|
|
Development of Containing 6Li Glass Scintillators for Neutron Detection
CHEN Yan-Ping, LUO De-Li
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1121–1128
 Abstract
Abstract(
2293 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(561KB)(
2035
)
Since the development of first generation glass scintillators for neutron detection in the 1950s, glass scintillators have played an increasingly unsubstitutional role in the fields of nuclear physics, high energy physics, industry detection (neutron spectrum measurement, neutron radiography, α, β, and γ-ray detection in extreme environments). Most researches were concentrated on containing 6Li, 10B silicate, phosphate, fluoro-oxide glass doped with lanthanide ions (Ce3+, Tb3+, Pr3+, etc.). This paper described performance characteristic, development history and luminescence mechanism of glass scintillators, then focused on studies about preparation methods, optical properties, neutron detection efficiency and luminescence delay time measurement of containing 6Li silicate glass, containing 6Li phosphate glasses, 6Li fluoxygen glasses and other glass scintillators, and pointed out future development trends and application fields of glass scintillators.
|
|
|
Graphene Applications in Solar Cells
JIANG Li-Li, LU Xiong
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1129–1137
 Abstract
Abstract(
5167 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(593KB)(
2931
)
Graphene has attracted much attention in fields such as physics, chemistry, and materials science, because of its unique properties and potential applications. Interests in graphene applications in solar cells have been motivated to meet the demand of improving the photovoltaic performance. Graphene applications in solar cells, such as graphene based transparent conducting electrodes, photoanodes, and accepter materials, are reviewed systematically. The further prospects and improvement of graphene applications are also discussed.
|
|
|
Effect of Nd2O3 Doping Content on the Properties of CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3
PENG Na, CHEN Shan-Hu, ZHOU Ju-Fa, CHEN Yao-Qiang, GONG Mao-Chu
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1138–1144
 Abstract
Abstract(
1643 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(652KB)(
1206
)
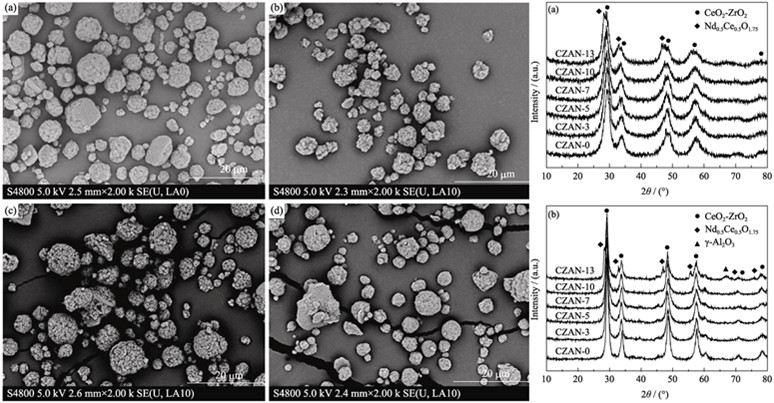
A series of CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3 (CZA) mixed oxides with Nd2O3 contents 0–13wt% were prepared by co-precipitation method and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption-desorption at low temperature, oxygen pulsing technique (OSC), H2-temperature programmed reduction (H2-TPR) and scanning electrical microscope (SEM). The results show that the solubility limit of Nd2O3 in the CZA solid solution is about 10wt%. With excessive Nd dopant, the single phase will separate resulting in the formation of Nd0.5Ce0.5O1.75 phase. Furthermore, the proper addition of Nd to CZA solid solution effectively restrains the sintering of oxide particles and greatly improves the thermal stability and redox property of the materials. When the doping amount of Nd2O3 in CZA solid solution is 10wt%, the sample has the best textural stability i.e. after calcination at 1000℃ for 5 h, the specific surface area and pore volume achieve 97.14 m2/g and 0.44 mL/g, respectively. For the CZA sample prepared with 7wt% Nd2O3 in CZA solid solution, the OSC is the highest in all samples, reaching 938.01 μmol/g and 821.72 μmol/g after calcination at 600℃ and 1000℃, respectively. Meanwhile, the mobility of bulk oxygen is the strongest and the sample has optimal reducibility at low temperature. After aging, the reduction peak temperature can be increased from 465℃ to 483℃. SEM image shows that all the prepared CZA samples have spherical particles and Nd2O3 can effectively prevent the agglomeration of particles in the process of high-temperature calcination.
|
|
|
Preparation of CdS-K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10 and Its Photocatalytic Property
CUI Wen-Quan, QI Yue-Li, LIU Yan-Fei, LIU Li, FAN Li-Hua, HU Jin-Shan, LIANG Ying-Hua
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1145–1152
 Abstract
Abstract(
1763 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(612KB)(
987
)
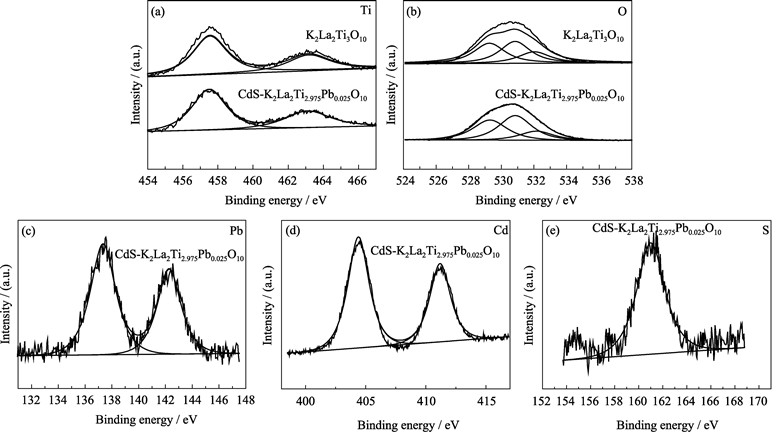
K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10 powder was synthesized via a stearic acid method. CdS-intercalated K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10 composite photocatalysts were synthesized via ion-exchange reaction, butylamine pillaring and sulfuration processes under the assistance of the microwave irradiation (designated as CdS-K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10). The photocatalysts were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS), ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflection spectra (UV-Vis), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and photoluminescence measurement (PL). The photocatalytic activities of CdS-K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10 for hydrogen production were also investigated under UV and visible light irradiation. The results reveal that the Pb ions doping and CdS-intercalated K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10 photocatalysts can widen the range of absorb visible light and greatly enhances the photocatalytic activity. The photocatalytic activities for hydrogen production of the CdS-intercalated K2La2Ti3-xPbxO10 prepared via a microwave assisted procedure are 230.15 and 3.35 mmol/(g cat) under UV light and visible light irradiation, respectively, after 3 h irradiation. The mechanism photocatalysis is deduced as well.
|
|
|
Preparation of Monolithic TiO2 Aerogel via Ambient Drying and Photocatalytic Degradation of Oily Wastewater
LI Xing-Wang, Lü Peng-Peng, YAO Ke-Fu, ZHAO Hai-Lei, ZHU Xiao-Hui
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1153–1158
 Abstract
Abstract(
1972 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(661KB)(
1161
)
The monolithic TiO2 aerogel was sucessfully synthesized at ambient pressure through Sol-Gel technique with TBT as the raw material and its photocatalyst property for degradation of the aqueous emulsion of crude oil in the Bohai Sea was investigated. During the ambient drying process, aging liquor and pinhole drying technology were found to be critical to the properties of TiO2 aerogels. It was shown that the pinhole drying was favorable in reducing the asymmetric stress on the framework of TiO2 gel in the drying process and the TEOS-Ethanol or TBT-Ethanol solution as the aging liquor for TiO2 wet-gel could enhance the strength of TiO2 gel skeleton. Combining these effects, the cracking problem of TiO2 alcohol gel in the drying could be solved and the high-performance TiO2 aerogel monolith was eventually achieved. The most integrated TiO2 aerogel block exhibited low density (0.184 g/cm3) and high specific surface area (389.5 m2/g). By calcinations at high temperature, the TiO2 aerogels changed from amorphous to anatase structure. The photocatalytic properties of the heat-treated TiO2 aerogels were investigated via the degradation experiment for the aqueous emulsion of crude oil in the Bohai Sea. The results of photocatalytic experiments showed that the catalytic degradation rate was up to 91% with the addition of TiO2 aerogel of 400 mg/L.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Photocatalysis of Rod-like ZnWO4 Nanocrystallites
ZHANG Xiao-Wei, CAO Li-Yun, HUANG Jian-Feng, Liu Yi-Jun, LI Jia
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1159–1163
 Abstract
Abstract(
7337 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(518KB)(
1198
)
The Wolframite ZnWO4 nanocrystallites were prepared by a facile, template-free microwave hydrothermal method using Na2WO4·2H2O and Zn(COOCH3)2·2H2O as starting materials. The phase, morphology and optical properties of as-prepared samples were characterized by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM), UV-Vis absorption spectra (UV-Vis) and photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL). Results indicate that ZnWO4 nanocrystallites have a preferential orientation growth along the (100) planes, and the morphology of ZnWO4 nanocrystallites change into rodlike structure with the increase of microwave hydrothermal time. An intense blue PL emission with a 460 nm wavelength is observed when the as-prepared ZnWO4 nanocrystallites are excited by a 295 nm wavelength, and they show a strong absorption in the ultraviolet region. The ZnWO4 nanocrystallites whose orientation degree of (100) planes is 0.24 with the particle sizes of 50–60 nm show the best photocatalytic properties.
|
|
|
Structure, Dielectric and Crystal Chemistry Properties of Bi1.5-xCaxZnNb1.5O7 Ceramics
WANG Hong-Ni, DING Shi-Hua, SONG Tian-Xiu, TU Wei, ZHANG Jing
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1164–1168
 Abstract
Abstract(
1696 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(486KB)(
1088
)
Bi1.5-xCaxZnNb1.5O7(0.00≤x≤0.50, BCZN) ceramics were prepared by solid phase reaction. The effects of Ca2+ substituting Bi3+ on the sintering properties, microstructure, dielectric and crystal chemistry properties of Bi1.5ZnNb1.5O7 based ceramics were investigated. The results revealed that when x≤0.25 mol, crystal structure of Bi1.5-xCaxZnNb1.5O7 ceramics via X-ray diffraction(XRD) was pure α-BZN phase. With the amount of Ca2+ ion increasing, the sintering temperature increased from 1000℃ to 1020℃, the density decreased from 7.011 g/cm3 to 6.353 g/cm3; and the grain size, lattice constant, resistivity all gradually decreased. For the crystal chemistry parameters, with the amount of Ca2+ ion increasing, AV(O')[Bi4], AV(O')[Bi3Zn], AV(O')[Bi2Zn2], AV(O')[Ca3Zn] all gradually increased, which coincided with the changes of lattice constant and dielectric properties.
|
|
|
Effects of Strain on Defects and Polarization in Tetragonal BaTiO3
ZHANG Si, MA Ying, ZHOU Yi-Chun
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1169–1173
 Abstract
Abstract(
1835 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(378KB)(
1081
)
The first-principle methods are used to calculate the effects of in-plane strain on the formation energies of neutral vacancies. It is shown that the formation energies of neutral O vacancy increase with compressive strain, while decrease for tensile strain. In other words, the O vacancy can be suppressed by compressive strain, which is contributed to the variation of the Ti–O bond. The formation energies of Ba–O divacancies and polarization of the tetragonal BaTiO3 are studied under different strain conditions. The strain changes the formation energies of Ba–O divacancies and the polarization of the systems containing Ba-O divacancies. More over, the results show that the polarization offset increases gradually when the strain changes from tensile to compressive strain. In other words the polarization imprint of BaTiO3 increase under compressive strain, but the changes are slight and negligible.
|
|
|
Study on Magnetic Properties of Dy0.15Fe1.85O3 Magnetic Nanoparticles at Low Temperature
ZHANG Mao-Run, SUN Jing-Jing, CHEN Jing
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1174–1178
 Abstract
Abstract(
1721 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(363KB)(
1017
)
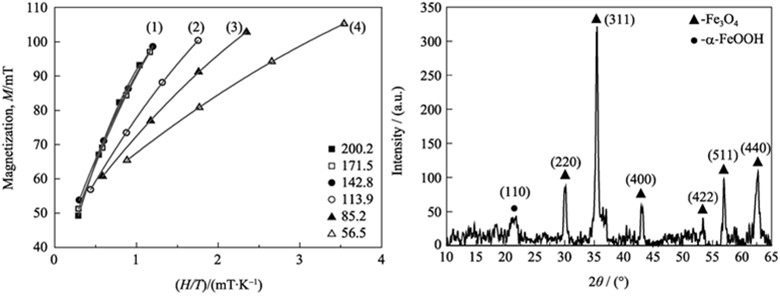
Dy0.15Fe1.85O3 magnetic nanoparticles were prepared by coprecipitation-phase transfer method, and the effect of temperature variation on the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles at low temperature were investigated. The chemical composition, morphology, crystalline structure and magnetic properties of the samples at low temperature were characterized by X-ray fluorescence spectrometer(XRF), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and super-conducting quantum magnetometer (SQUID). The results show that metal ions in the sample are mainly Dy3+ and Fe3+ whose mass fractions are 12.17% and 51.88%, respectively. The average diameter of the samples is ca. 15 nm. The magnetic particles are spherical with face-centered cubic spinel structure and complete crystalline. The saturation magnetization (MS) and coercivity (HC) of the samples increase with the decrease of temperature in the range of 56.5 K and 200.2 K. When the temperature exceeds or is equal to 142.8 K, the magnetic properties of the samples is at the superparamagnetic state. While the temperature is below 142.8 K, the superparamagnetic state is converted to ferromagnetic state.
|
|
|
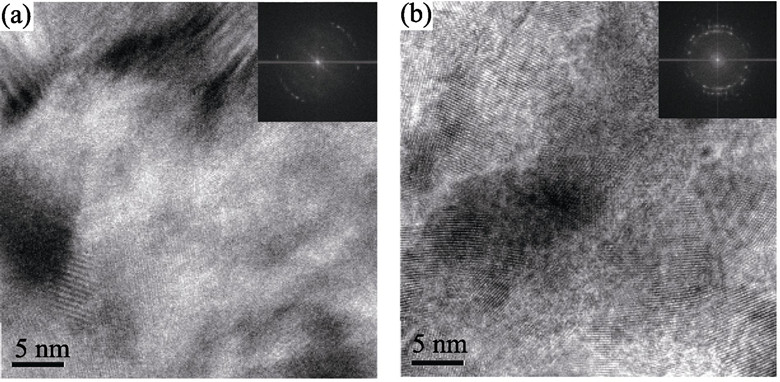
Effects of Rapid Quenching on Electrochemical Properties of MlNi3.55Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.3/5wt% Mg2Ni Composite Hydrogen Storage Alloy
TIAN Xiao, Tegus O, HAI Shan, YAO Zhan-Quan
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1179–1184
 Abstract
Abstract(
1813 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(451KB)(
1122
)
In order to improve the discharge capacity and the cycling stability of AB5-type hydrogen storage alloy, the effects of rapid quenching rate on the microstructures and electrochemical properties of MlNi3.55Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.3/5wt% Mg2Ni composite alloy were investigated by means of inductively coupled plasma (ICP), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and electrochemical measurements. The results show that the as-cast composite alloy is composed of the LaNi5 phase and a small amount of the Mg2Ni phase. However, the quenched composite alloys consist of the (La,Mg)Ni3 new phase and the LaNi5 phase. When the rapid quenching rate is higher than 15 m/s, nanocrystalline structure are formed and partial amorphous structure appeares in the composite alloys. Electrochemical studies show that the maximum discharge capacity and the capacity retention of quenched composite alloys increase firstly and then decrease with increasing rapid quenching rate. The maximum discharge capacity and the capacity retention after 100 cycles of the quenched composite alloy at 20 m/s is up to 344 mAh/g and 93.9%, respectively.
|
|
|
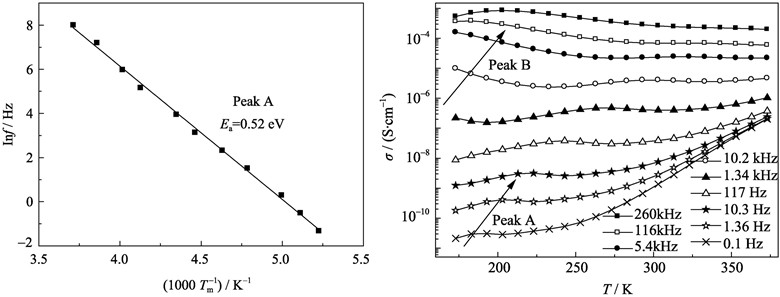
Investigation on Relaxation Properties of Deep Bulk Trap in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics
YANG Yan, LI Sheng-Tao, LI Xiao, WU Gao-Lin, WANG Qian, BAO Ming-Hui
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1185–1190
 Abstract
Abstract(
1600 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(568KB)(
1119
)
The relaxation properties of deep bulk trap in CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics prepared by solid state reaction and coprecipitation method were investigated. Dielectric spectra at frequency from 0.1 Hz to 107 Hz and in the temperature range from –100℃ to 100℃ were measured. With the analysis of dielectric spectra at different temperature, deep bulk trap relaxation in double Schottky barrier was studied. The relative position between deep bulk trap and Fermi level changed in double Schottky barrier under small AC signal, resulted in electron emission and capture of deep bulk trap, namely relaxation, which exhibited as a peak in dielectric frequency spectra. Furthermore deep bulk trap level, can be received based on frequency spectra analysis. Compared with the parameters of different samples, it is found that there exist deep bulk traps caused by interior defect at the levels with 0.52 eV and 0.12 eV lower than conduction band. The analysis of dielectric temperature spectra is similar, which can be complement for dielectric frequence spectra analysis.
|
|
|
Fabricating RE2Zr2O7 Buffer Layers by Low Cost Electrodeposition
CAI Zeng-Hui, LIU Zhi-Yong, LU Yu-Ming, CAI Chuan-Bing
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1191–1196
 Abstract
Abstract(
1541 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(469KB)(
980
)
Electrodeposition (ED), a novel and low cost method for epitaxial growth of La2Zr2O7 (LZO) and Gd2Zr2O7 (GZO) buffer layers on the biaxially textured Ni-5at%W (Ni-5W) substrate, was successfully developed to reduce the production cost of the second generation high temperature coated conductors. Combined with magnetron sputtering (MS) method, the architecture of MS-CeO2/ED-RE2Zr2O7 was obtained to replace the multilayers deposited only by MS system. Using electrodeposition, the full-width at half maximum (FWHM) values of phi (Ф) scans (in-plane texture) and omega (ω) scans (out-of plane texture) are 7.2° and 6.8°, respectively, for a typical LZO layer with 60 nm thickness. The corresponding values are 6.7° and 5.8° for 60 nm-thick GZO layers fabricated by the same method. YBa2Cu3O7-δ (YBCO) films with superconducting transitions are subsequently obtained on ED-LZO/Ni-5W, ED-GZO/Ni-5W and MS-CeO2/ED-LZO/Ni-5W structures by using pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) system.
|
|
|
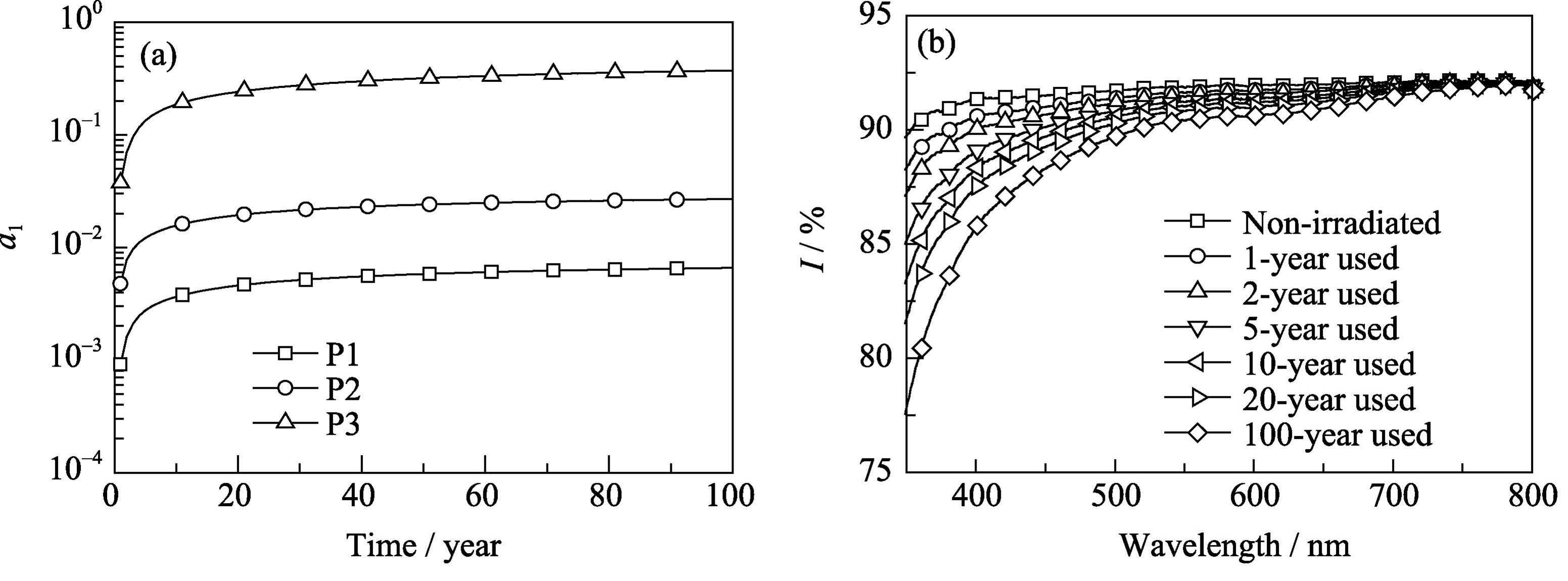
Study on Dynamic of Space Ionizing Radiation Induced Coloration in Glasses
DU Ji-Shi, ZHANG Tao, ZHAO Li-Li, SONG Li-Xin, HU Xing-Fang
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1197–1204
 Abstract
Abstract(
1624 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(634KB)(
981
)
Space ionizing radiation is mainly made up of the particles (proton and electron) with continuous energy distribution, and most of the particles have poor penetration capability in the glass, as a result, space ionizing radiation induced coloration in the glass inevitably changes complexly with depth in the glass. Based on this phenomenon, and considering the relaxation process of color centers induced by irradiation in the glass, a method applicable in the study on the dynamic of space ionizing radiation induced coloration in the glass was introduced in the paper. Selecting K9-HL glass as the studied object, using the numerical method and absorbed dose distribution of space ionizing radiation with depth in the glass simulated by Monte Carlo method, the process of space ionizing radiation (the orbital: perigee 350 km, apogee 425 km, orbital inclination 51.6°) induced coloration in this glass was studied. The method of anti-irradiation performance testing for the glasses used on the spacecrafts was discussed, and space ionizing radiation induced coloration distribution in the glass was analyzed. Key anti-irradiation technologies of the glasses on the spacecraft were proposed. Additionally, optical property K9-HL glass in the orbital shielded by silica glass anti-radiation layers of different thicknesses was studied.
|
|
|
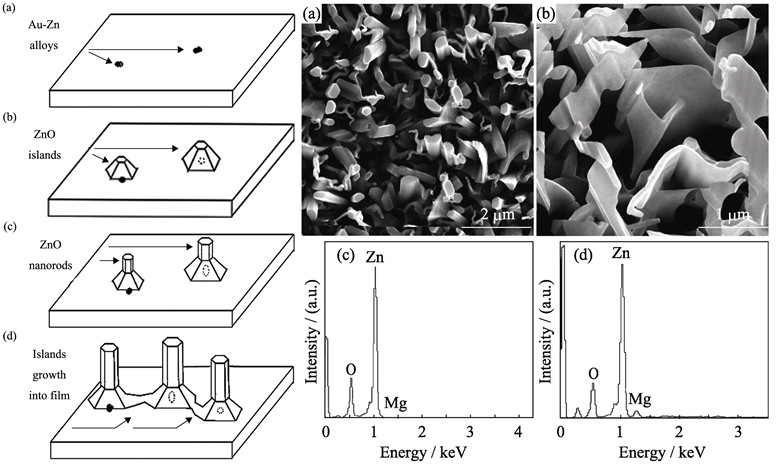
Growth and Photoluminescence of ZnO and Zn1-xMgxO Nanorods by High-pressure Pusled Laser Deposition
ZHANG Peng, WANG Pei-Ji, CAO Bing-Qiang
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1205–1210
 Abstract
Abstract(
1692 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(616KB)(
1154
)
The influence of the experimental parameters such as temperature, target, and thickness of catalyst layer on the growth of nanorods were systemically studied by a newly designed and home-built high-pressure pulsed laser deposition Zn1-xMgxO (PLD). The growth mechanism and photoluminescence properties of ZnO and Zn1-xMgxO nanorods were also investigated. It was found that c-orientated ZnO nanorod arrays grown on silicon substrate were obtained when the growth temperature was 925℃ and the thickness of gold catalyst layer was 2 nm. It was also proved that growth temperature and catalyst layer thickness were both crucial for the diameter and growth density of ZnO nanorods. A combination of vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) and vapor-solid (VS) mechanism was proposed to describe the growth of ZnO nanorods by high-pressure PLD. Zn1-xMgxO nanorods and nanobelts with random orientation were grown by doping the ZnO target with MgO. The bandgap of ZnO was effectively expanded together with defect-related levels formation in the forbidden gap, which also induced enhancement of visible peak emission.
|
|
|
Electroluminescent Characteristics of CdSe Colloidal Quantum Dots
LOU Teng-Gang, HU Lian, WU Dong-Kai, DU Ling-Xiao, CAI Chun-Feng, SI Jian-Xiao, WU Hui-Zhen
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1211–1215
 Abstract
Abstract(
1907 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(416KB)(
1280
)
Electroluminescent (EL) devices with an ITO/ZnS/CdSe/ZnS/Al structure were fabricated using chemically synthesized colloidal CdSe quantum dots (QDs) as active layer. The size of the CdSe QDs is about 4.3 nm measured by a transmission electron microscope. Scanning electron microscope characterization shows smooth surfaces of ZnS layers and Al electrodes. CdSe (111) and ZnS (111) diffraction peaks are observed in the X-ray diffraction patterns, verifying the incorporation of CdSe QDs and ZnS insulator materials in the devices. Room temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra reveal that the CdSe QDs’ emission peak is located at 614 nm. EL measurements at room temperature show a broad emission band ranging from 450 nm to 850 nm with a peak wavelength located at about 800 nm. Finally, the light emitting mechanism for the EL devices is proposed and the discrepancy between PL and EL spectra is interpreted.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characteristic of Hollow BN Fibers Derived from Organic Precursors
CHEN Ming-Wei, Ge Min, ZHANG Wei-Gang
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1216–1222
 Abstract
Abstract(
1880 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(563KB)(
1056
)
BN fibers with cylindrical hollow structures were prepared from organic polymeric precursors through melt spinning, curing and pyrolysis processes. The microstructure, solid phase and morphologies of the synthesized hollow BN fibers were investigated by XRD, SEM and TEM, respectively. Moreover, the dielectric properties of BN hollow fibers were also measured. The results show that heating temperature and heating rate are the key factors affected the structure and dielectric properties of BN hollow fibers. Moreover, the BN hollow fibers synthesized in the optimized process conditions have good resistance towards oxidation up to 950℃ in an oxidation atmosphere, and possess very low dielectric constant (ε′) and loss tangent (tanδ) less than 3.30 and 0.00064 (7-18 GHz), respectively.
|
|
|
Anisotropic Dielectric Properties of Short Carbon Fiber Composites
FU Jin-Gang, ZHU Dong-Mei, ZHOU Wan-Cheng, LUO Fa
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1223–1227
 Abstract
Abstract(
6422 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(403KB)(
1812
)
Dielectric materials based on short carbon fiber (Csf) dispersed inside epoxy resin (EP) matrix composites were prepared. The complex permittivity of two types of distributions over the frequency range from 2.6 GHz to 8.2 GHz was reported. The effects of orientation with different content and length of carbon fibers on dielectric properties were investigated. It is found that axial permittivity of carbon fibers is several times larger than their radial permittivity. The real and imaginary parts of complex permittivity increase gradually with increasing the Csf contents in the composites, and the fiber length also affects the anisotropic property greatly. The two layered transmission line model is used to explain the phenomena.
|
|
|
Effects of LaFeO3 Additions on the Dielectric and Ferroelectric Properties of (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 Ceramics
CHENG Hua-Lei, DU Hong-Liang, ZHOU Wan-Cheng, LUO Fa, ZHU Dong-Mei
2012 Vol. 27 (11): 1228–1232
 Abstract
Abstract(
5883 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(399KB)(
1982
)
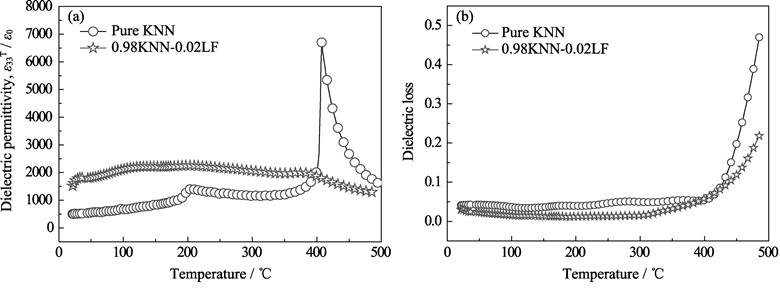
Pure (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 and 0.98(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-0.02LaFeO3 ceramics (abbreviated as KNN and 0.98KNN-0.02LF, respectively) were prepared by a solid state reaction approach, and their crystal structure, dielectric and ferroelectric properties were investigated. Pure KNN and 0.98KNN-0.02LF ceramics are the orthorhombic structure and pseudo-cubic perovskite structure, respectively. Dielectric measurements revealed that the dielectric permittivity curves of 0.98KNN-0.02LF ceramics present two anomalies compared with pure KNN: (i) The orthorhombic- tetragonal transition (TO-T) and the tetragonal-cubic transition (TT-C) shifts to lower temperatures. (ii) The phase transition temperature range around the temperature of the maximum dielectric permittivity (Tm) becomes more and more broad. In addition, 0.98KNN-0.02LF ceramics exhibited a very stable temperature dependence of dielectric permittivity with permittivity maximum near 2000 and dielectric loss less than 4% in the temperature range of 0–400℃. The relaxation behavior of the 0.98KNN-0.02LF ceramics is interpreted in terms of polar nanoregions (PNRs) caused by cations disorder. The P-E hysteresis loops further confirms the relaxor behavior in 0.98KNN-0.02LF ceramics.
|
|