|
|
Research Progress on Nanogenerators Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures
PAN Chun-Xu, LI Wei-Ping, ZHANG Yu-Peng, YU Chao-Zhi, LI De-Long
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 897–904
 Abstract
Abstract(
1211 )
 HTML
HTML(
27)
 PDF
PDF(742KB)(
1304
)
With the development of society and energy crisis, searching for new energy materials and developing new energy have been one of the eternal subjects. Since the piezoelectric nanogenerator based on ZnO was developed in 2006, many nanogenerators have been developed based on nanomaterials and nanostructures due to their different nano-effects. This paper reviews the scientific achievements on nanogenerators in nearly 10 years, and introduces the principles of the nanogenerators based on piezoelectric effect, triboelectric effect and modulation of the graphene band, which provide references for the development of new nanogenerator in the future.
|
|
|
Research Progress of Film/Bulk Oxide Magnetoelectric Composites
WANG Jing, WU Xia, DENG Chao-Yong, ZHU Kong-Jun, NAN Ce-Wen
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 905–911
 Abstract
Abstract(
922 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
1039
)
Composite ceramics of ferrites (e.g., CoFe2O4, NiFe2O4) and ferroelectrics (e.g., BaTiO3, Pb(ZrxTi1-x)O3) are classical magnetoelectric (ME) materials, which are also the first composites found to exhibit large room-temperature ME effect. These composites are generally fabricated via sintering at high temperature of over 1200℃. However, such high-temperature co-firing processing yields atom inter-diffusion and/or chemical reactions between two phases, or even microcracks. In this review, several low-temperature (normally below 800℃) synthesis routes of depositing the ferromagnetic (ferroelectric) films on ferroelectric (ferromagnetic) bulk single-crystals or ceramics are summarized. By such means, the above-mentioned problems can be avoided to improve the ME effect across the interface. Methods frequently used for characterizing the ME effect in these ceramics-based composites films are also discussed.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of A New Ferroelectric Ternary Solid Solution Pb(Lu1/2Nb1/2)O3-Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3
LIU Ying, LAI Fa-Chun, Huang Zhi-Gao, SHEN Dong-Quan, LONG Xi-Fa
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 912–916
 Abstract
Abstract(
816 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(604KB)(
893
)
Ceramics of (0.7-x)Pb(Lu1/2Nb1/2)O3-0.3Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3(PLN-PMN-PT) (0.38 ≤ x ≤ 0.46) ternary system were synthesized by means of a two-step columbite precursor method which can effectively suppress the pyrochlore phase. A morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region in the ternary systems was found in the range of 0.40 ≤ x ≤ 0.44 and the electric properties of the compositions near MPB region were investigated. Those compositions within MPB exhibit good comprehensive piezoelectric properties. The ceramic with composition of 0.29PLN- 0.3PMN-0.41PT shows a high Curie temperature of 270℃ and a high rhombohedral-tetragonal phase transition temperature of 135℃, whose piezoelectric coefficient d33, coercive field Ec and remnant polarization Pr are found to be 460 pC/N, 14.8 kV/cm and 34.6 μC/cm2, respectively. The large coercive field and high Tc enable it a promising candidate for application in the piezoelectricity field.
|
|
|
High Energy Density Spinel LiCr0.2Ni0.4Mn1.4O4 Cathode Material Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis Method
CHEN Ming-Zhe, GUO Xiao-Dong, ZHONG Ben-He, YAN Hui-Min, ZHANG Ji-Bin, LIU Ju
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 917–923
 Abstract
Abstract(
730 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(637KB)(
893
)
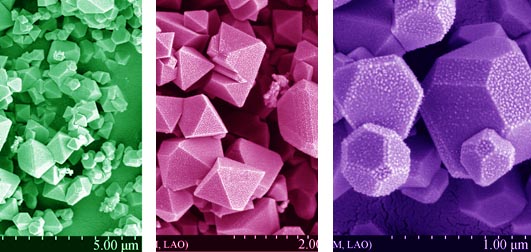
Cathode material of LiCr0.2Ni0.4Mn1.4O4 with high energy density and superior electrochemical properties was fabricated by means of spray pyrolysis. The material was characterized via thermogravimetric analysis (TG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in detail, and within the tolerance of current available electrolyte the discrepancy of different cut-off voltages (3.6-5.0 V, 3.6-5.2 V) was investigated. The results demonstrate that the obtained material is crystallized well without any formation of impurities, and a relative uniform particle size distribution is within micron and sub-micron. In the voltage window of 3.6-5.2 V, the initial discharge capacity can reach as high as 142.9 mAh/g at 0.5C, and its values of energy densitiy at 0.5C and 1C surpass 600 Wh/kg. If the cut-off voltage is set at 5.2 V, the degree of discharge and low-rate capacity are increased, while its high-rate capacity, cycling stability and working voltage platform are deteriorated seriously.
|
|
|
Influence of NH4HCO3 on Microstructure of Ni/La10Si5.8Mg0.2O26.8 Anode
XIANG Li, DING Xiao-Fang
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 924–930
 Abstract
Abstract(
619 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(1035KB)(
974
)
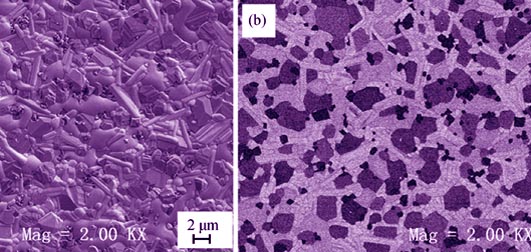
Apatite-type lanthanum silicates are a new type of oxide-ion conductors. In the present research, nanosized apatite-type lanthanum silicate (La10Si5.8Mg0.2O26.8) powder was prepared through Sol-Gel method by using citric acid and nitrates. The nanosized lanthanum silicate powder was mixed with nanosized NiO powder according to weight ratio of 4:6, and with different amounts of NH4HCO3 as pore-forming agent. Porous composite anodes of Ni/La10Si5.8Mg0.2O26.8 were fabricated through sintering at 1400℃ and then reduced in H2 atmosphere at 600℃. Phases, surface morphology and porosity of the samples were characterized by XRD, FE-SEM and Archimedes method, respectively. Resistance of the anodes at room temperature was determined by ac impedance spectroscopy. The results show that the prepared Ni/ La10Si5.8Mg0.2O26.8 porous composite anodes are micro-crack free and the mean thermal expansion coefficient before reduction is 10.7×10-6 K-1. With increasing amount of pore-forming agent NH4HCO3, sizes of Ni grains, apatite-type silicate grains and pores decrease, but the porosity increases within the range of 30%-45%. The resistance of the anodes decreases at first and then increases as the amount of NH4HCO3 increases. Considering all these characteristics, including phases, surface morphology, porosity and resistance, the anode made with the pore-forming agent NH4HCO3 at ratio of 30wt% is the best.
|
|
|
Effect of Sb Doping on Thermoelectric Property of N-type Half-Heusler Compounds
FAN Yi, LI Xiao-Ya, JIANG Yong-Fen, BAO Ye-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 931–935
 Abstract
Abstract(
835 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(468KB)(
1056
)
The effect of Sb doping on thermoelectric transport properties of N-type half-Heusler compounds Zr0.25Hf0.25Ti0.5NiSn1-xSbx (x=0, 0.002, 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03) was studied. Results show that with increasing Sb doping amount, the carrier concentration of the samples increases while the electrical resistivity decreases, especially sharply at low temperature range (~300 K). The Seebeck coefficient decreases, and the temperatures at which the Seebeck coefficient reaches climax move to higher ones. Therefore, the power factor increases by ~20%. The total thermal conductivity increases mainly due to the enhancement of electrical thermal conductivity, the lattice thermal conductivity remains almost unchanged. For the samples with x<0.01, the maximum ZT value is about 0.77 at 800 K, and among the samples, the one with x=0.005 performs the best in the whole temperature range.
|
|
|
Preparation and Tribological Behavior of Cu-based Electrical Contact Composite Containing NbSe2 in Vacuum
SUN Jian-Rong, LI Chang-Sheng, TANG Hua, HUA Xi-Jun
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 936–940
 Abstract
Abstract(
700 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(534KB)(
1003
)
Cu-graphite self-lubrication composite containing nano NbSe2 (0-9wt%) was fabricated by powder metallurgy technology. Friction property of the sample was investigated using micro-tribometer and ultra-low-temperature tribometer under atmosphere and vacuum conditions. The microstructure, phase and wear scar were also investigated by XRD and SEM. The results showed that tribological property was significantly improved after nano NbSe2 being added to the Cu-graphite self-lubrication composite. The composite with nano NbSe2 (5.5wt%) had smaller friction coefficient (μ=0.185) under vacuum dry friction conditions and higher carrying capacity than those of the composite without NbSe2. It was found that the wear could be attributed to adhesive wear together with contact fatigue wear.
|
|
|
Microstructure Evolution Induced by Ultraviolet Light Irradiation in Ti-Si Codoped Diamond-like Carbon films
JIANG Jin-Long, WANG Qiong, HUANG Hao, ZHANG Xia, WANG Yu-Bao, GENG Qing-Fen
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 941–946
 Abstract
Abstract(
707 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(455KB)(
1046
)
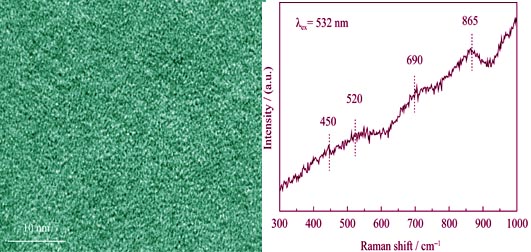
Titanium/silicon co-doped diamond-like carbon films were deposited on Si substrate by middle frequency magnetron sputtering using Ti80Si20 composite as target. The microstructure of the deposited films was characterized by ultraviolet and visible multi-wavelength Raman spectroscope. The influence of ultraviolet light irradiation on microstructure of the films was investigated by a combination of Raman and FTIR spectroscope. The mechanism of microstructural evolution of the films induced by ultraviolet light irradiation was discussed. The results show that the film dominated by amorphous structure displays inclusions of trans-polyacetylene, p-phenylene vinylene and sp hybridized carbine carbon chains. Ultraviolet light irradiation induces the relaxation and reconstruction of microstructure in the films, which leads to the increase of Si-O and C-O bonding, and the decrease of C=C and C-H bonding. Meanwhile, the size of sp2 clusters in the films decreases and the degree of disorder of sp2 clusters increases.
|
|
|
Preparation of Anti-reflection Coatings with Hollow Silica Nanoparticles by Self-assembly
SUN Zhi-Juan, CHEN Xue-Lian, JIANG Chun-Yue
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 947–955
 Abstract
Abstract(
1248 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(1021KB)(
1240
)
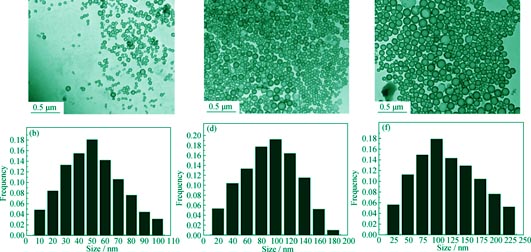
Using tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as raw material and polyacrylic acid (PAA) as nucleating material, hollow silica nanoparticles were synthesized on the basis of traditional method of Stöber. Using hollow silica nanoparticles, both single-layer anti-reflection coatings and broad-band double-layer anti-reflection coatings were prepared by self-assembly. The structure control of the hollow silica nanoparticles, the effect of deposition cycle, pH value of the hollow silica nanoparticle dispersion on transmittance of coatings, and the preparation of the double-layer anti-reflection coatings with a graded-refractive-index were investigated. The results show that the size and void fraction of the hollow silica nanoparticles can be controlled precisely by changing the amount of PAA and TEOS. The thickness and refractive index of the anti-reflection coatings can also be tuned accurately in the same way. The deposition cycles are reduced from 10 cycles to 2 cycles by acid pickling which simplifies the coating process. This new technique significantly increases the transmittance of glass substrate coated by single-layer anti-reflection coatings in the range of 350-800 nm under optimum conditions, and improves the maximum transmittance from 91.6% to 98.1% at optimized wavelength (λ=520 nm). Furthermore, glass substrate coated by double-layer anti-reflection coatings can increase the transmittance more than 5% in a much wider wavelength range (400-1500 nm).
|
|
|
Fabrication and Photocatalytic Performance of GaN/ZnO Composites
PENG Dan, ZHENG Xue-Jun, XIE Shu-Fan, LUO Xiao-Ju, WANG Ding
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 956–960
 Abstract
Abstract(
860 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(523KB)(
1235
)
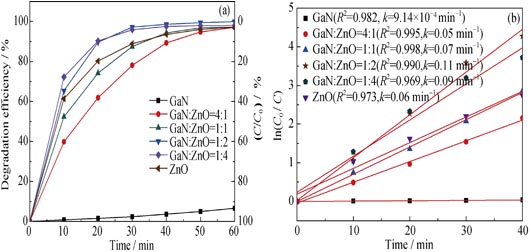
GaN powder was firstly synthesized by the Sol-Gel method using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and gallium nitrate [Ga(NO3)3] as surfactant and gallium source, respectively. Then, GaN/ZnO composites were prepared by solid phase method through mechanical mixing GaN powder and ZnO powder with different proportions. The composites were characterized by using X-Ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), high-resolution X-ray electron microscope (HRTEM) and photoluminescence (PL) spectra. The photocatalytic performance of GaN/ZnO composites as catalyst was tested by degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution under white light irradiation. The results show that the photocatalytic property of GaN/ZnO composites is obviously improved comparing with that of pure GaN and ZnO powders. The photocatalytic activity is analyzed by pseudo-first-order kinetics equation, showing that the best photodegradation rate constant k is 0.11 min-1 for the GaN/ZnO composites with GaN and ZnO mixing ratio of 1: 2.
|
|
|
Influences of the Dopants of Several Heavy Metal Oxides and GeO2 on Spectroscopic and Lasing Properties of Yb3+-doped Fluorophosphate Glasses
YANG Bin-Hua, LIU Xue-Qiang, ZHANG Wei, LI Xiang-Tan, ZHANG Li-Yan, HU Li-Li
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 961–966
 Abstract
Abstract(
587 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(403KB)(
957
)
Effects of the different metal oxides added with Ga2O5, TeO2, GeO2, WO3, Nb2O5 and Bi2O5 respectively on the spectroscopic and lasing properties of Yb3+-doped fluorophosphate glasses were comparatively investigated. Results show that the additions of TeO2, GeO2 and Ga2O5 can increase the absorption and emission cross sections of Yb3+-ions. Among the three glasses above, the TeO2-doped glass has the largest parameters up to 1.95 pm2 and 0.85 pm2, respectively. Meanwhile, the dopants of Ga2O5, Nb2O5 and GeO2 are beneficial to the improvement of lasing properties in fluorophosphate glasses. Laser parameters (SFL) of fluorophosphate glass doped with Ga2O5 is 1.237, the largest of all the glasses. Moreover, serious fluorescence trapping of Yb3+ is found in fluorophosphate glasses doped with TeO2 and GeO2, respectively, which strongly lessens the lasing properties.
|
|
|
Structure and Fluorescence Quenching of Li2O-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glasses
Doped with Trivalent Cerium
CHEN Yan-Ping, LUO De-Li, XU Qin-Ying, YANG Suo-Long, TANG Tao, WANG Xiao-Ying
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 967–971
 Abstract
Abstract(
666 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(518KB)(
1105
)
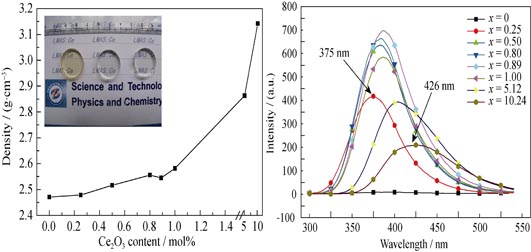
20Li2O-5MgO-20Al2O3-55SiO2 glass doped with different concentrations of Ce3+ ions was synthesized by using melt-quenching method. The glass density as a function of Ce3+ ions doping concentration was tested by Archimedes’ method. The structural characteristics of Ce3+-doped 20Li2O-5MgO-20Al2O3-55SiO2 were detected by using X-rays diffraction (XRD), high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) techniques. The photoluminescence excitation (PLE) and emission (PL) spectra were recorded in a spectrofluorimeter by photon counting techniques. Results showed that 5d energy level of Ce3+ ion was splitted to five components under the strong crystal filed surrounding Ce3+ ions. The higher the doping concentration of Ce3+ ions, the higher the degree of non-crystalline configuration of lithium magnesium aluminosilicate glass was. With the increase of the degree of non-crystalline configuration, the splitting width of 5d energy level increased, resulting in the redshift of excitation and emission spectra apparently. The PL emission intensity first increased, and then decreased with the increase of Ce3+ ions doping concentration. The concentration quenching processes were found to be the key reason for the reduction of the PL emission efficiency.
|
|
|
Effect of Metal Oxides on Fire Resistance and Char Formation of Intumescent Flame Retardant Coating
ZHOU You, LIU Xiu, WANG Fang, HAO Jian-Wei, DU Jian-Xin
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 972–978
 Abstract
Abstract(
1001 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(645KB)(
1101
)
Metal oxides (MO) can remarkably affect the char formation of intumescent flame retardants (IFR) during thermal decomposition, thereby improving the fire resistance property of IFR coatings. In present work, Fe2O3, ZnO and TiO2 were separately incorporated with caged bicyclic phosphates based IFR in epoxy coating, and their effects on fire resistance and char formation of the IFR coating were investigated. Back temperature test results showed that MO worked synergistically on improving fire resistance of the coating and their effectiveness of improvement followed the trend of Fe2O3>ZnO>TiO2. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), laser Raman spectroscopy (LRS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results revealed that MO promoted the formation of pseudo-graphic char with improved thermal stability which still survived at high temperature, and their effectiveness of promotion also followed the trend of Fe2O3>ZnO>TiO2.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Ordered Needle Coke with Graphene as an Inoculating Seed
XIE Xiao-Ling, CAO Qing, GUO Liang-Chen, ZHONG Cun-Gui
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 979–984
 Abstract
Abstract(
852 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(1129KB)(
1236
)
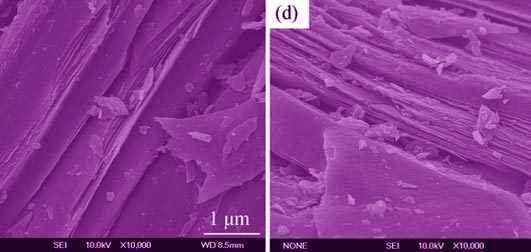
Anisotropic mesophase pitch of the highest content were produced by using graphene (GE) as structural directing agent, and refined coal tar pitch as the raw material, and which was applied to prepare semi-coke and needle coke thereafter with the utilization of temperature controlling program. The textures of mesophase pitch and semi-coke were investigated by polarizing microscope, and the structure and morphology of needle coke were analyzed by X-ray diffraction analyzer and scanning electronic microscope, respectively. Its electrochemical properties were observed by electrochemical workstation and the microcrystallite structure was analyzed by cyclic voltammetry. The results showed that addition of graphene obviously accelerated the formation of meso-sphere and enhanced structural orientation of needle coke and the electric transporting capability. Especially, nearly the same size and the largest number of meso-sphere in the pitch were obtained when the mass percentage of graphene in feedstock reached 0.2wt%; and lots of fibrous texture in semi-coke can be observed. At the same conditions, the existence of graphene made the degree of graphitization of needle coke increase by 200% and the charge transfer resistance decrease by 65.3%, as comparing with that without graphene.
|
|
|
Hierachical Zeolite-Zeolite Composite Prepared by a Vapor Phase Transport Method
ZHANG Qiu, Tan Wei, ZHENG Jia-Jun, ZHAO Qiang-Qiang, WANG Guang-Shuai, YI Yu-Ming, LI Rui-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 985–990
 Abstract
Abstract(
704 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(586KB)(
1004
)
A zeolite-zeolite composite composed of Y and ZSM-5 was successfully prepared by a vapor phase transport (VPT) method. The as-synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), N2 adsorption-desorption and FT-IR. The results display that the synthesis is influenced by the Y content, preparing condition of dry gel and transfering condition for VPT method. FT-IR spectra show the characteristic peaks of MFI framework on ZSM-5 precursor after hydrothermal pre-treatment for 16 h. The result can be attributed to the crystal nucleus or microcrystal of ZSM-5 zeolite, either of which may promote growth of ZSM-5 crystals during the VPT procedure, and depresse formation of ZSM-35 crystals. The mesopores structure, created in as-synthesized zeolite-zeolite composite, can be ascribed to the extracted aluminum from Y zeolite crystals by VPT procedure.
|
|
|
Study on the Injectable Magnesium-calcium Phosphate Cements
DAI Hong-Lian, HU Fu-Jian, FANG Cai-Ping, LI Shi-Pu
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 991–996
 Abstract
Abstract(
794 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
1088
)
Injectable magnesium-calcium phosphate cements (IMPC) was prepared using magnesium oxide (MgO), monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4), β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), glucose and phosphoric acid solution. The effects of liquid to powder ratio(LPR), contents of MgO and glucose on IMPC’s gelling and mechanical properties were investigated. The results showed that increase of LPR and glucose content resulted in increased IMPC setting time and injectability, and decreased compressive strength. With the MgO content decreasing, the setting time and the injectability were decreased, whereas the compressive strength was increased. To obtain optimal formula for the new IMPC, the MgO and glucose contents and LPR were selected based on orthogonal experiments, and the result was 26wt% MgO, 6wt% glucose and 0.30 mL/g LPR. The new IMPC has moderate hydration with low exothermic reaction and ideal hardening performance, indicating that it may be used as a novel bone adhesive material.
|
|
|
Synthesis of N-doped Mesoporous Titania with High Visible-light Photocatalytic Activity
WANG Hui-Lei, LIU Xiao-Heng
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 997–1002
 Abstract
Abstract(
689 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(587KB)(
1044
)
N-doped mesoporous titania was synthesized using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as template and Dimethyl Formamide (DMF) as nitrogen source. The physical and photophysical properties of the photocatalyst were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), FTIR, BET, transmission electron microscope (TEM), UV-Vis diffuse re?ectance spectra (DRS), and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS). PEG played an important role in the preparation process within mesoporous titania. The N-doped mesoporous titania possessed diameter of ca. 20 nm with anatase crystalline structure, and had absorption in the visible region. N-doped mesoporous titania samples showed excellent photocatalytic activity for methyl orange (MO) degradation under visible light irradiation, which could be attributed to synergistic effect between the retained alkoxyls and the nitrogen doping.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Carbon Fiber/Si3N4 Composites
WANG He-Yun, LIU Qian, ZHOU Yao, ZHOU Zhen-Zhen, LIU Guang-Hui
2014 Vol. 29 (9): 1003–1008
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(519KB)(
1091
)
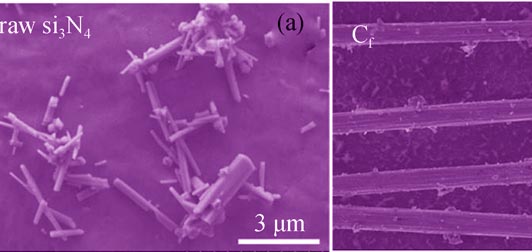
To investigate the effects of carbon fiber (Cf) adding content on the properties of Si3N4, Cf/Si3N4 composites with 0, 2wt% and 5wt% of short carbon fibers were prepared by hot-press sintering method, using Y2O3 as sintering additives. With long-time ball milling process, carbon fibers were well dispersed in mixed powders using ethanol as dispersion medium. Carbon fibers distribute uniformly in the composites and Si3N4 grains grow to a certain degree in the vertical direction to the pressure of hot-press. The interfacial by-product silicon carbide (SiC) phase forms due to the reaction between added Cf and Si3N4 particles or SiO2 layer on surface of Si3N4 particles during high temperature sintering. The sample with 2wt% Cf addition achieves a higher value of thermal conductivity (45.8 W/(m?K)), while the thermal conductivity of Si3N4 without Cf is only 37.1 W/(m?K). Therefore, the addition of Cf can improve the thermal conductivity of the composites. The fracture toughness of the composites has a slight increase with Cf adding. The measured hardness values for all samples are within a range of 16.6-16.8 GPa.
|
|