|
|
Progress on the Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica-based Nanotheranostics
SHI Jian-Lin, CHEN Yu, CHEN Hang-Rong
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 1–11
 Abstract
Abstract(
3086 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(7197KB)(
2024
)
Inorganic mesoporous nano-biomaterials have broad application potentials in molecular imaging, targeted drug delivery, tissue engineering, gene therapy, and non-invasive surgical therapy, etc., which are of great significance in the early diagnosis and efficient therapy of serious diseases such as cancer. This article reviews the most recent research advances and outlooks future development trends of mesoporous nanotheranostics based on clinical requirements, the principle of nano-synthetic chemistry and the design strategy of multifunctional mesoporous nano-biomaterials, by combining the recent achievements of our group. By integrating various functions into mesoporous silica nanoparticles to endow them with special capabilities, the mesoporous nanotheranostics could act as the contrast agents for clinical molecular imaging (magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescent imaging and the combinations of various imaging modalities), as well as the carriers for the encapsulation and delivery of drugs for the therapy of diseases (chemotherapy, gene therapy, photodynamic therapy and non-invasive surgical therapy). With the development of bio-nanotechnology and nano-synthetic chemistry, mesoporous nanotheranostics are expected to satisfy the clinical requirements following the systematic investigation of their biological effects and bio-safety, and finally find their applications in clinical practices to benefit human beings.
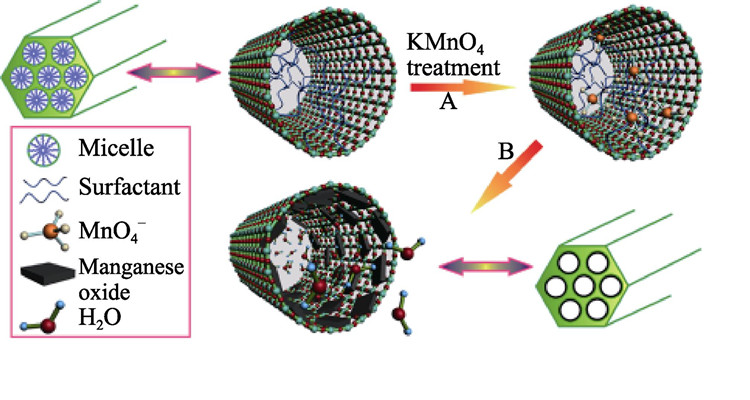
|
|
|
Progress on Biomedical Ceramic Coatings Prepared by Thermal Spraying
ZHENG Xue-Bin, XIE You-Tao
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 12–20
 Abstract
Abstract(
2452 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(4414KB)(
1841
)
Biomedical ceramic coatings on metallic substrates deposited via thermal spraying have attracted extensive attentions in the field of orthopedic implants due to their excellent mechanical strengths and biological properties. The studies on biomedical coatings for orthopedic implants are overviewed, and improvements of thermal sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings are summarized. Newly developed bioactive calcium silicate coatings are reviewed as well.
|
|
|
Application of Genomics/Proteomics Technologies in the Research of Biocompatibility of Biomaterials
Lü Xiao-Ying, HUANG Yan, YU Ya-Dong, YANG Ya-Min
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 21–28
 Abstract
Abstract(
1459 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(443KB)(
1412
)
Biocompatibility is a key scientific issue in the research area of biomaterials. With the development of molecular biology techniques, the evaluation of biocompatibility of biomaterials has deepened from the animal level and cellular level to molecular level. The development of biomics technologies provide effective tools for high-throughput evaluating molecular biocompatibility on whole scale, and understanding the interaction mechanism between biomaterial and human body. In this paper, current research of biocompatibility and the application of biomics technologies in biocompatibility study of biomaterials were reviewed.
|
|
|
Silicate Bioceramics for Bone Tissue Regeneration
WU Cheng-Tie, CHANG Jiang
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 29–39
 Abstract
Abstract(
3483 )
 HTML
HTML(
25)
 PDF
PDF(581KB)(
2188
)
Silicate bioceramics have received significant attention in the past several years. The main reason is that silicate bioceramics can efficiently stimulate the proliferation, differentiation and gene expression of tissue cells as well as the regeneration of bone tissue by release of Si-containing ionic products. Due to this significant advantage, silicate bioceramics, as a novel bioceramic system, have great potential to be widely used for repairing and regenerating bone tissues. In this paper, our researches in the past ten years are combined and the research advancements of silicate bioceramics are reviewed. The advantages and disadvantages of silicate bioceramics are summarized by comparing with conventional calcium phosphate bioceramics. Finally, a forward-looking perspective for silicate bioceramics on the applications of bone regeneration is also discussed.
|
|
|
Research on Preparation and Biological Properties of Dense Hydroxyapatite Spheres
LUO Hui-Tao, ZHI Wei, LU Xiong, LI Jin-Yu, FENG Bo, WENG Jie
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 40–44
 Abstract
Abstract(
1305 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(592KB)(
1343
)
By using carboxy methyl chitosan (CMCS) and gelatin (Gel) as adhesive, the nano-HA slurry which was fabricated via a precipitation process as the raw material, dense HA spheres with a uniform size distribution and good geometry were prepared successfully by means of Sol-Gel method. Dense HA spheres with a porosity of 4.7%±0.6% have a higher compressive strength (8.9±0.4) MPa than that of porous HA spheres (7.9±0.2) MPa with a porosity of 16.4%±0.5% (particles with diameter of 0.5 mm). The results of biomimetic mineralization and cell culture show that dense HA spheres have an excellent biological property.
|
|
|
Influence of Strontium on Hydroxyapatite Morphology and Luminescence Characteristics
ZHAO Xin, WANG De-Ping, QIU Wen-Qing, YE Song
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 45–50
 Abstract
Abstract(
1486 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(5261KB)(
1342
)
Strontium Hydroxyapatite (SrxCa10-x(PO4)6(OH)2, x=0, 3, 5, 10) powder with fluorescence property was successfully synthesized by a facile hydrothermal process. X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectra, field emission scanning electron microscope and photoluminescence excitation and emission spectra were employed to analyze phase change, characteristics and fluorescence property of samples. The experimental results indicate that the morphology of samples is spherical particle(D=1~2 μm), and with the amount of strontium changed from 0 to 100mol%, the morphology of spherical particle changes from short nanorods to nanosheets and then long nanorods. The samples show an intense and bright blue emission from 375 nm to 500 nm centered at 432 nm under long-wavelength UV light excitation (351 nm). The PL emission intensity firstly increases and then decreases with increasing the strontium content. When strontium content is 30%, the PL emission intensity reaches the maximum.
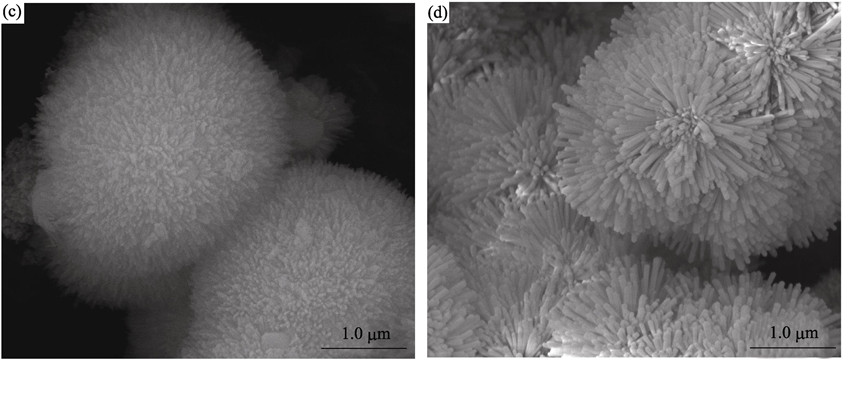
|
|
|
Fabrication of Micro-grooved Patterns on Hydroxyapatite Ceramics and Observation of Earlier Response of Osteoblasts to the Patterns
WANG Zhe, XIAO Zhan-Wen, FAN Hong-Song, ZHANG Xing-Dong
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 51–57
 Abstract
Abstract(
1223 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(635KB)(
1173
)
Hydroxyapatite (HAP) ceramic with orderly micro-patterned surface were fabricated by transferring micro-groove patterns from an aluminum alloy template, which was carved by an ultrasound-driven microprobe. The surface morphologies, phase compositions, and water wettability of samples were respectively analyzed with scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and contact angle measurements. The groove widths of three-kind samples were about 20, 40 and 60 μm, in lined with the designed values. Water wettability of the grooved HAP surfaces was found to be significantly increased by decreasing groove-width. Furthermore, the influences of the grooved HAP surfaces on the behavior of osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1) were examined by measuring cell orientation and counting the cell number. The results showed that the cells were oriented along the groove direction, and the cell orientation angles decreased with a decrease in groove-width, whereas no significant difference in the number of osteoblasts was observed. In summary, the groove-width of micro-patterned HAP has a distinct effect on the directed growth of osteoblast cells.
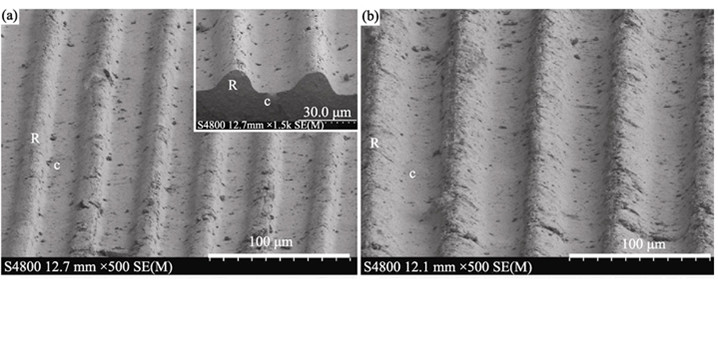
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Bionic Nano-silicon-substituted Hydroxyapatite
ZHAI Qian-Qian, ZHAO Shi-Gui, WANG Xiao-Hai, LI Xiu-Zhi, LI Wen-Jie, ZHENG Ya-Sen
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 58–62
 Abstract
Abstract(
1441 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(477KB)(
1279
)
To explore the synthesis condition of the bionic nano-silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite and the impact of the silicon content on its crystallization properties, hydroxyapatite of different silicon content were synthesized from Ca(NO3)2, (NH4)2HPO4 and Si(OCH2CH3)4(TEOS) via an aqueous precipitation reaction. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray fluorescence spectrum (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used for hydroxyapatite characterization. The results show that relative low temperature (40℃) is conducive to obtain pure bionic nano-silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite. Under this condition, SiO44- enters the lattice of hydroxyapatite and replaces part of PO43-. The more the content of silicon is, the lower the crystallinity is, the smaller the grain size is and the higher the lattice parameters a and c are.
|
|
|
Hydrothermal Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Fibers Precipitated by Propionmide
HAO Li-Jing, YANG Hui, ZHAO Na-Ru, WANG Ying-Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 63–68
 Abstract
Abstract(
1478 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(656KB)(
1711
)
Fibrous hydroxyapatite (HA) powder was successfully synthesized through hydrothermal method. Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate and diammonium hydrogen phosphate were added as precursors and propionamide (PA) as precipitant was used to control the degree of supersaturation of the reaction solution. XRD, FTIR, SEM and TEM were used to characterize the product. The synthesized HA powder was found to possess high crystallinity and regular morphology, as well as good dispersion. The effects of starting pH value and the concentration of precursors on the morphology, constitution, crystallinity and the growth characteristics of HA were investigated. The results show that the starting pH and concentration significantly affect the morphology at different extents, but not on the constitution and crystallinity. In fact, low starting pH controls orientation of fibrous HA while low concentration widens HA fibers.
|
|
|
Preparation and in vitro Properties of CaSiO3/TiO2 Composite Bioceramics
YU Hui-Xian, NING Cong-Qin
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 69–73
 Abstract
Abstract(
1268 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(1464KB)(
1366
)
CaSiO3 has attracted much attention as a bone substitute due to its strong ability to induce the formation of bonelike apatite in vitro. However, its poor chemical stability, biocompatibility, sintering and mechanical properties limit its further applications. In the present study, CaSiO3/TiO2 composites with initial CaSiO3/TiO2 molar ratios at 2:1, 3:1 and 5:1 were prepared by solid-state reaction method. CaSiO3/TiO2 ceramics sintered at 1100℃ with the crystal phases of CaSiO3 and CaTiSiO5 were found to have optimistic sintering behavior, mechanical properties and degradability compared with pure CaSiO3 ceramics. With the CaSiO3 content increased, the mechanical properties were enhanced while the in vitro bioactivity and biodegradability decreased. All these results suggest that CaSiO3/TiO2 composite ceramics maybe a prospective candidate for bone repair and the properties can be adjusted by changing their chemical compositions to adapt to bone regeneration.
|
|
|
Preparation and Optimization of Porous HA Ceramic Scaffolds by Wax Spheres Leaching Method
ZHAO Jing, LI Jin-Yu, ZHI Wei, LU Xiong, JIA Zhi-Bin, WENG Jie
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 74–78
 Abstract
Abstract(
1352 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(429KB)(
1146
)
Interconnectivity of tissue engineering scaffolds plays a very important role in biological performance in vivo. In this work, chitin sol and wax spheres were used for preparing porous hydroxyapatite (HA) ceramics scaffolds by particle leaching and gel-casting methods. Under the same mounded casting condition, the effect of ratio of slurry/wax pore former on porosity, shrinkage, interconnectivity, porous structure and compressive strength were investigated systematically. Porous HA ceramic scaffolds were evaluated by gravimetric method, stereomicroscope, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and universal testing machine. The results show that the present method is an effective method to fabricate a highly porous HA ceramic scaffolds. With increasing the ratio of slurry/wax spheres, the interconnectivity gets better and the optimal ratio of slurry/wax spheres is 1:1.2.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Supermagnetic Calcium Phosphate Composite Scaffold
ZENG Xiao-Bo, HU Hao, XIE Li-Qin, LAN Fang, WU Yao, GU Zhong-Wei
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 79–84
 Abstract
Abstract(
1369 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(634KB)(
1140
)
Supermagnetic calcium phosphate composite scaffold was fabricated by merging the superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) into the calcium phosphate scaffold, and then sintered in vacuum. Properties of the obtained magnetic scaffold were investigated by SEM, EDS, XRD and VSM. The stability of magnetic scaffold in water was assessed and Ros17/2.8 cells were cultured on the samples to evaluate the cell adhesion on the scaffold. The results demonstrated that the magnetic scaffold had a porous structure. The magnetic nanoparticles were uniformly distributed and firmly merged into the matrix. The content of magnetic nanoparticles could be accurately tuned, and the magnetic scaffold is stable in water. The composite scaffold maintained excellent magnetic properties, as the vacuum sintering procedure avoided the oxidation and phase transition of the magnetic nanoparticles. It is proposed that the magnetic materials might be a kind of potential bone tissue engineering scaffold in the future.
|
|
|
Research on Calcium Phosphate Cement Bone Adhesive
YANG Sheng-Bing, WANG Jing, LIU Chang-Sheng
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 85–90
 Abstract
Abstract(
1361 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(577KB)(
1249
)
Using citric acid and chitosan as hardening liquid, and calcium phosphate cement (CPC) as powder, gum-like adhesive bone cement is obtained after mixing the powder and liquid components together, which can be used as calcium phosphate cement bone adhesive (CPCBA). The effect of citric acid concentration on compressive strength, setting time and hydration products were investigated. In vitro cytocompatibility of the cements was also researched through cell culture on the cement surface. The results show that setting time is shorten and anti-washout is improved by introducing citric acid. Cohesion strength increases owing to chitosan chelated with calcium ion of CPC. The cements are transformed to hydroxyapatite after incubation 3 d in SBF and osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1) can attach and proliferate on the surface. Results indicate that the calcium phosphate cement bone adhesive is a suitable adhesive material for comminuted fracture.
|
|
|
Effects of Adding Carbon Nanotubes/Hydroxyapatite Composites on the Properties and Structure of Calcium Phosphate Cement
QIU Tian, HUANG Jing-Jing, ZHANG Miao, WANG Xian-Fu, LI Chen, LU Xiao-Ying, WENG Jie
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 91–96
 Abstract
Abstract(
1531 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(525KB)(
1241
)
The multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs)/ hydroxyapatite (HA) composites were synthesized by three different methods, namely physical blending (PB), chemical coprecipitation (CC) and bionic immersion (BI), and used as one of solid phase powders for the preparation of calcium phosphate cement (CPC). For the addition of MWNTs/HA composites, CPC had an increasing hydrophilicity and a decreasing initial and final setting time. However, the initial setting time and final of CPC made of MWNTs/HA powders still met the clinical requirements for the biomedical applications. The addition of MWNTs/HA composites synthesized by different methods had great effect on the compressive properties of CPC and HA crystallinity in CPC, but had no effect on the phase composition of CPC. Compared with blank CPC, CPC-CC and CPC-BI, CPC-PB had the best compressive mechanical properties and the highest HA conversion and content. Compared with blank CPC, the compressive strength and elastic modulus of CPC synthesized by PB method increased 48.23% and 41.87%, respectively.
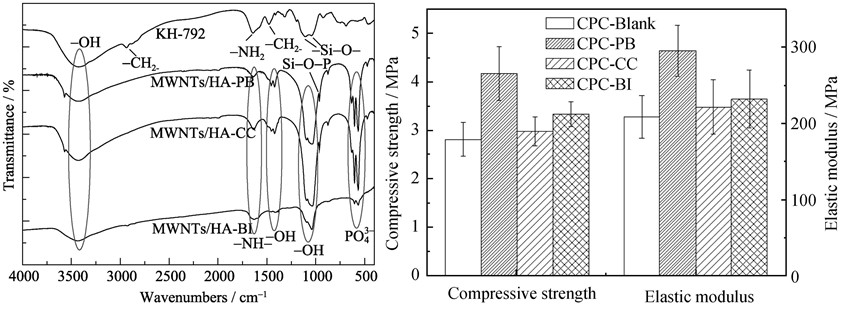
|
|
|
Preparation of Hierarchically Porous MBG/CPC Scaffold and Its Performance on Drug Loading and Release
DING Feng, LI Nan, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 97–102
 Abstract
Abstract(
1417 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(483KB)(
1136
)
Hierarchically composite scaffold (MBG/CPC) was successfully prepared by loading of mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBG) into macroporous calcium phosphate cement (CPC) with simply centrifuging method. It is revealed that MBG loading capacity on CPC and the BET surface area of MBG/CPC can reach 47.2% and 100.1 m2/g, respectively. In contrast, almost no MBG loading is detected by using traditional impregnation route. Drug loading and releasing tests show that DOX loading capacity on hierarchically composite scaffold MBG/CPC is 46 mg/g, which is 11.5 times of that on pure CPC. Importantly, a sustained drug release in vitro performance is presented on MBG/CPC.
|
|
|
Structural Properties and Wound Healing Effect of the Sol-Gel Bioactive Glass on Diabetic Skin Wounds
LIN Cai, MAO Cong, LI Yu-Li, ZHANG Juan-Juan, MIAO Guo-Hou, CHEN Xiao-Feng
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 103–108
 Abstract
Abstract(
1690 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(6812KB)(
1547
)
The 45S5 bioactive glass (45S5) was prepared by a melting process, while sol-gel bioactive glass (SGBG) was obtained by Sol-Gel method. The bioactive glasses were characterized by SEM、BET and XRD. Then the wound healing effect was investigated through the wound healing time, wound healing rate and histology examination. The results indicate that the bioactive glass can lessen the wound healing time and increase the healing rates of diabetic rats. Compared with the 45S5, SGBG can promote wound healing of diabetic rats more quickly and efficiently due to the larger surface area and nanostructure. Histological examination shows that bioactive glasses promote the proliferation of fibroblasts and growth of granulation tissue. All results suggest that bioactive glass can accelerate the recovery of skin wounds and SGBG with nanostructure has a better healing effect in diabetes- impaired models.
|
|
|
Research Progress on Biomineralization Mechanism of Freshwater Pearl
MA Yu-Fei, QIAO Li, FENG Qing-Ling
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 109–116
 Abstract
Abstract(
1649 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(838KB)(
1453
)
Calcium carbonate exists widely in many kinds of biominerals, and is one of the most widespread biominerals on the earth. The main component of the shell and pearl is calcium carbonate. In China, the majority of the freshwater pearls originated from Hyriopsis cumingii (Zhuji, Zhejiang Province) is with excellent quality and has outstanding pearly luster. The inorganic phase of this luster pearl is aragonite crystal and is regarded as aragonite pearl. Recently, the vaterite is observed in the freshwater cultured pearls, which is responsible for the lack luster and poor quality of the pearls. In the present paper, microstructure and property of the freshwater aragonite and vaterite pearl are introduced. In addition, in vitro growth of calcium carbonate crystal related to the pearl is reviewed. At last, the future research of nacre biomineralization is expected.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Zinc and Cerium Co-doped Titania Nano-materials with Antibacterial Activity
WANG Yu-Zheng, XUE Xiang-Xin, YANG He
2013 Vol. 28 (1): 117–122
 Abstract
Abstract(
4622 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
2480
)
Zinc and cerium co-doped titania (Zn/Ce-TiO2) nano-materials were synthesized by a Sol-Gel method at different calcination temperatures. Zn/Ce-TiO2 nano-materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS) and UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS). With the test of bacterial inhibition zone, the antibacterial properties of Zn/Ce-TiO2 nano-materials on E. coli. were investigated. The results show that crystallinity and the crystal phase of nano-materials are closely dependent on the calcination temperature. Zinc ions and cerium ions exist in the form of Zn2Ti3O8 and CeO2 phase, respectively. The Zn/Ce-TiO2 nano-materials synthesized exhibit enhanced antibacterial activity under visible light irradiation compared with it in the dark. Ultimately, the action mechanism of Zn/Ce co-doping is discussed.
|
|