|
|
Surface Protection of Polymer Materials from Atomic Oxygen: a Review
LI Hao-Geng,GU Hong-Yu,ZHANG Yu-Zhi,SONG Li-Xin,WU Ling-Nan,QI Zhen-Yi,ZHANG Tao
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 685–693
 Abstract
Abstract(
902 )
 HTML
HTML(
37)
 PDF
PDF(1954KB)(
1195
)
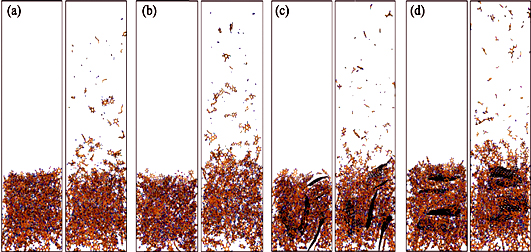
Polymers, as substrate of composite material on the surface of spacecraft, have such advantages as light mass and high strength. Atomic oxygen (AO) is one of the highest content particles of low earth orbit, and high-energy high-flux AO bombardment causes the polymers’ surface erosion and mass loss at different degree, resulting in polymers degradation. Thus, AO is one of major threats in space environment that reduces reliability of space devices and shortens their working life span. This review summarized current global protection technologies from AO in recent years. Among them, surface chemical modification method with advantages of body-modification and protection coating, providing organic/inorganic composite with modified layer through comprehensive protection performance. This review discussed the method to explore the AO protection reaction mechanism by computational simulation. Computational simulation combined with experiments may reveal nature of the protection, facilitate future researches on AO protection, and provide guidance for fabrication surface polymer materials used in domestic parts of the aerospace craft, especially the large-scale flexible space solar cell array
|
|
|
Recent Advancements in Interface between Cathode and Garnet Solid Electrolyte for All Solid State Li-ion Batteries
LI Dong, LEI Chao, LAI Hua, LIU Xiao-Lin, YAO Wen-Li, LIANG Tong-Xiang, ZHONG Sheng-Wen
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 694–702
 Abstract
Abstract(
1650 )
 HTML
HTML(
97)
 PDF
PDF(4432KB)(
2240
)
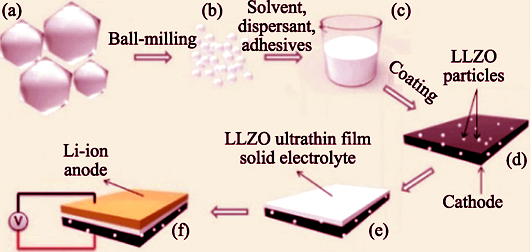
All-solid-state lithium battery (ASSLB) with inorganic solid state electrolytes is one of promising candidates for electric vehicles and large-scale smart grids for storage of alternative energy resources due to their benefits in safety, energy density, operable temperature range, and longer cycle life. As the key component in ASSLB, inorganic lithium-ion-based solid-state electrolytes (SSEs), especially the garnet-type solid electrolytes that own ionic conductivities in the order of 10 -3 S·cm -1 at room temperature and are relative safe vs. Li metal, have obvious advantages in ASSLB. However, interfacial instability and their poor solid-solid contact between garnet and cathode result in high interfacial resistance, low efficiency, and poor cycle performance. Based on these understandings and analyses of interface characteristics and issues, this work presents a brief review on modification of interface, covering composite cathode, composite electrolyte, interface engineering, and interface layer.Some approaches of improving interface wettability and future research directions of ASSLB are given as well, which endeavor to realize the practical applications of ASSLB.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Mn Doped Ni(OH)2
XIAO Min,XING Ru-Yue,YAO Shou-Guang,CHENG Jie,SHEN Ya-Ju,YANG Yu-Sheng
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 703–708
 Abstract
Abstract(
778 )
 HTML
HTML(
21)
 PDF
PDF(1116KB)(
858
)
Manganese doped Ni1-xMnx(OH)2 (x=0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) was prepared by buffer solution method. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements show that the samples are mainly composed of β-Ni(OH)2 with little amount of Mn3O4 phase. Cyclic voltammetry results show that the integral area of reduction peak of Ni0.8Mn0.2(OH)2 is the largest among the samples. The constant current charge-discharge tests show that the discharge capacity of Ni0.8Mn0.2(OH)2 reaches 271.8 mAh/g at the current density of 100 mA/g, which is higher than that of other samples and commercial β-Ni(OH)2 (253.6 mAh/g). At the current density of 300 and 500 mA/g, Ni0.8Mn0.2(OH)2 remains the highest discharge capacity of 294.7 and 291.5 mAh/g, respectively. Moreover, the cycling stability of Ni1-xMnx(OH)2 is superior to commercial β-Ni(OH)2. All data indicate that Mn doped Ni(OH)2 can improve the capacity and cycling stability of nickel electrodes, and greatly reduce the cost of nickel electrodes.
|
|
|
Electrospun FeMnO3 Nanofibrous Mats: Preparation and Electrochemical Property
SUN Xiao-Lu,SONG Xiao-Fei,LIU Yan-Hua,WU Yue,CAI Yi-Bing,ZHAO Hong-Mei
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 709–714
 Abstract
Abstract(
641 )
 HTML
HTML(
21)
 PDF
PDF(790KB)(
1032
)
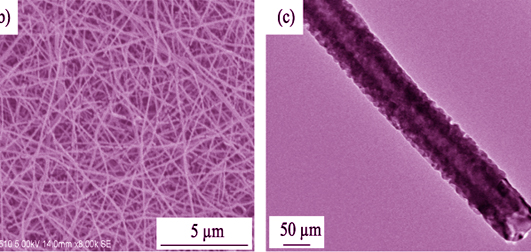
A uniform and stable precursor spinning solution was prepared by using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), ferric nitrate nonahydrate and manganese acetate tetrahydrate as raw materials, anhydrous ethanol and N,N-dimethylformamide as solvent, followed by magnetically stirred. The PVP/Mn(COOH)2/Fe(NO3)3 composite nanofibers were prepared by electrospinning technology. FeMnO3 nanofibrous mats were obtained after high temperature calcination, which was used as anode material for lithium battery. Apparent morphology and crystal structure of the samples were investigated by FT-IR, XRD, SEM, and BET specific surface area analyzers. All results showed that the fabricated FeMnO3 nanofibrous mats possessed good structural morphology with the specific surface area of 9.9 m 2/g. TG analysis showed that when temperature reaches 470 ℃, the TG curve becomes gentle while the mass loss is not obvious. Results form charge and discharge, cyclic voltammetry, and cycle performance tests, indicated that FeMnO3 nanofibrous mats had good electrochemical performance and electrical stability, with a specific capacity of 533 mAh/g at 50 mA/g after 37 cycles. After 50 cycles, the impedance is approximately 170 Ω, which remains essentially unchanged.
|
|
|
Dynamic Breakdown of ZnO Varistor Ceramics under Pulsed Electric Field
ZHU Zhi-Xiang,ZHANG Qiang,ZHU Si-Yu,LU Cheng-Jia,LIU Yi,YANG Jia,WU Chao-Feng,CAO Lin-Hong,WANG Ke,GAO Zhi-Peng,ZHU Cheng-Zhi
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 715–720
 Abstract
Abstract(
579 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1017KB)(
819
)
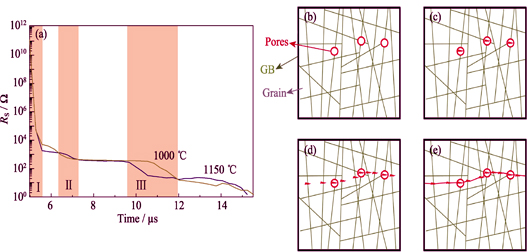
Electrical breakdown process of ceramics is a complex process related to electrical, thermal, and light effects. It has attracted lots of attentions. But the mechanism of dielectric breakdown is still under debate, especially for the solid ceramics. In this study, the ceramics with different grain size were sintered at different temperatures. A square pulsed voltage of 27 kV with the pulse width of 7 ms was generated to breakdown the ZnO ceramics with a thickness of 2 mm. Electric breakdown process of these ceramics were investigated using a homemade high-time- resolution electric detection system with the resolution < 1 ns. Compared the electric behaviors of ZnO ceramics with different grain sizes during the breakdown process, it is clear that the whole electric breakdown process could be divided into three main steps, all of which can completed within 7 ms. The first breakdown step is the pores breakdown due to the electric field concentration, and the second step is the grain boundaries breakdown, and then the bulk grain is broken-down leading to form the whole electrical breakdown channel. The data shows that the breakdown process of the grains has the longest duration, the grain boundary is the second, and the pores breakdown is the shortest. For the ceramics with different grain sizes, the breakdown durations of the grain boundaries are different. The duration and electrical breakdown speed of the three step processes are directly affected by the resistance uniformity and carrier concentration of the materials.
|
|
|
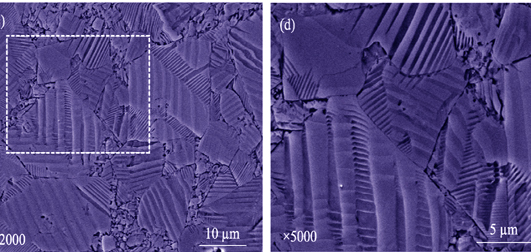
Influences of Sintering Methods on Microstructure and Physical Property of (K,Na,Li)(Nb,Sb,Ta)O3 Piezoelectric Ceramics
ZHANG Xiao-Chen, WANG Xue-Mei, WANG Chun-Lei
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 721–726
 Abstract
Abstract(
677 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(3977KB)(
927
)
(K,Na)NbO3-based ceramics (KNLNST ceramics) are a very promising type of lead-free piezoelectric materials. However, only limited studies were reported on them prepared by two-step sintering. Here, a comparison study was performed between two kinds of (K0.4425Na0.52Li0.0375)(Nb0.8825Sb0.08Ta0.0375)O3 ceramics that were prepared by either conventional sintering (CS) or two-step sintering (TSS). It was found that TSS largely increases the relative density ρ° and piezoelectric coefficient d33 from 95.0% and 363 pC/N of CS to 97.0% and 387 pC/N, respectively. KNLNST ceramics prepared by two kinds of sintering methods show significant differences between microstructure and domain structure. The KNLNST-CS ceramic has small grain sizes but distributed uniformly, and their domain patterns in most grains are simply a group or groups of parallel stripes. In contrast, the KNLNST-CS ceramic has a non-uniform grain-size distribution, with many large grains displaying broad bands, and existing fine strips.
|
|
|
Preparation and Luminescence Property of Eu 3+ Doped Porous Lanthanum Zirconate Powder
YANG Jin-Ping, JI Wen-Ling, ZHANG Hao, LIU Pan, CUI Yi, WEI Heng-Yong
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 727–733
 Abstract
Abstract(
675 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(9665KB)(
804
)
Pyrochlore type of lanthanum zirconate powder was prepared by Sol-Gel method using LaCl3 and ZrClO2·8H2O as raw materials, ethanol and deionized water as solvents, and the template P123 was introduced to control the pore structure in the powder. XRD, SEM and BET were used to determine the powder structure and morphology, and the luminescence property of Eu 3+ doped lanthanum zirconium samples were measured by fluorescence spectra. The results show that the introduction of template P123 is helpful to increase the number of large pores. When 6.56 g·mL -1 of P123 was used in the solution, there are lots of pores in the lanthanum zirconate particles, which have an average size of 43 nm and average capacity of 0.15 cm 3·g -1. The luminescence property of Eu 3+ doped lanthanum zirconium samples were significantly enhanced, and the quenching concentration increased from 9mol% to 11mol%.
|
|
|
Improvement on Size Uniformity of SiO2 Nanospheres Applied in Si Optical Resonance Nanopillar-arrays
PENG Xin-Cun, WANG Zhi-Dong, ZENG Meng-Si, LIU Yun, ZOU Ji-Jun, ZHU Zhi-Fu, DENG Wen-Juan
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 734–740
 Abstract
Abstract(
644 )
 HTML
HTML(
21)
 PDF
PDF(9609KB)(
966
)
Recently, optical resonances of nanostructured semiconductor were proved highly effective for light management in many optoelectronic devices. In this work, the monodispersed silica nanospheres with particle sizes of 270-330 nm were synthesized by modified two-step Stober method, and the nanosphere size uniformity was improved by optimizing the synthesis conditions. Then, the as-prepared nanospheres were self-assembled into monolayer as etching mask on the silicon substrate by means of constant temperature heating and evaporation. Finally, Si nanopillar-arrays were fabricated by inductively coupled plasma etching. The light reflectance spectra show that the fabricated Si nanopillar-arrays with diameters of 300-325 nm can excite the quadrupole Mie resonance, and the reflectance of lower than 5% was obtained in visible wavelengths, which show excellent light management performances and can further match the requirements of actual optoelectronic devices.
|
|
|
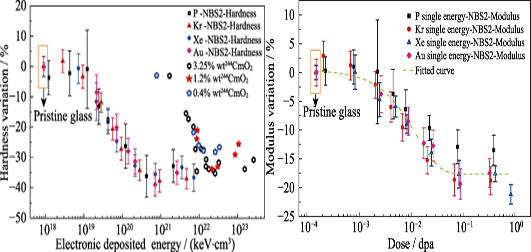
Mechanical Properties of Borosilicate Glass with Different Irradiation of Heavy Ions
ZHANG Xiao-Yang, PENG Hai-Bo, LIU Feng-Fei, ZHAO Yan, SUN Meng-Li, GUAN Ming, ZHANG Bing-Tao, DU Xin, YUAN Wei, WANG Tie-Shan
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 741–747
 Abstract
Abstract(
547 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(805KB)(
870
)
To understand the evolutions in mechanical properties of borosilicate glass under irradiation is significant for evaluating its performance after long-term interaction with irradiation environment. In this study, borosilicate glass samples were irradiated with 0.3 MeV P-ions, 4 MeV Kr-ions, 5 MeV Xe-ions and 8 MeV Au-ions, respectively. Modification of the samples’ mechanical properties before and after radiation was investigated with nano-indentation measurement. With increase of irradiation dose, both hardness and modulus of samples irradiated with P, Kr, Xe and Au ions drop and then saturate at 0.1 dpa. The trends of hardness variations for the sample irradiated with four kinds of ions at different energies are similar, and the change of modulus also follows the same rule. The maximum variation of NBS2 sample’ hardness and modulus are about 35% and 18%, respectively. The grazing incident X-ray diffraction (GIXRD) was employed to analyze the phase structure. The results indicate that borosilicate glass still remains amorphous after irradiation. The microstructure evolutions of irradiated borosilicate glasses were characterized by Raman spectroscopy. The decrease of network polymerization and the increase of structural disorder are suggested by Raman spectra. In addition, the results also suggest that the main factor for the evolutions of the hardness and modulus of the borosilicate glass under ion irradiation is the change of the deformation of glass network, which was caused by nuclear energy deposition in samples.
|
|
|
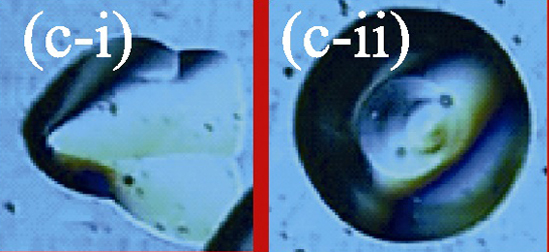
Correlation between Stacking Faults in Epitaxial Layers of 4H-SiC and Defects in 4H-SiC Substrate
GUO Yu, PENG Tong-Hua, LIU Chun-Jun, YANG Zhan-Wei, CAI Zhen-Li
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 748–754
 Abstract
Abstract(
1489 )
 HTML
HTML(
68)
 PDF
PDF(20268KB)(
1624
)
The morphology and causes of stacking faults (SF) in homoepitaxial layers of 4H-SiC were studied. According to characteristics of PL images and morphology images of 4H-SiC five kinds of SFs have been defined. In the PL images, the morphologies of SF I and SF II-V are trapezoidal and triangular, respectively. SF II lays inside the area of SF I. In the morphology images, SF I and IV are not seen, SF II-III are carrot shaped and SF V is triangular respectively. The results show that SF I is a kind of base plane SF which originates from the base plane dislocation (BPD) lines of the substrate, parallel to <1$\bar{1}$00> direction and moving along <11$\bar{2}$0> direction during epitaxial growing. SF II and most of SF III-IV originate from BPDs in substrate. One BPD converts into threading dislocation during epitaxial growing and propagates to the surface along <0001> direction, while other BPDs or partial dislocations originating from threading dislocation propagate in (0001) plane to form triangular base plane SFs. The rest of SF III-IV and SF V originate from TED or other defects in substrate. SF II-III display carrots morphology because a prism SF plane perpendicular to the (0001) plane is formed to intersect with surface during epitaxial growing process. SF IV is not seen in the morphology image because no prism SF plane is formed to intersect with surface. All results demonstrated that reducing BPDs of the substrate is especially important for reducing SFs in the epitaxial layers.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Metastable Vaterite Phase of CaCO3 via Ethanol-calcium Method and Ethanol-water Binary Solvent Method
CHEN Chuan-Jie, WEI Li-Geng, WU Yue, HU Cheng-Pei, HU Yuan-Cong, JIANG Jiu-Xin
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 755–760
 Abstract
Abstract(
588 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(1030KB)(
733
)
Ethanol-calcium method was proposed, and the metastable vaterite phase of CaCO3 was synthesized by this method, i.e. the complex compound between CaCl2 and ethanol reacted with Na2CO3 aqueous solution. Effects of aging time and reaction temperature on the polymorphs and morphologies of CaCO3 were investigated, and the comparative study on the synthesis of CaCO3 via ethanol-water binary solvent (EWBS) method at the same conditions was carried out. XRD results indicate that the fraction of vaterite in the product decreases with the aging time prolonging and reaction temperature increasing in both systems. However, the fraction of vaterite in the product prepared by ethanol-calcium method is much higher than that in the product prepared by EWBS method, and the stability of vaterite prepared by ethanol-calcium method is also much better. SEM observation shows that the morphologies of vaterite and calcite are their typical sphere and rhombohedra, respectively.
|
|
|
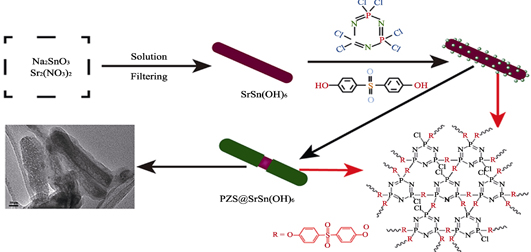
Strontium Hydroxystannate Nanorods Encapsulated by Hybrid Polyphosphazene: Synthesis and Flame Retardancy on Epoxy Resin
ZHANG Chong, GENG Xiao-Wei, GAO Xiang-Di, ZHANG Xin, GUO Rao, WANG Yu-Jing, XU Jian-Zhong, MA Hai-Yun
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 761–767
 Abstract
Abstract(
593 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(3007KB)(
1068
)
To develop a novel hybrid organic-inorganic flame retardant and smoke suppressant, strontium hydroxystannate (SrSn(OH)6) nanorods were synthesized via a co-precipitation method, and then the SrSn(OH)6 were encapsulated by cyclomatrixpolyphosphazene (PZS) to prepare a novel core-shell organic-inorganic hybrid nano-flame retardant (PZS@SrSn(OH)6). The micromorphology and chemical structure were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The thermal degradation of PZS@SrSn(OH)6 and EP/PZS@SrSn(OH)6 composites was investigated by thermogravimetry analysis (TGA). The flame retardancy properties were studied by limited oxygen index (LOI) and CONE calorimetry tests. The flame retardant mechanism was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), SEM, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and FT-IR. The results showed that PZS@SrSn(OH)6 exhibited high flame retardant and smoke suppression efficiency. Significant synergy between PZS and SrSn(OH)6 was found to enhance the flame retardancy of EP compared with pure EP, the LOI value was increased from 26.2% to 29.6% with 3wt% addition of PZS@SrSn(OH)6. CONE calorimetry tests indicated that 3% incorporation of PZS@SrSn(OH)6 brought about 29% and 37% maximum reduction in peak heat release rate and peak smoke production rate, and 242% improvement of char residue, respectively. A dense char structure is formed after combustion under elevated temperature for PZS@SrSn(OH)6, and the char layer blocks the exchange between the decomposed fragments and oxygen, then protect EP matrix and improve the flame retardancy.
|
|
|
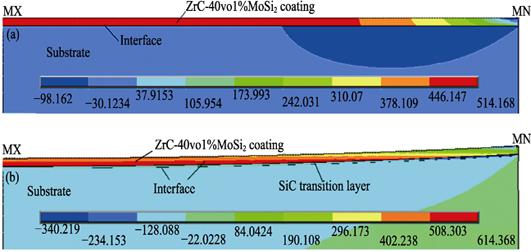
Residual Stresses of Plasma Sprayed ZrC-Based Coatings during Path-by-path and Layer-by-layer Deposition: Simulation and Experimental Verification
XIE Ling-Ling, NIU Ya-Ran, WANG Liang, CHEN Wen-Liang, ZHENG Xue-Bin, HUANG Zhen-Yi
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 768–774
 Abstract
Abstract(
531 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(3742KB)(
788
)
Commercial ANSYS14.5 software was used to simulate the residual stress characteristics in the deposition process of plasma sprayed ZrC-based coatings on the surface of C/C composite substrates. The simulation combined the mechanical model of composite beam adding laminate layer, and the finite element model of accumulation of path-by-path and layer-by-layer. Effects of SiC transition layer, second phase (SiC, MoSi2) and coating thickness on residual stresses of the ZrC-based coatings were analyzed and validated by experiments. All results show that the SiC transition layer effectively relieve thermal mismatch stress between the coating and the substrate. Stress of the coating decreases gradually with the increase of coating thickness, which conforms to the stress relaxation and superposition law. There exist tensile stress in the coating, and compressive stress in the substrate. Moreover, compressive stress concentration is found at the interface edge, which is easly induced cracks formation and propagation along the interface. Therefor, our simulation method in present study could simulate actual spray process and predict residual stress of the coatings accurately.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Theoretical Study of Conductive Mo1.33CT2 MXene
LIU Guo-Quan, JIANG Xiao-Juan, ZHOU Jie, LI You-Bing, BAI Xiao-Jing, CHEN Ke, HUANG Qing, DU Shi-Yu
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 775–780
 Abstract
Abstract(
881 )
 HTML
HTML(
35)
 PDF
PDF(2237KB)(
1195
)
In this work, Mo, Y, Al, and C were used as raw materials to synthesize a novel (Mo2/3Y1/3)2AlC MAX phase by spark plasma sintering (SPS) at 1550 ℃, and the corresponding accordion-like MXene was successfully obtained with a milder chemical etching method. The chemical composition and microstructure of the materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and energy dispersive spectrometer (DES). The final product was Mo1.33CT2 MXene with functional groups on the surface. At the same time, the electronic structure and electronic properties of the novel (Mo2/3Y1/3)2AlC MAX phase and the corresponding Mo1.33CT2 MXene were studied by the first-principles density functional theory. The calculated results show that all of them exhibit metallic properties, which are expected to be applied for energy storage, biosensors and electrocatalysis.
|
|
|
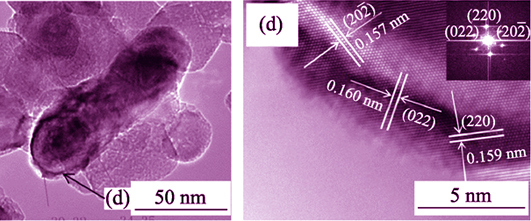
Preparation and Thermal Decomposition of Basic Magnesium Chloride Whiskers
GOU Sheng-Lian, NAI Xue-Ying, XIAO Jian-Fei, YE Jun-Wei, DONG Ya-Ping, LI Wu
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 781–785
 Abstract
Abstract(
657 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(2402KB)(
808
)
Basic magnesium chloride (BMC) whiskers were prepared by hydrothermal method using magnesium chloride and calcium hydroxide as raw materials. Subsequently, nano-MgO was obtained by pyrolysis of the resulting whisker. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images showed that the diameter of nano-MgO was between 20 and 40 nm. The corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern demonstrated the single-crystalline nature with the exposed plane of {111} and {110}. TG-DTG, SEM, XRD, and FT-IR analysis confirmed the four-step pyrolysis processes of BMC whisker. Results showed two molecules of crystal water lost during the first and second steps, respectively. Subsequently, two hydrogen chloride molecules were released in the third step. Finally, hydroxy water was dehydrated. The thermal decomposition kinetics of BMC whisker was studied by means of Satava and differential method. It indicates that the first step of the thermal decomposition of BMC whiskers is random nucleation and subsequent growth mechanism. The second step is two-dimensional diffusion. The third and the final steps are phase boundary reaction and one-dimensional phase boundary reaction mechanism, respectively.
|
|
|
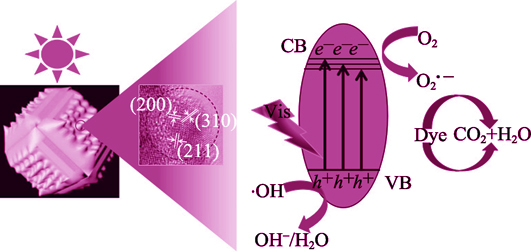
Synthesis of Cubic-relievo Ag3PO4 with High Visible-light Photocatalytic Activity
WEI Ju-Meng, LÜ Qiang, WANG Ben-Chi, PAN Jia-Le, YE Xiang-Ju, SONG Chang-Chun
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 786–790
 Abstract
Abstract(
578 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(5697KB)(
919
)
High visible-light photocatalytic activity silver phosphate (Ag3PO4) was successfully prepared via a facile water bath method. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images show that the products undergo three morphological changes during the reaction process, and the final product has uniform cubic-relievo morphology with an average particle size of about 1.6 μm. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicate that the samples are body-center cubic structure. In addition, the high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images show that several crystal facets are located in the surfaces of cubic-relievo Ag3PO4. UV-Vis absorption and photoluminescence (PL) spectra demonstrate that the products possess high visible-light responsive performance and weak PL emission intensity. The cubic-relievo Ag3PO4 exhibits significantly higher catalytic performance when applied on the photodegradation of methyl orange (MO) under visible-light irradiation in comparison to the cubic Ag3PO4, intermediate products or commercial nitrided TiO2 photocatalyst. This work indicates that the photocatalytic performance of the catalyst can be effectively improved by changing its surface structure.
|
|
|
Influence of Ammonium Hydrogen Carbonate to Metal Ions Molar Ratio on Co-precipitated Nanopowders for TGG Transparent Ceramics
LI Xiao-Ying, LIU Qiang, HU Ze-Wang, JIANG Nan, SHI Yun, LI Jiang
2019 Vol. 34 (7): 791–797
 Abstract
Abstract(
700 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(7030KB)(
931
)
Terbium gallium garnet (TGG) ceramics were successfully fabricated by air sintering at 1500 ℃ for 3 h combined with HIP post-treating at 1550 ℃ for 3 h under 150 MPa argon gas, where the TGG powders were synthesized by the co-precipitation method employing ammonium hydrogen carbonate (AHC) as precipitant. The influences of ammonium hydrogen carbonate to metal ions molar ratio (R value) on phase composition and morphology of the resultant powders as well as optical transmittance and Verdet constant of the TGG ceramics were investigated systematically. The precursors with R=3.6, 4.0 and 4.4 calcined at 1100 ℃ form pure TGG phase, whereas the precursor with R=3.2 treated at the same temperature yields the mixed phases of TGG and Ga2O3. The TGG powder with R=4.0 shows the best dispersity and homogeneity, giving rise to ceramic with the best optical quality. On the contrary, the powder with R=4.4 exhibits a strong agglomeration, which is closely related to the morphology of its precursor. High quality TGG transparent ceramics with the transmittance of 80.1% at 1064 nm can be fabricated by the nanopowder with R=4.0, and the Verdet constant of the TGG ceramics at 633 nm is rather close to that of the commercial TGG single crystals (-134 rad·T -1·m -1).

|
|