|
|
Progress of Calcium Sulfate and Inorganic Composites for Bone Defect Repair
YANG Guo-Jing, LIN Mian, ZHANG Lei, GOU Zhong-Ru
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 795–803
 Abstract
Abstract(
1247 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(886KB)(
1304
)
Treatments of bone defects caused by trauma, tumor and arthroplasty are challenging research area which has aroused great interests among biomaterial researchers to design and fabricate ideal artificial implants. Calcium sulfate has been used as biomedical bone cement for over a century, but its too fast bioresorption limits the applications in some clinical conditions. In this paper, its physicochemical properties, crystal polymorph and synthetic techniques are summarized. Furthermore, the recent research progress on calcium sulfate-based inorganic composite with hydroxyapatite, bioactive glasses, calcium phosphate cements and calcium silicate cements are reviewed. In addition, the development perspective on overcoming the shortcomings of calcium sulfate-base biomaterials is also discussed.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Translucent Hydroxyapatite Ceramics with Different Forms by Sol-Gel Method
LUO Hui-Tao, GUO Tai-Lin, ZHU De-Gui, ZHI Wei, DUAN Ke, ZHANG Cheng-Dong, QU Shu-Xin, WENG Jie
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 804–810
 Abstract
Abstract(
939 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(5534KB)(
1063
)
In order to fabricate translucent hydroxyapatite ceramics with different forms, using micro-sized HA powders as the raw material and chitin as adhesive, the ceramic green was prepared by Sol-Gel method. Subsequently, pure HA ceramics were obtained by normal pressure sintering. Translucent HA ceramics were then fabricated via hot isostatic pressing (HIP) sintering. The Sol-Gel method is easy to obtain shaped ceramic products. The so-produced HA ceramic spheres with a good sphericity and the HA ceramic fibers with a high aspect ratio have the density of 99.1% and the average grain size of 2.2 μm. Compressive strength of translucent HA ceramic spheres is 10.2 MPa whith It is higher than that of conventionally-sintered dense and porous HA ceramic spheres (8.9 and 4.7 MPa, respectively). Results of biomimetic mineralization and cell culture show that translucent HA ceramics have good biocompatibility.
|
|
|
Structural and Mechanical Properties of Composite Scaffolds Based on Nano-hydroxyapatite and Polyurethane of Alcoholized Castor Oil
LI Li-Mei, ZUO Yi, DU Jing-Jing, LI Ji-Dong, SUN Bin, LI Yu-Bao
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 811–817
 Abstract
Abstract(
894 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(948KB)(
1127
)
The interfacial interaction between two phases and homogeneous dispersion of inorganic phase in the organic matrix are critical factors for composite scaffolds with good structure and properties. Based on the modified soft-segment (alcoholized castor oil, ACO) of polyurethane (PU) and nano-hydroxyapatite (n-HA), porous n-HA/PU composite scaffolds were fabricated with in situ foaming method by controlling the process technology in this study. The results demonstrate that there exists good interfacial interaction between PU polymer matrix and polar n-HA due to increased hydroxyl number of modified polyurethane. Moreover, the n-HA filler can homogeneously disperse among the matrix and the miscibility is also dramatically improved. The micropore size of scaffolds is uniform, while the porosity, pore sizes and crystallinity are slightly decreased. FTIR and XRD analyses reveal that there are a large amount of hydrogen bond and chemical linkages between n-HA and ACO-PU matrix, which enhance the miscibility and stability of organic and inorganic phases. Correspondingly, the compressive strength and compressive modulus of scaffolds are significantly improved by alcoholized polyurethane and the uniformly dispersed n-HA particles. The nanocomposite scaffold can be used for further researches on regenerative medicine and bone tissue engineering.
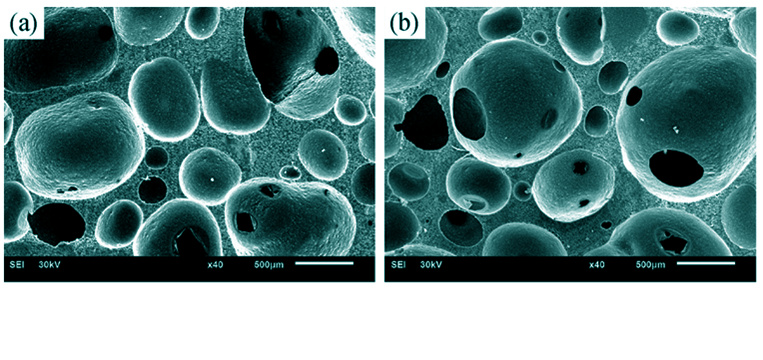
|
|
|
Effect of Fuel Amount on Synthesis of Gd0.8Sr0.2CoO3-δ Cathode Material by Glycine-nitrate Process
WANG Huan, ZHANG Hua, JIN Hong-Jian, ZHAO Wen-Wen
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 818–824
 Abstract
Abstract(
681 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(489KB)(
936
)
Gd0.8Sr0.2CoO3-δ (GSC) nano-powders as cathode materials were synthesized by glycine-nitrate process (GNP) with different glycine-to-metal ratios (G/M=1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5). The performance of GSC cathode calcined at different temperatures was characterized by XRD, SEM and AC impedance spectra. The actual flame temperatures of combustion measured ranging from 850℃ to 1150℃. The flame temperature for the sample of G/M 2.5 is the highest because of the most sufficient combustion which is in agreement with the calculation result of the ideal stoichiometric ratio (φ=1). Meanwhile, the fluffy foamy powder is obtained with fine grain size. Analysis of the AC impedance spectra shows that the area specific resistance (ASR) between GSC-2.5 cathode prepared at 1100℃ and Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 (SDC) electrolyte is mere 0.119 Ω·cm2. The electrical conductivity value of Gd0.8Sr0.2CoO3-δ cathode is higher than 100 S/cm in the temperature range from 500℃ to 800℃, which implies that GSC could be a promising cathode material for IT-SOFC.
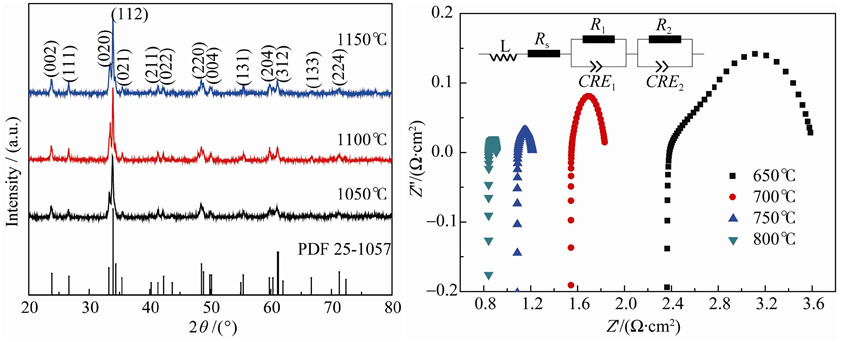
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Capacity of MnO2/SMWCNT/PANI Ternary Composites
XIAO Xing-Zhong, YI Qing-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 825–830
 Abstract
Abstract(
754 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(662KB)(
1068
)
Binary MnO2/acidified multi-walled carbon nanotube (SMWCNT) and ternary MnO2/SMWCNT/ polyaniline (PANI) composites were prepared by liquid-phase precipitation method. SEM images show that the morphology of the materials presents a typical porous structure. The electrochemical capacitive performance of the prepared samples in 0.1 mol/L K2SO4 solution was investigated by cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge/discharge tests. The binary MnO2/SMWCNT composites exhibits improved capacitance compared with the SMWCNT. Further, the ternary MnO2/SMWCNT/PANI composites display quasi-rectangular voltammogram shapes and high capacitor properties. The sample with the mass ratio of MnO2:SMWCNT:PANI=1:1:0.4 displays the best performance in all electrode materials. The specific capacitance of the sample reaches 318.6 F/g at the current density of 0.1 A/g, and its oxidation current density reaches 6.02 A/g. 92.7% current value is maintained after 100 cycles. The high electrochemical capacitors of the ternary MnO2/SMWCNT/PANI composites may be ascribed to their porous morphological structure and well-dispersed MnO2 particles on SMWCNT and PANI.
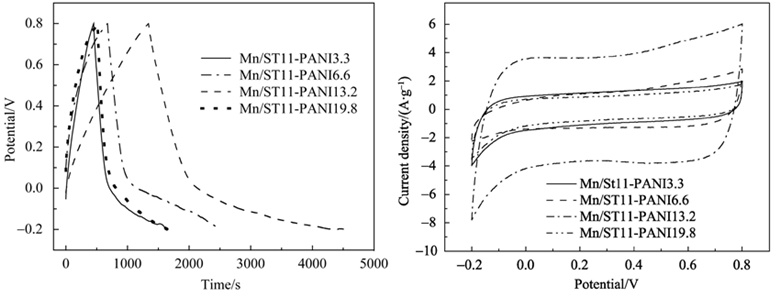
|
|
|
MoS2 Being Used as Negative Electrode for Asymmetric Electrochemical Capacitors
ZHAO Li-Ping, WANG Hong-Yu, QI Li
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 831–835
 Abstract
Abstract(
986 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(399KB)(
1219
)
MoS2 was adopted as a negative electrode material for the asymmetric electrochemical capacitors of MoS2/activated carbon (AC) using Li+-based organic electrolytes. This type of capacitors possesses the working voltage as high as 3.4 V. The physical properties of the negative electrode were characterized by XRD and SEM, etc. The charge storage mechanism at the negative electrode was studied and the effect of weight ratio of AC/MoS2 was investigated. The electrochemical performance tests reveal that the capacitors have relatively high energy density and power density, i.e., 28.7 Wh/kg and 1203.4 W/kg, respectively. The capacitors also show good cycle stability, displaying a 76.6% capacity retention after 1000 cycles at current density of 0.4 A/g.
|
|
|
PAN-based Activated Carbon Fiber/SnO2 Negative Electrodes for Lithium-ion Batteries
WANG Su-Qing, ZHANG Xue-Jun, TIAN Yan-Hong, Zhang Li, LI Ya-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 836–840
 Abstract
Abstract(
1090 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(555KB)(
1011
)
PAN-ACF/SnO2 composites were synthesized by a Sol-Gel method using SnCl2 and polyacrylonitrile- based activated carbon fiber (PAN-ACF) as raw materials, and electrochemical performance of the composites as negative electrodes for lithium ion batteries was investigated. The chemical composition and micro-structure of the composites were examined with X-ray diffraction (XRD). The structure features of PAN-ACF and PAN-ACF/SnO2 composites were analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The mass fraction of SnO2 was determined by thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA). The electrochemical properties of the composites were evaluated by galvanostatic charge-discharge, electrochemical impedance spectrum (EIS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV). The results indicate that SnO2 mass fraction in the PAN-ACF/SnO2 composites has certain influence on the morphology, structure and electrochemical performance of the product. The SnO2 in the composites has a tetragonal rutile structure with lattice constants of a = 0.4739 nm and c = 0.3181 nm. There are no obvious changes happened on the surface of PAN-ACF after charging and discharging process. When the composites are used as negative material for lithium ion batteries, the initial discharge capacity of composites with SnO2 mass fraction of 41.9% is up to 1824 mAh/g at current density of 50 mA/g, which remains 450 mAh/g after 20 cycles and tends to be stable, showing a good cycling performance.
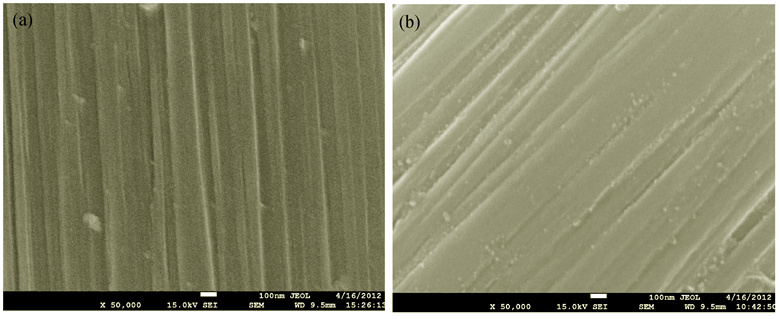
|
|
|
Theoretical Research on Optimization Dopant Regulation of La2BO4(B: B-site Element) Series Mixed Conductor Materials
REN Yu-Mei, CHEN Ning, ZHAO Hai-Lei, WANG Li-Jun, LI Fu-Sen
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 841–846
 Abstract
Abstract(
771 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1181KB)(
1013
)
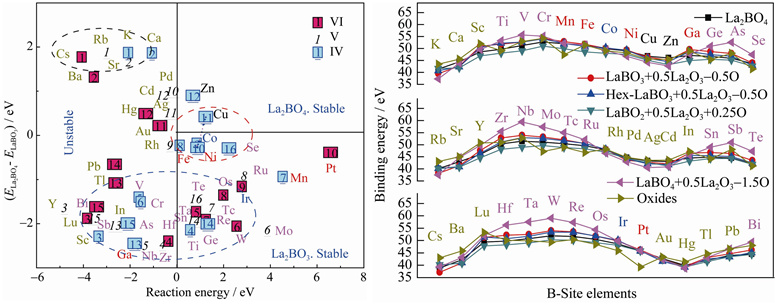
Following the current MGI (Material Genome Interactive) movement and based on the first-principles Density Functional Theory(DFT) calculation method, the K2NiF4 type La2BO4 as well as some other related virtual phases were calculated with B-site elements changed from the 4th to 6th periods. The total energy of these related virtual phases was obtained by geometry optimization task. By comparing the binding energy of virtual phases between the layered La2BO4 and the cubic LaBO3, the influence of several important B-site elements (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and Se) on structure stability of La2BO4 compounds was discussed. The results show that Cu is beneficial to the stability of La2BO4 phase, but not for Co, Ni and Fe elements in their synthesis process, and Fe was even trended to decompose to binary oxides. According to sufficient experimental data, the optimized stable area of B-doped elements was found. This results is helpful for studying the B-doped ingredient optimization of synthesis for solid oxide fuel cells materials.
|
|
|
Co-precipitation Synthesis and Thermal Stability of Zircon Encapsulated Carbon Black
PENG Cheng, ZHANG Chu-Xin, L? Ming, LI Zhi-Hong, WU Jian-Qing
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 847–852
 Abstract
Abstract(
946 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(4281KB)(
908
)
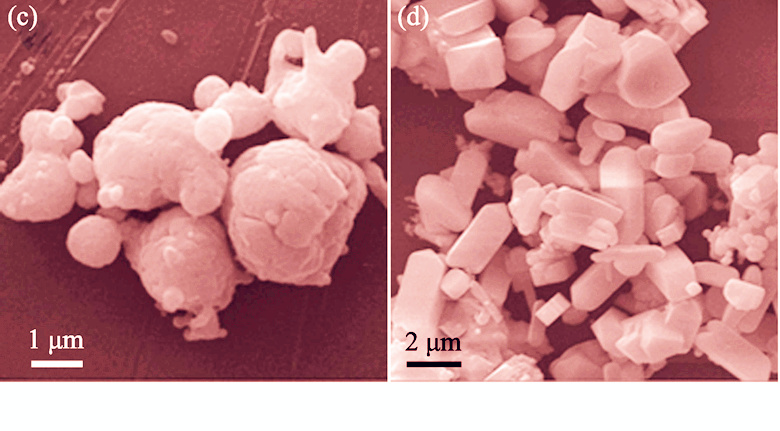
Zircon encapsulated carbon black powders were synthesized by a co-precipitation method using TEOS and zirconium oxychloride as starting materials. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electronic microscope (SEM), colorimeter and laser grain size analyzer were used to investigate the phase structure, morphology, thermal stability and size distribution of the prepared composite powders, respectively. The effect of experimental conditions including the pH of the precursor solution, the calcination temperature, the type and amount of mineralizers on their thermal stability was studied by orthogonal test. The optimal conditions were accordingly determined as follows: precursor solution pH=5, calcination temperature 1150℃ and 5% LiF mineralizer. Under these conditions, zircon encapsulated carbon black with embedded structures can be obtained. The composite powder has high thermal stability and adequate size distribution, and thus it is a good candidate material for black ceramic pigment. When calcined at 1000℃ in the frit glaze, the powder shows considerable tilting strength.
|
|
|
Degradation Behaviour of C/C composites by Atomic Oxygen Irradiation
TIAN Cong, CHENG Lai-Fei, LUAN Xin-Gang
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 853–858
 Abstract
Abstract(
662 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(6377KB)(
1105
)
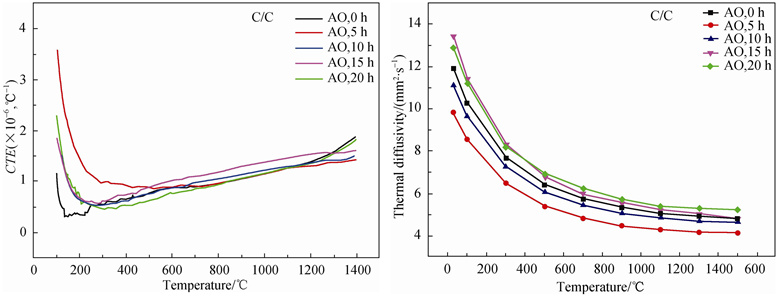
Erosion mechanisms of C/C composite and C/C-SiC composite (matrix modification for C/C composite using SiC) irradiated by atomic oxygen (AO) were studied by analyzing erosion morphology and mass loss rate. Thermal diffusivity coefficient, thermal expansion coefficient and flexural strength were determined before and after AO exposure test to discuss thermal physics and mechanics of AO damage. The results show that the erosion of C/C composite is the cooperation of chemical oxidation and mechanical erosion, which can be termed bombardment-induced surface chemical etching. The SiC components show good resistance to atomic oxygen erosion and hinder internal erosion. However, SiC components can also be damaged mechanically as the exposure time increasing. The mass loss rate of C/C composite is approximately proportional to the exposure time, while the mass loss rate of C/C-SiC composite is smaller than that of C/C composites and the increase of the mass loss rate slows down as the exposure time increasing. The changes of thermophysical property and mechanical property show that the overall performances of C/C and C/C-SiC have been changed to some extent after the AO exposure testing.
|
|
|
Structure and Property of Micro-arc Oxidation Coating Modified by Laser Melting and Solidifying on Aluminum Alloy
YU Jie, WEI Dong-Bo, WANG Yan, Lü Peng-Xiang, DI Shi-Chun
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 859–863
 Abstract
Abstract(
896 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(5346KB)(
997
)
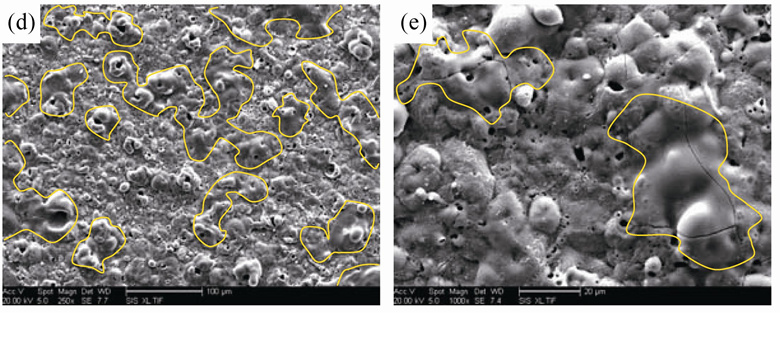
In order to improve performance and microstructure of micro-arc oxidation (MAO) coating, especially loose and porous characteristic, a laser melting and solidifying process (LSM) was introduced. Two kinds of samples were prepared: (1) MAO coatings, 18 μm average thickness, were produced on 6082 aluminum alloy by bipolar current pulse in Na2SiO3-KOH solution. (2) a melting process using a Nd:YAG laser was employed to modify above-mentioned MAO coatings to obtain MAO+LSM coating. Microstructure of two kinds of coatings (MAO coating and MAO+LSM coating) were examined by scanning electron microscopy. X-ray diffraction was used to determine the phase composition of the coatings. Coating hardness was tested by ultra-micro hardness tester, and corrosion performance was investigated by polarization test instrument. The results show that the MAO+LSM coating is composed of dense layer, intermediate layer and melting layer from inside to surface. The loose layer of MAO film is replaced by a dense and low porosity melting layer after LSM treatment. The occupancy of α-Al2O3 phase in MAO+LSM is improved compared with MAO coating. Hardness and anticorrosion performance of MAO+LSM coating are also further strengthened while the remelted coating keeps the same binding manner as MAO coating.
|
|
|
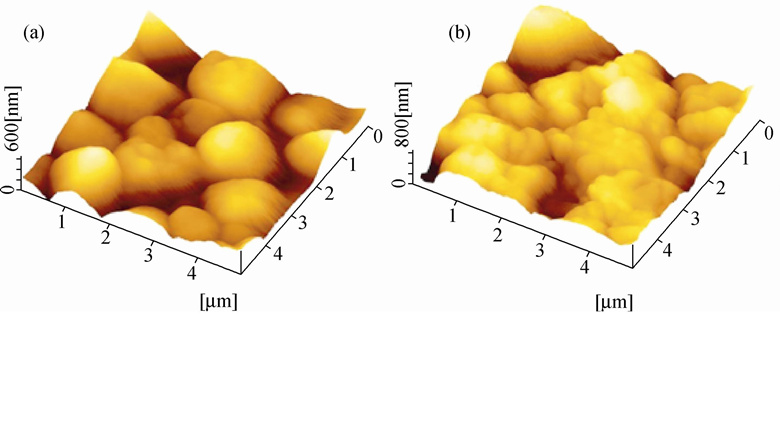
Study on Superhydrophobic Modification of Al2O3 Microfiltration Membrane
HOU Wei-Min, YU Yun, HU Xue-Bing, YU Yang, MI Le, SONG Li-Xin
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 864–868
 Abstract
Abstract(
849 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(725KB)(
1432
)
TiO2 nano-coating with superhydrophobic surface was initially prepared through depositing TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface of porous Al2O3 microfiltration membrane by multi-layer assembly technology, then followed by a fluorination surface treatment with 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane (PFDS). X-ray diffractometer (XRD), fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FTIR), atomic force microscope (AFM), water contact angle measurements (WCA) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) were used for membrane characterization. The crystalline structure of TiO2 nano-coating was analysed. The relationship among TiO2 nanoparticles deposition time, surface roughness and hydrophobicity was discussed. The influence of grafting time on the morphology and hydrophobicity was also researched. The result shows that with TiO2 nano-coating anatase structure is fabricated by annealing at 600℃ for 1 h, With the increase of TiO2 nanoparticles deposition time, the surface becomes rougher, and the state of water droplets on it transforms from Wenzel to Cassie contact. When the TiO2 nanoparticles deposition time is 50 min and the TiO2 coating is grafted for three times, an ideal superhydrophobic surface of micro-nanometer morphology is obtained with water contact angle of 174.5°.
|
|
|
Research for Patterned Sapphire Substrates of GaN-based LEDs
LI Cheng-Cheng, XU Zhi-Mou, SUN Tang-You, WANG Zhi-Hao, WANG Shuang-Bao, ZHANG Xue-Ming, PENG Jing
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 869–874
 Abstract
Abstract(
835 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(9371KB)(
1376
)
Patterned Sapphire Substrate (PSS) which can reduce the density of threading dislocation and enhance the effect of scattering is widely used to fabricate high-power Light-Emitting-Diode (LED) chip. In this paper, the finite- difference time-domain (FDTD) method was used to simulate and analyze the light extraction efficiency (LEE) of GaN-based micro-scale and nano-scale patterned sapphire substrates LED. The results show that the nano-patterned sapphire substrate (NPSS) has a significantly better LEE than that of micro-patterned sapphire substrate (MPSS). And in NPSS, the LEE of the pillar structure improveed 96.6% comparing to other nano-patterned structures. Large areas of table-like nano-sapphire patterned substrates are successfully prepared through soft embossing technology. The photoluminescence (PL) of the LED grown on table-like nano-sapphire patterned substrates is 8 times stronger than that of the LED grown on the unpatterned sapphire wafers.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Property of the Hierarchical Mesoporous ZnO Microspheres
LIU Wen-Kui, ZHOU Wei-Chang, ZHANG Qing-Lin, PAN An-Lian, ZHUANG Xiu-Juan, WAN Qiang
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 875–879
 Abstract
Abstract(
1023 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1264KB)(
1284
)
The zinc hydroxide carbonate (ZHC) precursor was synthesized by hydrothermal method in a autoclave using zinc nitrate hexahydrate, urea and tartaric acid as the source materials. Hierarchical porous ZnO microspheres have been successfully synthesized by calcining the microspheric ZHC. The result of scanning electron microscope (SEM) shows that the as-prepared ZnO microspheres with a diameter between 2-4 μm. The microspheres are assembled by numerous porous nanosheets which have the uniform thickness about 10 nm. The hierarchical ZnO microspheres were further charactered by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM), the results clearly show that the ZnO microspheres exhibit a typical wurtzite structure and are well crystallized. Brunauer-Emmett-Teller(BET) confirms that the ZnO microspheres are hierarchical mesoporous structures, the diameter of mesoporous on the nanosheets are in the range of 20-50 nm. The specific surface area of the ZnO microshperes is about 29.8 m2/g. The photocatalytic activity of the ZnO microspheres was evaluated by photode-gradation reaction of methylene blue (MB). The results show that the hierarchical porous ZnO microspheres exhibit high photocatalytic activity.
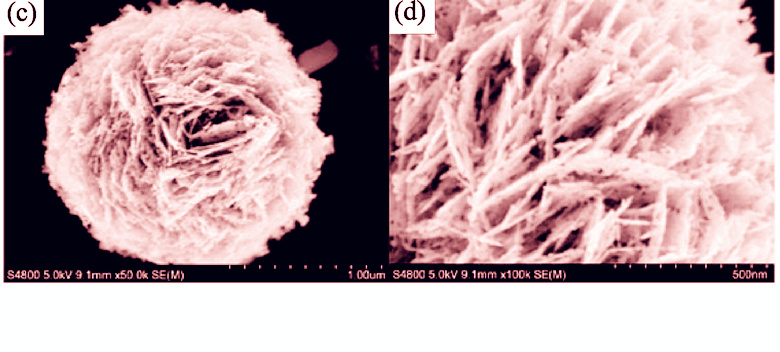
|
|
|
Effects of Fuel on Morphology and Photocatalytic Performance of ZnO Nanorods Synthesized by Solution Combustion Method
LI Jia-Ke, LIU Xin
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 880–884
 Abstract
Abstract(
862 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1034
)
ZnO nanorods was synthesized by solution combustion method using sucrose, citric acid, glycol (or urea) as fuel, and Zn (NO3)2 as oxidant. Effects of fuels (namely sucrose, citric acid, glycol or urea) on phase composition, morphology, specific surface area and photocatalytic performance of as-synthesized ZnO were investigated by means of XRD, SEM, BET and absorption spectrum. The results show that ZnO nanorods (average radial size less than 100?nm) with a hexagonal crystal structure can be synthesized at ignition temperature of 500℃. ZnO owns the best crystallization or the highest specific surface area (24.83 m2/g) when using urea or sucrose as fuel, respectively. Photocatalytic tests show that as-synthesized ZnO using sucrose as fuel owns the best photocatalytic performance. The photodegradation efficiency to methyl orange solution (10 ml/L) is 98.2% under the high-pressure mercury lamp irradiation for 60?min, and the reaction is described as the pseudo first order kinetics equation.
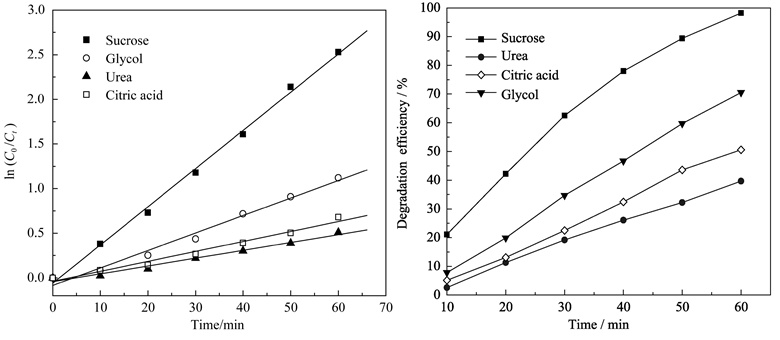
|
|
|
Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of La3Si8O4N11: Ln ( Ln =Ce3+, Sm3+) Nanofibers via Electrospinning
DING Di, WANG Hong-Zhi, LI Yao-Gang, ZHANG Qing-Hong
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 885–890
 Abstract
Abstract(
686 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(937KB)(
1037
)
Ce3+-doped and Sm3+ -doped La3Si8O4N11 nanofibers and microbelts were prepared by the electrospinning. The obtained samples were characterized by XRD, FE-SEM, EDS and PL. XRD patterns of sample nitrided at 1400℃ for 9 h were crystallized well and assigned to JCPDF card of the monoclinic La3Si8O4N11 crystal and the sample maintained La3Si8O4N11 phase after doping Ce3+ or Sm3+ ions. The obtained sample not only keeps the morphology of nanofiber but also assembles as film. Under ultraviolet excitation (343 nm), the emission spectra of Ce3+-doped La3Si8O4N11 sample consists a board peak near 430 nm and a shoulder at 460 nm, it results from Ce3+ 5d-4f transition. The dacay curve of Ce3+-doped La3Si8O4N11 nanofibers exhibits double-exponential decay curve. The fast and slow decay lifetimes of Ce3+-doped La3Si8O4N11 nanofibers are about 8.27 and 32.72 ns. The emission spectra of Sm3+ -doped La3Si8O4N11 shows four sharp peaks situated at 575, 600, 610 and 650?nm when excited at 409 nm results from Sm3+ 4f-4f transition.
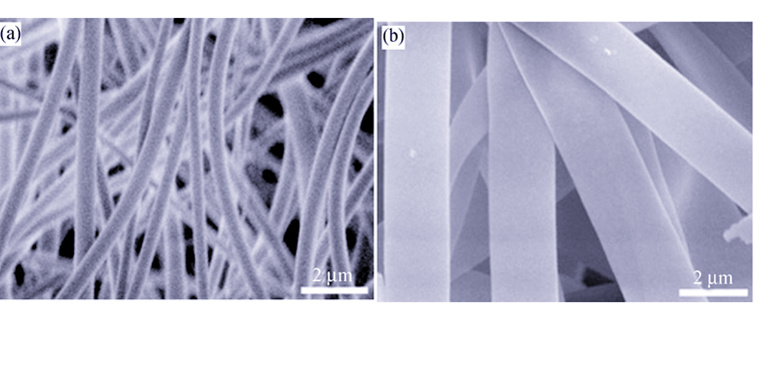
|
|
|
Defect Optical and Scintillation Properties of Lu2Si2O7:Ce Single Crystal Grown by Floating Zone Method
FENG He, REN Guo-Hao, DING Dong-Zhou, LI Huan-Ying, XU Jun, YANG Qiu-Hong, XU Jia-Yue
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 891–895
 Abstract
Abstract(
814 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(3669KB)(
978
)
Floating zone (Fz) method was employed to grow the Lu2Si2O7 (LPS):0.5%Ce single crystal. The crack, defect, optical and scintillation properties of LPS:Ce were studied. The electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), transmittance spectrum, X-ray excited luminescence (XEL) spectra, photoluminescence spectra and decay curves (from 77 K to 500 K) were recorded. The cleavage and thermal stress cracks are detected in the as-grown crystal. Two kinds of inclusions are found through the EPMA: one is [Si3O9]6- and anion radicals and the other is the excess SiO2. Part of Ce3+ in the LPS:Ce sample was oxidized into Ce4+ in the air growth atmosphere. Fz grown LPS:0.5%Ce sample presents high luminescence efficiency, which is 32000 ph/MeV. As the temperature increases, the photoluminescence curves move towards the longer wavelength direction and broaden, leading to the increasing self-absorption. The rollover point of the decay time locates at 450 K, indicating that the LPS:Ce scintillator is a kind of high performance scintillator which can be applied in the high temperature environment.
|
|
|
Preparation and Upconversion Luminescence of Nd3+/Yb3+ Co-doped La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2 Glass-ceramics
ZHANG Ming-Hui, YU Jian-Ding, PAN Xiu-Hong, CHENG Yu-Xing, LIU Yan
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 896–900
 Abstract
Abstract(
1620 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(566KB)(
1580
)
Nd3+/Yb3+ co-doped La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2 glass-ceramic samples were prepared by heat treatment of precursor glasses fabricated via aerodynamic levitation method. The thermal stability of the precursor glass was studied by DTA. The glass-ceramic samples were characterized by photoluminescence spectra, TEM and EDS. The effects of heat treatment on the upconversion luminescence were studied. The DTA curve shows that the glass transition temperature and the onset temperature of crystallization are 799℃ and 880℃, respectively. Five emission bands centered at 497, 523, 545, 603 and 657 nm are obtained at the excitation of 980 nm laser. The emission intensity can be increased by heat treatment. The glass-ceramic samples heat-treated at 880℃ for 50 min perform the strongest upconversion luminescence with intensity (at 545 nm) as 11 times high as that of the precursor glasses, which can be ascribed to the dense columnar crystals embedded in the glass matrix and the enrichment of Nd3+ ions in the crystals.
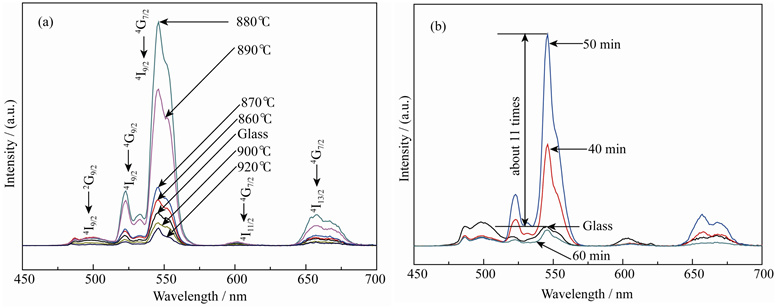
|
|
|
Effect of Surface Topography of Hydroxyapatite on Human Osteosarcoma MG-63 Cell
CHEN Xiao-Qin, CHEN Xue-Ning, ZHU Xiang-Dong, CAI Bing, FAN Hong-Song, ZHANG Xing-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (8): 901–906
 Abstract
Abstract(
1200 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(413KB)(
1405
)
The effect of surface topography of hydroxyapatite (HA) on Human osteosarcoma MG-63 cell lines response was investigated. HA discs with various pore sizes, different pore morphology and distribution were produced by single-axis pressing method. Cell morphology and proliferation were evaluated by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and MTT methods, respectively, and the differentiation potential was assessed by alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity testing and osteogenic gene expression (RT-PCR). The results showed that the HA discs with macroporous structure (>200 μm) would promote cell adhesion and proliferation, while osteogenic differentiation of MG-63 cells was facilitated by the HA discs with micropore structure (<100 μm). Moreover, the differentiation was also influenced by regularity and distribution of the pore. The irregular and alveolate micropore showed a stronger ability of osteogenic induction than smooth and shallow micropore structure.
|
|