|
|
Research Progress of Lithium-air Battery
WANG Fang, LIANG Chun-Sheng, XU Da-Liang, CAO Hui-Qun, SUN Hong-Yuan, LUO Zhong-Kuan
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1233–1242
 Abstract
Abstract(
3356 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(533KB)(
2814
)
With the increasing demand for high-performance battery by electric vehicle and the energy storage of power grid, the lithium-air battery with ultra-high specific energy has received more and more attention. To develop safe and practical lithium-air battery with good cycle performance, researchers have done plenty of exploratory work on the corresponding cathode materials, electrolyte, catalyst and waterproof oxygen permeation membrane, etc. Among all the work, finding stable electrolyte and minimizing discharge products’ passivation are the most critical issues. In this paper, based on the aprotic electrolyte architecture, the latest researches on the mentioned respects of the lithium-air battery are reviewed. In addition, the general development of other three architectures is introduced. At last, the future challenges in development of lithium-air battery are proposed.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Carbon-coated LaFeO3 and Electrochemical Properties of the Composites in Alkaline Solution
QI Wen-Juan, LUO Yong-Chun, KANG Long, ZHANG Guo-Qing
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1243–1250
 Abstract
Abstract(
1833 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(718KB)(
1324
)
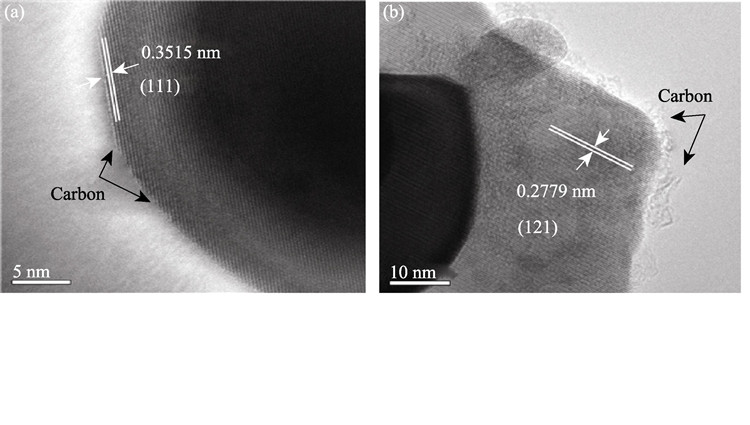
LaFeO3 nanostructure powders oxide was synthesized by sol-gel method and then LaFeO3/C composite materials containing different amounts of carbon were prepared by heat treatment using sucrose as a carbon source. The crystal structure, surface morphologies and electrochemical properties of the obtained composites coated with various carbon contents were investigated by the techniques of XRD, SEM, TEM, Raman spectroscope and electrochemical method. It was found that single phase nanostructure with perovskite-type LaFeO3 was obtained by Sol-Gel method and the crystal structure of LaFeO3/C could not be changed after coating carbon. Under high temperature, sourose was decomposed into amorphous carbon, which coated on the surface of LaFeO3 particles and formed network-like structure between LaFeO3 particles. Electrochemical measurements showed that the carbon- coated composites were superior in the electrochemical performance to the LaFeO3. LaFeO3/C electrodes possessed high discharge capacities, among which the sample adding with 5wt% carbon had the largest discharge capacity of 390 mAh/g. With increasing amount of carbon coated, the exchange current density I0 significantly enhanced, while effect of the coated carbon on the diffusion coefficient of ions was not obvious.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12/C Anode Materials
DONG Hong-Yu, ZHANG Zhi-Jun, YIN Yan-Hong, YANG Shu-Ting
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1251–1255
 Abstract
Abstract(
1677 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(406KB)(
1153
)
Li4Ti5O12 is a promising anode electrode material in Lithium ion batteries. Using polyacrylamide as template and carbon source, spinel Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12 and Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12/C were successfully synthesized by modified solid state method. The results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Field-emission scanning electron microscopy show that highly crystalline Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12 and Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12/C materials without any impurity are obtained. The shape and size of particles are modified by polyacrylamide. The electrochemical performances of materials are investigated in the range of 1.0–2.5 V. The Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12/C presents a higher specific capacity and better cycling stability than Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12. The charge and discharge specific capacity of Li4Ti4.95Al0.05O12/C material are 159.2 and 160.8 mAh/g at 0.2C rate.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of Yttrium Doped Barium Zirconate-cerate Proton Conductors
JIANG Hong, GUO Rui-Song, XU Jiang-Hai, GAO Yan-Ying, DENG Ya-Ping
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1256–1260
 Abstract
Abstract(
1866 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(552KB)(
1658
)
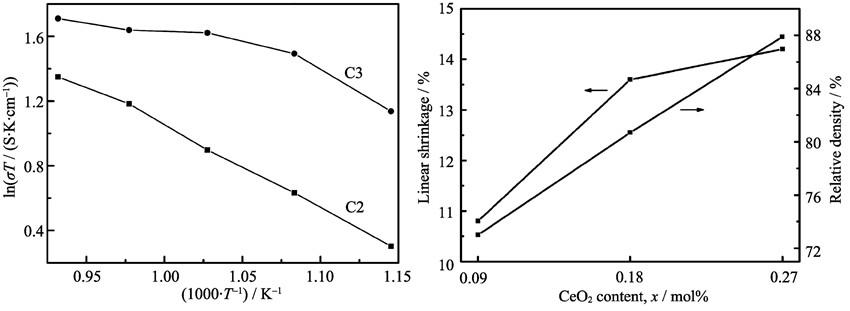
Yttrium doped barium zirconate-cerate (BaZr0.90-xCexY0.10O3-δ, x=0.09, 0.18, 0.27, BZCY) powders were synthesized by the conventional solid state reaction route. The x value was optimized to be 0.27 in the composition range. That is to say, the sample with x=0.27 had the best sinterability and conductivity among the three composites. The sintering behavior and electrical conductivity could be further improved by optimizing the addition content of ZnO sintering aid. ZnO was able to form a solid solution with BZCY, resulting in the enhancement of sinterability. As increasing the amount of ZnO, density of the sintered samples increased. However, conductivity did not increase monotonously with the addition of ZnO. When the content of ZnO was 2mol% (C3-Z2), the sample had the highest DC conductivity, reaching 9.27 mS/cm at 800℃ in wet H2 atmosphere. A small shift of the main peaks of the XRD pattern for the sample C3-Z2 was clearly observed compared with the standard patterns for BaCeO3 and BaZrO3. The XRD pattern of the sample C3-Z2 was in a good agreement with that of BaCe0.4Zr0.6O3 sample.
|
|
|
Template Synthesis of Mesoporous Nanocrystalline VN Electrode Materials and Its Supercapacitive Behavior
GAO Zhao-Hui, ZHANG Hao, CAO Gao-Ping, HAN Min-Fang, YANG Yu-Sheng
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1261–1265
 Abstract
Abstract(
1754 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
1020
)
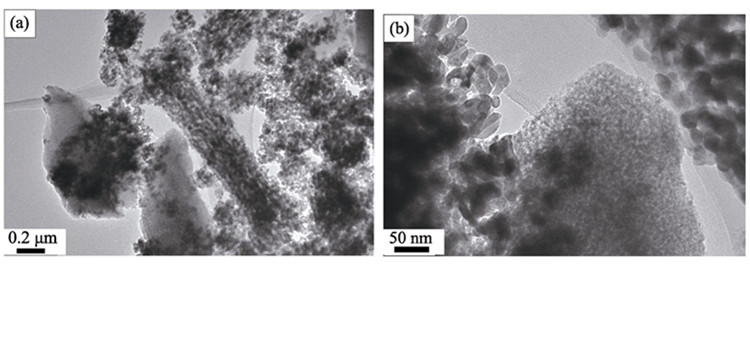
Using hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) as the template, mesoporous VN nanocrystalline was synthesized by NH3 reduction of precursor V2O5. The structure and surface morphology of mesoporous VN were characterized by XRD and TEM. Specific area and pore size distribution were studied by N2 absorption. The XRD result indicated that VN nanocrystalline belonged to the cubic crystal system. VN nanoparticles were in dimension of about 10 nm. N2 absorption result indicated that the surface area of VN sample was 88 m2/g, and most pores were distributed in the range of 2–6 nm. The supercapacitive behavior of VN electrode in 1 mol/L KOH electrolyte was studied by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and constant current charge-discharge measurements. The results showed that mesoporous VN electrode had both electrical double-layer capacitive properties and redox pseudocapacitive properties. The specific capacitance was of VN electrode 517 F/g at 1 mV/s scan rate, when the scan rate was up to 10 mV/s, its specific capacitance maintained 275 F/g.
|
|
|
Effects of Al2O3-doping on the Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of Ba4Sm9.33Ti18O54 Ceramics
YAO Xiao-Gang, LIN Hui-Xing, JIANG Shao-Hu, CHEN Wei, LUO Lan
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1266–1270
 Abstract
Abstract(
1519 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
1175
)
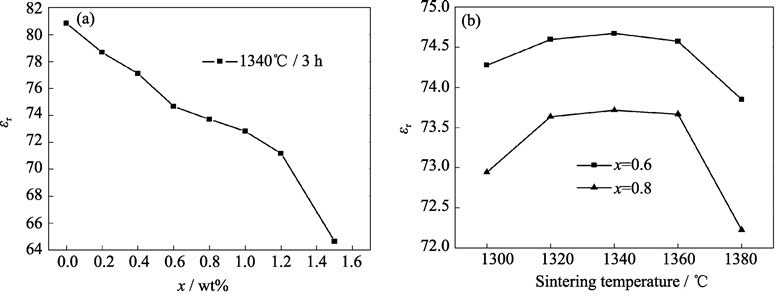
Ba4Sm9.33Ti18O54 (BST)• xwt%Al2O3 (x=0–1.5) microwave dielectric ceramics were prepared by solid state reaction method. The effects of Al2O3 on the microstructure and dielectric properties of BST ceramics were studied. With the increasing amount of Al2O3, the Sm2Ti2O7 phase observed in the undoped BST ceramics disappeared and new phases BaTi4O9 (x≥0.6) and BaAl2Ti5O14 (x≥1.0) were found in BST ceramics successively as identified by SEM and EDS analysis. It was showed that the disappearance of Sm2Ti2O7 phase and the formation of a small amount of BaTi4O9 phase significantly improved the Qf values of the BST ceramics, at the cost of dielectric constant. Further increasing the amount of Al2O3 produced more BaTi4O9 led to a slight decrease in Qf values. However, both the dielectric constant and Qf values were deteriorated with the appearance of BaAl2Ti5O14. BST ceramics with 0.6wt% Al2O3 doped sintered at 1340℃ for 3 h obtained the best dielectric properties: εr=74.7, Qf =10980 GHz, τf = –11.8×10-6/℃.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Sulfonated Graphene and Conducting Films
YUAN Wen-Hui, GU Ye-Jian, LI Bao-Qing, LI Li
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1271–1276
 Abstract
Abstract(
3312 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(511KB)(
2076
)
Graphite oxide (GO) was prepared from graphite by Hummers liquid oxidation method and the sulfonated graphene (S-GNS) was then prepared by pre-reduction, sulfonation and post-reduction. Glucose was also used to reduce the agglomeration among the graphene layers. The as-prepared sulfonated graphene was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscope (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), Thermo- gravimetric analysis (TG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscope (SEM), Transmission electron microscope (TEM) and Atomic force microscope (AFM), respectively. The experimental results indicate that the graphene of the p-phenyl-SO3H groups is successfully grafted into graphite oxide, and graphite oxide is completely reduced to sulfonated graphene. The sulfonated graphene possesses high thermal stability, smooth surface and few defects, and the thickness of single layer graphene is approximately 1.2 nm. Water solubility and dispersion results show that the sulfonated graphene can be dispersed into water with good water solubility. In addition, the BET specific surface area and the electrical conductivity of the sulfonated graphene film are up to 806.4 m2/g and 1150 S/m, respectively.
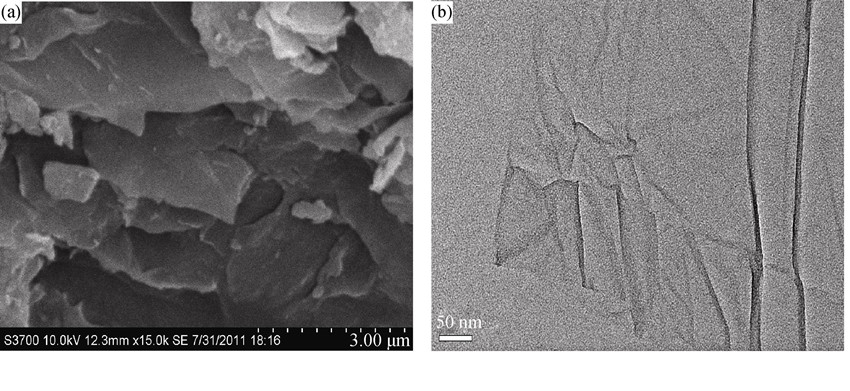
|
|
|
Preparation of Composite Additives Powder by Coprecipitation Method and Investgation of ZnO Varistor Ceramics
CHEN Pei-Rong, JI You-Zhang, YANG Qing
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1277–1282
 Abstract
Abstract(
1787 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(534KB)(
1013
)
ZnO varistor ceramic was prepared from composite additives powder synthesized by coprecipitation method. The coprecipitate precursor was investigated by thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis. Phase formation, morphologies, component elements and particle size distribution of the obtained powder were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope and dynamic laser scattering. Electrical properties of the prepared ZnO varistor ceramics were measured, then microstructure features of the ceramics were also observed. The results show that the mixture powder of each additive oxide is obtained by calcination of the precursor at 550℃, while the composite additives powder with pyrochlore-type composition of (Bi1.14Co0.26Mn0.29)(Sb1.14Cr0.57Ni0.29)O6.25 and average particle size of 0.26 μm is achieved at 650℃ for 1 h. ZnO varistor ceramic prepared from the resulted composite additives powder exhibits a higher breakdown voltage (Eb=330 V/mm), a higher nonlinearity coefficient (α=47) and a lower leakage current (IL=5 μA/cm2) than that prepared from conventional mixed oxide powder. The improvement in electrical properties is attributed to the more uniform microstructure.
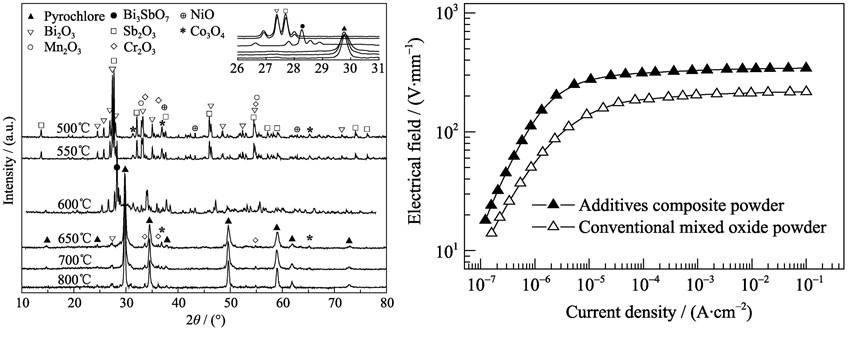
|
|
|
Photocatalytic H2 Evolution from Glycerol Solution over Bi3+-doped TiO2 Nanoparticles
SANG Huan-Xin, TIAN Ye, WANG Xi-Tao, TAO Lei
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1283–1288
 Abstract
Abstract(
1704 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(637KB)(
1174
)
TiO2 and Bi3+-doped TiO2 semiconductors were prepared by using Sol-Gel method. Their pore size distribution, crystal structure, surface composition, photo absorption properties and photocatalytic performance for H2 evolution from glycerol solution were investigated by techniques of N2 adsorption-desorption, XRD, FT-Raman, SEM, UV-Vis DRS and photocatalytic reaction. The results show that Bi3+-doped TiO2 appears anatase phase nanoparticles with mesoporous structure and has a much smaller crystallite size and much higher BET surface area than bare TiO2. These samples exhibit a visible-light absorption capability much higher than bare TiO2, which mainly originates from the doping process with the formation of new energy level of Bi3+ between conduction band and valence band of TiO2 to reduce the energy gap and the electron–hole recombination rate. The Bi3+-doped TiO2 samples display improved photocatalytic H2 production from glycerol solution, and 2%Bi-doped TiO2 shows a maximum H2 production rate of 3534.8 μmol/(h·gcat) under UV irradiation and 455.7 μmol/(h·gcat) under simulated-solar irradiation, respectively.
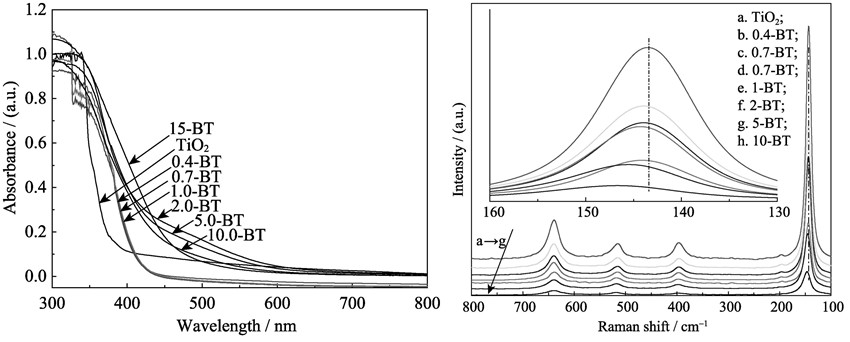
|
|
|
Characterization of PdHAp and Catalysis for Benzyl Alcohol Green Oxidation
WU Wei, YUAN En-Lin, ZENG Yi, LIU Zi-Wei, LIN Chu-Cheng, LI Yong-Sheng
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1289–1293
 Abstract
Abstract(
1519 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(528KB)(
1031
)
The PdHAp catalysts were prepared by simple ion-exchange method and calcium ions were replaced by palladium ions. As-prepared catalysts were applied for the green oxidation of benzyl alcohol. The catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), field emission transmission electron microscope (FE-TEM) and other techniques. The results show that some of the palladiums enter the crystal lattice of HAp, and the other palladiums were on HAp crystal surface in the form of nanoparticles. Pd nanoclusters show high dispersion of the catalysts. Palladium content is the key factor to determine catalysts’ performance. With the palladium content increasing, the catalytic efficiency was correspondingly improved. The catalysts have a good selectivity and possess excellent reusability.
|
|
|
Effects of pH Value on Composite Structure of Poly-titanium-ion/Montmorillonite and Its TiO2 Nano-particle
Lü Xia, PENG Tong-Jiang, SUN Hong-Juan, GU Chao-Jian
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1294–1300
 Abstract
Abstract(
1587 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(557KB)(
949
)
The montmorillonite composite structure samples were prepared using a hydrolysation-intercalation composite method with TiOSO4·2H2O as a precursor of TiO2 nano-particles and montmorillonite as substrate by controlling the pH value of the montmorillonite suspension. The changes of the structure, phase and crystal size of the samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction method. The results show that the pH value of montmorillonite suspension has a significant influence on the hydrolyzation of TiOSO4·2H2O, so the composite structure of hydrated- titanium-oxide/montmorillonite is affected. When the pH value of montmorillonite suspension is 0.5, the poly-titanium-ions are with the lower electrovalence and extent of polymerization and easily intercalate the interlayer space of montmorillonite, moreover, the structural layers of montmorillonite are separated best. The crystal size of anatase in the TiO2/montmorillonite composite samples calcinated at 700℃ is smallest and reaches 13.4 nm. After calcination at 1100℃, the relative content of anatase in the composite structure reaches 35%. Compared with pure TiO2 nano-particle sample, TiO2/Montmorillonite composite sample has a higher phase transition temperature from anatase phase to rutile phase and smaller crystal size of TiO2. Montmorillonite structure layer has a significant blocking effect on the TiO2 phase transformation and grain growth.
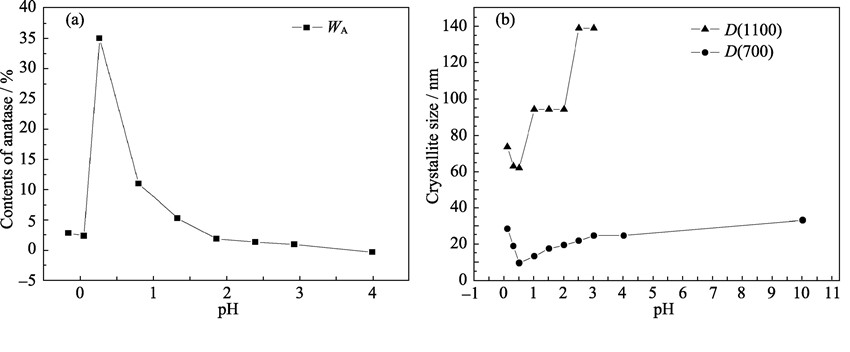
|
|
|
Study of the Photocatalytic Performance of Oxygen-deficient TiO2 Active in Visible Light
CAO Xiao-Xin, CHEN Yi-Lin, LIN Bi-Zhou, GAO Bi-Fen
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1301–1305
 Abstract
Abstract(
2152 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(470KB)(
1984
)
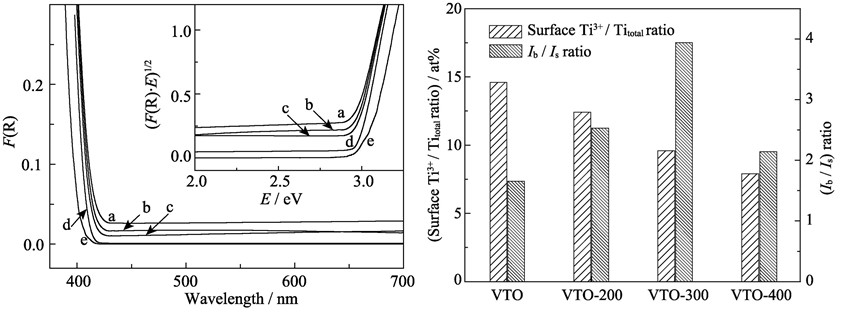
Oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide (TiO2-x) was prepared by heating TiO2 in H2 atmosphere, followed by the post-calcination in O2 at different temperatures. The physicochemical properties of the products were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), electron spin resonance (ESR), UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (UV-Vis DRS) and photoluminescence spectrum (PL). The photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared samples was determined by the degradation of gas-phase benzene under visible light (λ > 400 nm) irradiation. The results show that the TiO2-x post-heated at 300℃ exhibits the highest photocatalytic activity. After photocatalytic oxidation for 4 h, the conversion rate of benzene over the catalyst is up to 36.9% at steady state, which is 5.3 times as much as that on the untreated sample. The enhanced photocatalytic performance of the TiO2-x is related to the amount of the oxygen vacancies in matrix (single-electron-trapped oxygen vacancies). The postcalcination successfully reduces the surface oxygen vacancies (Ti3+), efficiently hindering the photoinduced carriers from recombination.
|
|
|
Oxidation Resistance and High Temperature Thermal Insulation of a Polymeric Precursor Derived BN/SiC Ceramics Foam
SHEN Zhi-Xun, GE Min, CHEN Ming-Wei, QIAN Yang-Bao, ZHANG Wei-Gang
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1306–1312
 Abstract
Abstract(
1784 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(781KB)(
1251
)
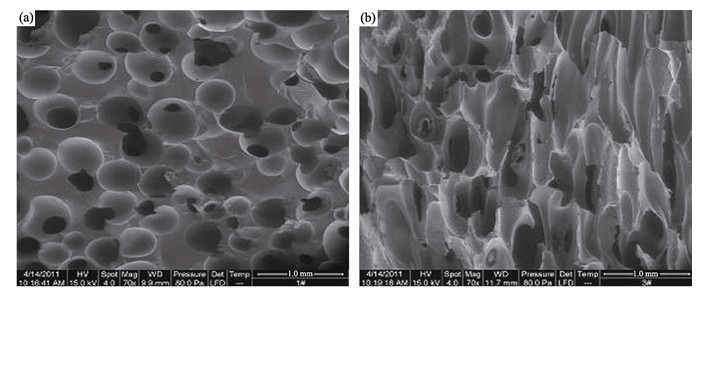
A kind of BN/SiC open-cell ceramic foams were fabricated from complex co-polymeric precursors of polycarbosilane and tris(methylamino)borane [B(NHCH3)3] using a high-pressure pyrolysis foaming technique. The obtained foams exhibited cell sizes ranging from 1 mm to 5 mm with bulk densities varying from 0.44 g/cm3 to 0.73 g/cm3, depending on the proportion of the starting precursors. Studies on the microstructure and thermal property of the porous ceramics showed that the addition of BN into SiC could improve dramatically the oxidation resistance from 800 to 1100℃. The compression strength of the composite foams was 5–10 times higher than that of pure SiC foam, which increased with increasing of BN content in the ceramic foams. Heat insulation performance of the ceramic foam fabricated from the starting precursors with a proportion of 1:1 in weight was analyzed by a device designed for insulation performance at high-temperature. When the temperature at the center point of hot surface of the foam was 1400℃, the temperature at the center point of the back achieved only 280℃. The heating history of the foam was simulated by finite-difference method, and the results showed that thermal conductivity of the composite foam was 4.0 W/(m·K), which was almost identical to the experimental result.
|
|
|
Study on Grain Fragmentation of Aluminum Nitride Microcrystal under High Pressure
LI Xiao-Lei, WANG Hong-Liang, ZHANG Qin-Shan, WANG Li-Ying, LI Shang-Sheng, SU Tai-Chao
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1313–1316
 Abstract
Abstract(
1574 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(369KB)(
974
)
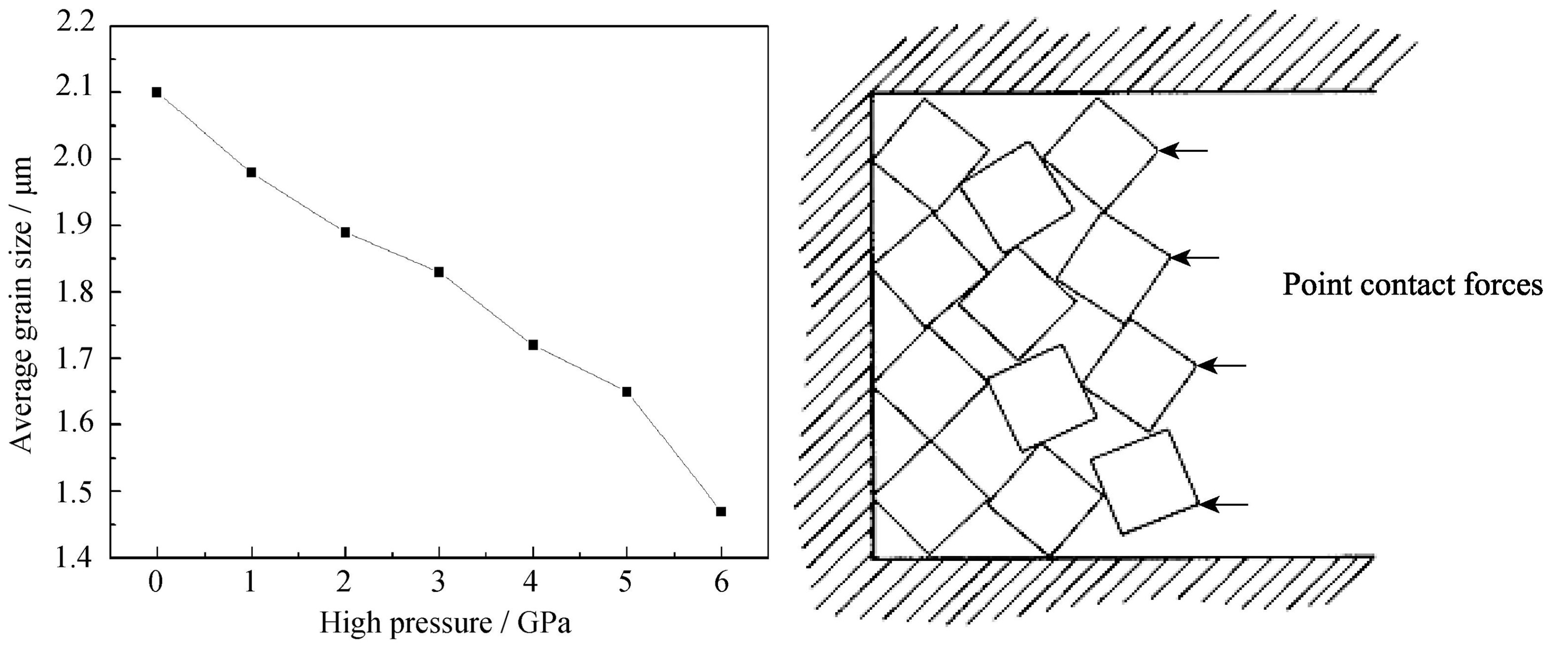
Grain fragmentation of AlN micron?powder under high pressure (2.0–6.0 GPa) was studied on cubic high pressure apparatus. Phase composition, grain size and microstructure of the samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that relative density of AlN microcrystal increases and open pore decreases with the rise of high pressure. “Cold-sintering” occurs in the AlN sample pressed at 6.0 GPa because its relative density reaches 88.72%. Obvious pressure-induced grain fragmentation is observed during the compacting of AlN powder under high pressure. The average particle diameter drops to 1.47 μm from 2.10 μm when high pressure is increased to 6.0 GPa from atmospheric pressure. Pressure-induced grain fragmentation can improve the surface free energy of AlN powder and increase sintering driving force. Meanwhile, it can activate sintering to improve AlN sintering rate because of the presence of defects (such as dislocation, crack, etc.) caused by high pressure.
|
|
|
Effects of Zn2+ and Cr3+ Doping on Nano-sized CoAl2O4 Spinel Pigments by Hydrothermal Processing
CHEN Yun-Xia, HU Qi, CAO Chun-E, LU Xi-Long, HONG Chen, SHEN Hua-Rong
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1317–1320
 Abstract
Abstract(
1630 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(416KB)(
1110
)
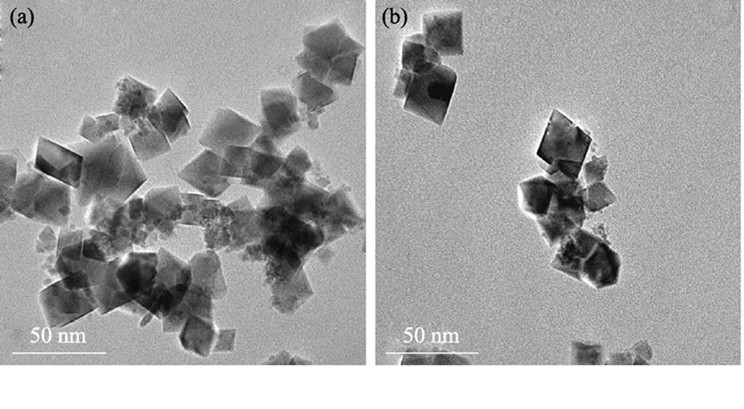
Nanosized spinel type cobalt blue pigments of CoAl2O4(AB2O4) were hydrothermally synthesized using CoCl2·6H2O, ZnCl2, AlCl3 and CrCl3·6H2O as raw materials. Colorimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and High resolution transmission electron microscope(HRTEM) were employed to investigate the effects of various amounts of Zn2+ doping at A site and Cr3+ doping at B site and various hydrothermal temperatures on the coloration, crystal phase compositions, crystal size and interplanar spacing of the CoAl2O4 spinels. The results indicated that Zn2+ and Cr3+ doping cause incomplete crystal growth and result in smaller particles than that of undoped spinels obtained at the same hydrothermal conditions. Zn2+ doping at A site lowered the synthesis temperature of the spinel crystalline colorants. Co0.95Zn0.05Al2O4 pigments with good coloration were obtained at 230℃. The hues of the as-prepared pigments changed from blue to green with increased amount of Zn2+ doping, and the coloration of samples became lighter. Similarly, the hues of the pigments also changed from blue to green with increasing the amount of Cr3+, but the coloration became deeper. Zn2+ doped spinels are of better coloration than that of Cr3+ doped.
|
|
|
Study on Properties of Ti:sapphire Crystals Doped Carbon Grown by the Kyropoulos Technique(KY)
HU Ke-Yan, XU Jun, WANG Chuan-Yong, LI Hong-Jun, ZOU Yu-Qi, YANG Qiu-Hong
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1321–1324
 Abstract
Abstract(
1683 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(419KB)(
1222
)
Ti:sapphire crystal is of great value in the domain of modern science and technology application. But growth of large Ti:sapphire crystals with a homogeneous titanium distribution and good optical quality is still a challenge. Carbon-doped Ti:sapphire crystal was grown by the Kyropoulos technique. The present work shows that by the utilization of KY growth technology, it is possible to grow carbon-doped Ti:sapphre, with 180 mm in diameter and 30 kg in weight, without macroscopic defects such as cracking. As-grown large crystals show high chemical homogeneities and the figure of merit is above 200, The study has the important practical significance of grown large Ti:Sapphire crystal with low infrared absorption loss and high figure of merit.
|
|
|
Preparation of Boron Carbide Spherical Films and Hollow Microsphere
YU Xiao-He, LU Tie-Cheng, LIN Tao, WANG Zi-Lei, TAO Yong, LIAO Zhi-Jun
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1325–1330
 Abstract
Abstract(
1579 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(573KB)(
1297
)
Boron carbide spherical-films were prepared by electron-beam evaporation deposition technique on steel ball substrates,combined with a independently designed magnetron rolling method. The boron carbide micro-shell was obtained after sintering, drilling and corrosion. The microcosmic appearance, microstructure, morphology, element composition of the boron carbide spherical films were investigated. The effect of annealing temperature (800–1100℃) on the boron carbide hollow micro-shells was also studied. The products were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope (XPS), atomic force microscope (AFM). The results show that the film is dense without any cracks and pores. Besides, the elemental distribution is well-proportioned. When the annealing temperature is over 900℃, the coating is self-standing formed into a hollow microsphere. The hollow microsphere annealed at 900℃ has the best micro appearance with a thickness over 10 μm.
|
|
|
Study on the Consolidation Process of Protein Foaming in the Preparation of Ceramic Foams
YIN Liu-Yan, ZHOU Xin-Gui, YU Jin-Shan, ZHAO Shuang, LUO Zheng, YANG Bei
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1331–1335
 Abstract
Abstract(
1501 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(479KB)(
1083
)
High porosity Si3N4 ceramic foams were fabricated by protein foaming method using egg white protein as foam agents. Atmosphere-, constant- and high-pressure consolidation processes were tested to prepare ceramic foams. The effects of air pressure on cellular structure, open porosity and pore size distribution of the as-prepared ceramic foams were investigated. The results showed that ceramic foams with average pore size and porosity of 210 μm and 78.6% was obtained by constant-pressure consolidation, which are the highest values among all the three groups. Moreover, SEM reveals that ceramic foams with uniformly ellipsoidal pores are produced by atmosphere- and constant-pressure consolidation processes, while ceramic foams with regular sphere pores are produced by high-pressure consolidation. The walls’ thickness of the pores increase with the increase of air pressure during consolidation process. As a result, the high-pressure consolidation process yields the highest compressive strength (nearly 50 MPa) of ceramic foams.
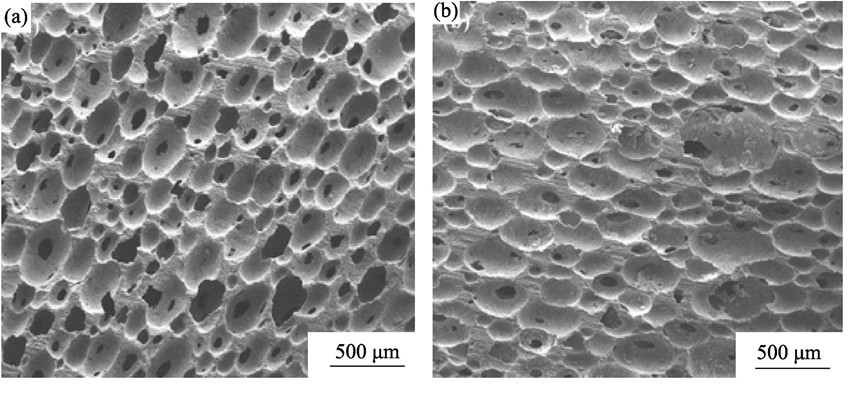
|
|
|
Design of Ultra-thin Absorbers Embedded with Fractal Frequency Selective Surface in Low Frequency
FAN Yue-Nong, NIE Yan, LIAO Zhang-Qi, WANG Xian, GONG Rong-Zhou
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1336–1340
 Abstract
Abstract(
5547 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(292KB)(
2022
)
Ultra-thin absorbers at low frequency bands composed of two traditional microwave absorbing material (MAM) rubber plates and fractal frequency selective surface (FSS) were designed. The absorbing properties of composite absorbers of different arrangement of MAM and FSS were investigated in detail in L and S bands. Two traditional MAM rubber plates and fractal FSS layers were fabricated for producing the multilayer microwave absorber (MMA) samples by using vulcanizing and laser etching methods, respectively. The reflectivity of MMA samples were measured by the NRL-arch testing systems. It is found that introducing FSS layers into the traditional MAM plates indeed could strengthen the absorbing properties of MMA samples at low frequencies. Moreover, after proposing double FSS layers in a proper arrangement, the MMA sample with the thickness of only 1.8 mm could obtain peak value of –9.35 dB and the reflectivity value of –3.49 dB at 1 GHz, respectively. As a result, the introduction of fractal FSS layers could provide another way to develop the absorbing properties at low frequency bands.
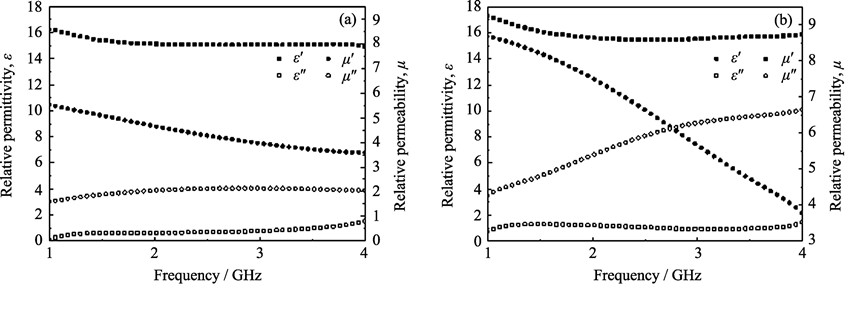
|
|
|
Preparation and Optimization of Long Persistent Luminescent Sr4Al14O25:(Eu,Dy) Phosphor Materials
QIU Tao, JI Zhen-Guo, KONG Zhe, LI Hong-Xia, ZHANG Er-Pan
2012 Vol. 27 (12): 1341–1344
 Abstract
Abstract(
5872 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(329KB)(
2056
)
Sr4Al14O25:(Eu,Dy) phosphor materials were prepared by solid state reaction. The dependence of long persistent luminescence from Sr4Al14O25:(Eu2+, Dy3+) on the amounts of H3BO3, the solid state reaction temperature, and the contents of Eu were studied. It was found that the addition of H3BO3 as the flux agent was critical for the formation of the blue-green emitting Sr4Al14O25 phase. Sr4Al14O25 phosphors with persistent luminescence of 490 nm and afterglow time more than 24 h was obtained for the sample prepared at 1400℃ with the doping amounts of H3BO3 of 10at% and Eu/Al atomic ratio of 0.03, respectively. Furthermore, the dependence of persistent luminescence intensity on Eu content indicates that the persistent luminescence process is mainly controlled by the electron transition rate from deep traps to Eu2+ levels.
|
|