|
|
Progress on Scintillation Crystals for Dual-readout Calorimeter
XIAO Xue-Feng, XU Jia-Yue, XIANG Wei-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 347–357
 Abstract
Abstract(
1077 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(585KB)(
1465
)
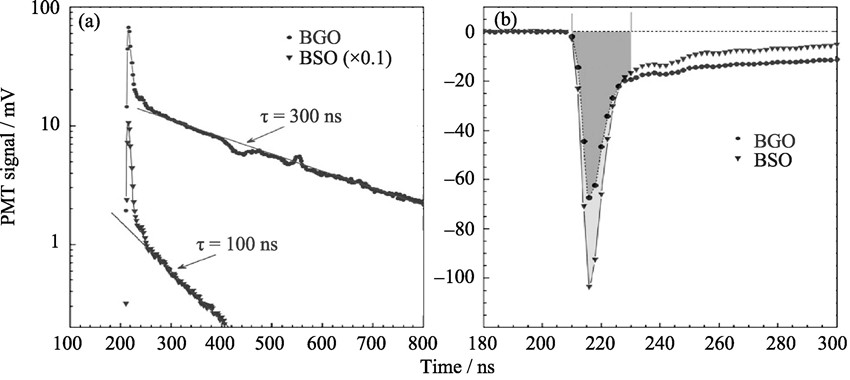
The dual-readout calorimeter is a new designed equipment to detect high-energy particles. It can collect the Cherenkov light and scintillation light at the same time, thus scientists can understand the particles comprehensively in the field of high-energy physics. Three types of dual-readout calorimeters have been designed so far: (1) Quartz fibers as Cherenkov emitter and plastic fibers as scintillator; (2) Undoped and doped scintillation crystals act as Cherenkov and scintillator respectively; (3) Scintillation crystal act as Cherenkov as well as scintillator. The last attracted much attention because it can avoid sampling fluctuations and enhance energy resolution of calorimeters. The progress on the scintillation crystals, including lead tungstate (PbWO4), bismuth germinate (Bi4Ge3O12), bismuth silicate (Bi4Si3O12) and lutetium aluminum garnet (Lu3Al5O12), were presented for the application of dual-readout calorimeter. Pr: PWO crystal and Bi4Si3O12 crystal have potential application in dual-readout calorimeter. It’s easy to separate the Cherenkov and scintillation light for Bi4Si3O12 crystal because the short-wavelength cut-off of Bi4Si3O12 crystal is small in comparison with Bi4Ge3O12 crystal. Bi4Si3O12 crystal shows more advantages and its properties can be further optimized by doping rare earth ions.
|
|
|
Quantitative Analysis for Phase Compositions of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC Ultra-High Temperature Ceramic Composites
ZHENG Qiang, WANG Xian-Hao, XING Juan-Juan, GU Hui, ZHANG Guo-Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 358–362
 Abstract
Abstract(
911 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(485KB)(
1567
)
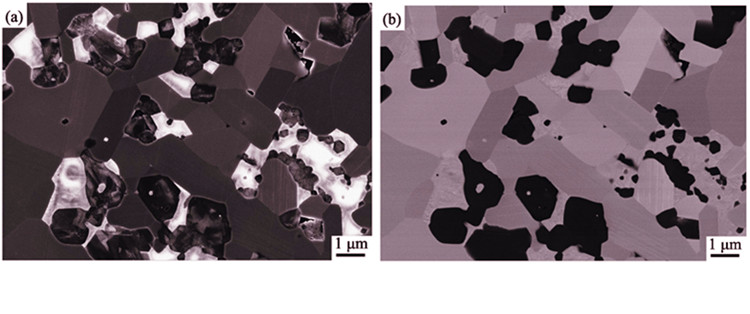
Three methods were applied and compared to perform quantitative phase analysis of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC ultra- high temperature ceramic composites: the K value method by powder X-ray diffraction, two SEM methods to combine secondary electron and backscattered electron images, and electron backscatter diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDS) mapping. K value method could be applied conveniently and simply, while the two SEM methods could not only be performed quantitative phase analysis but also reveal phase distribution and relationships. Results from the three methods all show significant deviation of phase compositions from the composite designing of reactive sintering, while they are largely consistent with each other. The content of impurity ZrO2 phase is detected more than 5vol%, and in contrast, the content of secondary ZrC phase is found substantially below the theoretical 5vol% level and even below 1vol% as calculated by the more sensitive K value method. These quantitative phase analysis could provide technical supports to study the true composite microstructure and phase designing.
|
|
|
Research on Microstructures and Properties of in-situ Synthesis of TiB2-TiC0.8-SiC Multiphase Ceramics
SUN Pei-Qiu, ZHU De-Gui, JIANG Xiao-Song, SUN Hong-Liang, XIA Zhao-Hui
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 363–368
 Abstract
Abstract(
773 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(688KB)(
1284
)
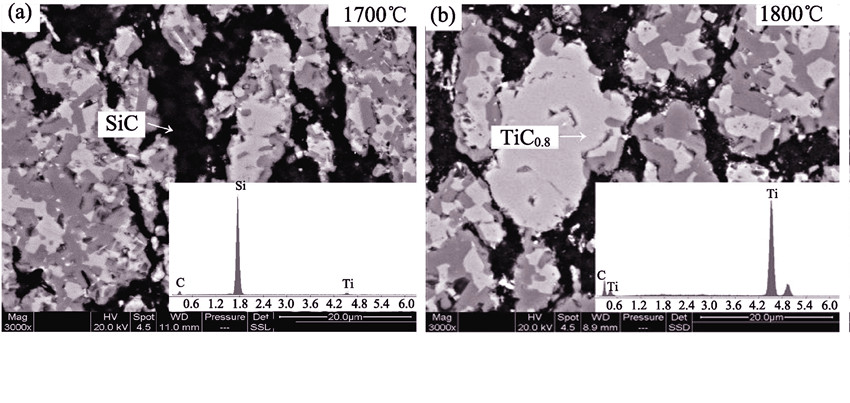
TiB2-TiC0.8-SiC multiphase ceramics were prepared by in-situ hot-pressing sintering. The phase composition and microstructures of the materials were characterized by optical microscope, X-ray diffraction technology and scanning electron microscope. The effects of sintering temperature on the phases, microstructures and mechanical properties of the ceramics were investigated. The results show that with the increase of sintering temperature, density, bending strength and fracture toughness of the ceramics are increasing significantly in the temperature from 1700℃ to 1950℃. Fully densified in-situ TiB2-TiC0.8-SiC multiphase ceramics with well-developed and optimized microstructure are obtained after sintered at 1900℃, in which the uniform distribution of lath-shape TiB2 and bulk TiC0.8 grains is obvious. The present study shows that Vickers hardness, fracture toughness and flexural strength of the TiB2-TiC0.8-SiC multiphase ceramics sintered at 1900℃ are 23.6 GPa, (7.0±1.0) MPa·m1/2 and 470.9 MPa, respectively. When sintering temperature was up to 1950℃, TiB2 and TiC0.8 grains grew up, and therefore the bending strength of multiphase ceramics was reduced. TiB2,TiC0.8 and SiC particles were incorporated to improve the particulate strength and toughness of composite material by the synergistic action of the mechanisms such as crack deflection, grain's pull-out and fine-grain toughening.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of AlMgB14-TiB2 Composite by Field-activated and Pressure-assisted Synthesis
LIU Wen, MIAO Yang, CHEN Shao-Ping, ZHUANG Lei, MENG Qing-Sen
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 369–374
 Abstract
Abstract(
989 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(511KB)(
1279
)
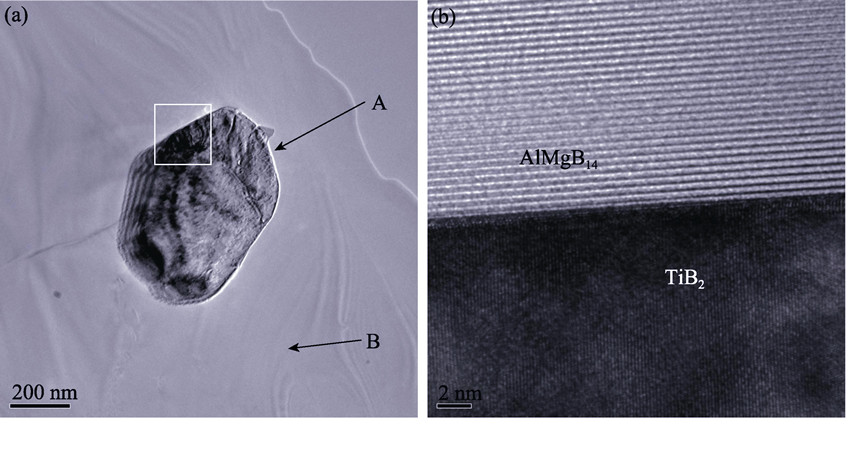
The pre-reacted AlMgB14 powders prepared by FAPAS were mixed with TiB2 powers and then subjected to the temperature of 1500℃, the axial pressure of 60 MPa, the heating rate of 100℃/min and dwelling time of 15 min. AlMgB14-30wt% TiB2 composites with ideal structures were successfully prepared. The microstructure and components of synthesized composites were observed and determined by scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results show that the micro-hardness of the AlMgB14-30wt% TiB2 composites is 31.5 GPa and the fracture toughness K1C could reach 3.65 MPa·m1/2, which is consistent with those prepared by mechanical alloying/hot pressing. The microstructure analysis shows that the main toughening mechanisms of AlMgB14-TiB2 composites are due to the hard phase dispersion strengthening, high-strength interface bonding. The FAPAS method might be used to synthesize AlMgB14-TiB2 composites at low costs with fast heating-up and efficiency.
|
|
|
Application of Doping Ceramics via Infiltration on Translucent Alumina Ceramics
LIU Guan-Wei, XIE Zhi-Peng, WU Yin
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 375–380
 Abstract
Abstract(
1017 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(537KB)(
1396
)
The feasibility to homogeneously incorporate additives and fabricate translucent alumina ceramics via liquid precursor infiltration technique was substantiated. Pre-sintered alumina compacts with various thickness values were infiltrated with aqueous yttrium nitrate solutions of different concentrations under various conditions. Line-scanning result of yttrium along the sample depth direction was investigated to characterize the doping homogeneity. It is found that better distribution homogeneity and more stringent control of a desired amount of dopants can be realized as the sample thickness and the solution concentration are decreased. By assuming all pores are open and completely saturated, the theoretical model is proposed to predict the amount of incorporated species by infiltration. Finally, translucent alumina ceramics were fabricated. Compared with ball-milling prepared counterparts, samples with improved microstructure and enhanced optical properties are achieved by infiltration.

|
|
|
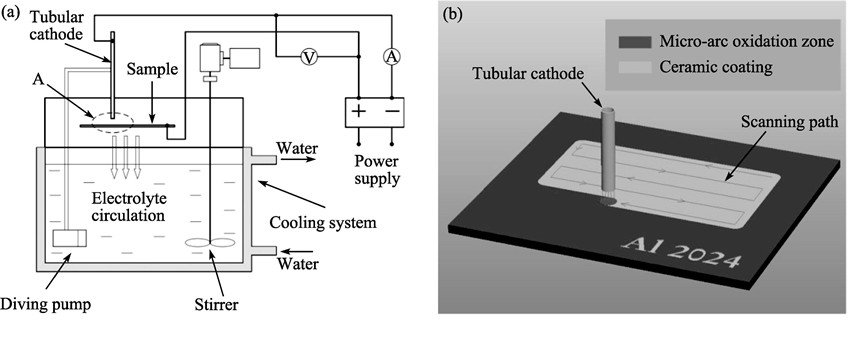
Study on Scanning Micro-arc Oxidation Technology Applied to 2024 Aluminum Alloy
Lü Peng-Xiang, WEI Dong-Bo, GUO Cheng-Bo, LI Zhao-Long, DI Shi-Chun
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 381–386
 Abstract
Abstract(
917 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(482KB)(
1245
)
The ceramic coating was formed on the part of the impaired surface of the 2024 alloy sample by scanning micro-arc oxidation using low pulsating power supply. It proposed a solution for local repairing impaired part of big workpiece using micro-arc oxidation technique. Microstructure and phase composition of coating were characterized by SEM, XRD and EDS. The nano indentation hardness and elastic modulus of coatings were tested by nano indenter. The corrosion resistance properties of coatings were determined by potentiodynamic polarization. The results show that under the continuous current mode, the bath voltage of scanning micro-arc oxidation (SMAO) raise fast and go into micro-arc oxidation stage immediately. The thickness of the coating formed by SMAO is 17 μm after a single scanning, indicating SMAO has high film efficiency. The coating, mainly composed of α-Al2O3 and γ-Al2O3, is dense in the inner layer and porous in the outer layer. There are a large number of micropores and micro-cracks on its surface. The nano indentation test results show that the nano indentation hardness and elastic modulus of coatings firstly increase and then decrease from interface to surface. The potentiodynamic polarization indicates that the SMAO and MAO coatings all have effective corrosion protective effect to 2024 aluminium alloy. And the MAO coating's performance is better than that of SMAO coating.
|
|
|
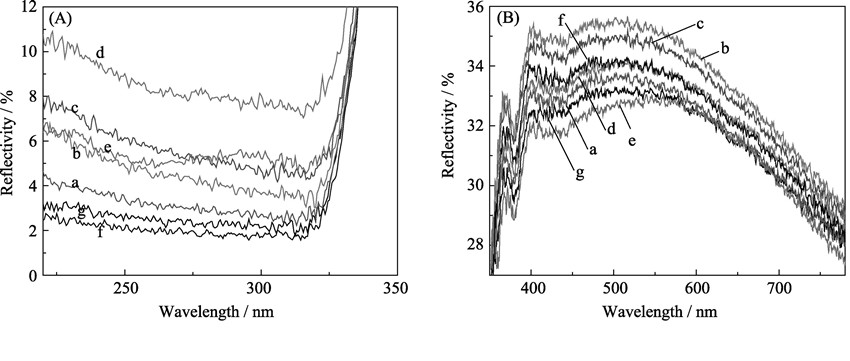
Influence of pH Value on the Performance of Composite Films Prepared from Chromium Residue by Hydrothermal Method
SUN Tong, LIU Lian-Li, XU Shu-Ying, PENG Xiao-Lin, YANG Hai-Long
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 387–392
 Abstract
Abstract(
738 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(483KB)(
1070
)
With chromium residue as main raw materials, the composite films were prepared by hydrothermal method. The samples were characterized by SEM, ICP, XRD, FT-IR and film thickness, and the influences of hydrothermal pH value on the performance of composite films were investigated using the films’ refractive index and reflectivity as evaluation indexes. The results show that the perfect three dimension networks are appeared on the film surface when pH value is above 11. At pH value of 9 or 10, Al2O3, Fe2O3, Fe(OH)3, Cr2O3, AlO(OH) and MgO crystals are formed in the sample, and the diffraction peak of them is strong. There are pores and surface absorbed water between internal nanoparticles in the samples. In the process of hydrothermal synthesis, the formation of chemical bonds force between the membrane material and basement are facilitated by the alkaline groups. Meanwhile, the thicker film is the smaller the refractive index of the film will be. At pH value of 11, the film is the thinnest and the refractive index is the biggest. At the initial pH value of 12, the refractive index of the film to ultraviolet light is weaker than glass substrate, and at the initial pH value of 11, the refractive index of the film to visible light is weaker than that of glass substrate.
|
|
|
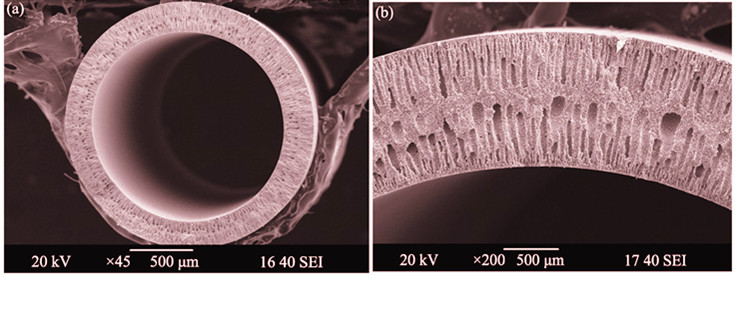
Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophobic Porous Yttria-stabilized Zirconia Hollow Fiber for Water Desalination
SHANG Shuang-Yin, FANG Hong, REN Chun-Lei, YANG Ping-Hua, CHEN Chu-Sheng
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 393–397
 Abstract
Abstract(
1004 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(547KB)(
1316
)
Porous yttrium-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) hollow fibers with an outer diameter of 1.92 mm, membrane thickness of 0.21 mm were prepared by a combined technique of phase inversion and sintering. The hollow fiber possessed a sandwich structure with long-finger like voids near the inner and outer walls and a thin porous sponge-like layer in the center. The porosity and average pore size of the YSZ hollow fiber were determined to be 54% and 0.56 μm, respectively. The surface of the hollow fiber was converted from hydrophilic to hydrophobic by grafting with fluoroalkylsilane (FAS). The as-prepared hydrophobic YSZ hollow fiber exhibited desired water desalination performance operating in the vacuum membrane distillation (VMD). A water flux as high as 48.3 L/(m2•h)was attained with a salt rejection of over 99.7% by exposing the shell side of the fiber to an aqueous solution of 4wt% NaCl at 80℃ and vacuuming the lumen side to a pressure of 4×103 Pa. The membrane distillation performance of the hydrophobic porous YSZ hollow fiber is comparable to the best of polymer membrane, which is promising for water desalination application.
|
|
|
Electromagnetic Properties of Novel Carbon Nanofibers
WANG Gai-Hua, DAI Bo, MA Yong-Jun, REN Yong
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 398–402
 Abstract
Abstract(
878 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(480KB)(
1351
)
Carbonized bacterial cellulose (CBC) with a three dimensional net-linked framework were synthesized from carbonized bacterial cellulose and investigated by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectrum and Transmission electron microscopy. The complex permittivity and permeability of CBC/paraffin wax composite with certain ratio of the composite were measured by vector network analysis in the frequency range of 0.1-18 GHz. It is found that the composite has high permittivity and dielectric loss, especially at the low frequency. The electromagnetic characteristics of the CBC/Fe3O4 complex absorbers synthesized by mixing a small quantity of CBC with Fe3O4 were also studied, aiming at improving the microwave absorbing properties of Fe3O4/Wax composite. When the sample’s thickness was 1.2 mm, the reflection loss reached a minimal value of -21 dB for CBC - Fe3O4/Wax and of -2 dB for Fe3O4/Wax as well.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Capacitance Characteristics of the Graphene Grafted Polypyrrole Composites
LIU Jian-Hua, ZHANG Shi-Lu, YU Mei, AN Jun-Wei, LI Song-Mei
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 403–408
 Abstract
Abstract(
1082 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(446KB)(
1306
)
The graphene grafted polypyrrole composites were in situ synthesized with the chemical grafting method. The testing and characterization of the structure and morphology indicated that the pyrrole monomer in the composites was grafted with the graphene lamellar layer on-chip evenly distributed through the amide bond, and a large number of the pyrrole grow into a chain connecting to the graphene layers. The synergistic effect of graphene and polypyrrole made the conductivity of the composites significantly improve from 0.22 S/cm to 3.32 S/cm. The capacitance value of graphene grafted polypyrrole composites reached 284 F/g, which increased by 52% compared with the specific capacitance of pure polypyrrole 186 F/g. It indicated the composites’s excellent characteristics of the capacitor.
|
|
|
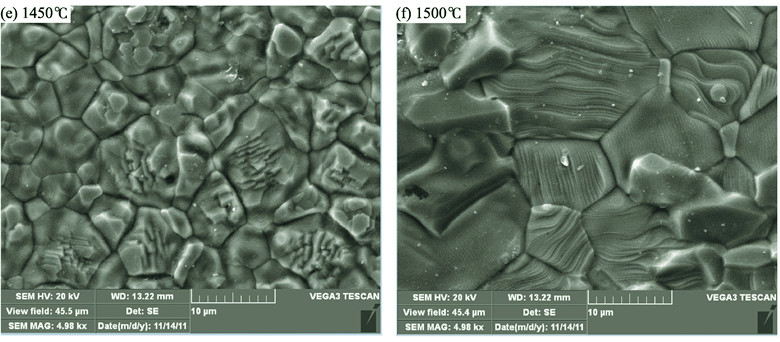
Research on the Sensitive Electric Properties of La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2Ox Electrolyte
GU Yuan-Yuan, CHEN Kang, JIANG Hao, JIAN Jia-Wen
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 409–414
 Abstract
Abstract(
790 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(501KB)(
1282
)
La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2Ox (LSGM) electrolytes were prepared from La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2Ox powders sintering at 1000-1500℃ for 4 h. Both the physical and electrical properties of the LSGM samples were tested. The results show that the linear shrinkage and relative density of the samples increase with sintering temperature rising, besides, the sample sintered at 1400℃ for 4 h shows the maximum value of 24.8% and 97%, respectively. Samples sintered at 1250℃-1500℃ for 4 h have uniform phase while that sintered at 1000℃ has a large amount of impurities. The sample sintered at 1400℃ for 4 h has the largest conductivity being 0.093 S/cm at 800℃. Based on this, a limiting-current-type O2 sensor based on LSGM was fabricated by screen-printing technique, and the I-V characteristics and response/recovery time were measured. It shows that the I-V curves have good current plateaus, and the limiting current exhibits a linear dependence on oxygen concentration. The response/recovery time are 10-15 s and 15-20 s, respectively, showing well reproducible response characteristics.
|
|
|
Sol-Gel Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of LiMnPO4/C Cathode Material
WANG Yan-Ming, WANG Fei, WANG Guang-Jian
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 415–419
 Abstract
Abstract(
1081 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(427KB)(
1512
)
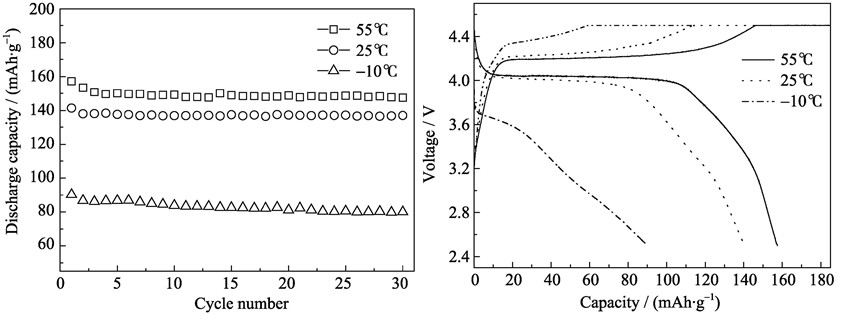
LiMnPO4/C composite as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries was synthesized via a Sol-Gel method using tributyl phosphate as both chelating agent and phosphor source while lauric acid as a carbon source. Crystalline structure and morphology of the composite were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results indicate that the LiMnPO4/C composite is well crystallized as an olivine structure without any detectable impurity phase at annealing temperature of 700℃. The spherical-like LiMnPO4/C microparticles are composed of large numbers of nanoparticles with the size ranging from 50 nm to 100 nm, which are covered with a thin carbon layer. Cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge-discharge tests reveal that LiMnPO4/C composite has superior electrochemical performance. The initial discharge capacities of LiMnPO4/C are 141 and 113 mAh/g at rates of 0.05C and 0.5C under room temperature, respectively, along with high cyclic stability and good charge-discharge performances under high and low temperatures.
|
|
|
Research on ZnO Nanorods Grown on Si Substrate Etched by TMAH as Si Solar Cell Antireflection Layer
WANG Tao, QU Xin-Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 420–424
 Abstract
Abstract(
974 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(411KB)(
1380
)
An antireflection layer grown on the Si surface of a solar cell can reduce reflection and increase absorption of light. As a result, it can increase the conversion efficiency of the Si solar cell. In this work, (100) Si wafers were anisotropically wet etched by tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide (TMAH) solution and the pyramidal structures were obtained. The minimum reflectivity of etched Si was lower than 6%. Then ZnO nanorods were grown on the Si substrate by a hydrothermal method. The minimum reflectivity of this structure was lower than 3%, better than that from the TMAH etched surface or ZnO nanorods covered surface only. This method has great potential because of its simplicity and high efficiency.
|
|
|
Preparation and Optical Storage Properties of λTi3O5 Powder
LIU Gang, HUANG Wan-Xia, YI Yong
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 425–430
 Abstract
Abstract(
1005 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(516KB)(
1248
)
The Ti3O5 powder was prepared by reducing TiO2 nanopartical in H2 atmosphere. The samples were investigated by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and UV-Vis diffusion reflectance spectra (UV-Vis). The results show that, single phase Ti3O5 can be obtained by increasing the H2 flow. When H2 flow increases from 0.3 mL/min to 0.8 mL/min, the single phase λ-Ti3O5 can be synthesized using SiO2-coated TiO2 (rutile, nanoparticle) as raw material at 1150℃ for 1 h. While using nano-TiO2 powders without SiO2-coated as raw material, the reduction product is multiphases composed of λ-Ti3O5 and β-Ti3O5. There is a high reflectivity contrast between λ-Ti3O5 and β-Ti3O5. When the multiphases sample is irradiated with 532 nm 20 ns-pulsed laser light at room temperature, Ti3O5 will transit from α phase to β phase, which shows a good optical storage performance.
|
|
|
Fabrication of TiO2/CdS Coaxial Heterojunction and Its Photocatalytic Properties
CAI Si-Long, SONG Ping-Xin, ZHANG Ying-Jiu, WANG Cai-Li, ZHANG Yue-Ping, AN Lu-Lu
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 431–435
 Abstract
Abstract(
954 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(406KB)(
1769
)
TiO2 nanotube arrays on titanium sheet were prepared by anodized oxidation method and filled with CdS in the interior of the annealed TiO2 nanotubes by direction current (DC) electrodeposition. The TiO2/CdS heterojunctions were characterized through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) and X-Ray diffraction (XRD). The results show that TiO2/CdS coaxial nanocables are orderly arrayed, their diameters are uniform and the chemical ratio of Cd and S is closed to 1:1. The TiO2 annealed at 450℃ in air is anatase and the deposited CdS is hexagonal phase. UV-visible absorption spectroscopy and methyl orange dye by photocatalytic degradation under UV light of the pure TiO2 nanotubes and TiO2/CdS heterojunction are investigated. Compared with the pure TiO2, TiO2/CdS heterojunction has an obvious red-shift on the edge of TiO2 absorption and their photocatalytic activity is obviously improved, with maximum degradation rate of methyl orange as 99.4%.
|
|
|
Preparation of La-doped BiFeO3 Thin Film and Its Photovoltaic Properties
XIE Yi-Jun, GUO Yi-Ping, DONG Wen, GUO Bing, LI Hua, LIU He-Zhou
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 436–440
 Abstract
Abstract(
1180 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(465KB)(
1558
)
The La3+ doped BiFeO3 (BFO) thin films were fabricated by Sol-Gel method. The precursor solution was synthesized by dissolving Bi(NO3)3, Fe(NO3)3 and La(NO3)3 in 2-methoxyethanol and BiFeO3 thin films were grown by chemical solution deposition on fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) glass substrate. The influence of La3+ doping on the band gap and photovoltaic properties of BiFeO3 was studied. The BiFeO3 thin films exhibited polycrystalline-phase perovskite structure. The lattice parameter of BiFeO3 decreased with La3+ addition increasing. The band gap of BiFeO3 doped with 10% La3+ doping was 2.71 eV, a little smaller than that of the undoped one. The bandgap of BiFeO3 increased to 2.76 eV with the increase of La3+ doping. The maximal open circuit voltage of 10% La3+-doped BiFeO3 prepared by modified method reached 0.4 V, showing good photovoltaic properties.
|
|
|
Study of Dielectric Relaxation Behavior of Co-doped BCZT Ceramics
XU Qin, DING Shi-Hua, SONG Tian-Xiu, PENG Yong, WU Xiao-Liang
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 441–446
 Abstract
Abstract(
5336 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(615KB)(
1255
)
Ba0.9175Ca0.08Nd0.0025(Zr0.18Ti0.8175-xYxMn0.0025)O3(BCZT-Y, x=0, 0.5mol%, 0.75mol%, 1.0mol%, 1.5mol%, 2.0mol%) ferroelectric ceramics was prepared by a solid phase reaction. The influence of Y3+ doping on the structure and dielectric properties of BCZT-Y ceramics was investigated. Results showed that with the Y3+ contents increasing, Y3+ ion substitution can be almost incorporated into the Ti4+ site, and the density of BCZT-Y ceramics increased from 4.029 g/cm3 to 6.058 g/cm3. The Curie temperature was shifted to lower temperature, and the εr-T peak was decreased and broaden. The ferroelectric relaxor characteristics were obtained while Y3+ ion content was further increased, which were consistent with the Lorenz-type formula fitting. It was found that the area of ferroelectric hysteresis loop became narrow and slant, the remnant polarization (Pr) and coercive field (Ec) reduced with the increase of Y3+ content.
|
|
|
Dielectric and Pyroelectric Properties of Y-doped Ba0.6Sr0.3Ca0.1TiO3 Ceramics by Solid-state Reaction Technique
CAO Sheng, MAO Chao-Liang, YAO Chun-Hua, CAO Fei, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 447–452
 Abstract
Abstract(
1480 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
2008
)
(Ba0.6Sr0.3Ca0.1)1-xYxTi0.999Mn0.001O3(0≤x≤0.007) ceramics were prepared by the solid-state reaction technique. The effects of Y doping on the microstructure, dielectric properties and pyroelectric properties were investigated. The average grain size decreases with the increase of Y concentration. The dielectric and pyroelectric properties measurement results show that the dielectric constant, dielectric loss, Tc and pyroelectric coefficient all initially increase and then decrease with Y concentration. And the pyroelectric figure of merit Fd can be improved by the Y doping. The specimen doped with 0.7mol%Y shows a higher maximum Fd value of 8.22×10-5 Pa-1/2 under 700 V/mm near 30℃ with the smallest average grain size of 3.1 μm, indicating its promising application in infrared thermal imaging arrays devices.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Al2O3/Steel-epoxy Laminated Composites
LI Wei-Xin, BAI Ming-Min, LU Ying, RAO Ping-Gen
2013 Vol. 28 (4): 453–459
 Abstract
Abstract(
1106 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(539KB)(
1692
)
A series of Al2O3/steel-epoxy laminated composites were prepared by using epoxy resin adhesive as binder via a simple process in a leaky mould at a pressure of 5 MPa. The results indicate that the interfaces of Al2O3/epoxy and steel/epoxy are joined tightly, and the laminated composites have much higher fracture toughness, impact toughness and energy consumption than the Al2O3 monolith, as well as having a close strength to Al2O3. The crack propagation behavior indicates that the improvement of toughness and energy consumption attribute to the mechanisms of crack blunting and arresting, crack bridging, interface debonding, ductile deformation of steel-epoxy mesh layer.
|
|