|
|
Preparation and Application of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanostructures
ZHAI Ying-Jiao, LI Jin-Hua, CHU Xue-Ying, XU Ming-Ze, LI Xue, FANG Xuan, WEI Zhi-Peng, WANG Xiao-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 897–905
 Abstract
Abstract(
2647 )
 HTML
HTML(
43)
 PDF
PDF(641KB)(
4980
)
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a new binary transition-metal compound,has attracted much attention due to its unique physical and chemical properties. MoS2 with different morphology structures were firstly reviewed, including inorganic fullerene-like, sphere-like, flower-like, wire, plate, rod, tube and so on. And then, the methods used to prepare MoS2 nanomaterials were discussed, including chemical vapor deposition method, sulfurization process, exfoliation, electrodeposition, hydrothermal method, and solvothermal method. The applications of MoS2 nanostructures in various fields were also summaried, such as lubrication, catalytic and photoelectric devices. Finally, the outlook for the research of this molybdenum disulfide nanomaterial was proposed.
|
|
|
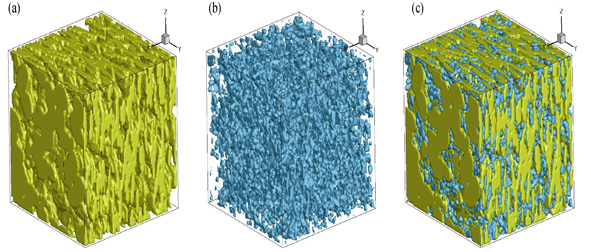
Numerical Reconstruction and Characterization Analysis of Microstructure of Lithium-ion Battery Graphite Anode
HE Shao-Yang, ZENG Jian-Bang, JIANG Fang-Ming
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 906–912
 Abstract
Abstract(
1159 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(546KB)(
26782
)
The real graphite anode of lithium-ion battery is of evident non-isotropic characteristic due to its cascading graphite flakes. An ellipsoid particle-based simulated annealing method is developed to numerically reconstruct the three-dimensional microstructure of graphite anode. The reconstructed anode is a composite of three clearly distinguished phases: pore (or electrolyte), graphite and solid additive, well representing the non-isotropic characteristic of real graphite anode. Characterization analysis of reconstructed electrodes gives information such as the connectivity, the specific surface area of solid or pore phase, and the pore size distribution. The results show that the size of graphite ellipsoids has important effects on the characteristics of electrode: 1) larger size graphite ellipsoids result in larger mean pore size and smaller specific surface area in the reconstructed electrode; 2) changing the polar radius of graphite ellipsoid particles has more pronounced influence on the characteristics of electrode than has changing its equatorial radius.
|
|
|
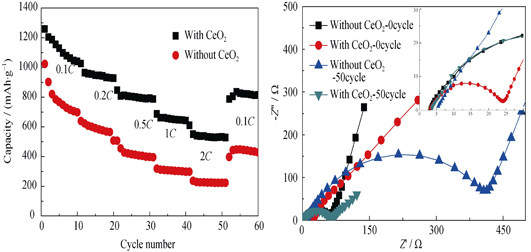
Effects of CeO2 Nano-crystal on Electrochemical Properties of Lithium/Sulfur Batteries
MA Guo-Qiang, WEN Zhao-Yin, WANG Qing-Song, JIN Jun, WU Xiang-Wei, ZHANG Jing-Chao
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 913–918
 Abstract
Abstract(
1184 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(445KB)(
1696
)
The CeO2 nano-crystal less than 10 nm was fabricated by using thermal decomposition method with Ce(OH)4 as the raw material. CeO2 nano-crystal with abundant -OH and -NO2 was used as the additive in the sulfur cathode. The additive can adsorb sulfur and lithium polysulfides during charge/discharge process, suppressing the dissloving and migrating of lithium polysulfides in the electrolyte. Thus the “shuttle effect” caused by dissloving of lithium polysulfides can be evidently inhibited, resulting in the enhanced cycle performance and the improved coulombic efficiency of Li-S battery. Furthermore, CeO2 nano-crystal with abundant -OH and -NO2 is beneficial to enhance the wettability between electrolyte and sulfur cathode, improving the utilization rate of active material. With 5wt% CeO2 nano-crystal added in the sulfur cathode, the discharge capacities at 0.1C and 0.5C (1C=1675 mA/g) after 100 cycles are as high as 750 mAh/g and 598 mAh/g, respectively, both much higher than those of the sulfur cathode without CeO2 nanocrystal. Simultaneously, the resistance of the cell is also reduced evidently before and after cycling owing to the addition of CeO2 nano-crystal in the cathode.
|
|
|
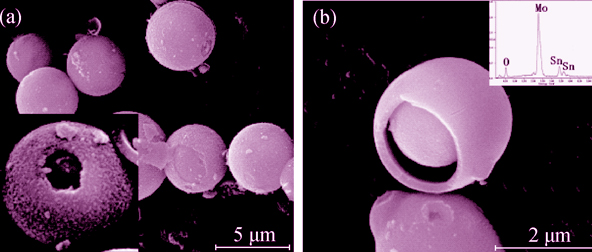
Morphology-controlled Synthesis of Hollow Core-shell Structural α-MoO3-SnO2 with Superior Lithium Storage
WANG Ya-Peng, LIU Jia-Jia, LIU Chun-Xiao, CHEN Wei-Wei, LI Ting-Ting, GUO Hong
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 919–924
 Abstract
Abstract(
741 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(969KB)(
1730
)
An effective approach of alcoholysis was employed to prepare hollow core-shell MoO3-SnO2 hybrid nanoparticle aggregates as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. The as-prepared samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, CV, and galvanostatical method. The results show that the unique hollow structures can shorten the distance Li-ion diffusion, and the hollow structure offers a sufficient void space, which sufficiently alleviates the mechanical stress caused by volume change. The as-obtained hollow core-shell MoO3-SnO2 hybrid electrodes can retain a discharge capacity of 865 mAh/g at current density of 50 mA/g after 100 charge-discharge cycles. Even at the current density of 1000 mA/g, the MoO3-SnO2 hybrid electrodes can still deliver a high reversible discharge capacity of 545 mAh/g. Therefore, the hollow MoO3-SnO2 hybrid electrode exhibits stable cyclability and good rate capability. This method is simple, low cost and mass-productive, and may also be used to prepare other advanced functional materials.
|
|
|
Nitrogen Doped Carbon Quantum Dots/Titanium Dioxide Composites for Hydrogen Evolution under Sunlight
WEI Jie, LI Xue-Dong, WANG Hong-Zhi, ZHANG Qing-Hong, LI Yao-Gang
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 925–930
 Abstract
Abstract(
1238 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(461KB)(
1791
)
Using acetonitrile as the solvent and glucose as the raw material, nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots (NCDs) were prepared by the solvothermal method. The size of NCDs is around 4 nm. The emission spectrum of NCDs showed red shift when the excitation wavelength of quantum dots increased from 330 nm to 470 nm. Titanium dioxide was coated by NCDs by mixing a certain proportion of NCDs, TiO2 and ultrapure water through 60 min ultrasonic and aging under 80℃ for 24 h. NCDs/titanium dioxide composites show good photocatalyst performance as compared with pure NCDs and pure titanium dioxide, because the NCDs can expand the absorption spectrum and reduce the photogenerated electrons and holes. The NCDs/TiO2 composites at the raw ratio of m(NCDs):m(TiO2)=15:85 show the best hydrogen evolution performance, using methanol as the sacrificial agent. The composite material displays good stability and certain photocatalytic performance after three cycles.
|
|
|
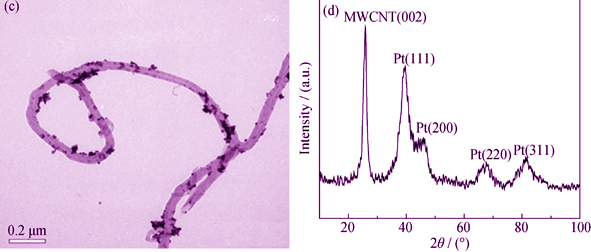
Effect of Modification Factors of MWCNTs Support on Electrocatalytic Performance of Pt Nanoparticles
XU Ming-Li, DUAN Ben, ZHANG Ying-Jie, YANG Guo-Tao, DONG Peng, XIA Shu-Biao, YANG Xian-Wan
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 931–936
 Abstract
Abstract(
683 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(521KB)(
1266
)
A simple and green method of modified multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) by methylene blue under ultraviolet irradiation was reported. The irradiation time, methylene blue dosage and ultraviolet wavelength were considered as the three main factors. The different factors of functionalized MWCNTs and their catalytic performance were systematically studied. TEM was used to indicate the catalyst morphology. Cyclic voltammetric and chronoamperometric experiments were used to study catalytic activity and stability for methanol in alkaline solution. The results showed that the optimal conditions of irradiation time, methylene blue dosage and ultraviolet wavelength are 6 h, 10 mg and 254 nm, respectively. Under these conditions, catalyst has the best dispersion of Pt nanoparticles on the surface of functionalized MWCNTs, realizing the best catalytic performance, with catalytic activity at 2-fold of that of the commercial Pt/C catalyst. This modification of MWCNTs provides a new way for achieving anode catalysts with high activity and low cost in the fuel cells.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Carbon Nanotubes/Titanium Dioxide Nanocomposites
MA Bao-Lu, ZHANG Yue
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 937–942
 Abstract
Abstract(
682 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(383KB)(
1209
)
CNTs/TiO2 nanocomposites were prepared by Sol-Gel method without any surfactant. The as-prepaired samples were characterizated by using X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscope, high resolution transmission electron microscopy, selected area electron diffraction and UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The degradation experiment of the methylene blue under UV-light was used to evaluate the catalytic activity of the CNTs/TiO2 catalysts, and the influence factors of catalytic efficiency such as CNTs doping concentration were studied systematically. The results suggest that the anatase titanium dioxide coat on the surfaces of CNTs uniformly in the form of C-O-Ti after annealing at 450℃, and the size of TiO2 nano-particle is about 16 nm. Moreover, CNTs/TiO2 nanocomposites show a distimctive photodegradation efficiency, CNTs/TiO2 nanocomposites with 1wt% CNTs present an increase of photodegradation efficiency by 11.7% as regarding to pure TiO2.
|
|
|
Preparation by Grinding-calcination and Photocatalytic Performance of La2O3/BiOCl Composite Photocatalysts
CHEN Jian-Chai, YU Chang-Lin, LI Jia-De, FANG Wen, HE Hong-Bo
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 943–949
 Abstract
Abstract(
839 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(598KB)(
1776
)
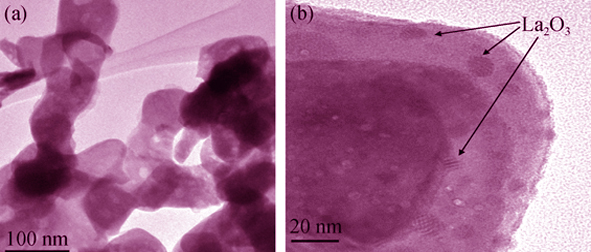
BiOCl nanoplates were firstly prepared by precipitation method and then La2O3/BiOCl composite photocatalysts with different La2O3 contents (1wt%, 2wt%, 4wt%, 8wt%) were synthesized by grinding-calcination procedure. The physical chemistry properties of the as-prepared photocatalysts were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscope (DRS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscope (FT-IR), and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscope. The photocatalytic activity of the samples was evaluated by photocatalytic degradation of high concentration acid orange II (40×10-6) under UV light (λ=254 nm) irradiation. Results showed that the as-prepared samples have good crystallinity. La2O3 particles with the size of 2-5 nm were closely combined with BiOCl nanoplate after grinding-calcination treatment. La2O3/BiOCl composite photocatalysts with 1wt% La2O3 calcined at 200℃ displayed the best photocatalytic activity which is 2.4 times of that of pure BiOCl. The produced La2O3/BiOCl has abundant surface OH groups and highly suitable adsorption of dye. Moreover, La3+ could capture the photon-generated electrons (e-) and prevent the recombination of photon-generated and holes (h+).
|
|
|
Preparation of Superparamagnetic Gold Nanocomposites with Different Diameters and Their Imaging and Therapy Applications
ZHAI Yun-Gang, DONG Wen-Jie, GAO Yong-Ping, NIU De-Chao, CHEN Jian-Zhuang, GU Jin-Lou, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 950–956
 Abstract
Abstract(
954 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(568KB)(
1269
)
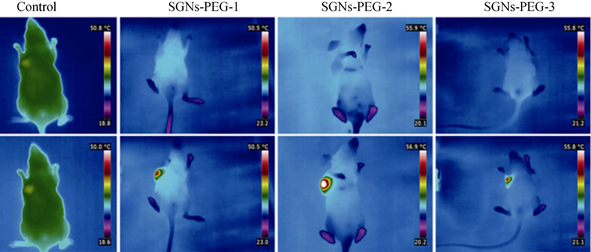
Superparamagnetic gold nanocomposites (SGNs), which have great potential in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and photothermal therapy (PT) on cancer, have been successfully synthesized via the in-situ reduction and the following seed-mediated growth route. It is found that the dimension of SGNs could be facilely tuned by changing the encapsulation amount of Fe3O4/tetrahydrofuran solution, and SGNs with diameters of 100, 150 and 200 nm were thus obtained. The as-synthesized SGNs present regularly spherical morphology, narrow size distributions and monodispersity in aqueous solutions. It is revealed that SGNs modified with SH-PEG are capable for simultaneous MRI and photothermal therapy. Especially, SGNs with average diameter of 150 nm exhibit the strongest absorption capacity and highest photothermal conversion efficiency with 808 nm laser. The temperatures in vitro and in vivo were increased by 37 ℃ and 25 ℃, respectively. Therefore, it is hopeful that tumor can be imaged well and killed efficiently under laser irradiation after intratumoral injection of such a kind of nanocomposites.
|
|
|
Magnesium Phosphate/PBS/Wheat Protein Biocomposite for Bone Repair
WANG Quan-Xiang, WU Ying-Yang, DONG Xie-Ping, MA Xu-Hui, WEI Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 957–962
 Abstract
Abstract(
788 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(515KB)(
1351
)
Magnesium phosphate was prepared through coprecipitation method, and biocomposite containing magnesium phosphate(MP), polybutylene succinate (PBS) and wheat protein (WP) was fabricated. In vitro degradability, bioactivity and cell responses to MP/PBS/WP composite were investigated. The results showed that the pH value changed from 7.4 to 7.51 after the MP/PBS/WP composite being soaked in Tris-HCl buffer solution for 10 d. The weight loss of the composite reached 58.43wt% after soaking for 12 w. Apatite layer could form on the composite surfaces after soaking in SBF solution for 10 d, indicating good bioactivity. In addition, the MP/PBS/WP composite could promote proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells. All data from this study show that the MP/PBS/WP composite has good degradability, bioactivity and cytocompatibility, showing a potential to be used as a new biomaterial for bone repair.
|
|
|
Influence on Processing and Magnetic Flux Properties of Single Grain YBCO Fabricated from Layered Precursor Powders
TANG Tian-Wei, QIU Fu-Jie, WU Dong-Jie, XU Ke-Xi
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 963–970
 Abstract
Abstract(
745 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(662KB)(
1267
)
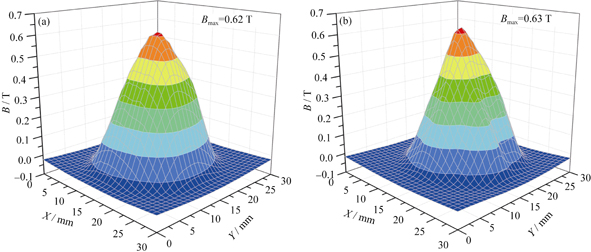
The fabrication of single domain Y-Ba-Cu-O(YBCO) bulk superconductors usually involves precursor pellets that contain a uniform distribution of YBa2Cu3O7-δ(Y123) and Y2BaCuO5(Y211) compounds. However, the concentration of Y211 phase particles in the fully melt processed superconducting bulk increases significantly with distance from the seed, leading to accumulation of Y211 phase particles and degradation of superconducting properties. By top seeded melt texture growth (TSMTG) process, single domain YBCO bulk superconductors at about 23 mm in diameters, and 9 mm in thickness were fabricated from layered precursor pellets and conventional precursor pellets, respectively. The growth morphology, microstructure and magnetic flux properties of both layered and conventional pellets were comparatively studied. The experiments suggest that the layered precursor pellets allow a sufficient growth in c growth sector, a more uniform distribution of Y211 phase in the matrix and a significant enhancement of the trapped field. Thus for the layered pellets, a trapped magnet field of 0.91 T is achieved at 77 K and the flux distribution is also of high symmetry. The present results are very valuable for further improving the properties of YBCO bulk superconductors.
|
|
|
Surface Properties of Magnesium-iron Hydrotalcite and Its Modified Products by Inverse Gas Chromatography
XU Jin-Fang, SHAO Meng-Meng, NI Zhe-Ming, XIAO Xue-Chun
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 971–976
 Abstract
Abstract(
688 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(472KB)(
1217
)
The magnesium-iron hydrotalcite was modified by three nonionic surfactants (Span-20, Tween-80, Triton X-100) combined with sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), respectively, and surface characterizations of modified hydrotalcites were investigated using inverse gas chromatography (IGC). The free energy of adsorption (-ΔG0), dispersive component of the surface energy (γsd) and acid-basic action free energy (-ΔGsp) were determined to explore the changes between MgFe-LDHs and modified hydrotalcites. The results show that the -ΔG0 of the modified hydrotalcites are lower than that of MgFe-LDHs, among which the -ΔG0 of the SDBS/Triton-LDHs is the lowest, indicating the best stability. The alkalinity of modifed hydrotalcites is weakened and the alkalinity of SDBS/Triton-LDHs is the weakest. In addition, the γsd decreases with temperature increase. Therefore, the compatibility with polymer can be improved by increasing the temperature in preparation of polymer/hydrotalcite materials.
|
|
|
Characterization and Toughening Mechanism of Crystallization of Canasite Glass-ceramics
LI Yao-Hui, WANG Jin-Zhen, HUANG You-Rong
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 977–983
 Abstract
Abstract(
807 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(567KB)(
1573
)
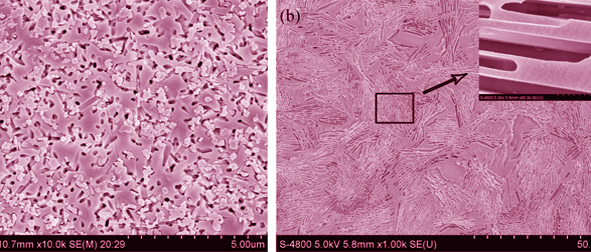
The R2O-CaO-SiO2-F system glass-ceramics were prepared through different heat treatment schedules. The crystallization, microstructure and mechanical properties, especially the crack propagation and toughening mechanism of the canasite-based glass-ceramics, were studied. The results show that CaF2 crystallites precipitate firstly during heat treatment at low temperature. After one-step heat treatment block-like xonotlite/canasite complex phases can be obtained. And after two-step heat treatment, the canasite-based glass-ceramics, composed of particularly interlocking blade-like crystals, are obtained with excellent mechanical properties. The micrographs suggest the orientation and interface of canasite crystals radically change the crack propagation, showing intercrystalline and transcrystalline cracks forming random-step or fold-like line. Based on these results, the blade-like canasite crystals at certain slenderness ratios, display favorable anti-cracking effect because of their bridging toughen mechanism. In addition, the residual stress between matrix and crystals also benefits relaxation of stress and deflection of crack. So, the excellent mechanical properties of the as-prepared glass-ceramics are resulting from multiple toughening mechanisms.
|
|
|
Effect of MgO/ Eu2O3 Co-doping on the Microwave Dielectric Properties of Al2O3 Ceramics
ZHANG Kang, LI Wei, LIN Hui-Xin
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 984–988
 Abstract
Abstract(
662 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(406KB)(
1377
)
Al2O3 ceramics co-doped with MgO/Eu2O3 were prepared by wet chemical process. The effects of the content of MgO/Eu2O3 co-doping on phase composition, microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of Al2O3 ceramics were explored. The experimental results show that suitable contents of MgO/Eu2O3 can promote densification and grain growth of Al2O3. As to the dielectric properties, the influence of MgO/Eu2O3 co-doping on the dielectric constant can be ignored. However, it has a significant impact on the dielectric loss. The Q×f value increases initially and then decreases as the Eu2O3 content increases. Optimized microwave dielectric properties with εr~9.82, Q×f ~225,225 GHz. can be attained for the samples co-doped with 0.05wt% MgO/0.10wt% Eu2O3 sintered at 1590℃ for 4 h This change of Q×f value may relate to the change of sample’s microstructure. Firstly, when the content of MgO/Eu2O3 increases, the grain size increases and the grain boundary decreases, which is beneficial to increase the Q×f value. Then, as the content of MgO/Eu2O3 keeps increase, the grain size decreases and the grain boundary increases, which may lead to decrease Q×f value. In addition, the presence of strain and second phase may also influence the change of Q×f value.
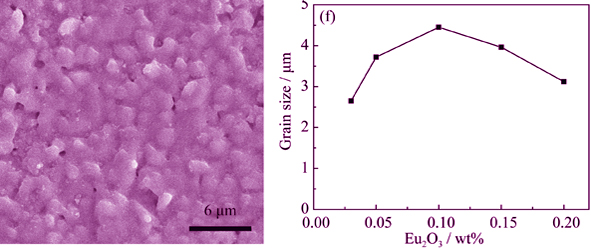
|
|
|
Preparation and High Temperature Stability of CaxSr1-xBi2Nb2O9 Lead-free Piezoelectric Ceramics
YAO Zhong-Ran, CHU Rui-Qing, XU Zhi-Jun, HAO Ji-Gong, LI Guo-Rong
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 989–994
 Abstract
Abstract(
607 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(511KB)(
1329
)
CaxSr1-xBi2Nb2O9 (x=0, 0.10, 0.25, 0.40) ceramics were prepared by solid-state reaction method, and their microstructure, electrical and temperature stability properties were systematically investigated. It is found that Ca-doping does not change the phase structure of SrBi2Nb2O9. With increasing Ca2+ contents, microstructure of the CaxSr1-xBi2Nb2O9 ceramics changes from sheet to long strips. The remnant polarization (Pr) increases firstly and then decreases, reaching the maximum value at x=0.01, while the coercive field (Ec) decreases gradually. Furthermore, Ca-doping can also improve the Curie temperature, which increases from 450℃ to 672℃ with increase of Ca2+ contents. The optimum electrical properties can be obtained at x=0.10 as 2Pr=14.8 μC/cm2, d33=22 pC/N and Tc=488℃. In addition, after annealing at 400℃, the piezoelectric constant (d33) of the ceramics remains 20 pC/N, showing good temperature stability for high temperature applications.
|
|
|
High Ion Conductivity in Garnet-type F-doped Li7La3Zr2O12
LIU Cai, WEN Zhao-Yin, RUI Kun
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 995–1001
 Abstract
Abstract(
2051 )
 HTML
HTML(
51)
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
4012
)
A novel garnet-type solid electrolyte, F-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO), was prepared via conventional solid-state reaction. Certain fluoride compounds were known to form the pure cubic garnet structure after continuous calcination at 900℃ and 1125℃, seperately. Fluorine ions doped in LLZO contributed to the stabilization of high ion conductivity garnet phase as well as the enhancement of sintering activity. The effects of fluorine ions were studied using the dopants LiF and CaF2. The 1.0wt% LiF-LLZO samples exhibited a total conductivity of 5×10-4 S/cm close to the bulk conductivity value of un-doped LLZO, while its activation energy was 0.26 eV, lower than that of other cation-doped LLZO samples. The strong intensity of the peaks indexed to (321), (400), (642), and (800) in XRD patterns indicated the growth of ceramic grains of F-doped LLZO in certain favorable crystallographic orientations during sintering process. In addition, a unique microstructure was revealed in the novel garnet-type oxide pellets, showing the grain boundary almost removed and closed pores formed, which resulted in the negligible grain boundary and the high total ion conductivity.
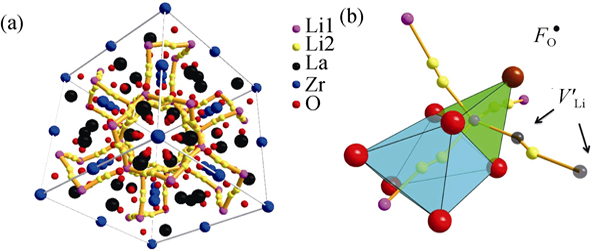
|
|
|
Facile Synthesis of Visible Light Activated Carbon-incorporated Mn Doped TiO2 Microspheres via Flame Thermal Method
SUN Tong, CHEN Yang, MA Xiao-Qing, LI Zhong, LI Hui, CUI Xiao-Li
2015 Vol. 30 (9): 1002–1008
 Abstract
Abstract(
770 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(433KB)(
1639
)
Carbon-incorporated Mn doped TiO2 (C/Mn-TiO2) microspheres with different Mn contents were prepared by a facile and novel flame assisted approach. The influence of the Mn contents on the morphology and performance was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) and Raman spectra, respectively. SEM and XRD results showed the existence of anatase TiO2 microspheres without post-heat treatment. XPS and Raman results confirmed Mn2+ substitution of Ti4+ in the resulted samples. UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra showed that the incorporation of Mn into TiO2 lattice could enhance visible light absorption. Improved photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible light illumination was demonstrated with the introduction of Mn dopant. The introduction of Mn resulted in the narrowed band gap in C/Mn-TiO2. This study offers not only an environmentally friendly product with high photocatalytic activity, but also a rapid and direct strategy without any particular skill.
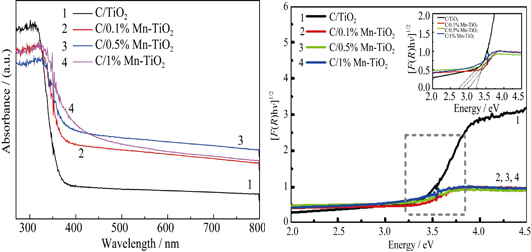
|
|