|
|
Research Progress on the Preparation of Ceramic Hollow Nanofibers by Electrospinning
LIU Peng-Chao, GONG Jing-Hua, YANG Shu-Guang, MA Jing-Hong, XU Jian
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 571–578
 Abstract
Abstract(
1115 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(678KB)(
1693
)
Ceramic hollow nanofibers possess unique one-dimensional tubular nanostructure, which have potential application prospects in the fields of microelectronics, catalysts, gas sensors and photoelectric transducers. The research progress on ceramic hollow nanofibers prepared by electrospinning is reviewed. The tendency of studies on fabricating ceramic hollow nanofibers through coaxial electrospinning, single capillary electrospinning and postprocessing is mainly introduced. And the discussion on the formation mechanism of hollow structure of ceramic nanofibers is presented with emphasis on single capillary electrospinning method, including phase transformation mechanism, gas evaporating mechanism and Kirkendall effect. The application prospect and disadvantages are also summarized.
|
|
|
Synthesis of ZnSe Nanomaterials via Solvothermal Method
WU Rong, JIANG Nan-Nan, LI Jing, JIAN Ji-Kang, CHANG Ai-Min
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 579–583
 Abstract
Abstract(
1180 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(338KB)(
1477
)
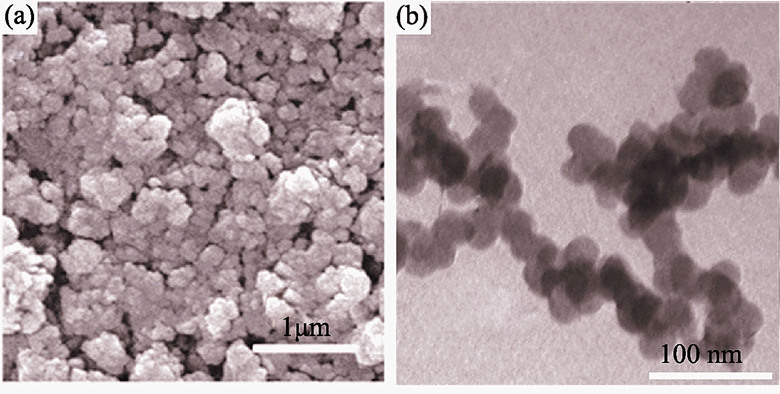
Sphalerite or wurtzite ZnSe nanomaterials were controllably synthesized by one-step solvothermal technique using ethanol amine (EA) as solvent, zinc acetate as zinc source and Na2SeO3•5H2O or Se powder as Se source. X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive spectrum (EDS), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were used to characterize the structures, compositions and morphologies of the products. The results show that sphalerite ZnSe nanoparticles with the diameter of 30 nm are synthesized by adopting Na2SeO3•5H2O as Se source, while wurtzite ZnSe nanoplates with thickness of 50 nm are prepared via Se powders as Se source. The above results indicate that the structures and morphologies of the ZnSe nanomaterials are dependent on the Se sources. It is also found that EA solvent and Se source play an important role in the formation of ZnSe nanomaterials. The optical properties of the as-prepared products are characterized by UV-Vis absorption and room-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra.
|
|
|
Preparation of One-dimensional Pt/SnO2 Nanofibers and NOx Gas-sensing Properties
XU Shuang, YANG Ying, WU Hong-Yuan, JIANG Chao, JING Li-Qiang, SHI Ke-Ying
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 584–588
 Abstract
Abstract(
892 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(490KB)(
1122
)
1D Pt/SnO2 hollow nanofibers were synthesized by electrospinning method to prepare and study the nanomaterials with the higher sensitivity and faster response to NOx at room temperature. The characteristics and morphology of material were studied by XRD, SEM and TEM. NOx gas sensor was tested at room temperature. The results show that the 1D Pt/SnO2 nanomaterials is hollow tubular and similar tubular structure. The sample with 0.3wt% Pt has the highest sensitivity, the fastest response to 9.7×10-5 V/V NOx, the sensitivity up to 109.6% and response time of 11.33 s. When the sample is doped with Pt 0.5wt%, its limit level is 2.91×10-6 V/V.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Continuous and Dense TAPO-5 Molecular Sieve Membranes by Steam-assisted Gel Conversion Method
WANG Jun-Fen, LIU Xu-Guang, ZHANG Ping-Ping, ZHANG Bao-Quan
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 589–593
 Abstract
Abstract(
883 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(489KB)(
1128
)
TAPO-5 molecular sieve membranes were synthesized by using steam-assisted gel conversion method. The as-synthesized TAPO-5 membranes were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), as well as UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscope (UV-Vis). Results were compared with those by conventional hydrothermal crystallization method. The influences of the aging conditions and crystallization time on the surface morphology, coverage and denseness of the membrane together with the crystalline structure of molecular sieve crystals were investigated. By using steam-assisted gel conversion method, continuous and dense TAPO-5 molecular sieve membranes could be fabricated on porous α-Al2O3 substrates after crystallization for 48 h because the pre-aged solid gel were favorable to the incorporation of Ti atoms into the tetrahedral framework and the intergrowth of TAPO-5 crystals.
|
|
|
Effect of Oleic Acid Surface Modification on Dispersibility of TiO2
Lü Yu-Zhen, ZHANG Sheng-Nan, DU Yue-Fan, CHEN Mu-Tian, LI Cheng-Rong
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 594–598
 Abstract
Abstract(
1457 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(696KB)(
1279
)
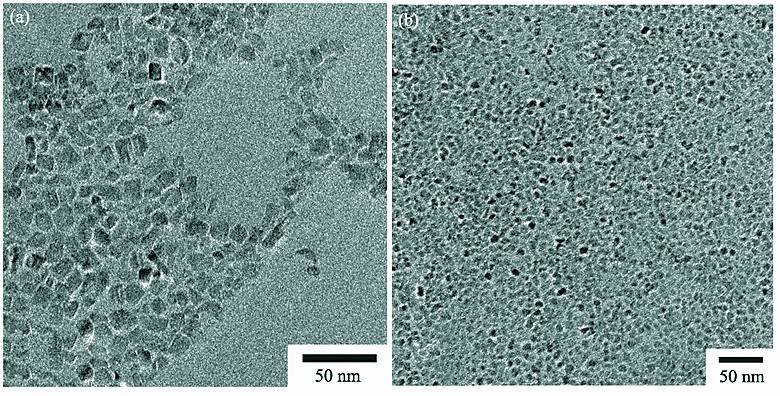
Oleic acid modified TiO2 nanoparticles were dispersed into transformer oil to prepare TiO2 nanoparticles modified transformer oil by ultrasonic treatment. The effect of surface modification on the dispersibility of TiO2 nanoparticles in the oil was investigated. The morphology, structure and surface modification state of TiO2 nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectra (FT-IR) and thermogravimetric method (TG). The results show that oleic acid is bound on the surface of TiO2 nanoparticles by bidentate coordination, and an effective modification layer is formed. With the increasing of modifying agent dosage, although the coordination pattern of oleic acid on the nanoparticle surface remains, the mass fraction of chemisorbed oleic acid obviously increases. The dispersibility and stability of TiO2 nanoparticles in the oil is dramatically improved. When the molar ratio of titanium salt to oleic acid is 1:24, TiO2 nanoparticles can be well dispersed in the transformer oil and keep transparent after aged for 30 d at room temperature.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Porous α-Al2O3 Based Ceramic Disk Substrates
CHEN Sheng-Bo, LIU Xu-Guang, ZHANG Bao-Quan
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 599–604
 Abstract
Abstract(
908 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(573KB)(
1076
)
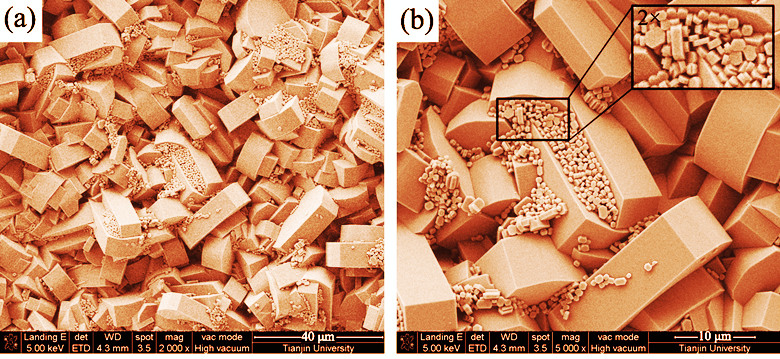
Porous α-Al2O3 based ceramics disks were prepared by dry pressure molding method. Influences of sintering temperature and SiO2 dopant on the structure, morphology and properties were investigated. It was founded that compressive strength and shrinkage ratio of α-Al2O3 ceramic disk both increased with increasing sintering temperature. The shrinkage ratio and compressive strength was less than 0.5% and stronger than 80 MPa, respectively, while the optimum sintering temperature was chosen to be 1180℃. The sintering of α-Al2O3 ceramic disk would be enhanced by doping SiO2, which crystallized into cristobalite phase from an amorphous phase during the sintering process. α-Al2O3 ceramic disk doped with 12wt% SiO2 sintered at 1180℃ exhibited a stronger compressive strength (110 MPa) and a shrinkage ratio of 1.2%. The ceramic disk possessed a smaller pore size but a wider pore size distribution than that of the pure α-Al2O3 ceramic disk. It was demonstrated that both α-Al2O3 and SiO2 doped α-Al2O3 ceramic disk substrates were favorable for the growth of ZSM-5 zeolite membranes. However, these ZSM-5 zeolite membranes showed different morphologies and crystal sizes, due to the difference in physicochemical properties of substrates.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of C/C-ZrC-SiC-ZrB2 Composites via Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis
XIE Jing, LI Ke-Zhi, FU Qian-Gang, LI He-Jun, YAO Xi-Yuan
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 605–610
 Abstract
Abstract(
1086 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(856KB)(
1102
)
C/C-ZrC-SiC-ZrB2 composites were prepared by precursor infiltration and pyrolysis (PIP) process using a mixture solution of organic ZrC, ZrB2 precursor and polycarbosilane as precursor. Microstructure, flexural property and ablation behavior of the composites were studied. The results show that the composites produced by PIP have a homogeneity distribution of ceramic phase. The flexural strength of the composites is 126.31 MPa. There are a large number of carbon fiber bundles pulled-out, and the composites exhibit a pseudo-plastic fracture behavior. After ablated for 120 s by oxyacetylene flame, the composites show no significant ablation, and their linear and mass ablation rates are –2.50×10-4 mm/s and –1.33×10-4 g/s, respectively. Different kinds of protective coatings form on the different regions of ablated surface, which can not only reduce the diffusion of oxygen and heat but also remedy defects effectively, and thereby greatly improves the ablation resistance of the composites.
|
|
|
Facile Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Graphene Nanosheets
LIU Yi, ZHAO Yu-Liang, GAO Zhao-Fen, JIANG Xia, ZENG Yu-Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 611–615
 Abstract
Abstract(
1336 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(379KB)(
1341
)
Graphene nanoplates (GNS) were prepared from oxided graphite by using thiosemicarbazide (CH5N3S) as a reducing agent. The microstructures and morphologies of products were subsequently characterized by XRD, FE-SEM, AFM and UV-Vis adsorption spectra. The performances of super-capacitor were characterized using cyclic voltammetry and constant current charge-discharge tests. The experimental results indicated that the as-prepared GNS possessed fair crystalline state and admirable aqueous dispersibility. An electrode prepared from GNS exhibited a specific capacitance of 75 F/g at a current density of 500 mA/g in 3 mol/L KOH electrolyte. Moreover, the GNS showed excellent electrochemical cycle performance.
|
|
|
Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Li1+2xMn0.3+xNi0.3-3xCr0.4O2 Synthesized by Spray-dry Method
ZHANG Qian, LIU Wei-Wei, FANG Guo-Qing, XIA Bing-Bo, SUN Hong-Dan, KANEKO Shingo, YANG Yu-Sheng, ZHENG Jun-Wei, LI De-Cheng
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 616–622
 Abstract
Abstract(
913 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(558KB)(
1060
)
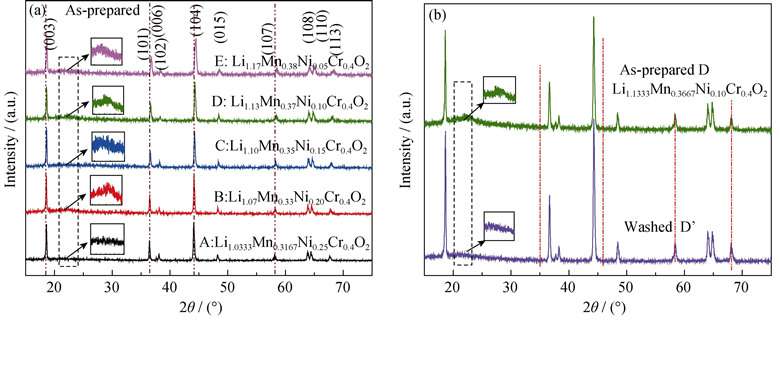
Lithium-rich layered solid solution materials, Li1+2xMn0.3+xNi0.3-3xCr0.4O2 (x=1/60, 1/30, 1/20, 1/15, 1/12), were synthesized by spray-drying process. Their crystal structures, element valences and the electrochemical performances were investigated by XRD, XPS, ICP, SEM, TEM and charge-discharge test. All samples have a typical solid solution feature in terms of their structure, and no impurity phase appears in their XRD profiles. Nevertheless, XPS results suggest that Cr3+ and Cr6+ co-exist in all samples. The presence of the Cr6+ in the as-prepared sample results in a high moisture absorption, which can be removed by water washed treatment. As to the electrochemical properties, the as-prepared samples have bad electrochemical performances due to the high moisture absorption. After washing with water, all samples exhibit solid solution behavior, and their initial specific capacities increase as the increase in the amount of Li and Mn. The discharge capacity of Li1.17Mn0.38Ni0.05Cr0.4O2 can reach 203 mAh/g with a capacity retention of 71% after 50 cycles.
|
|
|
Effect of BiYbO3 Solid Solution Limit on Electric Properties and Structure of BSPT Piezoceramics
SHI Wei, LENG Sen-Lin, LONG Yu, ZHU Jian-Guo, XIAO Ding-Quan
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 623–628
 Abstract
Abstract(
830 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(459KB)(
1171
)
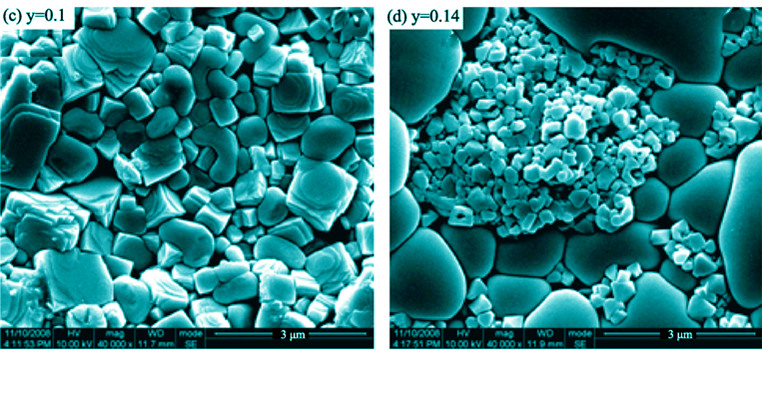
yBiYbO3-(0.36–y)BiScO3-xPbTiO3 (BSYPT-0.64/y) piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by traditional solid reaction method. The result of X-ray diffraction shows that the as-prepared BSYPT-0.64/y ceramics have single perovskite structure. However, scanning electron microscopy results show that the surface morphology of BSYPT-0.64/y ceramics becomes abnormal at y=0.1, and a large amount of tiny grains, with the grain size distributing from 0.3 μm to 0.5 μm, separate out on the surface of the ceramics at y=0.14. EDS analysis reveals that the major ingredients of these tiny grains are mainly Bi, Yb, Ti, Sc and O. The solid solution limit is therefore confirmed to be near y=0.1 for the BSYPT-0.64/y ceramics. By means of systematic piezoelectric, ferroelectric and temperature-dependent dielectric (Tc~450℃) characterizations, it is found that the occurrence of solid solubility limit-related BiYbO3 separation is not a key factor for affecting the electrical properties and structure of the ceramics, but a relatively isolated behavior. The degradation of structural and electrical properties is attributed to the decrease in Sc/Pb ratio when the BiYbO3 content is increased, which leads to a deviation from MPB in the BSYPT-0.64/y ceramics.
|
|
|
Effect of BaZrO3 Depant on the Structure and Electric Properties of (K0.49Na0.51)0.98Li0.02(Nb0.77Ta0.18Sb0.05)O3 Lead-free Piezoceramics
LI Yue-Ming, XIAO Zu-Gui, SHEN Zong-Yang, WANG Zhu-Mei, HONG Yan, PAN Tie-Zheng, Wu Fen
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 629–634
 Abstract
Abstract(
833 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(466KB)(
980
)
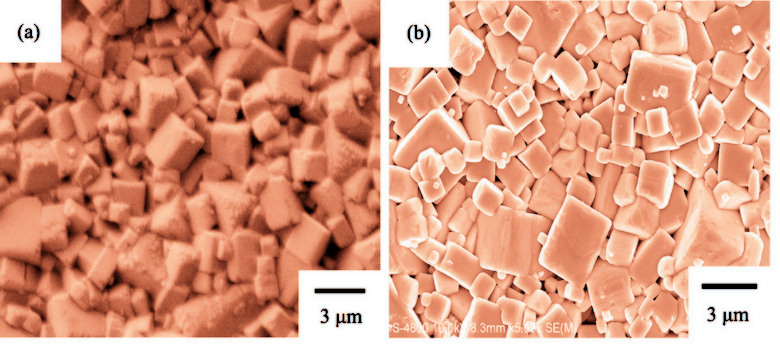
(K0.45Na0.55)0.98Li0.02(Nb0.77Ta0.18Sb0.05)O3-xBaZrO3 (NKNLST-xBZ, x = 0–0.020 mol) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by solid state reaction method. The effect of BaZrO3 doping amount on the piezoelectric, dielectric, electromechanical and ferroelectric properties were investigated systematically. The results revealed that the crystal structures transformed from orthorhombic phase to tetragonal phase with BaZrO3 doping amount increasing, and the coexistence of orthorhombic-tetragonal phases were observed in the x range from 0.005 to 0.008. Under the condition of two phases co-existence, the ceramic grain became small and uniform and dielectric loss tanδ significantly decreased, while the piezoelectric constant d33 and planar electro-mechanical coupling factor kp increased. The dielectric constant εT33 /ε0 of this system ceramics increased continuously with the increase of the BaZrO3 doping amount and the phase transition temperatures shifted to lower temperature. The optimized piezoelectric properties could be obtained at the x = 0.005 composition ceramic as follows: the piezoelectric constant d33 = 372 pC/N, planar electromechanical coupling coefficient kp = 47.2%, dielectric loss tanδ = 3.1%, a high dielectric constant εT33 /ε0 = 1470 and Curie temperature Tc=208℃.
|
|
|
Li2MnSiO4/C Nanocomposite Prepared by Resorcinol-Formaldehyde Assisted Sol-Gel Method
LIU Shuang-Ke, XU Jing, LI De-Zhan, HU Yun, XIE Kai
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 635–638
 Abstract
Abstract(
803 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(361KB)(
1042
)
Li2MnSiO4/C nanocomposite was prepared by a resorcinol-formaldehyde assisted Sol-Gel method. The crystalline structure, morphology and electrochemical performances of the products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and galvanostatic charge/discharge test. The results demonstrate that the as-prepared nanocomposite has a highly pure Pmn21 orthorhombic structure with uniformly distributed particle size of about 50 nm and exhibits good electrochemical performance. Li2MnSiO4/C cathode can deliver an initial discharge capacity of 105.7 mAh/g with 90.7% capacity retention over 50 charge-discharge cycles. It is also found that the crystalline structure of Li2MnSiO4 almost remains stable after charge-discharge cycling, indicating that the coated carbon layer formed by pyrolysis of resorcinol-formaldehyde can not only enhance the electronic conductivity, but also maintain the structural stability of the Li2MnSiO4/C nanocomposite.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Density-controllable TiO2 Nanowire Bundle Arrays and Their Application in Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cell
LIU Jun, WEI Ai-Xiang, ZHANG Chun-Xing
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 639–643
 Abstract
Abstract(
660 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(396KB)(
1078
)
Highly oriented single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanowire bundle arrays on transparent conductive fluorine- doped tin oxide (FTO) substrates were synthesized by hydrothermal method using the precursors of tetrabutyl titanate, deionized water and hydrochloric acid. The density of the TiO2 nanowire bundle can be tuned by changing the concentration of tetrabutyl titanate. Using the nanowire bundle array as the photoanode, CdS as sensitizer, the quantum dot sensitized solar cell (QDSSC) was assembled. The effects of nanowires density on photovoltaic performance of solar cell were investigated. It is found that the cell presents poor photovoltaic performance if the nanowires density is too high or too low. The optimal nanowires density for highest photovoltaic performance is 11.8×106/mm2 when the photoelectric conversion efficiency reaches 0.947%.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Performance of CoSeO3 Compound as a Cathodic Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction
ZHAO Dong-Jiang, MA Song-Yan, YIN Ge-Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 644–648
 Abstract
Abstract(
790 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(486KB)(
1061
)
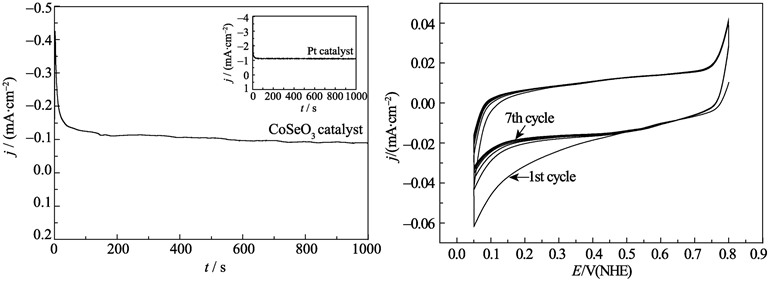
Novel CoSeO3 nanoparticles were successfully synthesized by low temperature refluxing method using dodecacarbonyltetracobalt [Co4(CO)12] and selenium (Se) as raw materials in glycol solvent. The crystalline structure, morphology and electrochemical performances of the as-prepared product were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and rotating disk electrode (RDE) technique. Results show that the as-obtained CoSeO3 compound presents the structural characteristics of monoclinic CoSeO3•H2O with the particle size of 26.7 nm and regular figure. The catalyst demonstrates significant electrocatalytic activity towards oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), showing an open circuit potential (OCP) of 0.80 V (vs NHE) in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution at 25℃. The transfer process of about 3.8 electrons is determined during the reduction per oxygen molecule by using Koutecky-Levich equation. The transfer coefficient, Tafel slope and exchange current density are 0.50, 119 mV and 1.98×10-6 mA/cm2 in the potential region of 0.64–0.76 V (vs NHE), respectively. The catalytic activity and electrochemical stability of the catalyst are compared with a commercial Pt catalyst.
|
|
|
Performances of GaN-based LEDs with AZO Films as Transparent Electrodes
CHEN Dan, Lü Jian-Guo, HUANG Jing-Yun, JIN Yu-Zhe, ZHANG Hao-Xiang, YE Zhi-Zhen
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 649–652
 Abstract
Abstract(
728 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(436KB)(
1129
)
Al-doped ZnO (AZO) thin films were prepared by pulsed laser deposition under different oxygen pressures. AZO films with highly transparent conductive properties were obtained at 0.1 Pa. AZO films were used on GaN-based light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as transparent contact layers. At a forward current of 20 mA, the 520 nm electroluminescence peak was evidently observed, with a high working voltage of 10 V. The brightness of the chip was enhanced as the forward current increased. Secondary ion mass spectra revealed that the high working voltage of the LED might be triggered by the change of material conductivity and the passivation layer formed at the AZO/GaN interface.
|
|
|
Substrate Effects on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiO2 Thin Films
WANG He, HE Hong-Bo, ZHANG Wei-Li
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 653–658
 Abstract
Abstract(
866 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(624KB)(
1103
)
The SiO2 films deposited respectively on K9 and two different orientations of Y3Al5O12 (YAG) crystals were manufactured by electron beam technology. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and nano-scratch tests were used to demonstrate the microstructures and mechanical properties of films. The crystal orientation of SiO2 thin films on K9 is noncrystalline structure and the other two, YAG (100) and YAG (111), are polycrystalline structures. The Young modulus of all films are similar. The nano-scratch tests show that the damage mechanisms of SiO2 thin films on K9 and YAG are different. The adhesive forces of the films on YAG (100) and YAG (111) are much less than homologous film on K9. The microstructures of the films and the divergences of the elastic modulus between films and substrates are taken to explain the different mechanical behaviors of the films on three substrates.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Cd/CdS-SiO2 Composite Film with High Third-order Optical Nonlinearity by Electrochemically Induced Sol-Gel Method
QING Sheng-Lan, GAN Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 659–664
 Abstract
Abstract(
756 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(427KB)(
1134
)
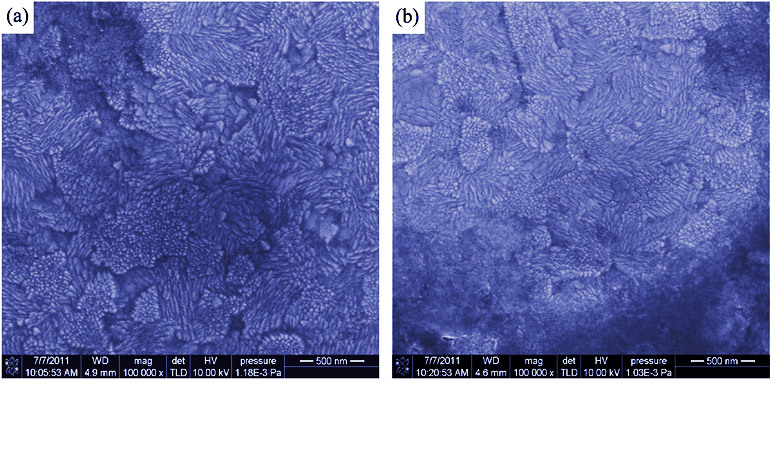
The sol was prepared with cadmium nitrate, thiourea and tetraethoxysilane as precursors by Sol-Gel method. The transparent film was prepared on ITO substrate by electrochemically induced Sol-Gel method using the as-prepared sol as electrolyte. SEM results showed that the film was made up of nano beams. While EDX results showed that the component elements of the film were Si, O, Cd, S and the atom ratio of Cd to S was more than 1. It could be inferred from both the EDX and cyclic voltammetry’s results that the film composite was Cd/CdS-SiO2. Z-scan test results showed that the film had third-order optical nonlinearity with self defocusing nonlinear refraction and saturated absorption properties at the wavelength of 1064 nm. The third-order nonlinear optical susceptibility of films could reach 1.18×10-14 (m/V)2 to 1.39×10-13 (m/V)2 which demonstrated that the third-order nonlinear optical properties of these films were excellent. Further analysis showed that the content of CdS in the film remarkably influenced the optical nonlinearity.
|
|
|
Numerical Simulation of the Influence of Different Rotation Speeds on the Capping of KDP Crystal
LIU Guang-Xia, WANG Sheng-Lai, DING Jian-Xu, SUN Yun, LIU Wen-Jie, ZHU Sheng-Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 665–670
 Abstract
Abstract(
652 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(438KB)(
903
)
The dependence of temperature and velocity distributions on rotation speed during KDP crystal growth process were numerical simulated via finite volume method and the Fluent software. It revealed that at the rotation speed of 9 r/min, the temperature value nearby the crystal was relatively higher, and the temperature distribution was stable, which resulted in single capping and slow capping speed. When rotation speeds reached 55 and 77 r/min, the temperature value nearby the crystal was comparatively low, which increased the supersaturation and accelerated the capping speed. The rotation speed between 9 and 50 r/min could bring temperature turbulence, and consequently led more capping. The capping speed was relatively moderate. The simulation result proved the rotation speed of 77 r/min was the optimum speed.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride/ZrO2-TiO2 Optical Film with Wide Band Gap and High Refractive Index
ZHANG Yu-Qing, ZHAO Li-Li, XU Shi-Long, ZHANG Chao, CHEN Xiao-Ying, SONG Li-Xin
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 671–676
 Abstract
Abstract(
1323 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(426KB)(
1763
)
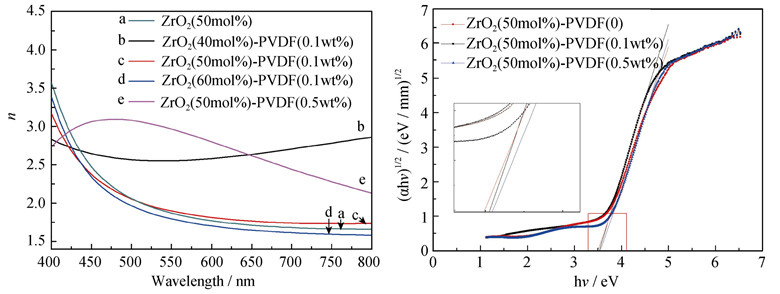
To improve the integrative properties of ZrO2-TiO2 optical film, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)/ZrO2-TiO2 film was coated on the K9 glass substrate by Sol-Gel method using ZrOCl2·8H2O and Ti(OBu)4 as precursor of Zr and Ti, respectively. Using PVDF as organic additive, PVDF/ZrO2-TiO2 optical films were characterized by SEM, FT-IR and contact angle. Then the optical properties of the PVDF/ZrO2-TiO2 optical films were investigated via Ultraviolet/ Visible/Near Infrared transmission spectrum, optical band gap (Eg) and refractive index. SEM images indicate that the optical films are successfully prepared on the glass substrates. The addition of PVDF in the optical films increases the contact angle between water and the films. Eg of ZrO2-TiO2 optical films are slightly widened with the increasing of ZrO2 content, and Eg of PVDF/ZrO2(50mol%)-TiO2 films are widened as the mass fraction of PVDF increases. In addition, refractive indexes of ZrO2-TiO2 optical films increase as the mole fraction of ZrO2 decreases, and refractive indexes of PVDF/ZrO2(50mol%)-TiO2 films increase as the mass fraction of PVDF increases.
|
|
|
Facile Approach to Preparation of Nitrogen-doped Graphene and Its Supercapacitive Performance
FENG Ya-Qiang, TANG Fu-Ling, LANG Jun-Wei, LIU Wen-Wen, YAN Xing-Bin
2013 Vol. 28 (06): 677–682
 Abstract
Abstract(
1685 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(426KB)(
2450
)
Nitrogen-doped graphene nanosheets (N-GNSs) with good morphologies were successfully synthesized by a facile solvothermal method. The result of X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) revealed that most oxygen containing functional groups on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) were removed during solvothermal reduction, and nitrogen atoms from dimethylformamide (DMF) were effectively doped into graphene structure in the form of pyrrolic-N and graphite-N. As an electro-active material, the N-GNSs exhibited superior capacitive behavior in 2 mol/L KOH electrolyte with a high specific capacitance of 181.3 F/g at the current density of 0.5 A/g. Also, it displayed good electrochemical stability with 92.5% of the initial capacitance over consecutive 2000 cycles. Therefore, the N-GNSs can be an attractive candidate as electrode materials for supercapacitors.
|
|