|
|
Research Progress of Hollow Structural Materials Prepared via Templating Method
BAO Yan, YANG Yong-Qiang, MA Jian-Zhong
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 459–468
 Abstract
Abstract(
1488 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(523KB)(
1899
)
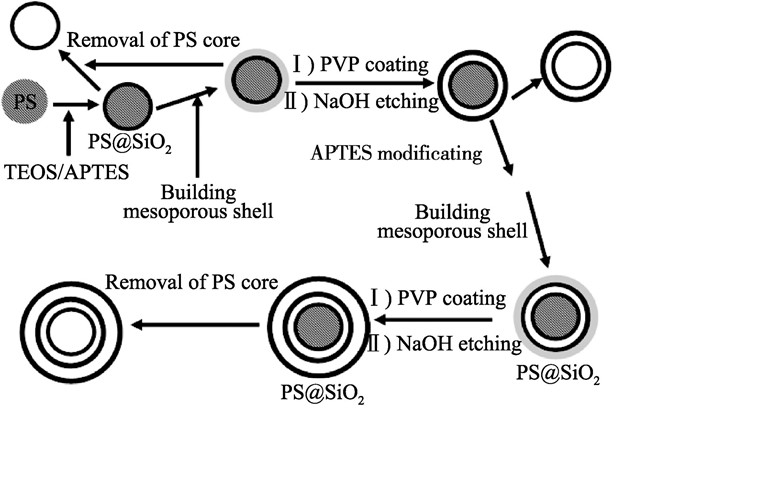
Hollow structural materials with low density and high surface area which can encapsulate small molecules, are widely used in environmental protection, drug delivery system, electronic and other fields. Because templating method is simple, and owns high repeat rate, good prediction and many other advantages, it is particularly interesting and frequently used to fabricate hollow structural materials with homogeneous, dense layers. Templating methods can be divided broadly into two classes according to the properties of templates used in synthesis, which can be called traditional templating methods and self-templating methods, respectively. In this review, a comprehensive overview of the preparation of hollow structural materials via templating methods was provided. The progress of two traditional templating methods: hard templates and soft templates were firstly summarized. The research and development of hollow structural materials prepared via four self-templating methods: Ostwald ripening, Kirkendall effect, galvanic replacement and chemical etching were mainly reviewed and commented in the later. At last, perspective on the future research and development of hollow structural materials prepared by templating methods were also discussed.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Porous Silicon Nitride with High Porosity by Carbothermal Reduction-reaction Bonding
LU Yuan, YANG Jian-Feng, LI Jing-Long
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 469–473
 Abstract
Abstract(
1029 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(379KB)(
3115
)
By using cheaper Si, SiO2 and carbon black as starting material, the porous silicon nitride ceramics with high porosity and uniform pore structure were prepared by carbothermal reduction-reaction bonding method. The influences of Si content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the samples were investigated. Microstructures and mechanical properties of porous silicon nitride ceramics were studied by XRD, SEM and three-point bending measurement. XRD analysis showed that only β-Si3N4 phase, minor of α-Si3N4 phase and glass phase Y3Si3O3N4 were detected in the samples. SEM analysis showed that porous silicon nitride ceramics obtained were composed of rod-like β-Si3N4 grains and uniform pores. Porous silicon nitride ceramics with different porosities and good mechanical properties were fabricated by changing the Si content.
|
|
|
In situ Synthesis and Growth Mechanism of SiC Nanowires in SiCO Porous Ceramics
PAN Jian-Mei, CHENG Xiao-Nong, YAN Xue-Hua, ZHANG Cheng-Hua, XU Gui-Fang
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 474–478
 Abstract
Abstract(
802 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(540KB)(
1163
)
SiC nanowires were in situ prepared in Ar atmosphere using polyurethane sponge as a porous template infiltrated with silicone resin. Characterizations of the samples were carried out by TG, XRD, SEM and TEM. The effects of the holding time on the synthesis of SiC nanowires were observed. The growth mechanism of SiC nanowires was discussed. The experimental results show that SiC nanowires were grown directly within the pores of the porous ceramics. The lengths of these nanowires are up to several tens of micrometers and single nanowire has a districtive diameter. The growth mechanism of the nanowires is supported by VS growth model. With the increase of the holding time, the amount of the nanowires increases and these nanowires present different morphologies. Furthermore, the specific surface area of the porous ceramics increases significantly and the volume resistivity decreases.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Microwave Absorbing Properties of PyC/BN Composite Powders
ZHOU Wei, XIAO Peng, LI Yang, LUO Heng, ZHOU Liang
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 479–484
 Abstract
Abstract(
911 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1064
)
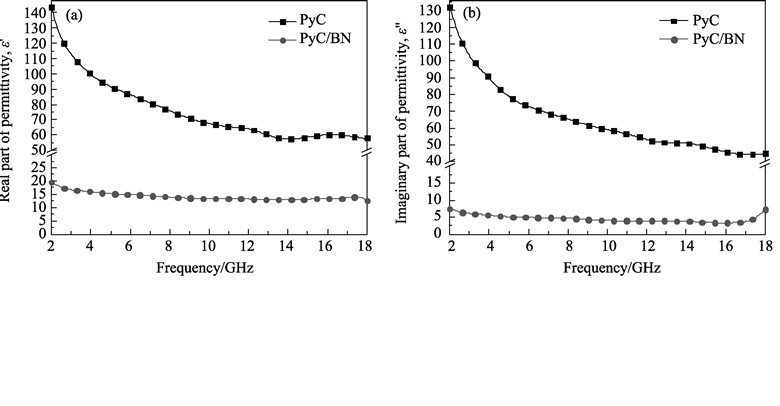
PyC/BN composite powders were synthesized via chemical reaction of boric acid, urea and PyC powders at 1750℃ for 6 h in nitrogen. The phases, chemical compositions, surface morphologies and oxidation resistance of PyC/BN composite powders were characterized by XRD, XPS, SEM and DTA/TGA instruments, respectively. The microwave absorption properties of PyC/BN composite powders were measured by using a microwave network analyzer in the frequency range of 2-18 GHz. The results show that generated h-BN particles are coated on the surfaces of PyC powders with the dimension from tens of nanometers to hundreds of nanometers. Compared with PyC powders, the oxidation resistance of PyC/BN composite powders is improved. The mass of PyC/BN composite powders remains over 50% at 1200℃ whereas PyC powders are oxidized completely at 940℃. Due to higher microwave impedance, electronic displacement polarization, interface polarization, multiple scattering and λ/4 destructive interference effect, the reflectivity peak of PyC/BN composite powders reaches -27.2 dB and the bandwidth of the reflectivity below -10 dB is 2.6 GHz under the same thickness (2 mm). And the reflectivity peaks are all less than -10 dB and multiple absorbing peaks appear with the increase of thickness. PyC/BN composite powders are supposed to be ideal microwave absorbers with lighter weight, high temperature resistance and strong microwave absorption.
|
|
|
Preparation and Gas Separation Performance of P25 Hybrid Carbon Membranes
SUN Mei-Yue, LI Lin, ZHANG Ping-Ping, XU Jia-Jia, YU Jiao-Zhu, WANG Tong-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 485–489
 Abstract
Abstract(
837 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(530KB)(
1181
)
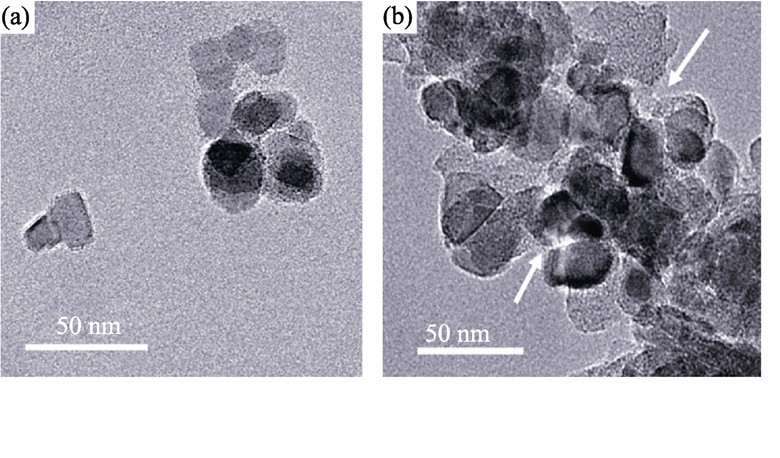
P25 hybrid carbon membranes were prepared by adding the commercial P25 particles into the precursor. Effects of P25 particles on the pyrolysis, carbon structure and gas separation performance of hybrid carbon membranes were characterized by means of TG, SEM, TEM and XRD. The results indicate that the thermal stability of polymer precursor is improved by the incorporation of P25 particles. Gas separation performances of hybrid carbon membrane are greatly improved with the addition of P25 particles due to the accumulate voids formed by the agglomeration of P25 particles and interfacial pores formed between P25 particles and carbon matrix. Molecular sieve mechanism is still conformed in the gas separation of hybrid carbon membranes. Gas permeability increases and gas selectivity remains with the increase of P25 loading. And the gas permeability reduces and gas selectivity increases as final carbonization temperature rises. The permeabilities of H2, CO2, O2, N2 and CH4 are 1769.2, 1558.6, 410.2, 55.5, 26.8 Barrer, respectively, for the hybrid carbon membrane prepared with 20wt% P25 loading and at 700℃ carbonization temperature.
|
|
|
Thermal Modulation Behavior inside the Hysteresis Loop of W-Mo Co-doping Vanadium Dioxide Film
ZHANG Yang, HUANG Wan-Xia, SHI Qi-Wu, SONG Lin-Wei, XU Yuan-Jie
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 497–501
 Abstract
Abstract(
942 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(403KB)(
1175
)
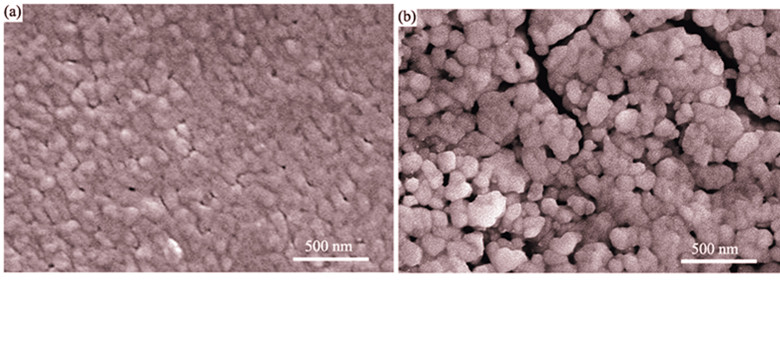
V1-x-yMoxWyO2 polycrystalline films were deposited on Si (100) substrate by an aqueous Sol-Gel method. XRD, SEM were used to detect the morphology and crystal structure of the films. In situ FTIR was carried out to analyze phase transition properties of the V1-x-yMoxWyO2 films. The results show that the prepared films are (011) oriented on Si substrate at room temperature, W6+ and Mo6+ substitute the position of V4+ in the sublattice. The infrared transmittance hysteresis cycles prove that, with the increasing of the W-Mo co-doping content, the phase transition temperature becomes low, while the temperature width of the hysteresis and the sharpness of the phase transition decrease, but the temperature width of the phase transition duration becomes wide. In the temperature range of the phase transition duration the infrared transmittance is modulated by the temperature path, and the infrared transmittance cycles are confined to the boundary of the infrared transmittance hysteresis cycles.
|
|
|
Research on Low-temperature Phase Structures and Electrical Properties of Dense PZT 95/5 Ferroelectric Ceramics
LAN Chun-Feng1, NIE Heng-Chang1, CHEN Xue-Feng, WANG Jun-Xia, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin, LIU Yu-Sheng, HE Hong-Liang
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 502–506
 Abstract
Abstract(
831 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(357KB)(
1170
)
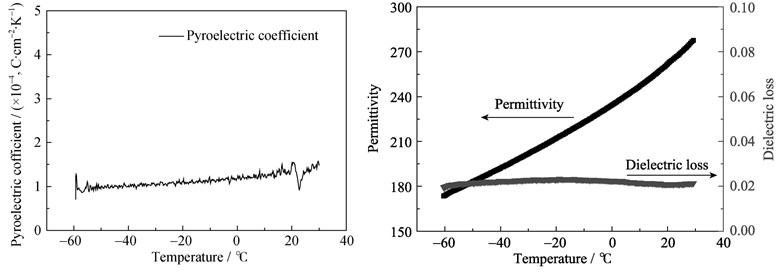
Dense PZT 95/5 ferroelectric ceramics were fabricated by solid-state reaction method. Low-temperature phase structures and electrical properties of dense PZT 95/5 ferroelectric ceramics were investigated. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results show that the phases of both poled and unpoled dense PZT 95/5 ferroelectric ceramics almost keep unchanged at different temperature. The remanent polarization calculated from the pyroelectric current and the resistance of dense PZT 95/5 ferroelectric ceramics changes little at low temperature (-60℃). However, when the temperatue is reduced from 30℃ to -60℃, the relative dielectric constant dramatically decreases from 278 to 173. According to the dynamic discharge model analysis, the sharp decrease of dielectric constant results in the remarkable increase of dynamic electric field at -60℃ which is 1.5 times higher than that at room temperature. This could be the dominant reason for the high dielectric breakdown probability of dense PZT 95/5 ceramics at low temperature under shock wave loading.
|
|
|
Research on the LiODFB Electrolyte’s Electrochemical Performance and Its Compatibility with LTO Electrode
ZHOU Hong-Ming,LIU Fu-Rong, LI Jian, FANG Zhen-Qi, LI Yan-Fen, ZHU Yu-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 507–514
 Abstract
Abstract(
1095 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(512KB)(
1405
)
1 mol/L LiODFB (LiPF6) EC+DMC+EMC (1:1:1 (wt%)) electrolyte’s thermal stability and corrosivity to the aluminum foil were tested by the electrochemical workstation. Cyclic voltammogram, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy rate and cycle performances of LTO/Li battery were measured. The compatibility between LiFePO4/LTO electrode and electrolyte was studied. Results show that at room temperature and 60℃, the stability of LiODFB electrolyte and its corrosivity to the aluminum foil are superior to that of LiPF6 electrolyte. LTO/Li cells with either LiODFB or LiPF6 for electrolyte have simple REDOX peak, and their first charge-discharge curves have stable charge-discharge platform. The difference battery performance between LiODFB and LiPF6 with LiFePO4/LTO as electrode at 0.5C and 1C rates is not significant at room temperature. LiODFB battery exhibits better cycle performance than LiPF6 battery at room temperature and especially at 60℃.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of SnO2/Graphene Anode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries
YU Zhen-Jun, WANG Yan-Li, DENG Hong-Gui, ZHAN Liang, YANG Guang-Zhi, YANG Jun-He, LING Li-Cheng
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 515–520
 Abstract
Abstract(
1568 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(520KB)(
2535
)
SnO2/graphene nanocomposites were in-situ prepared by using graphite oxide and SnCl2·2H2O as raw material, in which external reducing agent is not required. Compared with mechanical mixing method, it can avoid the congregation of SnO2 nanoparticles and graphene. The analysis results (XRD, TEM, etc) indicate that SnO2 nanoparticles are homogeneously dispersed on the surface of graphene layers with a particle size of 3-6 nm, and the thickness of graphene layers is about 1.5-2 nm. The main electrochemical performance can be concluded as follows. 1) The discharge capacity of SnO2/graphene anode electrode after 100 cycles at 200 mA/g, remains at 552 mAh/g, and the capacity retention is 4.4 times of bare SnO2. 2) The discharge capacities of SnO2/graphene anode electrode at 40, 400 and 800 mA/g are 724.5, 426.0 and 241.3 mAh/g, respectively. The excellent rate capability should be attributed to the high electric conductivity and two-dimensional nanostructures of graphene.
|
|
|
TiO2 Nanotube Based Dye-sensitized Photoanode
LUO Hua-Ming, LIU Zhi-Yong, BAI Chuan-Yi, LU Yu-Ming, CAI Chuan-Bing
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 521–526
 Abstract
Abstract(
1161 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(521KB)(
1419
)
A front-illuminated TiO2 nanotube-based dye-sensitized solar-cell (DSC) was presented. Highly ordered TiO2 nanotube membranes were fabricated by two-step anodic oxidation of Ti foil, and then they were transferred to fluorine-doped tin oxide glass substrates to produce a special kind of photoanode. A series of comparison were made between DSCs with different length of nanotubes. Front-illuminated DSC with 32.8 μm nanotube membrane showed an efficiency of 4.15% with TiCl4 treatment. The crystal phase evolution of the TiO2 nanotubes was researched using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD). Electrochemical Impedance Spectra (EIS) results indicated that the electron transportation efficiency had a strong dependence on the thickness of photoanode, and interfacial resistances decreased with the increasing of nanotubes length. These results could help us to understand the mechanism of the electron transportation and further improve the photoanode of DSCs.
|
|
|
Optimization of Photoelectrode for Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cell and Preliminary Study of Tandem Cell
LIU Feng-Juan, SHAO Jing-Zhen, DONG Wei-Wei, DENG Zan-Hong, WANG Shi-Mao, FANG Xiao-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 527–531
 Abstract
Abstract(
804 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(420KB)(
1121
)
Based on the preparation of flexible dye-sensitized solar cells (DSC) by cold isostatic pressing method, optimization of the paste and tandem DSC were investigated. The results presented that hydrothermal treatment of P25 paste could improve the stability of the paste and the efficiency of DSC obviously. Proper amount of 200 nm TiO2 particles was added to the P25 paste to enhance light scattering of photoelectrode. The highest conversion efficiency of 3.11% was obtained at the 4:1 ratio of P25 to 200 nm TiO2. Subsequently, N719 and N749 double-layer tandem DSC were studied. The results show that the efficiency of the double-layer tandem DSC is higher than that of N749 totally sensitized DSC but lower than that of N719 totally sensitized DSC. This may be caused by that thicker photoelectrode hampers the electronic transmission and dyes contact impacts the purity of dyes. The thickness of photoelectrode and cell structure need to be optimized.
|
|
|
Study on Smoke Catalytic Conversion by Sn-substituted Mesoporous Silica Composite in Wood Fire Retardance
XIA Liao-Yuan, WU Yi-Qiang, HU Yun-Chu
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 532–536
 Abstract
Abstract(
720 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(424KB)(
960
)
Sn-substituted mesoporous SiO2 (Sn-SiO2) was prepared by hydrothermal crystallization and characterized with XRD, N2 adsorption and TEM techniques. The results showed that the prepared materials exhibited an ordered mesostructures and high surface areas. The effect of poplar treated with Sn-SiO2 and APP on the combustion and smoke was studied by CONE calorimeter. The results show that the heat release rate (HRR), the total heat release (THR), the smoke production rate (SPR) and the total smoke production (TSP) decreased remarkably while the charring drastically increases, indicating that the compound of Sn-SiO2 and APP have excellent inflame-retarding and smoke inhibition effects for poplar. It is because APP, as catalyst, leads to the formation of carbon and the silica enhances the thermal stability of carbon at a high-temperature. Meanwhile, the Sn-SiO2 shows high catalytic activity for smoke and toxic gas produced by wood combust, which can reduce the concentration of CO effectively and avoid further casualties.
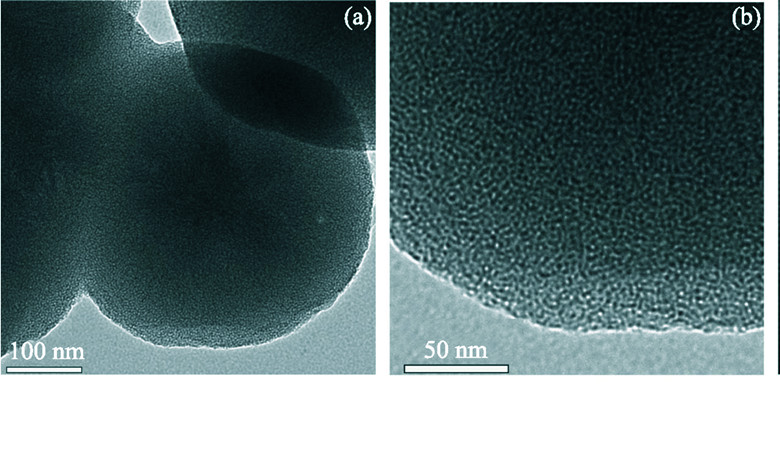
|
|
|
Effect of Solvents on the Structure and Properties of Mesoporous SiO2 Supported Phosphotungstic Acid
DAI Qun-He, SUN Ji-Hong, REN Bo, CHEN Dong, WU Xia
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 537–544
 Abstract
Abstract(
840 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(567KB)(
1082
)
HPW/BMMs catalyst was prepared by supported phosphotungstic acid on mesoporous SiO2 with two different mesoporous structures via impregnation method, and characterized by means of XRD, FTIR, nitrogen adsorption- desorption, TG and SEM. The effects of solvents, such as water, ethanol, acetone and acetonitrile, on the structure and properties of supported phosphotungstic acid were systematically investigated. The results showed that the mesoporous structures of BMMs were maintained in the catalysts synthesis process, however, the mesopores order degree, surface area and pore volume of the catalysts (HPW/BMMs) decreased as the increase of HPW loading. A new HPW species in HPW/BMMs appeared at lower loadings and disappeared as the increasing of HPW amount. In addition, the influence of aqueous solution on the Keggin structure of HPW in HPW/BMMs was remarkable, although the HPW crystal remained intact with the uniform dispersion. The acid density of the catalyst synthesis in water with 40% HPW loading (40HPW/BMMs-WA) was up to 1.381 μmol/m2. In contrast, when acetonitrile was used as solvent, the Keggin structure of HPW was more likely to be maintained, but the HPW crystal phase was severely destroyed with a low dispersing inside the mesoporous channels. In comparison, the effects of ethanol and acetone as solvent were not obvious. Furthermore, the acid reduced performances of the HPW/BMMs catalysts in etherification reaction between waste oils and methanol were preliminarily investigated.
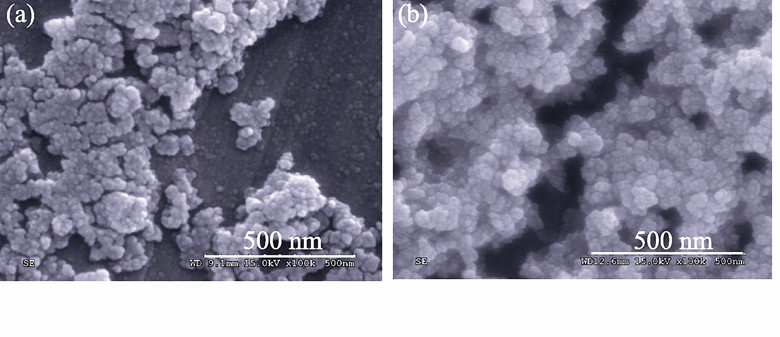
|
|
|
Preparation and Infrared Reflection Performance of Al/Cr2O3 Composite Particles
YUAN Le, WENG Xiao-Long, LU Hu, DENG Long-Jiang
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 545–550
 Abstract
Abstract(
942 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(714KB)(
1209
)
The composite pigments were prepared by co-precipitation coated Cr2O3 on the surface of flake aluminum powders. Phase structure, surface morphology and reflectance spectra of the composite pigment were characterized by XRD, FE-SEM, UV/VIS/NIR spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectrometer. The result shows that the influence of cover treatment with Cr2O3 on the reflectance spectra at various radiation wavelengths is different. The shorter the wavelength is, the stronger the influence is. When the molar ratio of Cr3+ to Al is 0.2:1.0, compared with the uncoated flake aluminum powders, its average reflectance of visible spectrum and brightness (L*) drop to 50% and 15, respectively. However, the infrared emissivity of 8-14 μm waveband increases less than 10%. It mainly ascribes to the difference of surface roughness and absorption coefficient for different radiation wavelengths. Thus, the composite particles play a vital role in designing the low infrared emissivity coating.
|
|
|
Photostimulated Luminescence and Radiation Hardness Properties of CsBr:(Eu2+,KOH)
MENG Jia, ZHAO Li-Li, SONG Li-Xin
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 551–556
 Abstract
Abstract(
752 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(444KB)(
1133
)
CsBr: (Eu2+, KOH) powders were prepared by solid-state reaction. The photo luminescence (PL) spectra, photostimulated luminescence (PSL) spectra, Raman spectra and PSL lifetime spectra were systematically investigated, and the influence of KOH-adding on photostimulated luminescence and radiation hardness properties were discussed. The results reveal that the probability of radiationless transition increase due to hydroxyl ion (OH-), with the increasing of concentration of KOH, the PSL decay time of CsBr:(Eu2+,KOH) shortens gradually. Furthermore, the vacancy concentration around Eu2+ decreases due to the existence of K+ and OH-, which avoid the concentration quenching by the aggregation of Eu2+ and improves the radiation hardness of CsBr: Eu2+.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Europium or Terbium Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanorods and Their Cytotoxicity
TAO Ting-Ting, WANG Jing-Xian, DONG Xiang-Ting, YU Wen-Sheng, LI Qing-Li
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 557–560
 Abstract
Abstract(
785 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(337KB)(
1081
)
Using CaCO3, Eu2O3, Tb7O4, HNO3 and NH4H2PO4 as starting materials, regulating pH value by NH3·H2O, europium-doped and terbium-doped hydroxyapatite (HA:Eu3+/ HA:Tb3+) nanorods were prepared by hydrothermal method using EDTA as a template. The synthesized materials were systematically characterized by XRD and FESEM. Their luminescence properties and cytotoxicity were studied by fluorescence analysis and MTT assay, respectively. The results show that the main emission peaks of HA:Eu3+ and HA:Tb3+ nanorods occur at 617 and 544 nm, which can emit bright red and green light, respectively. The cell survival curves show that the prepared HA:Eu3+ and HA:Tb3+ nanorods can be used as ideal biological tracer materials.
|
|
|
Nb Solution within Bi4Ti3O12 Sub-structure in the Intergrowth Bismuth-layered Compound Bi7Ti4NbO21
GAO Xiang, WANG Xian-Hao, XING Juan-Juan, GU Hui, ZHANG Fa-Qiang, LI Yong-Xiang
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 561–565
 Abstract
Abstract(
1043 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(367KB)(
1259
)
In intergrowth bismuth-layered compound Bi7Ti4NbO21, growth defects, such as disordered intergrowth with extra layers of Bi4Ti3O12 or Bi3NbTiO9 constituent sub-structures, or as the co-growth of Bi7Ti4NbO21 onto Bi4Ti3O12 grains, were frequently observed using high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM)[1]. In order to further find evidence to support the re-ordering picture that was proposed to explain formation of the intergrowth and associated defects, we employ the low- and medium-resolution high-angle annular-dark-field (HAADF) imaging combined with the quantitative energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDXS) analysis to probe into a heavily defected intergrowth structure. A gradual transformation from the ordered intergrowth of both sub-structures to the dominance of Bi4Ti3O12 sub-structure was observed. A substantial level of Nb solution could be detected in n-layered (n≥2) Bi4Ti3O12 sub-structure by spatially-resolved compositional quantification to differentiate the contribution from the adjacent single Bi3NbTiO9 layer. The presence of a finite Nb concentration in the Bi4Ti3O12 sub-structure indicates a substantial and uniform cations inter-change occurred between the two sub-structures, which is inherited most likely from the parent phases via the partially dissolved sintering melts[1].
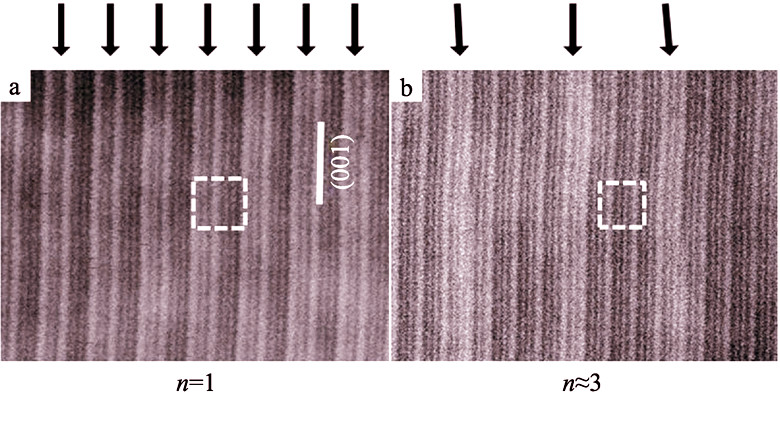
|
|
|
Rheological Properties of SiC-ZrB2 Composite Suspensions
LI Dan, YAO Xiu-Min, YANG Yong, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2013 Vol. 28 (5): 566–570
 Abstract
Abstract(
999 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(337KB)(
1437
)
The SiC-ZrB2 composite slurry was investigated as preliminary work for the preparation of high-performance SiC-ZrB2 reticulated porous ceramics (RPCs). The dispersions of SiC and ZrB2 powders were investigated, and the amounts of dispersant and adhesive were optimized, respectively. Based on these results, the investigation focused on the influences of the solid loading and the ZrB2 amount on the rheological behavior of suspensions. The suspension with 65wt% solid loading was chosen as the optimum for polymeric sponge replication process. And the ZrB2 amount should be less than 25wt%.
|
|