|
|
Recent Progress in Photocatalysis of g-C3N4
CHU Zeng-Yong, YUAN Bo, YAN Ting-Nan
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 785–794
 Abstract
Abstract(
2699 )
 HTML
HTML(
55)
 PDF
PDF(493KB)(
18139
)
Based on photocatalysts, solar energy can be converted into the energy that human can directly utilize, so as to solve the problems such as the depletion of the Earth’s resources and the deterioration of living environments. The unique structure of g-C3N4 gives it good photocatalytic performance. Its development and utilization have been a research hotspot recently. Generally, g-C3N4 can be used in the degradation of pollutions, hydrolysis to generate hydrogen and oxygen, organic synthesis and oxygen reduction. However, in practical, its performance is not satisfactory. Researchers have tried many new methods to improve its photocatalysis, which include physical coupling modification, chemical bonding modification and microstructural modification. The review summarizes its photocatalysis and improving methods, briefly illustrates the catalysis mechanism, and presents detailed discussions and analysis on the existing problems as well as potential applications.
|
|
|
Effects of Calcination Condition on Photocatalytic Properties of Nano-TiO2/Opal Composite and Its Mechanism
WANG Bin, ZHENG Shui-Lin, WEN Ming, ZHANG Guang-Xin
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 795–800
 Abstract
Abstract(
731 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(505KB)(
1061
)
Nanocrystalline TiO2 particles immobilized on opal by a hydrolysis precipitation method are used as a novel catalyst in photocatalysis. Effects of crystalline and size, BET specific surface area and porous properties on the photoactivity were investigated by characterizing samples obtained under various calcination temperatures and periods. Results reveal that there is still no evidence of rutile phase in XRD patterns when the calcination temperature increases to 800℃. This indicates that the opal support impedes the phase transformation. The photocatalytic reactivity of this nano-TiO2/opal composite catalyst was evaluated by degrading Rhodamine B (RhB) under ultraviolet light. The sample calcined at 600℃ for 2 h exhibits the smaller crystalline size and larger specific surface area with a concomitant higher activity of 97.24% for RhB degradation by 4 h irradiation under 250 W Hg lamp.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Co-doped TiO2 with Assistance of Ionic Liquid
ZHANG Li-Juan, DI Lan-Bo, LI Yan-Chun, ZHANG Xiu-Ling
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 801–806
 Abstract
Abstract(
917 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1197
)
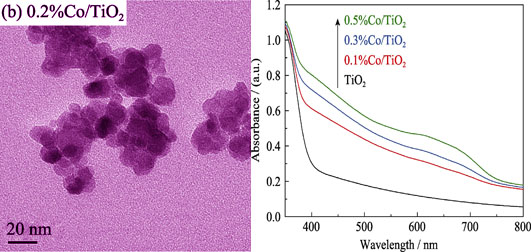
Co-doped mesoporous TiO2 photocatalysts were prepared by an ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimida-zolium tetrafluoroborate ([C4MIM]BF4) modified Sol-Gel method. The effects of Co doping on the surface area, crystalline phase, chemical binding states and compositions, and absorbance of the Co-doped mesoporous TiO2 photocatalysts were studied by N2 adsorption-desorption measurements (BET), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance absorption spectra (UV-Vis DRS). BET analysis showed that Co/TiO2 photocatalyst was mesoporous structure with large surface area. XRD patterns indicated that the Co-doped mesoporous TiO2 photocatalysts was anatase structure. XPS spectra indicated that the Co2+ replaced Ti4+ and entered into TiO2 lattice, which reduced the band gap of TiO2 and thereby extending the light response range to the visible region (UV-Vis spectra). Photocatalytic activity of the Co/TiO2 mesoporous photocatalysts was evaluated by photodegradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible light (λ>420 nm). Co-doped TiO2 exhibited obvious visible light activity for MB photodegradation, and 0.3%Co/TiO2 exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Photocatalytic Property of N-doped BiVO4 via Sol-Gel Method Using Corn Stem as Template
WANG Min, NIU Chao, DONG Zhan-Jun, CHE Yin-Sheng, DONG Duo, ZHENG Hao-Yan, YANG Chang-Xiu
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 807–813
 Abstract
Abstract(
922 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(655KB)(
1141
)
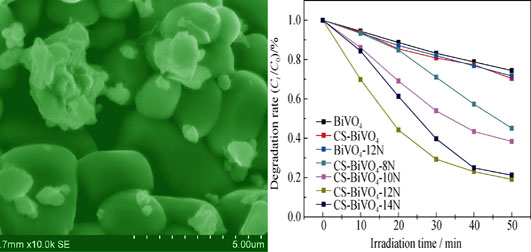
N-doped BiVO4 photocatalysts (CS-BiVO4-xN) were successfully prepared by Sol-Gel method taking the corn stem as template and C6H12N4 as N source. The samples were characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier infrared spectrum (FTIR), and UV-Vis absorption spectroscope (UV-Vis). The photocatalytic activity were investigated by degradation of methyl oran ge (MO) under visible-light irradiation. The results showed that N doping did not change the crystallinity of the BiVO4. The doped N replaced some of O atoms in BiVO4 and formed the -N-V-O band. The synergetic effect of impurity energy levels and oxygen vacancies led to narrower band-gap and red-shift of optical absorption band. Furthermore, the N doped BiVO4 with honeycomb like structure and smaller crystal sizes was prepared by using corn stem as template, which is beneficial to higher initial MO absorption and better photocatalytic activity. The degradation rate of MO under visible light illumination for 50 min is 80.9% in presence of CS-BiVO4-12N, which is much higher than those in presence of CS-BiVO4 (25.56%) and BiVO4-12N (28.34%).
|
|
|
Preparation and Application of Carbon Nanofibers-supported Palladium Nanoparticles Catalysts Based on Electrospinning
GUO Li-Ping, BAI Jie, LIANG Hai-Ou, LI Chun-Ping, SUN Wei-Yan, MENG Qing-Run
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 814–820
 Abstract
Abstract(
882 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
1163
)
Carbon nanofibers-supported palladium nanoparticle catalysts were prepared by electrospinning, chemical reduction and the subsequent high temperature carbonization methods. The experiments were carried out to investigate the influence of different reducing agents (sodium borohydride, hydrazine hydrate and hydrogen gas) on morphology of palladium nanoparticles and carbon nanofibers in detail. Catalysts were characterized by UV-Vis spectra, X-ray diffraction, fourier transform infrared spectrum, scanning electron microscope, field emission transmission electron microscope. Results show that the palladium nanoparticles are distributed uniformly on the carbon nanofibers with dimension of about 7 nm, and the catalyst is relatively flexible by using hydrogen gas as reducing agent. Then it was applied to the Heck coupling reaction to test catalytic properties and recyclability. Results indicate that the catalyst possesses excellent stability and recyclability.
|
|
|
Ambient Pressure Synthesis of Hierarchical Structured SAPO-5 Molecular Sieve with Special Morphology
ZHAO Xin-Hong, LI Xiao-Bin, CHEN Jing, QI Yong-Dong, WEN Juan-Juan, JI Dong
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 821–826
 Abstract
Abstract(
776 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(546KB)(
1069
)
Hierarchical structured SAPO-5 molecular sieve was ionothermally synthesized by microwave irradiation using a mixture solution of succinic acid, choline chloride and tetraethyl ammonium bromide as solvent and template under ambient pressure. The effects of the molar ratios of P2O5/Al2O3 and HF/Al2O3, silicon source, and crystallization time on the structure of SAPO-5 molecular sieve were systematically investigated. The resulting SAPO-5 molecular sieve was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscope (SEM), Transmission electron microscope (TEM), N2 physical adsorption-desorption and 29Si magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (29Si MAS-NMR) techniques, respectively. The results indicate that intra-crystalline and inter-crystalline mesopores coexist within the SAPO-5 molecular crystals, while 29Si MAS-NMR test shows that the incorporation of Si in the sample follows the SM3 mechanism. In addition, SEM images exhibit that hierarchical structured SAPO-5 molecular sieve with hexagonal nanometer-disc morphology can be synthesized under specific synthetic conditions.

|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Magnetic Carbon Composite Nanofibres
TANG Ying-Mao, MIAO Qing-Qing, XIAO Li-Ren, QIAN Qing-Rong, CHEN Qing-Hua
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 827–834
 Abstract
Abstract(
975 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(691KB)(
1161
)
Magnetic carbon composite nanofibres, using the mixed homogeneous solution consist of polyacrylonitrile (PAN), ferric acetylacetonate (AAI) and dimetbylformamide (DMF) as raw material, were prepared by electrospinning-calcination technology. TEM analysis showed that the carbon nanofibre diameter of sample CF900 was about 130-210 nm, in which magnetic nanoparticles were uniformly distributed. The magnetic properties of carbon composite nanofibres under different carbonization temperature was also investigated. Results showed that saturation magnetization (Ms) and remanent magnetization (Mr) increased with the increase of the temperature. When carbonization temperature was 900 ℃, the sample was of good magnetic property with high saturation magnetization (Ms=27.55 A·m2/kg). Moreover, the specific surface area (SBET) and total pore volume (Vtotal) were up to 354.0 m2/g and 0.315 mL/g, respectively.
|
|
|
Preparation of Zircon Whisker Using Carbon Black as Reducing Agent
WANG San-Hai, JIANG Wei-Hui, FENG Guo, LIU Jian-Min, MIAO Li-Feng, WANG Hong-Da
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 835–838
 Abstract
Abstract(
912 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(422KB)(
888
)
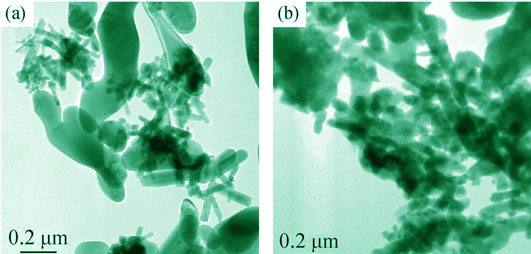
Zircon whisker was synthesized at 700 ℃ via non-hydrolytic Sol-Gel method using anhydrous zirconium tetrachloride (ZrCl4) as zirconium source, tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) as silicon source, lithium fluoride (LiF) as mineralizer, ethanol as solvent and carbon black as reducing agent. Thermogravimetric analysis and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA), X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were employed to characterize the influences of adding ways and amount of carbon black on the synthesis and morphology of zircon whisker. The results show that the carbon black added in form of suspension is favorable to the one-dimension growth of zircon. When 6wt% carbon black is added, optimized zircon whiskers are achieved along the growth direction of [001], which diameter and aspect ratio are in the range of 30-90 nm and 6-15, respectively. Because of carbon black reacting with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and monoxide, the adding way and amount of carbon black efficiently regulate the oxygen partial pressure in the reaction system. Reducing oxygen partial pressure can form more SiF4 gas, which is the basis of one-dimensional direction growth of zircon. However, excessively low oxygen partial pressure is against the ZrSiO4 formation. Therefore, appropriate oxygen partial pressure can promote the growth of zircon whisker.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Sodium Zirconium Phosphate Powder with Peculiar Morphology
CHEN Jun-Jun, WANG Jing, HUI Xiang
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 839–844
 Abstract
Abstract(
915 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(675KB)(
1040
)
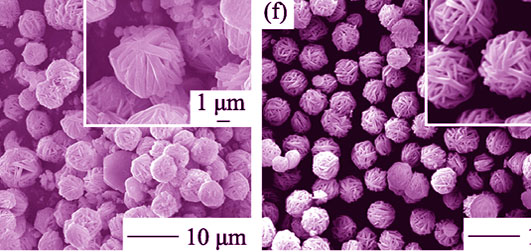
Single-phase Na2Zr(PO4)2 powders were directly synthesized by hydrothermal method using ZrOCl2•8H2O and sodium polyphosphate as raw materials, water as solvent. The effects of hydrothermal conditions and calcination temperature on the microstructure of sodium zirconium phosphate powders were investigated systemically by SEM, XRD and TG-DSC, etc. It is found that, when the molar ratio of raw materials is 1:2 (n(ZrOCl2•8H2O): n(Na5P3O10)) without adjusting pH value, slices being assembled coil-like Na2Zr(PO4)2 powders with good dispersion and uniform size can be obtained after 14 h hydrothermal treatment at 140℃. Appropriate extension of time and increase of temperature are beneficial to the powder formation. The higher the temperature, the shorter time the desired powders form. After calcination, Na2Zr(PO4)2 powders decompose and their morphology are destroyed. The growth mechanism of the sodium zirconium phosphate powders being prepared by hydrothermal method is explained by a basic growth unit model.
|
|
|
Preparation and Microwave Absorption Properties of CoFe2O4-graphene Nanocomposites
WU Xiao-Yu, LI Song-Mei,LIU Jian-Hua, YU Mei, WANG Bo
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 845–850
 Abstract
Abstract(
1166 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(591KB)(
1119
)
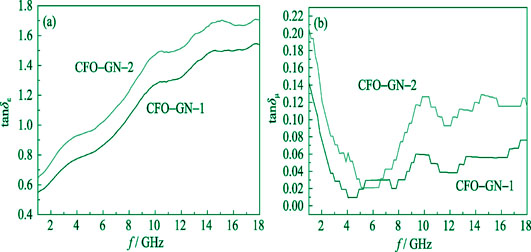
CoFe2O4-graphene (CFO-GN) nanocomposites were synthesized by in situ co-precipitation method, involving homogeneous co-precipitation of Co2+ and Fe2+ on the surface of graphite oxides and in situ thermal reduction of graphite oxides simultaneously. The morphology, structure, composition and microwave absorption properties of the nanocomposites were characterized and analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS), thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FT-IR) and vector network analyzer (VNA). The results indicate that the CoFe2O4 nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed on the interlayer and surface of the graphene sheets, CoFe2O4-graphene nanocomposites possess dielectric loss and magnetic loss, and exhibit excellent microwave absorption properties. The reflection losses of the nanocomposites with 88.62wt% and 74.53wt% CoFe2O4 are up to -11.0 dB and -12.4 dB, respectively, the bandwidths of reflection loss below -8 dB are 2.0 GHz and 4.3 GHz, respectively. The nanocomposites with higher content of graphene exhibit higher dielectric loss and reflection loss, wider absorption band, and thus exhibit better microwave absorption properties.
|
|
|
Red Emission Properties for (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3:Sm3+ Lead-free Piezoelectrics
SUN Hai-Qin, ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Qi-Wei, ZHANG Yin
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 851–854
 Abstract
Abstract(
662 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(372KB)(
923
)
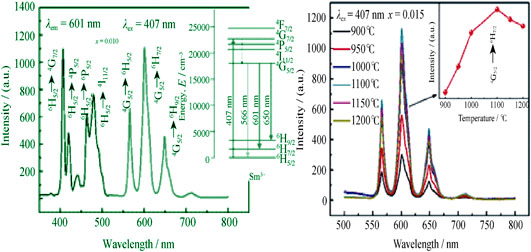
Sm3+ doped (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were fabricated by the conventional solid-state reaction method. Phase and crystallinity of the synthesized materials were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The influences of the Sm3+ dopant concentration, sintering temperature and charge compensation on photoluminescence properties were systematically investigated. The results showed that the (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 ceramics realized red-green emission by additives of Sm3+ ions, and the excitation bands were well adaptable to the emission band of commercial blue light-emitting diodes. The emission intensities were strongly dependent on the dopant concentration and sintering temperature with the optimal value at 0.015 mol and 1100℃ , respectively. The enhanced luminescence was observed for the Li+, Na+ and K+ doped compositions as compensators compared to the host matrix with only Sm3+ ions, indicating that host activator energy transfer of Sm3+ could be responsible for this enhancement. Among the compensators of Li+, Na+ and K+ ions, the K+ compensated (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-Sm3+ samples showed the remarkable improvement in photoluminescence properties. Hence, the Sm3+ doped (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 ceramics as a multifunctional material may have significantly technological promise for optical-electro integration devices.
|
|
|
Investigations on Optical Scatter Particles during CdSiP2 Crystals Growth
ZHANG Guo-Dong, LI Chun-Long, WANG Shan-Peng, ZHANG Xiang, ZHANG Xi-Xia, TAO Xu-Tang
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 855–858
 Abstract
Abstract(
779 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(393KB)(
1102
)
Polycrystalline charges of CdSiP2 (CSP) were synthesized by direct reaction method using P, Si, and Cd elements as the initial materials. Single crystals with the dimension of 8 mm in diameter and 40 mm in length were successfully grown by vertical Bridgman method. The dimension and the composition of the optical scatter particles in the CSP crystals were identified by SEM measurement. The results show that most of optical scattering particles are round-shaped with dimension of 2-8 μm. The EDS measurement result shows that the atomic percent of Si in the optical scattering particles is over 88%. The synthesis mechanism of CSP by single temperature zone method was studied by powder XRD. The results show that there is some unreacted silicon left when synthsized process is carried out below 1150℃. By optimizing the synthesis parameters and the Si inclusions were successfully restrained and the high optical quality CSP single crystal was obtained.
|
|
|
Near-infrared Luminescence Properties of Bi2O3-SiO2 Glasses and Glass Ceramics
LIU Jun-Fang, SU Liang-Bi, XU Jun
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 859–863
 Abstract
Abstract(
716 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(349KB)(
1006
)
Bi2O3-SiO2 glasses and glass ceramics were prepared by melting method. Infrared and VIS luminescence spectra, excitation spectra and fluorescence decay curves were measured. Near infrared (NIR) luminescence of Bi2O3-SiO2 glasses and glass ceramics was observed under 808 nm Laser Diode pumping. When the content of Bi2O3 is low (30mol%, 40mol%, 50mol%), NIR luminescence peak at 1336 nm (or 1300 nm) with full width at half maximum (FWHM) about 200 nm is observed. With the increase of Bi2O3 content, another peak at about 1070 nm with narrow FWHM appears and becomes the main peak, while the FWHM of the NIR emission centered at 1336 nm (or 1300 nm) decreases to only tens of nanometer. Two emission bands have different excitation bands and lifetime. We propose NIR emissions located at 1070 nm and 1336 nm (or 1300 nm) originate from different bismuth centers. The infrared emission peaked at about 1336 nm (or 1300 nm) derives from low valence Bi ions.
|
|
|
High Temperature Hydrogenation Behavior of Bulk Titanium Aluminum Carbide
CHEN Chen, ZHANG Hai-Bin, PENG Shu-Min, ZHAO Lin-Jie, ZHU Jian-Guo
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 864–868
 Abstract
Abstract(
911 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(708KB)(
948
)
Ti3AlC2 is a new type of nano-layered machinable ceramic with numerous salient properties. Therefore, recently it is considered to be a promising candidate for new generation reactors as the key structural material. In this work, the reaction product and material morphology between nano-layered Ti3AlC2 and hydrogen were investigated by XRD, SEM, EDS, XPS and Raman. The resulted gaseous products were calculated by Factsage sofeware. Under the condition of 700-1000℃, hydrogen atmosphere (low oxygen pressure), solid products are Al2O3, TiO2 and C and gaseous product is CH4. Hydrides are not detected in the current experiments. The SEM results indicate that the reacted samples keep intact and cracks are not formed on the surface, indicating the high temperature thermal stability of Ti3AlC2 in hydrogen. These results can be attributed to the formation of oxides on the surface of specimens.
|
|
|
Alumina Thin Film Coated Ammonium Dinitramide Fabricated by
Atomic Layer Deposition
GONG Ting, QIN Li-Jun, YAN Rui, HU Lan, JI Yue-Ping, FENG Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 869–874
 Abstract
Abstract(
975 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(447KB)(
1301
)
To deposit alumina thin films on ammonium dinitramide (ADN) by atomic layer deposition (ALD), trimethylaluminum and water were used as the precursors. The surface morphology and chemical compositions of the ALD alumina coated ADN were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS). The hygroscopic property of the ALD alumina coated ADN was studied by a vapor adsorption analyzer (VSA). The possible mechanism of ALD alumina film growth on the surface of ADN was discussed. The characterization results indicate that the ALD alumina film completely covers the surface of ADN. The thickness of the alumina film can reach hundreds of nanometers. After 48 h of air exposure, the shapes and topologies of the alumina coated ADN particles are maintained. The hygroscopicity of the ADN samples coated by 200 and 400 cycles of ALD alumina are 40.99% and 40.75%, respectively. Although the ALD alumina coating completely covers the surface of ADN and successfully maintains the shapes and topologies of ADN particles in a wet environment, the hygroscopicity of the ALD alumina coated ADN is not improved.
|
|
|
Surface Behaviors of U2N3+xOy Films in CO Atmosphere
LUO Li-Zhu, LU Lei, LIU Ke-Zhao, ZHAO Dong-Hai
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 875–879
 Abstract
Abstract(
580 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(466KB)(
1063
)
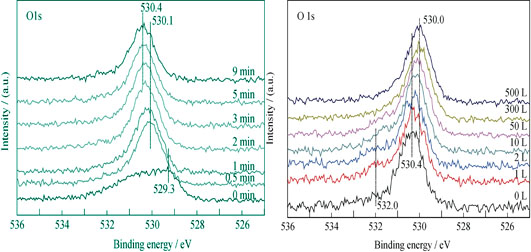
U2N3+xOy films were deposited on Si substrate by magnetic sputtering deposition method. The behaviors of U2N3+xOy after exposure to CO atmosphere was analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) to explore its CO corrosion mechanism. Under ultra-high vacuum (UHV) condition, it is found that CO atmosphere is oxidative on the surface of U2N3+xOy film. The dissociated carbon in forms of amorphous is segregated on the outmost surface rather than diffuses inside, and the diffusion of the dissociated oxygen resulted in oxidation of U2N3+xOy, leading to the formation of uranium oxy-nitrides in higher valence state on the surface and an N-rich layer as an intermediacy in the subsurface. The diffusion of oxygen in the film is suppressed on the very surface by the product of uranium oxides or uranium oxy-nitrides in higher valence state due to the potential barrier. The distance of the N-rich layer to the outmost surface dominates the intensity variation of satellites at 386.7 eV and 397.5 eV, which is enlarged with the oxidation process. All abore chemical changes play a very important role for understanding the corrosion mechanism of U2N3+xOy films.
|
|
|
Oxygen Gas-assisted Synthesis of Boron Nitride Nanotubes
LI Juan, WU Hao, CHEN Yong-Jun, XU Sheng-Ming
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 880–884
 Abstract
Abstract(
581 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(664KB)(
1059
)
Wool-like products were fabricated on the stainless-steel substrates by directly heating amorphous B powder at high temperature (1300℃) at 50 mL/min ammonia gas with different flow of oxygen gas (10, 15, 20, 40 mL/min). It was found that B powder could be oxidized by trace oxygen gas to form the intermediate B2O2 vapor, which can act as highly active boron source for the growth of BN nanotubes. When an appropriate amount of oxygen was introduced, the obtained nanotubes had an average diameter of about 80 nm and the lengths of several hundred micrometer. Both the diameter and the yield of BN nanotubes could be influenced dramatically by the flow rate of oxygen. With the increase of oxygen flow, the diameter of nanotubes was gradually increased, and the yield of nanotubes was improved obviously at first and then turned down. The formation mechanism of these nanotubes is governed by a vapor-liquid- solid (VLS) growth model.
|
|
|
Effect of Sintering Additive Composition on the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Si3N4/SiC Ceramics
HU Hai-Long, ZENG Yu-Ping, ZUO Kai-Hui, XIA Yong-Feng, YAO Dong-Xu
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 885–890
 Abstract
Abstract(
1480 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(423KB)(
2831
)
Two compositions of the Y2O3-Al2O3 (YA) and Y2O3-MgO (YM) systems were chosen to investigate the effect of sintering additive composition on the mechanical and tribological properties of gas pressure sintered Si3N4/SiC ceramics. The relative density, flexural strength, fracture toughness, hardness, coefficient of friction and wear rate were verified to depend substantially on the sintering additive composition. Compared with YM, the Si3N4/SiC ceramics with YA exhibit superior sinterability and show preferable mechanical and tribological properties, especially for the Si3N4/SiC ceramics with 20wt% SiC addition. These properties can be primarily attributed to the higher relative density and the grain size with smaller aspect ratio.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Flower-like Hierarchical TiO2 Microspheres from Titanium Sulfate and Hexafluorosilicic Acid
SHI Guo-Dong, SONG Jun, YANG Liu-Liu, ZHANG Li-Xiong
2014 Vol. 29 (8): 891–896
 Abstract
Abstract(
1942 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(774KB)(
2718
)
Flower-like hierarchical TiO2 microspheres assembled by nanosheets with exposed {001} facets were prepared through a cost-effective hydrothermal synthesis method, using cheap Ti(SO4)2 as the feedstock and hexafluorosilicic acid as the capping agent. These hierarchical microspheres were assembled by numerous and cross-linked nanosheets. The fine structure of hierarchical microspheres could be easily controlled by adjusting the concentration of hexafluorosilicic ions. The growth process of the microspheres was examined through XRD and SEM characterizations, and a possible formation mechanism was proposed. Compared with other solvothermal synthesis methods, this cost-effective hydrothermal synthesis route is attractive and can be potentially applied in the production of flower-like TiO2 hierarchical microspheres in large scale. The as-prepared flower-like TiO2 hierarchical microspheres exhibit good photocatalytic ability to degrade methyl orange dye.
|
|