beneficial for the formation of amorphous during cooling process, without changing the main crystalline phase precipitation. For Y2O3 single doping, Y is mainly dissolved in the zirconium oxide, stabilizes t-ZrO2, and inhibits precipitation of the cordierite, and exerts little effect on the grain size. For both Y2O3 and La2O3 mixed doping, Y and La mainly locate in the glass phase, strengthen the grain boundary, of which La promotes the grain growth of ZrO2 and mullite. The appropriate doping amount of Y2O3 and La2O3 should be in the range of 1.0wt%-2.0wt% and 0.6wt%-1.2wt%, respectively.
|
|
|
Prediction of Sintering Process for ZrO2 Ceramics Based on Master Sintering Curve Theory and Its Expansion
CHEN Cheng, LI Chen-Hui, KE Wen-Ming, SHI Yu-Sheng, HE Zhi-Yong, ZHANG Qi-Fu
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 53–57
 Abstract
Abstract(
779 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(420KB)(
1666
)
Yttria stabilized zirconia compacts fabricated by cold isostaitc pressing were sintered in an in-situ measurement instrument under different heating rates (2, 5 and 8℃/min) and pressureless condition. The images were obtained by the in-situ measurement instrument and subsequently analyzed by using Image-Pro Plus 6.0. Based on the shrinkage data and corresponding master sintering curve, the sintering activation energy was eventurely calculated to be 685.7 kJ/mol. Besides predicting the final density of the compacts, the master sintering curve (EMSC) was extended and modeled presenting relationship between temperature and relative density in the sintering process under different heating rates. This study provides possibility for predicting the sintering schedule, which ensures the accuracy and repeatability of sintering time and temperature.
|
|
|
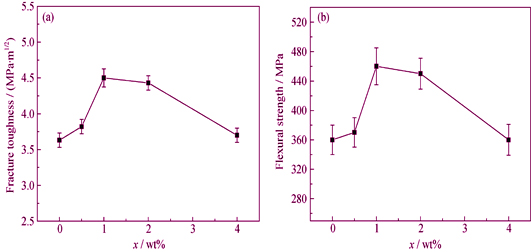
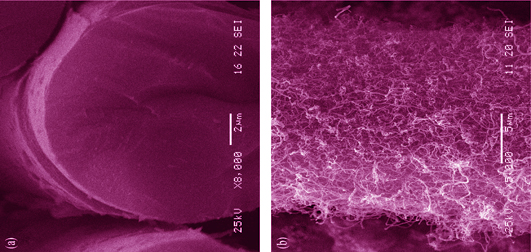
Fracture Behavior of SiC/SiC Composites with Different Interfaces
ZHAO Shuang, YANG Zi-Chun, ZHOU Xin-Gui
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 58–62
 Abstract
Abstract(
1145 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(480KB)(
1887
)
SiC fiber reinforced SiC matrix composites (SiC/SiC) are promising materials for high temperature structural applications. In this work, SiC/SiC composites with Pyrolytic Carbon (PyC) interface or Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) interface were fabricated by polymer infiltration and pyrolysis (PIP) process. Overall mechanical properties and interfacial shear strength of the SiC/SiC composites were characterized and crack growth processes were observed in situ by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results indicate that flexural strengths of two types of SiC/SiC composites are similar, but the fracture toughness of the SiC/SiC composite with PyC interface is twice as much as that of the SiC/SiC composite with CNTs interface. Cracks propagate along the fibre-matrix interface in the SiC/SiC composite with PyC interface, which can be deflected or arrested by the PyC interface, hence the composite exhibits a pseudo-ductile fracture behavior. However, the CNTs interface fails to cease the crack in the SiC/SiC composite with CNTs interface, so the initial crack propagates rapidly through the fibers leading to final main crack, and a brittle fracture mode.
|
|
|
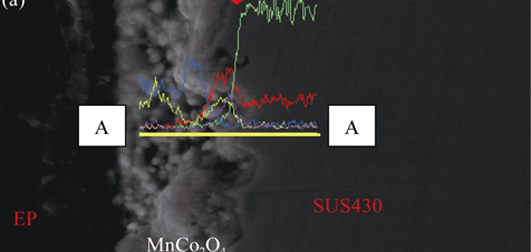
Surface Modification of SUS430 Interconnect with MnCo2O4 Coating
CAO Xi-Wen, LUO Ling-Hong, XU Xu, CHENG Liang, SHI Ji-Jun, YU Hui
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 63–68
 Abstract
Abstract(
884 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(442KB)(
1407
)
Nano-scale MnCo2O4 powder was prepared by means of Sol-Gel method. XRD and TEM were employed to analyze phase composition and microstructure of the MnCo2O4 powder. A paste was made of the powder by adding a proper amount of ethyecellulose as binder and terpilenol. The paste was coated on the SUS430 substrate by screen printing method. The MnCo2O4 coating on SUS430 alloy was sintered under the atmosphere of 95%N2 + 5%H2 at 900℃ for 3 h and then at 800℃ in air for 10 h. SEM was employed to observe the surface and cross-section of the sample with coating. The oxidation resistance and the area specific resistance(ASR) value of the sample was characterized at 750℃ in air. Finally, EDS was employed to analyze the cross-section of the sample. The results show that the powder is in single cubic spinel phase. The grains are homogeneous with size of about 150 nm. The coating that is dense contacts to alloy matrix closely with uniform thickness. After oxidation at 750℃ for 1000 h in air, the weight gain of SUS430/MnCo2O4 sample is 0.15 mg/cm2, which is only one-sixth that of the SUS430 alloy. The ASR value is 0.026 Ω·cm2, two order of magnitude lower than that of SUS430 alloy. EDS results show that Cr is mainly distributed in interface between the coating and alloy, with no distribution in the coating. The MnCo2O4 coating can effectively reduce the oxidation rate and improve the conductivity of SUS430 alloy significantly at high temperature, and restrain the volatilization of Cr successfully.
|
|
|
Effect of Plating Solution Flow Pattern on Preparation of Electroless Copper- Plated Carbon Foam under Vacuum and Ultrasonic Conditions
YANG Liu, LIU Xiu-Jun, LI Tong-Qi, HAN Rui-Lian, FENG Zhi-Hai
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 69–74
 Abstract
Abstract(
575 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1627
)
Electroless plating with assistance of vacuum and ultrasonic is an effective method to coat copper onto the inner surface of bulk carbon foam. However, it is difficult to obtain uniform copper coating. In present work, the copper coating’s uniformity was improved by forcing plating solution inside the carbon foam on basis of vacuum and ultrasonic assistance during eletroless plating process. And effect of the flow pattern on plated copper’s properties was investigated. Compared with one-direction flow of plating solution, a bidirectional flow made the weight gain rate of single cut piece >7.10% and the total weight increased up to 7.68%. The copper coating at thickness >5 µm; with better uniformity was compact, smooth and no CuO or Cu2O. The mechanical and electrical properties of Cu/carbon foam were evenly enhanced. The compression strength was increased from 0.70 MPa to 1.54 MPa, and the conductivity from 700 S/cm to 1724 S/cm.
|
|
|
Microstucture and Heat Resistance of Coated Yellow Iron Oxide Pigment
PAN Guo-Xiang, CHEN Jian, NI Zhe-Ming, CAO Feng, HU Shuang-Shuang, LIN Kai, LI Jin-Hua, ZHU Zeng-Lin
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 75–80
 Abstract
Abstract(
1065 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(566KB)(
1864
)
Poor heat resistance of iron oxide yellow pigment limits its application in plastics processing and coil coatings. Yellow iron oxide pigments coating with aluminum hydroxide were synthesized by a precipitation method using yellow iron oxide as precursor. Structure of the composite pigment is characterized using XRD, FT-IR, TG-DTA, SEM-EDS, and TEM. The effect of pH on structure and heat resistance of the pigments was investigated. All results show that iron oxide yellow coating layer is amorphous aluminum hydroxide when pH is 4. When pH increases to 6, 8 and 10, the surface coating layer is boehmite phase. The heat resistance of coated yellow iron oxide pigments is greatly improved, and the color difference value of pigments after treatment at 240 ℃ for 30 min is low, owing to the surface coating layer of boehmite structure. After coating, the iron oxides yellow maintains the original acicular structure, and pigment does not aggregate. When pH is 10, the coated iron oxides yellow composed both large stick and needle like structure, possibly because of the nucleation formation of AlOOH in the reaction process. This result may explain the special endothermic peaks of 246 ℃ appeared on the DTA curves. This research might provide theoretical and practical guidance for developing heat resistant yellow iron oxide pigments.

|
|
|
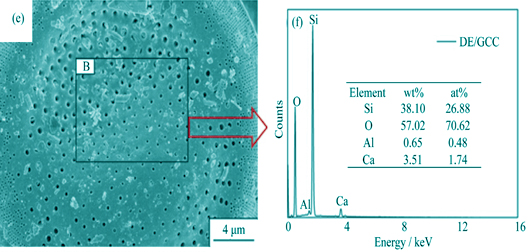
Preparation and Characterization of Humidity Control Material Based on Diatomite/Ground Calcium Carbonate Composite
HU Zhi-Bo, YAN Yang, ZHENG Shui-Lin, SUN Qin, YIN Sheng-Nan
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 81–87
 Abstract
Abstract(
621 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1288
)
Humidity control material is a kind of healthy environmental friendly material. The diatomite/ground calcium carbonate composite humidity control material (DE/GCC) was prepared by calcinations using diatomite (DE) and ground calcium carbonate (GCC) as raw materials. The obtained samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscope, Fourier transform infrared spectroscope and low-temperature nitrogen adsorption method to determine the mineral compositions, functional groups, microstructure, surface element compositions and pore structure, respectively. The moisture absorption performance of samples were tested under high relative humidity conditions (RH=70%, 80%, 90%) and the constant temperature of 30℃. The moisture absorption dynamics and humidity control mechanism were analyzed. It is indicated that the calcium silicate and calcium hydroxide are formed in the DE/GCC during the calcinations process. Compared with the raw materials, the content of mesopore increases in the DE/GCC sample, which is in favor of the capillary condensation. After 36 h test in the environment with relative humidity of 70%, 80% and 90%, the moisture contents of DE/GCC reach 7.213%, 11.159% and 14.701%, which are about 2.1, 2.9 and 3.0 fold as those of DE, respectively. The moisture absorption kinetics follows the pseudo-second-order model.
|
|
|
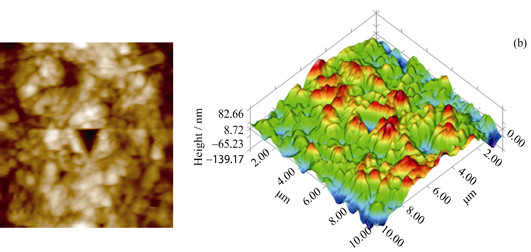
Bionic Remineralization of Acidic Etched Enamel Induced by Using Mesoporous Bioactive Glass in Natural Oral Saliva
DONG Zhi-Hong, NIE Zhi-Ping, ZHOU Chang-Chun
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 88–94
 Abstract
Abstract(
627 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(575KB)(
1258
)
Acidic etched enamel was treated with mesoporous bioactive glass (M58S) to induce enamel remineralization in natural oral saliva. By simulated brushing teeth, the M58S was adhered on the enamel surface. Then the samples were rinsed by water and immersed in natural oral saliva for different periods. Characterized by XRD, SEM, FIB-TEM, EDX, SAED, and nanoindentation, the samples showed that a new mineralized phase appeared on the surface of the treated samples after soaking for 6 h. After soaking for 24 h, a compact and homogeneous mineralized layer at the thickness of about 100 nm formed with similar structure to apatite, and ratio of calcium to phosphate which was close to the enamel’s. Under pressure of 300 µN, mineralized layer showed a scratch limited value with microhardness at (3.37±0.62) GPa and elastic modulus at (60.48±4.56) GPa, both close to 75% value of original enamel. These results indicate that mesoporous bioactive glass can rapidly repair etched enamel and prevent teeth from caries. Therefore, the mesoporous bioactive glass may be used as bionic remineralization materials.
|
|
|
Effect of Dopamine on Hydroxyapatite Deposition for Dental Restoration
XU Jin-Mei, LIU Xin-Ling, GAO Yan-Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 95–99
 Abstract
Abstract(
1045 )
 HTML
HTML(
22)
 PDF
PDF(516KB)(
1543
)
A novel and biomimetic restoration method for teeth by soaking in a simulated oral environment was reported. A biocompatible polydopamine (PDA) layer was deposited on the surface of dentin via dopamine polymerization to functionalize the surface to induce deposition of hydroxyapatite crystals. The samples were characterized by means of XPS, XRD, SEM and EDS. Results show that the coating of polydopamine layer induces the growth of hydroxyl apatite crystal on dentin surface, and improve the binding force between the hydroxyl apatite layer and the dentin surface. The optimized concentration of dopamine solution is 2 mg/mL for the uniform deposition of PDA layer on the dentin surface.
|
|
|
Tribological Behavior of Vacuum Plasma Sprayed B4C-Mo Composite Coating
LIN Chu-Cheng, KONG Ming-Guang, ZHU Hui-Ying, HUANG Li-Ping, ZHENG Xue-Bin, ZENG Yi
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 100–106
 Abstract
Abstract(
972 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
1322
)
A B4C-Mo composite coating was fabricated using a vacuum plasma spray technique, and its wear behavior was compared with that of a pure B4C coating. The microstructure of the composite coating was much more homogeneous and compact as a result of the formation of a (B, Mo) C transition phase, which effectively improved the interface between B4C and Mo splats. For this reason, the wear resistance of the composite coating was much superior to that of the pure B4C coating. The distribution of nano-sized Mo in the composite coating might also contribute to the improved tribological properties.
|
|
|
Effect of Phase Composition of Calcium Phosphate (CaP) on Bioactivity of Osteon-like Composite Scaffolds
CHEN Xue-Ning, FAN Hong-Song, WANG Hong-Jun
2016 Vol. 31 (1): 107–112
 Abstract
Abstract(
1135 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(417KB)(
964
)
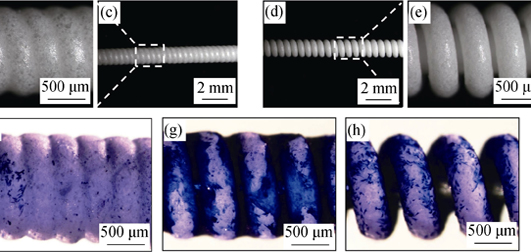
From compositional perspective, natural bone is a kind of inorganic and organic composite material; while from structural perspective, the basic structural unit of cortical bone is vascularized osteon. In this study, based on the biomimetic principle, a tissue-engineered construct was created to stimulate the basic building block of cortical bone-osteon with complex structure. To achieve this goal, a bi-layered polycaprolactone (PCL)/CaP composite scaffold was produced via a novel two-step fabrication process in the combination of electrospinning and twin screw extrusion. Its inner hollow tube was made of electrospun nanofibers, allowing the formation of a confluent layer of endothelial cells (MS-1) to resemble the Haversian canal, and its outer layer consisted of spiral PCL/CaP microfilament with high porosity, facilitating the proliferation and differentiation of pre-osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1) to form bone-like tissues. To explore the effect of material composition on scaffold bioactivity, three composite scaffolds with different outer layers were fabricated, including PCL, PCL/biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) and PCL/β-tricaclium phosphate (β-TCP). And then the influences of scaffold composition on the behaviors of pre-osteoblasts were further investigated. Compared to PCL and PCL/β-TCP, significantly more cell growth and higher calcium deposition are found on PCL/BCP scaffolds, precisely controlling the spatial distribution of different cells. Taken together, this bi-layered PCL/BCP scaffold partially mimics the complex structure of osteon, showing a promising potential in the orthopedic application.
|
|