|
|
Research Progress on Transition Metal Compound Used as Highly Efficient Counter Electrode of Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
WANG Gui-Qiang, WANG De-Long, KUANG Shuai, ZHUO Shu-Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 907–915
 Abstract
Abstract(
1347 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1146KB)(
1383
)
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSC) has been considered as one of the most promising alternatives to conventional photovoltaic device due to its low cost, simple fabrication process and high conversion efficiency. Pt-loaded conducting substrate has been widely exploited as the standard counter electrode for DSC. However, Pt is expensive and rare, so it is most desirable to seek a low-cost substitute for Pt in counter electrode of DSC. Transition metal compound has been demonstrated to be one of the most promising counter electrode materials for DSCs owing to its low cost, simple fabrication, broad variety of materials and good catalytic activity. This article provides a review of transition metal compound counter electrodes for DSC and a brief outlook on the future development of transition metal compound counter electrodes.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Na-β-Al2O3 Nanopowders by PVP Sol-Gel Process
ZHANG Hao, ZHANG Gao-Xiao, WU Xiang-Wei, WEN Zhao-Yin
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 916–920
 Abstract
Abstract(
815 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(631KB)(
1106
)
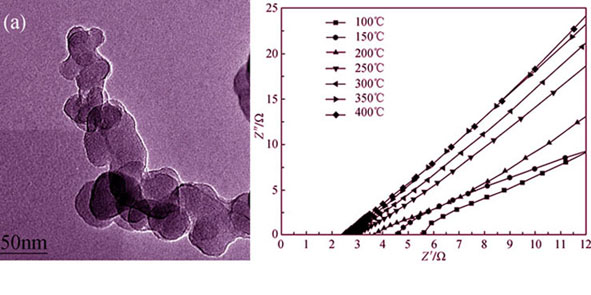
As the key material of the β-Al2O3 electrolyte of sodium sulfur battery(SSB), the properties of Na-β-Al2O3 powders play an important role in the performance of SSB. In this study, nanosized Na-β-Al2O3 powders were prepared by Sol-Gel process with polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) as the chelating agent. The phase formation temperature of the Na-β-Al2O3 by the PVP-based process was reduced to 900℃, which was much lower than those of conventional SSR and most chemical synthesis methods. The new method can effectively inhibit the performance decline of the Na-β-Al2O3 ceramics induced by the volatilization of Na2O at high temperature in the conventional method. The powders were characterized by XRD, SEM and TEM techniques. It was demonstrated that the phase was pure and the particles were well dispersed with diameter of 60-70 nm, which were helpful to the good performance of Na-β-Al2O3 ceramics. In addition, the conductivities of the Na-β-Al2O3 ceramics sintered by the as-prepared powders were measured by AC impedance spectroscope and the evaluation of the spectra was carried out with increasing temperature from room temperature to 350℃. The electrical conductivity of the ceramics at 350℃ reached 0.22 S/cm.
|
|
|
Thermoelectric Properties of Ni-doped ZnO Synthesized by Sol-Gel Processing
WU Zi-Hua, XIE Hua-Qing, ZENG Qing-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 921–924
 Abstract
Abstract(
1253 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(699KB)(
1256
)
Zn1-xNixO nanoparticles were prepared by Sol-Gel processing. Scanning electron microscope observations indicated that nanoparticles were mainly flake structure with many honeycombed passages on the surface of nanoparticles. For the sintered samples, the solubility limit of Ni in the Zn1-xNixO wurtzite structure was found to be 0.05. All doped samples showed n-type semiconducting conductivity. The increase of x led to a significant decrease in absolute value of Seebeck coefficient (|S|). Over the entire temperature range, the thermal conductivity of Zn1-xNixO samples was much lower than that of bulk ZnO sample. The highest ZT (0.045) was obtained for Zn0.925Ni0.075O at 750 K.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of La0.75Sr0.25Mn0.5Cr0.5-xCuxO3-δ for SOFC Anode Material
SUN Lin, LU Jun, YIN Jie-Wei, YIN Yi-Mei, MA Zi-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 925–930
 Abstract
Abstract(
883 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(826KB)(
1050
)
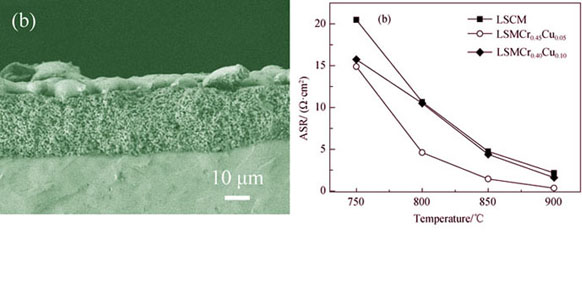
New perovskite oxides La0.75Sr0.25Mn0.5Cr0.5-xCuxO3-δ (LSMCr0.5-xCux, x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.20) were developed as anode materials for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). Phase analysis, chemical compatibility with YSZ electrolyte and microstructure of LSMCr0.5-xCux were characterized by X-Ray diffusion (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM), respectively. The total conductivities of LSMCr0.5-xCux in different atmospheres were measured by four-terminal DC method, and the AC electrochemical impedance spectra measurements were carried out using symmetrical cell method. The as-prepared LSMCr0.5-xCux powders are pure rhombohedral perovskite phase confirmed by XRD, and the size of particles increase with increasing Cu content. No third impurity phase is observed when LSMCr0.5-xCux (x=0, 0.05, 0.10) and YSZ are heat-treated in air at 1200℃ for 3 h, indicating good chemical compatibility between the anode materials and YSZ electrolyte. The total conductivity of doped materials increases remarkably with increasing Cu content in air and in 5% H2-Ar atmosphere. In addition, the impedance spectra show that the ASR (anode surface resistance) value of LSMCr0.5-xCux in wet 5% H2-Ar atmosphere is lower than that of undoped LSCM and reaches the minimum value (0.38 Ω·cm2) at 900℃ when x is 0.05.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Flake Graphite Anode Materials with Slightly Expanded Interlayer
HE Yue-De, JIAN Zhi-Min, LIU Hong-Bo, XIAO Hai-He
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 931–936
 Abstract
Abstract(
876 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(529KB)(
1211
)
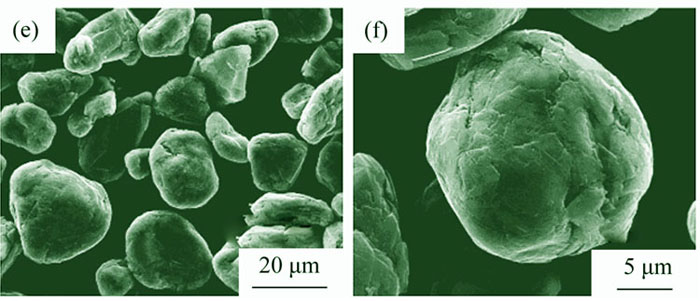
Correlation among preparation method, crystal structure, morphology and electrochemical performance of graphite with a slightly expanded interlayer were investigated. The structure and morphology of the samples were characterized by XRD and SEM analysis, respectively. The specific surface area (BET) and tap density were tested by the related equipments, The electrochemical behavior of the samples was studied using galvanostatic charge/discharge test, cyclic voltammograms, and electrochemical impedance spectra. The results indicate that average interlayer distance d002 of modified graphite expands slightly, and average in-plane crystallite size La and Lc decrease, while spherical graphite particles become smoother. Electrochemical measures show that the initial columbic efficiency of graphite increases from 91.6% to 92.7%, and reversible capacity increases from 345.5 mAh/g to 379.8 mAh/g, while both cycling performance and rate discharge capacity are improved. The intercalation potential of modified graphite is mild increased, lithium-ion can deintercalate from graphite more easily, and the electrochemical reversibility of graphite is improved, compared with that of the raw graphite. The improvement can be ascribed to the reduction of activation energy of deintercalation reaction for modified graphite.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Porous Silicon/Carbon Composite as Negative Electrode Materials
YU Xiao-Lei, YANG Jun, FENG Xue-Jiao, GAO Peng-Fei, WANG Jiu-Lin, NULI Yan-Na
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 937–942
 Abstract
Abstract(
1023 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(680KB)(
1994
)
Lotus root-like porous silicon / carbon composite was synthesized via magnesiothermic reduction and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method, using mesoporous silica SBA-15 as silicon source. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurements were used to study the effects of the raw material ratio, mixing-pressing method and reaction temperature on the phase composition and morphology of the lotus root-like porous silicon. The optimal synthesis condition of porous silicon is that the uniformly mixed precursors with the excess amount of 20wt% Mg powder after ball-milling are directly reacted at 750℃ for 4 h. The electrochemical tests reveal the porous silicon/carbon composite material maintains the reversible capacity of 1633.1 mAh/g at a current density of 0.5 A/g after 70 charge-discharge cycles, and attains 580.1 mAh/g even at 8 A/g.
|
|
|
High-performance SiO/C/G Composite Anode for Lithium Ion Batteries
SHI Chang-Chuan, YANG Xue-Lin, ZHANG Lu-Lu, ZHOU Yong-Tao, WEN Zhao-Yin
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 943–948
 Abstract
Abstract(
1123 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(575KB)(
2196
)
Silicon monoxide/carbon/graphite (SiO/C/G) composite with high capacity and excellent cycling performance has been successfully synthesized via high-energy mechanical milling and followed pyrolysis of silicon monoxide/sucrose/natural graphite mixture. The phase composition and morphology of the samples were characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). Nano-sized (<50 nm) SiO particles were bonded by amorphous carbon and homogenously dispersed on graphite flakes in the as-prepared composite. After 100 cycles, the composite electrode kept a reversible capacity of 1108.9 mAh/g with the capacity retention of 103.8%. Uniform distribution of SiO particles in the amorphous carbon matrix, better buffering effect of carbon matrix and enhanced electrical conductivity are responsible for the superior electrochemical performance.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Carbon Nanotubes/Cobalt Manganese Oxides Composite Materials for Lithium Air Batteries
ZHANG Zhi-An, ZHOU Geng, PENG Bin, LU Hai, JIA Ming, LAI Yan-Qing, LI Jie
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 949–955
 Abstract
Abstract(
958 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(889KB)(
1187
)
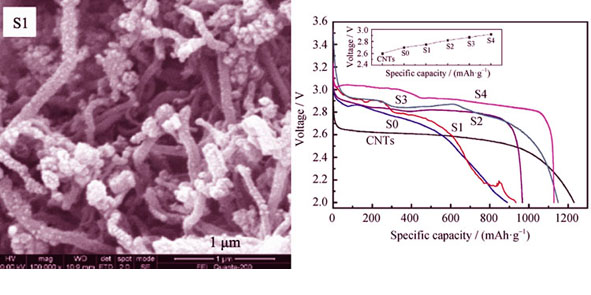
Carbon nanotubes/cobalt manganese oxides composites with different Co/Mn ratios were prepared by precipitation method. The as-prepared products were characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, BET, FT-IR, discharge performance, charge performance and cycle profiles. The results show that the products are CNTs/Co3O4 and CNTs/Mn3O4 when Co/Mn ratios are 4:0 and 0:4, respectively, while CNTs/(Co, Mn)(Co, Mn)2O4 is obtained at Co/Mn ratios of 3:1, 2:2 and 1:3. The products show high dispersion with oxides attaching to CNTs closely, and CNTs/Mn3O4 has the best morphology performance. With increasing content of Mn, the discharge performance improves. CNTs/Mn3O4 has the highest discharge voltage of 2.92 V. For charge processes, the product with higher content of Co reveals better charge properties. The lowest voltage is about 3.8 V. Meanwhile, the product with Co/Mn ratio of 3:1 has a minor charge-discharge voltage difference(△V) of 1.05 V, which still keeps excellent electrochemical performance after 5 charge-discharge cycles.
|
|
|
Effect of Nb5+ -doped YBCO Film Synthesized by Low-fluorine MOD Method
MAO Lei, SUO Hong-Li, LIU Min, ZHANG Zi-Li, YE Shuai, MA Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 956–960
 Abstract
Abstract(
701 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(619KB)(
1011
)
Nb5+-doped YBCO film was fabricated successfully by low-fluorine metal organic deposition (MOD) method. The effective pinning centers in doped film are attributed to Nb-containing nanoparticles with the size of 20-30 nm. Measurement results show that the texture and critical temperature of the doped film are not influenced obviously by the nanoparticles. In addition, a significant enhancement of Jc is observed for YBCO films with nanoparticles compared to that of pure YBCO film by the field dependence of Jc values. The self-field critical current density reaches as high as 3.4 MA/cm2, and the peak pinning force (Fp) of the doped film is greatly increased than the pure one, which reaches at 3.25 GN/m3.
|
|
|
Mechanism of Residual Stresses in Anodic Oxidized Film on Lead Substrate under Electric Field
LI Jian-Zhong, WEI Li-Hua, WANG Bo, SUN Xiu-Li, TIAN Yan-Wen
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 961–966
 Abstract
Abstract(
663 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(938KB)(
934
)
Mechanism of residual stresses generated in anodic oxidized film on lead alloy substrate was investigated using CrO3 solution with the influence of electric field. The stresses formation process, their relationship with surface morphology and structure of oxidation film were discussed in details based on the results of SEM, XRD and Raman tests. It is indicated that Cr2O72- and HCrO4- ions are absorbed on lead alloy surface in the initial formation process of oxidation film. Then PbCrO4 is formed on the interface of Cr2O72- and Pb. HCrO4- oxidizes Pb into PbO under electric field. At the same time, the stresses are generated gradually in the oxide film and increase quickly with current density increase. However, enhanced oxygen evolution promotes the formation of PbO or β-PbO2 with the increase oxidation time. Meanwhile, the growth of crystalline grain for lead oxides is believed to be mismatched with the developing inner stresses, releasing inner stresses, which lead to residual stresses decreasing in oxidation film. The film is cracked because stresses gradient increases remarkably in oxidized film due to the crystal lattice difference in different lead oxides.
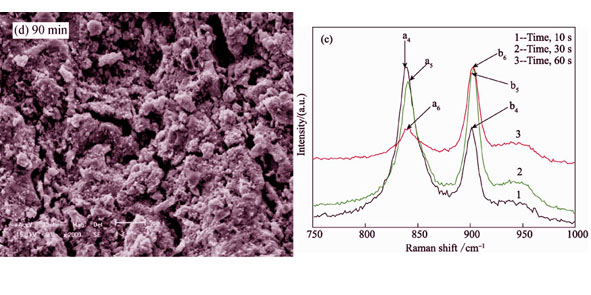
|
|
|
Electrical Properties of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 Lead-free Piezoceramics by Pressureless Sintering
ZHANG Dong-Sheng, TIAN Ai-Fen
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 967–970
 Abstract
Abstract(
963 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(576KB)(
1277
)
Lead-free piezoceramics K0.5Na0.5NbO3 were prepared by pressureless sintering. The effects of sintering temperature on the density and electrical properties of KNN ceramics were investigated. The results show that the density of the KNN ceramics changes dramatically in a narrow temperature range of 1065-1120℃. The density of the ceramic sintered at 1100℃ reaches 4.35 g/cm3 (95% of the theoretical density). The ceramic sintered at 1100℃ shows the best electrical properties: the maximum piezoelectric coefficient of about 118 pC/N, the maximum relative dielectric constant of 538, the minimum dielectric loss of 4.70%, the remanent polarization of 15.37 μC/cm2 and the coercive electric field of 13.16 kV/cm. The phase transformation temperature from orthorhombic to tetragonal is about 206℃, and the Curie temperature is 410℃.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Core-shell SiC/SiO2 Nanowires at Low Temperature
ZHAO Chun-Rong, YANG Juan-Yu, DING Hai-Yang, LU Shi-Gang
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 971–976
 Abstract
Abstract(
879 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(777KB)(
1191
)
Core-shell SiC/SiO2 nanowires were synthesized with formaldehyde resin as the carbon source and SiO2 nano-powder as the silicon source at 1300℃ under argon atmosphere via the carbothermal reduction. The component, morphology and structure of the synthesized core-shell nanowires were systematically studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, transmission electronic microscope, high-resolution transmission electron microscope, and Raman spectroscope. The results show that the synthesized products are high-purity nanowires and it is found that the nanowires are quite uniform. The length of the nanowires can reach several millimeters, and the core-shell SiC/SiO2 nanowires consist of a single crystalline β-SiC core with a diameter of about 30 nm and a uniform amorphous SiO2 outer shell with a thickness of 12 nm. Compared to the single crystalline β-SiC, the emission spectrum from the photoluminescence of the as-synthesized core-shell SiC/SiO2 nanowires has blueshift at room temperature. The formation mechanism of the core-shell SiC/SiO2 nanowires is also discussed. The SiC core is grown in high temperature based on the vapor-solid mechanism. During cooling, the amorphous SiO2 shell is formed by the reaction between SiO and CO gas.
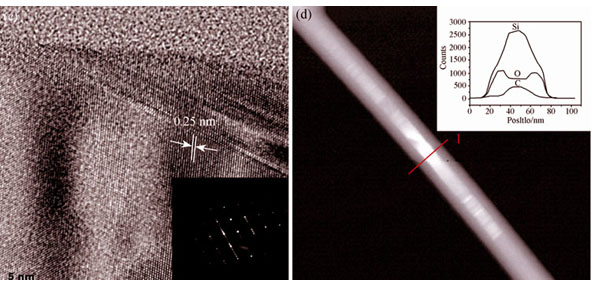
|
|
|
Exchange Coupling in CrPtMn-based Top-pinning Spin Valves
BAI Ru, QIAN Zheng-Hong, LI Jian-Ping, SUN Yu-Cheng, ZHU Hua-Chen, LI Ling-Wei, LI Yuan, HUO De-Xuan, PENG Ying-Zi
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 977–981
 Abstract
Abstract(
756 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(347KB)(
1070
)
The exchange coupling effect between the ferromagnetic pinned layer and antiferromagnetic pinning layer is considered to be one of the key factors for fabricating high performance spin-valves. In this study, the dependence of the exchange coupling field (Hex) in CrPtMn-based spin valves on the deposition pressure and subsequent anneal treatment has been investigated. It is found that the Hex for the as-deposited spin valves changes little by varying the sputtering pressure during the deposition of the CrPtMn pinning layer, and the Hex value is roughly 7.96×103 A/m. However, after the as-deposited spin valves are annealed at 240℃ for 2 h, the Hex correlates and increases with an increase of the sputtering pressure during the CrPtMn deposition. The exchange coupling Hex for annealed spin valves shows good thermal stability with a strength of 2.39×104 A/m at room temperature. The Hex gradually decreases with increasing temperature, and finally disappears at 315℃ which is its blocking temperature.
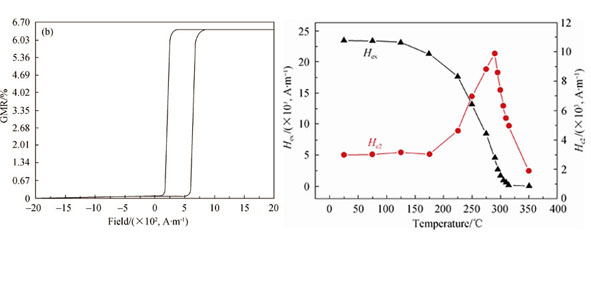
|
|
|
Preparation and Converse Magnetoelectric Effect of AlN/FeCoSiB Magnetoelectric Composite Films
TONG Bei, YANG Xiao-Fei, LIN Geng-Qi, CHEN Shi, OUYANG Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 982–986
 Abstract
Abstract(
960 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(447KB)(
1133
)
AlN/FeCoSiB magnetoelectric (ME) composite films were prepared by RF magnetron sputtering successfully. The influences of annealing on piezoelectric property of AlN film and magnetic property of FeCoSiB film were discussed. The converse magnetoelectric (CME) response was investigated in detail. The results demonstrate that after annealing at 500℃, the AlN film possesses the highly (002) preferred orientation and typical columnar microstructure. Pronounced magnetic field sensitivity of FeCoSiB film is improved greatly through annealing at 300℃. The CME coefficient (αCME) reaches the maximum of 62.5 A/(m·V) at the bias magnetic field (Hdc) of 875 A/m. In addition, the magnetic induction (B) has an excellent linear relationship to the driven AC voltage (Vac) (Linearity of 1.3%). These make the AlN/FeCoSiB ME composite films exhibit promising potential in magnetic and electric field detecting application.
|
|
|
Luminescence Properties of High Y3+-doped Ce:Li6Lu(BO3)3 Scintillators
SUN Dan-Dan, PAN Shang-Ke, REN Guo-Hao, WU Yun-Tao, SHANG Shan-Shan, ZHANG Guo-Qing
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 987–991
 Abstract
Abstract(
693 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(445KB)(
948
)
To decrease the high effective atomic number (Zeff) of Ce:Li6Lu(BO3)3 crystal, Y3+, which has a lower atomic number, is introduced to substitute Lu3+. The Ce:Li6Lu1-xYx(BO3)3(0≤x≤1) solid solutions were prepared by the solid-state synthesis method. Based on the X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) analysis, Ce: Li6Lu1-xYx(BO3)3 (0≤x≤1) solid solutions and Li6Gd(BO3)3 crystal have the similar XRD patterns and belong to the space group P21/c. The luminescence intensity of X-ray stimulated luminescence (XSL) spectrum of Ce:Li6Lu1-xYx(BO3) (0≤x≤1) decreases with the increasing of the content of Y3+. In the case of x=0.5, the Zeff of Ce:Li6Lu0.5Y0.5(BO3)3 is similar to that of Ce:Li6Gd(BO3)3, while the luminescence intensity of Ce:Li6Lu0.5Y0.5(BO3)3 is as much as 1.4 times of Ce:Li6Gd(BO3)3. The XSL and PL spectra of Ce:Li6Lu0.5Y0.5(BO3)3 indicate that the emission band around 400?nm can be fitted into two peaks, 391 nm and 419 nm, which correspond to the electronic transition from 5d energy level to 2F5/2 and 2F7/2 of Ce3+ ions, respectively. The decaying time of Ce:Li6Lu0.5Y0.5(BO3)3 is about 19.6 ns. When x=0.50-0.70, Ce:Li6Lu1-xYx(BO3)3(0≤x≤1) is suitable for using as neutron detection material.
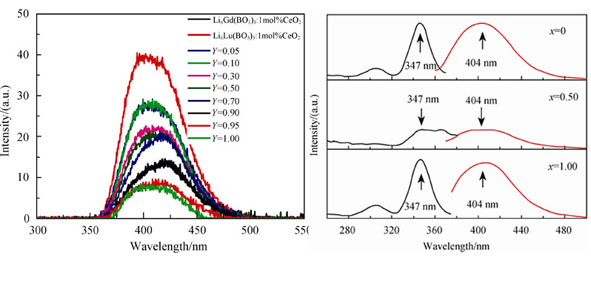
|
|
|
Pd Loaded Mesoporous ZrO2-TiO2 Composite and Its CO Catalytic Oxidation Property
GONG Yun, CHEN Hang-Rong, CUI Xiang-Zhi, JIANG Wan, SHI Jian-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 992–996
 Abstract
Abstract(
686 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(475KB)(
1059
)
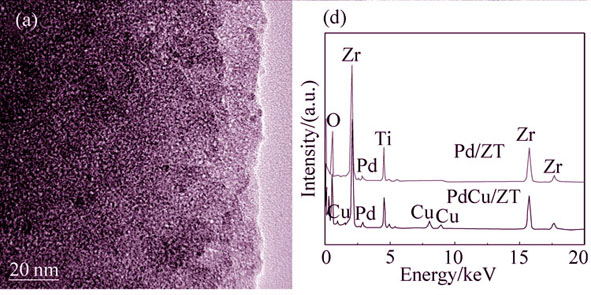
Mesoporous Pd/ZrO2-TiO2 and PdCu/ZrO2-TiO2 composites with high CO catalytic oxidation performance were successfully synthesized by using mesoporous ZrO2-TiO2 as catalyst support. Both XRD and TEM results indicated that the Pd or Cu species could be homogeneously dispersed in the ZrO2-TiO2 support. The effects of different factors on the CO oxidation property were investigated, including the different kinds of catalyst supports, preparation methods and catalytic promoters. It was found that mesoporous ZrO2-TiO2 as the catalyst support exhibited higher catalytic performance for CO oxidation than mesoporous Al2O3 or SBA-15. In addition, the low-temperature catalytic activity of Pd/ZrO2-TiO2 catalyst prepared by one-step route was greatly enhanced in comparison with traditional impregnation method. More importantly, the co-loaded PdCu/ZrO2-TiO2 catalyst via one-step process showed the optimal catalytic activity for CO oxidation, and the corresponding complete conversion temperature reduced to 170℃, which was attributed to the interaction between the Pd and Cu species according to the O2-TPD analysis.
|
|
|
Photocatalytic Properties of Magnetic Activated Carbon Supported F-doped TiO2
LIN Xiao-Xia, JI Xiang, FU De-Gang, HAO Ling-Yun
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 997–1002
 Abstract
Abstract(
938 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(651KB)(
1426
)
Fluorine-doped TiO2 (F-TiO2) prepared by Sol-Gel method was coated on magnetic activated carbon, and the magnetically separable composite photocatalyst (F-TMAC) was synthesized. The prepared samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, UV-Vis, XPS and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The photocatalytic activity was determined by degradation of 100 mg/L reactive brilliant red (X-3B) in a 200 mL aqueous solution with 0.2 g catalyst. The results showed that the photocatalytic activity of such type catalyst was better than that of Degussa P25. The degradation ratio of X-3B was 99.8% under 18 W UV lamp irradiation and 83.1% under 250 W visible lamp irradiation, respectively. Furthermore, the photocatalyst can be separated easily by an external magnetic field with good reuse performance. The degradation ratio of X-3B was decreased by 6% after 5 cycles.
|
|
|
Third-order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Silver Quantum Dots Doped in Sodium Borosilicate Glass
ZHAO Xiu-Li, LIANG Xiao-Juan, LUO Hong-Yan, CHEN Zhao-Ping, XIANG Wei-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1003–1008
 Abstract
Abstract(
708 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(531KB)(
1042
)
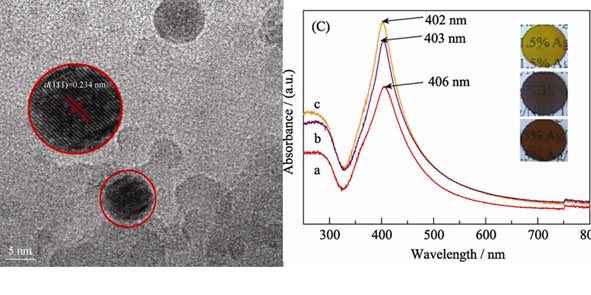
Silver quantum dots doped in sodium borosilicate glass were synthesized through Sol-Gel method using tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), boracic acid, metallic sodium as precursors. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) analyses revealed that silver quantum dots were cubic crystalline phase; size and distribution of the quantum dots were measured by transmission electron microscope (TEM) as well as high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM). The results showed that spherical shape formed uniformly in the glass, and the size of these quantum dots ranged from 5 nm to 13 nm. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectrometer obtained surface plasma resonance (SPR) absorption peaks as that of the Ag quantum dots at about 406 nm. Nonlinear optical properties of silver quantum dots doped glass were investigated by using Z-scan technique at the wavelength of 800 nm with femtosecond Ti: sapphire laser radiation. The values of nonlinear refraction index γ, nonlinear absorption coefficient β and the third-order nonlinear optical susceptibility χ(3) of the glass were estimated to be –1.72×10-17 m2/W, 9.96×10-11 m/W, 1.01×10-11 esu, respectively.
|
|
|
Effect of Carbon Source and Adding Ratio on the Microstructure and Properties of Solid-state Sintering Silicon Carbide
YAO Xiu-Min, LIANG Han-Qin, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1009–1013
 Abstract
Abstract(
786 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(812KB)(
1240
)
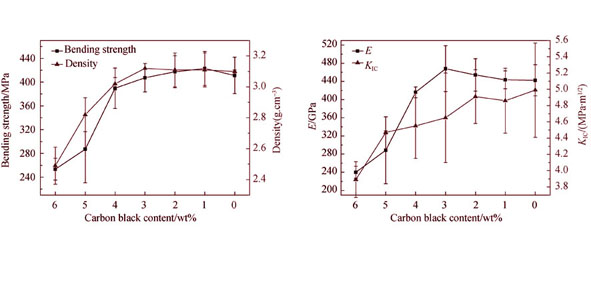
With 6wt% total carbon additive amount, the microstructure and properties of pressureless solid-state sintered SiC(SSiC) were studied with different carbon sources and carbon source adding ratio. It is found that SSiC ceramics with inorganic carbon (carbon black) as carbon source have finer SiC grains and lower density. As the carbon additive amount derived from organic carbon source (phenolic resin) increases, the grain size of SiC grains in SSiC ceramics increases, the distribution of carbon phase in the ceramics is more homogeneous, the density and the mechanical properties of SSiC ceramics increase. When the carbon additive amount derived from organic carbon source is 3.0wt%, the ceramics with highest density have the largest elastic modulus, which is up to 486 GPa, the fracture toughness of it is 4.65 MPa·m1/2. When the carbon additive amount derived from organic carbon source is over 3.0wt%, the abnormal grain growth of SiC grains appears in the ceramics, the fracture strength and toughness further increase. At the same time, the thermal diffusion coefficient of SSiC ceramics with different carbon sources and adding ratio is also discussed.
|
|
|
Ablation Resistance Properties of Ultra-high Temperature Composites C/C-SiC-ZrB2 by Slurry Impregnation Method
FAN Qian-Guo, CUI Hong, YAN Lian-Sheng, ZHANG Qiang, MENG Xiang-Li, YANG Xing
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1014–1018
 Abstract
Abstract(
795 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1019KB)(
1214
)
The ultra-high-temperature composites C/C-SiC-ZrB2 were prepared by slurry impregnation method. The composites consist of the carbon fiber as the reinforced phase, C and SiC as the matrix, and the micro-particle ZrB2 as the ultra high temperature phase. The ablation resistance properties of the composites were assessed by arc wind tunnel testing. The ablation mechanism was studied through XRD, SEM and EDS measurements. The results indicate that compared with C/C-SiC composites, the C/C-SiC-ZrB2 composites show better ablation resistance properties, and the properties increases with the content of ZrB2 increase. A ZrO2-SiO2 glassy melting layer formed at high temperature plays an important role in antioxidant ablation.
|
|
|
Effects of Chromite Additive on the Microstructure and Performance of Bauxite-based Fracturing Proppant
GAO Feng, WU Yao-Peng, LIU Jun, HE Hong-Wei, KANG Li-Tao, LIANG Wei
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1019–1024
 Abstract
Abstract(
855 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(763KB)(
1006
)
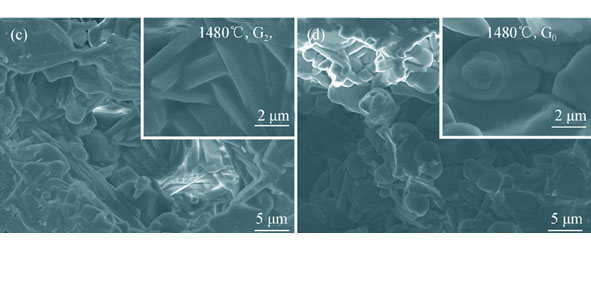
High-strength fracturing proppant was prepared by pressureless sintering process using bauxite (67wt% Al2O3) and chromite as raw materials. The influence of chromite content (0-5wt%) on phase composition, microstructure and breakage ratio were studied by XRD, SEM, EDS and the column compression method, respectively. The results indicate that the additive of chromite promotes the formation of solid solution of chrome-corundum (Al2-2xCr2xO3,0<x<1)and rod-shape mullite phases, both of which are believed to strengthen the fracturing proppant. Additionally, liquid phase is formed by excessive ferrum located between the ceramic grains at relatively high sintering temperatures, which is important for accelerating the sintering densification. The sintering temperature decreases with the addition of chromite. The optimized proppant sample with 2wt% chromite doped, sintered at 1420℃ for 2 h shows a breakage ratio of only 1.8% under the pressure of 69 MPa. Furthermore, 2 wt% chromite doping decreases the sintering temperature by 60℃ (from 1480℃ to 1420℃). This process enables the production of high-strength fracturing proppant from low-rank mineral materials and demonstrates a promising practical application.
|
|
|
Preparation of BIT-layered Double Hydroxide and the Study of Antifungal Properties
ZHANG Yi-Xuan, LI Song-Mei, LIU Jian-Hua, YU Mei
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1025–1032
 Abstract
Abstract(
768 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(834KB)(
1070
)
Mg-Al layered double hydroxides, loaded with 1,2-benzisothiazolin-3-ketone(Mg2Al-BIT LDH), were synthesized via coprecipitation method. The resulting compounds were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscope and scanning electron microscope. Drug release kinetics were studied in the medium with pH at 4.8 and 7.2. The results showed that BIT was successfully inserted into the LDH inter layers, with a drug loading rate of 44.35%。The release kinetics process was in line with the quasi-second-order equation. The results showed that the antifungal effects of BIT were worse than that of Mg2Al-BIT LDHs in the final phase of the mold test due to its consumption, dissolution and precipitation, suggesting Mg2Al-BIT LDHs nano-hybrid a better anti-mildew duration.
|
|
|
Microstructure of Al2O3/Ti-Al Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Aluminum Thermal Reduction Processing
ZHANG Xiao-Wei, LIU Hong-Xi, JIANG Ye-Hua, PHAM THI Hong-Nga
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1033–1039
 Abstract
Abstract(
726 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1054KB)(
1111
)
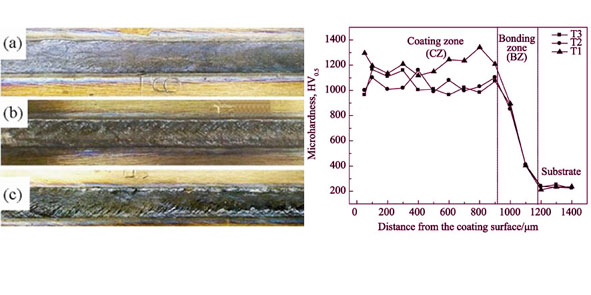
With composite powders of Al and TiO2 systems as reactants, Al2O3 reinforced Ti-Al matrix intermetallic composite coatings were prepared on the TC4 alloy substrate by laser in-situ synthesis processing. The effects of laser power, laser scanning speed and laser spot size on laser energy density were analyzed, respectively. The macroscopic morphology, cross-section microstructure, and micro-hardness of Al2O3/Ti-Al composite coatings were characterized by optical microscope (OM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS) and micro-hardness tester. The results show that scanning speed has the greatest impact on laser energy density firstly, then the laser spot size, and then the weakest is laser power. With the scanning speed increases, Al2O3/Ti-Al composite coatings surface become rougher, “fish-scale shape” morphology are more obvious, and the thickness of bonding-zone decreases. The reinforced phase of composite coating is composed of k-Al2O3 and α-Al2O3, while the matrix phase is composed of α-Ti and α2-Ti3Al. And with the increase of laser scanning speed, k-Al2O3 changes into α-Al2O3 partially. The morphology of Al2O3 reinforcement tends to change from dendrite shape to fiber. The micro-hardness of samples has a smooth transition tendency from the substrate to the coating surface. The micro-hardness distribution of coating cross section is uniform, and the average micro-hardness is significantly higher than that of the substrate.
|
|
|
Characterization of Tritium Retention in Plasma Sprayed B4C/Mo Coatings
LIN Chu-Cheng, ZHU Hui-Ying, MASAO Matsuyama, WANG Hu, HUANG Li-Ping, ZHENG Xue-Bin, ZENG Yi
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1040–1044
 Abstract
Abstract(
1193 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(331KB)(
1435
)
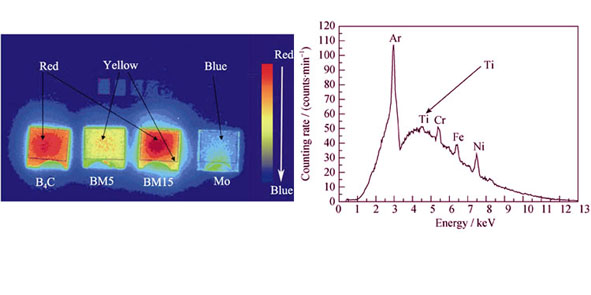
Quantification of the amount and depth of tritium retained on plasma facing materials (PFMs) surface is of great importance for selecting PFMs with high safety in the nuclear system. In the present study, potential PFMs of B4C/Mo coatings were prepared and the depth profiles of tritium in the coatings were measured both by imaging plate (IP) technique and β-ray induced X-ray spectrometry (BIXS). The IP images showed that the amount of adsorbed tritium in the coatings followed the order of B4C > BM15 > BM5 > Mo, which was along with the X-ray spectra also illustrating that most tritium penetrated into the bulk of the B4C coating while on the surface only for the other three coatings. The cross-sectional morphologies of the coatings were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM), which demonstrated that B4C coatings had the highest porosity while the other three coatings were denser despite of the existence of smaller-sized pores and cracks. All the results suggest that pores and microcracks in the as-sprayed coatings provide passageway for tritium penetration and adsorption, which are the key factors that affect the amount of tritium adsorbed. Furthermore, the content of Ti contamination in the coatings also plays an important role in controlling tritium adsorption.
|
|
|
Rapid Low-cost Synthesis and Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Mesoporous Mn3O4 Nanorods
HU Ying-Ying, WEN Zhao-Yin, JIN Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (9): 1045–1050
 Abstract
Abstract(
784 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(475KB)(
1026
)
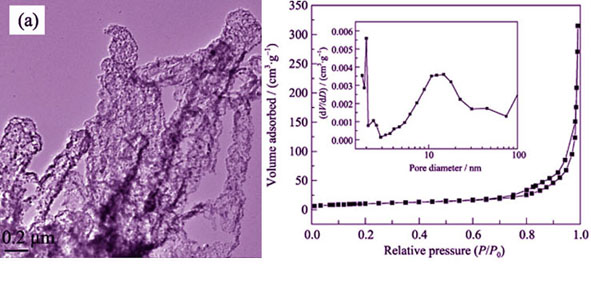
Mesoporous Mn3O4 nanorods, as anode materials for Li-ion batteries, were fabricated by a novel process using only ethanol and manganese acetate tetrahydrate as the reaction precursors. The as-prepared mesoporous Mn3O4 nanorods were characterized by X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry-differential scanning calorimetry, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller surface area analyzer. The results indicate that the average diameter of mesoporous Mn3O4 nanorods is about 150 nm, and their pore size is mainly distributed in the range of 6–20 nm with the BET specific surface area as high as 37.3 m2/g. The Mn3O4 nanorods anode displays reversible capacities of 676.1 and 662.4 mAh/g after 100 cycles at a current rate of 141 mA/g, demonstrating a higher capacity and more stable cyclability than Mn3O4 nano-powders. Furthermore, excellent rate capability is realized with the mesoporous Mn3O4 nanorods. A capacity of 850 mAh/g is retained after 80 cycles at various current densities.
|
|