|
|
Research Progress of Graphene Composites
KUANG Da, HU Wen-Bin
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 235–246
 Abstract
Abstract(
6373 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(578KB)(
6727
)
Graphene has recently attracted much interest in material field due to its unique two-dimensional structure and outstanding properties. Various preparation methods of graphene are briefly compared. The physical and mechanical properties of graphene are then introduced. Graphene-based composite becomes one of the most important research frontiers in the application of graphene. A comprehensive review is presented to introduce the latest progress of the graphene related composites, including graphene-polymer composites and graphene-based inorganic nanocomposites, especially introducing the fabrication methods and outstanding performances of the bulk metal-matrix/ graphene composites.
|
|
|
Research Progress on the Application of C/SiC Composites in Scramjet
MA Qing-Song, LIU Hai-Tao, PAN Yu, LIU Wei-Dong, CHEN Zhao-Hui
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 247–255
 Abstract
Abstract(
1241 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(737KB)(
1700
)
Scramjet is crucial to develop hypersonic technology. The hypersonic vehicles with scramjet as power device are of much significance for national defense security and space transportation. In this paper, the requirements for thermal protection materials of scramjet were analyzed and current status of the application of C/SiC composites in scramjet was reviewed. At last, the development proposals and key problems needed to be solved for C/SiC composites were offered in order to meet the demands of scramjet.
|
|
|
Ablation Properties of ZrB2-SiC Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Coatings
ZHOU Hai-Jun, ZHANG Xiang-Yu, GAO Le, HU Jian-Bao, WU Bin, DONG Shao-Ming
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 256–260
 Abstract
Abstract(
980 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(471KB)(
1379
)
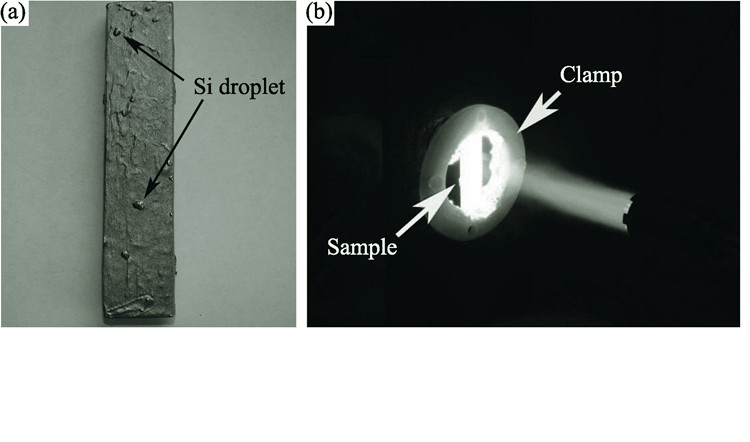
To improve the anti-ablation properties, the ZrB2-SiC ultra-high ceramic coatings were successfully fabricated on the C/C composites surface by slurry dipping and liquid silicon infiltration process. Their ablation resistances properties were determined by using an equipment of oxygen-propane torch test. The results show that the bonding strength between the coating and C/C matrix is relatively high due to the formation of reactive SiC layer. The ZrB2-SiC coating has a well protection from oxygen-propane fire ablation at 1500℃ for 600 s. The whole coating keep integrity avoiding the C/C matrix from oxidation and ablation during the test. The microstructure indicates that ZrB2-SiC coating has some ZrO2 phase and ultra-high temperature ceramics phase after the test, which proves that the coating also has much longer life for the protection of C/C composites at high temperature airflow erosion environment. The anti-ablation forms of the ZrB2-SiC coating are mainly thermo chemistry corrosion and mechanical erosion.
|
|
|
Nanocarbon-coated α-Al2O3 Composite Powders Synthesized by High-energy Ball Milling
WU Xiao-Xian, LI Hong-Xia, LIU Guo-Qi, NIU Chong-Chong, WANG Gang, SUN Jia-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 261–266
 Abstract
Abstract(
729 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1149KB)(
1249
)
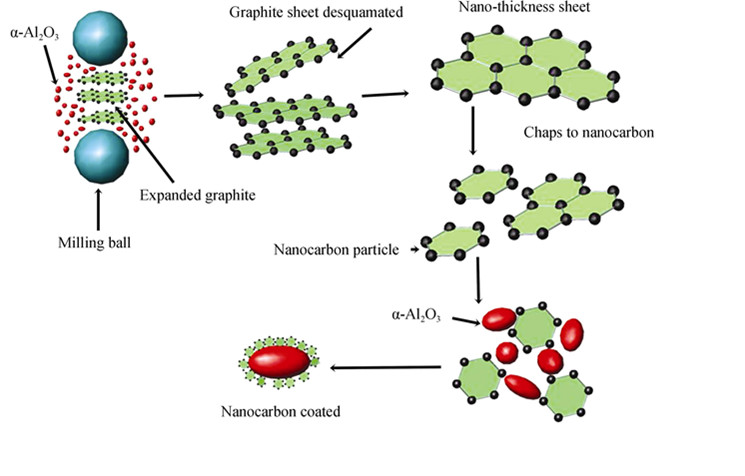
Nanocarbon-coated α-Al2O3 composite powders were synthesized by high-energy ball milling using expanded graphite and α-Al2O3 as raw materials. The effects of milling time and speed on phase composition and microstructure of the composite powders were investigated. X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) were employed to characterize the phase composition, morphology and microstructure of the composite powders. The results show that nanocarbon with a size of 20–50 nm coated on the α-Al2O3 particles when the expanded graphite and α-Al2O3 with a weight ratio of 1:2 were milled for 5 h at a speed of 600 r/min. By increasing the milling time, the (002) diffraction peak of graphite gradually disappeared, and nano-graphite sheets desquamated from expanded graphite and then chaped to nanocarbon particles. Milling for the same time, higher milling speed was beneficial to synthesize nanocarbon particles, but when milling speed reached certain value, the size of nanocarbon cannot become smaller again. Nanocarbon-coated α-Al2O3 composite powders cannot be synthesized using a milling speed of 480 r/min even milled for 5 h. The morphology and microstructure of the composite powders were basically the same when the composite powders were milled at 600 and 700 r/min for 5 h.
|
|
|
Preparation of Porous Carbon by Copolymerization for Electric Double-layer Capacitors
SUN Li-Hong, LIU Hong-Bo, XIA Xiao-Hong, HE Yue-De
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 267–272
 Abstract
Abstract(
667 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(453KB)(
1099
)
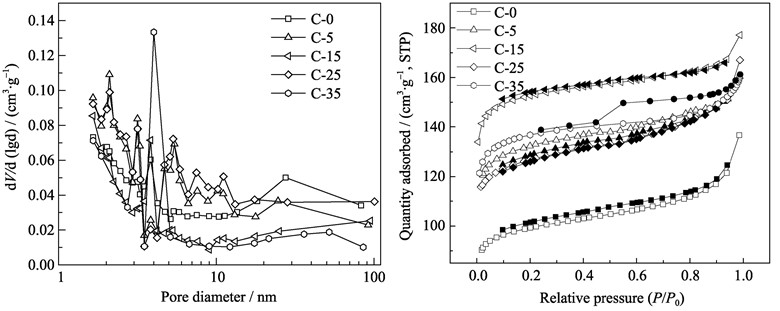
Porous carbons were prepared by chemical blending using phenolic resin (PF) and epoxy-terminated prepolymer (QS) as carbon precursor and thermally decomposable polymer, respectively. Chemical reaction of PF with QS was manifested by FT-IR spectra and a higher decomposition temperature of QS in TG curves. In the curing reaction, epoxy groups of QS reacts with the phenolic hydroxyl of PF to form ether linkage. The influences of the content of QS on specific surface area, pore structure and electrochemical performance were investigated. As the content of QS increases, the specific surface area, total pore volume and micropore volume increases firstly and then decreases, reaching the maximum value of 609.0 m2/g, 0.28 cm3/g and 0.22 cm3/g, respectively when w(QS)/w(PF)=15%. The performances of prepared samples are better than that of porous carbon prepared by polymer blend method at the same condition. When the porous carbon used as the electrodes in electric double layer capacitor (EDLC), a satisfied speci?c capacitance of 177.5 F/g in 30wt% KOH aqueous electrolytes is acquired and the capacitance maintenance achieves 78% when the current density increases to 20 mA/cm2.
|
|
|
Preparation of FTO-free and Coal Based Carbon Counter Electrodes for Dye Sensitized Solar Cells
MENG Fan-Ning, WANG Chun-Lei, WU Ming-Xing, LIN Xiao, WANG Tong-Hua, MA Ting-Li
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 273–277
 Abstract
Abstract(
732 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(382KB)(
1225
)
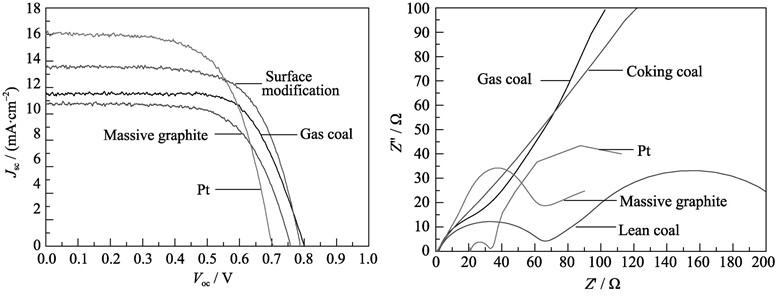
The coal-based carbon counter electrodes (CEs) with low-cost and high-performance were prepared from different coal powders such as gas coal, coking coal and lean coal, and they were used to substitute both conductive glass substrate and catalyst layer. The effects of impregnation and surface modification of the coal-based carbon CEs on their structure and photovoltaic performance were investigated. XRD, SEM and electrochemical impedance spectroscope were used to character the structure and performance of coal based carbon CEs. Results show that the coal based carbon CE after impregnated is the integrative CE with porous top surface and dense bottom. The solar cell with coal based carbon CE with surface modified demonstrates high photovoltaic performance with open circuit photo-voltage (Voc) of 0.79 V, short circuit photocurrent density (Jsc) of 13.48 mA/cm2, fill factor (FF) of 0.67, and solar-to-electricity conversion efficiency (η) of 7.16%, which is 30% higher than that of the cell with graphite electrode, and comparable to that of the cell with Pt electrode. The results indicate that the as-prepared coal based carbon CE is a promising CE candidate for substitute conventional?Pt/FTO counter electrode.
|
|
|
Application of Modified Foam Graphite Anode with Low Potential in Marine Benthic Microbial Fuel Cell
LU Zhi-Kai, FU Yu-Bin, XU Qian, LIU Yuan-Yuan, ZHANG Ye-Long
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 278–282
 Abstract
Abstract(
693 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(417KB)(
1225
)
Foam graphite is a novel anode material and its modification is one important way to increase the performance of marine benthic microbial fuel cell. The electrochemical performance of mixed-acid modified foam graphite anode was investigated. The results showed that the hydroxyl and carboxyl groups were introduced on foam graphite surface after modification. The contact angle of modified anode decreased 24.5°, resulting in higher wettability and better attachment for bacteria. Its exchange current density reached 6760.8 mA/m2 and the kinetic activity was improved 53.7-fold higher than the original one. Additionally, the present study also found that the anode potential of modified decreased 100 mV, and its open circuit potential reached 865 mV (plain anode 750 mV). The power density of modified cell reached 358.1 mW/m2, 2.4-fold higher than unmodified foam. Three months discharge showed that the modified anode and its cell have relatively stable performance. Meanwhile, the paper primarily analyzed the reasons why the anode potential was lower and kinetic activity was higher after modification. The results gave some enlightenments to constructing a novel marine benthic microbial fuel cell with higher output voltage and power.
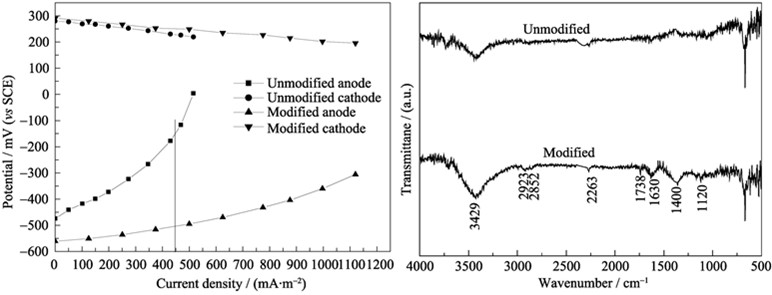
|
|
|
Modification and Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Inverse Opal Membranes
WU Jun, Wang Ai-Jun, CHEN Sheng-Li, YUAN Gui-Mei, WANG Xiao-Dong, ZHANG Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 283–286
 Abstract
Abstract(
949 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(399KB)(
1270
)
The surface of TiO2 inverse opal material was modified by Liquid Phase Deposition(LPD) method, and a layer of TiO2 nanoparticles was deposited on the inverse opal framework in order to increase the specific surface area. The photo-catalytical degradation of Rhodamine B was used as the probe-reaction to investigate the photocatalysis activity of the TiO2 inverse opal membranes, and the influences of boric acid concentration of the LPD solution on surface morphology and photocatalysis activity of TiO2 inverse opal membranes were investigated. The results showed that the photocatalysis activity of TiO2 inverse opal membrane modified by LPD method was improved which was about 6 times higher than that of the unmodified TiO2 inverse opal when the boric acid concentration of PLD solution was 0.0183 g/mL.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Synthesis and Photocatalytic Properties of Cu-doped BiVO4 Microsheets
LIU Guo-Cong, JING Zhen, ZHANG Xi-Bing, LI Xian-Feng, LIU Hong
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 287–292
 Abstract
Abstract(
1039 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(673KB)(
1398
)
Using Bi(NO3)3·5H2O, NaVO3 and Cu(NO3)2·3H2O as raw materials, Cu-doped BiVO4 microsheets were synthesized by ultrasonic-hydrothermal process with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) as template. The as-prepared samples were investigated by XRD, XPS, SEM, HRTEM, UV-Vis and BET tests. The results reveal that uniform and well crystallized Cu/BiVO4 microsheets in monoclinic crystal structure, with length of 1.0–2.0 μm, width of 0.5–2.0 μm and thickness of 200–300 nm, could be obtained via an ultrasonic-hydrothermal route assisted by 2.0 g CTAB. Compared with BiVO4 particles, Cu/BiVO4 nanosheets show a little red shift in the absorption band, resulting in a narrowed band gap (<2.4 eV). For 5.0wt% Cu/ BiVO4 microsheet, its photodegradation rate constant K is 5.89 ×10–2 /min and the best photocatalytic activity is found with a 100% degradation of methylene blue (MB) with 10 mg/L concentration under visible-light irradiation for 60 min.
|
|
|
Preparation and Photocatalytic Property of NiO/ZnO Heterostructured Nanofibers
CAO Tie-Ping, LI Yue-Jun, WANG Chang-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 295–300
 Abstract
Abstract(
1413 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(469KB)(
1971
)
Heterostructured NiO/ZnO composite nanofibers were prepared by electrospinning technique employing polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and Zinc acetate as precursors and then solvothermal growth of NiO nanostructures on as-electrospun ZnO nanofibers substrate. The morphology and structure of NiO/ZnO composite nanofibers were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) and PL spectra. Photocatalytic activity was tested via rhodamine B (RB) degradation as the model reaction. The results showed that the as-fabricated sample were composed of NiO nanoparticles assembling uniformly on the surface of ZnO nanofibers to form NiO/ZnO heterostructures. Compared with the pure ZnO nanofibers, NiO/ZnO composite nanofibers exhibited enhanced photocatalytic activity in the decomposition of RB under ultraviolet light. This material also shows good catalytic stability and the decolorizing efficiency of RB solution remains as high as 89% after 3 times recycle. Moreover, it is easily separated, removed from the system after reaction and reuse.
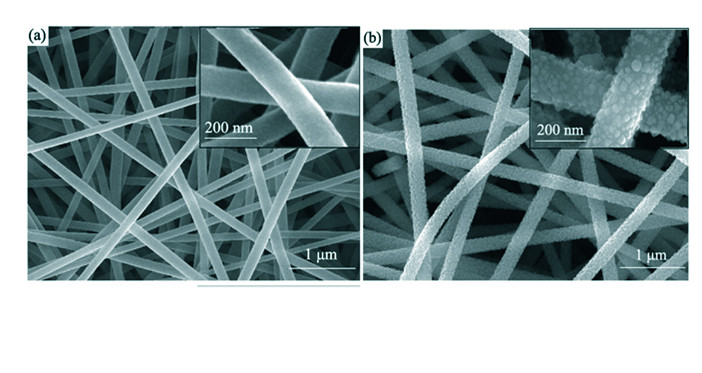
|
|
|
Alignment Growth Mechanisms of Rod-like ZnO on Zinc Substrates
LIU Chang-You, WANG Jin-Fang, SUN Xiao-Yan, WANG Ze-Wen, JIE Wan-Qi
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 301–306
 Abstract
Abstract(
790 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(647KB)(
1152
)
Discontinuous films of ZnO particles were prepared on zinc substrates by air pre-oxidation process. The arrays of rod-like ZnO nano-/micro- crystals on zinc substrates were synthesized through hydrothermal processing with N2H4·H2O solution. It is found that the rod-like ZnO nano-/micro-crystals align well on the substrate surface with a unique crystallographic orientation. The experimental results suggest a free alignment growth mechanism for rod-like ZnO nano-/micro-crystals on zinc substrates. The crystallization habit of ZnO nano-/micro-crystals is to grow along with the c axis fast under hydrothermal conditions, thus the well alignment of rod-like ZnO nano-/micro-crystals only depends on the state of ZnO nuclei on the substrate surface. The states of ZnO nuclei on the substrate surface with a unique crystallographic orientation well agree with others, which regulates the alignment of rod-like ZnO nano-/micro-crystals. In temperature-dependent photoluminescence spectra, the "negative thermal quenching" phenomenon of near band-gap edge excitons is observed in the temperature ranging from 30 K to 60 K, which identify two non-radiative processes and one negative thermal quenching process.
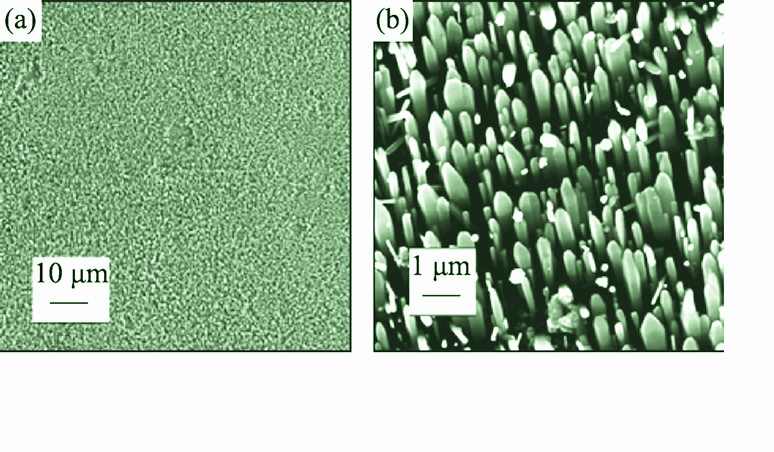
|
|
|
Study on Methods to Strenthen and Toughen Sapphire Crystal by Carbon Doped Grown by Temperature Gradient Technique (TGT)
HU Ke-Yan, XU Jun, TANG Hui-Li, LI Hong-Jun, ZOU Yu-Qi, YANG Qiu-Hong
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 307–311
 Abstract
Abstract(
913 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(345KB)(
1170
)
Mechanical properties of carbon-doped sapphire crystals with different carbon concentrations were studied at room temperature. The present work showed that the fracture strength and fracture toughness of as grown crystals were significantly improved by carbon doping and the visible-infrared optical property did not adversely affect. When the concentration of doped carbon was 5×10-3, the fracture strength and fracture toughness were increased to 752 MPa and 2.81 MPa·m1/2 in average, respectively, and the transmition of visible-infrared was about 80%. Appropriate carbon dopant in the crystals played the roles of clearance ions and created blocking effect to the sapphires cracking, which improved fracture strength and fracture toughness of sapphires at room temperature. However the mechanical properties and optical properties declined when carbon dopant was excessive, due to carbon inclusions grown from composition segregation.
|
|
|
Optoelectrical Properties and Back Contact Characteristic of VSe2 Thin Films
YANG Jia-Yi, GAO Jing-Jing, WANG Wen-Wu, ZENG Guang-Gen, LI Wei, FENG Liang-Huan, ZHANG Jing-Quan, WU Li-Li, LI Bing
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 312–316
 Abstract
Abstract(
728 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(424KB)(
1096
)
VSe2 thin films were prepared by using electron beam evaporation method and subsequently annealed at different temperatures. The structural, morphological. optical and electrical properties of VSe2 thin films were characterized by XRD, SEM, optical transmission spectra, Hall coefficients and in situ conductivity measurements. And the back contact characteristic of CdTe solar cells with VSe2 was investigated by dark J-V measurements. The results show that the films are crystallized in a stable hexagonal phase after annealing. The direct optical band gap value Eg for the films, showing p-type conduction mechanism, is found to be about 2.35 eV. The roll-over phenomenon in CdTe solar cells is eliminated and the device performance effectively improves when VSe2 is used as a back contact.
|
|
|
Preparation and Magnetoelectric Coupling Effects of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3/CoFe2O4 Laminated Ceramics
YUAN Chang-Lai, XUAN Min-Jie, XU Ji-Wen, LIU Xin-Yu, ZHOU Chang-Rong, YANG Yun
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 317–320
 Abstract
Abstract(
600 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(372KB)(
1010
)
The Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3-CoFe2O4 laminated composite ceramics composed of the piezomagnet CoFe2O4, and the piezoelectrics Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 with the sintering agents CuO and CeO2, were prepared by the interfacial solid-state melt infiltration technique. It is found that a good interfacial bonding between the piezomagnet and piezoelectrics is obtained. With the increasing thickness ratio of piezomagnet to piezoelectrics, the magnetostriction coefficient (–λ) of the laminated ceramics increase, the piezoelectric coefficient (d33) decrease, and the magnetoelectric coupling coefficient (αE) increases firsty and then decreases. The values of –λ and d33 of the laminated ceramics are in the range from 67×10-6 to 134×10-6 and 205 pC/N to 340 pC/N, respectively. At dc magnetic field of 100 mT along with ac frequency of 230 kHz and the thickness ratio of 2, a maximum value of αE=3200 mV/(cm·mT) is achieved for the laminated ceramics.
|
|
|
Effect of LiSbO3 Content on the Microstructure and Piezoelectric Properties of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 Lead-free Ceramics Doped with BiMnO3
JIANG Min-Hong, LIU Xin-Yu, CHEN Guo-Hua, ZHU Gui-Sheng, XU Ji-Wen, MA Jia-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 321–325
 Abstract
Abstract(
804 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(431KB)(
1100
)
Lead-free (0.996–x)KNN-0.004BM-xLS (x=0, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06) ceramics were prepared by the traditional ceramic sintering processing. The effect of LS content on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of KNN-BM lead-free ceramics was investigated. The results show that the ceramics have a single orthorhombic phase structure when x≤0.02, a co-existed phases orthorhombic and tetragonal phases structure at 0.03≤x≤0.05, and a single tetragonal phase structure at x=0.06. The morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) for the ceramics is identified in the composition range of 0.03≤x≤0.05. With increasing the LS content, both d33 and kp of the ceramics firstly increase and then decrease. At x=0.05, d33 and kp reach their maximum values which are 230 pC/N and 0.42, respectively. The To-t and Tc of the ceramics shift to the low temperature with the increasing of the LS content. The To-t and Tc of the ceramics are 455 and 215℃ at x=0, 385 and 150℃ at x=0.02, 370 and 75℃ at x=0.06, respectively.
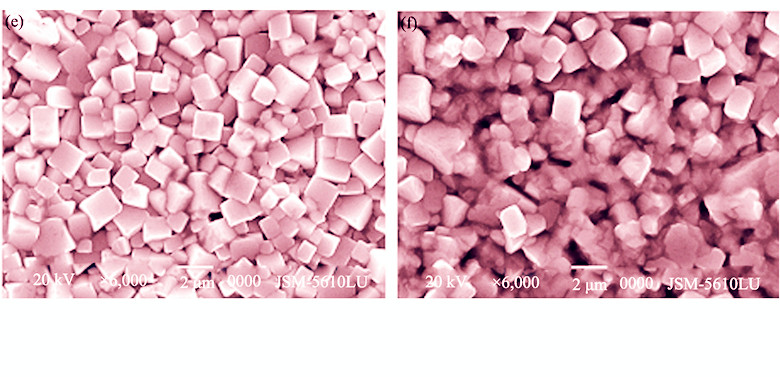
|
|
|
Piezoelectric and Dielectric Properties of [(NaxK(1–x))0.985Bi0.015](Nb0.97Ti0.03)O3 Ceramics
JIANG Xiang-Ping, YI Wen-Bin, CHEN Chao, TU Na, LI Xiao-Hong, ZHAN Hong-Quan
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 326–330
 Abstract
Abstract(
879 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(409KB)(
1095
)
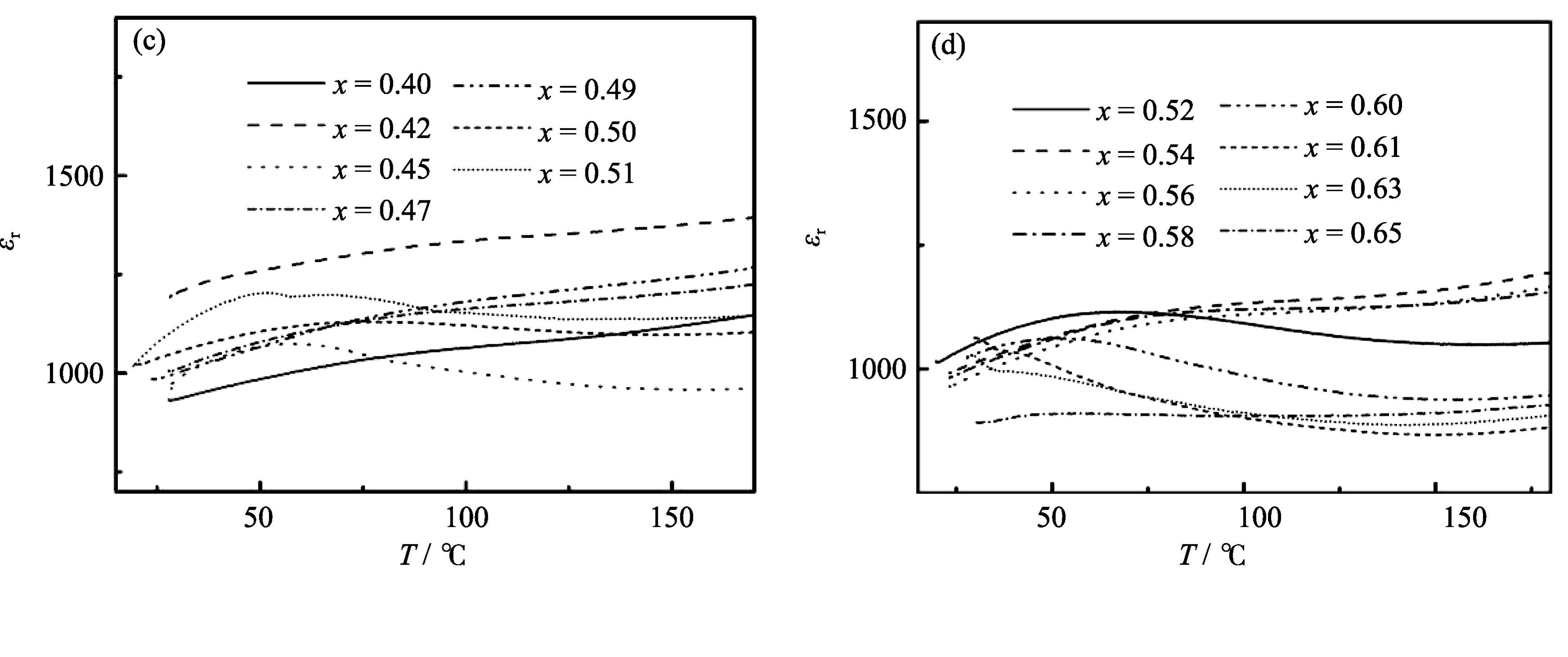
[(NaxK(1–x))0.985Bi0.015](Nb0.97Ti0.03)O3 (x=0.40–0.65) lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were synthesized by solid-state reaction method. The influences of different x value on the phase structure, microstructure, piezoelectric and dielectric properties of samples were studied in detail. The results indicate that all samples possess pure perovskite structure and the Curie temperature of all samples are in the temperature range of 340–365℃. The ceramic sample with x=0.40 is in the tetragonal symmetry at room temperature and with the increase of x content, the phase structure of samples change gradually from pure tetragonal phase to coexistence of tetragonal and orthorhombic phase, while the ceramic sample with x=0.65 has tetragonal phase. The polymorphic phase transition (PPT) from orthorhombic to tetragonal symmetry near room temperature locates in the composition of 0.45≤x≤0.63 in which the ceramic samples possess relatively high piezoelectric activity. The ceramic sample (x=0.60) with optimum piezoelectric properties (d33=253 pC/N, kp=0.43, TC=359℃) is a promising lead-free piezoelectric material.
|
|
|
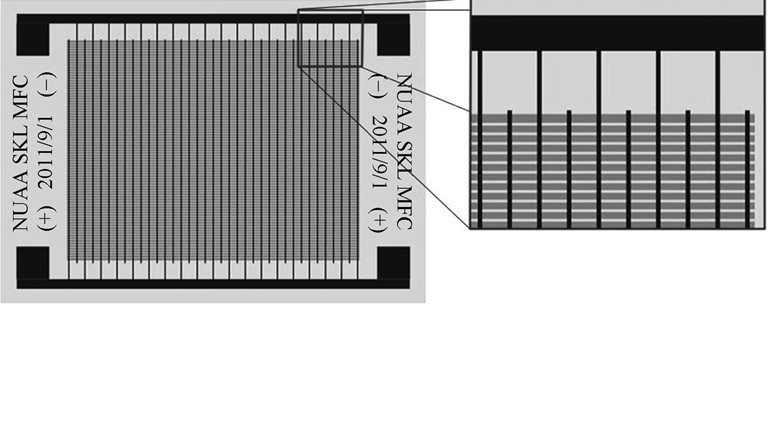
Fabrication of Flexible Piezoelectric Fiber Composite Actuator by Arrangement-casting Method
LI Shi-Cheng, ZHU Kong-Jun, QIU Jin-Hao, PANG Xu-Ming
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 331–335
 Abstract
Abstract(
706 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(479KB)(
1098
)
The structure of piezoceramic fiber composite actuator was designed, consisting of interdigitated electrode plates, binder and piezoceramic fiber composite layer. The flexible, planar piezoceramic fiber composite actuators were prepared by arrangement-casting method. The electrical and mechanical properties of the PZN-PZT ceramics were tested. Piezoelectric properties of piezoceramic fiber composite were estimated by iso-strain mixing formulas. The strain properties of the actuator were tested using dynamic response system based on LabVIEW. The piezoelectric constant d33, Curie temperature Tc and elastic compliance coefficient s33 of the PZN-PZT ceramics are found to be 520 pC/N, 320℃ and 20.5×10–12 m2/N, respectively. Theory of piezoelectric constants and of piezoceramic fiber composite are 509 and –156 pC/N, respectively. Test results show that the actuator is capable of producing large, directional in-plane strains. 100 parts-per-million longitudinal strain and 58 parts-per-million transverse strain were generated under a 300 V peak-to-peak applied voltage cycle. The stretching of the longitudinal and transverse directions are 3.6 μm and 1.7 μm, respectively, indicating the actuator has a high electromechanical property.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Li1.035Mn1.965O4 and Al-doped Li1.035Al0.035Mn1.930O4 as Cathode Materials for Li-ion Batteries by a Wet-chemical Technique
KONG Long, LI Yun-Jiao, LI Wei-Jian, Li Pu-Liang, LI Hua-Cheng
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 336–340
 Abstract
Abstract(
4249 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(348KB)(
1775
)
Spinel Li1.035Mn1.965O4 and Al-doped Li1.035Al0.035Mn1.930O4 cathode materials were synthesized by a simple wet-chemical technique and heat treatment. The structure and the morphology of the two samples were investigated by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The XRD patterns show that both of the two samples exhibit a well-defined spinel structure. The TEM result demonstrates that the Li1.035Al0.035Mn1.930O4 powder possesses a good crystalline state. The galvanostatic charge/discharge tests indicate that the Li1.035Al0.035Mn1.930O4 material delivers an excellent cycling ability and a nice rate capability, maintaining 96.4% of its initial capacity after 100 charge-discharge cycles at 0.5C and keeping 79.6% of the reversible capacity at 0.5C discharge rate when discharges at 4C rate.
|
|
|
Preparation of Manganese Dioxide for Oxygen Reduction in Zinc Air Battery by Hydro thermal Method
HUANG You-Ju, LI Wei-Shan
2013 Vol. 28 (3): 341–346
 Abstract
Abstract(
2773 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(370KB)(
1884
)
δ-MnO2, α-MnO2 and β-MnO2 nano-particles were obtained by a hydrothermal method with changing molar ratios of K+/H+ at low temperature of 180℃, and the molar ratios of K+/H+ were 3.4, 0.85 and 0.24, respectively. The as-prepared samples were characterized by SEM, XRD, FTIR, BET, TG and electrochemical method. The results indicate that the concentrations of K+ ion and H+ ion have great effects on the crystalline structures, morphology and specific surface area of the as-prepared products. Among the three as-prepared samples used as cathodic materials in zinc air battery, the rate performances of the δ-MnO2 and α-MnO2 are superior to that of the as-prepared β-MnO2. The oxygen reduction currents of δ-MnO2, α-MnO2, and β-MnO2 at –0.35 V are 56.28, 56.01 and 40.88 mA/cm2, respectively.
|
|