|
|
Fabrications of TiO2Photoanodes for Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
CHEN Wei, LIU Yang-Qiao, LUO Jian-Qiang, JIN Xi-Hai, SUN Jing, GAO Lian
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 561–570
 Abstract
Abstract(
1133 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(611KB)(
1269
)
Flexible dye-sensitized solar cell (FDSSC) is a type of dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) based on flexible substrates, such as plastics and metals, etc. The advantages of FDSSC over rigid DSSC involve bendability, lower cost, ease of large-scale production and wider application, which make it attract much attention. The fabrication methods for FDSSC photoanodes are generally categorized to low-temperature fabrications and high-temperature fabrications, including chemical additive method, mechanical compression, electrophoretic deposition, lift-off method, and some new technologies. This paper reviewed the above fabrication methods and the performance of the cells was discussed by taking into account the mechanisms for electron transfer and recombination. Finally, the future development of FDSSC was prospected.
|
|
|
Research Progress of Porous Ceramics Produced by Freeze Casting Technique
LIU Gang, YAN Yan
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 571–583
 Abstract
Abstract(
1338 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(1347KB)(
1349
)
Freeze casting, a novel technique for ceramics achieving unique porous microstructures with excellent mechanical properties, progressed very quickly in the past decade and has become a very hot research field. The present review summarizes the freeze casting history and introduces the basic principles, characteristics, processing affecting factors, and potential applications. Furthermore, several perspectives are given in the end.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Mesoporous Carbon Using Halloyiste As Template
ZHOU Shu-Hui, CHUAN Xiu-Yun
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 584–588
 Abstract
Abstract(
617 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(429KB)(
1136
)
Mesoporous carbons with“core-shell”structure were synthesized using halloysite as template and sucrose as carbon precursor by a template method. Field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), nitrogen adsorption, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectra and Thermogravimetry (TG) were employed to cheracterize the as-synthesized materials. Results indicate that the morphology and structure of the templated carbons are similar to that of halloysite. The carbons exhibit higher specific surface area (945 m2/g and 1147 m2/g), higher pore volumes and mesopore volume fraction than that of halloysite. The carbons present high purity and amorphous structure. Raising the carbonization temperature, the Raman characteristic parameter (R) of the carbons decreases and their decomposition temperature increases from 563℃ to 623℃. At the same time, the formation mechanism of the carbons and their pores is also discussed.
|
|
|
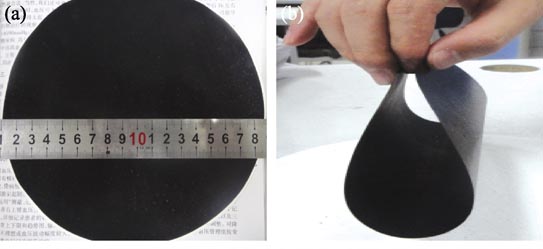
Fire Retardancy of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites Coated with POSS/Clay/MWCNTs Hybrid Buckypaper
LU Shao-Wei, ZENG Xian-Jun, ZHANG Chun-Xu, WANG Ji-Jie, NIE Peng
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 589–593
 Abstract
Abstract(
673 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(451KB)(
914
)
A hybrid buckypaper consisting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), clay and polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane(POSS) was fabricated through vacuum filtration method. The as-prepared buckypaper (or hybrid buckypaper) can be incorporated onto the surface of fiber reinforced polymer composite as surface fire shields. The morphology and pore size distribution of the MWCNTs buckypaper were characterized with field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and Barret-Joyner-Halenda(BJH) method. The fire retardant performance of composite laminates coated with (or without) the buckypaper was thoroughly evaluated by cone calorimeter testing at a radiant heat flux of 50 kW/m2. Compared with the contral composite, the peak heat release rate (PHRR) of composite surface coated MWCNTs buckypaper or the hybrid buckypaper reduced more than 20.2% and 35%, respectively. The CO production rate and the smoke production rate reduced obviously. The formation of compact char material can be observed on the surface of the composite residues and analyzed by FESEM, the fire retardant property of composite can be improved by surface coated hybrid buckypaper.
|
|
|
Mechanical Properties of Reaction-bonded Si3N4/SiC Composite Ceramics
HU Hai-Long, YAO Dong-Xu, XIA Yong-Feng, ZUO Kai-Hui, ZENG Yu-Ping
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 594–598
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
1124
)
With Y2O3:Al2O3 (A 2:3; B 3:1 total amount 15wt%) as sintering additives and SiC as the second phase, high flexural strength Si3N4/SiC composite ceramics were prepared via nitridation of Si powder. The phase composition, relative density, microstructure as well as mechanical properties were investigated. The experimental results showed that the α→β-Si3N4 phase transformation could be completed at 1700℃ for 2 h with sintering additives A or B. With the sintering additive A and 5wt% SiC addition, the maximum relative density of 94.8% and maximum flexural strength of 521.8 MPa were obtained for the Si3N4/SiC composite ceramics. As compared with the specimen without SiC addition which flexural strength was 338.7 MPa, flexural strength of the above mentioned Si3N4/SiC composite ceramics was improved by 54.1%. SiC powder can effectively improve the mechanical properties of the specimen and the fracture of Si3N4/SiC composite ceramics followed the typical intergranular fractural mode.
|
|
|
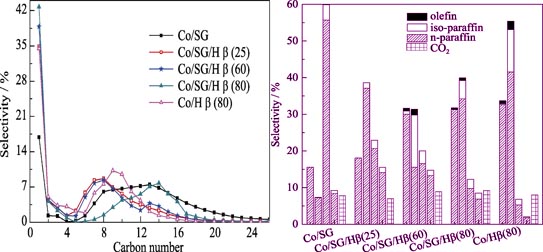
Hβ Modified Co/SiO2 Catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis of Jet Fuel-range Hydrocarbons
LI Yu-Ping, WANG Tie-Jun, MA Long-Long, WU Chuang-Zhi, DING Ming-Yue
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 599–604
 Abstract
Abstract(
641 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(490KB)(
1016
)
Bi-functional catalysts were prepared using hybrid supports, mesoporous SiO2(SG) and microporous Hβ zeolites with different Si/Al ratios of 25, 60 and 80 for direct jet fuel-range hydrocarbon synthesis (C8-C18). The textual and structural properties of the catalysts were studied by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction(XRD), H2-temperature-programmed desorption(H2-TPR) and N2 physisorption. The results showed that catalysts supported on tailor-made SiO2 and Hβ hybrid maintained both meso- and micro-pores with acid centers. With the decrease of Si/Al ratio, the bands corresponding to the characteristic adsorptions of Co/SG/Hβ catalysts shifted to the lower wave numbers, which accompanied by increased acidity. SiO2 decreased the acidity of Hβ and the interaction between Co and support, resulting in high Co dispersion, reduction and CO conversion for Co/SG/Hβ. The microporous structure and acidity of Hβ accelerated the hydrocracking/hydroisomerizaion reaction, which contributed to the high selectivity to jet fuel-range isoparaffins. The increased BET surface area and microporous volume with moderate acidity of Co/SG/Hβ(80) were essential for its high CO conversion (95.7%) and selectivity to jet fuel-range hydrocarbons (42.3%, including 27.6% of isoparaffins).
|
|
|
Fabrication of TiO2/WO3 Micro-nanofibers Composites and Their Photocatalytic Activity
MENG Shu-Qian, ZHOU De-Feng, ZHU Xiao-Fei, YANG Guo-Cheng, LI Zhao-Hui
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 605–613
 Abstract
Abstract(
919 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(786KB)(
1192
)
PVP/Ti(OC4H9)4/N5H37W6O24·H2O precursors with different Ti/W molar ratios were successfully synthesized by a simple combination method of Sol-Gel and electrospinning techniques. The electrospun precursors was converted into TiO2/WO3 micro-nanofibers via calcination at different temperatures in air. The obtained samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-Vis) techniques. Photocatalytic activity was evaluated by degradation of methylene blue (MB) under ultraviolet light irradiation. The results showed that WO3-doped TiO2 micro-nanofibers with Ti/W molar ratio of 12:1 and TiO2/WO3 micro- nanofibers with Ti/W molar ratio of 4:1 after calcination at 500℃ exhibited better photocatalytic degradation activity than that of pure TiO2 micro-nanofibers.
|
|
|
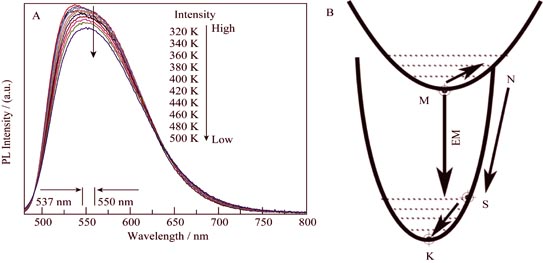
Packaging Technologies and Luminescence Properties of Ce:YAG Single Crystal for White Light-emitting Diode
XIANG Wei-Dong, ZHAO Bin-Yu, LIANG Xiao-Juan, CHEN Zhao-Ping, XIE Cui-Ping, LUO Le, ZHANG Zhi-Min, ZHANG Jing-Feng, ZHONG Jia-Song
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 614–620
 Abstract
Abstract(
995 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(463KB)(
1061
)
The Ce:YAG single crystal for white light-emitting diode (WLED) application was grown by the Czochralski method. The thermal stability and optical properties of samples were characterized by absorption spectrum, photoluminescence spectra and temperature-dependent PL spectra. The photoelectric performance of WLEDs fabricated by the Ce:YAG single crystal were also measured. It is found that the Ce:YAG single crystal shows a broad emission band from 500 nm to 700 nm under blue light (wave length 466 nm). Absorption peaks, located at 202, 219, 247.3, 347.4 and 455.5 nm, are due to 4f→5d transition, and the energy of 5d orbits is divided into 21954, 29154, 40437, 45662 and 49505 cm-1. As the temperature increases, the PL intensity is reduced because of a higher energy of the 2F7/2, and the damping upon PL intensity by the Ce:YAG single crystal (13.28%) are much lower than that by commercially available phosphors (30%). When the current is at a standard state and the luminous flux of emission blue light is around 3.7 lm, the most suitable thickness for the Ce:YAG single crystal is 0.5 mm. Since the WLED fabricated by the Ce:YAG single crystal prepared in present work meets all requirements in related GB codes, and its performance is better in comparison with that of the commercially available one, the Ce:YAG single crystal will possibly be used to fabricate new-type WLED devices.
|
|
|
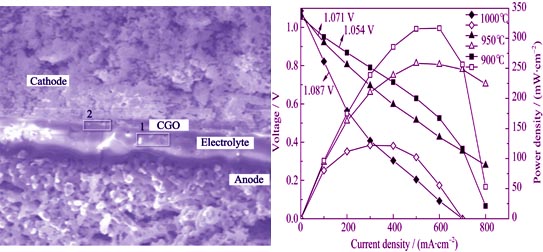
Fabrication and Characterization of Functionally Graded Cathodes Based on in-situ Formed La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ for Intermediate Temperature SOFCs
GUO Mi-Lan, TU Heng-Yong, LI Si-Lin, YU Qing-Chun
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 621–626
 Abstract
Abstract(
637 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(635KB)(
1258
)
Precursor powders of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ (LSC) and composite powders of LSC precursor and Ce0.8Gd0.2O2-δ (CGO) were prepared by Sol-Gel process. The precursor powders of LSC were characterized by TGA, XRD, BET and exhibited homogeneity and high specific surface area. XRD analysis indicated that single phase of LSC can be formed after calcination at high temperature in Ar and annealing at 850℃ for 2 h in air, which corresponds to the fabrication and annealing condition of functionally graded cathode before SOFC stack operation. Functionally graded cathode of LSC/CGO precursor and LSC precursor were sintered at 900--1000℃ in Ar, which were deposited on NiO/YSZ anode supported half cell with YSZ as electrolyte layer and CGO as barrier layer. Microstructural analysis by SEM and EDX indicated that graded cathode contacted well with CGO layer. It was found that SrZrO3 was formed at the YSZ-CGO boundary. The test of single SOFC cells with in-situ formed LSC showed that cell performance was improved with decrease of the sintering temperature. In comparison, the best cell performance was achieved at the sintering temperature 900℃.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Activation Graphene/Sulfur Complex Cathode Material for Lithium-sulfur Batteries
CHEN Fei-Biao, WANG Ying-Nan, WU Bo-Rong, XIONG Yun-Kui, LIAO Wei-Ling, WU Feng, SUN Zhe
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 627–632
 Abstract
Abstract(
864 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(614KB)(
1275
)
Novel accordion structure activation graphene/sulfur (AG/S) complex cathode materials were prepared by solution-based reaction-deposition method using activation graphene (AG) as precursors. SEM, EDX and TEM measurement were conducted. The result indicated that the AG/S had accordion structure with a uniform S coating on accordion structure AG. At the same time, sulfur was also found to be deposited on the interlayer of AG. Constant current charge-discharge tests showed that the AG/S complex cathode material with 65wt% sulfur delivered a high initial discharge specific capacity of 1452.9 mAh/g at the current density of 400 mA/g, with 909.7 mAh/g remained after 200 cycles. Meanwhile, an initial discharge specific capacity of 1309.9 mAh/g could be obtained for the material at the larger current density of 1000 mA/g, keeping 717.1 mAh/g after 200 cycles at the same current density. The rate performance, coulombic efficiency and cycling stability of the AG/S complex cathode materials were confirmed to be excellent, which may be originated from the homogeneous distribution of the sulfur with small powder size in the composites, the excellent electrical conductivity of AG and the fixation effect of the functional groups on the surface of AG for S.
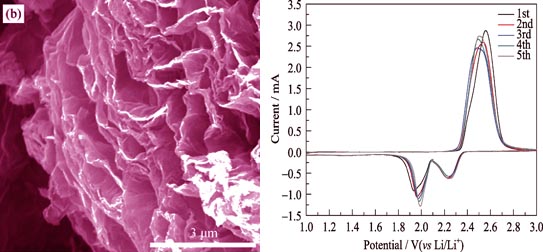
|
|
|
Influence of Ta2O5 Additive on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of NiCuZn Ferrites
SUN Ke, LI Yao, YANG Yan, LAN Zhong-Wen, YU Zhong, GUO Rong-Di
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 633–638
 Abstract
Abstract(
727 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(616KB)(
1012
)
NiCuZn ferrites doped with Ta2O5 additive were prepared by solid-state reaction method. The influence of Ta2O5 additive on the microstructure, static magnetic properties and high frequency losses (Pcv) of NiCuZn ferrites were investigated. The results reveal that Ta2O5 can refine the grain of NiCuZn ferrites, and consequently reduce the sintering density. At the same time, the saturation induction and initial permeability of samples reduce monotonously with the increase of Ta2O5 content. The coercive force and resonance frequency, however, increase gradually. Furthermore, the high frequency losses (Pcv) firstly decrease and then increase, and the dominant factor of Pcv transforms from residual loss (Pr) to hysteresis loss (Ph), so the Pcv has a valley value when Ta2O5 content is 0.12wt%. The lowest Pcv is 139 mW/cm3 at the conditions of 100℃, 3 MHz and 10 mT, where Ph and Pr are 93 mW/cm3 and 46 mW/cm3, respectively.
|
|
|
Structure of Antireflective Films with Si-O-P Bonds and Impact Factors on Its Performance
WANG Yan, WANG Hong-Ning, CHEN Ruo-Yu
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 639–644
 Abstract
Abstract(
763 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(472KB)(
1071
)
An antireflective (AR) film was successfully prepared by dip-coating on silica glass substrate. During the preparation, aqueous colloidal silica (ACS) was used as silica source, orthophosphoric acid as adhesion promoting agent and hydrogen peroxide as activating agent. The structure, formation mechanism and performance of the film were investigated by FTIR, XRD, FESEM, TEM and AFM. The hydrogen peroxide in silica sol repairs the surface Si-O- bonds of colloidal silica particles greatly. As a result, their stabilities and reaction activities are improved. During the heat-treatment of the film, the orthophosphoric acid is firstly transformed into the chain of metaphosphoric acid and subsequently reacted with surface Si-OH from colloidal silica particles and the substrate, resulting in the formation of the numerous Si-O-P cross-linkings and the stable silicophosphate gel structure. When molar ratio of H3PO4: H2O2: EtOH: SiO2 is 0.49: 0.52: 30: 1, the average transmittance of the film in the visible light is 98%, and the pencil hardness grade reaches 6H.
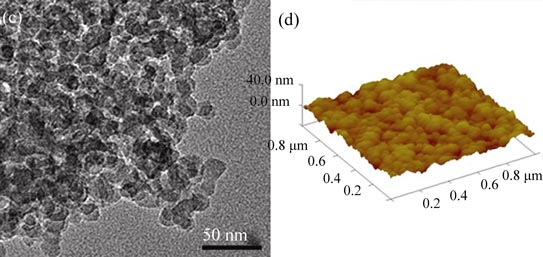
|
|
|
Fast Fabrication of Highly Ordered Porous Anodic Alumina Membranes by Hard-mild Anodization
HAO Ai-Wen, HUANG Li-Qing, CHENG Long, Li Xin, ZHANG Wei-Wei, SHAN Dong-Zhi, FENG Xue-Hong
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 645–649
 Abstract
Abstract(
786 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(394KB)(
999
)
A hard-mild anodization combined method (HA-MA) for rapidly fabricating highly ordered porous anodic alumina (PAA) membranes is presented in this paper. Firstly, by using hard-anodization (HA), the ordered pit arrays on aluminum surface were rapidly prepared and then, by using mild anodization (MA), ordered PAA membranes were fabricated on the ordered pit arrays aluminum surface. The effect of HA parameters, such as anodization voltage and duration, on the order degree of as-fabricated PAA membranes were investigated. The results showed that the optimum HA voltage and duration in 0.3 mol/L sulfuric acid at -1.5℃ were 80 V and 10 min, respectively. The order degree and mechanical stability of as-fabricated PAA membranes were similar to that of PAA membranes fabricated by two-step MA method, but its total process duration was within 4.5 h, which cost only about 1/4 time as that of by two-step MA method, The HA-MA method greatly improved the fabrication efficiency of ordered PAA.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Multi-shell Hollow Biphase Bioceramic Microsphere Composites
YANG Yong-Zhu, ZHANG Lei, YANG Guo-Jing, GAO Chang-You, GOU Zhong-Ru
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 650–656
 Abstract
Abstract(
641 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(608KB)(
1010
)
A series of hollow bioceramic microspheres with two or three shell layers were fabricated via alginate microsphere template and layer-by-layer coating techniques. The Na2SiO3-alginate mixture hydrosol beads were firstly injected into the Ca(NO3)2 aqueous solution under mild stirring to form calcium silicate hydrate-coated alginate microspheres. The composite microspheres were dispersed into the beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) -containing alginate hydrosol and wollastonite (CaSiO3)-containing alginate hydrosol in turn while gently stirring. The microspheres were filtered, dried in vacuum and finally calcined at 850℃ for 2 h to obtain the multi-shell hollow bi-phase ceramic microspheres. The microstructure and chemical composition of the microspheres were characterized by SEM, EDX, XRD and FTIR analysis. In vitro biodegradation behavior of the two-shell hollow microspheres was tested in weak acidic Tris buffer and confirmed a unique controlled release characteristic for the silicate and phosphate groups. These results suggest that the rational design of the two- or multi-shell layer allows the preparation of bioceramic composites composed of β-TCP and CaSiO3 with stage adjustable biodegradation and these biomaterials are potential candidates for improving bone regeneration and repair.
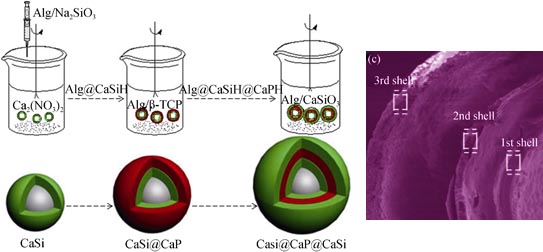
|
|
|
Synthesis and Properties of a Bridged Siloxane for Protection of Architectural Glazed Tiles of the Qing Dynasty in the Forbidden City
HAN Xiang-Na, HUANG Xiao, LUO Hong-Jie
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 657–660
 Abstract
Abstract(
527 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(402KB)(
920
)
The architectural glazed tiles of the Qing dynasty in the Forbidden City are the most important glazed ceramic of China. But some serious deterioration such as color change, dirty, craze crack, efflorescence and glazed layer spallation are observed in some tiles. In this paper, a bridged siloxane (BSQ) protective material focusing on glazed layer spallation issue was designed and synthesized starting with isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Important properties including water absorption, contact angle, color change, water vapor diffusion and compressive strength of the treated glazed titles were examined. Furthermore, the chemical attack tests and freeze-thaw cycles were also evaluated. It shows that the BSQ treatment can modify the tile surface to hydrophobic, increase the strength of tile body and thus mitigate glazed layer spallation.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterizations of Co-doped Lithium
Manganese Oxide Spinel Li1.035Mn1.965O4
LI Yun-Jiao, XU Hu, KONG Long, LI Hua-Cheng, LI Chun-Xia, ZHANG Xian-Zhen, HAN Qiang
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 661–666
 Abstract
Abstract(
1532 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(454KB)(
3445
)
Spinel powders of Li1.035CoxMn1.965-xO4 (x=0-0.100) systems were synthesized by a simple wet chemical process with post heat-treatment. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns reveal that the Co doping does not affect the Fd3m space group of the cathode materials. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images show that the Li1.035CoxMn1.965-xO4 cathode materials have a uniform and nearly cubic morphology with a narrow size distribution. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) results demonstrate that the Li1.035Co0.035Mn1.930O4 powder has a good crystalline state. The electrochemical testing results indicate that the prepared Co-doped Li1.035CoxMn1.965-xO4 samples show a better cycling ability and rate capability at room temperature than that of Co-free Li1.035Mn1.965O4. In particular, the Li1.035 Co0.035Mn1.930O4 sample delivers a reversible specific capacity of 113 mAh/g in 1st cycle and retains 93.8% of its initial capacity after 100 cycles at 0.5C rate. When discharging at 4C rate, the Li1.035Co0.035Mn1.930O4 powder maintains 86 mAh/g, which is 76.1% of the reversible capacity at 0.5C. Comparatively, the Li1.035Mn1.965O4 powder maintains only 64.8% of its reversible capacity at 0.5C discharge rate. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results show that Co ion doping can enhance the electrical conductivity and the Li-ion diffusion coefficient. These results indicate a superior cycling and rate performance compared with the pristine one.
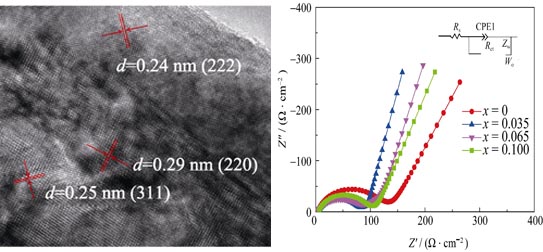
|
|
|
Sol-Gel Preparation of PHFBMA/PFG/Silica Coatings with Durable
Shortwave-band Antireflective Performance
ZHANG Qing-Hua, HUI Hao-Hao, YANG Wei, WEI Yao-Wei, WANG Jian, XU Qiao
2014 Vol. 29 (6): 667–672
 Abstract
Abstract(
1231 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(518KB)(
2732
)
A new silica shortwave-band antireflective (AR) coating with durable optical performance on fused silica substrate was prepared by a base-catalyzed Sol-Gel process using tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) as a precursor. 1H, 1H, 12H, 12H-perfluoro-dodecane-1, 12-diol (simplified as PFG) was used to control the structure and size of the silica particles in the sols, and hence decreased the refractive indices of the coatings. After Poly (2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4-hexafluorobutyl) methacrylate (PHFBMA) being introduced into the silica sols, the AR coatings could retain a transmission about 99.9% at about 300 nm. At the same time, the transmission stability of the coatings was improved significantly, which were tested in a moisture environment and an organic-containing vacuum chamber, respectively.
|
|