|
|
Recent Progress on Defect Dipoles Characteristics in Piezoelectric Materials
DU Gang, LIANG Rui-Hong, LI Tao, LU Xiao-Rong, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 123–130
 Abstract
Abstract(
1780 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(551KB)(
36447
)
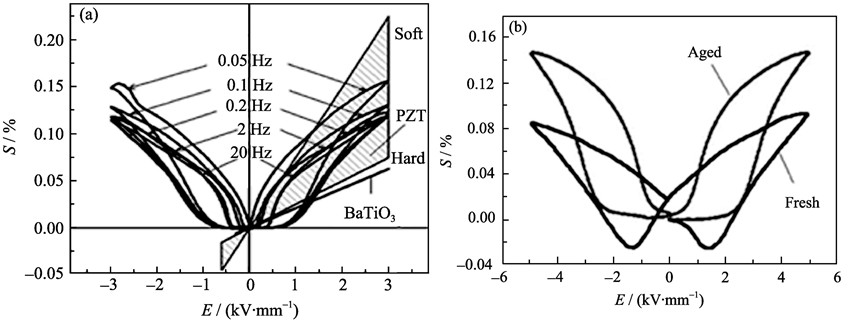
Defect dipoles which have pronounced effects on properties of piezoelectric materials can be introduced either by partially modifying with acceptor impurities or volatizing of cation elements in perovskite lattice during sintering. The formation mechanism of defect dipoles and responses under external fields were reviewed in the present paper. Besides, the main physic mechanisms of ferroelectric aging, hysteresis loop abnormalities and electro- shape-memory effects in piezoelectric materials were discussed in detail from the defect dipoles viewpoints. Based on a defect mediated reversible domain switching mechanism, large recoverable electro-strain, as well as constricted hysteresis loops were obtained in unpoled aged ferroelectric crystals and/or ceramics, which indicated that aging was not always a detrimental effect, and may be promising for future novel applications. Furthermore, the defect dipole relaxation process was briefly described and the development trends of the high reliability piezoelectric actuators were proposed.
|
|
|
Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Mechanical Properties of Bi3.15(Eu0.7Nd0.15)Ti3O12 Ferroelectric Thin Films
JIANG Da-Dong, ZHENG Xue-Jun, GONG Yue-Qiu, ZHU-Zhe, PENG Jin-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 131–135
 Abstract
Abstract(
891 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(420KB)(
1281
)
Bi3.15(Eu0.7Nd0.15)Ti3O12 (BENT) thin films were deposited on Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si(111) substrates via metal- organic decomposition (MOD) and annealed at 600℃, 650℃, 700℃ and 750℃. The hardness and elastic modulus were measured by nanoindentation, and the residual stress was measured by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The grain sizes of the BENT thin films increase with the annealing temperatures increasing. With the grain size increasing from 37 nm to 46 nm, the hardness decreases from 8.4 GPa to 3.1 GPa and the elastic modulus decreases from 171.5 GPa to 141.6 GPa. While the annealing temperature increases from 600℃ to 750℃, the residual stress decreases from -743 MPa to -530 MPa. The BENT thin film annealed at 600℃ shows the largest hardness and elastic modulus.
|
|
|
Raman Spectroscopy and Microwave Absorbing Properties of CNTs/Al2O3-TiO2 Composite Absorbing Coatings with Different Diameters
WANG Liu-Ying, XU Zhuo, HUA Shao-Chun, LIU An-Min, GUO Qin, LIU Gu
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 136–140
 Abstract
Abstract(
852 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(349KB)(
1195
)
CNTs/AT13 composites were prepared by mixing Al2O3-TiO2 ceramics (AT13) and carbon nanotubes with different diameters in an ultrasonic bath. CNTs/AT13 coatings were prepared by micro-plasma spraying. Raman spectra of CNTs/AT13 composite powders and sprayed coatings with different CNTs diameters were studied. The values of D peak to G peak of the composite coatings increased compared with CNTs/AT13 composite powders. With increasing the diameter of CNTs, the ratio of D peak to G peak of the composite coatings is smaller and the graphitization degree of CNTs was higher. The microwave absorbing properties of the sprayed CNTs/AT13 coatings with different thicknesses were investigated in the frequency range of 2-18 GHz. when the coating thickness is 1.0 mm, the microwave absorbing ability is poor. With thicker coating, the microwave absorbing ability of the CNTs/AT13 coatings are enhanced. When the coating thickness increases to 1.5 mm, with increasing of the CNTs diameters, the experimental reflectivity peak first decrease and then increase while the resonant frequency moves to the high frequency. The reflection peak of 30-50 nm CNTs/AT13 composite coating is -23.98 dB, and the frequency bandwidth for less than -5 dB and -10 dB is 6.40 GHz and 3.36 GHz, respectively. With increasing diameters of CNTs, the frequency bandwidth for less than -5 dB decrease, the frequency bandwidth for less than -10 dB increase. When the coating thickness increases to 2.0 mm, the resonant frequency of the CNTs/AT13 composite coating moves to low frequency.
|
|
|
Influence of pH Value in Electrolyte on Photovoltaic Performance of CIGS Thin-films Prepared by Electrochemical Method
SUN Bao-Ping, PANG Shan, HU Bin-Bin, YANG Guang-Hong, WAN Shao-Ming, DU Zu-Liang
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 141–145
 Abstract
Abstract(
781 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(523KB)(
1113
)
Cu(In1-x,Gax)Se2 (CIGS) films were prepared by one-step electrodeposition method on FTO glass substrates, and the influence of electrolytic pH on the chemical composition, structure and photovoltaic performance of CIGS thin-films were studied in detail. The results showed that the stoichiometry of In and Ga in the film could be effectively regulated by changing the pH value of the electrolyte. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results showed that the CIGS thin-films had good crystallinity and uniform particle size distribution when the pH value was 2.0. The effect of different stoichiometries of the CIGS thin-films on the kinetics of photo-charges was also studied. The CIGS thin film with a stoichiometric ratio of 0.3 for Ga/(In + Ga) presented the strongest surface photovoltaic effect.
|
|
|
Effect of Heat-treatment Temperature on Upconversion Luminescence of β-NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ Nano/Microparticles
DING Ming-Ye, LU Chun-Hua, HUANG Wen-Juan, JIANG Chen-Fei, NI Ya-Ru, XU Zhong-Zi
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 146–152
 Abstract
Abstract(
1150 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(735KB)(
1235
)
β-NaYF4:20%Yb3+,2%Er3+ nano/microparticles were successfully synthesized by solvothermal and thermal decomposition method. According to the results obtained with TG-DTA, the as-synthesized samples were heat-treated at different temperatures in air. The microstructure, morphology and upconversion luminescence property of annealed samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, FT-IR and photoluminescence (PL) spectra. The results show that the total upconversion luminescence intensity of nano/microparticles firstly increases and then decreases with a rise of temperature. Comparing with the as-prepared samples, appropriate heat treatment temperature (580℃) can improve upconversion luminescence property of nanoparticles. The results in present research indicate that the improvement of crystallization, the decrease in the concentration of defects and the decomposition of the organic molecules on the surface of the particles induce the enhancement of upconversion luminescence. However, the intensity of upconversion luminescence decreases sharply under higher temperature treatment (>580℃), which may be due to the phase transition (β→α) and the existence of Na2CO3. The differences in luminescence property between nanoparticles and microparticles are mainly attribute to different agglomeration degree of particles during thermal treatment.
|
|
|
Photocatalytic Property of Eu/BiVO4 Photocatalyst by Citric Acid Sol-Gel Method
WANG Min, LIU Qiong, SUN Ya-Jie, CHE Yin-Sheng, JIANG Chen-Zhi
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 153–158
 Abstract
Abstract(
1026 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(833KB)(
1296
)
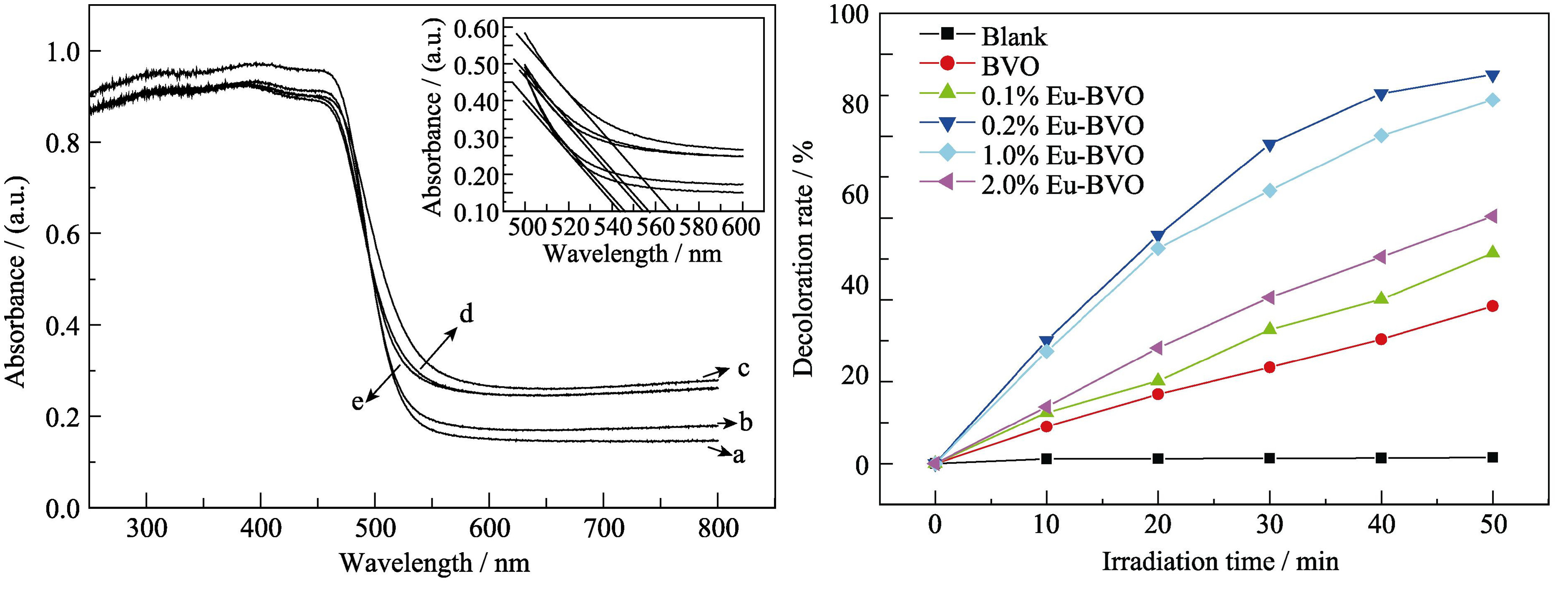
Eu3+-doped BiVO4 photocatalyst was synthesized by complexing Sol-Gel method using citric acid as chelate, and characterized with X-ray photoelectron spectroscope(XPS), X-ray diffraction(XRD), scanning electron microscope(SEM), specific surface area (BET) and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscope(DRS). The photocatalytic activity was evaluated by photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange (MO) solution under visible light. It revealed that pure BiVO4 and all the Eu3+ dopedsamples were monoclinic phase and no peaks of any other phases or impurities were detected. It was also found that doping Eu3+ increased the amount of V4+ and oxygen vacancies. In addition, the light absorption edges of Eu3+ doped BiVO4 had extended a red shift compared with that of pure BiVO4. However, Eu3+ doping had little influence on morphology and specific surface area. The appropriate amount of Eu3+ doping could signifcantly increase the photocatalytic activity and the highest photocatalytic degradation rate was about 95% when the Eu3+ doping amount was 0.2%, which was more 62% than that of pure BiVO4 under 50 min visible light irridation.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Effective and Qualified Cu-doped ZnSe Quantum Dots and Their Optical Properties
ZHENG Jin-Ju, CAO Sheng, GAO Feng-Mei, WEI Guo-Dong, JIA Long, YANG Wei-You
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 159–164
 Abstract
Abstract(
1256 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(566KB)(
1351
)
Effective Cu-doped ZnSe quantum dots (ZnSe:Cu d-dots) with high qualities were synthesized by a growth-doping strategy. The effect of the ratios of Zn to Se precursor within the raw materials on the quality of the ZnSe cores and ZnSe:Cu d-dots was studied. The photoluminescence (PL) properties of ZnSe:Cu d-dots in Cu doping process were investigated systematically. The results suggested that the optical performance and stability of the d-dots could be remarkably improved by further coated with a homogeneous ZnSe shell on the fabricated surface-doped ZnSe:Cu d-dots. In addition, the obtained ZnSe:Cu d-dots could be changed to be water-soluble by ligand exchange. It implied that these novel d-dots could be a promising candidate to substitute for the conventional quantum dots containing Cd elements, suggesting their potentially environment-friendly applications in the fields of solid state lighting and diagnostics.
|
|
|
Spectral Properties of ~2 μm Emission of Tm3+ Doped Bi2O3-SiO2-PbO Glass
WANG Xin, LI Ke-Feng, FAN Si-Jun, BAI Gong-Xun, HU Li-Li
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 165–170
 Abstract
Abstract(
741 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(476KB)(
1251
)
Silicate glasses 33Bi2O3-50SiO2-17PbO doped with 0.1%,0.25%, 0.5%, 0.75% and 1% Tm2O3 were prepared by the conventional melting method. Thermal property was studied by the DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimeter) method. Its Tx-Tg value is 138℃. According to the absorption spectra and Judd-Ofelt theory, J-O strength parameters, radiative transition properties, the radiative lifetimes and the branching ratio of some excited state energy levels were calculated. Analysis on the relationship between 3F4 lifetime and Tm3+ doped concentration showed that the critical concentration for self-quenching is 3.54×1020 ions/cm3. The absorption and emission cross-sections of Tm3+:3F4→3H6 transition were obtained using McCumber theory. The maximum absorption cross-section is 3.7×10-21 cm2 at 1658 nm and the maximum emission cross-section is 7.2×10-21 cm2 at 1842 nm. The results show that Tm3+ doped 33Bi2O3-50SiO2-17PbO material is an ideal candidate to realize ~2 μm laser.
|
|
|
Influence of Calcining Process on Optical Properties of Al-doped-ZnO Powders
WANG Zhi-Yong, PENG Chao-Qun, WANG Ri-Chu, WANG Xiao-Feng, LIU Bing
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 171–176
 Abstract
Abstract(
889 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(499KB)(
1243
)
AZO precursors (x(Al) =5.5mol%, 6.5mol%) were successfully synthesized by the polyacrylamide gel rout. The influence of calcining process on the optical properties of Al-doped-ZnO powders were investigated. It was found that Al concentration in the solution decreased with increasing calcination temperature. The ZnAl2O4 phase was detected in the AZO powders after calcined at 750℃. With increasing calcination temperature, the wavelength of UV absorbance peak was moved from 366 nm to 377 nm, while the peak displayed blue shift and the intensity was improved with prolonging calcination time. The room temperature photoluminescence spectra showed that emission peaks were composed of ultraviolet peak (354 nm), detectable ultraviolet peak (406 nm) and blue emission peak (430 nm).
|
|
|
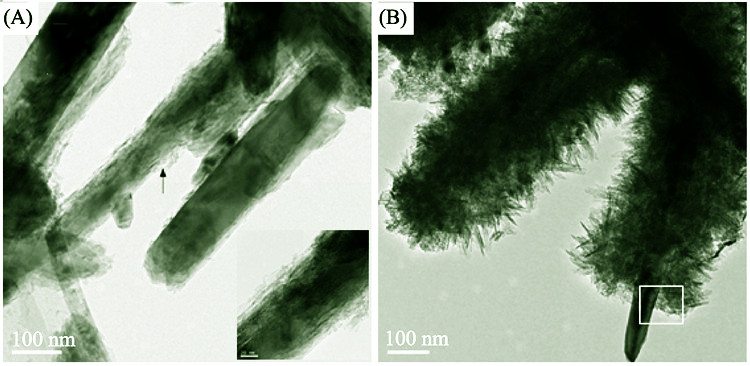
Microstrcture Characterization and Properties of TiO2/α-FeOOH Nanocomposites
WANG Yan-Fei, WANG Wei, ZHENG Yi-Fan, LI Guo-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 177–183
 Abstract
Abstract(
775 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(644KB)(
1091
)
A series of TiO2/α-FeOOH nanocomposites were prepared by hydrolysis precipitation method at different temperatures using TiCl4 as Ti source and α-FeOOH as support. The phase composition, morphology, microstructure and optical properties of the samples were investigated by XRD, HRTEM, STEM and UV-DRS. The results show that with the temperature gradually increasing from 30℃ to 90℃, the core-shell structure first gets better and then worse, and the best core-shell structure is formed at 45℃. The shell is composed of fine grains of rutile TiO2 and the large grain of α-FeOOH serves as the core, and the nanocomposites coated continuous and dense. The interaction between TiO2 and α-FeOOH is not only physical adsorption, a coherent lattice structure is formed at the interface between TiO2 and α-FeOOH, which leads to a large lattice distortion and a good composite structure. UV-DRS results show that the largest red shift of absorption peak is observed for the composite with good core-shell structure, indicating that the TiO2/α-FeOOH nanocomposites can greatly expand the range of spectral response and thus improve the utilization of sunlight.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of ZnO Hollow Micro-spheres with Excellent Property of Blue Emission
SUN Yong-Jiang, WANG Li, JIANG Xue-Hui, CHEN Ke-Zheng
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 184–188
 Abstract
Abstract(
886 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
1173
)
With the assistance of glucose and citrate, hollow micro-spheres of zinc citrate were prepared through low-temperature hydrothermal route, and then hollow micro-spheres of ZnO were obtained by calcinating the precursor at 500℃ in air. The composition, structures and morphologies of products were characterized by XRD, TG-DSC, SEM, TEM and IR. It was investigated that the precursor hollow micro-spheres with average diameter of 2 μm and thickness of 200 nm were prepared by the hydrothermal route. ZnO hollow micro-spheres prepared by calcinating the precursor with average diameter of 1 μm and thickness of 100 nm were composed of nanoparticles with diameter of 20-30 nm. The room-temperature photoluminescence property of the sample was studied. Under excitation wavelength of 325 nm, the as-prepared ZnO hollow micro-spheres possess excellent properties of blue emission, locating at 469 nm.
|
|
|
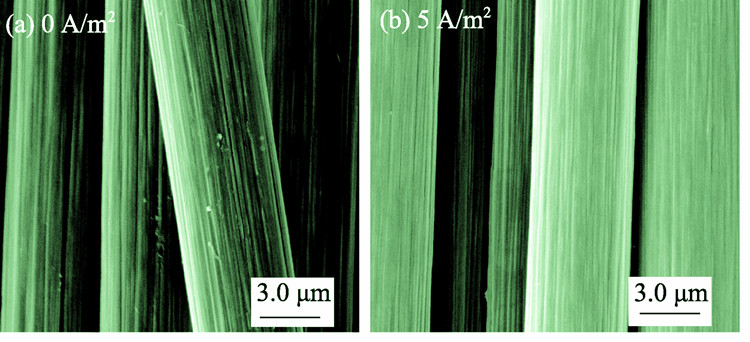
Effect of Fiber Surface Structure on Absorption Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composites
QIAN Xin, ZHI Jian-Hai, WANG Xue-Fei, ZHANG Yong-Gang, YANG Jian-Xing
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 189–194
 Abstract
Abstract(
1153 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(658KB)(
1138
)
Carbon fibers with different surface structures were obtained through changing the treatment intensities in the process of electrochemical oxidation, and then oxidized carbon fibers were used as reinforcements to manufacture carbon fiber/epoxy composites. The relationship between fiber surface structure and the moisture absorption of carbon fiber/epoxy composites after hygrothermal aging treatment was studied. Results show that a significant increase happen to the surface activity of carbon fiber after electrochemical oxidation, and there is also a large extent of elevation in the relative content of oxygen-containing functional groups especially -OH group which increases from 18.62% to 34.84%. The moisture absorption mechanism of carbon fiber/epoxy composites varies with the change of hygrothermal aging conditions. Temperature is considered to be a leading factor in the moisture absorption process. Results also indicate that the higher the surface activity of carbon fiber, the greater composite materials get the equilibrium moisture content. There is an obvious decline in the ILSS values of carbon fiber/epoxy composites with the increase of moisture uptake content.
|
|
|
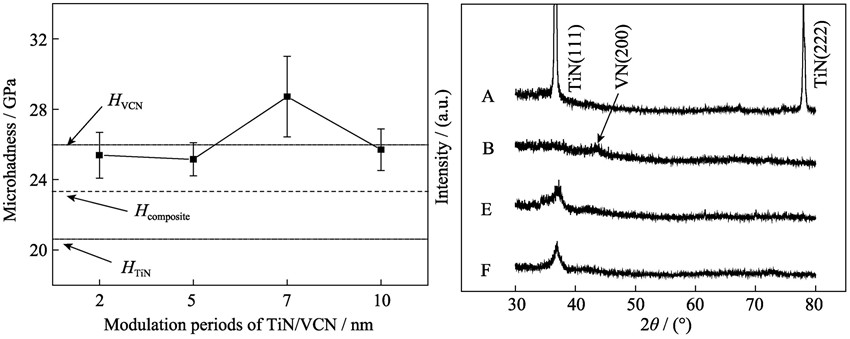
Mechanical Properties and Tribological Performance of TiN/VCN Multilayers
CAO Jun, XU Jun-Hua, YU Li-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 195–200
 Abstract
Abstract(
996 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(364KB)(
1089
)
Monolithic TiN, VCN films and TiN/VCN nano-multilayer films with different modulation periods were prepared by magnetron sputtering. Microstructures, mechanical properties and friction properties at room and high temperature of these films were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), nano-indentation, and CSM high temperature ball-on-disc tribometer. The results show that the TiN/VCN multilayer films are mainly nanocrystalline with δ-NaCl fcc structure. Maximum hardness of TiN/VCN multilayer films is 28.71 GPa, about 23% higher than the value calculated by the rule of mixtures. Based on these data, a mechanism of the superhardness in this system is proposed. Friction coefficients of TiN/VCN multilayers are similar to that of TiN films at room temperature, but lower than that of TiN films when testing temperature is increased to 700℃. Wear rates of TiN/VCN multilayers at room and high temperature decrease about 3×10-14 m3/(N·m) comparing to that of single layer film. The lubrication mechanism of Magnéli phase (V2O5) is discussed in terms of crystal chemistry and thermal measurement methods. In conclusion, compared to TiN films, the friction and wear properties of TiN/VCN multilayer films are greatly improved.
|
|
|
Influence of Substrate Temperature on the Morphology, Composition and Growth Rate of SiC Films Deposited by PECVD
YU Fang-Li, BAI YU, QIN Yi, YUE Dong, LUO Cai-Jun, YANG Jian-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 201–206
 Abstract
Abstract(
988 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(532KB)(
1024
)
SiC films were deposited on the surface of single crystal Si(100) and polycrystalline Cu by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). The effect of substrate temperature on the composition, structure and growth rate of as-deposited films was studied by high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results showed that the as-deposited films were amorphous and the growth rate of films decreased with increasing substrate temperature from 60℃ to 500℃. In addition, the growth rate of films deposited on the Si(100) wafer was higher than ones deposited on the polycrystalline Cu under the same deposition conditions. Meanwhile, it was found that the Si/C ratio of films decreased with the increase of substrate temperature. When the substrate temperature was controlled at about 350℃, the Si/C ratio in film was nearly equal to 1:1.
|
|
|
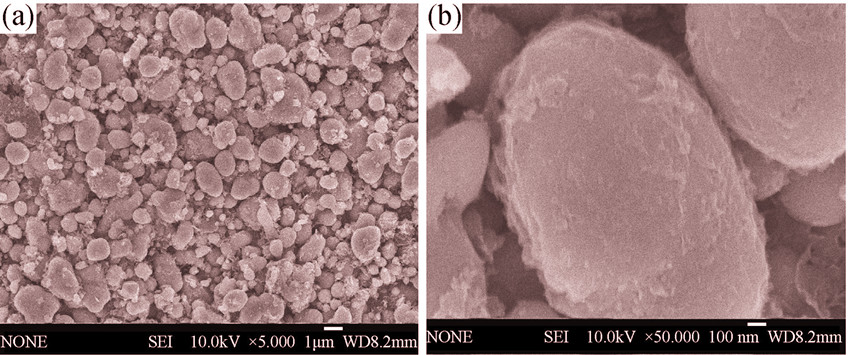
Synthesis of FePO4 from Fe2O3 and Its Application in Synthesizing Cathode Material LiFePO4
WANG Tao, YIN Ye, LIU Hao-Wen
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 207–211
 Abstract
Abstract(
1152 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(419KB)(
1747
)
FePO4 was synthesized by rheological phase method using Fe2O3, NH4H2PO4 and H2NCONH2 as row materials. The influence of temperature on the synthesis process was investigated. Taking prepared FePO4 as iron source, LiFePO4 was also synthesized by rheological phase method. The structure and morphology of as prepared FePO4 and LiFePO4 were characterized by XRD and SEM, respectively. XRD results indicate that FePO4 is belong to the triclinic system, with α-quartz structure and LiFePO4 is belong to the orthorhombic system, with olivine structure. SEM results showed that the FePO4 particles were layered distribution, while the LiFePO4 particles seemed like spherical. Both of the particles were well dispersed, and the average particle sizes were about 2 μm. Electrochemical properties of the obtained LiFePO4 cathode material were investigated by galvanostatic charge-discharge test, cyclic voltammetry(CV) and alternating current(AC) impedance methodes, the initial discharge capacity could reach 163.4 mAh/g, indicating excellent electrochemical performance. All the above results indicated that the prepared iron phosphate is an ideal iron source for the synthesis of lithium-ion battery cathode material LiFePO4.
|
|
|
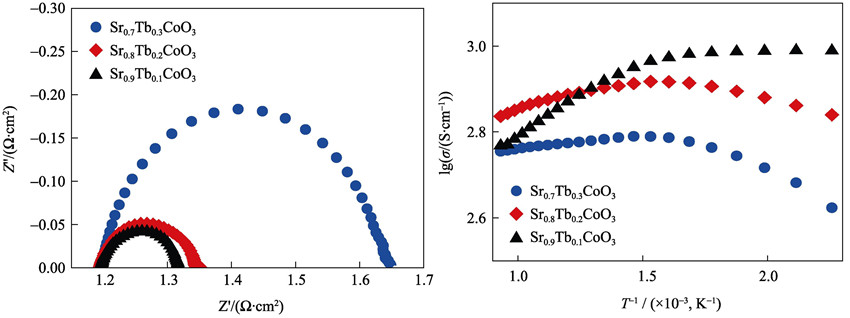
Preparation and Characterization of Sr1-xTbxCoO3-δ (x≤0.3) Cathode Materials for Intermediate-temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
LIU Tao
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 212–216
 Abstract
Abstract(
729 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(450KB)(
1058
)
Cathode materials consisting of Sr1-xTbxCoO3-δ (STC, x≤0.3) were prepared by solid-state reaction from stoichiometric proportions of SrCO3, Co3O4 and Tb4O7. Crystal structure, weight loss processes, electronic conductivity, polarization resistance and cell performance were investigated by XRD, ND, TGA, Van Der Pauw DC four-probe method and electrochemical method, respectively. XRD shows the presence of two structural phases in the series belonging to Pm-3m for Sr0.9Tb0.1CoO3-δ and I4/mmm for Sr0.8Tb0.2CoO3-δ and Sr0.7Tb0.3CoO3-δ. Electronic conductivity measurements show that the conductivities of STC were all higher than 407 S/cm in the temperature range of 500℃ to 800℃. AC impedance measurements in symmetrical cells with LSGM as an electrolyte show that the polarization resistance (Rp) and the activation energy (Ea) increase with increasing Tb content. Sr0.9Tb0.1CoO3-δ, with the largest concentration of oxygen vacancies exhibits the best cathode characteristics with maximum power density of 836 mW/cm2.
|
|
|
Microstructure and Electrochemical Hydrogen Storage Characteristics of CeMg12+100wt%Ni +Ywt%TiF3 (Y=0, 3, 5) Alloys Prepared by Ball Milling
HU Feng, ZHANG Yang-Huan, ZHANG Yin, HOU Zhong-Hui, DONG Zhong-Ping, DENG Lei-Bo
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 217–223
 Abstract
Abstract(
5727 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(554KB)(
1156
)
The nanocrystalline and amorphous CeMg12+100wt%Ni+Ywt%TiF3(Y=0, 3, 5) alloy samples were synthesized by ball milling technology. The infulence of TiF3 on microstructure and electrochemical properties of milling alloys were investigated. The electrochemical performance of prepared alloy samples was studied through discharge capacity, cycle stability and electrochemical kinetic, meantime. By using electrochemical PCT (pressure-concentration- isotherm) curves the change law of electrochemical performance of ball-milled alloys was further explained from the view of thermodynamics. The result showed that TiF3 was helpful for enhancing the nanocrytstalline and glass forming ability of milled CeMg12+100wt%Ni+Ywt%TiF3(Y=0, 3, 5) hydrogen storage alloys, improving the electrochemical and kinetic properties. On the other hand, in milling process, addition of TiF3 reduced the hot stability of alloy hydride to some degree, accelerating the electrochemical dehydriding reaction.
|
|
|
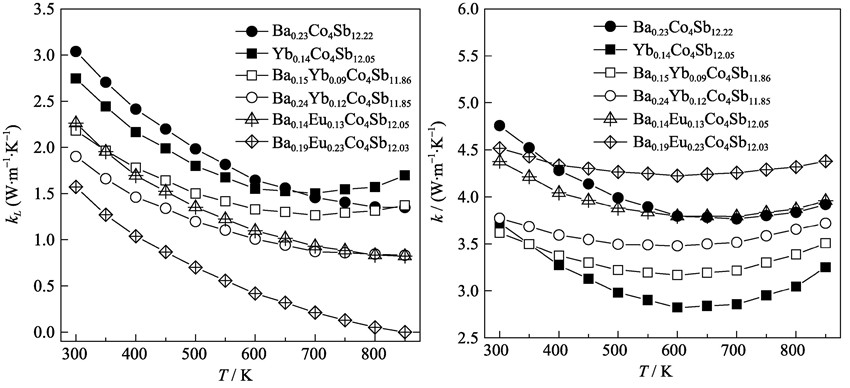
Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties of BaxEuyCo4Sb12 with Very High Filling Fraction
WU Ting, BAI Sheng-Qiang, SHI Xun, CHEN Li-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 224–228
 Abstract
Abstract(
726 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(353KB)(
981
)
Filled skutterudite is one of the most promising thermoelectric materials for power generation applications. We report the high-temperature thermoelectric properties including electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity in single-phased polycrystalline dual-element-filled skutterudites BaxEuyCo4Sb12(0<x<0.2, 0<y<0.3). The double-filled skutterudites are synthesized by the melting-quenching-annealing method and the bulk pellects are sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS). High total filling fractions (x+y>40%) with very large power factor of BaxEuyCo4Sb12 over 60 μW/(cm•K2) at high temperature is obtained. The combination of Ba and Eu fillers inside the voids of the skutterudite structure provides a broad range of resonant phonon scattering and consequently a strong suppression in the lattice thermal conductivity is observed. The lattice thermal conductivity values for BaxEuyCo4Sb12 system are dramatically decreased and the lowest value is about 1.7 W/(m•K) at room temperature. Consequently, enhanced thermoelectric figure of merits (ZT) for Ba and Eu dual-element-filled CoSb3 skutterudites are obtained at elevated temperatures, in particular ZT=1.3 at 850 K for Ba0.19Eu0.23Co4Sb12.
|
|
|
Effects of TiO2 Interlayers on the Optical Switching of VO2 Thin Films Grown by Sol-Gel Process
ZHANG Yu-Bo, HUANG Wan-Xia, SONG Lin-Wei, YAN Jia-Zhen, SHI Qi-Wu, ZHANG Yang
2013 Vol. 28 (2): 229–234
 Abstract
Abstract(
888 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(473KB)(
1060
)
Thermochromic VO2 and VxW1-xO2 films were deposited on TiO2/mica substrates. The TiO2/mica substrates were fabricated via Sol-Gel process, and the hydrophilicity of the TiO2/mica substrate was improved under UV light irradiated. The V2O5 sol was deposited on the TiO2/mica substrate by the spin coating method, and then it was annealed. SEM and XRD analysis were applied to analyze the morphology, phases and microstructure of the films. FTIR was used to study the thermochromic properties. The results suggest that VO2/TiO2 grow preferentially along single orientation. VxW1-xO2/TiO2 composite film is impossible to fabricate single orientation films. TiO2 interlayers are favorable to compact the VO2 thin films and reduce the transition temperature. It will make the hysteresis width of VxW1-xO2/TiO2 composite film reduce to about 4℃ particularly.
|
|