|
|
Heteroepitaxial Growth of Single Crystal Diamond Films on Iridium: Procedure and Mechanism
WANG Yang, ZHU Jia-Qi, HU Zhong-Bo, DAI Bing
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 909–917
 Abstract
Abstract(
1893 )
 HTML
HTML(
77)
 PDF
PDF(2466KB)(
1394
)
Due to its unique physical and chemical property, diamond is widely used in many fields such as detectors and optoelectronic devices. Many scholars’ attention is drew into single crystal diamond because of its potential to significantly increase the functionality of these devices. Presently, single crystal diamonds grown heteroepitaxially on iridium (Ir) substrates reach the largest size and an excellent growth quality. In this paper, substrates with different structures for nucleation and growth processes of epitaxial diamond are introduced. The mechanisms of diamond nucleation by Bias Enhanced Nucleation (BEN) method and growth undergoing an Epitaxial Lateral Overgrowth (ELO) process are described, including technique of Patterned Nucleation and Growth(PNG). Limitations of current study are pointed out, and the future development of heteroepitaxial theory and experiment are also forecasted in this paper.
|
|
|
ZrB2-SiC Composites Toughened by Interlocking Microstructure and Chopped Carbon Fiber
ZHANG Zhao-Fu,SHA Jian-Jun,ZU Yu-Fei,DAI Ji-Xiang
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 918–924
 Abstract
Abstract(
688 )
 HTML
HTML(
28)
 PDF
PDF(5053KB)(
989
)
ZrB2-SiC ceramics present better oxidation resistance and mechanical properties than monolithic ZrB2 ceramics. However, the small damage tolerance and poor crack growth resistance, which result in the low fracture toughness, limit the engineering application of ZrB2-SiC ceramics. Focusing on this issue, microstructure design and introduction of toughening phase are two effective approaches to improve the fracture toughness of ZrB2-SiC ceramics. In this work, ZrB2-SiC and Cf/ZrB2-SiC composites were toughened respectively by interlocking microstructure and chopped carbon fibers via reactive hot pressing. For the ZrB2-SiC composites, the interlocking microstructure formed by in-situ ZrB2 platelets presented excellent self-enhancing effect. The ZrB2-SiC composites had high bending strength and fracture toughness. However, the composite exhibited typical brittle fracture characteristics. Compared with ZrB2-SiC composite, the flexural strength of Cf/ZrB2-SiC composite decreased, but the fracture toughness was comparable with the ZrB2-SiC composite. Furthermore, the critical crack size and the work of fracture of Cf/ZrB2-SiC composites significantly improved, and the composite presented the non-catastrophic failure mode.
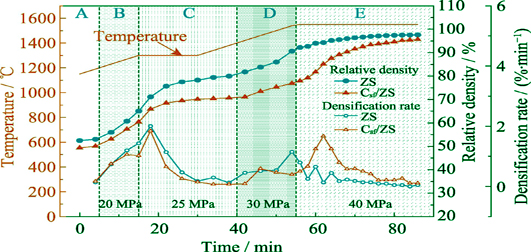
|
|
|
Litchi-like Superparamagnetic Hydroxyapatite Microspheres with Hierarchically Mesoporous Microspheres
XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo,LIU Xue,LIAO Xiao-Ling
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 925–932
 Abstract
Abstract(
655 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(4040KB)(
791
)
Due to the fact that the conventional bioceramic microspheres lack target function, novel litchi-like porous microspheres composed of a core of CaCO3 and a tunable magnetic-hydroxyapatite (HA) shell were successfully prepared in this study. Antitumor drug, doxorubicin (DOX), was effectively loaded on the HA microspheres which possess magnetic targeting function. In addition, the HA shell, which had favorable biocompatibility and pH response characteristics, could be used to control release of loaded DOX from the litchi-like superparamagnetic microspheres in a simulated acidic tumor cell environment, effectively killing tumor cells and reducing toxic side effects to normal cells. The smart design presented in this study, which incorporates a tunable superparamagnetic shell and a controlled architecture, allows the sensitive release of drugs for efficient antitumor activity.
|
|
|
Sodium Magnesium Fluoride Particles of Different Morphologies: Prepared by EDTA-assisted Hydrothermal Method
XU Yun-Qing,WANG Hai-Zeng
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 933–937
 Abstract
Abstract(
1091 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(1809KB)(
787
)
Different morphologies of sodium magnesium fluoride particles were prepared by EDTA-assisted hydrothermal method using sodium fluoride, magnesium chloride hexahydrate as main materials and EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt) as auxiliary agent. Influence of solution pH, reaction temperature, time and complexing agent on the morphology and phase of the products was investigated, and the formation mechanism was discussed. Samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The results show that the EDTA not only provides sodium ions as raw material, but also forms complex with magnesium ions as a complexing agent in the reaction system. Reaction temperature, pH and complexing agent have great influences on the morphologies and phase of the products. The obtained products have microcube crystals with a smooth surface and micron-sized hollow spheres polymerized with nanoparticles. And the products have high crystallinity with crystal dimension ranging from 1 μm to 3 μm.
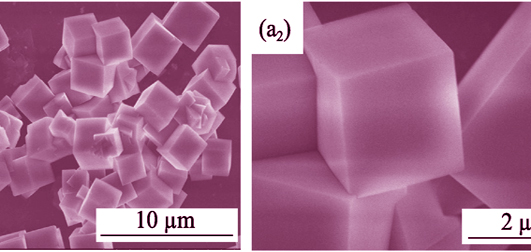
|
|
|
Influence of Al-modification on CMAS Corrosion Resistance of PS-PVD 7YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings
FAN Jia-Feng,ZHANG Xiao-Feng,ZHOU Ke-Song,LIU Min,DENG Chang-Guang,DENG Chun-Ming,NIU Shao-Peng,DENG Zi-Qian
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 938–946
 Abstract
Abstract(
672 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(5659KB)(
1001
)
7YSZ thermal barrier coatings with feather-like columnar structure were prepared by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD), and were carried out with Al-modification. After that, the as-sprayed and Al-modified 7YSZ TBCs were conducted with thermal cycling, heated at 1050 ℃ for 5 min and air-cooling for 5 min, respectively. And the CMAS corrosion tests were carried out at 1200 ℃. Microstructure, element and phase composition of the coating were analyzed by SEM, EDS and XRD. Corrosion mechanism of CMAS and the corrosion resistance mechanism of Al-modified coating were investigated. The results showed that the Al-modified coatings kept good thermal stability. And the coating had no apparent spallation, after 5200 thermal cycles. The as-sprayed coating was destroyed by CMAS, and "wave" deformation was observed. The 7YSZ coating was completely permeated by CMAS. Dense corrosion-resistant layer of α-Al2O3 was formed on the surface of the coating by Al-modification, and the corrosion of the coating was significantly improved. It was found that α-Al2O3 layer not only protected the coating by separating CMAS, but also had positive effect on the thermochemical reaction in CMAS corrosion. Due to formation of α-Al2O3 layer, the oxides of CaO, Al2O3 and SiO2 were hard to penetrate the coating. However, the penetration of MgO was not significantly affected by Al-modification. In addition, a mathematical model based on Fick's second law was established to evaluate the effect of Al-modification on the CMAS corrosion resistance of 7YSZ coatings.
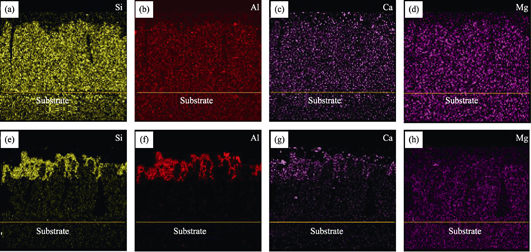
|
|
|
Simulation and Experimental Verification of Thermal Property for Aluminum Nitrides and Copper Clad Laminates under Space Thermal Environment
HE Duan-Peng,GAO Hong,ZHANG Jing-Jing,WU Jie,LIU Bo-Tian,WANG Xiang-Ke
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 947–952
 Abstract
Abstract(
760 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(2762KB)(
1199
)
Aluminum nitrides (AlN), which possess high thermal conductivity, high electrical resistivity, good dimensional stability and excellent mechanical property, have been considered the preferred materials as a new generation of high-performance ceramic substrate and packaging materials. In this paper, the application potential of ceramics in space electronic systems is discussed. And the basic capabilities of AlN were analyzed. Heat transfer property of AlN and its copper clad laminate were of selective and theoretical analysis, which were further verified by simulation. Finally, the thermal conductive performance of AlN in the simulated space thermal cycle environment was discussed. The results show that the thermal conductivity is up to 174.1 W·m -1·K -1 and the thermal diffusivity of copper clad laminates is higher than that of pure aluminum nitrides. The simulation results of thermal characteristics are in agreement with the theoretical calculation. The final space environment simulation tests indicate that the thermal conductive capabilities of aluminum nitrides remain extremely stable.
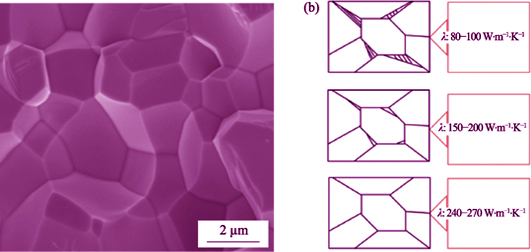
|
|
|
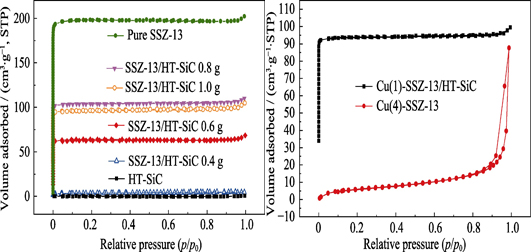
Cu-SSZ-13/SiC-waste Composite: Synthesis and Application for NH3-SCR
LUO Qing,YUAN Qing,JIANG Qian-Qin,YU Nai-Sen
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 953–960
 Abstract
Abstract(
612 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(1469KB)(
1083
)
Solar cell wafer cutting process produces a lot of silicon carbide-based waste named HT-SiC. Herein, we developed a novel catalyst through a one-pot hydrothermal process combined with an ion-exchange method to synthesize Cu-SSZ-13/HT-SiC composite and applied in denitration catalytic reaction. TMAdaOH and Cu-TEPA were used as templates to prepare the precursor for Cu-SSZ-13, respectively. Results showed that, with participation of HT-SiC, SSZ-13 crystal was successfully obtained by using TMAdaOH template, while it would get only amorphous structure by using Cu-TEPA template. NH3-SCR(Selective Catalytic Reduction, SCR) exhibited catalytic activity and stability of Cu-SSZ-13/HT-SiC in medium and high temperature zones was more effective than those of Cu-SSZ-13 without HT-SiC, and NO consumption by the former was about 11-fold of the latter at 500 ℃. Moreover, compared with Cu-SSZ-13/α-SiC catalyst prepared with pure SiC (α-SiC), Cu-SSZ-13/HT-SiC shows better catalytic activity in the whole temperature range. These favorable performances are attributed not only to the good thermal conductivity and thermal stability of SiC, but also to the 7.34wt% Fe component contained in HT-SiC, which acts as an active site for reducing NO in NH3-SCR. This method not only provides a way to reuse the SiC waste, but also enhances denitrification activity of Cu-SSZ-13 in medium and high operating temperature.
|
|
|
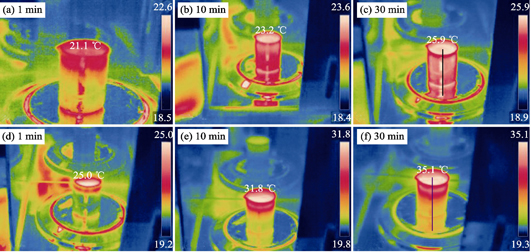
Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties of Titanium Dioxide (B)/Glass Fiber Cloth
ZHU Ben-Bi,ZHANG Wang,ZHANG Zhi-Jian,ZHANG Jian-Zhong,IMRAN Zada,ZHANG Di
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 961–966
 Abstract
Abstract(
595 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(2305KB)(
929
)
Titanium dioxide (B)/glass fiber cloth (B-T/GFC) composites with photothermal enhanced photocatalytic properties were prepared by using a facile chemical synthesis and Sol-Gel method, using the glass fiber cloth and TiH2 as substrate and precursor, respectively. XRD, SEM and TEM were employed to investigate the composition, structure and morphology of B-T/GFC composite. Different properties of the materials were studied by spectrophotometer, optical contact angle measuring instrument and solar simulator. The results show that the composite surface is composed of anatase black TiO2 with a disordercoating of about 1 nm. Meanwhile, the B-T/GFC composite with high hydrophobicity has strong absorption ability in the wavelength range from 250 nm to 2000 nm. Compared with glass fiber cloth, the B-T/GFC composite reveals better photothermal ability under sunlight with one solar intensity (1 kW/m 2). The photocatalytic degradation ability of B-T/GFC composite in organic pollutants cutting waste solution is better than those of pure black TiO2 (B-T) and P25. After irradiation for 2 h, the degradation of COD over B-T/GFC composite is about 1.3 times higher than that of P25. The B-T/GFC composite possessing excellent photothermal enhanced photocatalytic properties performance may lead to a range of novel applications.
|
|
|
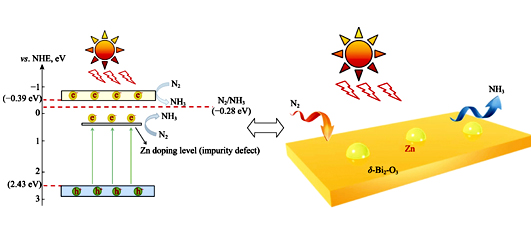
Zn doping 2D Layered δ-Bi2O3 Nanosheets for Photocatalytic Nitrogen Fixation
GAO Xiao-Ming,SHANG Yan-Yan,LIU Li-Bo,NIE Wei
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 967–973
 Abstract
Abstract(
712 )
 HTML
HTML(
21)
 PDF
PDF(9371KB)(
967
)
Surface traps are formed by doping element into catalyst, which effectively inhibits the recombination of photogenerated carriers and achieves excellent photocatalytic nitrogen fixation performance consequently. Two-dimensional Zn-δ-Bi2O3 nanosheets were prepared via solvothermal method using Bi(NO3)3·5H2O and Zn(CH3COO)2 as raw materials. The morphology, element composition and light-harvesting capability were characterized by XRD, SEM, EDS, XPS, TEM, and UV-Vis DRS. The results show that Zn doping attributs to interstitial deposition, and Zn-δ-Bi2O3 microspheres are assembled from 2D nanosheets. The ability of photocatalytic nitrogen fixation over photocatalyst was explored under room temperature and atmospheric pressure with visible light irradiation. The results show that the ammonia production over 4wt% Zn-δ-Bi2O3 could reach 301.6 μmol·L -1 after 3 h irradiation. The mechanism of photocatalytic ammonia synthesis was investigated by means of fluorescence, photocurrent and impedance spectra. Zn doping not only broadens the utilization range of visible light-harvesting, but also inhibits the recombination of photogenerated electron-hole pairs, and thus improves the performance of photocatalytic nitrogen fixation.
|
|
|
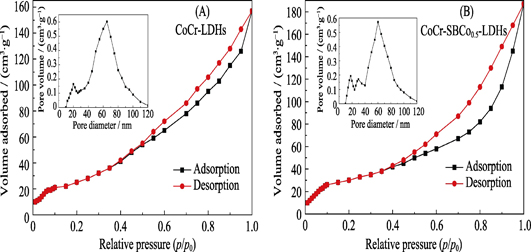
Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue by Schiff-base Cobalt Modified CoCr Layered Double Hydroxides
ZHANG Xiao-Feng,ZHANG Guan-Hua,MENG Yue,XUE Ji-Long,XIA Sheng-Jie,NI Zhe-Ming
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 974–982
 Abstract
Abstract(
743 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(3090KB)(
1010
)
A series new material of cobalt (Ⅱ) with Schiff-base intercalated cobalt-chromium layered double hydroxides (CoCr/SBCo-LDHs) were successfully prepared via coprecipitation. Their structure and property of the CoCr-LDHs and CoCr/SBCo-LDHs materials were thoroughly characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), UV-Vis DRS, scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electrons microscope (TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope (EDX), X-ray photoelectron spectroscope, and specific surface area analyzer. Using H2O2 as photocatalytic additive, the effects of different intercalation amount, catalyst dosage and initial concentration of methylene blue (MB) solution on photocatalytic activity were investigated, and the kinetics and main active groups of photocatalytic degradation process were explored. Experimental results show that H2O2 can improve the photocatalytic performance of hydrotalcite materials. Under the condition of the Xenon lamp simulated sunlight and MB initial concentration of 25 mg/L, the photocatalytic degradation rate of MB by 20 mg CoCr/SBCo0.5-LDHs and H2O2 was 99%. The photodegradation process of MB conforms to the quasi-first-order kinetic model, and the active groups playing major role are h + and ·OH.
|
|
|
Near-infrared Afterglow Enhancement and Trap Distribution Analysis of Silicon-chromium Co-doped Persistent Luminescence Materials Zn1+xGa2-2xSixO4:Cr3+
WANG Kai, YAN Li-Ping, SHAO Kang, ZHANG Cong, PAN Zai-Fa
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 983–990
 Abstract
Abstract(
784 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(1403KB)(
1158
)
Co-doping of silicon in zinc gallate spinel persistent luminescent phosphor was adopted to enhance the afterglow properties. Firstly, a series of silicon-chromium co-doping zinc gallate spinel samples were prepared by high temperature solid state reaction method. Phosphor with chemical formula of Zn1+xGa2-2xSixO4:Cr 3+ (x = 0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.5, 1) was obtained with the raw materials of ZnO, Ga2O3, SiO2, and Cr2O3. The experimental results show that the introduction of suitable concentration of silicon improves the afterglow performance effectively. The strongest afterglow intensity was obtained for sample with x = 0.2, which is 3 times higher than ZnGa2O4:Cr 3+, and the afterglow duration is up to 24 h. Through further trap distribution analysis, it is shown that the introduction of silicon in the ZnGa2O4 host can regulate the distribution of trap depths. Particularly, besides the antisite defects, the co-doping of silicon can induce the formation of aliovalent substitution defects and interstitial defects, as well as tune the band gap value, thereby achieving the purpose of improving the afterglow performance.
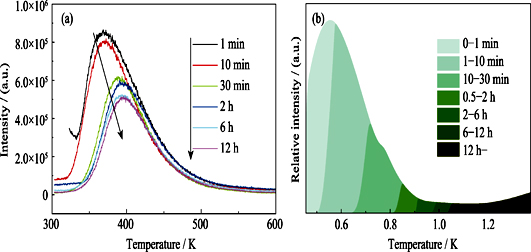
|
|
|
Preparation and Photodetection Property of ZnO Nanorods/ZnCo2O4 Nanoplates Heterojunction
ZHANG Zhi-Ming,FANG Xiao-Sheng
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 991–996
 Abstract
Abstract(
942 )
 HTML
HTML(
33)
 PDF
PDF(8115KB)(
962
)
Heterojunction-type nanostructures based on ZnO nanomaterials are one of the important candidates for constructing high-performance ultraviolet (UV) photodetectors. In this work, a novel ZnO nanorods/ZnCo2O4 nanoplates heterojunction was designed and prepared, and the electrical properties and photodetection properties of the as-prepared heterojunction were investigated. ZnCo2O4 nanoplates were constructed into uniform thin film on ITO glass substrate using oil/water interface self-assembly. Next, ZnO nanorod arrays with uniform orientation and proper density were grown on ZnCo2O4 nanoplates thin film using hydrothermal method with the help from ZnO seed layer. As a result, high-quality ZnO nanorods/ZnCo2O4 nanoplates heterojunction was achieved. This heterojunction has a high rectification ratio of 673.7. Under reverse bias, this heterojunction has a light-dark current ration of more than two orders of magnitude. The UV-visible rejection ratio of this heterojunction is 29.4, which indicates its selective detection of UV light. These results effectively prove the potential of this ZnO nanorods/ZnCo2O4 nanoplates heterojunction in constructing high-performance UV photodetectors.
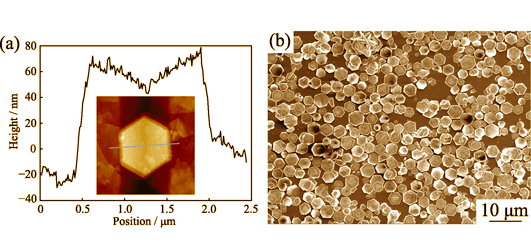
|
|
|
Influence of Ce 3+ Substitution on the Structure and Electrical Characteristics of Bismuth-layer Na0.5Bi8.5Ti7O27 Ceramics
HU Hao, JIANG Xiang-Ping, CHEN Chao, NIE Xin, HUANG Xiao-Kun, SU Chun-Yang
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 997–1003
 Abstract
Abstract(
849 )
 HTML
HTML(
35)
 PDF
PDF(4080KB)(
910
)
The structure and electrical properties of Ce 3+-doped intergrowth bismuth layer-structured piezoelectric ceramics Na0.5Bi8.5-xCexTi7O27 (NBT-BIT-xCe, 0≤x≤0.1) prepared by conventional solid-state reaction process were systematically studied. In this study, all the ceramic samples were found to possess a single bismuth layer structure, and with the increase of x content, there is an increasing trend towards the lattice distortion of the sample, while the average grain size decreased. As demonstrated by dielectric spectrum and DSC method, two dielectric anomalies of the samples occur, which corresponds to ferroelectric phase transitions of the ceramics. And Ce 3+doping significantly reduces concentration of oxygen vacancy and dielectric loss in materials, improving piezoelectric constant (d33) of ceramic samples. The resultant ceramics with x=0.06 reached the optimal performance, possessing a d33 up to 27.5 pC/N with the Curie temperature of 658.2 ℃ and tanδ=0.39%.
|
|
|
Phototransistor Based on Single TaON Nanobelt and Its Photoresponse from Ultraviolet to Near-infrared
TAO You-Rong,CHEN Jin-Qiang,WU Xing-Cai
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 1004–1010
 Abstract
Abstract(
496 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(14855KB)(
937
)
TaON nanobelts (NBs) were controllably synthesized by Ta2O5 NBs template-conversion method. The typical NBs have cross-sections of 40 nm×200 nm-400 nm×5600 nm, and lengths up to about 0.5 cm. A field effect transistor (FET) based on single TaON NB was fabricated on SiO2/Si substrate. The electronic mobility and on-off ratio of the nanobelts are 9.53×10 -4cm 2/(V·s) and 3.4, respectively. The FET shows good photoresponses from 254 nm to 850 nm. Under irradiation of 405 nm light (42 mW/cm 2), the responsivity is 249 mA/W at a bias of 5.0 V, and the photoswitch current ratio is 11. Therefore, the phototransistor shows a good photodetectivity, and TaON NBs may become good candidates for fabricating optoelectronic devices. Additionally, Ta2O5@TaON composite NBs were also synthesized, and a FET based on the single NB was fabricated. Under irradiation of the same light, its photoresponse is weaker than TaON NB, but it is still a good optoelectronic material.
|
|
|
Electrocaloric Effect in Pb0.3CaxSr0.7-xTiO3 Ceramics Near Room Temperature
HAN Liu-Yang, GUO Shao-Bo, YAN Shi-Guang, RÉMIENS Denis, WANG Gen-Shui, DONG Xian-Lin
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 1011–1014
 Abstract
Abstract(
817 )
 HTML
HTML(
23)
 PDF
PDF(434KB)(
862
)
The electrocaloric (EC) effect is strongly related to interaction of polarization and temperature changes, showing great potential in high-efficient solid state refrigeration. This work focuses on the Pb0.3CaxSr0.7-xTiO3 (PCST(x), x = 0.00, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15) ceramics in which the influence of Ca content on dielectric and ferroelectric property under electric field was studied, and the EC temperature change was calculated through indirect method. Substitution of Ca largely modifies the diffused phase transition behaviors of PCST ceramics, which the diffusion exponent of PCST(0.05) increases with electric field up, indicating a promising wide temperature range of large electrocaloric effect. Thus, the largest adiabatic temperature change (1.71 K) is obtained near the room temperature in PCST(0.05) by indirect method. With an electric field of 8 kV/mm, PCST(0.05) ceramic shows good EC effect in a wide temperature range that the adiabatic temperature change is larger than 1 K from 5 ℃ to 70 ℃.
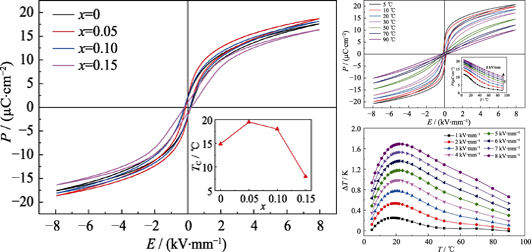
|
|
|
Preparation and Mechanical Property of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Silicon Carbide Matrix Composites
MENG Xiang-Wei,WU Xi-Shi,PEI Bing-Bing,ZHU Yun-Zhou,HUANG Zheng-Ren
2019 Vol. 34 (9): 1015–1020
 Abstract
Abstract(
877 )
 HTML
HTML(
27)
 PDF
PDF(2110KB)(
898
)
In this study, high-strength silicon carbide (SiC) matrix composites reinforced by short carbon fiber (Csf) (SiC/Csf) were fabricated by slip casting and reaction sintering. The effects of the dispersant (tetramethylammonium hydroxide, TMAH) content and mixing time on the viscosity of the slurry were investigated. In addition, the influences of the volume fraction of Csf and particle size of SiC powder on the mechanical property were also studied. It is found that the viscosity of slurry with 0.1wt% TMAH is the lowest and the mixing time is preferably controlled at 6 h. The composites with 35vol% Csf shows the highest flexural strength of (412±47) MPa. The composites with 5 μm SiC powder achieves the highest flexural strength of (387±40) MPa. Grain composition demonstrates that the sample prepared by a mixture of 5 and 50 μm SiC powder at a ratio of 2 to 1 shows relatively excellent mechanical properties with the flexural strength up to (357±41) MPa.
|
|