|
|
Research Progress on Crystal Growth Mechanism of Titania/Titanate Nano-powder Materials
ZHAO Bin, LIN Lin, CHEN Chao, HE Dan-Nong
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 683–690
 Abstract
Abstract(
1088 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(911KB)(
1514
)
Chemical and physical properties of titania/titanate nanomaterials should be strongly influenced by their crystalline phases, grain sizes, morphologies and microstructures. The process of crystal growth contains phase transition and morphological evolution behavior. In this review, the crystal phase transition mechanisms and morphology evolution models were elucidated based on the recent research works of crystal phase and morphology controlled synthesis of titania/titanate nano-powder materials, which included Ostwald Ripening, Ostwald’s step rule, Oriented Attachment Growth, Kirkendall Effect, etc. These phase transition mechanisms and morphology evolution models not only offer explanations for the formation of titania/titanate nano-powder materials with different phases and morphologies, but also give a guidance of phase and morphology controlled synthesis of titania/titanate nano-powder materials.
|
|
|
Preparation of Nano-scaled TiO2-xNx Photocatalyst by PEALD in-situ Doping
RAO Zhi-Peng, WAN Jun, FENG Jia-Heng, LI Chao-Bo, XIA Yang
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 691–695
 Abstract
Abstract(
900 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(513KB)(
1142
)
TiO2-xNx photocatalyst was deposited by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) system using in-situ doping method. X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM), photoluminescence (PL), UV-Vis spectra were used to characterize the photocatalyst, and the variation of water contact angles and photocatalytic decomposition property of TiO2-xNx nano films to methylene orange (MO) solution under visible light were investigated. The results show that the incorporated nitrogen structures could be adjusted by plasma powers, and substitutional atoms are mainly formed in the TiO2 films deposited at the plasma power of 50 W, which is about ~1.22at%. The crystal type is anatase (101). No defect is observed in the TiO2-xNx films, and the recombination rate of the photo-generated electron-hole pairs is lower, which is conducive to the improvement of the photocatalytic efficiency. This method solves the problem of the formation of oxygen vacancies in the classic ALD growth process to prepare TiO2-xNx photocatalysts and the TiO2-xNx nano films realize visible absorption and visible light photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation (λ<800 nm).
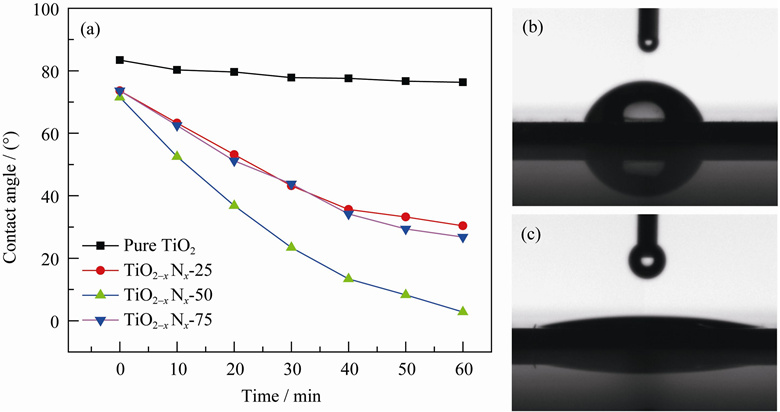
|
|
|
Spectra Properties and Energy Transfer of Bi/Tm Co-doped TiO2-BaO-SiO2-Ga2O3 Glasses
TANG Han, XIA Hai-Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 696–700
 Abstract
Abstract(
573 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(636KB)(
951
)
Bi, Tm singly doped and Bi/Tm co-doped titanate glasses were prepared by the conventional melt quenching method. The enhanced emission of Tm3+: 3H4→3F4 transition at ~1485 nm, and the quenched emission of Tm3+: 3F4→3H6 transition at ~1810 nm were observed in Bi/Tm co-doped glasses under 808 nm excitation. Under 980 nm excitation, no Tm-relevant emission was observed in Tm singly doped glasses, while the emission of Tm3+: 3F4→3H6 transition at ~1810 nm was observed in Bi/Tm co-doped glasses. These results indicated that the energy transfer occurred between active Bi ions and Tm3+ in Bi/Tm co-doped glasses, in which the energy corresponding to Bi-related emission level excited the Tm3+ from 3F4 to the 3H4 level under 808 nm excitation and from 3H6 to the 3H5 level under 980 nm excitation. The energy transfer processes were studied based on the Inokuti-Hirayama model, and the energy transfer of electric dipole-dipole interaction was confirmed to be dominant in Bi/Tm co-doped glasses. The energy transfer efficiency from Bi to Tm ions was estimated to be ~60% from the obtained lifetime of emission. Broadband emission covering 1200-1600 nm indicates Bi/Tm co-doped titanate glasse as potential material for broadband optical fiber amplifiers and tunable lasers.
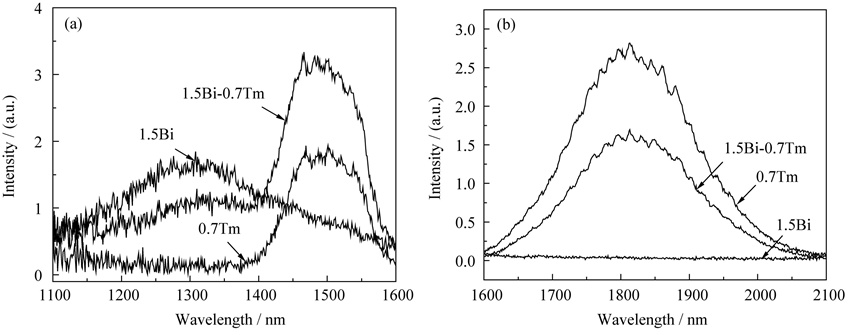
|
|
|
Preparation of Polycrystalline Cu(In,Ga)Se2 Thin Film with Nano-metal Oxide: the Chemical Reaction Process and Its Properties
ZHENG Chun-Man, WEI Yong-Tao, XIE Kai, HAN Yu
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 701–706
 Abstract
Abstract(
714 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(892KB)(
1068
)
Polycrystalline Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS) thin film was prepared by non-vacuum method with nano-metal oxide as starting materials. The evolution of the composition and structure during the preparation process was investigated by field emission scanning electron microscope, high resolution transmission electron microscope, energy dispersive analysis and X-ray diffraction. The properties of CIGS film was characterized using Hall Effect tester and absorption spectroscopic analysis. The results show that the nano-metal oxide is consist of CuO, In2O3, Ga2O3 and copper-indium, copper-gallium binary alloy oxides. The metal oxides gradually transform into Cu11In9 and Cu9In4 during the reduction reaction. Moreover, it forms a large number of pores, which is benefit for the selenide reaction. The selenium vapors enter the film along the pore, react with the reduction product and form CIS and CGS in the selenide process. Then, the polycrystalline CIGS film with the chalcopyrite structure forms. The carrier concentration, mobility and the resistivity of CIGS film are about 2.3×1015 cm-3, 217 cm2/(V·s) and 36 Ω·cm, respectively. The obtained thin film is a p-type semiconductor with a bandgap of about 1.15 eV.
|
|
|
Domain Switching, Retention and Imprint of NBT-KBT100x Piezoelectric Thin Films under Different External Fields
ZHU Zhe, ZHENG Xue-Jun, ZHANG Dan-Shu
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 707–712
 Abstract
Abstract(
661 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(513KB)(
895
)
MOD method was used to prepare (1-x)Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-xK0.5Bi0.5TiO3 (NBT-KBT100x) relaxor piezoelectric thin films. The surface morphology, the initial domain structures, domain switching, retention and imprint of NBT-KBT100x thin films were observed by PFM under different external fields. The results show that the NBT-KBT17 thin film presents the most single domain grains. Moreover, the LPFM phase and amplitude images of NBT-KBT17 thin film are also obtained, which indicates that the piezoelectric response is significant at d31 mode. The single grain with larger size of NBT-KBT17 thin film is selected to write the domain by opposite DC voltages. The written single grain is then placed in environment for different duration to detect the domain evolution and retention of the thin film. Although the depolarization phenomenon is observed in small area, the original domain states are still stable, showing low retention loss. The phase and amplitude-electric voltage hysteresis loops of NBT-KBT17 thin film capacitor are observed by PFM under the mechanical force. The observations indicate that the hysteresis loop and butterfly curve has a migration, which means the imprint is produced by the external force. Finally, the formation mechanism of imprint is explained by space charge principle.

|
|
|
Preparation and Performance of SrCo1-xGaxO3-δ Cathode Materials for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
XIONG Ming-Wen, YIN Yi-Mei, YUAN Xian-Xia, MA Zi-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 713–719
 Abstract
Abstract(
734 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1802KB)(
992
)
Cathode materials of SrCo1-xGaxO3-δ (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFC) were synthesized by an Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetie Acid (EDTA)-citrate complexing method. The obtained samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, thermal expansion measurement, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and the effects of Ga-doping on performance and properties of materials were evaluated. The results show that all the samples have brownmillerite structure. The thermal expansion coefficient (TEC), electrical conductivity and the amount of adsorbed oxygen on the surface of the cathode materials gradually decrease with Ga content increasing. Among the as-abtained samples, SrCo0.8Ga0.2O3-δ shows the lowest area specific resistance (ASR) of 0.73 Ω•cm2 at 600℃, the single-cell with it as cathode demonstrates a maximum power density of 0.484 W/cm2 at 650℃.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Properties of Lithium Ion-sieve Precursor Li4Mn5O12
XU Hui, CHEN Chang-Guo, SONG Ying-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 720–726
 Abstract
Abstract(
960 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(492KB)(
1141
)
Adsorption method is the most promising method for extraction of lithium from salt lakes. A new kind of MnO2 ion-sieves with high Li+ selective adsorption property were synthesized. Spinel-type Li4Mn5O12 precursors were synthesized by EDTA-citrate complexing method using LiNO3 and Mn(NO3)2·4H2O as starting materials. MnO2 ion-sieves with Li+ selective adsorption property were prepared by the acid treatment process to extract Li+ from the spinel Li4Mn5O12 precursors. As-prepared samples were characterized by thermo gravimetric, XRD, SEM, FT-IR and Li+ selective adsorption measurements, respectively. The results show that calcination time has a considerable effect on the structure and composition of precursors. The precursor calcined at 400℃ for 24 h has a pure phase of Li4Mn5O12. Final MnO2 ion-sieve and Li4Mn5O12 precursor are about 200 nm spherical pellets and have the same structure of spinel. The maximum adsorption capacity of ion-sieve is about 43.1 mg/g and has the good selection for Li+.
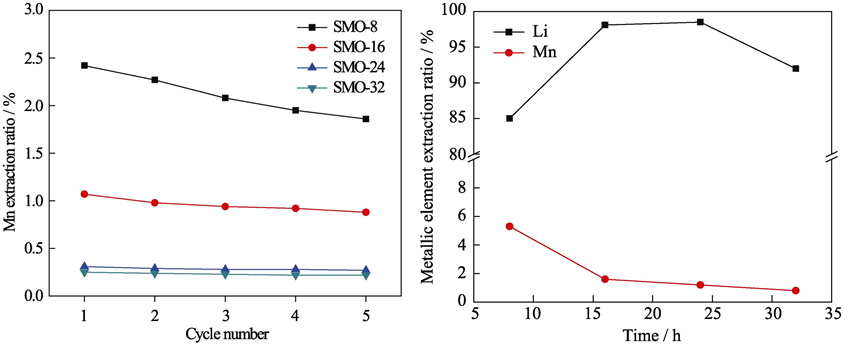
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Ge4+-doping Li4Ti5O12 Anode Material for Li-ion Battery and Its Electrochemical Properties
QIU Cai-Xia, YUAN Zhong-Zhi, LIU Ling, CHENG Si-Jie, LIU Jin-Cheng
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 727–732
 Abstract
Abstract(
1364 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(467KB)(
1340
)
The spinel Li4Ti5-xGexO12 (x=0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15) electrode materials were successfully synthesized by Sol-Gel method using Ti(OC4H9)4, CH3COOLi•2H2O and GeO2 as raw materials. The crystalline structure, morphology and electrochemical properties of the obtained materials were characterized by XRD, SEM, half cell charge-discharge tests, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and AC impedance. The results showed that doping with certain amount of Ge4+ did not change the basic structure of Li4Ti5O12, but greatly affected its mophology and particle size. Ge-doped Li4Ti5O12 has relatively high rate capability due to the smaller particle size. In this study, Li4Ti4.9Ge0.1O12 represented the highest initial discharge capacity and the best cycling performance among all samples. At the charge-discharge rate of 0.2C, its first discharge capacity was 172.43 mAh/g, and at 5C rate, its discharge capacity remained at 140.62 mAh/g after 100 cycles with a capacity retention of 97.3%.
|
|
|
Study on the MoN/Nitrogen-doped Graphene Sheets Composite for Lithium Ion Capacitor Electrode Materials
MA Wen, HAN Peng-Xian, KONG Qing Shan, ZHANG Ke Jun, BI Cai Feng, CUI Guang Lei
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 733–738
 Abstract
Abstract(
863 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(539KB)(
1118
)
Molybdenum nitride/nitrogen-doped graphene sheets (MoN/NGS) composite was prepared via a simple hydrothermal method followed by calcination at 800℃ under ammonia atmosphere. The phase structure and morphology of samples were characterized by XRD and SEM. The electrochemical properties of composite electrodes were studied by performing cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge and discharge, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy test. The MoN/NGS electrode deliveres specific capacitance of 422 F/g at the current density of 0.05 A/g, and its capacitance retention remains more than 80% after 900 cycles. The energy density remains as high as 32.5 Wh/kg when the power density is 3000 W/kg. It should be noted that such improvement should be attributed not only to the presence of NGS in the composite offering an effective conducting network but also to the hybrid structure of MoN/NGS composite providing a favorable and fast ion transport and diffusion.
|
|
|
Electrochemical Capacitance Performance of One-dimensional Nano-α-Co(OH)2 Employing Cobalt-cholate Supramolecular Nanofibers Self-template Method
CAI Long-Cheng, LI Juan, HUANG Jian-Bin
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 739–744
 Abstract
Abstract(
652 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(684KB)(
1139
)
Nano-α-Co(OH)2 was prepared via a facile strategy, in which the cobalt-cholate self-assembled spramolecular nanofibers as self-template were obtained by mixing sodium cholate solution with cobalt nitrate solution, and then the samples were obtained by adding depositing reagents NH3•H2O under ambient conditions. The composition and microstructure of the as-prepared samples were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), infrared spectroscope (FT-IR), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results indicate that the as-prepared materials are pure phase α-Co(OH)2 with one-dimensional nanofiber crossing loose network–like struture whose diameter is 100-200 nm. The electrochemical capacitive properties of the products were investigated using cyclic voltammetry and impedance spectroscopy in 6 mol/L KOH aqueous solution. The specific capacitance is up to 1200 F/g at a constant current charge/discharge test of 1 A/g within 0-0.5 V potential region, and stably keep 75% of initial capacitance after over 800 charge-discharge cycles. Its special nanostructure, with fast electrochemical response property, allows easy penetration of electrolyte and effective utilization of electrode material. This self-templating approach is therefore believed to provide a simple and convenient route to fabricate nanomaterials for application in supercapacitors.
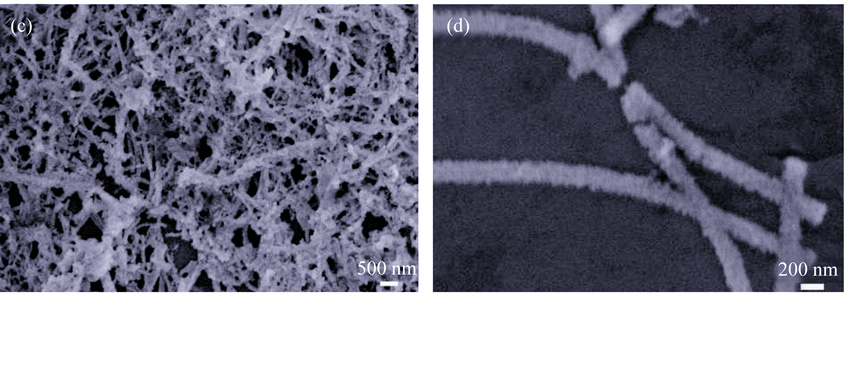
|
|
|
Magnetic Field Induced Chain Alignment of Ferroparticles in Magnetic Fluid
LI Yan-Qin, BU De-Cai, LI Xue-Hui
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 745–750
 Abstract
Abstract(
717 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(402KB)(
1207
)
Chain alignment of suspended-ferroparticles in a carrier fluid exposed to the external magnetic field was investigated theoretically and experimentally. The results show that without the external magnetic field the ferroparticles were randomly distributed and when exposed to uniform magnetic field the turned out to be a chained-alignment pattern along the external magnetic field orientation at intensity of 11.1 kA/m. With the external uniform magnetic field intensity up to 28.6 kA/m, more ferroparticles closely aggregated to a chained-alignment pattern along the magnetic field direction. When the magnetic field intensity reached 28.7 kA/m in the gradient magnetic field, a large number of ferroparticles gathered around the coils and formed complex clusters, while a small number of ferroparticles demonstrated a chain-alignment pattern along r direction with weaker magnetic field intensity. When the magnetic field gradient was gradually increasing from 1.73 kA/m2 to 5.11 kA/m2, the cluster pattern of ferroparticles turned out to be dense along the axis. This research may enhance the applications of magnetic fluid in the fields of mechanical engineering, bioengineering and thermodynamic engineering.
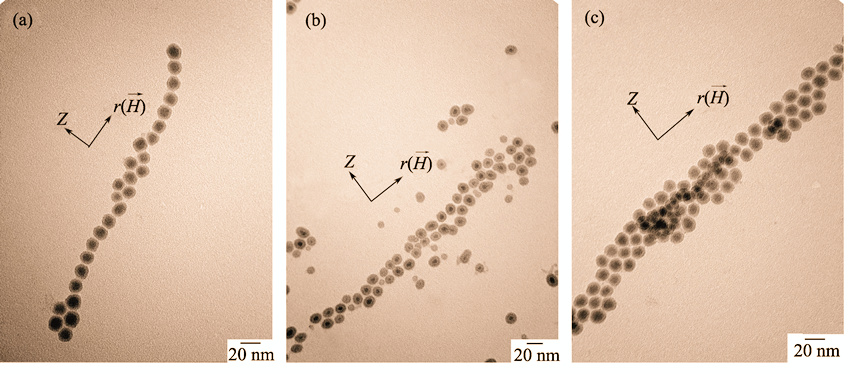
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Nano-hydroxyapatite/PLGA Composites with Novel Surface-modified Nano-hydroxyapatite
JIANG Li-Xin, JIANG Liu-Yun, MA Chi, HAN Chong-Tao, XU Li-Juan, XIONG Cheng-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 751–756
 Abstract
Abstract(
995 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(5414KB)(
1100
)
Nano-hydroxyapatite (n-HA) was modified by a new method of combining silane coupling reagent (KH550) with surface-grafting L-lactide LLA. Then, the surface-modified n-HA (g-n-HA) was introduced into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) to prepare a series of g-n-HA/PLGA composites with the concentration of 3wt%, 10wt%, 20wt% and 30wt%. The properties of the g-n-HA/PLGA composites were characterized and compared with PLGA and n-HA/PLGA composites. The results show that n-HA is successfully modified by KH550 and L-LA. The g-n-HA particles could disperse more uniformly in PLGA matrix and promote PLGA to crystallize. The obtained g-n-HA/PLGA composites has better mechanical properties than those of n-HA/PLGA composites with the same amount of n-HA. Moreover, the bending and tensile strength of g-n-HA/PLGA composite containing 10wt% g-n-HA are 14.4% and 11.3% which is higher than that of pure PLGA, respectively. Therefore, the g-n-HA/PLGA composite is promising for bone fracture internal fixation material in future.
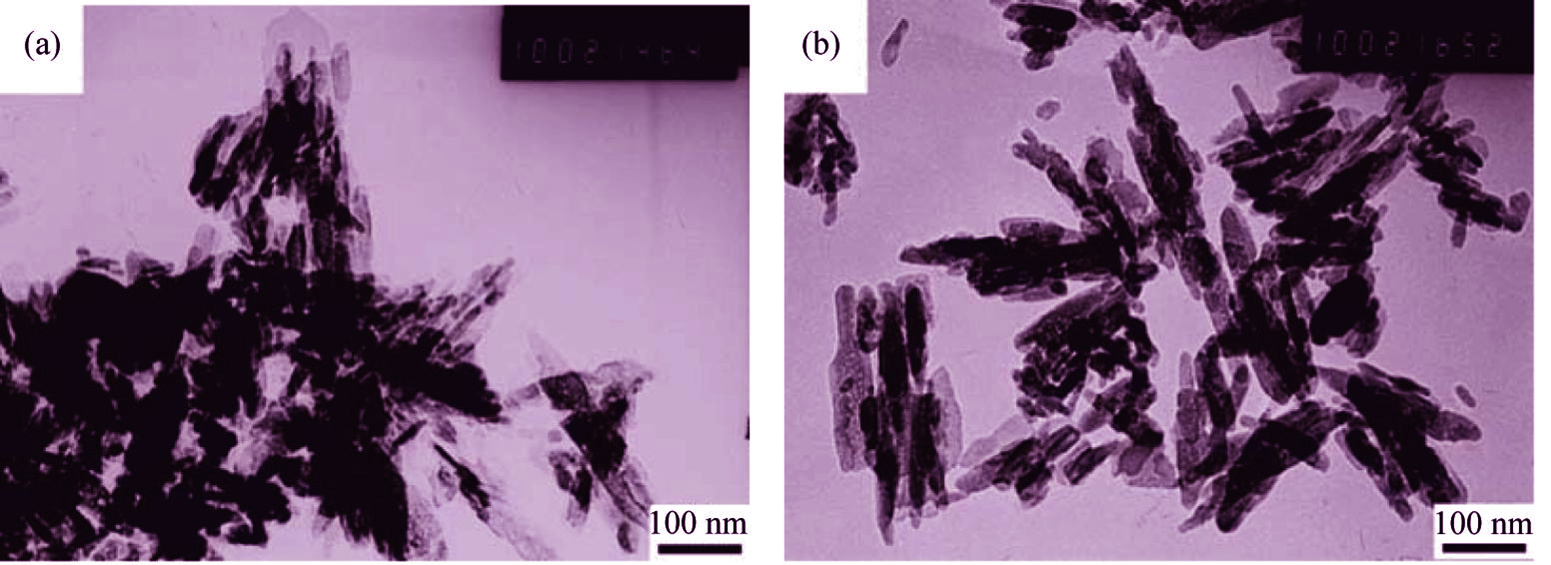
|
|
|
Research of the Preparation Technology for the SiC Whisker
CHEN Yang, WANG Cheng-Guo, GAO Ran-Ran, ZHU Bo
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 757–762
 Abstract
Abstract(
749 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1063KB)(
983
)
SiC whiskers were prepared on graphite matrix using common and low-cost hydrogen silicone oil (H-PSO) as raw material, and the influence of different process parameters on the growth of SiC whisker was studied based on the crystallization fraction using orthogonal test method. The process parameters include heat treatment temperature (T), holding time (t), flow of protective atmosphere (f) and porosity of matrix (P). The morphology and structural characteristics of SiC whisker were also analyzed by SEM, TEM, RAMAN and XRD. The results show that the temperature is the most important factor that influences the growth of SiC whisker, followed by gas flow, porosity, holding time in proper sequence. The bigger gas flow in safe range makes generation reaction of SiC whisker sufficient, and smaller porosity benefits SiC crystal nucleus to grow up. Higher temperature and longer time are favorable to whisker continued growth. The SiC whisker is of core-shell structure with SiC phase as core and silicon oxide as the shell.
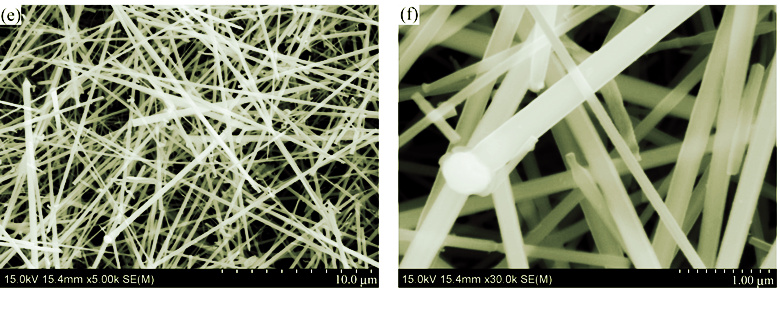
|
|
|
Preparation of Ordered Porous Ceramic Joint on C/SiC Composites and Its Joining Technique
WANG Hao, ZHOU Qing-Jun, JIAN Ke, SHAO Chang-Wei, ZHU Yi-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 763–768
 Abstract
Abstract(
846 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1010KB)(
1000
)
Mono-dispersed silica spheres were prepared as template by st?ber method. Based on this template, the ordered nanoporous ceramic joints on the C/SiC composites were successfully fabricated for the first time by preceramic polymer techniques and the condition was optimized. Two different joining methods, directly soaking (DSM) and soaking after the first joining (SJM), were used for joining the ordered nanoporous ceramic joints of the C/SiC composites. The result shows that the bending strength of the joints by DSM and SJM is about 20.5 and 82.4 MPa, respectively, suggesting SJM more suitable for joining C/SiC composites.
|
|
|
Influence of V Content on Microstructure, Mechanical and Friction Properties of TaVN Composite Films
XU Jun-Hua, XUE Ya-Ping, CAO Jun, YU Li-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 769–774
 Abstract
Abstract(
4561 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(502KB)(
1093
)
A series of TaVN composite films with different V contents were fabricated by magnetron sputtering technique. The microstructures, mechanical properties, friction properties at different temperatures were investigated by X-ray diffraction, nano-indentation, CSM high-temperature ball-on-disc tribo-meter, respectively. The results show that the microstructure of TaVN films has fcc structure. With V content increasing, the preferential orientation changes from (111) to (200), and the hardness increases to a peak value (32.3 GPa) and then decreases. At room temperature, the friction coefficient of TaVN films decreases as V content increases, which may be related to the formation of V2O5. When the temperatures increase from room temperature to 800℃, the friction coefficient increases and then decreases. The friction mechanisms of TaVN composite films and TaN film at high temperature are compared based on the crystal chemistry theory.
|
|
|
Hydrogen Permeation Properties of Alumina Coating on 316L Stainless Steel
LI Shuai, HE Di, LIU Xiao-Peng, ZHANG Chao, WANG Shu-Mao, YU Qing-He, QIU Hao-Chen, JIANG Li-Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 775–779
 Abstract
Abstract(
1337 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(387KB)(
1228
)
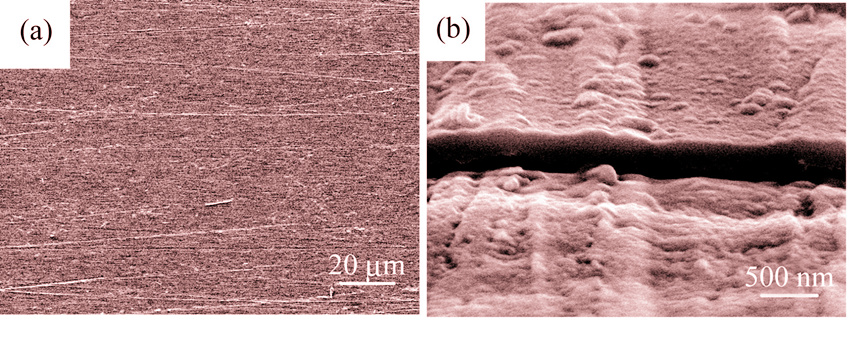
Alumina coatings were deposited on 316L stainless steel by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). The phase and microstructure of coatings were examined by XRD and SEM, and the hydrogen permeation behavior of coating was measured by a gas-phase hydrogen permeation apparatus. The results show that the alumina coating is amorphous after thermal annealing at 973 K, and the coating is smooth, intact and 190 nm of thickness. The hydrogen permeation pressure exponents of the coating are 0.56-0.78, which indicates the hydrogen permeation of coating is surface and diffusion limited. The apparent hydrogen permeability of the coating is P = 1.99×10-6 exp(-117×103/RT) mol/(m·s·Pa1/2). The permeation activation energy of the coating is 117 kJ/mol, which is much higher than that of 316L stainless steel with value of 66.6 kJ/mol. Thus, the alumina coating effectively suppresses the hydrogen permeation in 316L. Furthermore, the hydrogen permeation reduction factors (PRF) of the alumina coating on 316L are 59–119 at temperatures 873–973 K, and the alumina coating offers excellent hydrogen permeation suppression performance.
|
|
|
Investigation on Crystallization Behavior of Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Prepared by High-gravity Combustion Synthesis
YANG Zeng-Chao, LIU Guang-Hua, XU Li-Hua, LI Jiang-Tao, GUO Shi-Bin
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 780–784
 Abstract
Abstract(
655 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(555KB)(
1095
)
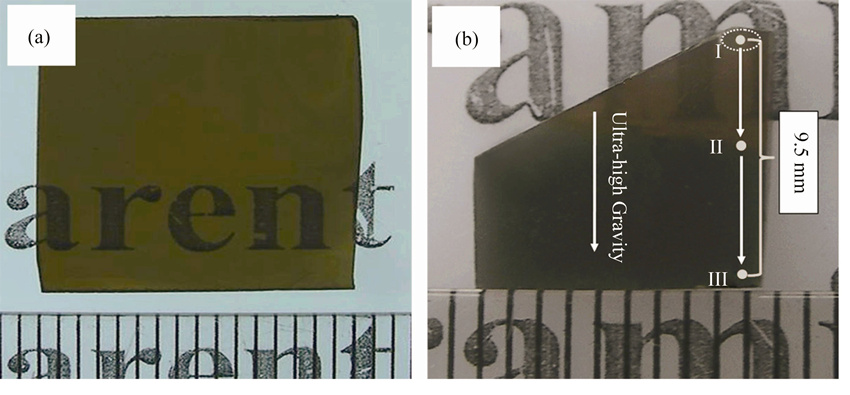
The crystallization behavior of Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 glass prepared by high-gravity combustion synthesis was investigated by isothermal annealing experiments. The effect of annealing condition on the crystallization behavior of the glass was discussed according to the Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 ternary phase diagram. From experimental results, the crystallization behavior of the glass strongly depended on the annealing temperature and the content of SiO2. After being annealed at 1050℃, the sample showed a graded phase distribution along the high-gravity direction, consisting of Al6Si2O13 glass-ceramic, pure glass and χ-Al2O3 glass-ceramic. At annealing temperature of 1100℃, Y3Al5O12 and Y2Si2O7 were precipitated as the major crystalline phases. When the annealing temperature further increased to 1200℃, the predominant crystalline phase was Y3Al5O12. The research provides a possible way to prepare Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 glass-ceramics by integrating high-gravity combustion synthesis with post annealing treatment.
|
|
|
Mechanical and Optical Properties of Ion-exchange Strengthened Glass Coated with Sol-Gel Derived ZrO2-SiO2 Film
ZHANG He, ZHOU Jue-Hui, ZHANG Qi-Long, YANG Hui
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 785–779
 Abstract
Abstract(
1528 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(341KB)(
1532
)
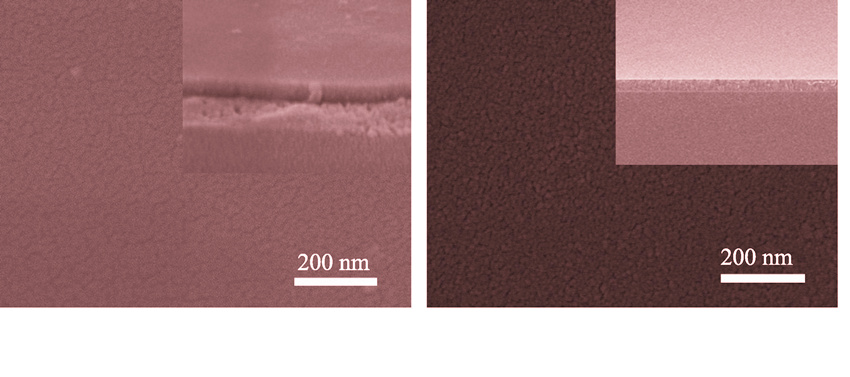
ZrO2-SiO2 films of different SiO2 content were deposited on soda-lime glass substrates through a Sol-Gel process, which was followed by an ion-exchange strengthening process. Phase presents, surface morphology and ion-exchange depth were determined by X-ray diffractometer, scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive spectrometer analysis, respectively. The mechanical and optical properties of coated glass were studied. Homogeneous, continuous and dense films are obtained. Pure ZrO2 film belongs to tetragonal structure, while other films with SiO2 have an amorphous structure. ZrO2-SiO2 films with high ratio (H/E≥0.1) and elastic recovery (We≥60%) were thought to be favourable bending strength. Light transmittance increased, while hardness and Young’s modulus decreased with the increasing SiO2 content in films. Typically, chemical strengthened 0.5ZrO2-0.5SiO2 film coated glass exhibited high bending strength of 393 MPa and high hardness of 18 GPa, and a negligible optical loss in visible region for thin thickness (~45 nm).
|
|
|
Microstructure and Thermal Characterization of Multilayer Insulation Materials Based on Silica Aerogels
SHENG Chen, YU Yun, YU Yang, MI Le, TANG Gen-Chu, SONG Li-Xin
2013 Vol. 28 (7): 790–794
 Abstract
Abstract(
1301 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(312KB)(
1745
)
A new kind of MLIMs are prepared, whose spacer is made from Al2O3 fiber mat, and silica aerogels is implanted on the surface of Al2O3?fiber through Sol-Gel process. In high vacuum (10-3 Pa), the effective thermal conductivity of the new MILMs could be reduced by 21.8%, at the same time, the weight could be reduced by 67.2%. Furthermore, this MLIMs shows good insulation performance in high temperature of 1200 K and low vacuum (100 Pa).
|
|