|
|
Progress in Research and Development of Solar-grade Silicon Preparation by Electron Beam Melting
TAN Yi, SHI Shuang, JIANG Da-Chuan
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 785–792
 Abstract
Abstract(
769 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(472KB)(
1571
)
Electron beam melting is an effective method to remove volatile impurities in silicon due to its characteristics of high energy density and high vacuum degree, which has huge advantages and wide application prospects in preparation of solar-grade silicon. Currently it has been successfully applied in industry and become one of the key procedures for preparation of solar-grade silicon by metallurgical route. Based on the thermodynamic principle of the volatile impurities removal, the removal efficiency and mechanism are summarized in this paper. According to current problems of this technology combined with our own experience, the emphasis of current research is reviewed from the points of numerical simulation, energy-saving melting technology and coupling with directional solidification technology. The future development direction of this technology is also proposed.
|
|
|
Development on the Preparation and Application of Onion-like Carbon
ZHENG Yan-Bin, JIANG Zhi-Gang, ZHU Pin-Wen
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 793–801
 Abstract
Abstract(
1777 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(515KB)(
2209
)
Due to unique structure, onion-like carbon has excellent physical and chemical properties that brodens the application in carbon and carbon-based composite materials. The classification and the structure of onion-like carbon were firstly introduced. Its advantages and disadvantages of traditional preparation methods, including arc discharge, plasma, electron-beam radiation, chemical vapor deposition, nanodiamond annealing in vacuum, thermolysis, were summarized. Then, some new synthetic methods developed in recent years were also presented. Subsequently, the application of onion-like carbon on anode materials of lithium ion secondary battery, counter electrode materials of dye-sensitized solar cell, electrodes materials of electrochemical hydrogen storage and super capacitor, friction and wear, and catalyst fields was summarized. Finally, deficiencies of preparation and application on onion-like carbon were pointed out and future research were put forward.
|
|
|
Research Progress on TeO2 Crystal and Its Utilization in Infrared Devices
ZHU Yong, YUE Shi-Hai, WANG Wei, YIN Xue-Ji, GE Zeng-Wei
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 802–808
 Abstract
Abstract(
926 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(447KB)(
1790
)
TeO2 crystal has excellent acousto-optic properties and double b decay properties of high natural abundance of 130Te isotope. It can be used in high-performance acousto-optic devices and also for the research of neutrino and dark matter. Recently, the above applications raise the requirements for the size and quality of TeO2 crystal. Structure and physical properties of TeO2 crystal are briefly introduced in this article, and then the recent progress on the preparation of large sized TeO2 crystal with high quality and its application in infrared devices are reviewed. Finally, its preparation and application in future of TeO2 crystal are discussed.
|
|
|
Growth and Scintillation Properties of Ce:Li6Lu(10BO3)3 Crystal
LIU Wei, PAN Shang-Ke, LI Huan-Ying, JIANG Yong, CHEN Xiao-Feng, REN Guo-Hao
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 809–813
 Abstract
Abstract(
558 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(397KB)(
1394
)
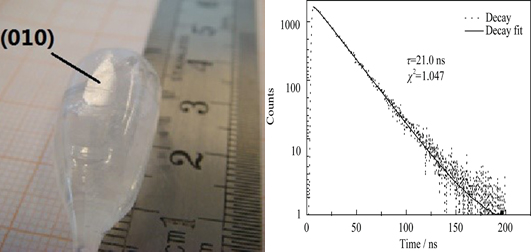
To improve the neutron detection efficiency, Ce:Li6Lu(10BO3)3 crystal was grown by Czochralski method from the raw materials enriched with 10B isotopes. The X-ray excited luminescence of Ce:Li6Lu(10BO3)3 crystal presents an emission band from 360 nm to 480 nm corresponding to 5d - 4f transitions of Ce3+ ions. The scintillation efficiency of Ce:Li6Lu (10BO3)3 crystal was 3.9 times as large as that of BGO crystal, and the photoluminescence decay time excited by 350 nm and scintillation decay time excited by 137Cs γ-ray source were 21.0 ns and 31.7 ns, respectively. The relative light output of Ce:Li6Lu(10BO3)3 crystal excited with 662 keV γ-ray from 137Cs was 20% that of CsI(Tl) crystal and the energy resolution was measured to be 9.7%. In the neutron energy spectrum excited by moderated 252Cf neutron source, the obvious full energy peak of neutron was observed and the energy resolution was 33%. With the relatively high scintillation efficiency, fast decay time and good neutron detection efficiency, Ce:Li6Lu(10BO3)3 crystal is a promising fast scintillator for neutron detection applications.
|
|
|
Flat Panel X-ray Imaging of LuAG:Ce,Mg Ceramic Scintillators
HU Chen, LIU Shu-Ping, FENG Zhao-Dong, QIN Xiu-Bo, SHI Yun, PAN Yu-Bai
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 814–818
 Abstract
Abstract(
940 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(397KB)(
1677
)
(Lu, Mg, Ce)3Al5O12 (LuAG: Ce, Mg) transparent ceramic scintillators (LuAG: 0.3at% Ce, 0.2at% Mg) with high optical and scintillation efficiency were fabricated by solid-state reaction method combined with vacuum sintering. The ceramic scintillator with dimension of 20 mm×20 mm×0.05 mm was packed with graphite substrate of 25 mm×25 mm×4 mm by graphite powders contained silica gel. Laser cutting of cubic array with dimension of 50 μm×50 μm and distance of 10 μm was performed. Flat panel X-ray imaging based on as prepaired ceramics was demonstrated. The images were good quality with a high resolution. The quality of the photos were evaluated by line-pair pattern method and knife edge method, respectively. MTF value of 17.5% was at 10 lp/mm for the ceramic scintillators after laser cutting, while resolution of 9 lp/mm achieved at 10% MTF by knife edge measurement. Based on above data, LuAG:Ce,Mg ceramics are proved to be a promising scintillator in flat panel X-ray imaging.
|
|
|
The Electronic and Optical Properties of Tetrahedral Doped Co1-xRexCr2O4 (Re = Li, Na, K, Rb) Spinel
YANG Zhi-Huai, ZHANG Yun-Peng, ZHANG Mei-Guang, XU Qiang, ZHANG Ya-Ni, ZHANG Rong
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 819–824
 Abstract
Abstract(
728 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(501KB)(
1705
)
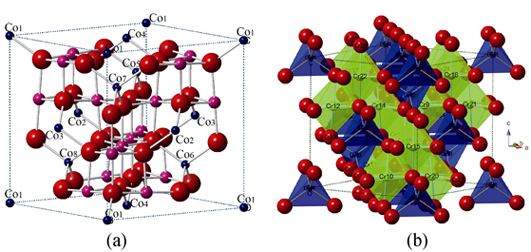
The structure parameters, electronic density of states, and optical properties of Re (Re = Li, Na, K and Rb) doped tetrahedral Co(1-x)RexCr2O4(x=0.125) system were investigated by using plane-wave ultrasoft pseudopotential method with generalized gradient approximation. The obtained data indicate that monovalent ions doping results in a slight tetrahedral lattice distortion, leading to the stability of the system being reduced and the Rb doped system the most stable. The calculated electronic density of states demonstrates that the conduction bands of doping system are mainly dominated by Co-3d and Cr-3d electrons and the peak of Co-3d in conduction band shifts down when compared to the pure CoCr2O4. Moreover, the Fermi levels of the doping system get into the deeper valence band along with the doping concentration increases. Finally, the doped systems present a red shift phenomenon and a strong absorption in the low energy region according to the absorption spectral calculations, suggesting that doping system can greatly improve the absorption and photo catalytic efficiency of visible light for CoCr2O4.
|
|
|
Preparation and Visible Light Responsive Photocatalytic Activity of Bi2MoO6/Ni-Fe LDH Composites
QU Ting, HUANG Qiang, ZHAO Zhen-Bo
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 825–832
 Abstract
Abstract(
1067 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(693KB)(
1770
)
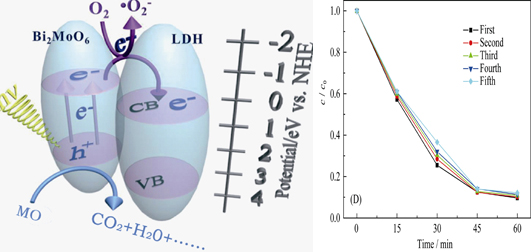
Bi2MoO6/Ni-Fe LDH composites were prepared by hydrothermal method and co-precipitation. The morphology and structure of the sample were characterized by XRD, FT-IR, SEM, TEM, XPS and N2-physisorption. Photocatalytic degradation activity and mechanism of the samples were investigated by the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange (MO), methylene blue, butyl rhodamine B and phenol under visible light irradiation. The results showed that BET specific surface area of the composites increased with the LDH content increase. Photocatalytic degradation activity of MO under visible irradiation exhibited significant enhancement. After visible light irradiation for 60 min, the Bi2MoO6/Ni-Fe LDH composites with LDH content of 4.5wt% showed the highest degradation rate of 91%, higher than that of Bi2MoO6 and Ni-Fe LDH by 52% and 16%, respectively. And the composites photocatalytic degradation followed first-order reaction kinetics. The composites decolorizing rate still remained 88% after 5 times recycle, showing high catalytic stability.
|
|
|
Application of Transmission Electron Backscattered Diffraction in Nanomaterials Research
LIU Zi-Wei, HUA Jia-Jie, LIN Chu-Cheng, JIANG Cai-Fen, ZENG Yi
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 833–837
 Abstract
Abstract(
865 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(430KB)(
1690
)
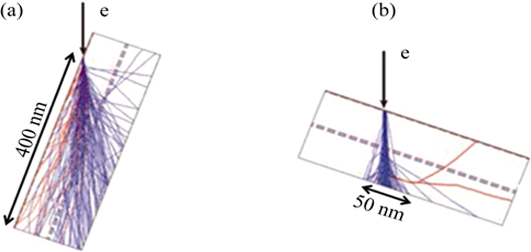
To improve the spatial resolution of electron backscatter diffraction technique, by which phase identification and orientation analysis of the nano scale grain or ultrafine powders can be achieved, a special specimen holder for transmission electron backscatter diffraction techniques (t-EBSD) accompanied by adjusting position and angle of EBSD detector, was newly designed. The new sample holder could fix the STEM samples, enabling clear TEM Kikuchi diffraction patterns to be successfully collected by EBSD detector. Then the effect of sample thickness on Kikuchi diffraction pattern was investigated. Based on the newly designed holder, the t-EBSD mapping of zirconia coating was acquired with the mean angle deviation (MAD) at only 0.38, successfully identified the cubic phase of less than 30 nm zirconia coating. Put the ultrasonic dispersed TiO2 powder on copper mesh, the point analysis of t-EBSD could identify the anatase and the rutile of TiO2, distinguishing minimum size of anatase phase TiO2 less than 20 nm. Therefore, the minimum resolution of phase identification in scanning electron microscopy is improved from about 100 nm to less than 30 nm, demonstrating the electron backscatter diffraction technology a very promising way in nano materials research.
|
|
|
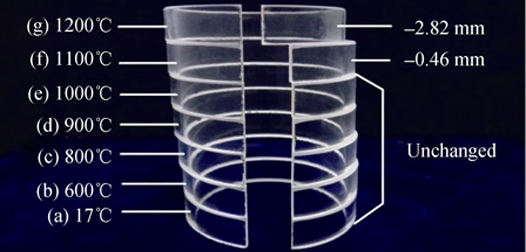
Evaluation of Elastic Modulus of Quartz Glass Tube at High Temperature by Modified Split Ring Method
LIU Zhao, BAO Yi-Wang, WEI Chen-Guang, WAN De-Tian
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 838–842
 Abstract
Abstract(
638 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(415KB)(
1413
)
Quartz glass tubes are widely used in chemical, mechanical, optical, and other fields, especially for the cases of high temperature. However, scarcity of evaluation techniques of elastic modulus at high temperature causes a barrier for analysis of thermal stress and structure design. Although a split ring method has been used at room temperature, its application at high temperature is scarcely reported due to the difficulty of the deformation measurement. In this study, a combination of the split ring method and relative method was utilized to solve deformation measurement problem, thus evaluating the elastic modulus of quartz glass tubes at various temperatures. The results indicate that the elastic modulus datum increases from room temperature to 800℃, reaches the peak value of 87.20 GPa at 800℃, and then gradually decreases, and then sharply decreases when temperature higher than 1100℃. These results demonstrate that the quartz glass tube measurement by improved split ring method for determining high-temperature elastic modulus is accurate and reliable, which could be used to evaluate other brittle tubes at high temperature.
|
|
|
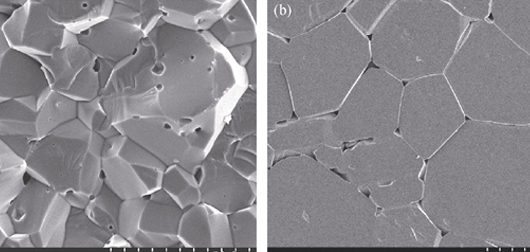
Preparation of MgO·1.5Al2O3 Transparent Ceramic by Pressureless Sintering and Hot Isostatic Pressing
YUAN Ze, WANG Hao, TU Bing-Tian, LIU Xin, XU Chun-Lai, WANG Wei-Ming, FU Zheng-Yi
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 843–847
 Abstract
Abstract(
820 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(389KB)(
2664
)
Possessing unique optical and mechanical properties, magnesium aluminate spinel transparent ceramic has been regarded as an important multifunctional material. In this study, pure phase MgO·1.5Al2O3 ceramic powders with uniform and fine particle size were synthesized through solid-state reaction. A two-step structural refinement procedure, including XRD Rietveld analysis by Fullprof software and further refinement by spinel solid solutions structure modeling program SIDR, was utilized to resolve the crystal structure of synthesized powders. After refinement, the crystal structure was finally determined to be (Mg0.46Al0.54)IV[Mg0.26Al1.64□0.09]VIO4. Using the synthesized MgO·1.5Al2O3 ceramic powders, high performance transparent ceramic was fabricated by pressureless vacuum sintering and subsequent hot isostatic pressing sintering (HIP). The relative density of the sample HIP-sintered at 1850 ℃ for 4 h under 180 MPa Ar could reach 99.75%. In the meantime, the in-line transmittance measurement of the 2-mm-thick sample displayed good optical transparency from ultraviolet to middle-infrared wavelengths with the maximum transmittance 65% in visible region and 80% in infrared region. The MgO·1.5Al2O3 transparent ceramic also exhibited good mechanical properties of Vickers hardness ((12.75 ± 0.12) GPa) and Young's modulus (277 GPa).
|
|
|
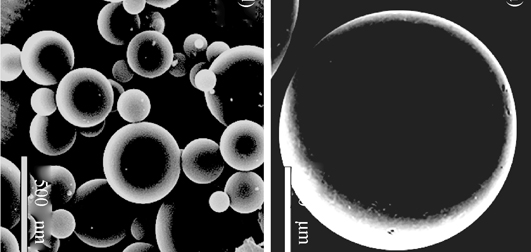
Facile Preparation, Structural Control and Spheroidization of Mesoporous Carbons Using Hydrolyzed Water Glass as a Template
ZHANG Chuan, WANG Ji-Tong, LI Xu, LONG Dong-Hui, QIAO Wen-Ming, LING Li-Cheng
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 848–854
 Abstract
Abstract(
727 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(909KB)(
1430
)
Mesoporous carbons (MC) with controlled pore structure were synthesized using hydrolyzed water glass (sodium silicate) as hard template precursor. The mixture of carbon precursor (resorcinol-formaldehyde) sol and silica sol followed by Sol-Gel process generated a polymer/silica dual hydrogels. After ambient drying, carbonization and HF etching, mesoporous carbons with developed mesoporous structure were obtained. The hydrolysis conditions of water glass including hydrolysis temperature and hydrolysis time, and the weight ratio of RF polymer to silica were studied respectively to investigate their effects on the mesoporous structure. The microstructures of the mesoporous carbons were characterized by N2 adsorption, SEM and TEM observations. It was found that as-prepared mesoporous carbons displayed disordered mesoporous channels which replicated from the initial colloidal silica networks. The average mesopore size could be precisely adjusted in the range from 6 nm to 12 nm by tuning the hydrolysis time and hydrolysis temperature, while the total porosity could be controlled by changing the weight ratio of polymer precursor to silica. Furthermore, with the assistant of suspension polymerization and spray drying technologies, spherical mesoporous carbons with millimetre and micrometer-sized particles were produced, respectively. The present work provides a low-cost approach for deliberately controlling the mesoporous structure and spherical morphology to mesoporous carbons that can be extended to many different applications.
|
|
|
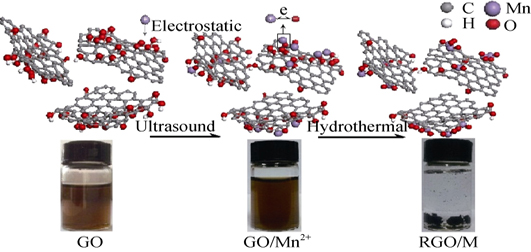
One-step Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide/MnO2 Composites
HOU Yuan, ZHANG Bang-Wen, XING Rui-Guang, BULIN Chao-Ke
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 855–860
 Abstract
Abstract(
988 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(558KB)(
1817
)
Reduced graphene oxide/MnO2 (RGO/M) composites were successfully prepared via one-step hydrothermal routine, in which graphene oxide serviced as the oxidant and Mn2+ as the reducer. The morphology and microstructure of the nanocomposites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscope (XPS), Raman spectra (RS), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscope and field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM). In addition, the electrochemical properties of the composite were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge/discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques for supercapacitor applications. The results indicate that the RGO/M composites displayed controllable specific capacitance in acidic electrolytes by adjusting the molar ratio of GO to manganous chloride at a specific hydrothermal reaction condition. In the optimal case, a specific capacitance of 277 F/g can be obtained in 1 mol/L H2SO4 at a scan current density of 1 A/g, with a capacitance retention of 98% after 500 cycles.
|
|
|
Amorphous SnO2-C Composite Fibers and Their Electrochemical Performance
YANG Qi, HU Wen-Bin
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 861–866
 Abstract
Abstract(
660 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(403KB)(
1507
)
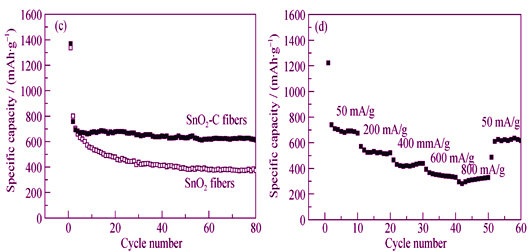
SnO2-C composite fibers with excellent electrochemical performance were successfully synthesized by using tin(II)2-ethylhexanoate as starting material through electrospinning technique and subsequent calcination in inert atmosphere. The experimental results of X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscope, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) show that SnO2-C composite fibers with diameters of 100-300 nm have amorphous structure and carbon content of ~38%. The electrochemical test results show that SnO2-C composite fibers exhibit initial discharge specific capacity, charge specific capacity and coulombic efficiency of 1370.1 mAh/g, 757.5 mAh/g and 55.28%, respectively, at current density of 50 mA/g. After 80 cycles at current density of 50 mA/g, the specific capacity of SnO2-C composite fibers remains at 611.6 mAh/g without apparent capacity reduction. Their high specific capacity and excellent cyclic performance are attributed to their one dimensional (1D) structure with homogeneous distribution of SnO2.
|
|
|
Electrochemical Performance of Nano-fibrous Selenium Cathode Synthesized by Reverse Solvent Method for Rechargeable Li-batteries
GUO Jing, JIN Jun, WEN Zhao-Yin, LIU Yu
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 867–871
 Abstract
Abstract(
686 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(343KB)(
1308
)
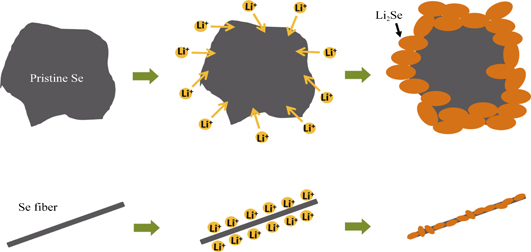
Nano-fibrous selenium of high purity and crystallinity with a diameter of 100 nm were synthesized by the reverse solvent method. The structure and morphology of products were characterized by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope, respectively. Since the size of elemental selenium is reduced, the inactivaton effect induced by the coverage of fully insulated discharge product Li2Se on Se particles surface is mitigated, thus greatly improving the utilization coefficient of active materials and alleviating the capacity fading of lithium-selenium batteries. Compared with the pristine selenium cathode, Se fiber electrode presents higher specific capacity and better cycling stability which delivers an initial specific discharge capacity of 465 mAh/g at 0.1C (1C=675 mAh/g) and maintains a capacity of 213 mAh/g after 40 cycles. Meanwhile, Se fiber electrode shows higher electrochemical activity than pristine Se electrode due to its shorter lithium ion diffusion path, resulting in a substantially enhanced rate capability of Se fiber electrode.
|
|
|
Powder Metallurgic Synthesis of Mid-temperature Lead-free AgSn18SbTe20 Thermoelectric Materials and Processing Influence on Thermoelectric Performance
XING Zhi-Bo, LI Jing-Feng
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 872–876
 Abstract
Abstract(
676 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(511KB)(
1401
)
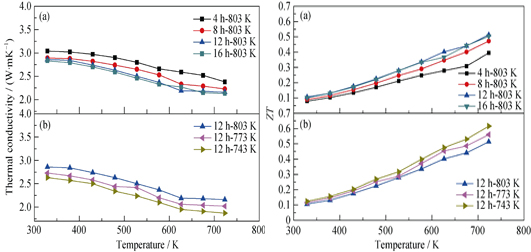
Lead-free thermoelectric materials gain increasing attention for environmentally friendly power- generation applications derived from waste-heat sources. In this work, mid-temperature lead-free p-type AgSn18SbTe20 thermoelectric materials were fabricated by a process combining mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). Electrical conductivity, Seeback coefficient, power factor and thermal conductivity of the sintered samples were measured in the temperature range from 300 K to 723 K, and the thermoelectric figure of merit, ZT, values were calculated. The phase structures and morphologies of the samples were observed. The effects of milling time and sintering temperatures on thermoelectric properties were investigated. And the results show that properly prolonging milling time and decreasing sintering temperature can enhance thermoelectric performance of the materials. The ZT value can be enhanced by 59% through optimizing the processing parameters, resulting in a relatively high ZT up to 0.62 at 723 K when the materials are milled for 12 h and sintered at 743 K.
|
|
|
Porous Alumina Ceramics with Unidirectional Oriented Pores Fabricated by Ionotropic Process of Sodium Alginate
SUN Yang, XUE Wei-Jiang, SUN Jia-Lin, ZHOU Guo-Zhi, HUANG Yong
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 877–881
 Abstract
Abstract(
838 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(429KB)(
1525
)
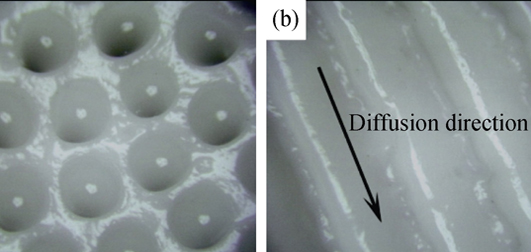
Alumina ceramic bodies with high porosity characterized by highly ordered and unidirectional oriented pores were successfully fabricated using the ionotropic process of sodium alginate by solvent exchange subsequently with freeze-drying. It is important to point out that the whole process and raw materials are eco-friendly. The average unidirectional pore size of samples sintered at 1500℃ for 2 h is 200 μm with minor porosity in the pore walls with average pore size of 0.3-0.5 μm. The properties of samples can be adjusted by controlling the solid loading in slurry. As the solid loading increasing from 5wt% to 15wt%, the density and compressive strength increased from 0.87 g/cm3 to 1.16 g/cm3 and from (18.9±3.2) MPa to (44.2±5.4) MPa, respectively with permeability decreasing from 2.57×10-11 m2 to 2.16×10-11 m2. In addition, with the solid loading increasing from 5wt% to 15wt%, the conductivity of the direction parallel and perpendicular to the unidirectional pores increased from 2.1 W/(m·K) to 3.1 W/(m·K) and from 1.3 W/(m·K) to 1.7 W/(m·K), respectively.
|
|
|
Microwave Dielectric Properties of LaPO4 Ceramics Synthesized by a Hydrothermal Method
XIE Hui-Dong, LI Fei, CHEN Chao, XI Hai-Hong, SHI Ling
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 882–886
 Abstract
Abstract(
691 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(376KB)(
1492
)
Lanthanum orthophosphate (LaPO4) ceramics were obtained by using hydrothermal prepared powders and solid-state reaction prepared powders in a sintering temperature range of 1030-1340℃ and 1300-1460℃, respectively. The sintering and microwave dielectric properties of hydrothermal processed LaPO4 ceramics were compared with those of solid-state reaction processed LaPO4. The results showed that hydrothermal processed LaPO4 had a higher sinterability and better microwave dielectric properties due to its much finer particle size when compared with solid-state reaction processed LaPO4. The best microwave dielectric properties of the hydrothermal processed LaPO4 ceramics were obtained when the ceramics sintered at 1260℃ for 2 h with a permittivity~10.2, a Q×f value about 129704 GHz (at 10.2 GHz) and a temperature coefficient value of -58.6×10-6/℃. The Q×f value of hydrothermal processed LaPO4 ceramics was 2.47 times greater than that of solid-state reaction processed LaPO4 ceramics, while the sintering temperature of the former was 140℃ lower than that of the latter in the literature.
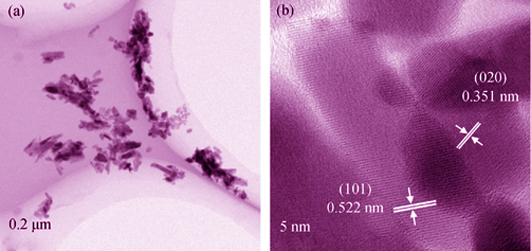
|
|
|
Growth and Characterization of Sulfur-doped GaSe Single Crystals
HUANG Chang-Bao, NI You-Bao, WU Hai-Xin, WANG Zhen-You, XIAO Rui-Chun, QI Ming
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 887–890
 Abstract
Abstract(
591 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(298KB)(
1204
)
It is difficult to obtain high quality sulfur-doped GaSe single crystal due to the intensive convection and solution diffusion in the melt. High quality GaSe0.89S0.11 single crystal with dimensions of ϕ20 mm×60 mm was successfully grown by Bridgman method using modified furnace with crucible rotation technique. The crystal was characterized by using energy dispersive spectrometer, X-ray diffractometer, nanoindentation, and Fourier infrared spectrometer. The measured results indicate that the sulfur-doped GaSe crystal with sulfur level of 2.38wt% shows significantly improved mechanical properties. The infrared transmission tests indicate that it has slightly higher transmittance in the range of 0.62-12.5 µm than the pure GaSe crystal. The results demonstrate that the modified Bridgman method could be used to produce high quality sulfur-doped GaSe crystals.
|
|
|
TiO2 Nanowires Infiltrated with Graphene-decorated Mesoporous TiO2 for Enhanced Dye-sensitized Solar Cell
CHEN Ang-Ran, ZHAO Wei, CUI Hou-Lei, ZHI Jian, HUANG Fu-Qiang
2015 Vol. 30 (8): 891–896
 Abstract
Abstract(
783 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(420KB)(
1391
)
Novel hybrid dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) were fabricated and characterized, employing a composite photoanode of TiO2 nanowires infiltrated with graphene-decorated mesoporous TiO2. Combining the merits of the high dye loading of mesoporous TiO2, high light harvesting capability with the carrier transport of TiO2 nanowires and the high electron collection efficiency from graphene, the overall performance of such photoanode was significantly improved. The obtained DSSCs showed a power conversion efficiency of up to 7.58%, about 1.5 times higher than the pristine TiO2 nanowires, which was quite competitive compared with the similar 1D structured photoanode of DSSCs.
|
|