|
|
Research Progress of Direct Growth of Two-dimensional Hexagonal Boron Nitride on Dielectric Substrates
ZHANG Xing-Wang, GAO Meng-Lei, MENG Jun-Hua
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1245–1256
 Abstract
Abstract(
1464 )
 HTML
HTML(
86)
 PDF
PDF(19728KB)(
2145
)
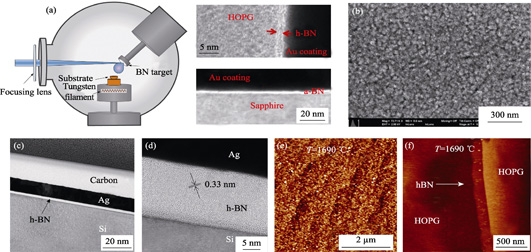
In recent years, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) two-dimensional (2D) atomic crystal has attracted considerable attention due to its unique structure, novel property and potential applications. The synthesis of high quality h-BN determines how far we can go for property research and practical applications. However, the sizes of h-BN domains obtained by mechanical exfoliation were limited to several micrometers. Transition metal substrates are usually used in the CVD growth of 2D h-BN layers, and thus a transfer process is required for fabricating h-BN-based electronic devices. Therefore, it is strongly desirable to directly synthesize 2D h-BN on dielectric substrates. In this article, we review recent process on the direct growth of h-BN by CVD, MOVPE, PVD on different dielectric substrates, including silicon-based substrates, sapphire, quartz, etc. Several approaches, such as, increasing substrate temperature, oxide-assisted nucleation, and surface nitridation were adopted to directly grow h-BN on dielectric substrates. Besides, we also summarized the main applications of 2D h-BN grown on dielectric substrates.
|
|
|
Degradation Mechanism of Silver Nanowire Transparent Conductive Films: a Review
YE Chang-Hui, GU Yu-Jia, WANG Gui-Xin, BI Li-Li
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1257–1264
 Abstract
Abstract(
1252 )
 HTML
HTML(
69)
 PDF
PDF(10982KB)(
1747
)
Silver nanowire transparent conductive film is one of the new indium-free electrode materials. It has attracted increasing attention from academia and industry due to its superior optoelectronic properties and excellent flexibility. It has been employed in a wide variety of applications in displays, touch panels, solar cells, smart heaters, electromagnetic interference shielding, and so on. However, silver nanowire transparent conductive film has a serious stability issue in service, for example, break or spheroidization above 300 ℃ under fulfidation, accelerating the degradation under ultraviolet light, pores for mation or even breakdown due to electromigration. In this review, the degradation phenomena is thoroughly introduced, the degradation mechanisms is analyzed, and the remedy strategy of degradation is discussed.
|
|
|
Defect Evolution and Microcracks of 8YSZ Double-layer Thermal Barrier Coatings by Water Immersion Ultrasound Macroscopic Detection
WANG Lin, DING Kun-Ying, LIN Xiao-Ping, LI Ze, ZHENG Run-Guo, YANG Lian-Wei
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1265–1271
 Abstract
Abstract(
485 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(6068KB)(
985
)
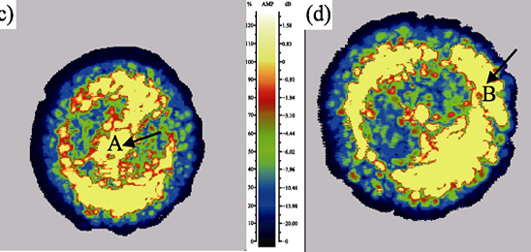
Evolution of internal structure of 8wt% Y2O3-ZrO2 (8YSZ) thermal barrier coatings during thermal shock was detected by PASCAN-64 water immersion ultrasonic equipment and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that echo signal obtained by reflection of the ultrasonic wave which is incident from vertical top coating to the bond coating mainly reflect evolution of the structure of top coating, and the echo signal obtained by reflection of ultrasonic wave which is incident from vertical basement to interface between bond coating and top coating mainly reflect evolution of structure of TGO layer, while the microstructure evolution of the whole coating is reflected by transimission signal obtained by transimission of the ultrasonic wave from vertical top coating to substrate. When porosity of the coating top coating is less than 11%, the maximum transverse size of the coating top coating is less than 50 μm and the TGO layer is mainly dense α-Al2O3, the amplitude of the echo signal dB is less than 0. Uniform distribution of signals can be observed from corresponding images, indicating that the coating is in good condition. When the porosity of top coating is more than 44%, the maximum transverse size is more than 100 μm, and the TGO layer is mainly composed of oxides of Cr and Co with sparse structure and thickness of more than 5.2 μm. From the image, the area whose amplitude dB is greater than 0 is connected into pieces, which indicates the imminent failure of the coating. Water immersion ultrasound technology can accurately reflect the evolution of internal structure of thermal barrier coatings, and it is a good nondestructive testing method for internal defects of thermal barrier coatings.
|
|
|
Carbon Fiber Preform's Structure on Mechanical Property of C/C Composites and Bolts
PANG Sheng-Yang, WANG Pei-Yao, HU Cheng-Long, ZHAO Ri-Da, TANG Su-Fang
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1272–1278
 Abstract
Abstract(
581 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(5505KB)(
833
)
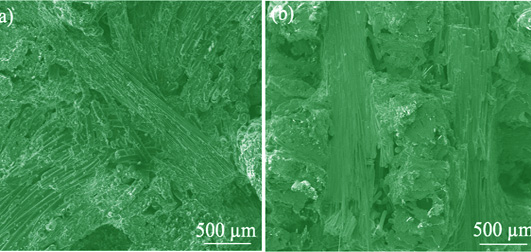
The C/C composites reinforced by 2D-preforms were fabricated using an electro-coupling chemical vapor infiltration (E-CVI) technique. The effects of different preform's structure on the mechanical properties of C/C and their bolts were investigated. The results show that the C/C composites reinforced by different preforms parameters exhibit different mechanical behaviors. For needle-punched preforms, as the needle-punched density decreasing from 35 pin/cm 2 to 25 pin/cm 2, the tensile and flexural strengths of C/C composites increased from 60.1, 119.9 MPa to 69.5, 176.8 MPa, respectively. With the carbon yarn tow changing from 12 K to 3 K, the tensile and flexural strengths of C/C composites increased from 69.5, 176.8 MPa to 105.5, 184.4 MPa, respectively. For bidirectional stitched preforms, the tensile and flexural strengths of C/C composites are 68.1 and 123.7 MPa, respectively. The different mechanical behaviors is mainly attributed to structural integrity of long fibers, and the distribution and quantity of large pores. The mechanical properties of bolts are impacted by their bulk materials and surface status, which are slightly lower than those of their counterparts.
|
|
|
Argon Ion Etching on Property of YBa2Cu3O7-x Thin Films Prepared by TFA-MOD Process
LUO Zhi-Yong, LIAO Chu-Jian, CAI Chuan-Bing, LIU Zhi-Yong, LI Min-Juan, LU Yu-Ming
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1279–1284
 Abstract
Abstract(
448 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(4782KB)(
837
)
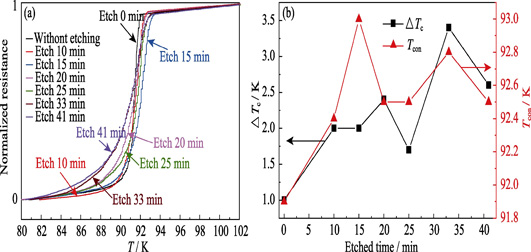
An impurity layer composed by Ba-Cu-O heterogeneous phase and a-axis YBCO crystal grains exists on the surface of the YBCO film after high-temperature crystallization, due to the unique growth mechanism of the YBCO film prepared by the TFA-MOD method. For the research of zero resistance superconducting welding and conventional resistance welding, we etched the YBCO film with Ar ion, decreasing the thickness of the film and removing the impurity layer without destroying the superconductivity and crystal structure. The Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to research the states of the film with difference etching time. The results showed that the surface impurity layer of the 1.3 μm YBCO film was about 220 nm. The YBCO film was still crystal and c-axis oriented, though over etching. After etching, the oxygen vacancy defects in the film increased, causing the decrease of superconducting transition and current carrying performance. It can be solved by oxygen-absorbing treatment.
|
|
|
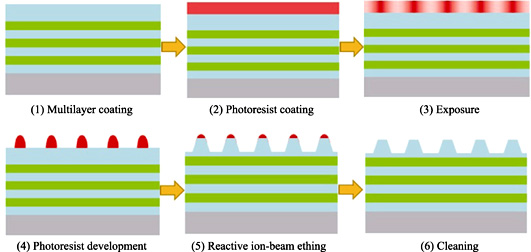
Cleaning Methods for Multilayer Dielectric Pulse Compression Gratings
ZOU Xi, JIN Yun-Xia, KONG Fan-Yu, WANG Yong-Lu, ZHANG Yi-Bin, SHAO Jian-Da
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1285–1289
 Abstract
Abstract(
477 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(3852KB)(
725
)
Two cleaning methods for multilayer dielectric pulse compression gratings (MDG) were studied. The first method is SPM (Sulfuric-Peroxide Mixtures, 98wt%H2SO4+30wt%H2O2) + megasonic, and the second method is Oxygen plasma + HPM (Hydrochloric/Peroxide Mixture, 37wt%HCl+30wt%H2O2+DIH2O) + megasonic. To compare the cleaning effectiveness, the element content of sample surface, diffraction efficiency, surface roughness, temperature rising and laser damage induced threshold (LIDT) were measured. The 1-on-1 LIDT of samples cleaned by the first and the second methods are 7.55 and 5.32 J/cm 2 respectively, with 1064 nm laser pulse (12 ns, s-polarized) at incidence angle of 70°. In addition, the sample cleaned by the second method has lower surface contamination content, but the sample cleaned by the first method has better performance in diffraction efficiency, surface roughness and temperature rising. By further analyzing, we find that element Fe brought by oxygen plasma cleaning process in the second method is the factor that affects the damage performance and temperature rising. Therefore, the cleaning method based on the first one, the SPM + megasonic is better for improving the laser damage performance of MDG.
|
|
|
Micro-tube Sapphire Crystal Grown by the Edge-defined-film Fed Method
WANG Dong-Hai, XUE Yan-Yan, LI Na, ZHOU Shi-Ming, XU Xiao-Dong, LI Dong-Zhen, XU Jun, WANG Qing-Guo
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1290–1294
 Abstract
Abstract(
864 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1083KB)(
1000
)
Sapphire rod with micro-tube (inner diameter: 470 μm) and sapphire plate with micro-tube (inner diameter: 160 μm) were grown by the edge-defined-film fed method (EFG). Profile curves of the small liquid menisci were investigated on the base of numerical solution of the Young-Laplace equation. By inserting Mo wires, new type of die was designed to form and sustain size of micro-tube in the volume of the crystal. Two problems were solved at the same time: 1) obtaining high quality sapphire crystal; 2) forming and sustaining necessary micro-tube sizes in the volume of the crystal. The crystal were transparent, colorless, no cracking and good XRC value of 3.8 arcmin, demonstrating the high quality of the as-grown crystal.
|
|
|
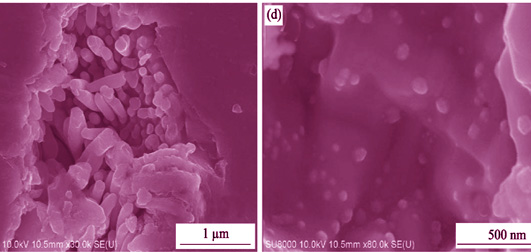
Ultra-fast Synthesis of Cu2S Thermoelectric Materials under Pulsed Electric Field
GONG Hao, SU Xian-Li, YAN Yong-Gao, TANG Xin-Feng
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1295–1300
 Abstract
Abstract(
716 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(2195KB)(
1249
)
Cu2S shows excellent thermoelectric properties as a material with phonon liquid-electron crystal characteristics. However, traditional preparation methods are cumbersome and difficult to afford bulk Cu2S with uniform composition, high density and excellent thermoelectric properties. In this study, a novel method named Pulsed Electric Current Sintering was introduced to synthesize and sinter Cu2S materials in one step consuming only 30 s. The synthesis of Cu2S under intense pulsed electric field includes three steps. A small amount of CuS and Cu2S forms in the first step; most of Cu2S and part of Cu1.96S are produced in the second step; finally, the remained Cu1.96S and Cu react to form completely pure Cu2S. The Cu2S bulk obtained by this method is a dense bulk with homogeneous composition, and contained abundant multi-scale microstructures. The thermoelectric performance is optimized by regulation of Cu-deficient Cu2-xS. The maximum ZT of Cu1.97S bulk at 873 K is 0.72, which is 49% higher than that of the pristine sample.
|
|
|
High-quality Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 Nanocubes: Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance as Cathode Material for Aqueous Sodium-ion Battery
WANG Wu-Lian, ZHANG Jun, WANG Qiu-Shi, CHEN Liang, LIU Zhao-Ping
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1301–1308
 Abstract
Abstract(
698 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1979KB)(
1250
)
High-quality Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 (HQ-FeHCF) nanocubes were synthesized by a simple hydrothermal method. Its structure, morphology and water content are characterized. Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 exhibits regular cubic shape with a uniform size of ca. 500 nm, which belongs to the face-centered cubic phase. Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 shows discharge capacities of 124, 118, 105, 94, 83, 74 and 64 mAh·g -1 at 1C, 2C, 5C, 10C, 20C, 30C and 40C rate, respectively, in the aqueous ternary electrolyte of NaClO4-H2O-Polyethylene glycol. Its capacity retention remains 100% after 500 charge/discharge cycles at the rate of 5C. The full battery with Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3 as cathode and NaTi2(PO4)3 as anode was fabricated, which delivers a specific energy density of 126 Wh·kg -1 (based on the active electrode materials) with a voltage output of 1.9 V. Furthermore, 92% of its initial discharge capacity retains after 140 charge/discharge cycles at a rate of 5C, and its Coulomb efficiency is close to 100%.
|
|
|
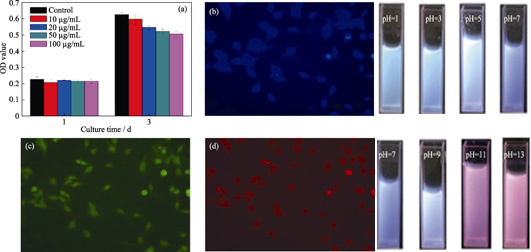
One-step Synthesis of Specific pH-responsive Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Luminescence Mechanism
GAO Dong, ZHANG Yu-Liang, SUN Jing, FAN Hong-Jun
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1309–1315
 Abstract
Abstract(
710 )
 HTML
HTML(
27)
 PDF
PDF(7744KB)(
1195
)
Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (CDs) were synthesized via a facile one-step solvothermal reaction using citric acid, formamide and water. Subsequent characterizations indicate that the nitrogen-doped CDs are featured by good water solubility, bright blue emission and typical excitation-dependent emission. However, unlike from conventional pH response of most CDs, the as-prepared CDs possess unique pH response. Apart from that fluorescence intensity varies with the pH value, the prepared CDs can generate excitation-independent red emission in alkaline conditions. Through scientific research towards fluorescent property of prepared CDs in different alkaline environments as well as solution with different hydroxyl content, combined with chemical composition and surface states based on Raman spectrum, FT-IR and XPS, the fluorescent mechanism of the unique pH response are attributed to a large number of hydroxyl groups in strong alkaline environment bonded to the surface of CDs, thus changing the surface states of CDs, further forming a new stable luminescence center. Finally, cytotoxicity tests and cell imaging experiments showed that the prepared CDs have low cytotoxicity, and can be used as fluorescent probe for cell imaging, indicating their potential application in the field of biological imaging.
|
|
|
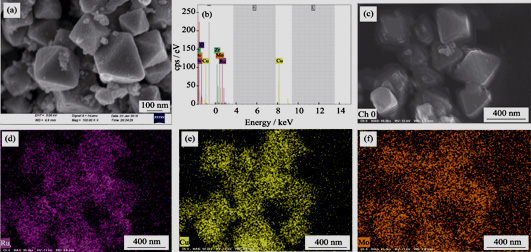
Preparation and Dehydrogenation Property of NH2-UIO-66 Supported RuCuMo Nanocatalyst
ZHANG Yi-Qing, LIU Li, ZHANG Shu-Juan, WAN Zheng-Rui, LIU Hong-Ying, ZHOU Li-Qun
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1316–1324
 Abstract
Abstract(
815 )
 HTML
HTML(
26)
 PDF
PDF(4335KB)(
1020
)
Amine-functionalize metal organic framework (NH2-UIO-66) was successfully synthesized by solvothermal method with zirconium salt and 2-aminoterephtalic acid. Tri-metallic RuCuMo nanoparticles (NPs) were immobilized by a facile impregnation-reduction method to prepare RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 catalysts. The structure, morphology, composition and specific surface area of the above catalysts were characterized. Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 catalyst exhibits the highest catalytic activity comparing with Ru, RuCu and CuMo counterparts as well as pure tri-metallic RuCuMo NPs in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane at room temperature, and the correspoding activation energy (Ea) and turnover frequency values (TOF) are 30.1 kJ?mol -1 and 180.83 mol H2 min -1(mol Ru) -1, respectively. Addition of Cu and Mo can significantly enhance the catalytic activity of Ru counterparts, owing to the synergistic effect among Ru, Cu and Mo atoms, bi-functional effect generated between RuCuMo NPs and NH2-UIO-66 support, and the amine as anchoring groups in the NH2-UIO-66 framework, which facilitate the formation and stabilization of ultra-small RuCuMo NPs by preventing their aggregation. The addition of non-noble metals Cu and Mo provides an important approach for the improvement of catalytic activity and industrial application.
|
|
|
TiO2@SiO2 Composites: Preparation and Photocatalytic Antimicrobial Performance
CHEN Yi-Fan, TANG Xiao-Ning, ZHANG Bin, LUO Yong, LI Yang
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1325–1333
 Abstract
Abstract(
850 )
 HTML
HTML(
32)
 PDF
PDF(2578KB)(
1116
)
Carrier SiO2 was synthesized through Sol-Gel method, and the photocatalytic antibacterial material of TiO2@SiO2 composite was prepared by hydrolysis method. The synthesized composites were characterized. The photocatalytic properties of the composites were investigated by degrading methyl orange with UVA irradiation. After 3 h irradiation, all of composites with different amount of titanium doping can reach 99.9%. And the optimal catalytic efficiency of the composite is obtained when the titanium doping ratio (molar ratio) is 0.58. Antibacterial effect of composites on Escherichia coli, measured by plate coating method, shows that the antibacterial properties are improved with the increase of titanium content, which reach up to 92% under UVA irradiation. Moreover, the composites also exhibit favourable antibacterial properties under visible irradiation. Though fluorescence detection of bacterium, it is proved that the reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by the composites migrate into the cells and cause the oxidative damage of the cells, which is a significant basis for the antibacterial mechanism of photocatalytic materials.
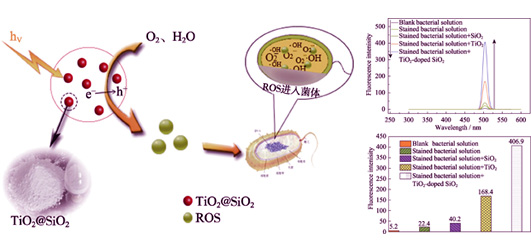
|
|
|
Preparation of CeO2/Flake-like CdS Composites as High-Performance Photoanodes for Photoelectrochemical Cathodic Protection
WEI Ke-Nian, LIU Zhan, ZUO Shi-Xiang, YAN Xiang-Yu, WU Feng-Qin, LI Xia-Zhang, YAO Chao, LIU Xiao-Heng
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1334–1340
 Abstract
Abstract(
436 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(1862KB)(
846
)
CeO2/CdS nanocomposites with the function of storing electrons and physical barrier were fabricated for photocathodic protection through a stepwise synthetic route. The obtained smples were characterized by XRD, TEM, UV-Vis and PL. The photoelectrochemical properties of CeO2/CdS with different mass ratios were investigated under white light irradiation. The maximum photocurrent density of CeO2/CdS (mass ratio 0.2 : 1) is 700 μA·cm -2 and the potential of the 304 stainless steel coated with CeO2/CdS (mass ratio 0.2 : 1) shifts to -650 mV (vs. SCE), which is significantly lower than the corrosion potential (-200 mV vs. SCE). The above results indicate that the CeO2/CdS composites exhibit remarkable photo cathodic properties which are attributed to the heterostructure of CeO2 nanoparticles and CdS nanosheets, and the structure facilitates the separation of photo-induced electron and hole. Furthermore, the CeO2/CdS composites can also provide cathodic protection for 12 h in the dark.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Property of Yb:CaF2 Laser Ceramics from Co-precipitated Nanopowders
WEI Jia-Bei, TOCI Guido, PIRRI Angela, PATRIZI Barbara, FENG Ya-Gang, VANNINI Matteo, LI Jiang
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1341–1348
 Abstract
Abstract(
576 )
 HTML
HTML(
19)
 PDF
PDF(1601KB)(
922
)
Transparent ytterbium doped calcium fluoride ceramics (Yb:CaF2) were successfully fabricated by vacuum sintering and hot pressing post-treatment from coprecipitated powders. In-line transmittance of 5at% Yb:CaF2 transparent ceramics fabricated by pre-sintering at 600 ℃ for 1 h and hot pressing post-treatment at 700 ℃ for 2 h, reaches 92.0% at the wavelength of 1200 nm. Microstructure, spectroscopic characteristics and laser performance of the ceramics were measured and discussed. The sample shows a homogeneous microstructure with average grain size of 360 nm. Furthermore, the absorption cross section at 977 nm and the emission cross section at the 1030 nm of the ceramics are calculated to 0.39×10 -20 cm 2and 0.26×10 -20 cm 2, respectively. Finally, the laser behavior was tested, finding a maximum output power of 0.9 W while the highest slope efficiency was 23.6%.
|
|
|
C/SiOC Composites by a Modified PIP Using Solid Polysiloxane: Fabrication, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
WU Qing-Qing, WANG Zhen, DING Qi, NI De-Wei, KAN Yan-Mei, DONG Shao-Ming
2019 Vol. 34 (12): 1349–1356
 Abstract
Abstract(
690 )
 HTML
HTML(
36)
 PDF
PDF(3820KB)(
850
)
A modified polymer infiltration and pyrolysis method (PIP) was developed to enhance the densification of C/SiOC composites, using molten MK resin (polymethylsilsesquioxane) as precursor. Organic sulfonic acid was added as cross-linking agent to lower the curing temperature. The cross-linking mechanism and ceramization behavior of MK resin was studied. A high ceramic yield of about 85wt% and low free carbon content below 3wt% are achieved, with excellent high-temperature stability of the derived SiOC. The modified PIP approach presents a high densification efficiency. After only 8 PIP cycles, the final C/SiOC composites possess a density of about 1.81 g/cm 3. Compared with those composites fabricated by conventional PIP process, the C/SiOC composites prepared by modified PIP process show a much denser microstructure with much more improved densification efficiency. Bending strength of the as-fabricated C/SiOC composites is of (312±25) MPa, showing obvious non-brittle fracture behavior.
|
|