|
|
Research Progress on Oxide/Oxide Ceramic Matrix Composites
WANG Yi, LIU Hai-Tao, CHENG Hai-Feng, WANG Jun
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 673–680
 Abstract
Abstract(
1449 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(584KB)(
1610
)
Oxide/Oxide ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) possess great potential in combustion environments of gas turbines, such as combustion chamber, scramjet nozzle and so on for their favorable performances (high strength and modulus, excellent oxidation resistive properties, etc.). In this paper, reinforced fibers and ceramic matrices for Oxide/Oxide CMCs are summarized, and it is pointed out that both single crystal oxide fibers and mullite ceramic matrix have great application potential. The improvement approaches of their mechanical properties, interphases and porous matrix, are reviewed based on the adjustment of the fiber/matrix bonding. The key problems, notch sensitivity, creep tolerance and ablation resistence, which limit their applications, are analyzed, and their future development is prospected.
|
|
|
Research Development on Novel Anode of Solid Oxide Direct Carbon Fuel Cells
WANG Hong-Jian, CAO Tian-Yu, SHI Yi-Xiang, CAI Ning-Sheng
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 681–686
 Abstract
Abstract(
710 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(268KB)(
1097
)
Solid oxide direct carbon fuel cells (SO-DCFCs) can convert the chemical energy of the carbon fuel directly into electricity with high efficiency, wide fuel applicability and convenience for CO2 capture. SO-DCFCs show promising development in the situation that the energy and environmental issues become increasingly prominent. One of the key issues in SO-DCFC development is the anode which can accelerate carbon conversion, mass transportation within the electrode and impurities tolerance. This paper systematically summarized and analyzed the anode structural features, operating process, material characteristics of three types of SO-DCFC anode, including porous solid anode, molten carbonate anode and liquid metal anode. The liquid metal anode was particularly focused on due to its distinctive advantages in current collection, performance stability and the CO ratio in exhaust gas. Finally, the development trends of the anode for SO-DCFC in the future are discussed.
|
|
|
Preparation and Reaction Kinetics of Carbon Nanotubes/Aluminum Composite Powders Using Polymer Pyrolysis Method
XU Run, LI Xin-Da, LI Zhi-Qiang, ZHAO Ren-Yu, FAN Gen-Lian, XIONG Ding-Bang, TANG Jie, XU Yong, ZHANG Di
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 687–694
 Abstract
Abstract(
863 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(593KB)(
1005
)
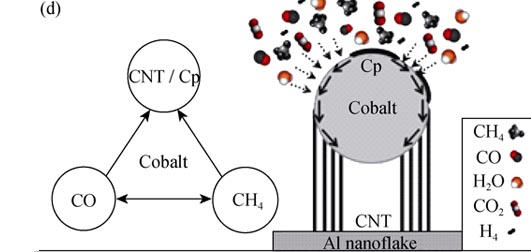
The method of polymer pyrolysis chemical vapor deposition (PP-CVD) was used to in situ grow carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on the micro and nano sized flake like aluminum powder substrates. The vapor species were in situ produced by pyrolysis of polyethylene glycol (PEG) including the carbon sources, which was the main difference between the PP-CVD and conventional CVD methods, while the catalyst nanoparticles were produced by the reaction between citric acid (CA) and cobalt nitrate (Co(NO3)2) on aluminum powder surfaces. The reaction mechanism of PP-CVD was studied with the analysis of experiments and reaction kinetics modeling, revealing the influence of the vapor species produced by pyrolysis of PEG and CA and surface vapor-solid reactions on catalyst nanoparticles on CNT growth rates. The CNTs growth rates increases with the increase of reaction temperature and initial partial pressure of CO, which is influenced by the content of PEG and CA, and decreases with the increase of catalyst density and initial partial pressure of H2. The variation trends of the simulated CNTs average length with reaction temperature and time are consistent with the experimental results. Thus, this work provides new theoretical basis to the further optimization of fabricating CNTs/aluminum composite powders.
|
|
|
Effect of SiC Content on B4C-SiC Composites Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying-hot Pressing
ZHANG Zhi-Xiao, DU Xian-Wu, XING Wei-Hong, WANG Wei-Min, ZHANG Jin-Yong, FU Zheng-Yi
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 695–700
 Abstract
Abstract(
746 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(567KB)(
1068
)
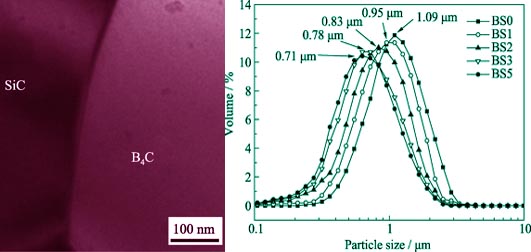
Dense B4C-SiC composite ceramics were fabricated through mechanical alloying using coarser B4C and SiC powders as starting powders, and subsequent hot pressing sintering at 1950℃ without any sintering aid. The influences of the content of SiC on mechanical properties of the composite ceramics were studied through determining relative density of composite ceramics, Vickers hardness, flexure strength and fracture toughness. Combined with the microstructure and component analysis technologies of XRD, SEM and TEM, the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties of the composite ceramics was investigated. The results indicate that the relative density and fracture toughness of the composite ceramics are improved with increase of SiC content, and reach the maximum value at 96.1% and 4.6 MPa•m1/2, respectively, with SiC content of 50wt%. However, with the increase of SiC, the Vickers hardness and flexure strength are enhanced firstly and then decreased. The maximum values are 25.5 GPa and 480 MPa, respectively, with SiC content of 20wt%. Homogeneous dispersion of SiC phase in B4C matrix is one of the reasons why the composite ceramics possess higher flexure strength. Fracture toughness of the composite ceramics is significantly higher than that of monomeric B4C. The main reasons are attributed to powerful interfacial bonding between B4C and SiC as well as the higher fracture toughness of SiC.
|
|
|
Effects of Nitrogen Pressure on Microstructure and Mechanical Performance of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics
ZHANG Jun-Xi, XU Zhao-Yun, WANG Bo, QIN Yi, YANG Jian-Feng, ZHAO Zhong-Jian, HU Wei, SHI Zhi-Wei
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 701–705
 Abstract
Abstract(
689 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(379KB)(
1120
)
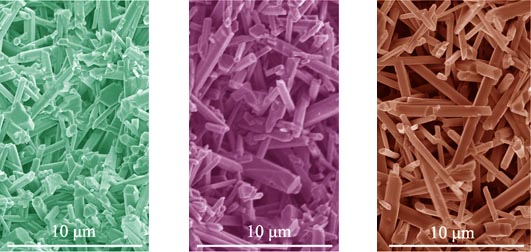
Porous silicon nitride ceramic was fabricated by using α-Si3N4 as raw material and Y2O3 as a sintering additive, with nitrogen pressure of 0.12 MPa, 0.32 MPa and 0.52 MPa. Effects of the nitrogen pressure on grain morphology and mechanical properties of the resultant porous Si3N4 ceramics were characterized by SEM, XRD and flexural strength. With the increasing of nitrogen pressure, sintering shrinkage decreased, with a corresponding increased porosity. Due to the increase of nitrogen pressure, the viscosity of liquid phase increased due to increased N solubility, leading to the low densification in the sintering. Fibrous β-Si3N4 grains were developed in the porous microstructure and the grain morphology and aspect ratio were greatly affected by the nitrogen pressures. The high viscosity of the liquid phase in nitrogen at high pressure led to restraining of the β-Si3N4 nucleation, and preferential growth of β-Si3N4. Due to the formation of elongated β-Si3N4, flexural strength of the porous Si3N4 ceramic was improved by the increase of nitrogen pressure, while decreased with the increase of porosity. The porous Si3N4 ceramics with porosity of 58% and flexural strength of 140 MPa were obtained at the nitrogen pressure of 0.52 MPa.
|
|
|
Controllable Synthesis of One-dimensional β-SiAlON Materials
PENG Ben, QIU Gui-Bo, YUE Chang-Sheng, ZHANG Mei, GUO Ming
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 706–710
 Abstract
Abstract(
521 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(445KB)(
878
)
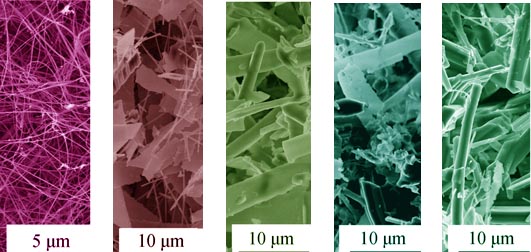
β-SiAlON whiskers, belts and rods were prepared at 1650-1850 K in N2 atmosphere, respectively, by using Si, Al and Al2O3 powders as raw materials which were pressed into cuboid and burying in Si3N4 grains. The effects of growth conditions on the controllable synthesis of one-dimensional β-SiAlON preparation were investigated in detail, and their growth mechanisms were explored according to the thermodynamic calculations. The results showed that one-dimensional β-SiAlON could be controllably synthesized only by adjusting sintering temperatures. Specifically, β-SiAlON whiskers with 200-400 nm in diameter and 100-1000 in aspect ratio could be obtained at 1650 K. Increasing growth temperature from 1700 K to 1800 K, β-SiAlON belts with thickness of about 200 nm, width of 1-4 μm and length-width ratio in the range of 10-20, were produced. Further increasing temperature to 1850 K, β-Sialon rods were synthesized accordingly. Vapor-solid (VS) growth mechanism was put forward to elucidate the growth of one-dimensional β-SiAlON based on their thermodynamic calculations and microstructures.
|
|
|
Preparation of Ultra-fine NdB6 Powders by Combustion Synthesis and Its Reaction Mechanism
DOU Zhi-He, ZHANG Ting-An, WEN Ming, SHI Guan-Yong, HE Ji-Cheng
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 711–716
 Abstract
Abstract(
601 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(428KB)(
1424
)
Ultrafine powders NdB6 were prepared by combustion synthesis with B2O3, Nd2O3 and Mg as raw materials. The effects of reaction atmosphere, sample pressure and raw materials ratio on the reaction product morphology and phases were studied. Characterizations by XRD and SEM show that the products consist of NdB6, MgO and a little amount of Mg3B2O6 and Nd2B2O6. After reaction with sulphuric acid at low concentration to eliminate the latter three components, the pure NdB6 is obtained (purity 99.1%). As the preparation pressure increases, the NdB6 particle sizes become small. When the sample pressure is 20 MPa, the average particle size is less than 500 nm. The preparation reaction process is as follows: firstly, Mg reduces Nd2O3 to generate Nd and MgO; and then, the reaction between Mg and B2O3 are ignited to generate B and MgO; at the same time, the generated Nd and B are reacted to produce NdB6. The apparent activation energy of the reaction is 691.59 kJ/mol and the reaction order is 3.2.
|
|
|
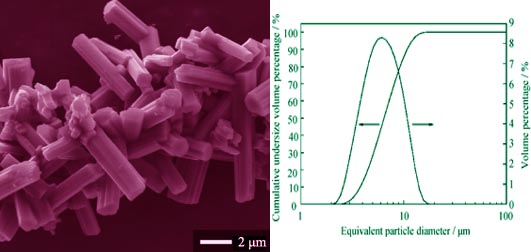
Effects of Gel Aging on Synthesis of ZrB2 Powders
YANG Bi-Yun, LI Jun-Ping, WANG Ting-Yu, LI Rui-Xing, FENG Zhi-Hai, CAI Hong-Nian
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 717–721
 Abstract
Abstract(
672 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(338KB)(
962
)
ZrB2 particles were synthesized by a Sol-Gel method using zirconium n-propoxide, boric acid, acetic acid and D-fructose. D-Fructose acts as both a modifier and a carbon source for carbothermal reduction reaction. For comparison, both nascent state gel and aged gel were used to clarify the aging-time-dependent mechanism for ZrB2 synthesis. As a result, a single phase ZrB2 powder with a uniform size and shape distribution can be obtained from the aged gel with a boron and carbon to zirconium molar ratio of 3.5-4 and 7, respectively, after reduced at 1550 ℃ for 2 h. Besides, the synthesized ZrB2 particles exhibit prism-like morphology with average particle size of ca. 4-7 μm in length, 1 μm in diameter of excircle of the cross-section and 4-7 in aspect ratio, when initial raw materials ratio n(B)/n(Zr) is 3.5-4 and n(C)/n(Zr) is 7. The median diameter D50 is 6.46 μm and specific surface area is about 2.53 m2/g. Furthermore, a complete carbothermal reduction of ZrO2 can be achieved using the aged gel.
|
|
|
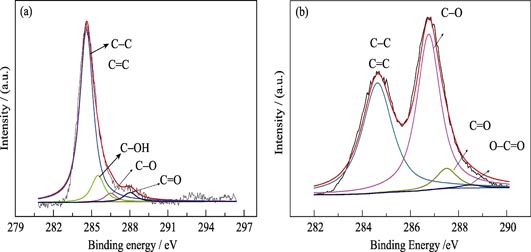
Preparation and Electrocatalytic Properties of Pd/PMo12-GN Composite towards Formic Acid Oxidation
HUANG Xiao-Ling, LIN Zhou, LIAN Xing-Yi, ZHANG Xiao-Feng, LIN Shen
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 722–728
 Abstract
Abstract(
709 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
1102
)
The Pd/PMo12-GN composite film was prepared by electrochemical reduction, in which GN prepared from GO reduction under UV irradiation and simultaneously functional embellished by PMo12. The as-prepared composite was characterized by X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscope, scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope. It was shown that Pd/PMo12-GN composite was successfully prepared and Pd particles were uniformly-dispersed with a small particle size on the PMo12-GN substrate. Cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometric curves, CO-stripping curves and EIS were used to discuss the electrocatalytic activities of the Pd/PMo12-GN composite film. The results indicated that the as-prepared composite film presented better electrocatalytic activity, stability, CO tolerance ability, and electric conductivity towards formic acid oxidation as compared with commercial Pd/C catalyst. The enhancement in electrochemical performance of the Pd/PMo12-GN composite film can be attributed to the synergistic effect of highly dispersed Pd nanoparticles on the PMo12-GN substrate and higher oxidation power of PMo12 which promotes the removal of the poisonous species on the Pd surface.
|
|
|
Influence of Deposition and in situ Annealing Time on Composition and Optical Band Gap of h-BN Films Deposited by PECVD
QIN Yi, ZHAO Ting, WANG Bo, YANG Jian-Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 729–734
 Abstract
Abstract(
536 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(510KB)(
870
)
Series of h-BN films were grown by RF plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) technique using high purity nitrogen and diborane as the precursor gases. The optimized experimental conditions for preparing h-BN films were explored. Based on these explorations, influences of deposition time and in situ annealing time on the composition and optical band gap of the films were investigated. All specimens were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscope, utraviolet-visible spectrophotometer and field emission scanning electron microscope. The results show that the deposition time has a significant impact on the quality and optical band gap of the samples, and the optical band gap exhibits an exponential relation with the varied thickness of the films. Moreover, in situ annealing at 700℃ can affect the crystal quality, but almost not the phase and optical band gap of the h-BN films.
|
|
|
Nonlinear Optical Properties of Silver Composited Ge-In-S-CsI Chalcogenide Glasses
XU Yin-Sheng, CHENG Jun-Wen, QI Jia-Ni, LU Shan-Shan, LU Ke-Lun, XU Jian-Wei, SHAO Qi-Fen, DAI Shi-Xun
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 735–740
 Abstract
Abstract(
629 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(418KB)(
989
)
In this study, the Ag doped 70GeS2-20In2S3-10CsI chalcogenide glasses were synthesized by vacuumed melting-quenching technique. The third nonlinear optical properties were studied using Z-Scan technique at 800 nm. After being introduced Ag into the glass, both the linear and nonlinear refraction index γ increased from 2.204 to 2.2087 and from 23.3×10-18 to 30.5×10-18 m2/W, respectively. Besides, the nonlinear response time increased from 70 fs to 79 fs. The further heat treatment also enhanced the nonlinear refraction index up to 44.3×10-18 m2/W, 2 folds higher than that of As2Se3. Meanwhile, the nonlinear absorption coefficient β decreased because the bandgap decreased with the thermal heat treatment. However, the highest figure of merit (FOM) is 3.3, which is enough for the nonlinear optics. Large nonlinear refraction index, high FOM, and fast response time ensured that the Ag-composited chalcogenide glass and glass ceramics can find applications in nonlinear optics.
|
|
|
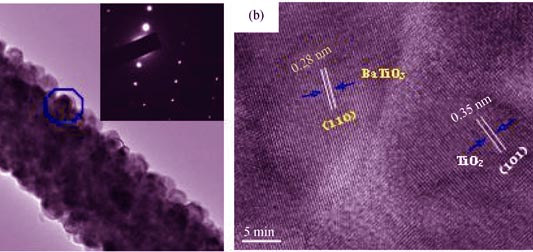
Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of BaTiO3/TiO2 Heterostructured Nanofibers
LI Yue-Jun, CAO Tie-Ping, MEI Ze-Min
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 741–746
 Abstract
Abstract(
746 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(512KB)(
1267
)
Heterostructured BaTiO3/TiO2 composite nanofibers were fabricated by in situ hydrothermal method using TiO2 nanofibers as both template and reactant. The morphology and structure of BaTiO3/TiO2 composite nanofibers were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM). Photocatalytic activity was tested via rhodamine B and phenol degradation as the model reaction. The results showed that the as-fabricated sample was composed of BaTiO3 nanoparticles assembling uniformly on the surface of TiO2 nanofibers to form BaTiO3/TiO2 heterostructures. Compared with the pure TiO2 nanofibers, BaTiO3/TiO2 composite nanofibers exhibited enhanced photocatalytic activity in the decomposition of rhodamine B under UV illumination. The degradation of both RB and phenol followed first-order reaction kinetics, and the composite showed higher photoactivity than did the pure anatase TiO2.The composite nanofibers also showed good catalytic stability and the decolorizing efficiency of RB solution remained as high as 96% after 5 times recycle. Moreover, the catalyst was easily separated and removed from the system after reaction and reuse.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Co-S alloys
HU Li-Na, ZHAO Xiang-Yu, LI Jia-Jia, YANG-Meng, MA Li-Qun, ZHANG Li-Yan
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 747–752
 Abstract
Abstract(
620 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(525KB)(
973
)
The Co-S alloys were prepared by a hydrothermal method and the process parameters were optimized. The surface morphology and phase structure of Co-S alloys were characterized by SEM and XRD. The electrochemical properties of Co-S alloys were investigated by galvanostatic charge and discharge tests, cyclic voltammetry and AC impedance. The results indicated that the as-prepared Co-S alloy, which was synthesized using a 70% packing volume of the reaction solution at 160℃ for 12 h, showed good crystallinity. This alloy consisted of metallic Co and Co9S8 phases with a cross-linked lamellar morphology of about 50 nm in thickness. It possessed a maximum discharge capacity of 536 mAh/g at charge and discharge current density of 150 mA/g and a good cycling stability with capacity retention rate of 77.4% after 50 cycles. The redox reactions between Co and Co(OH)2 were the main reaction during charge and discharge. Partial dissolution of Co reduced the active material and led to capacity decay.
|
|
|
Influence of Growth Temperature and Oxygen Pressure on Laser-induced Voltage Effect of La0.67Sr0.33MnO3:Ag0.08 Thin Films
YAN Yi-Zhi, YIN Xue-Peng, LIU Xiang, CHEN Qing-Ming
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 753–757
 Abstract
Abstract(
560 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
1154
)
La0.67Sr0.33MnO3:Ag0.08 (LSMO:Ag0.08) polycrystalline ceramics were prepared by chemical co-precipitation method, and then La0.67Sr0.33MnO3:Ag0.08 thin films were prepared on vicinal cut LaAlO3 (LAO) substrates by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technique. Effects of growth temperature and oxygen pressure on structure, electrical transport properties and laser-induced voltage (LIV) effect were investigated. The results show that the maximum LIV peak (Up), the figure of merit (Fm) and anisotropy Seebeck coefficient (ΔS) are obtained for LSMO:Ag0.08 thin films when growth temperature and oxygen pressure are 790 ℃ and 45 Pa, respectively. The LIV enhancement of LSMO:Ag0.08 thin films is due to the anisotropy of the Seebeck coefficient, which is produced by long range cooperative Jahn-Teller distortions under optimal growth temperature and oxygen pressure conditions.
|
|
|
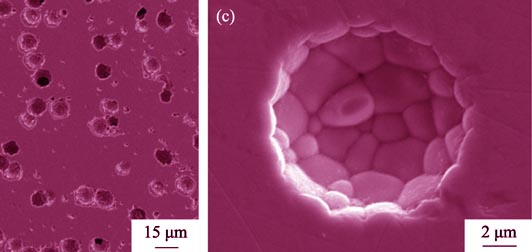
Investigation on the Mechanical and Ferroelectric Properties of the Porous PZT 95/5 Ceramics
ZENG Tao, BAI Yang, SHEN Xi-Xun, WANG Bao-Feng, DONG Xian-Lin, ZHOU Zhi-Yong
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 758–762
 Abstract
Abstract(
611 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(387KB)(
1016
)
Porous lead zirconate titanate (PZT95/5) ceramics were prepared by adding pore formers. The effects of pore structures including porosity, pore size and pore shape on the mechanical and ferroelectric properties of the porous PZT95/5 ceramics and their mechanisms were investigated, and the relationships between the microstructures and the mechanical and ferroelectric properties were revealed. The results showed that increase in porosity improved the acoustic impedance matching between ceramics and encapsulating materials by reducing the sound impedance values. With increase in porosity, the yield stress and remnant polarization (Pr) of the porous PZT95/5 ceramics decreased, while the coercive electric field increased. The porous PZT95/5 ceramics with spherical pores exhibited higher yield stress and remnant polarization (Pr) than that with irregular pores. The porous PZT95/5 ceramics with larger pore size exhibited lower yield stress and remnant polarization. However, compared with pore shape, pore size had minor effects on the yield stress and remnant polarization properties of the porous PZT95/5 ceramics. The effect of pore structure on the yield stress could be explained by stress concentration theory. The microscopic internal stress combined with space-charge theory was used to explain the variation of the remnant polarization with the pore structure.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of MnFe2O4 with Different Morphologies and Their Application in Water Treatment
DUAN Lian-Feng, ZHANG Yu, WANG Li-Min, JIN Song-Zhe, WU Hua
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 763–768
 Abstract
Abstract(
823 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(462KB)(
1156
)
Manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) with rough surface was synthesized by a simple solvothermal method. The average diameter of particles was about 150 nm, and the tubes of rough surface about 10 nm. Here, magnetic MnFe2O4 particles with different morphologies (cube, polyhedron and octahedron) were successfully prepared by controlling CTAB concentration. Both of the samples with different morphologies exhibit ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature. The saturation magnetization (Ms) and coercivity (Hc) of MnFe2O4 with non-smooth surface are 58.7 Am2/kg and 6.23 kA/m, respectively. The particles with rough surface also show good performance in removal of pollutants like Congo red (92.4 mg/g), CrVI (54.4 mg/g), and PbII (84.4 mg/g) from waste water by adsorption experiments. Because the particles are recollected by magnetic separation, the waste water purification rate can be improved, which expands the applications of magnetic materials.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Copper-substituted Hydroxyapatite Micrspheres
XIAO Dong-Qin, WANG Dong-Wei, REN Jun-Chen, DUAN Ke, YAO Ning, LU Xiong, ZHENG Xiao-Tong, WENG Jie
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 769–775
 Abstract
Abstract(
1319 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(590KB)(
6385
)
As the second essential trace element in human body, copper plays vital roles in metabolism and antimicrobial. Therefore, synthesis of copper-substituted hydroxyapatite (Cu-HA) is expected to create bioceramics with improved biological and antimicrobial properties. In this study, Cu-HA was prepared by hydrothermal reactions using Ca(NO3)2∙4H2O, Cu(NO3)2∙3H2O and Na2HPO4∙12H2O. Products were characterized by scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscope and atomic absorption spectrometry. Results show that copper is incorporated into the HA crystals. Correspondingly, the products retain HA structure but their morphologies transform from ribbons to flower-like microspheres. Moreover, when Cu/(Cu+Ca) (molar ratio) of the reaction solution is greater than 0.05, the thermal stability of the HA product is decreased.
|
|
|
Microwave-assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Calcium Phosphate Microspheres and Polyhedra
CHEN Feng, SUN Tuan-Wei, QI Chao, WU Jin, CUI Da-Xiang, ZHU Ying-Jie
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 776–780
 Abstract
Abstract(
1573 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(754KB)(
2295
)
Synthetic calcium phosphate (CaP) has been investigated as promising biomaterial due to its excellent biocompatibility. CaP nanosheet-assembled microspheres were prepared using Ca(CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in aqueous solution by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min. Meanwhile, CaP polyhedral were prepared using Ca(CH3COO)2, NaH2PO4•2H2O and PLA-mPEG in mixed solvent of water and ethylene glycol (EG) by microwave-assisted solvothermal method at 120℃ for 30 min. The products were characterized with X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and thermogravimetric analysis (TG). EG showed a significant effect on the chemical composition and morphology of the product. The hemoglobin protein adsorption properties of the as-prepared products were investigated. The Hb adsorption amount increased with increasing Hb initial concentration, and were decreased with increasing volume of EG.
|
|
|
Compact Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 Thin Films Fabricated by a Simple Sol-Gel Technique
ZHANG Ke-Zhi, TAO Jia-Hua, LIU Jun-Feng, HE Jun, DONG Yu-Chen, SUN Lin, YANG Ping-Xiong, CHU Jun-Hao
2014 Vol. 29 (7): 781–784
 Abstract
Abstract(
1633 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
2415
)
Cu2ZnSn(S1-xSex)4 (CZTSSe) thin films with a compact and crack-free morphology and large-grain are obtained via a green Sol-Gel process and post-selenization. The fabrication of CZTSSe films is simplified by predigesting preparation process of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) precusor solution and avoiding using sulfurization. Low-toxic ethylene glycol is selected as solvent, and Cu(CH3COO)2, Zn(CH3COO)2, SnCl2•2H2O and thiourea are used as raw materials. Energy dispersive X-ray analyzer (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectra results indicate that all of CZTSSe thin films with the kesterite structure are of Cu-poor and Zn-rich states. Optical band gap (Eopt) of the CZTSSe thin films decreases from 1.51 to 1.14 eV with increasing Se content.
|
|