|
|
Research Progress in Calcium Phosphate Microspheres for Bone Defect Repair
LI Bo, XU Wen-Feng, LIAO Xiao-Ling
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1009–1017
 Abstract
Abstract(
1254 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(701KB)(
1389
)
Calcium phosphate ceramic microspheres have attracted many research interests in various application fields, such as separation, catalysis, sensor, tissue engineering and drug delivery, due to their excellent permeability, high surface area ratio, low density and stable mechanical properties. In this paper, current advances of calcium phosphate ceramic microspheres in bone regeneration applications, such as bone tissue engineering and anabolic drug delivery, were comprehensively reviewed. Calcium phosphate ceramic microspheres were classified into four main categories according to their solid, porous, hollow or flow-like structures. The corresponding preparation methods and specific applications were summarized. Advantages and disadvantages of such microspheres were evaluated and future improvements were proposed. This review is intended to provide a comprehensive guide to the design and fabrication of calcium phosphate microspheres aiming at repairing bone defects.
|
|
|
Coloration of Ce-doped Multicomponent Silicate Glasses by Electron Irradiation
FU Xin-Jie, SONG Li-Xin, LI Jia-Cheng
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1018–1022
 Abstract
Abstract(
679 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(444KB)(
1155
)
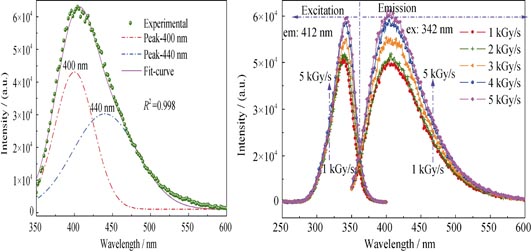
The coloration of Ce-doped multicomponent silicate glass (type K509) irradiated by 10 MeV electrons was investigated by absorption spectra, electron paramagnetic resonance and photoluminescence spectra. The results show that non-bridging oxygen hole centers (HC1 and HC2) are induced in K509 glasses after electron irradiation, leading to significant degradation of visible transmission. The concentration of color center grows in an exponential law with the increase of radiation dose at the same dose rate, and decreases in exponential decay law with radiation dose rate at the same total dose. According to photoluminescence spectra, the concentration of Ce3+ ions has a negative correlation with radiation dose, and has a positive correlation with dose rate, which proves the mechanism of radiation-hardness in cerium-doped glasses. Ce3+ ions capturing holes induced by electron irradiation to form Ce4+ inhibits the formation of hole trapped color centers, HC1 and HC2, which avoids additional absorption in visible light range. The energy level diagram of Ce3+ in K509 glasses is also obtained by Gaussian resolution of the broad asymmetric emission spectra of Ce3+.
|
|
|
Gene Transfection of Bioactive Glass Fibers
LIU Hui, CHEN Xiao-Feng, LI Xian, LI Yu-Li, LIN Ze-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1023–1028
 Abstract
Abstract(
684 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(438KB)(
929
)
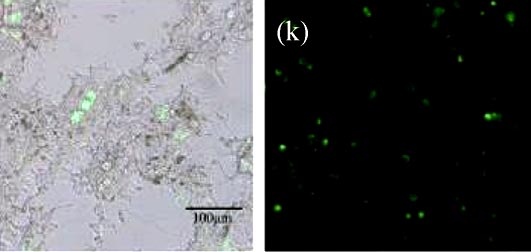
Bioactive glasses (BGs) exhibit potential applications for gene transfection because of their composition including Ca and P. Here, bioactive glass fibers (BGFs) with mesopores or hierarchical nanopores, were prepared by electrospinning process using BGs Sol-Gel precursor and its effect on mediating gene transfection was investigated. The results indicate that BGF acts as a gene vector by releasing Ca2+ and PO43-, and then reunioning them along with plasmid DNA in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM). BGFs have a dose-dependent manner in transfection efficiency. When using 1 μg/mL plasmid, the transfection efficiency of BGF with concentration at 1000 μg/mL is higher than 50% of lipofectamine LTX_PLUS. The transfection mechanism of BGF is similar to that of calcium phosphate (CaP) system. Furthermore, BGF’s sufficient ions releasing ensures stability and effectiveness to be applied in gene transfection, which makes BGF a promising candidate for gene delivery in replace of traditional gene carrier, the nano-calcium phosphate system.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Properties of Hollow CaSi2O2N2:Eu2+ Luminescence Fibers
CUI Bo, WANG Hong-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, ZHANG Qing-Hong
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1029–1033
 Abstract
Abstract(
622 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(465KB)(
1103
)
Hollow Eu2+ doped CaSi2O2N2 and Ca-Si-O-Eu nanofibers were prepared through electrospinning combined with gas-reduction-nitridation method. The Ca-Si-O-Eu precursor was smooth and uniform, has a length arrange from ten to hundred micrometers. The as-obtained sample not only keeps the hollow structure but also assembles to a film. XRD patterns reveal that the sample nitrided under 1300℃ for 5 h are crystallized well and maintained CaSi2O2N2 phase after Eu2+ doping. The emission spectra of Eu2+ doped CaSi2O2N2 under the 400 nm ultraviolet light irradiation has a board peak centered at 550 nm, which results from Eu2+ 5d-4f transition. In comparison with CaSi2O2N2:Eu phosphor powders and fiber film, the hollow CaSi2O2N2:Eu phosphor fiber film has stronger emission intensity under PL measurement.
|
|
|
Preparation and Optical Properties of AgIn Alloy Quantum Dots Doped Glass
YIN De-Wu, LIU Zhen, YANG Xin-Yu, ZHANG Xi-Yan, XIANG Wei-Dong
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1034–1038
 Abstract
Abstract(
592 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(393KB)(
1055
)
Indium-silver alloy quantum dots doped sodium borosilicate (NBS) glass was prepared by Sol-Gel method with controlled atmosphere technology. The morphology and microstructure of AgIn alloy quantum dots in the glass were characterized by means of X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), high- resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) and electron diffraction (SAED). The fluorescent properties of the glass by fluorescence spectrometer were studied. The results showed that indium-silver alloy quantum dots with an average grain size of 5 nm were finely dispersed in the sodium borosilicate glass after heat-treated at 600℃. Indium- silver alloy quantum dots in the glass exhibited a fluorescence peak at around 435 nm which nominated AgIn quantum dots doped NBS glass as the candidate glass for laser sources, nonlinear media and photonic applications.
|
|
|
Optical Characteristics of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Surface Modification Using Polyethylene Glycol
TAN Man-Lin, WANG Yan-Tao, ZHANG Wei-Li, FU Dong-Ju, LI Dong-Shuang, WANG Xiao-Wei, MA Qing, CHEN Jian-Jun, LI Ting-Kai
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1039–1043
 Abstract
Abstract(
881 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(382KB)(
1107
)
Surface of Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles prepared by Sol-Gel method was modified by a polymer reactant, PEG (polyethylene glycol, Mw=2000). The structure and optical properties of the PEG modified nanoparticles were then investigated by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy. Results showed that the added PEG polymers were successfully coated on the surface of ZnO nanoparticles, without obvious variation being found in the ZnO crystal structure. The ZnO particles tend to have a smaller size, better stability and better dispersible uniformity after PEG coating. Furthermore, a defect state emission peak with significantly reduced intensity was found at the range of 400-500 nm in photoluminescence spectra, indicating that the surface defects of ZnO nanoparticles could be well improved by PEG modification.
|
|
|
Effects of Mo Doping on Properties of Pt/C as Catalyst towards Electro-oxidation of Ethanol
LI Lin, YUAN Xian-Xia, XIA Xiao-Yun, DU Juan, MA Zhong, MA Zi-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1044–1048
 Abstract
Abstract(
600 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(405KB)(
1105
)
Direct Ethanol Fuel Cells (DEFCs) have attracted lots of interest with the merits of high energy density and environmental benignity. Thus, development of novel efficient catalyst with high activity and excellent durability is of great importance for the future large-scale application of DEFCs. A series of Mo-doped Pt/C catalysts were synthesized with microwave assisted technology, and the effects of Mo content on the activity as well as durability of the resulted catalyst towards ethanol oxidation were comparatively investigated by using cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and chronoamperometry. The result shows that the Pt2Mo/C catalyst demonstrates a comparable onset potential to Pt/C, the highest current density and the slowest deterioration towards ethanol oxidation, implying that the Pt2Mo/C catalyst is best one to achieve highest activity and best durability.
|
|
|
Optical Properties of ZnS:Co+Cr Nanocrystals Synthesized by a Low Temperature Hydrothermal Process
WANG Xiao-Xiao, YANG Lin, LIU Hong, CHEN Qiang, XIAO Ding-Quan, ZHU Jian-Guo
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1049–1054
 Abstract
Abstract(
649 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(480KB)(
1218
)
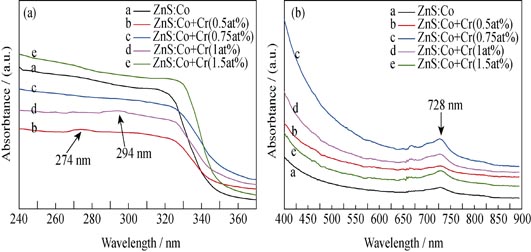
Water-soluble ZnS:Co+Cr nanocrystals (NCs) were synthesized by a low temperature hydrothermal process using 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA) as capping agent. X-ray diffraction, laser particle size analyzer, transmission electron microscope (TEM), UV-Vis spectrophotometer, fluorescence spectrophotometer, XPS were used to characterized crystalline structure, morphology, particle size and optical properties of the samples. It is found that the ZnS:Co+Cr NCs are monodisperse and show zinc blende structure with an average particle size of about 9.3 nm. The absorption edge of ZnS:Co+Cr NCs is observed at 320 nm from the UV-Vis absorption spectra, furthermore the characteristic absorption peak at 728 nm of Co2+ is observed. The photoluminescence characteristics indicate that ZnS:Co+Cr NCs shows the maximum PL intensity value under the condition: Cr-doping concentration of 0.75at% and the hydrothermal reaction temperature of 160℃. As confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscope(XPS) , the Cr2+ dopants are partialiy oxidized into Cr3+.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Hollow Spheres-like Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 Composite Photocatalysts
LI Xiao-Yan, YAN Jian-Hui, ZHANG Li, ZHOU Ming-Jie, LIU You-Nian
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1055–1060
 Abstract
Abstract(
911 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(556KB)(
1188
)
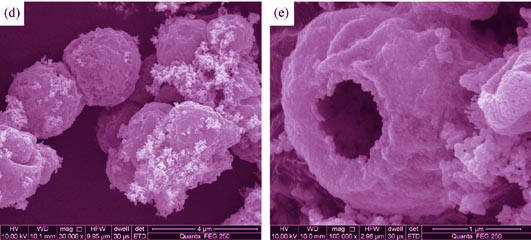
Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 composite hollow spheres with high specific surface area were synthesized by hydrothermal method, using glucose as template and Zn(NO3)2·6H2O, Cu(NO3)2·3H2O, Al(NO3)3·9H2O as raw materials. The samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, HRTEM, BET, DRS and PL spectra. The results showed that Zn- doped CuO/CuAl2O4 composites possessed hollow microspheres shape with specific surface area up to 214.97 m2/g and diameter of about 2 μm after calcined at 600℃. The Zn doped photocatalysts exhibited enhanced absorption intensity, decreased electron-hole recombination. Further photocatalytic activities of the samples were greatly increased. The influences of calcination temperature and Zn doping content on photocatalytic activities of the samples were investigated by measuring the degradation rate of methyl orange (MO) under simulated sunlight irradiation. The sample doped with 0.5wt% Zn which was calcined at 600℃ showed the highest efficiency. Under visible light irradiation for 60 min, the decolorizing efficiency of 25 mg/L MO by 0.5 g/L photocatalyst reached 97%.
|
|
|
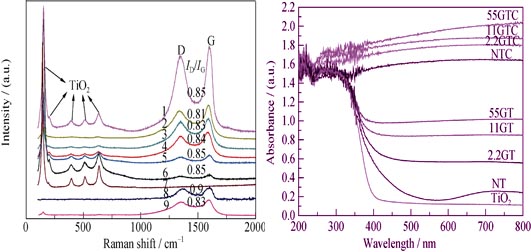
Synthesis of Graphene/Ni/TiO2/CNTs Composites and Photocatalytic Activities
LV Hui, CHEN Ai-Ping, SUN Xiu-Li, TANG Jun, LI Chun-Zhong
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1061–1066
 Abstract
Abstract(
905 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(517KB)(
2242
)
TiO2 nanoparticals doped with nickel were coated on graphene by solvo-thermal method. Then the CNTs were grown by in-situ chemical vapor deposition using nickel as catalyst. Finally, the graphene/Ni/TiO2/CNTs nanocomposites was obtained. The prepared graphene/Ni/TiO2/CNTs nanocomposite photocatalyst was characterized by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope and Raman spectra. The photocatalytic activities of the samples were investigated by the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange under UV and visible light. The results indicated that the photocatalytic activities increased from Ni/TiO2, graphene/Ni/TiO2, to graphene/Ni/TiO2/CNTs by the addition of graphene and CNTs. And the photocatalytic activities of graphene/Ni/TiO2/CNTs increased with the graphene amount increase. For the sample graphene/ Ni/TiO2/CNTs with the highest graphene content, its photocatalytic degradation of MO under UV irradiation reached 98%, and its photocatalytic degradation of MO under visible light irradiation was 3.5 fold higher than that of sample Ni/TiO2.
|
|
|
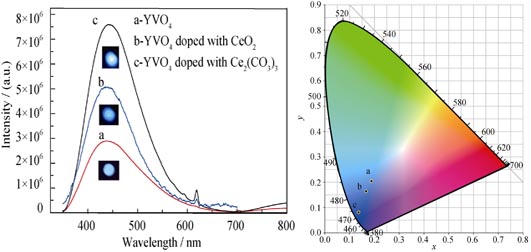
Blue-emitting Properties of Ce3+ Doped YVO4 under Ultraviolet Excitation
ZHANG Shou-Chao, RUAN Yong-Feng, JIA Guo-Zhi, FENG Zhi-Hui, LIU Zhi-Peng, PEI Li-Bin
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1067–1072
 Abstract
Abstract(
761 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(518KB)(
1112
)
YVO4 and YVO4:Ce3+ single crystals doped with 2.0at% CeO2 (or Ce2(CO3)3) were grown by using the Czochralski method. XRD pattern shows that Ce3+ ion enters the YVO4 lattice by occupying the Y3+ sites and the YVO4 crystal structure change little by the addition of Ce ions. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) shows that the Ce (3d) peak splits into five peaks located at 882.0, 885.8, 902.9, 908.0 and 915.9 eV, which indicates that the Ce3+ and Ce4+ ions coexist in both kind of samples. The excitation spectra of YVO4 and YVO4:Ce3+ crystals are both in the range from 260 nm to 360 nm, due to the charge transfer transition of the O2--V5+ ion pairs of VO43- polyhedron. YVO4 and YVO4:Ce3+ single crystals radiate a wideband blue light centered at 440 nm when excited by 325 nm ultraviolet light, the former corresponds to 3T2→1A1 and 3T1→1A1 transition of VO43-, while the latter corresponds to 5d→4f transition of Ce3+. In YVO4: Ce3+ crystal, the wave functions of Ce3+ overlaps effectively to the π orbital of VO43-, via this interaction the energy can be transfer effectively from VO43- to Ce3+, so that the blue-emitting intensity of Ce3+ is improved significantly. Experimental results show that YVO4: Ce3+ crystal is a potential blue-emitting material for white-emitting LED under ultraviolet excitation.
|
|
|
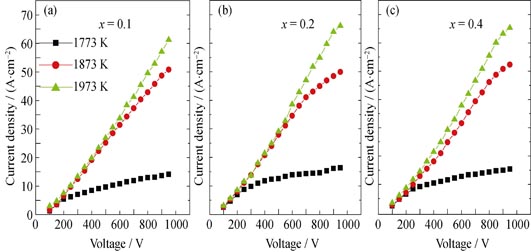
Synthesis and Properties of Single Crystal Ce1-xPrxB6 by Floating Zone Melting
ZHANG Fan-Xing, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Jiu-Xing, LIANG Chao-Long, HUANG Ying-Kai
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1073–1076
 Abstract
Abstract(
647 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(476KB)(
1009
)
High-quality single crystals Ce1-xPrxB6 (x = 0.1, 0.2, 0.4) hexaborides were successfully prepared by the reactive spark plasma sintering (SPS) combining with the floating zone melting method using powder of CeB6 and PrB6 as raw materials. The thermionic emission properties of the (100) plane of single crystals were investigated. Results show that the (100) plane of Ce0.8Pr0.2B6 single crystal has the maximum emission current density, 66.07 A/cm2 at 1873 K, which is higher than the current reported CeB6 single crystal, increased by about 20%. In addition, the thermal emission current density of (100) plane of Ce0.9Pr0.1B6, Ce0.6Pr0.4B6 single crystals are 65.81 A/cm2 and 65.31 A/cm2, respectively. The (100) plane of Ce0.8Pr0.2B6 single crystal has the lowest work function of 2.61 eV, while the work functions of other single crystals are in the range of 2.64-2.753 eV. Therefore, single crystals Ce1-xPrxB6 hexaborides have good thermionic emission and low work function, which promises good prospects in the application as a hot cathode material.
|
|
|
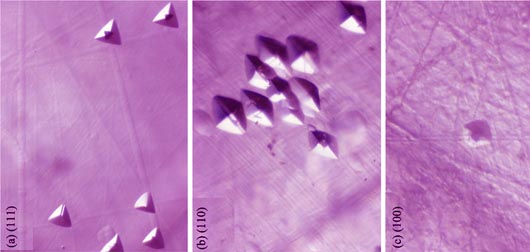
Growth, Structure and Transmission Spectrum of A New Type GYSGG(GdxY3-xSc2Ga3O12) Crystal
CHENG Mao-Jie, SUN Dun-Lu, LUO Jian-Qiao, ZHANG Hui-Li, CHEN Jia-Kang, ZHANG Qing-Li, YIN Shao-Tang
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1077–1081
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(447KB)(
1258
)
A new GYSGG (Gd0.63Y2.37Sc2Ga3O12) crystal with high quality was successfully grown by Czochralski method. The structure and transmission spectrum were investigated. The lattice constant of GYSGG was larger than those of the currently used crystals GGG and CaMgZr:GGG, ranging in YSGG and GSGG. The crystal substrate with various lattice constants can be obtained for applications by adjusting the proportions of Gd and Y in the GYSGG crystal. Further, the rocking curves of three different crystalline faces exhibit symmetric shape and small full width at half maximum (FWHM), suggesting that the crystal has good crystalline integrity. The dislocation etching pits of three different crystalline faces were also investigated. The transmission spectrum indicates that the crystal has a wide band in transmission, from which the refractive index curve is calculated and sellmeier equation coefficients are fitted. Therefore, the GYSGG is not only an excellent laser host crystal, but also a window material with wide wave band, suggesting that it has potential applications as new magnetic bubble substrate with an adjustable and larger lattice constant.
|
|
|
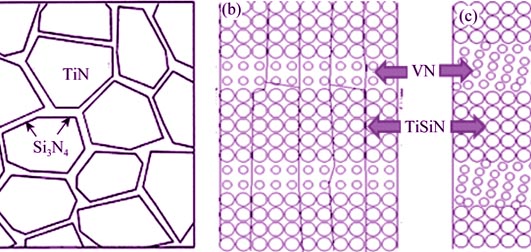
Influence of VN 2-D Inserted Layers Thickness on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of TiSiN Nanocomposite Film
XUE Zeng-Hui, LI Wei, LIU Ping, MA Feng-Cang, LIU Xin-Kuan, CHEN Xiao-Hong, HE Dai-Hua
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1082–1086
 Abstract
Abstract(
648 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(465KB)(
999
)
Using V and TiSi targets, a series of TiSiN nanocomposite films being inserted by VN nano-layers with different thickness were prepared by RF magnetron sputtering method. Using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) and nano-indentation techniques, the influences of VN inserted layer thickness on microstructure and mechanical property of TiSiN nanocomposite film were investigated. The results show that, when the VN inserted layer thickness is small, the TiSiN film transforms from nanocomposite structure into nanomultilayered structure, leading to the decrease of hardness. As the VN inserted layers thicken, the hardness of film renewedly increases. When the VN inserted thickness is 0.5 nm, the film presents columnar crystals which continuously crosses through the nanomultilayers. TiSiN and VN layers exhibit coherent epitaxial growth structure, and the hardness accordingly reaches 37.2 GPa. With further increase of the VN inserted layer thickness, the coherent epitaxial growth structure is broken and the hardness of film decreases.
|
|
|
Effect of Annealing Temperature on Metal/Dielectric Multilayers for Fabricating Broadband Pulse Compression Gratings
WU Jian-Bo, JIN Yun-Xia, GUAN He-Yuan, KONG Fan-Yu, LIU Wen-Wen, LIU Shi-Jie, YI Kui
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1087–1092
 Abstract
Abstract(
658 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(688KB)(
1105
)
Metal/dielectric multilayers were prepared by physical vapor deposition process using gold as the metal material, HfO2 and SiO2 as high and low refractive index materials, respectively. These stacks were used to fabricate broadband pulse compression gratings. Influences of annealing temperature on the surface root-mean-square roughness, reflectivity and resistance to chemical cleaning damage were investigated. The experimental results indicated that surface root-mean-square roughness of these multilayers changed only slightly after annealing. Their resistance to chemical cleaning damage improved with the annealing temperature increase, whereas their reflectivity decreased. The metal/dielectric multilayers annealed at 250℃ for 10 h could not only endure the process of chemical cleaning, but also slightly decrease the reflectivity, suggesting that it is an optimal annealing process for metal/dielectric multilayers.
|
|
|
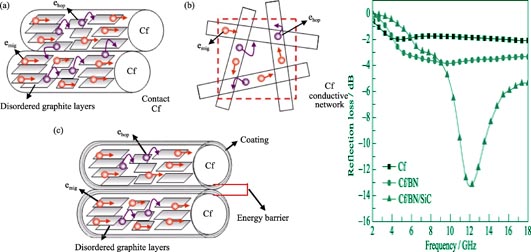
Microwave Absorbing Properties of Carbon Fibers Modified with BN/SiC Composite Coatings
ZHOU Wei, XIAO Peng, LI Yang, LUO Heng, HONG Wen
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1093–1098
 Abstract
Abstract(
929 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1098
)
BN coating were prepared firstly on carbon fibers by dip-coating process using boric acid and urea as raw materials. Then, SiC coating were deposited on BN coating surface by chemical vapor deposition process using methyltrichlorosilane as precursor. Finally, BN/SiC composite coatings modified carbon fibers were obtained. The oxidation resistance, dielectric and microwave absorption properties, and microstructure of the BN/SiC composite coatings modified carbon fibers were investigated. The results showed that the thickness of the BN and SiC coating on the surface of carbon fibers were about 0.1 μm and 0.7 μm, respectively. After being modified by BN/SiC composite coatings, the initial and final oxidation temperatures of the modified carbon fibers were increased from 560℃ and 780℃ to 790℃ and above 1200℃, respectively. The dielectric properties of the modified carbon fibers changed significantly, and the microwave absorption properties were improved. Compared with the uncoated carbon fibers, the lowest reflectivity of the BN/SiC composite coatings modified carbon fibers with the thickness of 2 mm reduced to -13.3 dB, and the bandwidth (less than -10 dB) increased to 2.5 GHz.
|
|
|
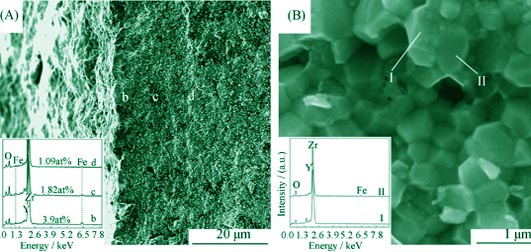
Preparation of Antistatic Ceramics Employing Fe-infiltration in Sintered Zirconia Body
LI Yong, XU Xie-Wen, YANG Xian-Feng, XIE Zhi-Peng
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1099–1104
 Abstract
Abstract(
679 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(550KB)(
1075
)
Antistatic ceramic with good mechanical performance has wide application in fields of aerospace, petrochemical engineering, electronics and textile. Antistatic ceramic ZrO2 was fabricated via an innovative surface modification method based on embedding Fe-infiltration into the 3Y-TZP ceramic at high temperature, which showed good antistatic and mechanical properties. In addition, microstructure and morphology of as-prepared samples were characterized by XRD, SEM and XPS. Furthermore, the antistatic mechanism of ZrO2 ceramics was investigated. The effects of infiltration temperature and infiltration time on vickers hardness and surface resistivity of specimen were evaluated. Experimental results showed that the surface resistivity and hardness decreased with the increase of infiltration temperature and infiltration time, in which the surface resistivity decreased from more than 1014 ?/□ to 8.3×107 ?/□, and the hardness of ZrO2 ceramics decreased from 12.7 GPa to 11.23 GPa after infiltration at 1000℃ for 4 h. Analysis results indicated that there was a phase transformation of ZrO2 from t-ZrO2 to m-ZrO2 in the infiltration process. It was also found that Fe, Fe3O4 and FeO located in the interface of infiltration layer, which were attributed to the antistatic property of ZrO2 ceramics.
|
|
|
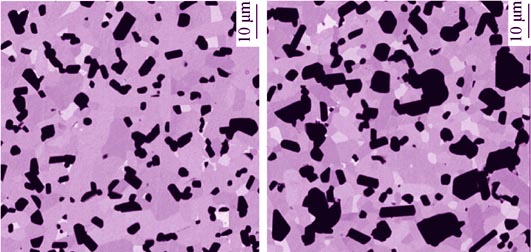
Comparative Study on Quantitation of Phase Component and Phase Composition of HfB2-SiC-HfC Ceramics
HU Dong-Li, XING Juan-Juan, ZHENG Qiang, GU Hui, NI De-Wei, ZHANG Guo-Jun
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1105–1109
 Abstract
Abstract(
731 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(349KB)(
1093
)
Phase component and phase composition of two pressureless-sintered HfB2-SiC-HfC ultra-high temperature ceramic samples were quantitatively analyzed. The results obtained by two different methods were compared. The phase component and phase composition for HfB2, SiC and HfC phases are in consistence, suggesting that the two methods respectively based on X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) are both applicable to the phase quantification for ceramic composites. Trace WB phase was also detected and further quantified by the backscattered electron (BSE) method. XRD-K value method was successfully extended to quantify the low-solution phase components. Quantitative results of stable W solute levels in HfB2 and HfC phases in both samples, which were prepared with different milling media and WC contents, indicate that the liquid phase plays a key role in the reactive-densification process. The loss of W by the SiC milling makes Si3N4 to be more suitable milling medium.
|
|
|
Degradation Effect of Super Acid Modified Fe2O3-TiO2-N on Acrylic Acid under Visible Light
HAN Zhi-Yue, DU Zhi-Ming, ZHANG Ying-Hao, ZHAO Lin-Shuang, CONG Xiao-Min
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1110–1114
 Abstract
Abstract(
709 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(291KB)(
997
)
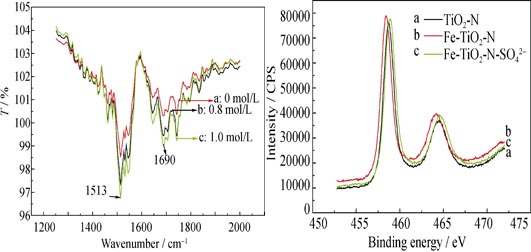
Super acid modified Fe2O3-TiO2-N was prepared by hydrolysis precipitation method and sulfuric acid impregnation method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) showed that the catalysts were anatase, Fe2O3 were highly decentralized in the catalysts with amorphous form, and modification of SO42- inhibited grain growth. Ultraviolet-visible spectra (UV-Vis) showed that Fe and N co-doping made the visible light absorption to the red shift, and sulfuric acid impregnation treatment made the light absorption to the blue shift. Diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared (DRIFT-IR) spectra showed that sulfuric acid impregnation can improve the surface acidity of catalysts. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) showed that the valence of S was +6 in the catalysts. Its photocatalytic activity on the degradation of acrylic acid under visible light was studied. The one hour degradation rate of super acid modified Fe2O3-TiO2-N catalyst under visible light was improved 57% than that of the N-doping sample under the same condition.
|
|
|
Morphology Evolution in Hydrothermal Synthesis of Mesoporous Alumina
LI Yan-Hui, PENG Cheng, ZHAO Wei, BAI Ming-Min, RAO Ping-Gen
2014 Vol. 29 (10): 1115–1120
 Abstract
Abstract(
1215 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(655KB)(
1110
)
Boehmite with varied morphologies was successfully synthesized from aluminum ammonium sulfate hydrate and urea, as well as poly-glycol-2000 by hydrothermal method. The experimental results show that boehmite microspheres, microfibers and 3D hierarchical structured AlOOH can be fabricated only by adjusting hydrothermal temperature. SEM images indicate that boehmite decomposes into γ-Al2O3 phase after heat-treatment through a topotactical process. TEM studies present that the mesopores are formed in γ-Al2O3 particles. Based on these investigations, a temperature-dependent morphology formation mechanism is proposed. Besides, the as-synthesized alumina excited at 325 nm shows emission in the range of 380 nm to 500 nm, centered at 409 nm and 467 nm.
|
|