|
|
Magnetoelectric Properties of Low Temperature Sintered CoFe2O4-(PZN-PZT) Multiferroic Composite Materials
FAN Gui-Fen, XU Xing, WANG Kai, LV Wen-Zhong, LIANG Fei, JIN Shan-Long
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 561–566
 Abstract
Abstract(
914 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(476KB)(
1001
)
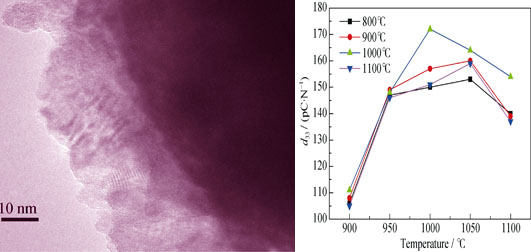
CoFe2O4-(PZN-PZT) multiferroic composite ceramics were prepared by low temperature sintering using traditional ceramic method. The influences of mixed mode, PZT shell and composition on structure, magnetic and magnetoelectric coupling properties were studied. XRD and TEM results show that CoFe2O4/PZT core-shell nanostructured particles are prepared by the Sol-Gel method. A 10-20 nm thick PZT shell formed on the surface of CoFe2O4 particle. EDS analyses show that low temperature sintering and barrier layer effectively inhibit the elements diffusion of the two phases. SEM images and magnetoelectric property measurement show that PZT shell coated on CoFe2O4 particles and the stirring process improve the magnetic particles content in com-position, match the sintering process perfectly, and improve the magnetoelectric coupling properties effectively. The coated and stirred sample CoFe2O4-(PZN-PZT) with volume ratio of 4:6 which sintered at 1000℃ show maximum magnetoelectric coupling coefficient of (18.3 mV/(cm·Oe)) at 10 kHz.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electromagnetic Absorption Performance of Ni-RGO
XU Shuang-Shuang, CHEN Gong, ZHANG Hai-Qin, CHEN Yuan, ZHAO Yan
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 567–574
 Abstract
Abstract(
964 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(652KB)(
1367
)
Electroless plating was utilized to deposit nickel nanoparticles on the reduced graphene oxide (RGO). By adjusting the nickel salt precursor concentration, three kinds of Ni-RGO with different nickel contents were synthesized, namely Ni-RGO-1, Ni-RGO-2 and Ni-RGO-5. Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction were employed to study the surface morphology and crystal structure of as-prepared Ni-RGO. The electromagnetic performance of graphene oxide and Ni-RGO was characterized. The results indicated that the permittivity of Ni-RGO was above 8, almost three times higher than that of pristine graphene oxide. Ni-RGO-1 exhibited the best electromagnetic wave absorption performance, although the concentration of nickel precursor is the lowest one among three samples. The minimal reflection loss was up to -24.5 dB for Ni-RGO-1 with a thickness of 2 mm.
|
|
|
Analogous Three-dimensional MoS2/Graphene Composites for Reversible Li Storage
LIANG Pei, XING Song, SHU Hai-Bo, ZHANG Lin, HU Chen-Li
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 575–580
 Abstract
Abstract(
1068 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(499KB)(
1025
)
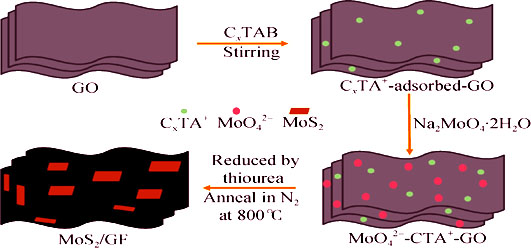
MoS2/GF composites were synthesized by hydrothermal method using graphene oxide (GO), sodium molybdate and thiourea as raw materials with assistance of different cationic surfactants (C14TAB, C16TAB, C18TAB). The investigation of as-prepared samples by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy demonstrate that the composites have presented different morphologies and microstructures which may be resulted from the cationic surfactants. Electrochemical performances for reversible Li+ storage of the composites reveal that the capacities, cycling stability and rate capability are influenced by different morphologies and microstructures. Comparison to C16TAB and C18TAB assistance, the composite synthesized with C14TAB assistance delivers a high first discharge capacity of 955 mAh/g and reversible capacity of 751 mAh/g after 50 cycles, shoowing excellent rate capability. The improvement in the electrochemical performances of the composites synthesized with C14TAB assistance is attributed to its special particle-on-sheet structure and synergistic interactions between graphene and MoS2.
|
|
|
One-pot Synthesis and Application in Asymmetric Supercapacitors of Mn3O4@RGO Nanocomposites
WANG Chao-Fei, LU Shuang, CHEN Hui-Long, GONG Fei-Long, GONG Yu-Yin, LI Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 581–587
 Abstract
Abstract(
911 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(573KB)(
924
)
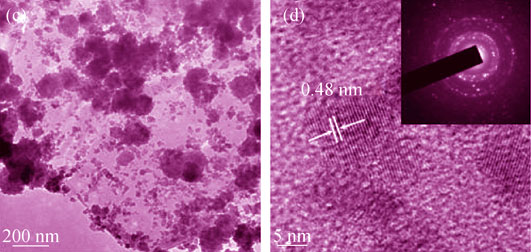
Supercapacitors have attracted dramatic attentions in recent years for their apparent advantages, such as fast charge/discharge rate, high power density and high stability. However, it is still a challenge to improve their energy density for their practical applications. One of the strategies to overcome this drawback is to broaden the working voltage of the devices through assembling asymmetric supercapacitors. Herein, Mn3O4@RGO nanocomposites were successfully synthesized by using one-pot approach with Mn(Ac)2 and GO in the mixed solvent of ethanolamine and water (3:1) without adding any surfactant. The asymmetric supercapacitors (Mn3O4@RGO//RGO) assembled with Mn3O4@RGO and RGO exhibit excellent performances in energy storage. The asymmetric supercapacitors can achieve a maximum energy density of 21.7 Wh/kg at power density of 500 W/kg and a maximum power density of 8 kW/kg at energy density of 11.1 Wh/kg, based on the total mass of active materials. The Mn3O4@RGO//RGO supercapacitors also demonstrated excellent durability retaining 88.4% of their specific capacitances even after 5000 charge/discharge cycles. The excellent performances of Mn3O4@RGO//RGO devices in energy storage can be attributed to high density of Mn3O4 nanoparticles grown directly on the surfaces of RGO nanosheets, which can dramatically improve the conductivity of materials.
|
|
|
F127 Template on Pore Structure and Electrochemical Performances of Mesoporous SnO2
ZHAI Li-Li, ZHANG Jiang, LI Xuan-Ke, CONG Ye, DONG Zhi-Jun, YUAN Guan-Ming
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 588–596
 Abstract
Abstract(
917 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(726KB)(
1079
)
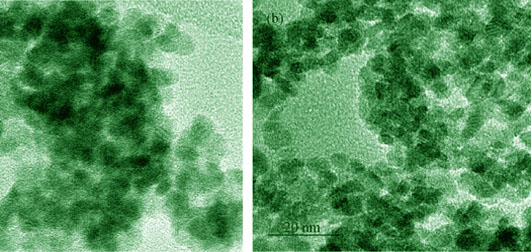
Mesoporous SnO2 was synthesized via a hydrothermal process using tin chloride (SnCl4·5H2O) and urea ((NH2)2CO) as raw materials, with a block polyether F127(EO106-PO70-EO106) as a template. The analysis results (XRD, TEM, BET, etc) show that the amount of F127 has significant influence on pore structure of mesoporous SnO2. With increasing dosage of F127, specific surface area and pore volume of the mesoporous SnO2 increase with pore size distribution relatively broad. The results of the electrochemical tests indicate that existence of mesopores not only provide the path for deinsertion and insertion of Li+, but also buffer the huge volume expansion of tin dioxide, which consequently improves the electrochemical performances of mesoporous SnO2 as an anode material. When the amount of F127 is 6.0 g, the as-prepared 6F-SnO2 with a BET specific surface area of 124 m2/g and average pore size of 4.94 nm, displays optimal cycle performance and rate performance which the reversible capacity of the 6F-SnO2 maintains 434 mAh/g at 60 mA/g after 30 cycles. In addition, the cyclic voltammetric test reveals that the reversible reduction of partial Li2O with high activity can provide additional reversible capacity.
|
|
|
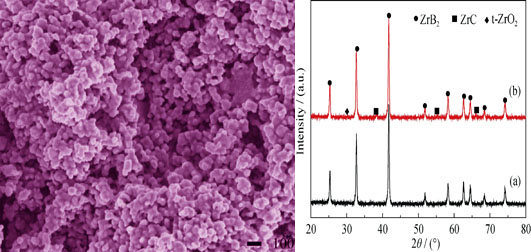
Synthesis of ZrB2 Nanoparticles by Using Xylitol
ZHAO Yue, LI Jun-Ping, WANG Ting-Yu, LI Rui-Xing, FENG Zhi-Hai, CAI Hong-Nian
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 597–601
 Abstract
Abstract(
746 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(423KB)(
971
)
ZrB2 nanoparticles were synthesized synergistically by Sol-Gel method and carbothermal reduction reaction using zirconium n-propoxide, acetic acid, boric acid and xylitol as starting materials. In the reaction system, xylitol acted as a carbon source for the carbothermal reduction reaction and chelated boron, leading to the formation of coordination compound through its polyhydroxy reaction with boric acid. According to the Fourier Transform infrared spectra and thermal analysis of gel precursor, the effects of sol and gel reaction processes on the carbothermal reduction reaction temperature and gelation time were discussed. The results show that the polyhydroxy compound of xylitol is beneficial to initiate reactions and gelation, which makes the threshold throughout the whole chemical processes easy to overcome. The gel does not need aging treatment and the reaction temperature is lowered. Besides, a single phase of equiaxed ZrB2 nanoparticles could be obtained from nascent state gel calcined at 1450℃ with n(xylitol)/n(zirconium n-propoxide) of 1.4. The average diameter and oxygen content of ZrB2 nanoparticles are ca. 50 nm and 1.36wt%, respectively.
|
|
|
Direct Brazing of Al/Al2O3 without Wettability of Molten Metal
CHEN Fan, SHI Kai-Cheng, SUN Shi-Yang, ZHAO Bo-Wen, SHANG Hai-Long, LI Ge-Yang
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 602–606
 Abstract
Abstract(
648 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(399KB)(
931
)
Al2O3 cannot be directly brazed with aluminum due to the poor wettability of aluminum on alumina below 850℃. Based upon effect of sputtered aluminum wetting on Al2O3, a direct brazing method was proposed to utilize sputtered Al-based films as brazing fillers on alumina. The results show that direct brazing of Al2O3 by Al and Al-Cu alloy can be achieved at 680℃ in vacuum with vacuum level only of 0.1 Pa. Through this method, the shear strength of joint with pure Al as brazing filler is 115 MPa and that with Al-1.6at% Cu is up to 163 MPa. When the Cu content in the Al-Cu alloy increases to 14.3at%, the shear strength of joint decreases to 127 MPa, due to the joint fracture generating at the interface caused by the interfacial segregation of Cu. Moreover, the principle of this direct brazing method not based on wettability of molten metal is analyzed.
|
|
|
Wetting Properties and Interface Reaction Mechanism of Ag-Cu Brazes on Dual-phase Membrane Ceramic
ZHANG Li-Li, LI Ke,YU Chen-Chen, ZHANG Yu-Wen, WU Cheng-Zhang, DING Wei-Zhong
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 607–612
 Abstract
Abstract(
670 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(522KB)(
1032
)
A reactive air brazing Ag-CuO alloy was evaluated for brazing dual phase oxygen membrane Ce0.8Gd0.2O2-δ- NdBaCo2O5+δ (CGO-NBCO). Contact angle tests were observed between Ag-Cu brazes and CGO-NBCO in air and the interfacial microstructures of the used samples were evaluated by SEM. The results indicate that the wetting angle decreases from 35° to 20° with the content of Cu increased from 6.6mol% to 15.8mol%. It is found that there are copper oxide-enriched zones formed in the junction of the alloy and substrate. The wettability between Ag-CuO alloy and oxygen membrane CGO-NBCO is improved due to the interfacial reaction between Cu oxides in braze and the surface layers of CGO-NBCO substrates to form compounds of Ba-Cu-O, Co-Cu-O and Nd-Ce-Cu-O oxides. The new formed interface reaction layers promote the wettability of the rest braze.
|
|
|
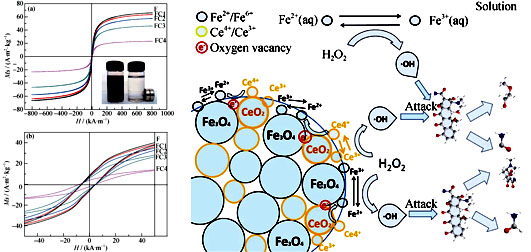
Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction for Degradation of Ofloxacin with Magnetic CeO2/Fe3O4
HU Xiao-Dan, ZHOU Zhi-Wei, ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Xiao-Hong, ZHANG Hai-Qian
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 613–620
 Abstract
Abstract(
1041 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(746KB)(
1184
)
CeO2/Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles were prepared for promoting the catalytic activity of Fe3O4, which is applied as the catalyst of heterogeneous Fenton reaction system for the degradation of ofloxacin. Several factors that affected the degradation efficiency of the system such as CeO2 content, H2O2 concentration and pH were investigated. The mechanism of catalytic degradation was also explored via the measurement of iron ion and kinetics fitting. The results show that the catalytic activity of CeO2/Fe3O4 is better than that of Fe3O4. The degradation efficiency of ofloxacin increases with the addition of CeO2 content, H2O2 concentration or solution acidity increase. The degradation effect of ofloxacin is the best for CeO2/Fe3O4(molar roction=0.780)-H2O2 catalytic system when H2O2 concentration is 100 mmol/L and pH is 3, which accords first order kinetics model. The catalytic ability of CeO2/Fe3O4 is strengthened through surface catalytic reaction and electronic transfer of oxygen vacancies of CeO2 during catalytic reaction.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Characterization of Y-doped ZrO2 Nanofiltration Membranes by Aqueous Sol-Gel Process
DA Xiao-Wei, QIU Ming-Hui, FAN Yi-Qun
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 621–626
 Abstract
Abstract(
678 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(479KB)(
1320
)
Crack-free tubular yttria-stabilized-zirconia (YSZ) nanofiltration membranes was fabricated via an aqueous Sol-Gel process, using zirconium oxychloride as precursor and water as solvent. This procedure was completely free of organic solvent and thus was environmentally friendly. The influences of precursor concentration and calcination temperature on the particle size of sols, crystal and pore structure were investigated. The results revealed that the sol prepared with lower precursor concentration and calcined at 400℃, has higher content of monoclinic phase, thus leading to the increase of pore size. Subsequently, addition of 8mol% yttrium into the sol inhibits phase transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic and grain growth, as well as avoid membrane cracking. In addition, retention experiment result shows that the YSZ nanofiltration membrane exhibits a molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) of 860 Da and a water permeability of 200 L/(m2·h·MPa). Furthermore, ions retention properties of YSZ nanofiltration membrane towards four solutions like NaCl, Na2SO4, CaCl2, and MgCl2, were conducted at pH 6 and a transmembrane pressure of 0.8 MPa. The retention properties of YSZ nanofiltration membrane towards CaCl2 and MgCl2 solutions reach maximum values of 65% and 78%, respectively.
|
|
|
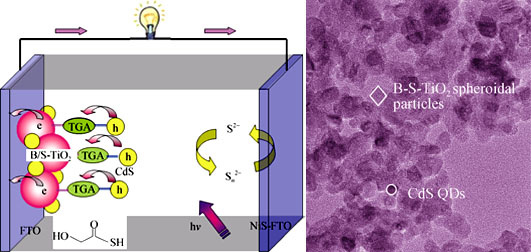
Boron and Sulfur Co-doped TiO2 Nanofilm as High Efficiency CdS Quantum-dot-sensitized Solar Cells
LI Ling, XIAO Jun-Ying, CUI Mi-Dou, TAI You-Yi, PANG Yong-Wen, HAN Song, LI Xiao-Wei
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 627–633
 Abstract
Abstract(
930 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(485KB)(
1005
)
B and S co-doped TiO2 was prepared by a typical hydrothermal synthesis. Then the obtained B-S-TiO2 was dissolved in organic solvent to form paste and then coated on FTO conducting glass by screen printing to prepare nanofilm. The CdS/B-S-TiO2 composite electrodes was obtained by chemical bath deposition (CBD) using B-S-TiO2 nanofilm and CdS quantum dots (QDs). The obtained samples were characterized by EDS, XRD, TEM and UV-Vis. The results show that B and S do not change the structure of anatase TiO2. Noticeable shifts of absorbance edge towards longer wavelength were observed and the absorbance intensity of the B-S-TiO2 nanofilm increases significantly. Furthermore, NiS was prepared as counter electrode by CBD and a modified polysulfide redox couple, ((CH3)4N)2S/((CH3)4N)2Sn, was employed as electrolyte to assemble CdS quantum-dots (QDs)-sensitized solar cells. The measurements show that the cells have an enhanced energy conversion efficiency under AM 1.5 G illuminations which increased from 3.21% to 3.69%, about 14.9% increment, with a significantly high open voltage (Voc) of 1.218 V, a high filled factor (ff) of 88.7%, and a short-circuit photocurrent (Jsc) of 3.42 mA/cm2.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Property of Spherical Lu3Al5O12:Eu3+ Phosphor
LI Jin-Kai, TENG Xin, CAO Bing-Qiang, LIU Zong-Ming
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 634–640
 Abstract
Abstract(
734 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(979KB)(
1006
)
Spherical phosphors of (Lu0.95Eu0.05)3Al5O12 ((Lu0.95Eu0.05)AG) with good dispersion was achieved through precursor synthesis via homogeneous precipitation method using urea as the precipitant, followed by annealing. The size of spherical particle can be effectively controlled by adjusting the urea concentration. Based on it, the synthesis, phase evolution and photoluminescent properties of the (Lu0.95Eu0.05)AG phosphors were tested by XRD, FE-SEM, TEM, BET, PLE/PL, and fluorescence decay analyses. The results showed that the precursors were converted into phase-pure (Lu0.95Eu0.05)AG garnet at a relatively low temperature of 1100℃. The (Lu0.95Eu0.05)AG garnets possessed high theoretical densities which were suitable for the application of scintillation material. The phosphors exhibited strong orange red emissions at 592 nm (the 5D0→7F1 magnetic dipole transitions of Eu3+) upon UV excitation into the charge transfer band (CTB) at 235 nm, with CIE chromaticity coordinates of (0.63, 0.37). The intensity of 592 nm emission increased with the particle size increase, while the lifetime of 592 nm emission decreases at a higher particle size. Thus, the spherical phosphors of (Lu0.95Eu0.05)AG garnet developed in the present work were expected to be a new type of phosphor which may be widely used in lighting and displaying areas.
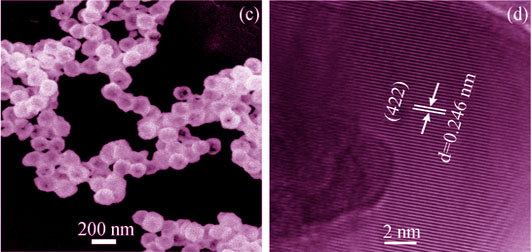
|
|
|
Synthesis and Optical Properties of Copper Doped Y2Ba2O5 Pigments with High Near-infrared Reflectance
JIANG Jun, YAO Bo-Long, GAO Xv-Rui, WANG Li-Kui, LI Hong-Ping, DENG Li-Duo
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 641–646
 Abstract
Abstract(
875 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(441KB)(
1097
)
A series of environmentally benign near-infrared reflective green nano-pigments were synthesized via Sol-Gel method with a general formula of Y2Ba(2-x)CuxO5(x=0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75 and 1.0). The crystal structure, morphology and optical properties of the synthesized pigments were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), UV-Vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectra, and high accuracy spectrophotometer. Analysis results demonstrated that Cu ion was successfully introduced into the Y2Ba2O5 lattice of which grain size decreased from 62.1 nm to 54.7 nm. The systematic substitution of Cu2+ for Ba2+ in Y2Ba2O5 changed color from white to green (a*=-21.61) and decreased band gap from 2.30 eV to 2.04 eV. These pigment samples revealed the uniform spherical-like morphology with an average size of 150-300 nm. When Cu2+ was introduced, the infrared reflectance of pigment sample was decreased. However, the pigment still displayed high near infrared reflectance (68.80%) and solar reflectance (45.95%), while the doping of Cu2+ up to x=0.50. Therefore, such green high near-infrared reflectance from these Y2Ba(2-x)CuxO5 powders have great potential in serving as cool pigments for building coatings.

|
|
|
Fabrication and Luminescence Properties of Polycrystalline Ce, Pr Co-doped LSO Thin Films by Sol-Gel Method
ZHANG Xiao-Xin, XIE Jian-Jun, FANG Ling-Cong, LIN De-Bao, CHEN Xu, SHI Ying
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 647–651
 Abstract
Abstract(
676 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(461KB)(
921
)
Lutetium oxyorthosilicate (Lu2SiO5, LSO) films co-doped with Ce3+ and Pr3+ was synthesized on cleaned silicon (111) substrates by Sol-Gel route with a spin-coating technique. XRD patterns indicated that the films were crystallized into A-type Lu2SiO5 phase at 1000℃, followed by a phase transition to B-type Lu2SiO5 at 1100℃. SEM observations revealed that the surface of the films was smooth, homogeneous and crack-free when the samples were calcined under 1100℃. The average grain size of the crystal particles was 200-300 nm and the thickness of the thin film was about 320 nm when the coating layer number up to 10. The energy transference from Pr3+ to Ce3+ in Lu2SiO5 host was observed and discussed. The luminescence intensity of Ce3+ can be improved after Pr3+ co-doping.
|
|
|
Role of Fluxes in the Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+ Oxynitride Phosphors by Microwave Sintering
HAN Bin, WANG Yi-Fei, LIU Qian, HUANG Qing
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 652–660
 Abstract
Abstract(
664 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(635KB)(
1119
)
Eu2+ activated Ba3Si6O12N2 oxynitride green phosphors were synthesized by microwave sintering method with the aid of fluxes, namely BaCl2, H3BO3, KF, and NH4F. We employed a combination of X-ray diffraction, photoluminescence spectra and scanning electron microscopy measurements, in conjunction with detailed quantum efficiency (QE), life time and thermal quenching studies of luminescence properties to understand the origins of the improved luminescence properties. The results showed that the photoluminescence intensity of the phosphors was increased obviously by using varied fluxes and the intensity rise was recorded in order of fluxes as following: H3BO3 > KF > BaCl2 > no flux > NH4F. The maximum emission intensity of the Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+ phosphor was achieved at containing 1.0wt% H3BO3, due to the high crystallinity, narrow particle-size distribution and smooth surface, which showed low thermal quenching, shorter life time and increased external quantum efficiency, compared with that of the sample with other fluxes or without flux.
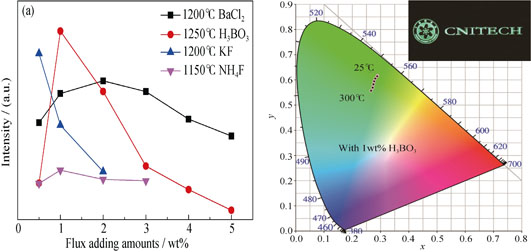
|
|
|
Effect of Residual Phase and Grain Size on Corrosion Resistance of SiC Ceramics in Mixed HF-HNO3 Acid Solution
LIU Ze-Hua, QI Qian, YAN Yong-Jie, ZHANG Hui, LIU Xue-Jian, LUO Hong-Jie, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 661–666
 Abstract
Abstract(
826 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1047
)
Effect of residual phase and grain size the corrosion resistance of SiC ceramics in mixed HF-HNO3 acid solution was investigated. Three kinds of fabrication methods (SSiC-solid state sintered SiC, LPS SiC-liquid phase sintered SiC and RB SiC-reaction bonded SiC) were adopted to prepare SiC ceramics. Besides, the grain size in SiC ceramics was adjusted under different sinter temperatures. Compared to RB SiC and LPS SiC ceramics, SSiC ceramics showed a better corrosion resistance for the good corrosion resistance of residual graphite and ‘island’ structure of residual phase in ceramics. The grain size of SiC ceramics sintered at temperature between 2100℃ and 2160℃ increase from 2 μm to 6 μm, and the absolute values of Y intercept, which reflect the corrosion of SSiC ceramics with none residual phase, are 9.22 μg/cm2 (2100℃), 5.81 μg/cm2 (2130℃) and 0.29 μg/cm2 (2160℃), which demonstrate that large grain size is beneficial to the corrosion resistance of SiC ceramics.
|
|
|
Optimizing the Charge Transfer Process by Synthesizing NiO Microspheres on Ni Foam through Microwave-assisted Method
HAN Dan-Dan, JING Xiao-Yan, XU Peng-Cheng, TAN Ao, CHENG Zhen-Yu
2016 Vol. 31 (6): 667–672
 Abstract
Abstract(
793 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(431KB)(
864
)
The porous nickel oxide microsphere on Ni foam was adopted to optimize the charge transfer process to improve electrochemical performance by a microwave-assisted method. Microstructure and morphologies of the resulting materials were investigated by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope. Results showed that the as-prepared NiO microspheres with nickel sulfate had average diameter of ~2 µm. The ultrathin secondary nanoflakes composed of nanowire building blocks were interconnected with each other forming a highly open net-structure. Because of enhanced electron transfer capability, charge transfer resistances of the porous microsphere were reduced and the electrochemical performances were improved, the charge-discharge measurements tested at a discharge current of 0.5 A/g showed higher rate specific capacitance (455 F/g). The impedance characterization illustrated lower electronic and ionic resistance of porous NiO due to its superior surface properties for enhanced electrode electrolyte contact during the faradaic redox reactions.
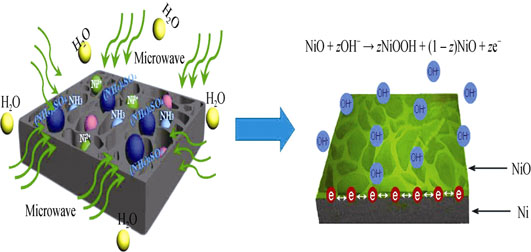
|
|