|
|
Applications of Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) in the New Generation of High-K Gate Dielectrics
ZHU Xin-Hua, LI Ai-Dong, LIU Zhi-Guo
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1233–1240
 Abstract
Abstract(
1016 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(608KB)(
1752
)
Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) Z-contrast image has some advantages such as high image resolution (directly revealing the real positions of atoms in crystal), high compositional sensitivity and directly interpretable images, it becomes a powerful tool for investigating the microstructure of materials at atomic scale. In this review, the formation mechanisms, methods and features of the Z-contrast STEM images are introduced, and its applications in the new generation of high-k gate dielectrics (e.g., Hf-based metals oxides, rare-earth oxides and epitaxial perovskite oxides) are also reviewed. After aberration-correction the spatial resolution of the Z-contrast STEM images is as high as the sub-Å level, this technique is invaluable for characterizing the interfacial structures between high-K gate dielectrics and semiconductors. The related results are also introduced.
|
|
|
Effect of CeO2-based Solid Solutions on Hydrogen Storage Kinetic Properties of Mg2Ni Alloy
ZHANG Guo-Fang, ZHANG Yang-Huan, LIU Zhuo-Cheng, XU Jian-Yi, ZHANG Yin
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1241–1245
 Abstract
Abstract(
644 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(390KB)(
1481
)
Nanosized Ce1-x(Eu0.5La0.5)xO2 and Ce1-x(Fe0.5La0.5)xO2 solid solutions were synthesized via hydrothermal method, and the doping effect was characterized by analyzing the structure and spectrum features of the solid solutions. The results showed that the cell parameters of the solid solutions increased, the absorption edge of the UV diffuse reflectance spectroscopy was drifted, and the characteristic Raman F2g vibration peak shifted to lower wave numbers. Then the mixtures of Mg2Ni alloy powders and the solid solution additives were ball-milled to obtain composites. XRD results showed that the fraction of amorphous and nanocrystalline in the as-prepared composites was increased. The hydrogen storage kinetic measurements demonstrated that surface activity and degree of reversibility of the composites was optimized, and the diffusion rate and diffusion coefficient of hydrogen atoms in the bulk of Mg2Ni were increased.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Performance of Anode for Microtubular Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
YANG Nai-Tao, SHEN Yi-Chi, YAN Wei, MENG Xiu-Xia, TAN Xiao-Yao, MA Zi-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1246–1252
 Abstract
Abstract(
672 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(545KB)(
1533
)
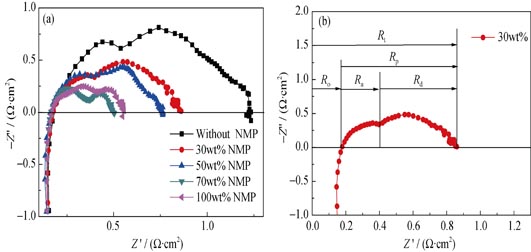
NiO-YSZ hollow fibers were fabricated via a phase-inversion spinning technique. An YSZ electrolyte film was dip-coated on the outer surface of the fiber and then co-sintered at 1450℃ to form electrolyte/anode hollow fiber half cell. The microstructure of the NiO-YSZ anode was modulated by controlling NMP/ethanol ratio of the inner coagulant during spinning process. Experimental results showed that, with the 1-Methy 1-2-Pyrrolidinone (NMP) content increase from 0 to 30wt%, 50wt%, 70wt% and 100wt%, the microscopy of the anode hollow fibers evolved from a sandwiched structure, i.e. finger-like pore/sponge voids/finger-like pore morphology, to a finger-pore-penetrating structure, leading to porosity increase of the anode. Meanwhile, gas tightness of YSZ electrolyte film, mechanical strength of the reduced dual-layer hollow fibers, and conductivity of anode could decrease. Microtubular fuel cells were fabricated by coating a porous Ag cathode onto the dense YSZ electrolyte film. The concentration polarization in the H2/air cell decreased with increasing the length of the finger-like pores. The microtubular SOFC made from the anode hollow fibers with 70wt% of NMP-ethanol as the inner coagulant demonstrated the minimum polarization resistance and the highest output performance with 662 mW/cm2 power density.
|
|
|
Effect of Electrolyte Surface Microstructure on Interfacial Polarization Resistances of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Cathodes
SONG Shu-Xiang, WANG Yun-Long, XIA Chang-Rong
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1253–1256
 Abstract
Abstract(
631 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(383KB)(
1239
)
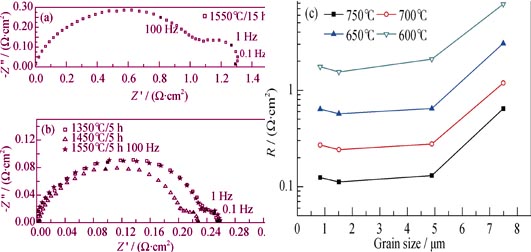
The interfacial polarization resistance (Rc) associated with cathode in solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) is affected by the electrolyte conductivity. In this work, the effect of electrolyte surface microstructure on the cathode performance was demonstrated by analyzing electrochemical impedance spectra of symmetric cells which consist of porous (La0.85Sr0.15)0.9MnO3-δ (LSM) and La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3-δ (LSCF) electrodes with Sm0.2Ce0.8O2-δ (SDC) electrolytes. The SDC electrolytes exhibited different surface microstructures, i.e. different grain sizes and grain boundary densities as a result of various sintering conditions. SEM was used to investigate the SDC surface microstructure parameters and the relationships between these parameters and the polarization resistance ware discussed. It is found that Rc is greatly affected by the SDC surface microstructures and decreases with the decrease of grain size, or the increase of grain-boundary density. Moreover, it is demonstrated that the oxygen ion transfer is significantly increased by decreasing grain size for the oxygen reduction at the LSM cathode.
|
|
|
Surface Modification of Li-rich Layered Li(Li0.17Ni0.2Mn0.58Co0.05)O2 Oxide with TiO2(B) as the Cathode for Lithium-ion Batteries
LIU Qin, YUAN Wen, GAO Xue-Ping
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1257–1264
 Abstract
Abstract(
918 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(564KB)(
19707
)
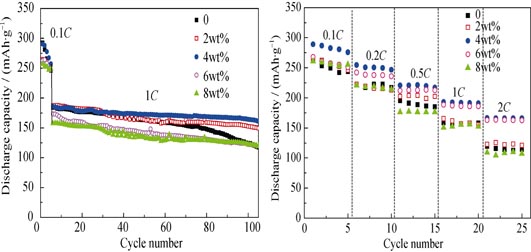
The Li-rich layered Li(Li0.17Ni0.2Mn0.58Co0.05)O2 oxide was prepared by a spray-drying method. Subsequently, the surface modification with TiO2(B) nanocrystallites (2wt%, 4wt%, 6wt%, 8wt%) was introduced into the Li-rich layered Li(Li0.17Ni0.2Mn0.58Co0.05)O2 oxide by precipitation method. It is demonstrated that there is no obvious change in the crystallographic structure of the Li-rich layered Li(Li0.17Ni0.2Mn0.58Co0.05)O2 oxide based on the analysis of XRD, SEM and TEM, while only the surface of the oxide is modified with TiO2(B) nanocrystallites. It is indicated from DSC curves that the thermal stability of Li-rich layered oxide is obviously improved by the surface modification with TiO2(B) nanocrystallites. Correspondingly, the large discharge capacity of 296.4 mAh/g and high coulombic efficiency of 84.5% are obtained at 0.1C rate (1C=300 mA/g) in the first cycle for the Li-rich layered oxide after the surface modification with TiO2(B) nanocrystallites (4wt%). Moreover, the capacity retention after 100 cycles is increased from 69.5% for the pristine sample to 80.2% for the TiO2(B)-modified sample. Even at 2C rate, the large discharge capacity of 166.5 mAh/g is still obtained for the TiO2(B)-modified sample. Apparently, it is demonstrated from the above results that the surface modification with TiO2(B) nanocrystallites can improve the thermal stability and electrochemical performance of the Li-rich layered Li(Li0.17Ni0.2Mn0.58Co0.05)O2 oxide.
|
|
|
Preparation and Performance of KNN-based Upconversion Transparent Ceramics
GENG Zhi-Ming, LI Kun, SHI Dong-liang, SHI Xia-Yu, HUANG Hai-Tao, CHAN Helen Lai Wa
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1265–1269
 Abstract
Abstract(
898 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(444KB)(
1526
)
Upconversion transparent ceramics K0.5(1-y)Na0.5(1-y)LiyNb1-yBiyO3-Er0.005Yb0.005x(Er3+/Yb3+:KNNLB, x=0-3, y=0-0.09) were fabricated by hot-press sintering process using LiBiO3 as additives. The microstructure, optical transparency and upconversion fluorescence were investigated.The results show that the crystalline phase of the ceramics is orthorhombic-perovskite structure.The ceramics are well densified, and the grain size of the ceramics is about 0.5 μm.These ceramics present good transparency in the infrared and the long-wavelength visible regions, but the optical transparency declines rapidly in the visible region as the amount of Yb3+ and Er3+ ions increases.The transparency of the ceramics with y = 0.06 and x = 0 reaches 45% in the visible region and over 95% in the infrared region(the thickness of the sample is 0.5 mm).The strong upconversion fluorescence is observed when the ceramics are excited by the 900 nm-wavelength light of an xenon lamp.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Luminous Property of Periodical Gradient Si-rich SiNx Thin Films
CHEN Xiao-Bo, YANG Wen, DUAN Liang-Fei, ZHANG Li-Yuan, YANG Pei-Zhi
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1270–1274
 Abstract
Abstract(
625 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1422
)
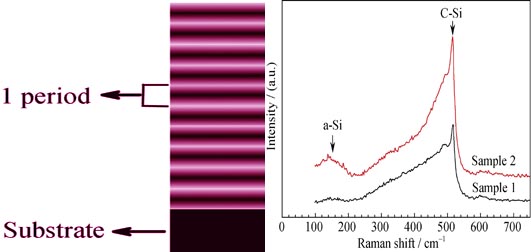
Periodic gradient Si-rich SiNx (G-SRSN) thin films and single-layer Si-rich SiNx (S-SRSN) thin films were deposited on monocrystalline silicon wafers and quartz substrates by combination of magnetron co-sputtering and rapid photo-thermal annealing. Raman spectroscope, grazing incident X-ray diffraction (GIXRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscope and photoluminescence (PL) were used to analyze the structure, bonding configurations and luminescence of the films. Raman, GIXRD and TEM results show that the crystalline fractions of G-SRSN and S-SRSN thin films are 41.7% and 39.2%, respectively. Quantum dots density of G-SRSN thin film is 4.4 times higher than that of S-SRSN thin film. The FTIR spectra demonstrate that both G-SRSN and S-SRSN films are Si-rich SiNx, but Si content of the former is lower than that of the later. PL spectra suggest that the G-SRSN thin films possess a lower radiative recombination defect density than the G-SRSN thin films.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of CaTiO3:Pr3+/TiO2-mica Fluorescent Pearlescent Pigments
ZHOU Wei-Ming, CHEN Qing-Hua, KE Mei-Zhen, WU Nan, LUO Yong-Jin, ZHANG Hua-Ji, QIAN Qing-Rong
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1275–1280
 Abstract
Abstract(
649 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(509KB)(
1340
)
Double-layer of titanium dioxide and Pr-doped calcium hydroxide were coated on the surface of mica by liquid phase deposition, and followed by calcination to form the Pr-doped calcium titanates fluorescent layer. The resultant CaTiO3:Pr3+/TiO2-mica fluorescent pearlescent pigments were characterized by photoluminescence excitation (PLE) and emission (PL), automatic colorimeter (AC), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), respectively. The fluorescent pearlescent pigments obtained at the calcium oxide cladding ratios of 5.3%, the praseodymium/calcium nitrate molar concentration of 0.2%, and the calcinations temperature of 900 ℃, show good pearl property with homogeneous, dense and smooth surface, and relatively high fluorescence intensity. The excitation spectrum of these fluorescent pearlescent pigments consists of three bands at 264, 304 and 380 nm. The maximum emission wavelength is found to be a red light of 613 nm, corresponding to the transition for 1D2→3H4.
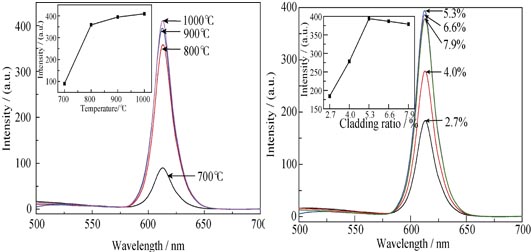
|
|
|
Syntheses and Photoluminescence Properties of Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+ Phosphors
PENG Xia,LI Shu-Xing, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren, LI Hui-Li
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1281–1286
 Abstract
Abstract(
742 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
1406
)
Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+ phosphors were prepared by carbothermal reduction and nitridation method using Sr2CO3, Si3N4 and Eu2O3 as raw materials, and C as main reduction agent. The influence of C, Sr2CO3 and Eu2+ contents on phase composition and photoluminescence properties of as-prepared phosphors were investigated. The experimental results indicate that single-phase Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+ is produced with molar ratio nc/nSi3N4=9/5. Excessive Sr2CO3 addition contributes to the N contents of the as-prepared phosphors, which enhances emission intensity. There is an asymmetric wide emission peaks between 550 nm and 700 nm due to the electron transfer of Eu2+ from 4f65d1 to 4f7 excited by 450 nm. Increasing Eu2+ concentration from 1.5mol% to 20mol%, the luminescence intensity hits the maximum value at Eu2+ concentration of 2mol% followed by continuous decline. Meanwhile the emission peak position is red-shifted from 608 nm to 641 nm, and the CIE chromaticity coordinates varies from (0.606, 0.393) to (0.656, 0.343), which indicates that Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+ is a promising phosphor for white LEDs.
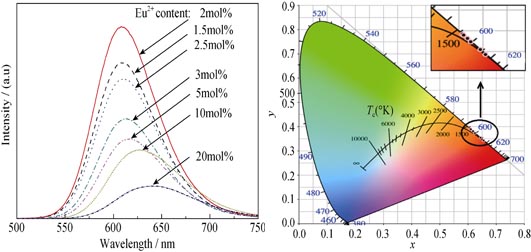
|
|
|
CO2 Methanation over Ru/TiO2 Catalysts under UV Irradiation and Heating
CHEN Shu-Qing, Lü Gong-Xuan
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1287–1293
 Abstract
Abstract(
749 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(522KB)(
1602
)
CO2 hydrogenation was carried out over Ru/TiO2 catalysts prepared by wet impregnation method. It was found that CO2 methanation (CO2 + 4H2 → CH4 + 2H2O) could be catalyzed by Ru/TiO2 both under UV irradiation and heating. Results showed that CH4 was the only C-contained product under UV irradiation in temperature range from 150-350℃, while both CH4 and CO (minor product) were formed at temperature higher than 400℃ under heating conditions. This indicated that reaction temperature affected obviously on selectivities of products. For all the catalysts with different Ru loadings, CO2 conversion increased firstly and then decreased from 150℃ to 550℃, and corresponding maximum value of CO2 conversion of 77.58% was achieved at 350℃ over 1.5wt% Ru/TiO2 catalysts. Further increasing of reaction temperature over 400℃ led to the increase of CO selectivity. Based on reaction data, XRD, XPS and N2 adsorption-desorption characterization results, we found that CO2 hydrogenation occurred in different ways under UV irradiation and heating conditions (150-550℃). Under UV irradiation, excited electrons were firstly trapped by Ru site and then these electrons reduced CO2 species, which was adsorbed on Ru surface to form CH4 via RuC intermediate. However, under heating condition (150-550℃), H2 was first decomposed into H atoms over Ru site, then the adsorbed CO2 species on Ru site was reduced by H atoms to form RuC intermediate. Finally, RuC reacted with H atoms to produce CH4. Although CO2 hydrogenation was taken place via same intermediate under UV irradiation and heating conditions, the RuC intermediate was formed in different ways, i.e., the activation of CO2 was induced in the different routes, therefore the different selectivities of products were obtained under UV irradiation and heating at temperature higher than 400℃ consequently.
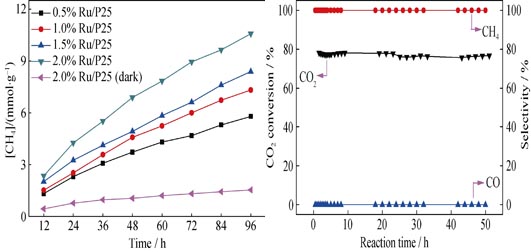
|
|
|
Promotional Effect of Tungsten Incorporation on Catalytic Performance of Ti0.8Zr0.2Ce0.2O2.4/Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by NH3
FU Wei-Liang, SHEN Yue-Song, ZHU She-Min, SHEN Shu-Bao
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1294–1300
 Abstract
Abstract(
757 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(621KB)(
1219
)
Series TZC/ATS catalysts and the tungsten-added samples, with Ti0.8Zr0.2Ce0.2O2.4 (TZC for short) as active component and Al2O3-TiO2-SiO2 (ATS for short) as catalyst carrier, were prepared by extrusion method. Effects of tungsten incorporation on catalytic performance and tolerance towards K2O and CaO poisoning of TZC/ATS for deNOx by NH3 selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) were mainly studied, and anti K2O and CaO poisoning abilities between the TZCW0.4/ATS and the V2O5(WO3)/TiO2 were comparatively analyzed. Moreover, the specific surface, solid-phase structure, morphology and surface acidity of the catalysts were characterized by techniques of N2-BET, XRD, SEM and NH3-TPD, respectively. Results showed that the TZCW0.4/ATS catalyst exhibited the highest catalytic activity and the best stability for deNOx by NH3-SCR when the Ti/Zr/Ce/W molar ratio of the active component was 4:1:1:0.4. Furthermore, tungsten incorporation greatly enhanced the anti K2O and CaO poisoning abilities of the TZCW0.4/ATS catalyst, and these anti-poisoning abilities of the TZCW0.4/ATS were much stronger than those of the V2O5(WO3)/TiO2. The promotional effect on catalytic deNOx performance was caused by increased specific surface area and enhanced surface acidity of the TZCW0.4/ATS catalyst after tungsten incorporation.
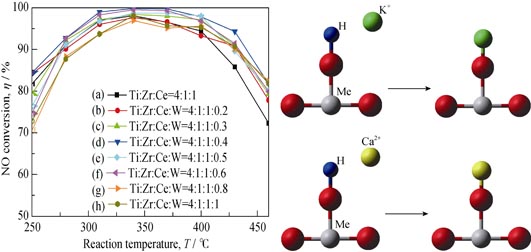
|
|
|
Synthesis and Thermophysical Properties of (La1-xMgx)2Ce2O7-x
YANG Bin, LI Lin-Yan, FAN Min-Guang, LI Bin, XU Sheng-Ming, WANG Jian-Long, LIN Xu-Ping
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1301–1305
 Abstract
Abstract(
608 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(350KB)(
1226
)
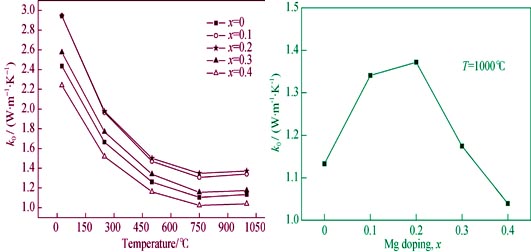
Doping magnesium into La2Ce2O7 can increase its thermal expansion coefficient (TEC) and decrease its thermal conductivity (TC), thus improve its performance for thermal barrier coating (TBC). (La1-xMgx)2Ce2O7-x ceramics were prepared by Sol-Gel method. Powder X-Ray diffraction results revealed that (La1-xMgx)2Ce2O7-x showed the identical structure as La2Ce2O7 (defect-fluorite type), and the crystal parameter decrease with increasing x value in the range of 0≤x≤0.4, and MgO occurred in the product when x?0.4. The TEC of (La1-xMgx)2Ce2O7-x sample (0≤x≤0.4) with the same composition increases with the increasing temperature, whereas the TC presents the opposite trend. At the same temperature, the TEC of the (La1-xMgx)2Ce2O7-x sample (0≤x≤0.4) with different composition increases with increasing x value whereas the TC increases firstly and then decreases with the increasing of x value, where x=0.2 nearby as turning point. In addition, possible mechanisms of the influence of Mg doping on the structure, crystal parameter, TEC and TC of La2Ce2O7 are discussed.
|
|
|
Effect of Sodium Citrate Amount on Morphology and Anion Exchange Property of Co2+-Ni2+-Fe3+-CO32- LDHs
MA Xiang-Rong, LIU Zong-Huai
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1306–1312
 Abstract
Abstract(
761 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(506KB)(
1429
)
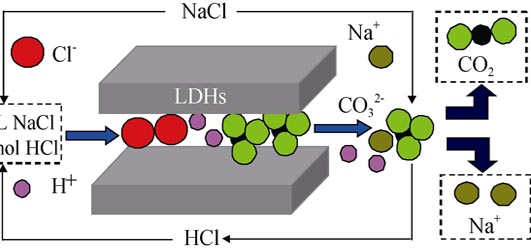
Co2+-Ni2+-Fe3+- -LDHs (layered double hydroxides, LDHs) materials were synthesized by using trisodium citrate (TSC) assisted homogeneous precipitation technology. The influences of TSC amount on the basal spacing and morphology of the obtained materials were investigated by changing TSC amount from 0.6 mmol/L to 3.0 mmol/L. Then the deintercalation of carbonate ions from a Co2+-Ni2+-Fe3+- -LDHs (layered double hydroxides, LDHs) materials were synthesized by using trisodium citrate (TSC) assisted homogeneous precipitation technology. The influences of TSC amount on the basal spacing and morphology of the obtained materials were investigated by changing TSC amount from 0.6 mmol/L to 3.0 mmol/L. Then the deintercalation of carbonate ions from a Co2+-Ni2+-Fe3+-![]() -LDHs materials with different basal spacing and shape morphology were investigated by socking in a NaCl-HCl mixed solution. The results indicated that LDHs with basal spacing of 0.776 nm and well-defined hexagonal shapes was obtained when TSC optimized amount was between 0.6-1.0 mmol/L, exhibiting a good anion exchange property. Thus a series of materials intercalated by -LDHs materials with different basal spacing and shape morphology were investigated by socking in a NaCl-HCl mixed solution. The results indicated that LDHs with basal spacing of 0.776 nm and well-defined hexagonal shapes was obtained when TSC optimized amount was between 0.6-1.0 mmol/L, exhibiting a good anion exchange property. Thus a series of materials intercalated by![]() , , ![]() , , ![]() , , ![]() and CH3(CH2)11 and CH3(CH2)11![]() anions were obtained. When TSC amount was up to 1.5 mmol/L, a new layered structure of LDHs with basal spacings of 0.770 nm and 0.691 nm was observed with rose-like morphology consisting of reunion hexagonal shapes, decreasing its anion exchange property. When TSC amount was further increased to 3.0 mmol/L, the layered structure of LDHs with a basal spacing of 0.681 nm was observed with ball-shaped like morphology consisting of reunion hexagonal shapes, leading to its anion exchange property disappear. anions were obtained. When TSC amount was up to 1.5 mmol/L, a new layered structure of LDHs with basal spacings of 0.770 nm and 0.691 nm was observed with rose-like morphology consisting of reunion hexagonal shapes, decreasing its anion exchange property. When TSC amount was further increased to 3.0 mmol/L, the layered structure of LDHs with a basal spacing of 0.681 nm was observed with ball-shaped like morphology consisting of reunion hexagonal shapes, leading to its anion exchange property disappear.
|
|
|
Wettability and Wetting Process in Cu/Ti3SiC2 System
LU Jin-Rong, ZHOU Yang, LI Hai-Yan, ZHENG Yong, LI Shi-Bo, HUANG Zhen-Ying
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1313–1319
 Abstract
Abstract(
645 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(442KB)(
1187
)
Effects of wetting temperature and Ti3SiC2 constituent elements Si and Ti on the wettability of Cu/Ti3SiC2 system were investigated in vacuum via sessile drop technique. The results show that the wettability of Cu/Ti3SiC2 system is fairly well at elevated temperature because of the reaction between Cu and Ti3SiC2. The reaction zone in Cu/Ti3SiC2 interface becomes larger and deeper with the temperature increasing, and which leads to the decrease in contact angle. Its reaction rate is accelerated when the temperature exceeds 1250℃. The minimum contact angle of 15.1° is measured at 1270℃. XRD and SEM results indicate that the reaction products are TiCx and CuxSiy, and the reaction layer is mainly consisted of Cu, Ti3SiC2, TiCx and CuxSiy depending on the wetting temperature. The wettability of Cu/Ti3SiC2 system is improved by the reaction layer. Adding alloying element Si or Ti to Cu is harmful to the wettability between Cu and Ti3SiC2 since Si inhibits the decomposition of Ti3SiC2 and Ti hinders the infiltration of Cu into Ti3SiC2.
|
|
|
Bioinspired Polydopamine Functionalization of Titanium Surface for Silver Nanoparticles Immobilization with Antibacterial Property
TAN Ying, Tan Guo-Xin, NING Cheng-Yun, RONG Xi-Cang, ZHANG Yu, ZHOU Lei
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1320–1326
 Abstract
Abstract(
1076 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(695KB)(
1746
)
A bioinspired polydopamine (PDA) layer was deposited on titanium surface by simply dipping the substrate into an alkaline dopamine solution. The in vitro bioactivity of the polydopamine coated titanium was assessed by incubation in simulated body fluids (SBF). The results showed that surface-anchored catecholamine moieties in polydopamine enriched the interface with calcium ions, facilitating the deposition of hydroxyapatite. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were metallised on the PDA-grafted titanium surface in mild aqueous environments. About 14% silver release as Ag+ ions were found after 5 d when the surfaces were exposed to deionized water. The AgNPs showed an efficient microbicidal activity against Staphylococcus Aureus bacterial strains, while not significantly affecting osteoblast cells (MC3T3-E1) viability.
|
|
|
In situ Biomimetic Fabrication and Characterization of Nano-hydroxyapatite/ Chitosan Composite Microspheres
LI Jian, HAN Zhi-Jun, WEI Yan, NIU Lu-Lu, LIU Yu, LU Guo-Yun, HUANG Di
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1327–1332
 Abstract
Abstract(
760 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
1271
)
To solve the problem that nano-hydroxyapatite (nHA) crystals aggregation and non-uniformly distribution in nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan (CS) composite microspheres, nHA/CS microspheres were prepared through in situ biomimetic method in water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions. The physical and chemical properties of the composite microspheres were investigated by scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), X-ray energy-dispersive spectroscope (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FTIR) and laser particle size analyzer. The results indicate that the composite microspheres are spherical with average size of 8.62 μm and disperse uniformly. Moreover, the nHA crystals are dispersed uniformly within composite microspheres and bonded with CS matrix. The composite microspheres have great potential in bone tissue engineering and drug delivery system.
|
|
|
Improved Visible-light Photocatalytic Activity of Bi-crystalline Mesoporous Titania Codoped with Carbon and Silver
LU Qiang, ZHANG Zhi-Bo, DONG Chang-Qing, ZHANG Xiao-Yuan, CUI Fang-Ming
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1333–1338
 Abstract
Abstract(
666 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(332KB)(
1386
)
A bi-crystalline mesoporous titania (meso-TiO2) with anatase and rutile composite nanocrystal frameworks was prepared and then modified by carbon doping (C-meso-TiO2), silver nanoparticle loading (Ag-meso-TiO2), and carbon-silver codoping (Ag-C-meso-TiO2). The visible-light photocatalytic activities of the samples were evaluated by the degeneration of aqueous methylene blue (MB) solution under visible-light irradiation (wavelength >420 nm). The prepared bi-crystalline mesoporous samples showed obviously higher visible-light photocatalytic activity than that of the commercial anatase titania nanoparticles (NPs). Ag-C-meso-TiO2 exhibited the highest visible-light photocatalytic activity which could be attributed to the band gap narrowed by the doped carbon and the plasmon electron transfer from Ag NPs to the titania matrix, and the corresponding MB degeneration rate reached 65% after 180 min visible-light irradiation while that of the commercial titania NPs just reached 7%.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Hot-pressed Al2O3/Al-steel Mesh-Al Laminated Composites
BAI Ming-Min, LI Wei-Xin, LI Yan-Hui, ZHAO Wei, RAO Ping-Gen
2014 Vol. 29 (12): 1339–1344
 Abstract
Abstract(
541 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(405KB)(
1173
)
Al2O3/Al-steel mesh-Al laminated composites with “sandwich” Al-steel mesh-Al layer as interlayer, which was consisted of two Al foils and one steel mesh, were prepared by vacuum hot pressing at 580℃ and 1.5 MPa. The results indicate that the interface of Al2O3/Al is bonded tightly and no reaction is observed. Intermetallic compound (IMC) is detected in Al/steel interface which improves the connection conditions between the steel and Al. The laminated composites have much higher fracture toughness, work-of-fracture than that of the Al2O3 monolith, as well as having a close strength to Al2O3. Crack blunting and arresting, crack bridging, interface debonding, and ductile deformation of “sandwich” Al-steel mesh-Al layer are the main reasons for improving the toughness and work-of-fracture of laminated composites. Low-velocity impact results suggest that the Al2O3/Al-steel mesh-Al laminated composites have good impact resistance.
|
|