|
|
Recent Progress on Bismuth Layer-structured Ferroelectrics
ZHANG Fa-Qiang, LI Yong-Xiang
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 449–460
 Abstract
Abstract(
1852 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(781KB)(
2218
)
As an improtant lead-free ferroelectric/piezoelectric system, the past few decades have attracted increasing attention of bismuth layer structured-ferroelectrics (BLSF) due to its comprehensive advantages in the areas of high temperature, high frequency and ferroelectric random access memory (FRAM). In this paper, the recent progresses on the study of this system were reviewed. Firstly, as the basic of other researches, the key issues in strucutre design and microstructure study were dicussed in detail. Then special emphasis was put on ferroelectric/ piezoelectric performance and film technology. Additionally, some new research fields that were closely related to ferroelectric were introduced. In the end, the research directions were also extracted according to the authors’ knowledge.
|
|
|
Research Status and Outlook of High Temperature Radar Absorbing Materials
DING Dong-Hai, LUO Fa, ZHOU Wan-Cheng, SHi Yi-Min, ZHOU Liang
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 461–469
 Abstract
Abstract(
2109 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(561KB)(
1818
)
Traditional radar adsorbing materials characterized by thin broad, light and strong can not fully satisfy requirements of advanced weapons with heat resistance, anti-oxidation, high strength and fracture toughness. Recently, high temperature radar absorbing materials have attracted much attention. Research progresses of three high temperature absorbers, including C, SiC and ZnO, were reviewed. Then ways to improve their microwave properties and mechanisms of their temperature respond behaviors were introduced. In addition, the coating and structural microwave absorbing materials were compared. On this basis, superiorities, research status and main problems of continuous fibers- reinforced ceramic matrix composites were elaborated. Based on these progresses, potential development directions of high temperature microwave absorbing materials were proposed.
|
|
|
Research on Microwave Absorption Properties of FeCo/Graphite Nanocomposite
LI Jia, LIU Hong-Bo, YANG Li
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 470–474
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
1142
)
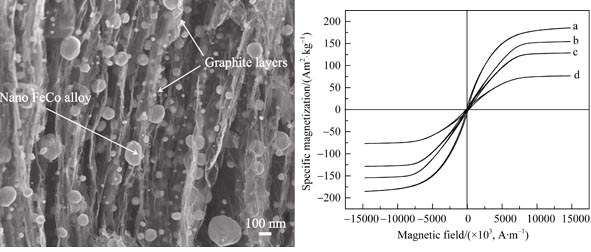
Fe3+Co2+/graphite oxide composites were firstly prepared by absorbing Fe3+ and Co2+ into the layers of graphite oxide based on absorption property of graphite oxide. And then FeCo/graphite nanocomposites were synthesized by reducing the Fe3+Co2+/graphite oxide compounds with H2. The crystal structure, morphology and magnetic properties were characterized by XRD, SEM and magnetic loop analysis, and the microwave absorption properties, caused by content variation of FeCo alloy, was investigated. Results indicated that the FeCo/graphite nanocomposite was two-phase material composed by graphite and nano FeCo particles. With diameter ranging from 30 nm to 150 nm, the FeCo particles dispersed both on the surface of and between the graphite layers, which made the FeCo/graphite nanocomposite a typical soft magnetic material. With the FeCo alloy content decrease, the saturation magnetization and magnetic loss increased but the dielectric loss decreased. With proper FeCo alloy content, the synergistic effect of dielectric loss and magnetic loss could lead to the FeCo/graphite nanocomposite displaying good microwave absorption property.
|
|
|
Effects of H3PO4 Treated Porous SiO2 on Proton Conductivity and Performances of EDL-TFTs
WAN Xiang, LIU Yang-Hui, ZHANG Hong-Liang
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 482–486
 Abstract
Abstract(
653 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(466KB)(
1302
)
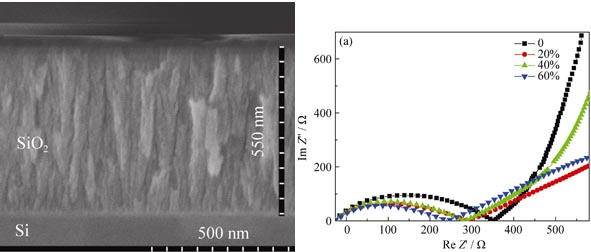
Porous SiO2 films were deposited by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition and were treated by H3PO4 solution with various concentrations. Then indium-zinc-oxide (IZO) electric-double-layer thin-film transistors (EDL- TFTs) were fabricated by using such porous SiO2 films as the gate dielectrics. The effects of H3PO4 treatments on the proton conductivity and EDL capacitance of porous SiO2 films and on the performances of EDL-TFTs were investigated systematically. The proton conductivity and EDL capacitance of SiO2 films increase with the H3PO4 concentration increase. A high proton conductivity of 1.51×10-4 S/cm and a large EDL capacitance of 6.33 μF/cm2 are obtained for porous SiO2 films which were treated with 60% H3PO4 solution. The operating voltage decreases and the on/off ratio increases with the increasing H3PO4 concentration. The EDL-TFTs gated by porous SiO2 films treated with 60% H3PO4 solution show the best performance with a low operating voltage of 1.2 V, a high mobility of 20 cm2/(V·s), and a large on/off ratio of 4×106. Such EDL-TFTs are promising for biosensors and chemical sensors in the future.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) Powders by Solvothermal Method
ZHOU Chao, FENG Qing, GAO Yan-Min
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 487–492
 Abstract
Abstract(
675 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(557KB)(
1292
)
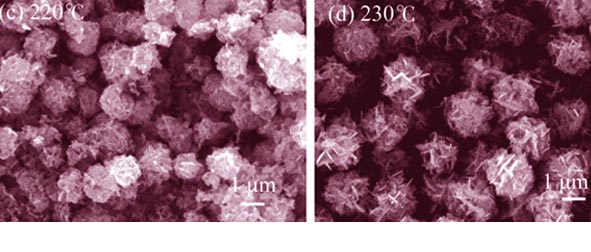
Cu2ZnSnS4(CZTS) powderss were synthesized by a facile solvothermal method in ethylene glycol with the presense of polyvinylpyrrolidone(PVP), using CuCl2·2H2O, Zn(Ac)2·2H2O and SnCl4·5H2O as metal precursor, thiourea as sulfur source. The effects of reaction temperature and time on crystal structure, composition, morphology and absorption spectra of CZTS powders were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Raman spectroscope, transmission electron microscope (TEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDS) and UV-Vis spectroscope. The results reveal that the reaction temperature and reaction time have a certain influence on the morphology and optical properties of the as-synthesized CZTS powders. The optimum solvothermal reaction condition is 230℃, 24 h. Under this condition, crystallization of the synthesized CZTS powders is pure and complete, and the particles are uniform and monodispersed sheets-contanimg microspheres. Elements’ atomic ratio of CZTS powder is close to stoichiometric coefficient and band gap of the products is about 1.52 eV, which is close to the optimum value for solar photoelectric conversion. In addition, a possible reaction mechanism of CZTS particle preparation is also inferred.
|
|
|
Effect of Hydrogen and Cu Interlayer on the Optical and Electrical Properties of GZO Thin Film
LV Kun, ZHU Bai-Lin, LI Ke, HU Wen-Chao, XIE Ming, WU Jun
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 493–497
 Abstract
Abstract(
509 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(460KB)(
981
)
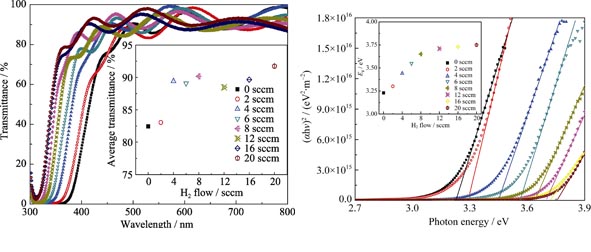
By method of magnetron sputtering, GZO thin films were deposited in H2+Ar atmosphere and GZO/Cu/GZO thin films were deposited in Ar atmosphere. Effects of H2 flux and Cu interlayer thickness on the optical and electrical properties of the films were investigated, respectively. Furthermore, GZO/Cu/GZO films were also deposited in H2+Ar and the properties of films were investigated as a function of Cu interlayer thickness. The results show that introduction of H2 into deposition atmosphere can effectively decrease the resistivity and enhance the transmittance of GZO films. The best figure of merit is obtained for the films deposited at H2 flux of 20 sccm. With increasing Cu interlayer thickness, both the resistivity and transmittance of the GZO/Cu/GZO multilayer film are decreased. After introducing H2 into deposition atmosphere, the transmittance of GZO/Cu/GZO multilayer film is remarkably decreased although its resistivity is further decreased with increasing Cu interlayer thickness. In addition, it is found that the energy gap (Eg) of the films increases with H2 flux increasing, while it decreases with Cu interlayer thickness increasing.
|
|
|
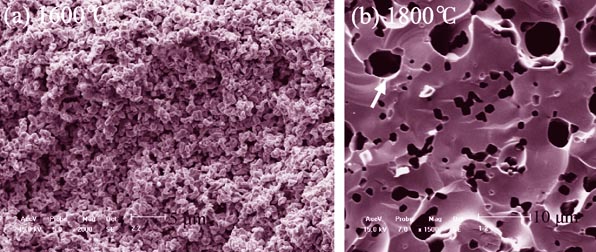
Preparation of Tungsten Boride Ceramic by Pressureless Sintering
CAO Xiao-Zhou, WANG Chao, XUE Xiang-Xin, YANG He
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 498–502
 Abstract
Abstract(
1023 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(444KB)(
1040
)
WB2 ceramic was prepared by a two-step sintering method. Firstly, WB2 powder was synthesized by solid phase reaction using the mixed boron and tungsten powder as raw materials at high temperature. Secondly, WB2 ceramic was prepared by pressureless sintering using the above synthesized powder. The effect of boron/tungsten molar ratio on the phase composition of synthesized product, and the effect of temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of WB2 ceramic were investigated. The results showed that phase-pure WB2 could be obtained with B/W molar ratio of 2.5. The apparent porosity decreased, the relative density increased and the mechanical properties were improved greatly with the increase of sintering temperature. When the sintering temperature was up to 1800℃, the porosity, relative density, flexural strength and Vickers micro-hardness of WB2 ceramic were 5.2%, 86.0%, 72 MPa and 2088.5 MPa, respectively. The main fracture model of WB2 ceramic was changed from intergranular fracture to transgranular fracture.
|
|
|
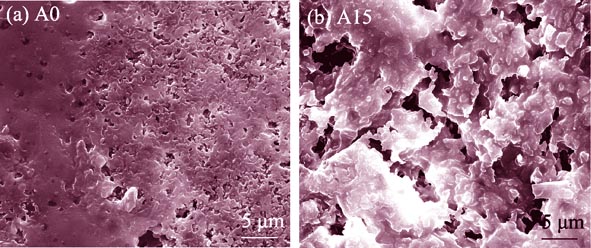
Effects of AlN Content on the Thermal Properties and Thermal Shock Resistance of BN Matrix Composite Ceramic
TIAN Zhuo, DUAN Xiao-Ming, YANG Zhi-Hua, JIA De-Chang, ZHOU Yu
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 503–508
 Abstract
Abstract(
590 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(490KB)(
955
)
Using BN, SiO2, AlN as the raw materials, BN matrix composites ceramics were fabricated by hot-press sintering. Effects of AlN content on the thermal properties and thermal shock resistance of the composites were studied. It was found that thermal expansion coefficient of the composites decreased at first and then increased with the increase of AlN addition. When 5vol% AlN was used as the raw materials, the produced composite exhibited the minimum coefficient of thermal expansion, which was 2.22×10-6/K. Thermal conductivity of the composites increased at first and then decreased, and reached the highest value when 10vol% AlN was used as raw materials. The residual strength after thermal shock of the composites without AlN increased with the increase of thermal shock temperature difference. Residual strength of composite ceramic after thermal shock showed downward trend with the introduction of AlN. For composite ceramic adding with 5vol% AlN, the residual strength was 219.7 MPa and the residual strength was 88.9% after thermal shock from 1100℃ to ice water, showing a good thermal shock resistance.
|
|
|
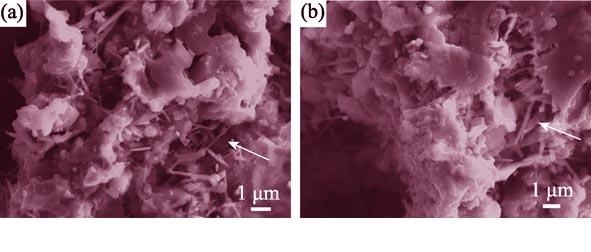
Effects of SiC on Phases, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Porous Al2TiO5 Fabricated by Reaction Sintering
CUI Hong-Zhi, LI Shu-Hai, CUI De-Yun
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 509–514
 Abstract
Abstract(
479 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(592KB)(
1456
)
Porous aluminium titanate (AT) composites were fabricated by sintering with γ-AlOOH, TiO2 and SiC as raw materials. Effects of the particle size and the content of SiC on phases, microstructures, compressive strength, porosity and pore size distribution of products were investigated. Results show that the phases of the products are composed of Al2TiO5(AT), Al6Si2O13, TiC, SiO2, Al2O3 and a small amount of unreacted TiO2. When SiC is added into γ-AlOOH and TiO2 mixture, it reacts with TiO2 and forms TiC and SiO2. The small TiC particles distribute and disperse in the walls and shelves of porous products. Moreover, SiO2 reacts with Al2O3, decomposted from γ-AlOOH, to form Al6Si2O13 whiskers which distribute crisscross between Al2TiO5 grains or in the pores. The Al6Si2O13 whiskers along with TiC particles contribute greatly to improving the compressive strength of the products, particularly with small SiC particles. When SiC particles are big, the packing patterns of powder mixtures are changed and the porosities of the products are increased. However, when SiC content is beyond 5wt%, both the porosities and compressive strength of the products decrease due to the formation of more low-melting point SiO2, and some SiO2 fills in the pores of the porous products, and some exists on the surface of Al2TiO5 grains and weakens the bonding strength.
|
|
|
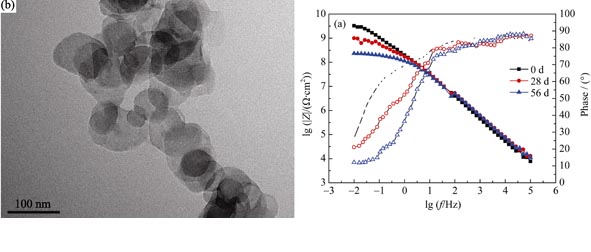
Preparation and Anti-mildew Properties of TPN-SDS-layered Double Hydroxide Nanohybrids
LI Yan-Yun, LI Song-Mei, LIU Jian-Hua, YU Mei
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 515–522
 Abstract
Abstract(
695 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(556KB)(
934
)
MgAl-TPN-SDS-LDHs nanohybrids were synthesized by coprecipitation process. The anti-mildew durability of TPN were improved when nanohybrids was introduced in alkyd resin coating due to inhibition release rate of TPN. The non-ionic, poorly water-soluble chlorothalonil (TPN) was firstly incorporated into micelles derived from negatively charged surfactants-sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). The negatively charged micelles were then encapsulated in nanoparticles of MgAl-layered double hydroxides. The as-prepared nanohybrids were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscope, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope and UV-VIS absorption spectrum. The results showed that MgAl-TPN-SDS-LDHs nanohybrids were successfully prepared, with TPN loading rate at 34.49wt%. The release kinetic of TPN from TPN-SDS-LDHs nanohybrids was investigated in butyl acetate and the release process fitted the pseudo-second-order kinetic equation. The alkyd resin coating containing TPN-SDS-LDHs nanohybrids showed better anti-mildew durability than coating containing TPN in fungus test.
|
|
|
Effect of Pretreatment Temperature and Sodium Chloride Concentration on Energy Dissipation Characteristics of ZSM-5/Water System
SUN Yue-Ting, XU Jun, LI Yi-Bing, XU Xiao-Qing, LIU Cheng
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 523–528
 Abstract
Abstract(
568 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(453KB)(
1032
)
Research and development of new materials with high energy dissipation density is of intriguing interest in protective engineering fields. With ultra-large specific surface area, nanoporous material enables a high-efficiency energy dissipation system by interaction with liquids, which has a promising application in vehicle crash safety and anti-explosion for armored vehicles. In this paper, ZSM-5 zeolite / NaCl solution system, a mixture with ZSM zeolite immersed in sodium chloride solution was experimentally investigated. Its energy dissipation characteristics and working mechanism were explored by quasi-static compression experiments. Effect of pretreatment temperature of ZSM-5 zeolite (600–1100℃) and NaCl concentration of the solution (0–2 mol/kg) were examined parametrically. Results show that the energy dissipation density of ZSM-5 zeolite / NaCl solution system can reach 12 J/g, as a reusable system under quasi-static loading. Its performance characteristics can be finely tuned by pretreatment of ZSM-5 and adding different concentrations of NaCl. The energy dissipation density increases with pretreatment temperature and decreases with NaCl concentration, while its working pressure increases with both of them. This work is of significance for the development of intelligent, controllable and efficient energy dissipation devices.
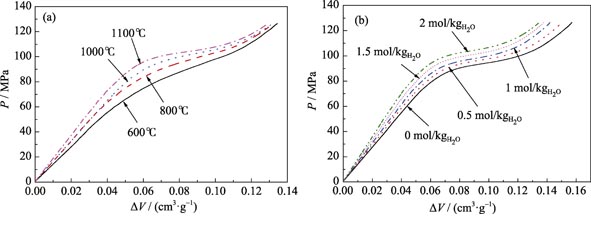
|
|
|
Effect of Temperature on Microstructure and Cr(VI) Adsorption Capacity of MgAl Metal Oxides
XU Li-Hua, ZENG Hong-Yan, LIAO Meng-Chen, XU Sheng, ZHANG Zhi-Qing, Li Qiao
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 529–533
 Abstract
Abstract(
551 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(422KB)(
1089
)
The adsorption properties of Cr(VI) on the double oxides (LDO) from calcined MgAl hydrotalcites (LDH) were investigated. The effect of temperature on the adsorption performances of the LDO was studied, and the adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics were studied at different adsorption temperatures. The samples were characterized by XRD and FT-IR to clarify the adsorption mechanism.The results indicated that CrO42– had intercalated into the interlayer structures of Mg-Al hydrotalcites. Moderately increasing temperature was beneficial for the reconstruction of LDH crystalline structure from LDO. In the temperature range of 20℃–60℃, adsorption capacity of the LDO was increased with temperature rising, it reached 91 mg/g in the temperature range from 50℃ to 60℃. The experimental data were well fit to the Langmuir equation. The negative values of ΔGo indicated that the adsorption process was spontaneous, and positive values of ΔHo and ΔSo showed the endothermic and entropy-increasing nature of the process. The adsorption was consistent with the pseudo-second order kinetic model. The active energy value was 20.04 kJ/mol, which implying that the internal diffusion was the rate-determining step in the chemical adsorption.
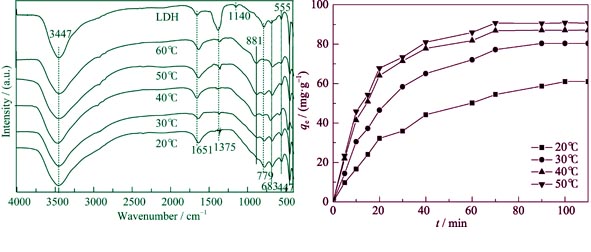
|
|
|
Fabrication and 2D-mapping of Pr: Lu3Al5O12 Scintillator Ceramics with High Light Yield and Fast Decay Time
SHEN Yi-Qiang, SHI Yun, PAN Yu-Bai, FENG Xi-Qi, WU Le-Xiang, KOU Hua-Min, ZHANG Zhi-Ming, WEI Long
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 534–538
 Abstract
Abstract(
682 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(421KB)(
956
)
Pr:LuAG ceramics were fabricated by a solid state reaction method using vacuum sintering with or without sintering aids (TEOS and MgO). The inline transmittance of the Pr:LuAG ceramics sintered with sintering aids reached ~80% in visible light range, while the ceramics without sintering aids were 5 times higher light output (1196 pe/MeV) and faster decay (73% fast decay component) although lower transmittance in visible light region (~70%, 2.0 mm thick) comparatively with the energy resolution of 8.4%. The Pr:LuAG cermics were cut and polished to 1.9 mm×1.9 mm× 1.0 mm pixels to form ceramics arrays, by using the 4×4 ceramics arrays, 2D mapping was accomplished. The position signals were clearly identified, which were better than that of commercial BGO (Bi4Ge3O12) crystals. It is proved that Pr:LuAG ceramics is promising in PET (Positron Emission Tomography) imaging.
|
|
|
Rietveld Structure Refinement and Raman Spectroscopy of Pyrochlore-type Oxygen-rich Ce2Zr2O8 Phase
XIE Hua, WANG Lie-Lin, LUO De-Li
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 539–544
 Abstract
Abstract(
710 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(490KB)(
1083
)
Pyrochlore-type oxygen-rich Ce2Zr2O8 phase was prepared successfully by graphite reduction method. In order to compare the structure between Ce2Zr2O8 and Nd2Zr2O7, the pyrochlore Nd2Zr2O7 was selected as the substitute of CeZrO3.5+δ, the oxide precursor of Ce2Zr2O8. Experimental results show that excessive oxygen in the Ce2Zr2O8 structure mainly occupies the oxygen vacancies from the precursor structure. Oxygen ions diffusion in the precursor CeZrO3.5 structure does not destroy the ordering cation sublattice. Meanwhile, Zr-O ligands are transformed from octahedrons of co-top connection in the precursor to cubes of co-edge connection in the Ce2Zr2O8. The antiphase boundary density and Raman bands in comparison with?the precursor are improved significantly, suggesting the structure of Ce2Zr2O8 phase is in a metastable state. The characteristic structure facililates rapid adsorption or release of oxygen ions, providing structural feasibility for ideal candidate materials for automobile exhaust purification. However, the structure of Ce2Zr2O8 indicated that the radiation resistance and chemical stability may be downward when An2Zr2O7 pyrochlore under self irradiation condition transforms to the oxygen-rich phase An2Zr2O8.
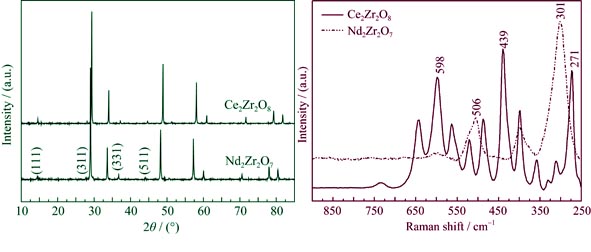
|
|
|
Synthesis of NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ Upconversion Nanoparticles Using Hydrogel Networks as a Template
QIU Mu-Shu, LIN Min, ZHAO Ying, DONG Yu-Qing, LU Tian-Jian, XU Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 545–549
 Abstract
Abstract(
663 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(432KB)(
1108
)
Hydrogel network structures were used as nano-sized reactors for synthesizing NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ upconversion nanoparticles with controlled size. By adjusting the crosslinking density, hydrogel networks with different sizes were prepared and used as reactor to control the size of synthesized nanoparticles. The particle size and upconversion luminescence property of the nanoparticles were characterized using XRD, TEM and photoluminescence (PL) spectra. The results show that the size of synthesized NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+ nanoparticles is around 10 nm. The diameter and the luminescence intensity decrease with increase of hydrogel crosslinking density. The increased crosslinking density reduces Ostwald ripening and increases pore pressure, which limit the growth of nanoparticles. The decreased particle size results in broken bonds on the particle surface and particle scattering. Besides, the hydrogel may also quench the fluorescence of the nanoparticles. This research provides a simple and environmentally friendly method for synthesizing uniform upconversion nanoparticles.
|
|
|
Effects of Reaction Temperature on Structure and Optical Properties of Hydrothermally Prepared (NH4)xWO3-y and WO3·1/3H2O
WANG Kun, KANG Li-Tao, CHEN Shi, DONG Li, LIANG Wei, GAO Feng
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 550–556
 Abstract
Abstract(
1873 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
3474
)
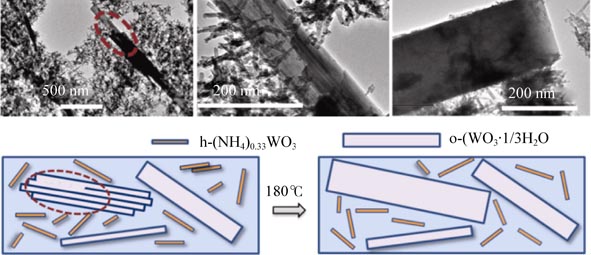
Effects of reaction temperature on phase, microstructure and optical property of hydrothermally prepared (NH4)xWO3-y and WO3·1/3H2O were studied in this work. XRD results show that the sample prepared at 100℃ is hexagonal (NH4)xWO3-y (h-(NH4)xWO3-y). At higher reaction temperatures of 140℃ and 180℃, the hexagonal (NH4)xWO3-y gradually and partially transforms into orthorhombic WO3·1/3H2O (o-WO3·1/3H2O). SEM and TEM images illustrate that both (NH4)xWO3-y and WO3·1/3H2O crystallites show a short-rod shape with a [001] growth direction (c axis). The phases of crystallites seem to be strongly related to crystallite sizes; nano- and micro-sized crystallites adopt h-(NH4)xWO3-y and o-WO3·1/3H2O, respectively. Based on XRD, SEM and TEM results, a mechanism is extracted to explain the transformation from h-(NH4)xWO3-y to o-WO3·1/3H2O. Optical measurements indicate that the h-(NH4)xWO3-y nano-rods prepared at 100℃ exhibit a low infrared light transmittance of 25.5%, and maintaining a high luminous transmittance (67.6%), mainly due to the fice crystallite sizes.
|
|
|
A Modified Vertical Bridgman Method for Growth of GaSe Single Crystal
HUANG Chang-Bao, NI You-Bao, WU Hai-Xin, WANG Zhen-You, CHENG Xu-Dong, XIAO Rui-Chun
2014 Vol. 29 (5): 557–560
 Abstract
Abstract(
1028 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(372KB)(
2030
)
As growing ε-GaSe single crystal, volatile component and curving solidification interface spoil the qualities of crystals. The GaSe single crystal in Φ19 mm×65 mm size was grown by modified vertical Bridgman method. The crystallinity and optical properties of as-grown crystals were measured by XRD and transmission spectra, respectively. The FT-IR measurements indicated wide transparency over the spectral range (0.65-16 μm) and low absorption coefficient (<0.3 cm-1) in grown GaSe crystal.
|
|