|
|
Composite Anodes with Ni Impregnated LST-SSZ for Direct Methane Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
LIU Ya-Di, YUAN Chun, ZHOU Yu-Cun, ZOU Jie, XIN Xian-Shuang, WANG Shao-Rong
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1121–1126
 Abstract
Abstract(
712 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(550KB)(
1089
)
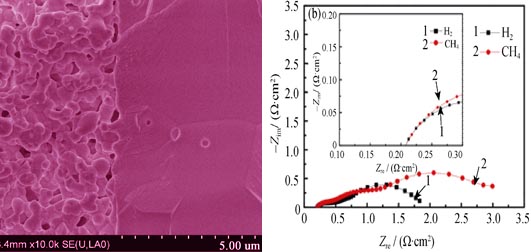
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) is one of the most attractive energy conversion devices because of their high efficiency, low pollution, and fuel flexibility. La0.2Sr0.8TiO3 (LST) anode material shows its potential utilization in direct oxidation of methane fuel without carbon formation. In this paper, LST powders were synthesized by traditional solid-state method, and then mixed with scandia-stabilized zirconia (SSZ) in mass ratio of 5: 5 to prepare the composite anode materials. Symmetrical cells with LST-SSZ composite anode were fabricated and measured. Their polarization resistances in hydrogen at 700℃, 750℃ and 800℃ were 5.3, 3.0 and 2.0 ?·cm2, respectively. Considering the insufficient conductivity of LST, 10wt%Ni was impregnated into the composite anode to improve the anode performance. The polarization resistance of the symmetrical cell with 10wt% Ni impregnation load is obviously reduced. The maximum power density of a cathode supported single cell with 10wt%Ni-LST-SSZ composite anode are 225 mW/cm2 and 175 mW/cm2 in hydrogen and in methane at 750℃, respectively, and the single cell shows its stability running in methane fuels.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Corrugated SnO2 by Cotton Fibers Template Method and Its Electrochemistry Performance
YU Ji, XIA Yuan
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1127–1132
 Abstract
Abstract(
717 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
843
)
Corrugated SnO2 was prepared by an effective template using cotton fibers which were sacrificed during preparation. The as-prepared SnO2 samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, CV, galvanostatical method and EIS. The results show that the corrugated SnO2 is composed of nanopaticles with size of 16-21 nm. The as-obtained corrugated SnO2 electrodes can deliver a discharge capacity of 614 mAh/g at current density of 70 mA/g after 50 cycles. Even at the current density of 3 A/g the products can still deliver a high reversible discharge capacity of 405 mAh/g. As lithium storage materials, the corrugated SnO2 shows stable cyclability and good rate capability.
|
|
|
Zinc Molybdate-carbon Composites as Counter Electrode Materials for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
TANG Bei-Bei, GUO Ming-Xing, JIANG Wei, YIN Shu-Hui, ZHANG Man-Xia, WANG Liang, ZHANG Yi-Ming, ZHENG Lei, MENG Yue-Qi
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1133–1138
 Abstract
Abstract(
869 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(471KB)(
1187
)
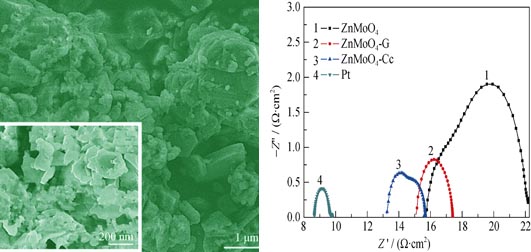
Sheet-like structured zinc molybdate (ZnMoO4) was firstly synthesized by hydrothermal method. Then, graphite (G) and conductive carbon (Cc) modified ZnMoO4 (denoted as ZnMoO4-G and ZnMoO4-Cc) were fabricated by dispersing ZnMoO4 into graphite (G) and conductive carbon (Cc) solutions, respectively. The obtained ZnMoO4-G and ZnMoO4-Cc composites were used as electrocatalysts for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs), exhibiting promising potential as counter electrode materials. The experimental results demonstrated that the DSC assembled with sole ZnMoO4 showed an overall light conversion efficiency of 4.19%, while the DSCs made of ZnMoO4-G and ZnMoO4-Cc counter electrodes displayed power conversion efficiencies of 6.56% and 7.36%, respectively. The solar cell performance obtained by ZnMoO4-Cc counter electrode was comparable to Pt-based DSCs (7.81%). Various characterization techniques, such as electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS), cyclic voltammetry (CV) and Tafel polarization curve, were employed to evaluate the electrocatalytic activity of all investigated materials. Among all investigated counter electrodes, the high solar cell performance obtained by ZnMoO4-Cc counter electrode could be attributed to superior electrical conductivity of conductive carbon material and excellent electrocatalytic activity of sheet-like structured ZnMoO4-Cc.
|
|
|
Effects of Different Amount of Se-doping on Microstructures and Thermoelectric Properties of n-type Bi2Te3-xSex
ZHANG Qi-Hao, XU Lei-Lei, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1139–1144
 Abstract
Abstract(
1283 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(555KB)(
1365
)
A hydrothermal method combined with a subsequent spark plasma sintering technique was successfully utilized to synthesize selenium (Se) doped bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3-xSex) (0≤x≤0.45). The influence of Se-doping on the composition and morphology of n-type Bi2Te3-xSex was studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope. Thermoelectric properties of the as-prepared bulk Bi2Te3-xSex nanocomposites were investigated in detail. Results showed that the grain became finer by the Se-doping. With increasing Se doping content, the electrical conductivity of bulk Bi2Te3-xSex increased firstly and then decreased. Se-doping effectively reduced the thermal conductivity and improved the Seebeck coefficient to some extent. Consequently, a maximum ZT value of 0.57 was obtained from bulk Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 at 475 K, which was increased by 159% as compared with pure bulk Bi2Te3.
|
|
|
Structure and Dielectric Properties of Sc3+- and Ru4+-doped BZN Based Ceramics
ZHANG Qian, DING Shi-Hua, SONG Tian-Xiu, PENG Xiao-Song, LIU Xu, JIANG Xu-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1145–1150
 Abstract
Abstract(
503 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(455KB)(
986
)
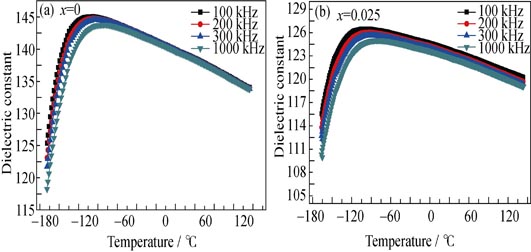
The dense Bi1.4Sc0.1ZnNb1.5-xRuxO7 ceramics were prepared by traditional solid state reaction. The effect of Sc3+ and Ru4+ co-substitution on the phase structure, crystal chemistry and dielectric properties of Bi2O3-ZnO- Nb2O5 were investigated. The results reveal that all doped samples show a pure α-BZN phase structure. When x=0.055 mol, the intensity of X-ray diffraction becomes weak and diffraction peaks broaden. With the increase of x, the lattice constant a and the average distance R(A-O') of the ceramics decrease. The bond valance calculation show that the AV(O')[A4] and oxygen ξ parameter of 48f(O) increase, but the AV(O)[A2B2] gradually decreases with the amount of Ru4+ increasing. Meanwhile, the dielectric constant of samples decreases and the dielectric loss increases. The dielectric relaxation characteristics are weakened at room temperature while the relaxation behavior at low temperature is obvious. With increasing dopant, Tm shifts toward higher temperature. The εr-T curves of samples are fitted by the modified Curie-Weiss’s (C-W) formula. The calculations show that the degree of dielectric relaxation (γ) decreases from 1.57 to 1.33 when the Ru4+ content increases from 0 to 0.04 mol.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Properties of Highly Pure BiFeO3 Using A Method of Solid State Reaction-molten Salt Synthesis with Non-equilibrium Process
WU Xing, LI Hai-Feng, ZHOU Jin-Ling, HUO Min-Feng, CHENG Cheng, SHEN Xu-Gen, YAN Chun-Jie
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1151–1155
 Abstract
Abstract(
831 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(493KB)(
1087
)
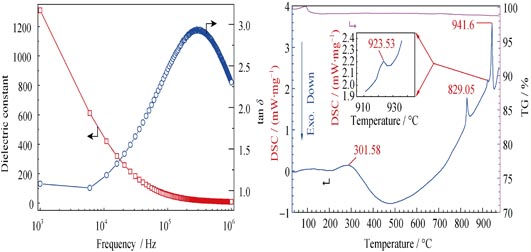
High pure Bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) powders were prepared by a solid state reaction-molten salt synthesis method (SSR-MSS method) using shock heating and chilling non-equilibrium process (SHCN process). The structure, morphology and electromagnetic properties were characterized by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscope (FTIR), Thermogravimetry-Differential Scanning Calorimetry (TG-DSC) and Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM). The results indicated that SHCN process was better to get higher purity of BiFeO3 powders than conventional equilibrium process (C process), but still has a certain number of impurity phases like Bi25FeO39 and/or Bi2Fe4O9 as found in the products prepared by either SSR-SHCN process or MSS-SHCN process. In contrast, single-phase BiFeO3 powders could be obtained by SSR-MSS-SHCN process. The micro-nanoscale BiFeO3 powders presented antiferromagnetism, superparamagnetism, and/or weak ferromagnetism behavior at room temperature, but not spin-glass state at low temperature (5 K).
|
|
|
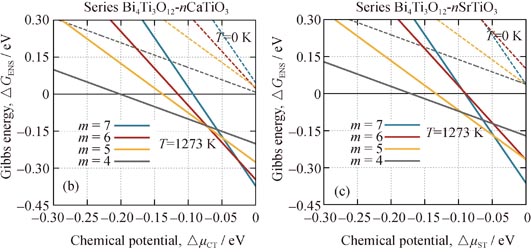
Phase Competition in Bismuth Layered Structure Based on First Principles Thermodynamics
QIU Rui-Hao, LI Yong-Xiang, ZHANG Wen-Qing
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1156–1160
 Abstract
Abstract(
651 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(463KB)(
1096
)
The difficulties of synthesis of pure Aurivillius phases largely impede them from extensive application. In this work, the first principles thermodynamics approach was applied to investigate the phase competition relation of three homologous Aurivillius series CaBi2Nb2O9-nNaNbO3, Bi4Ti3O12-nSrTiO3 and Bi4Ti3O12-nCaTiO3, in order to uncover the thermodynamic mechanism of the phase stability. The competition among different phases was analyzed by the relative Gibbs energy as a function of chemical potential of perovskite unit. The analysis reveals that most phases are able to overcome others to be the most stable ones in a certain range as chemical potential increases, which can be applied to interpret the relevant experimental phenomena including the phase mixture and disordered structures. Temperature dependence of phase competition evolutions are also studied based on the configurational and vibrational entropy effect, the former effect changes the competition relations of different phases, while the latter only increases the stable range of the lower phases.
|
|
|
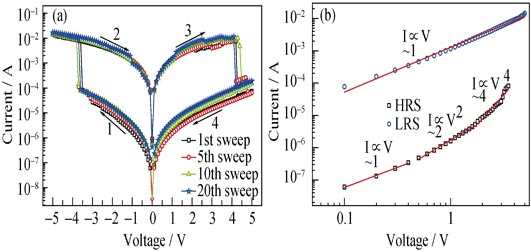
Deposition of Amorphous Zinc Oxide Thin Film at Room Temperature and Its Resistive Switching Characteristics
ZHANG Tao, XU Zhi-Mou, WU Xing-Hui, LIU Bin-Bing
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1161–1166
 Abstract
Abstract(
790 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(454KB)(
1111
)
Amorphous zinc oxide thin film was prepared through Sol-Gel method using deep-ultraviolet photochemical activation instead of high temperature annealing. The XRD patterns showed that the zinc oxide film was amorphous. XPS analysis showed that the film was mainly composed of ZnO. The Al top electrodes were deposited on irradiated thin film by DC magnetron sputtering to get Al/a-ZnO/FTO structured device. The influence of deep-ultraviolet irradiation time on switching properties was investigated to understand the mechanism of deep-ultraviolet irradiation. The results illustrate that the device after sufficient irradiation (12 h) has bipolar resistive switching property. The distribution of threshold voltage is very concentrated (-3.7 V<Vset<-2.9 V, 3.4 V<Vreset<4.3 V) which meets the need of low voltage operation of the memories. Both HRS and LRS have not obviously attenuated for at least 4000 s. The resistive switching behavior of the Al/a-ZnO/FTO device can be explained by the trap-charged space-charge-limited current mechanism.
|
|
|
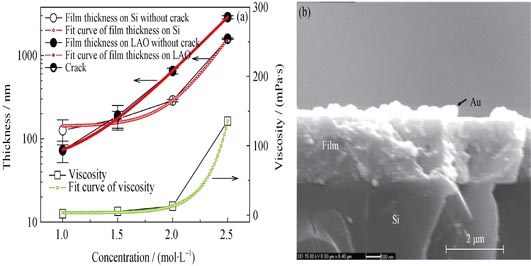
Influence of Thickness on Performances of YBa2Cu3O7-δ Films Prepared by Metal Organic Solution Deposition
RUI Run-Sheng, LIU Zhi-Yong, BAI Chuang-Yi, GUO Yan-Quen, JIN Xiao-Yan, CAI Chuan-Bing
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1167–1172
 Abstract
Abstract(
704 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(555KB)(
1044
)
Trifluoroacetate metal organic deposition (TFA-MOD) is one of the most promising technology routes for fabrication of YBa2Cu3O7-δ (YBCO) coated conductors. In this paper, high-boiling point organic solvent diethanolamine (DEA) was added to modulate and to improve the properties of precursor solution by suppression the defect in the final films. And the thickness of single coated film was increased by increased concentration of the metal ions in the precursor solution. It is revealed that an exponential relationship was found between the thickness of precursor film after low-temperature decomposition and the ion concentration, as well as the viscosity of precursor solution vs the ion concentration. Optimizing the ion concentration and dip-coating parameters, smooth and crack-free YBCO films after crystallization are achieved with the thickness more than 1.3 μm. The films show homogeneous microstructures while dispersive heterogeneous particles appear in the surface of the thick films. Critical current density (Jc) measurement shows a decrease of Jc due to the increase of the thickness of YBCO films prepared by high concentration precursor solution, while critical currents (Ic) are distinctly improved. For instance, the Ic value of YBCO film prepared by 2.5 mol/L precursor solution is 4.7 times of that by 1.0 mol/L precursor solution.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Pore Structure of Mesozeolite FAU
FENG Chun-Feng, MA Li, MA Jing-Hong, LI Rui-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1173–1178
 Abstract
Abstract(
893 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(478KB)(
1325
)
Mesoporous zeolites X and Y with FAU structure were hydrothermally synthesized using an organos-ilane surfactant (TPOAC) as mesopore-generating agent, which was added into the conventional synthesis system of the crystalline microporous aluminosilicates. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, high-resolution transmission electron microscope, N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and thermogravimetric analysis were used to characterize their structural and textural features. The results showed that the presence of TPOAC led to nanoscale zeolite crystals and abundant intracrystal mesopores at diameter of 5~6 nm, forming the meso-zeolites X and Y with micropores, intra- and inter-mesopores. Both mesoporous zeolite X and Y displayed not only inherent topological and microporous structure of zeolite FAU, but also different morphology from conventional zeolite FAU crystals.
|
|
|
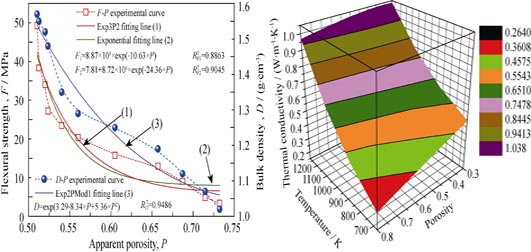
Fabrication, Properties and Nonlinear Thermal Conductivity Model of Highly Porous Mullite Ceramics
LUO Xue-Wei, LI Hai-Feng, XIANG Wu-Guo, YUAN Hui, CHENG Cheng, SHEN Xu-Gen, YAN Chun-Jie
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1179–1185
 Abstract
Abstract(
829 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(678KB)(
1188
)
Highly porous mullite ceramics were prepared by bauxite and silica fume as raw materials and corn starch as the pore-forming agent. The phase and morphology were characterized by XRD and SEM, respectively. The influence of corn starch content on apparent porosity, bulk density and flexural strength were studied. Thermal conductivity of porous mullite was measured at 473-1273 K. A new nonlinear thermal conductivity model and several models between bulk density, flexural strength and apparent porosity were established. The results indicate that, bulk density and flexural strength of porous mullite decrease with porosity increase and conform to the exponential function relationship. Thermal conductivity of porous mullite increases with the rise of temperature and the measured values are in good agreement with values calculated by nonlinear thermal conductivity model. The new model can accurately reflect the thermal conductivity correlations for temperature, porosity, radiation and mean pore size.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Ribbon-shaped Mesophase Pitch-based Carbon Fibers with Different Crystal Orientations
XIONG Xiao-Qing, YUAN Guan-Ming, LI Xuan-Ke, DONG Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Zhong-Wei, WANG Jun-Shan
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1186–1192
 Abstract
Abstract(
642 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(572KB)(
911
)
Using mesophase pitch as the raw material, with the rectangular-section spinnerets at different aspect ratios (length divided by width), ribbon-shaped mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers with various cross-section sizes and crystal orientations were prepared by adjusting the spinning rate. Effects of the heat-treatment temperature and aspect ratio of spinnerets on structure and properties of the ribbon-shaped carbon fibers were investigated. The results show that the aspect ratio of spinneret and the spinning rate of pitch fibers have a significant influence on the crystal orientation of carbon fibers. Within the specified spinning rate of pitch fibers, the crystal orientation of carbon fibers varies from a parallel-fold structure to a vertical-radial structure with the decrease of the aspect ratio of the spinnerets. The electrical conductivity and the mechanical property of ribbon-shaped carbon fibers significantly increase with the increase of heat-treatment temperature. With increase in spinning rate, there is no obvious change in the room-temperature axial electrical resistivity along the longitudinal direction of fiber, whereas obvious changes in the mechanical property are observed. At 30:1 of the aspect ratio of the spinneret and 75 m/min of spinning rate, the tensile strength and young’s modulus of the graphite fibers heat-treated at 2500℃ are up to 2.53 GPa and 234.77 GPa, respectively.
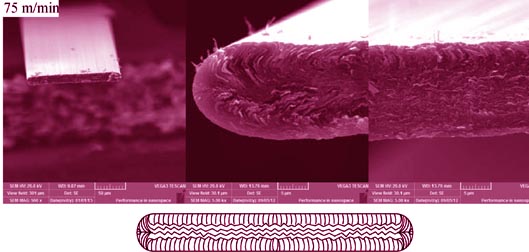
|
|
|
One-step Synthesis of Flower-like Bi2WO6-rGO Composite Photocatalysts
GUO Dan, WANG Ping, ZHENG Qi-Ying, WANG Jin
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1193–1198
 Abstract
Abstract(
835 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(467KB)(
2018
)
A one-step hydrothermal method was developed for fabrication of flower-like Bi2WO6-rGO composite photocatalysts with high-efficiency visible-light photocatalytic activity. Photocatalytic experimental results for the decolorization of methyl orange (MO) aqueous solution indicated that all the resulted Bi2WO6-rGO photocatalysts exhibited a much higher photocatalytic performance than the pure Bi2WO6, and the Bi2WO6-rGO (0.5wt%) showed the highest photocatalytic activity with a k = 5.0×10-2 /min, a value as 1.7 times as that of the pure Bi2WO6. The enhanced performance can be attributed to the cooperation effect of rGO nanosheet which promoted the effective transfer of photogenerated electrons and provided large surface area for absorbing organic pollutants. This work may provide new insights into design and fabrication of high-performance graphene-based photocatalytic materials.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Jumbo-size Single Crystalline Bi2Se3 Nanoplates and Nanoribbons by Vapor Transportation
LI Xiao-Shuai, WANG Zeng-Mei, ZHU Ming-Fang, WANG Shan-Peng, TAO Xu-Tang, LU Jun, CHEN Xing-Tao, XU Jia-Le
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1199–1203
 Abstract
Abstract(
703 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(347KB)(
1172
)
Low-dimensional Bi2Se3 nanomaterials were discovered to be new three-dimensional (3D) topological insulators (TIs) recently, which have broad application prospect in the field of microelectronic devices and sensors. Single crystalline Bi2Se3 nanoplates (NPs) and nanoribbons (NRs) with jumbo size were synthesized in the vacuum quartz tube via vapor transportation. The crystal structure, composition and morphology of the as-prepared Bi2Se3 NPs and NRs were analyzed by XRD, EDS, Raman and SEM. It is found that both of the two specimens are well-crystallized in the direction of {001} with a high purity. Bi2Se3 NPs have a large lateral size of 15-180 μm, while Bi2Se3 NRs have a large length of 860 μm and a width of about 5 μm. Besides, the probable growth mechanism is proposed based on the analysis of the SEM images of Bi2Se3 NPs and NRs prepared at different temperatures and the binding energy difference along different directions. Bi2Se3 has a quicker growth speed along <001> and directions in relatively high temperature to form single crystalline NPs with large lateral size, while it grows faster along directions in relatively high temperature to form single crystalline NPs with large lateral size, while it grows faster along  direction in lower temperature to get single crystalline NRs with large length. All these results not only improve the preparation process of Bi2Se3 nanomaterials with jumbo size, but also promote the commercial use in the field of microelectronic devices. direction in lower temperature to get single crystalline NRs with large length. All these results not only improve the preparation process of Bi2Se3 nanomaterials with jumbo size, but also promote the commercial use in the field of microelectronic devices.
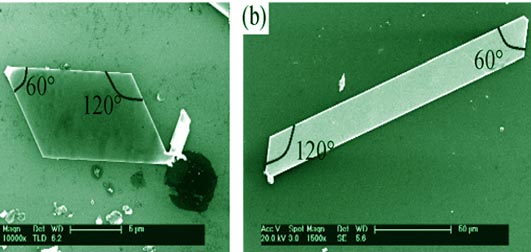
|
|
|
Visible Light Photocatalytic Properties of Bi2O3 Modified BiPO4 Nanorod Composite Photocatalyst
DU Quan-Chao, Lü Gong-Xuan
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1204–1210
 Abstract
Abstract(
774 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(595KB)(
1500
)
BiPO4 nanorod composite photocatalyst with controllable morphology was synthesized by using Bi2S3 nanorods as a template. This composite catalyst exhibited excellent photocatalytic performance for methylene blue (MB) degradation under visible light irradiation. UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy results showed that the Bi2O3 modified BiPO4 catalyst had higher visible light absorption. X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy results indicated that as-prepared BiPO4 catalyst was nanorods with diameter of about 30 nm and length of 200-500 nm. Surface modification with small amount Bi2O3 could significantly promote visible light degradation efficiency of MB, which was about 1.7 times higher than that of the unmodified BiPO4 catalyst. Photocurrent and N2 adsorption experiments showed that the photocurrent and BET specific surface area increased significantly after surface modification. Bi2O3 modification not only enhanced visible light absorption ability of catalyst but also presented a center for the enhancement of electron transfer. The results showed BiPO4 catalyst with Bi2O3 modification was a high activity photocatalytic material.
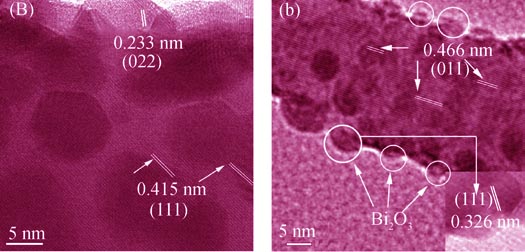
|
|
|
Luminescence Property and Energy Transfer of Ce3+, Eu3+ Co-doped Lu3Al5O12 Polycrystals
LUO Jia-Liang, WU Yun-Tao, REN Guo-Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1211–1217
 Abstract
Abstract(
664 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(600KB)(
1417
)
The (Ce0.01EuxLu0.99-x)3Al5O12 (x=0.2%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%) scintillating polycrystalline powders were prepared by high temperature solid state reaction method, and the sample structure and luminescence property, especially energy transfer between Ce3+ and Eu3+, were studied. A pure cubic phase was confirmed in all samples by X-ray diffraction (XRD). X-ray excited luminescence (XEL), photoluminescence excitation and emission spectra (PL) were employed to study the influence of increasing Eu3+ concentration on the luminescent property of Ce3+ and Eu3+ as well as the energy transfer from Ce3+ to Eu3+. The variation of the integral intensity of luminescence of Ce3+ in XEL with increasing Eu3+ concentration illustrated energy transfer from Ce3+ to Eu3+. The luminescence behavior of Ce3+ and Eu3+ in the host of Lu3Al5O12 under UV-visible light was studied by PL, and emission peak of Eu3+ under 340 nm excitation of Ce3+ directly indicated the energy transfer from Ce3+ to Eu3+. In addition, thermoluminescence spectra (TL) were utilized to identify the energy transfer from Ce3+ to Eu3+, and also the shifting of the thermoluminescence peaks with Eu3+ concentration increasing, was explained by two paths of the electrons transfering from Ce3+ to Eu3+ under thermal excitation.
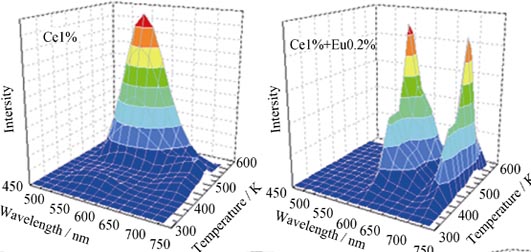
|
|
|
Effect of Sb on Structure and Physical Properties of GeSbxSe7-x Chalcogenide Glasses
WEI Wen-Hou, FANG Liang, YANG Zhi-Yong, SHEN Xiang
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1218–1222
 Abstract
Abstract(
798 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(492KB)(
1272
)
GeSbxSe7-x (x = 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0) chalcogenide glasses were prepared by the melt-quenching technique, and the effect of Sb on glass structures and physical properties were systematically investigated. Raman spectra of these glasses show that the glass structure gradually changes from Se chains or Se rings dominated to SbSe3/2 pyramids and GeSe4/2 tetrahedra cross-linked, and the degree of cross-linkage of glass network improves with Sb content increase. Meanwhile, the glass transition temperature, density, elastic moduli, and refractive index increase with Sb content increase. The transmittance spectra indicate that replacement of Se with Sb leads to gradually reducing the optical bandgap.
|
|
|
Structure and Optical Properties of CuInSe2 and Cu0.9In0.9Zn0.2Se2 Thin Films Deposited by One-step Radio-frequency Magnetron Sputtering
WANG Wei-Jun, HE Jun, ZHANG Ke-Zhi, TAO Jia-Hua, SUN Lin, CHEN Ye, YANG Ping-Xiong, CHU Jun-Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1223–1227
 Abstract
Abstract(
633 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
1510
)
CuInSe2 (CIS) and Cu0.9In0.9Zn0.2Se2 (CIZS) thin films were deposited by Radio-Frequency (RF) magnetron sputtering process. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results indicate CIZS film deposited at 300℃ (CIZS-300) is (220) preferred orientation which is different from (112) preferred orientation of other films. Cu-poor and appropriate temperature are major factors for (220) preferred orientation of grains. The Raman spectra show a strong peak around 171 cm-1 and a weak peak around 206 cm-1, which corresponding to A1 and B2 modes. Substitution of Zn for Cu leads to a broadening and blue-shift of A1 Raman mode. The band gap Eopt of CIZS film increases due to a reduced Se p-Cu d interband repulsion with Zn doping. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) measurement demonstrates that the surface morphology of CIZS is more compact and smoother than that of CIS thin films.
|
|
|
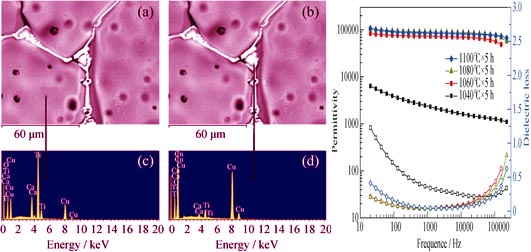
Preparation and Electrical Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Thin Ceramic Sheets via Water-based Tape Casting
LI Wei, XIONG Zhao-Xian, XUE Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (11): 1228–1232
 Abstract
Abstract(
723 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(410KB)(
1250
)
Thin ceramic sheet of CaCu3Ti4O12 has a great significance for preparation of multiplayer ceramic chip capacitors. In this work, a simple plan was made to achieve CaCu3Ti4O12 thin ceramic sheets with excellent dielectric properties. Thin ceramic sheets of CaCu3Ti4O12 were prepared via water-based tape casting at various sintering temperatures. The CaCu3Ti4O12 samples sintered at 1080℃ exhibit a great performance on dielectric properties with high permittivity (εr=98605) and low dielectric loss (tanδ=0.028) which are better than those of samples prepared by conventional dry pressing. Meanwhile, the complex impedance spectra were measured to explain the mechanism of special electrical behaviors of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics. These testing results indicate that the CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics via tape casting exhibits a better performance of giant permittivity and lower dielectric loss than other reports, which provides a possibility for the application of the CaCu3Ti4O12 in modern micro-electronics technology.
|
|