|
|
Application and Development of Hybrid Perovskite Materials in the Field of Solar Cells
WANG Yan-Xiang, LUO Jun, GUO Ping-Chun, ZHAO Xue-Guo, YANG Zhi-Sheng, ZHU Hua, SUN Jian
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 673–682
 Abstract
Abstract(
1698 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(675KB)(
2893
)
The hybrid perovskite is a new kind of photoelectric material. The development in a highly-efficient perovskite solar cell with long-term durability, following the first attempt at a perovskite sensitizer in 2009, has attracted many researchers attention. The power conversion efficiencies of organolead halide perovskite solar cells have been improved from 3.1% to 19.3% in 2014. In this paper, the structure of organolead halide perovskite and its application in the inorganic-organic hybrid perovskite solar cells are reviewed. The development, device structure and preparation method of the organolead halide perovskite solar cell are summarized. Finally, the long-term stability, environmental problems and development tendency of perovskite solar cells are briefly described.
|
|
|
Modification Strategies for Semiconductor Photocatalyst Based on Energy Band Structure Theory
WANG Dan-Jun, ZHANG Jie, GUO Li, SHEN Hui-Dong, FU Feng, XUE Gang-Lin, FANG Yi-Fan
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 683–693
 Abstract
Abstract(
1601 )
 HTML
HTML(
42)
 PDF
PDF(834KB)(
2802
)
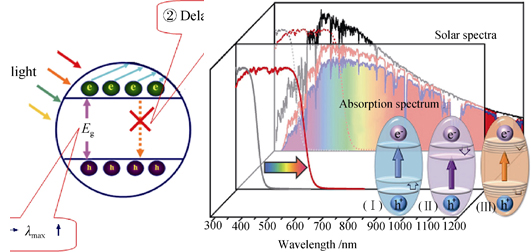
Design and controllable synthesis of catalyst and its property tuning are an interesting subject for physical chemistry, materials chemistry and catalytic chemistry. As a new environmental-purifying technology, semiconductor photocatalytic oxidation technology has arosen worldwide attention. However, conventional photocatalyst exhibits poor utilization of solar energy and low efficient of photogenerated charge separation, which restricts the practical application of the technology. Therefore, it is still a challenging topic to design and synthesize visible-light-response photocatalytic materials with higher utilization efficiency of solar energy. Besides tuning synthesis method (by controlling particle size, morphology, crystallinity and other microstructures, etc), modification is a crucial strategy for the activity enhancement of photocatalyst. In this paper, we reviewed the basic mechanism for the photocatalyst modification from the view of semiconductor energy structure. Taking consideration of the basic mechanism and process of photocatalysis, there are two key modification strategies: chemical structure modification (energy band modification) to broaden the light absorption and surface modification (surface sensitization, semiconductor combinations and noble metal deposition) to increase life-time of carrier. Suitable band structure is responsible for the visible-light harvesting and effective separation of carrier of semiconductor photocatalyst.
|
|
|
Effect of Calcination Temperature of Cu-Mn/γ-Al2O3 Catalysts on Performance for Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene
ZHENG Yi-Fan, ZHONG Shu-Bin, LV De-Yi, ZHOU Huan, HUAN Chang-Yong
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 694–698
 Abstract
Abstract(
952 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(378KB)(
1481
)
Cu-Mn/γ-Al2O3 catalysts were prepared by impregnation method and calcined at different temperatures (300-600℃), which were characterized by XRD, BET, H2-TPR and XPS. Their performances for catalytic oxidation of toluene were evaluated in a fixed-bed tubular reactor, and the correlation of catalytic activity with active phases or mole ratios of both Cu+/(Cu++Cu2+) and Mn4+/(Mn4++Mn3+) was discussed. Among all catalysts, the Cu-Mn/ γ-Al2O3 catalyst calcined at 550℃ shows the best catalytic activity, with a lowest reaction temperature (T95 is 286℃) and 100% selectivity of CO2. The generation of new phase (Cu1.4Mn1.6O4) and more amount of Cu+ and Mn4+ ions present on the surface of the catalyst calcined at 550℃ are responsible for its high activity.
|
|
|
Preparation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Property of Eu-doped TiO2 Hollow Microspheres
LIU Yang-Long, ZHENG Yu-Ying, SHANG Peng-Bo
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 699–705
 Abstract
Abstract(
846 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(608KB)(
1738
)
Pure TiO2 and Eu-doped TiO2 hollow microspheres were prepared by Sol-Gel method and characterized by techniques such as XRD, SEM, TEM, HRTEM, BET and XPS. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) in aqueous solution was used as a probe reaction to evaluate their photocatalytic activity. The experimental results show that the dosage of TBOT has a great effect on the morphology of TiO2 hollow microspheres. When the dosage of TBOT is 1.5 mL, the obtained hollow microspheres disperse well and show clear structure. XRD pattern indicates that TiO2 hollow microspheres calcined at 400℃ present anatase structure and Eu-doped ones can restrain the anatase phase from converting to rutile phase. The experimental results suggest that Eu-doped can obviously improve the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 hollow microsphere and when the doping of Eu is 0.7%, the photocatalytic degradation reaches the best because of its highest surface area and smallest crystallize size and pore diameter.
|
|
|
Influence of Ionic Liquids on Structure and Properties of Magnetically Separable TiO2 Photocatalytic Materials
LI Yan-Chun, ZHANG Xiu-Ling, ZHAN Zhi-Bin, DI Lan-Bo
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 706–712
 Abstract
Abstract(
628 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(575KB)(
1182
)
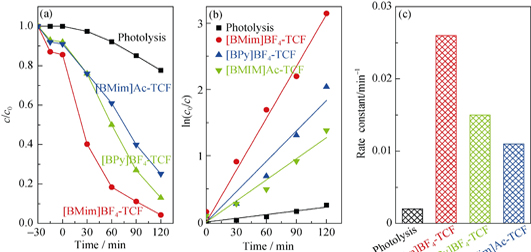
Magnetically separable TiO2/CoFe2O4 (TCF) photocatalytic materials were prepared by Sol-Gel method with the assistance of ionic liquids [BMim]BF4, [BPy]BF4 and [BMim]Ac, respectively. The influence of ionic liquids on structure and properties of the magnetically separable TiO2 was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption-desorption measurement (BET), transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results showed that anatase TiO2 was formed in [BMim]BF4-TCF and [BPy]BF4-TCF after calcination at 200 ℃, while anatase TiO2 was not formed in [BMim]Ac-TCF and TCF until the calcination temperature was increased to 400 ℃. When the calcination temperature was increased to 800 ℃, TiO2 in [BMim]BF4-TCF predominantly existed in the form of anatase structure (92.6%). These results indicated that BF4- anions in ionic liquids might reduce the crystallization temperature of anatase and improve the thermal stability of anatase at high temperatures. Samples prepared with the assistance of [BMim]BF4 or [BPy]BF4 exhibited larger specific surface areas (125.7 and 120.3 m2/g) than that of prepared by using [BMim]Ac (77.8 m2/g) or without addition of ionic liquid (63.7 m2/g). Photocatalytic activity of the samples was tested by photodegradation of methylene blue (MB) under simulated sunlight. MB photodegradation rates after 2 h irradiation over [BMim]BF4-TCF, [BPy]BF4-TCF, [BMim]Ac-TCF calcined at 400 ℃ were 96%, 87% and 64%, respectively.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution of Graphene-ZnIn2S4 Nanocomposite Spheres
ZHOU Min-Jie, ZHANG Na, HOU Zhao-Hui
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 713–718
 Abstract
Abstract(
962 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(467KB)(
2037
)
Graphene-ZnIn2S4 nanocomposite spheres were prepared via a facile photocatalytic reduction method. The samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, FT-IR, XPS and DRS. The results showed that the graphene oxide was reduced to graphene and ZnIn2S4 nanospheres were loaded on the surface of graphene sheets through a photocatalytic reduction process. The experimental results for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of the samples indicated that the amount of evoluted H2 under simulated sunlight irradiation using graphene-ZnIn2S4 nanocomposite spheres was 1540.8 μmol, 9.8 times of the pure ZnIn2S4 nanospheres, under optimal technological condition with the graphene content of 2.0wt% for 24 h. The enhanced performance can be attributed to the graphene which effectively promoted the transfer of photogenerated electrons. Furthermore, a detailed photocatalytic hydrogen evolution mechanism of graphene-ZnIn2S4 nanocomposite spheres was investigated.
|
|
|
Preparation and Luminescence Properties of Flexible Eu3+ Doped SiO2 Fibrous Membranes
ZHANG SHU-XIAN, CUI BO, WANG HONG-ZHI, LI YAO-GANG, ZHANG QING-HONG
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 719–724
 Abstract
Abstract(
535 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(485KB)(
1395
)
Eu3+ doped SiO2 fibrous membranes were prepared by Sol-Gel and electrospinning methods. The obtained samples were chacterized by SEM, XRD, FT-IR, TG, PL, etc. By heat-treatment, the organic components were removed slowly and the diameters of the Eu3+ doped SiO2 fibers decreased. SEM images exhibit that the surface of the fibers retains smooth and uniform after heat-treatment. By controlling the heating rate, the Eu3+ doped SiO2 fibrous membranes present relatively high tensile strength at about 4.31 MPa after heat-treatment at 750℃. The samples exhibit no cracks after bending and recovering process. By excited by 392.6 nm light, the emission peaks between 570-670 nm are observed, which attributes to the 5D0→7FJ transition. The strongest emission peak situates at 616 nm results from Eu3+ 5D0→7F2 transition. The optimal heat-treatment temperature is 750℃. PL spectra also show that the luminescence intensity attains the highest value at the concentration of 8mol% Eu3+ doped.
|
|
|
Cubic Mesoporous Silica Thin Films Coated on Titanium to Induce Carbonated Hydroxyapatite Deposition
ZHANG Zhen-Rong, YAO Yi-Yuan, LUO Kai, WAN Long, LIU Xuan-Yong
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 725–731
 Abstract
Abstract(
673 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(580KB)(
1522
)
Cubic mesoporous silica thin films were synthesized on pure titanium by dip-coating method and then their bioactivity were evaluated through the induced deposition of bone-like carbonated hydroxyapatite (CHA) layer in vitro. The composition, microstructure and morphology of the films were characterized by small-angel X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectrum, nitrogen adsorption, electron microscopes and energy dispersive spectroscopy, etc. The surface Zeta potential of the films was investigated by electrokinetic analyzer for solid surface analysis. The results reveal that the films have three-dimensional cubic mesostructure. The mesoporous silica films are covered with a thin CHA layer after being soaked in a simulated body fluid (1.5 SBF) for 14 d, indicating its good bioactivity. The unique mesostructure and the presence of abundant electronegative silanol groups in physiological solution may be responsible for the bioactivity.
|
|
|
High-performance LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Cathode Material Prepared by Sol-Gel Method in Non-aqueous Solvent
XIA Shu-Biao, ZHANG Ying-Jie, DONG Peng, XU Ming-Li, YAO Yao
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 732–738
 Abstract
Abstract(
872 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(546KB)(
1943
)
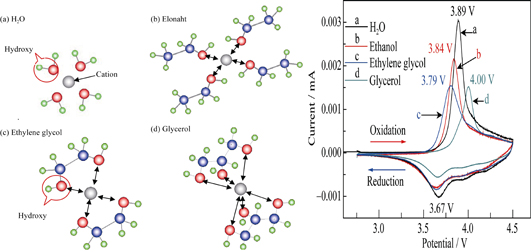
Lithium ion battery cathode material LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 was prepared by Sol-Gel, respectively, using water, ethanol, ethylene glycol, glycerol as a solvents. Through TG / DSC analysis of the thermodynamic properties, the sintered condition of the sample was selected as pre-treatment at 550℃for 6 h and then ??sintering at 750℃ for 24 h. XRD patterns show that the 018/110 peak of the samples prepared by organic solvent is splitted obviously, but the peak shifts to a small angle, which indicates that the lattice spacing increases. SEM results show that the average particle size of the samples prepared by organic solvent is 0.4 μm, which is smaller than that of the sample (0.5 μm) prepared by using water. Some of the single crystals present in the sample prepared by using ethanol and ethylene glycol as solvent. The electrochemical performance test results show that the charge-discharge performance of samples prepared in the organic solvent is lower than that of the sample prepared in the water. However, the initial discharge capacity (197.33 mAh/g) of the samples prepared using ethanol as a solvent (200.66 mAh/g) is closed to that of the sample prepared by using water as solvent, and cycle performance has greatly improved at 1C rate. After 50 cycles at 1C rate, the capacity retention rate of the sample prepared by using water is increased from 87.1% to 94.4% as compared with the sample prepared by using ethanol. The presence of large crystal particle is beneficial to improve the cycle performance of the NCA material.
|
|
|
Effect of Nickle Substitution on the Performance of Lithium Ion Battery Material LiMnTiO4
ZHANG Xu, WANG Yu, LI Yue, YANG Meng, ZHAO Xiang-Yu, MA Li-Qun
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 739–744
 Abstract
Abstract(
594 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(498KB)(
1298
)
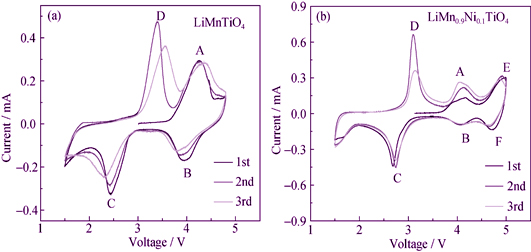
Spinel LiMn1-xNixTiO4(x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) cathode materials were prepared by Sol-Gel method. The surface morphology and phase structure of LiMn1-xNixTiO4 (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) were characterized by FESEM and XRD. FESEM analysis indicated all the samples consisted of irregular particles and XRD patterns showed that all the materials had impurity TiO2, but there were no impurities related to Ni element. Electrochemical studies of doped and undoped spinels were carried out by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and constant current charge-discharge. CV results showed that LiMnTiO4 had two couples of sharp redox peaks corresponding to Mn3+/Mn4+, Mn2+/Mn3+ redox reactions. However, after Ni substitution, there appeared the third redox coupled, which was related to the Ni3+/Ni4+ redox reaction. LiMn1-xNixTiO4 (x=0.1, 0.2, 0.3) exhibited improved electrochemical properties compared with LiMnTiO4. When the Ni substitution was 0.1, the first discharge capacity of LiMn0.9Ni0.1TiO4 was 171.6 mAh/g at current density of 30 mA/g, and after 48 charge-discharge cycles, the discharge capacity was 162.8 mAh/g, with the capacity retention of 82.7%. The Ex XRD pattern of LiMn0.9Ni0.1TiO4 showed that the material structure had no changes after the first cycle, and there was no transition between cubic phase and tetragonal phase.
|
|
|
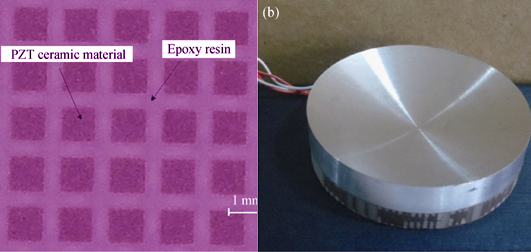
Properties of a Lens-focused Transducer Based on Piezoelectric Composites
HE Min, HAO Qi, WANG Ke-Xin, ZENG De-Ping, YE Fang-Wei, LI Fa-Qi, WANG Zhi-Biao, HE Hong-Ying
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 745–750
 Abstract
Abstract(
709 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(389KB)(
1759
)
To broaden the bandwidth of focused transducer with suppressing the multimode coupling phenomenon, and improving the electro-acoustic conversion efficiency, 1-3 piezoelectric composites as the ultrasonic emission material was used to replace Pb-based lanthanum doped zirconate titanates ceramic. A new type of lens-focused transducer was designed and produced based on 1-3 piezoelectric composites. Through the comparative study of frequency characteristic, it is proved that the 1-3 piezoelectric composites lens-focused transducer can not only increase the bandwidth of the transducer which is 3.13 times of the one based on Pb-based lanthanum doped zirconate titanates, but also suppress the radial vibration obviously to obtain a single pure vibration modes. Besides, the electro-acoustic conversion efficiency of the former lens-focused transducer is 1.88 times of the latter one. These results provide a theoretical and experimental foundation for the realization of ultrasonic transducer of high efficiency on reliability and stability.
|
|
|
Measurement of Microwave Dielectric Properties of Diamond Films Using Split-cylinder Resonator Method
SU Jing-Jie, YANG Zi, LI Yi-Feng, TANG Wei-Zhong, AN Xiao-Ming, GUO Hui
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 751–756
 Abstract
Abstract(
840 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(355KB)(
1299
)
Regarding to the difficulties in measuring microwave dielectric properties of diamond films due to their characteristics of low dielectric loss and small thickness, a split-cylinder resonator apparatus was established. By measuring dielectric performances of sapphire samples with different diameters, the capability of the split-cylinder resonator for measuring low dielectric loss materials was demonstrated, and the influence of sample’s diameter on measurement results was studied. Then by using the split-cylinder resonator apparatus, dielectric properties of high quality diamond films prepared by two different methods, microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD) and DC arc plasma jet, were measured in the Ka band. Results show that the diamond film deposited by MPCVD method has a higher quality than that of the diamond film deposited by the DC arc plasma jet method, which is consistent with the results of their Raman and UV-visible absorption spectra. The results indicate that both the relative dielectric constant and the loss tangent of the sample deposited by MPCVD method are lower than those of the sample prepared by DC arc plasma jet method.

|
|
|
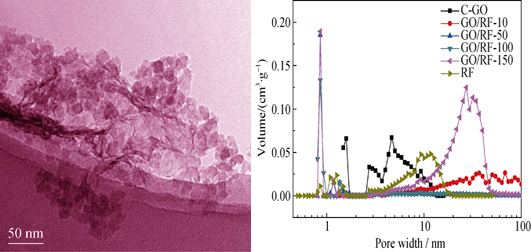
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Graphene/Carbon Aerogels
YI Shang-Qi, LIU Hong-Bo, XIA Xiao-Hong, HUANG Gui-Rong, MA Qian, CHEN Yu-Xi
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 757–762
 Abstract
Abstract(
1040 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(451KB)(
1730
)
Graphene/carbon aerogels (RF) were prepared via a Sol-Gel process in graphene oxide (GO) solution using resorcinol (R) and formaldehyde (F) as carbon precursor. The structure, morphology and pore-size distribution of the samples were characterized by XRD, Raman spectrum, SEM and N2 adsorption desorption method. The results indicate that graphene can act as nucleation and growth sites for carbon aerogels. At low mass loading level of RF, a macroporous structure is formed, and the structure of carbon aerogels originates from sheet-structure of GO precursor. With increasing the mass of RF, RF carbon aerogel results in dispersed and thickened carbon platelets. At high mass loading levels, carbon spheres are obtained. Meanwhile, with increasing the mass of RF, the specific surface area of the aerogel increases firstly and then decreases, reaching the maximum value of 841 m2/g when w(GO)/w(RF)=1︰50. Electrochemical measurements show that GO/RF-100 has the highest specific capacitance of 169 F/g in 6 mol/L KOH aqueous electrolytes.
|
|
|
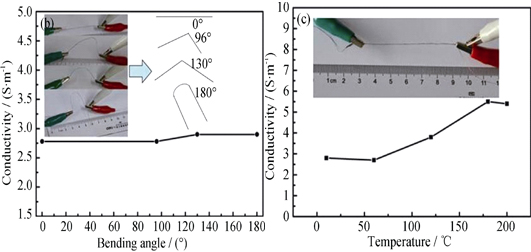
Preparation and Electrical Properties of Graphene Coated Glass Fiber Composites
LIU Guo-Qiang, SHI Fu-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, ZHANG Qing-Hong, WANG Hong-Zhi
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 763–768
 Abstract
Abstract(
1294 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(415KB)(
1829
)
The graphene coated glass fiber composites were obtained from the electrostatic adsorption of graphene oxide on bovine serum albumin (BSA) modified the glass fibers, and the subsequent reduction of graphene oxide coated glass fibers by hydroiodic acid at low temperature of 40℃. The phase structure and functional groups of graphene oxide were studied by XRD and FT-IR, respectively. SEM images showed that the graphene wrapped effect was improved with pH decreasing, when pH of graphene oxide dispersion was less than 6. Zeta potential of graphene oxide and BSA molecule were tested by Particle size/Zeta potential instrument, which showed that the isoelectric points of graphene oxide and BSA were smaller than 3 and 5.3, respectively. Conductivity of graphene wrapped glass fiber composites reached 4.5 S/m, and conductive glass fibers maintained original conductivity after different levels of bending. Moreover, due to the reduction of graphene, the conductivity increased slightly after the heat-treatment above 100℃. These results prove that the conductive glass fibers can be used at high temperature.
|
|
|
Effect of B2O3 Doping and Phosphate Impregnation on Oxidation Resistance and Mechanical Properties of Mesocarbon Microbead Composites
LEI Zhuo-Yan, WANG Zhi, FAN Heng-Bing, MA Wen-Bin, CHEN Jian, WANG Xu
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 769–773
 Abstract
Abstract(
556 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(446KB)(
1319
)
Mesocarbon microbead/carbon nanotubes (MCMB/CNTs) composites were modified by adding B2O3 powders and phosphate impregnation and the MCMB/CNTs were prepared using in-situ thermal polymerization. The morphology, flexural strength and oxidation resistance behavior were studied using scanning electron microscope (SEM), three-point bending tests, thermo gravimetric analysis (TG) and isothermal oxidation method. The results show that the oxidation resistance and flexural strength of the composites are enhanced with proper amount of B2O3. When the ratio of B2O3 is beyond 2%, the flexural strength of the sample begins to decrease. The sample with 2% B2O3 impegnated with phosphate reachs the highest flexural strength of 66 MPa, and the initial mass loss temperature of the samples is 520℃. After isothermal oxidation at 500℃ for 60 min, the mass loss and the flexural strength of the sample are 5% and 50.3 MPa, respectively.
|
|
|
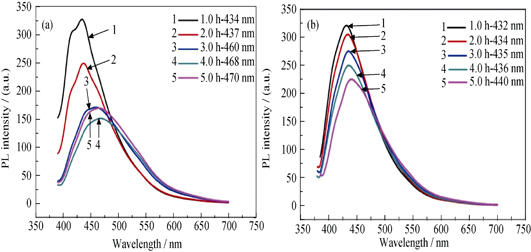
Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Oil-Soluble PbSe Quantum Dots
YANG Feng-Jiu, LU Meng-Chen, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Yan, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 774–778
 Abstract
Abstract(
657 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(304KB)(
1351
)
Oil-soluble PbSe quantum dots (QDs) with uniform morphology and narrow size distribution were obtained via a facile hydrothermal approach. The cubic PbSe QDs with nearly spherical shape and average diameter of (4.0 ± 0.5) nm were obtained. The as-synthesized PbSe QDs showed a strong and a relatively narrow band edge emission in the near purple region at 435 nm and a small full width at half maximum (FWHM) approximately of 80 nm. The photoluminescence (PL) spectra moved to low energy region and FWHM became broad when the reaction time extended and the synthesis temperature increased. The PL spectra exhibited less intense and well defined features at long wavelength which were ascribed to low energy transitions as varying Pb/S molar ratios. In addition, the defect luminescence of PbSe QDs became more obvious with the synthesis temperatures and Pb/S molar ratios increasing. The PL spectra of PbSe QDs shifted to long wavelength (low energy region), because small particles coalesced into form large particles during reaction, which was in agreement with the Ostwald ripening principle. The defects of PbSe QDs may result from thermodynamically instable and lower densities of capped oleic acid.
|
|
|
Nitrogen-doped Carbon Paper as Electrodes for Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
HE Zhang-Xing, LIU Jian-Lei, HE Zhen, LIU Su-Qin
2015 Vol. 30 (7): 779–784
 Abstract
Abstract(
681 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(311KB)(
1756
)
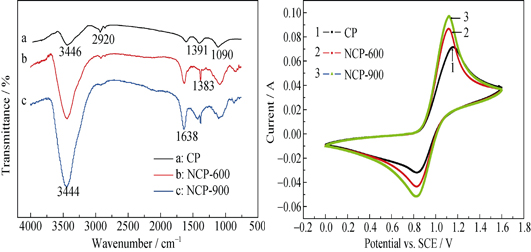
To improve the electrochemical activity of carbon paper (CP) for vanadium redox flow batteries, CP was modified by heat treatment in atmosphere of NH3 at 600 (NCP-600) and 900℃ (NCP-900), respectively. The FTIR results indicate that the nitrogenous groups have been introduced on the surface of CP by modification successfully. Compared with the pristine sample, the water contact angle of NCP-900 decreases from 120.5° to 99.7°, indicating the improved hydrophilicity of CP by nitrogen doping. The SEM results show that there is no obvious morphology change on the surface of CP after nitrogen doping, which do not affect the mechanical property. The electrochemical activity of CP is enhanced significantly by nitrogen doping. The oxidation current peak of V(Ⅳ)/V(Ⅴ) couple on NCP-900 is 92.1 mA, much higher than that of pristine sample (68.9 mA). The cells with NCP-900 and pristine sample as electrodes were assembled and the charge-discharge performance was evaluated. The energy efficiency of cell with NCP-900 as electrode at a current density of 20 mA/cm2 is 83.73%, 2.59% larger than that with the pristine sample. The improved electrochemical performance of nitrogen-doped carbon paper is due to the increased active sites and the enhanced hydrophilicity provided by the introduced nitrogenous groups.
|
|