|
|
Comment on Experiment Fundament of Veprek’s nc-TiN/a-Si3N4 Model and Its “Exceed Diamond Hardness”
LI Ge-Yang
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 1–8
 Abstract
Abstract(
848 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(627KB)(
1771
)
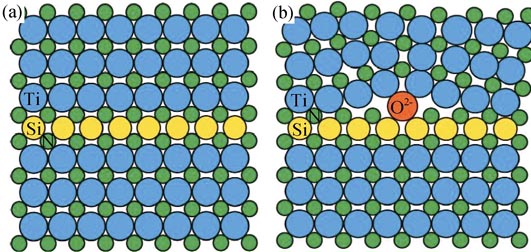
Since hardness exceeding that of diamond was reported by Vepreke, TiN/Si3N4 nanocomposite film has attracted much attention from the scientific community and resulted in a ballooning number of publications over the past 15 years. This paper commented on the Veprek's microstructure model and “superhardness” of this kind of films from experimental fundamental aspects. In term of the microstructure, the model of nc-TiN/a-Si3N4 proposed by Veprek, in which equiaxed nanocrystalline TiN (nc-TiN) were embedded in an amorphous Si3N4(a-Si3N4) matrix, was short of sufficient experimental evidence. Direct transmission electron micrographs observations showed that the TiN nanocrystals still had a columnar morphology instead of equiaxed morphology. Si3N4 interface tissue had a thickness of about 0.5-0.7 nm and existed in the crystalline state. Low-energy coherent interfaces are formed between Si3N4 and neighbouring elongated TiN grains. As far as the preparation technology, the hardness exceed diamond has not been repeated by others in this material up to now. Veprek attributed it not only to the lack of a sufficiently high temperature and partial pressure of nitrogen, but also to the unavoidable oxygen in preparation. However, those critical conditions were imposable to satisfy in technology. For the samples, although Veprek declared their films received the hardness exceed diamond (up to 138.9 GPa), they have not confirmed by any others, and moreover, these samples have disappeared now.
|
|
|
Nitrogen-doped Porous Carbon for CO2 Adsorption
CHEN Ai-Bing, YU Yi-Feng, ZANG Wen-Wei, QI Guo-Lu, YU Yun-Hong, LI Yue-Tong
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 9–16
 Abstract
Abstract(
1107 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(494KB)(
1862
)
CO2 is regarded as a greenhouse gas. Its capture and storage has important practical significance. Porous carbon materials doped with N atoms can greatly change the surface chemical properties, strengthen basic surface, which have wide application in the field of CO2 adsorption. In this paper, based on the latest research progresses of N-doped carbon materials, the direct synthesis, post treatment strategies, etc. and pore structure of N-doped porous carbon for adsorption, separation or diffusion of CO2 were introduced in detail. The relationships between the physical structure parameters, surface chemistry of N-doped carbon materials and CO2 adsorption separation performance were systematically summarized. It was also pointed out the existing problems and the solutions of various treatment methods. Preparation and industrialization of high performance CO2 adsorbents provide theoretical support for the directional design.
|
|
|
Effects of Alkali/Char Ratio and Activation Temperature on Ultramicropores of Rice Husk Active Carbon
LI Da-Wei, MA Teng-Fei, TIAN Yuan-Yu, ZHU Xi-Feng, QIAO Ying-Yun
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 17–22
 Abstract
Abstract(
764 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(490KB)(
1525
)
Porous carbons were prepared by KOH activation of rice husk char at alkali/char ratios of 0.6︰1 to 3︰1 and activation temperatures from 640℃ to 780 ℃. The obtained porous carbons were characterized using N2 adsorption and desorption technique, CO2 adsorption, TG-FTIR analyses. The results indicate that the ultramicropore size of the prepared porous carbons is mostly in the range of 0.42-0.70 nm. As the alkali/char ratio increases, the volume of ultramicropores first rises and then diminishes, whereas the volume of ultramicropores tends to decrease monotonously with the increase of activation temperature. A microporous carbon with ultramicropore volume of 0.149 mL/g, ultramicropore fraction of 36.3%, pore volume of 0.411 mL/g, and specific surface area of 774 m2/g, can be produced by activation at 640℃ at the alkali/char ratio of 1︰1. The ultramicropore volume of the porous carbons and their CO2 uptake at 104 Pa display a strong linear relationship.
|
|
|
Microwave Abosrbing Properties of CNTs Composites Attached with Fe3O4/CNTs Hybrid Buckypaper
LU Shao-Wei, LI Qian, XIONG Xu-Hai, MA Ke-Ming, XU Wei-Kai, JIA Cai-Xia
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 23–28
 Abstract
Abstract(
904 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(553KB)(
21788
)
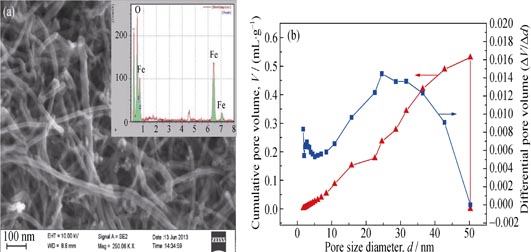
A naval hybrid buckypaper was fabricated by vacuum filtration method with monodispersed solution of Fe3O4 decorated carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which was easy to be infiltrated by resin and can be co-cured with polymer composites. The morphology, element composition, pore size distribution, and magnetic of hybrid buckypaper were characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), Barret-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) and vibrating sample magnetometer. The electromagnetic parameters of CNTs composite and hybrid buckypaper attached CNTs composite were investigated in the frequency range of 8.2-18 GHz with wave guide method and the reflection loss can be calculated. The hybrid buckypaper with only absorbing thickness of 0.1 mm attached CNTs composite possesses much broader absorbing bandwidth and larger reflectivity than those of CNTs composite, nearly all of which reflectivity is below -10 dB in frequency range of 8.2-18 GHz and the minimum value is -43.18 dB at 15.42 GHz.
|
|
|
Quasi-solid-state Dye-sensitized Solar Cells Employing Fibers Stacked Paper Carbons as Efficient Counter Electrodes
XU Shun-Jian, LUO Yu-Feng, ZHONG Wei, XIAO Zong-Hu, LOU Yong-Ping, OU Hui
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 29–34
 Abstract
Abstract(
565 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(514KB)(
1212
)
Three types of paper carbons (PCs) were introduced into quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) as counter electrodes. The PCs were respectively prepared using printed paper, filter paper and facial tissue as raw materials by one-step pyrolysis. Results show that each PC consists of carbon fibers with radial size of ~10 μm, and has low crystallinity as well as well-developed porous structure. As a result, each type of PC displays more excellent catalytic activity for tri-iodide (![]() ) reduction than graphite, which brings about higher efficiency for use in QDSCs. In three PCs, PC fabricated from printed paper possesses the highest surface area and the most outstanding catalytic activity. This is mainly attributed to unique carbonaceous ramentums on carbon fibers in printed paper derived PC. Each type of PC in QDSCs not only provides catalytic active sites for ) reduction than graphite, which brings about higher efficiency for use in QDSCs. In three PCs, PC fabricated from printed paper possesses the highest surface area and the most outstanding catalytic activity. This is mainly attributed to unique carbonaceous ramentums on carbon fibers in printed paper derived PC. Each type of PC in QDSCs not only provides catalytic active sites for ![]() reduction, but also serves distinctive function to improve the ion conductivity of quasi-solid-state electrolyte. Consequently, PCs based QDSCs have higher short-circuit current density (Jsc) and open-circuit voltage (Voc) compared with traditional Pt based QDSCs. The higher Jsc and Voc cover the insufficiency of fill factor, resulting in comparable efficiencies with traditional Pt based QDSCs. reduction, but also serves distinctive function to improve the ion conductivity of quasi-solid-state electrolyte. Consequently, PCs based QDSCs have higher short-circuit current density (Jsc) and open-circuit voltage (Voc) compared with traditional Pt based QDSCs. The higher Jsc and Voc cover the insufficiency of fill factor, resulting in comparable efficiencies with traditional Pt based QDSCs.

|
|
|
Effect of Vacuum Rapid Annealing Treatment on Performance of CIGS Solar Cells
TIAN Li, ZHANG Xiao-Yong, MAO Qi-Nan, LI Xue-Geng, YU Ping-Rong, WANG Dong
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 35–40
 Abstract
Abstract(
707 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(422KB)(
1382
)
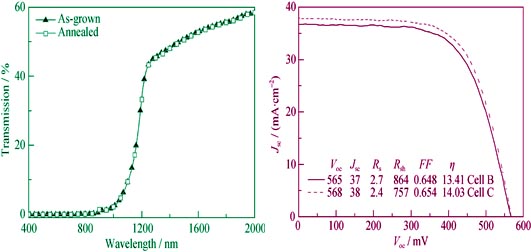
CIGS absorber layers were prepared by sequential sputtering/selenization method. Based on that, CIGS solar cells were fabricated with a structure of glass/Mo/CIGS/CdS/i-ZnO/ZnO:Al/Ni-Al grid. The influences of annealing treatment on the performance of CIGS solar cells were investigated. By optimizing annealing condition, the cell efficiency increased from 4.91% to 14.01%. Further investigation revealed that the post-annealing treatment had two advantages. Firstly, it facilitated the diffusion of Cd ions into CIGS surface to substitute the Cu vacancies. Thus, the surface of CIGS converted from p-type to n-type conduction, leading to the shift of p-n junction from CIGS/CdS interface into the CIGS layer. Therefore, the recombination centers at the p-n junction were greatly reduced. Secondly, most H2O molecules being adsorbed on the CIGS surface were eliminated by annealing, which improved the uniformity of electrical properties and band-gap of CIGS layer, resulting better performance of CIGS solar cell.
|
|
|
Tribological Properties of Graphene-based Fe3O4 Nanocomposite Materials
QIAO Yu-Lin, ZHAO Hai-Chao, ZANG Yan, ZHANG Qing
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 41–46
 Abstract
Abstract(
683 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(551KB)(
1637
)
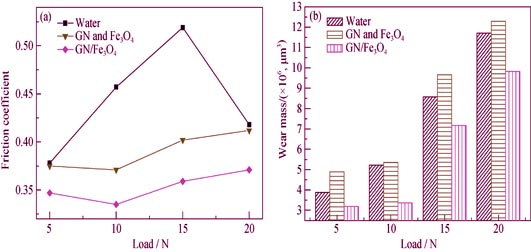
Graphene-based Fe3O4 nanocomposite materials were prepared by the melthod of Liquid-phase Ultrasonic Exfoliation. Morphologies of nanocomposite materials were characterized by means of SEM and TEM. Its tribological properties as a pure water additive were investigated using multi-functional reciprocating friction and wear tester. The lubrication mechanism was discussed based on results of analyses of SEM, XPS. The results showed that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles with size of 20-90 nm were densely and randomly deposited on interlamination and surface of graphene sheets. The nanocomposite materials as a pure water additive displayed good friction-reducing and antiwear performance. Compared with pure water, the graphene-based Fe3O4 nanocomposite could reduce the friction coefficient of 26.7% and the wear mass of 35.4% under condition of 10 N of load and 0.01wt% of concentration. The prosperity was attributed to the effect of adsorption membrane and boundary lubrication film containing graphene and Fe3O4 which inhibited oxidation of Fe and reduce wear on the frictional surface.
|
|
|
Microcapsulation of TiO2 precursor and Its Performance as Inhibitor of Erosion
LI Hong-Guang, YAN Jun, WANG Ming-Qiu, MENG Sheng-Hao, DU Shi-Guo
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 47–52
 Abstract
Abstract(
591 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(543KB)(
1416
)
As erosion and wear of gun bore become increasingly serious with the increase of muzzle velocity, chamber pressure and rate of fire, the demand for their high effective inhibitor is urgent. TiO2 precursor microcapsules with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as wall material were prepared by interfacial crosslinking method in W/O/W multiphase emulsion. The microcapsules were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), particle size analyzer, fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), thermogravimetric analyzer (TG). The results showed that the microcapsules were dispersive spherical particles at average size of 10 μm with integral and dense shell. The microcapsules were composed of about 35% solid TiO2 and aldol resin layer. Its anti-erosion effect was tested by erosion tube method, and showed that the combustion law of propellant was not affected after application and the anti-erosion efficiency was 35% when added 2.5wt% microcapsules relative to propellant mass.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Application of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as High Efficiency Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent
WANG Jun, ZHANG Bao-Lin, YANG Gao, WANG Lei, XIE Song-Bo, LI Xuan, GAO Fa-Bao
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 53–58
 Abstract
Abstract(
844 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(504KB)(
1572
)
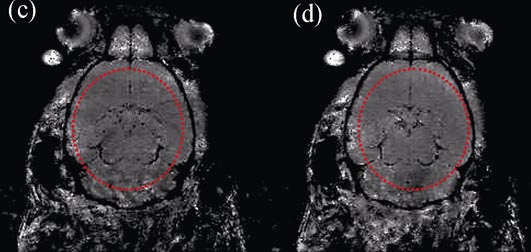
Iron oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by thermal decomposition of iron (III) acetylacetonate (Fe(acac)3) in poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), which was used as the solvent, reducing agent and modifying agent. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) analysis indicates that the nanoparticles have magnetite crystal structure. The results of transmission electron microscope (TEM) show that the shapes of iron oxide nanoparticles coated with PEG are equiaxial with uniform morphology. Particles and Zeta potential analyses show that the surface of iron oxide nanoparticles is negatively charged, and their hydrodynamics size dispersed in deionized water is 20 nm. Iron oxide nanoparticles show superparamagnetic behavior at room temperature and high r2/r1 ratio. MTT studies show that PEG-SPIONs have low cytotoxicity. In vivo magnetic resonance imaging reveals their excellent contrast effects of the PEG-SPIONs. This work demonstrates that iron oxide nanoparticles coated with PEG can be excellent T2 MRI contrast agents.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Nanocrystalline Potassium Sodium Niobate Ceramics
WANG Chao, CHEN Jing, CHEN Hong-Li, HOU Yu-Dong, ZHU Man-Kang
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 59–64
 Abstract
Abstract(
749 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(448KB)(
1685
)
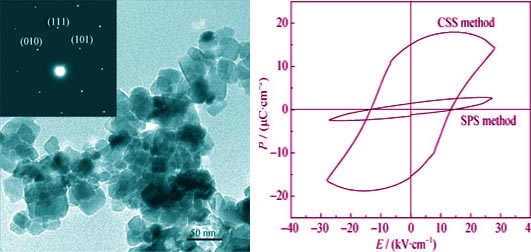
Using average 30 nm grain sized potassium sodium niobate powders obtained by a novel Sol-Gel method as starting materials, nanocrystalline potassium sodium niobate ceramics with pure orthorhombic phase, relative density of above 99% and grain size of 40 nm were prepared by spark plasma sintering method under sintering temperature of 900 ℃, sintering pressure of 30 MPa and sintering time of 1 min. The phase structure, micro-morphology, dielectric properties and ferroelectric properties of the ceramics were investigated. The results show that, differently from common micro-grain ceramics, dielectric constant of nanocrystalline potassium sodium niobate ceramics decreases to 341, which changes little with the temperature, and the ceramics have obvious dielectric relaxation (dispersion factor γ is 1.60), and a well saturated ferroelectric hysteresis loop with coercive field of 13.5 kV/cm and remanent polarization of 1.5 μC/cm2. The abnormal properties can be attributed to the significant increasing content of grain boundary in nanocrystalline potassium sodium niobate ceramics, and it can be expected that if potassium sodium niobate ceramic has the critical size at room temperature, it would be less than 40 nm.
|
|
|
Effect of Reynolds Number of Molten Particle on Splat Formation in Plasma Spraying
CHEN Dan, WANG Yu, BAI Yu, WANG Yun-Hui, ZHAO Lei, Fu Qian-Qian, WANG Hai-Jun, HAN Zhi-Hai
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 65–70
 Abstract
Abstract(
869 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(526KB)(
1385
)
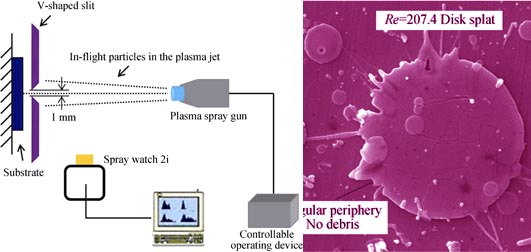
Effect of Reynolds number on the flattening behavior of in-flight particles was investigated by slit method. Molten 6wt%-8wt% yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) particles with different Reynolds numbers were collected. The morphology of splats was examined using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and 3D laser microscope. Meanwhile, the behavior of spreading, heat transfer and solidification of YSZ droplets with different Reynolds numbers were simulated by CFD software Fluent. The results show that the flattening behavior of molten particles is significantly influenced by Reynolds number when Ohnesorge number exceeds 0.2. The splat tends to splash with the increase of Reynolds number. At a lower Reynolds number, the splats exhibit a regular disc-shape. However, when Reynolds number reaches 450±20, splats begin to splash. In addition, for the original molten particles with the same diameters, the flattening ratio of molten particles in supersonic atmospheric plasma spraying (SAPS) is approximately 1.3 times as much as that in atmospheric plasma spraying (APS).
|
|
|
Interconnectivity of Bioceramic Scaffolds with Different Porous Structures and Their Fluid Velocity Distribution Analyzed by Micro-CT Computer Modeling
LUO Pin-Feng, ZHI Wei, ZHANG Jing-Wei, SHI Feng, DUAN Ke, WANG Jian-xin, LU Xiong, WENG Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 71–76
 Abstract
Abstract(
649 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(548KB)(
1404
)
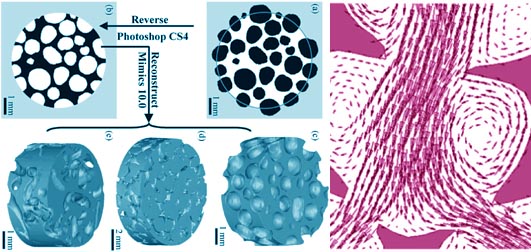
Pore interconnectivity is a key parameter for bone tissue engineering scaffolds, which controls penetration of body fluid with proteins and cells, and tissue ingrowth. The present study investigated the porous characteristics of hydroxyapatite (HA) scaffolds prepared via three processes (HA sphere packing, wax sphere-leaching and HA fiber aggregation) by micro-computed tomography (μCT) from following three procedures: (1) modeling of the porous structure by image reconstruction; (2) analysis of porosity along longitudinal direction; and (3) simulation of fluid flow across the scaffold by finite element analysis (FEA). Image analyses revealed that, the scaffolds prepared by the above two methods featured relatively regular porosity distributions, whereas that by HA fiber aggregation had an irregular distribution. Fluid velocity distribution by FEA suggested that scaffolds prepared by HA sphere packing and wax sphere leaching readily allowed penetration of fluid due to their favorable pore interconnectivity. The fluid velocity vector distribution predicted that circular flows dominated near the pore wall in the scaffold prepared by wax sphere leaching. These circular flows may impede the material exchange between cells attached to the pore wall and the body fluid, which may illustrate that the inferior in vivo osteogenic activity of scaffolds prepared by wax sphere leaching when compared with those produced by HA sphere packing.
|
|
|
Synthesis of ZrN Nanopowder via Soft Urea Pathway
MA Xi-Fei, KANG Zhuang, HUANG Xiao, ZHANG Guo-Jun
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 77–80
 Abstract
Abstract(
1015 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(424KB)(
1533
)
High pure ZrN nanopowder was synthesized from Z-U or ZO-U precusors by using ZrCl4 and ZrOCl2·8H2O as zirconium source, urea as solid N source. The preceramic precursors characterized by FT-IR were prepared via coordination between zirconium ions and urea molecules. Both precursors were further pyrolyzed at relatively low temperatures to yield ZrN. XRD and SEM techniques were used to examine the microstructures of the ceramic powders, while TG-DTA was used to study the pyrolysis process. It appears that the crystal water has strong effect on the coordination chemistry of Zr ions, resulting in obvious differences in molecular structures of two precursors. Such structural differences have strong effects on purity and morphologies of the as-prepared ZrN nanopowder. Apparently, the Z-U precursor from ZrCl4 is more liable to acquire high pure ZrN nanopowder.
|
|
|
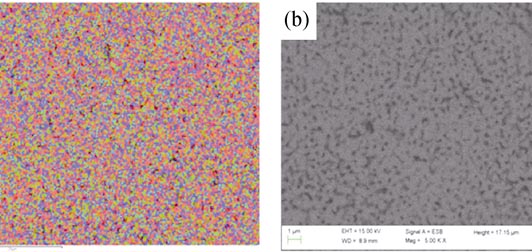
Synthesis and Characterization of Thorium-doped Nd2Zr2O7 Pyrochlore
WANG Lie-Lin, XIE Hua, CHEN Qing-Yun, WANG Qian, LONG Yong, DENG Chao, ZHANG Ke-Xin
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 81–86
 Abstract
Abstract(
689 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(456KB)(
1478
)
A2Zr2O7 zirconate pyrochlores are proposed as potential host phases for the immobilization of high level nuclear waste because of their chemical and radiation stabilities. Thorium-doped pyrochlore Nd1.8Th0.2Zr2O7.1 was synthesized at 1200℃ for 12 h by citrate polymer precursor method using zirconium nitrate, thorium nitrate, neodymium nitrate and citrate acid as raw materials. The phase compositions of the products were characterized by XRD, SEM, FT-IR and Raman spectrum. The results reveal that neodymium ions are substituted by thorium ions at the A position of A2Zr2O7, which maintain the single pyrochlore structure. The lattice parameter decreases for Nd2Zr2O7 pyrochlore with the addition of 20at% Th because the effective ionic radius of Th4+ is less than that of Nd3+. The mean grain sizes of these samples are about 50 nm and the bulk densities are more than 95% of theoretical values. With thorium content increase, the degree of structural disorder in Nd1.8Th0.2Zr2O7.1 pyrochlore increases.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Visible-light Photocatalytic Activities of Bi2Sn2O7
GAO Er-Ping, WANG Wen-Zhong
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 87–92
 Abstract
Abstract(
885 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(564KB)(
1652
)
Bi2Sn2O7 photocatalysts with rods and microspheres composed of particles were successfully synthesized via a facile hydrothermal route. Adding order change of the raw materials resulted in different forms of nucleation, thus affected the final morphology of the products. The as-prepared Bi2Sn2O7 was a special kind of complex oxide with pyrochlore structure, which possessed visible photocatalytic performance with the band gap of 2.61 eV. Photocatalytic activities of the products were evaluated by degradation of RhB under visible light. Bi2Sn2O7 exhibited high Photocatalytic activities with degradation rate of 98% within 100 min. Particularly, microsphere shaped Bi2Sn2O7 composed of particles possessed higher photocatalytic activities. Under condition of different free radicals quenchers, ·O2- and h+ were recognized as primary active species responsible for RhB degradation.
|
|
|
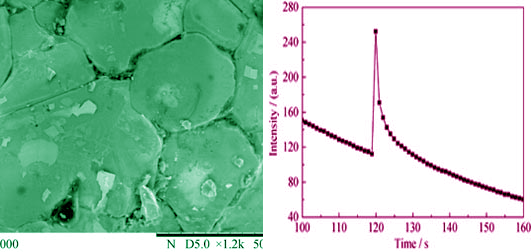
Mechanoluminescence of Persistent Luminescent SrAl2O4: (Eu2+, Dy3+) Material Prepared by Electron Beam Reduction
SHEN Dong-Dong, JI Zhen-Guo
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 93–96
 Abstract
Abstract(
758 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(377KB)(
1549
)
Long persistent luminescent SrAl2O4: (Eu2+, Dy3+) was prepared by electron beam reduction. The as- prepared material was mechanically ball-milled into fine powder, and the powder was mixed with wear resistant epoxy resin. Then, the epoxy resin mixed persistent luminescent was coated on quartz glass plate by screen printing with thickness of about 1000 nm. The mechanoluminescent properties of the as-persistent luminescence film was characterized by falling ball impact technique with a homemade device for measuring mechanoluminescence intensity based on a single avalanche diode and a pico-amper meter. It is found that electron beam reduced SrAl2O4: (Eu2+, Dy3+) shows strong mechanoluminescence with high signal/background ratio of 1.25 and high signal/noise ratio. Further study found that intensity of the mechanoluminescence produced was proportional to exponential of the initial height of the ball (i.e., the final kinetic energy of the ball before impact) before falling down, and a decay curve was similar to that of persistent photoluminescence. These results indicate that mechanoluminescence is caused by impact energy of the ball which promotes electrons into traps, and then release via normal long persistent luminescent.
|
|
|
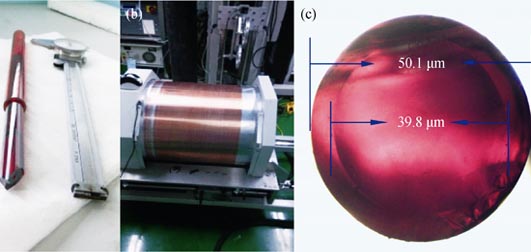
Preparation and Applications of Low-loss As-S Chalcogenide Glass Fibers
XU Yan-Tao, GUO Hai-Tao, YAN Xing-Tao, LU Min, LIN Ao-Xiang, LI Fu, YANG Jian-Feng, ZHAN Huan
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 97–101
 Abstract
Abstract(
656 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(415KB)(
1326
)
High-purity As-S glasses were prepared by repetitive distillation and open-type dynamic distillation methods. The intensities of impurities’ absorptions were obviously reduced at 2.9 μm, 4 μm and 6.3 μm. Chalcogenide glass tubes with precise wall thickness and fine surface properties were prepared by tube-rotating technique and the fibers with core of 40 μm, cladding of 50 μm and error of 1% in diameter were drawn by rod-in-tube method. The fiber had good mechanical and optical performances, which general optical loss was less than 0.5 dB/m and the bending radius was less than 4 mm based on the bending test. The line-plane-switching fiber bundle which format was 64×9 quadrate array to implement 192×3 linear array was made from these chalcogenide glass and long-array infrared push-broom image was successfully demonstrated. The results prove that the fibers and bundle have excellent properties and push-broom infrared system based on the line-plane-switching fiber bundle being feasibility.
|
|
|
Effect of Carbon Content on Mechanical Properties of SiC/B4C Prepared by Reaction Sintering
GAO Xiao-Ju, CAO Jian-Wu, CHENG Lai-Fei, YAN Dong-Ming, ZHANG Cong, MAN Peng
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 102–106
 Abstract
Abstract(
631 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(392KB)(
1395
)
SiC/B4C composite was obtained by reaction sintering with Si infiltration, and the effects of carbon content on mechanical properties and the microstructure were investigated. The results showed that the mechanical properties of the SiC/B4C composite improved firstly and then worsened with increasing carbon content. The optimum comprehensive properties of the composite were obtained by addition of 10vol% carbon. The hardness, bending strength, and fracture toughness of the composite were 19.63 GPa, 358 MPa and 3.96 MPa·m1/2, respectively. In addition, at carbon levels below 10vol%, the microstructure became more uniform as the carbon content increased. However, at carbon levels above 10vol%, the addition of carbon led to a fracture mode transformation, from combination of intergranular and transgranular to transgranular, which contributed to a change in the mechanical properties of the SiC/B4C composite.
|
|
|
Large-scale Fabrication of Tellurium Nanowire Arrays by Magnetron Sputtering with Controllable Morphology
ZHANG Zhi-Wei, DENG Yuan
2015 Vol. 30 (1): 107–112
 Abstract
Abstract(
840 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
1465
)
A convenient template-free magnetron sputtering method was employed for fabrication of highly ordered single crystalline tellurium nanowire arrays at moderate substrate temperature (200℃). The phase, morphology and microstructure of the as-prepared films were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM). The results indicate that the produced nanowire arrays are composed of single-crystalline Te nanowires, which grow along the [101] direction with needle like morphology. These nanowires have an average diameter of 100 nm and length up to about 1 μm. Working pressure and substrate temperature are both essential for the formation of Te nanowire arrays, which balance the diffusion and growth of Te along [101] direction and (101) plane. The growth mechanism of such nanostructure is proposed, including an absorbing-combining-nucleation-growth process.
|
|