|
|
Research Progress of Thermal Controlled Cracking of Hard-Brittle Plate
WANG Hai-Long, WANG Yang, WANG Xiang-Wei, ZHANG Hong-Zhi
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 923–930
 Abstract
Abstract(
731 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(2456KB)(
1621
)
Thermal Controlled Cracking Method (TCCM) has developed for more than 60 years with great success. The research progress of TCCM in the past 60 years was reviewed in two directions, i.e. Premade Trajectory Cutting (PTC) and Non-Premade Trajectory Cutting (NPTC) respectively. For PTC, cutting velocity, trajectory deviation and sectional quality are the main process parameters to be optimized. For NPTC, cutting velocity and sectional quality are the main process parameters to be optimized. The crucial technique for optimizing these above parameters is to adopt new techniques for generating advanced heating source, cooling source and better process flow. These new techniques are expected to provide enormous promotion for the developing of TCCM.
|
|
|
Research Progress of Ni-based Composite Catalysts for Methane Dry Reforming
ZHANG Peng, ZHANG Qing, LIU Jing, GAO Lian
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 931–941
 Abstract
Abstract(
1066 )
 HTML
HTML(
19)
 PDF
PDF(2136KB)(
1837
)
Methane Dry Reforming (DRM) catalysis converts the two greenhouse gases, CO2 and CH4 into syngas, which can be further utilized for liquid fuels production through Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. The DRM reaction is therefore of significance for both energy and environments. The key issue to promote industrialization of DRM reaction is to develop suitable catalysts. Nickel based composite catalysts have received extensive attention due to their outstanding catalytic activities comparable to those of precious metals and their bargain price. However, nickel based catalysts usually undergo severe deactivation due to the coke deposition and metal sintering during long-term reaction at high temperature, which seriously limit their industrial applications and development of the engineering of DRM. Many researches have been carried out to address this issue. In this review, the recent research progress in the activity, coke resistance, and sintering resistance of Ni-based composite catalysts are introduced from the aspect of catalyst components, structures, preparation methods, and simulations. The research trends of DRM catalysts are also predicted based on the recent research progress in single-atomic catalysis and the in-situ characterization techniques for catalysis.
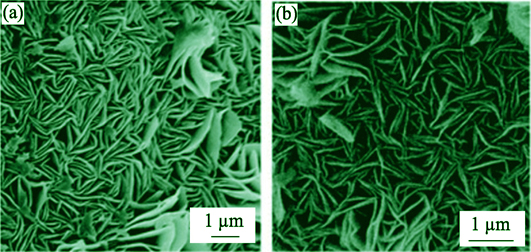
|
|
|
Reductive Preparation of Blue TiO2 via Deposition of Aluminum
SHENG Peng, ZHAO Guang-Yao, XU Li, LIU Shuang-Yu, WANG Bo, LIU Hai-Zhen, MA Guang, HAN Yu, CHEN Xin
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 942–948
 Abstract
Abstract(
838 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(1609KB)(
1140
)
Improving catalysis efficiency and reducing production cost attract extensive interest for the study of photocatalyst. Herein a blue titania crystal with aluminum atoms modified on the surface was prepared by aluminum reduction and deposition. The blue titania displays a unique core-shell structure with crystallization nuclei inside and with oxygen vacancies and aluminum atoms outside. And the blue titania shows excellent photocatalytic and electrochemical performance under simulated sunlight. Under high vacuum, with vapored aluminum atoms being deposited on titania nanocrystals, Ti4+ is reduced to Ti3+, which creates a large number of oxygen vacancies on the surface. Additionally, moderate amounts of aluminum atoms coated on titania become photo-induced charge carrier traps, facilitating the separation and transport of charge carriers, which enhances the photocatalytic capability. TiO2-Al0.36 exhibits the best photocatalytic performance, degrading methyl orange in 8 min, and it shows excellent photochemical property with the photocurrent of 1.47 mA·cm-2, which is more than 8 times as high as that of pristine titania (0.17 mA·cm-2).
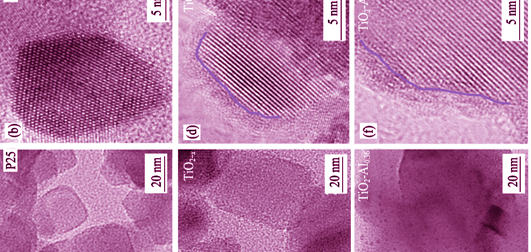
|
|
|
Preparation and Visible-light-driven Photocatalytic Performance of Porous Rod-like FeVO4
JIANG Hai-Yan, XIA Yun-Sheng, LI Yu-Zhen
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 949–955
 Abstract
Abstract(
775 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(2035KB)(
1321
)
Pure triclinic porous FeVO4 with multiple morphologies were fabricated by adopting hydrothermal strategy using Fe(NO3)3 and NH4VO3 as inorganic source and NH3 solution as pH adjuster. The samples were characterized by means of techniques such as X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. It was found that hydrothermal temperature and pH of the precursor solution exerted a great effect on the crystalline structure and the particle morphology of the product. Porous triclinic FeVO4 nanorods were generated hydrothermally at 180℃ and pH of 4 or 7, sheet-like FeVO4 was obtained at pH 4.0 and hydrothermal temperature of 120℃. However, the mixture of Fe2O3 (in majority) and FeVO4 (in minority) was prepared when pH of the precursor solution was raised to 10 at 180℃ or the hydrothermal temperature was raised to 240℃ at pH 4.0. Among the FeVO4 samples, porous FeVO4 nanorods with the highest surface area of 10.4 m2/g exhibited the best visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance for the degradation of MO. It is concluded that such an excellent photocatalytic performance is attributed to its higher crystallinity, surface area, and surface oxygen vacancy density, porous structure, and lower bandgap energy.
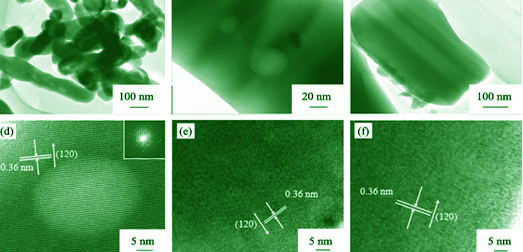
|
|
|
Preparation of High-performance Cu-SAPO-34 Catalysts without Removal of Templating Agents
KONG Xiang-Li, QIU Ming-Hui, YANG Lu, WANG An-Ran, FAN Yi-Qun, KONG De-Shuang, GU Chang-Jun, HUAN Xiu-Hua, KONG Ling-Ren
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 956–962
 Abstract
Abstract(
701 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(1007KB)(
1148
)
The pollution of nitrogen oxides has become a serious environmental problem. Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) with zeolites is one of the most effective ways to remove nitrogen oxides. To reduce the cost of the catalysts’ preparation, a facile fabrication method of high-performance Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts without removal of templating agents was proposed. Zeolite slurry containing templating agents was directly applied as a raw material to prepare the Cu-SAPO-34 catalyst followed by pretreatment, ion exchange and one-time calcination. As prepared catalysts were systematically investigated by XRD, BET, TG, ICP, XPS, SEM, TPR, TPD, and NH3-SCR. In the ion exchange process, different pH conditions were studied and optimized. The optimized catalyst with Cu content of 2.43% performed a cubic crystal, high acidity and catalytic activity. The NO conversion rate was more than 80% in the range of 200~450℃, and the highest value was 97.8% obtained at 300℃. Compared with the catalyst prepared from commercial SAPO-34, the as-prepared Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts without removal of templating agents exhibited similar microstructure and catalytic performance. These results indicate that the presence of a small amount of templating agent in the SAPO-34 zeolites makes no difference to fabricate high-performance Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts. It is a feasible method to prepare high-performance Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts without removal of templating agents.
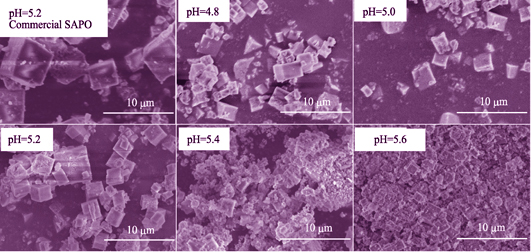
|
|
|
Synthesis of Pure-silica BETA Zeolite by the Method of Seed-direct Steam-assisted Crystallization
FENG Shou-Ai, ZHOU Jun, YANG Xuan-Yu, LIU Hong, HUANG Jiang-Feng, BAI Jia-Feng, CHENG Xiao-Wei, DENG Yong-Hui
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 963–968
 Abstract
Abstract(
821 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(2115KB)(
1296
)
The pure-silica zeolite BETA has a promising prospect in the field of cigarette harm reduction and petrochemical industry. In present work, the single-template method, named as the seed-direct steam-assisted crystallization (SAC), was used to synthesize the pure-silica zeolite BETA. And then the samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), nitrogen adsorption, and Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The results revealed that BETA seeds, template (TEAOH) and alkalinity exert great effects on the synthesis of pure-silica zeolite BETA. The BETA zeolite with polymorph A enrichments (58%-68%) is synthesized by SAC method, which can not be affected by the change of molar ratio of the raw materials. The pure-silica zeolite BETA possesses the hydrophobic properties, which can be used in the separation of organic/H2O, and the removal of harmful organic materials in cigarette smoke.
|
|
|
High-temperature Insulation Property of Opacifier-doped Al2O3-SiO2 Aerogel/Mullite Fiber Composites
ZHU Zhao-Xian,WANG Fei,YAO Hong-Jun,DONG Jin-Xin,LONG Dong-Hui
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 969–975
 Abstract
Abstract(
822 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(2236KB)(
1762
)
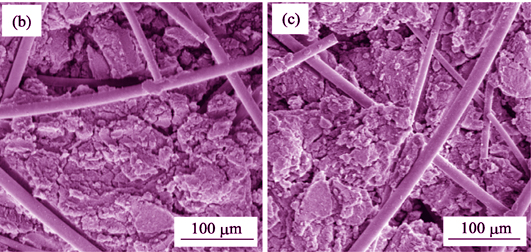
Infrared opacifier-doped Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel/mullite fiber composites were successfully prepared through a mixed Sol-Gel and supercritical drying process by using TiCl4 and ZrOCl2·8H2O as the source of TiO2 and ZrO2, respectively. Effects of two kinds of infrared opacifier on microstructure, mechanical property and thermal conductivity of composites were studied. The results show that introduction of infrared opacifier effectively prevent the aerogels from collapse and agglomeration when exposed to high temperature, leading to high-level retention of porosity. The aerogel/mullite fiber composites demonstrate a typical structure of aerogel filled fibrous fiber with marvelous properties—low density (0.21-0.24 g·cm-1) and high bending strength performance (0.98-1.26 MPa), which expands brilliant potential in many areas of application. When exposed to high temperature of 1050℃, the thermal conductivity of TiO2 and ZrO2 doped composites can be significantly reduced from 0.098 W·m-1·K-1 to 0.085 W·m-1·K-1 and 0.076 W·m-1·K-1, respectively, which could be attributed to outstanding scattering and absorbing ability of the infrared opacifiers to the infrared electromagnetic wave. All results indicate that the addition of infrared opacifiers is a promicsing approach to enhance high-temperature properties of aerogel materials.
|
|
|
Ga2O3 MOSFET Device with Al2O3 Gate Dielectric
LV Yuan-Jie, SONG Xu-Bo, HE Ze-Zhao, TAN Xin, ZHOU Xing-Ye, WANG Yuan-Gang, GU Guo-Dong, FENG Zhi-Hong
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 976–980
 Abstract
Abstract(
787 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(463KB)(
1863
)
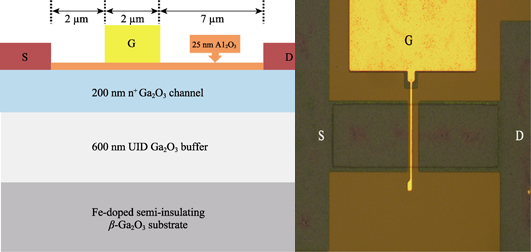
n-typed β-Ga2O3 was homoepitaxially grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) on a Fe-doped semi-insulating (010) Ga2O3 substrate. The structure consisted of a 600 nm undoped (UID) Ga2O3 buffer layer and 200 nm Si-doped channel layer. High-temperature Ohmic alloy experiments were taken on two kinds of n-typed β-Ga2O3 with Si donor concentrations of 3.0×1017 and 1.0×1018 cm-3. It’s hard to realize good Ohmic contact on the β-Ga2O3 epitaxial layer with donor concentrations of 3.0×1017 cm-3. The lowest Ohmic value of 9.8 Ω•mm was obtained on the substrate with donor concentrations of 1.0×1018 cm-3. Metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) was fabricated based on homoepitaxial β-Ga2O3 film with donor concentrations of 1.0×1018 cm-3, in which Al2O3 grown by atomic layer deposition (ALD) was used as gate dielectric. The drain saturation current of the fabricated device reached 108 mA/mm at Vgs of 2 V, and a high peak transconductance of 17 mS/mm was obtained. Due to poor gate leakage, the three-terminal off-state breakdown voltage was just 23 V at Vgs = -12 V. The breakdown characteristics can be improved by introducing HfO2 with high dielectric constant or Al2O3/HfO2 composite structure.
|
|
|
Floating Zone Growth and Thermionic Emission Property of [100], [110], [111] CeB6 Single Crystal
WANG Yan, ZHANG Jiu-Xing, YANG Xin-Yu, ZHAO Jing-Jing, NING Shu-Yu, LI Zhi
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 981–986
 Abstract
Abstract(
550 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(8843KB)(
1086
)
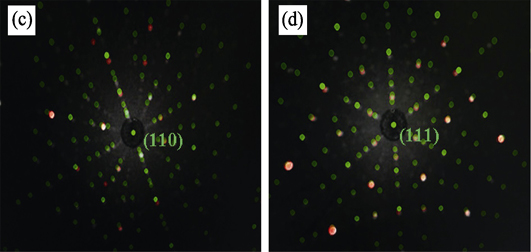
High-quality CeB6 single crystal was successfully prepared by optical floating zone method combining spark plasma sintering. [100], [110], [111] CeB6 single crystals were obtained by X-ray Laue directional system equipped with precision cutting system. The structure and crystal quality of [100] CeB6 single crystal was given emphasis to analyze and characterize. The results show that [100] CeB6 single crystal exhibits good quality with the full width at half-maxmium (FWHM) of 0.24o. With the increase of the cathode temperature from 1773 K to 1973 K, the maxmium emission current density of [100], [110], [111] single crystal improved by 3.6, 4.2 and 2.5 times, respectively. [100] CeB6 single crystal possesses the best thermionic emission performance: the maxmium emission current density reaches 64.77 A·cm-2 at 1973 K and applied voltage of 4 kV, which is larger than that of reported values in the literature up to now, and the effective work function is 2.821 eV. Therefore, [100] CeB6 single crystal with excellent thermionic emission properties will have proming application prospects.
|
|
|
Recycling Polycrystalline Silicon Solar Cells
LI Jia-Yan, CAI Min, WU Xiao-Wei, TAN Yi
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 987–992
 Abstract
Abstract(
856 )
 HTML
HTML(
24)
 PDF
PDF(2204KB)(
1403
)
Recovering Si material from the degraded solar cells is significant for environmental protection and material recycling. In this tudy, the optimal conditions for recycling degraded solar cells by chemical etching and ultrasonic cleaning were investigated. The samples were tested by EDS, SEM and XPS, The results showed that Al electrodes were completely removed from cells by reaction with 10wt% NaOH solution for 18 min, with less silicon corrosion lost. After that, Ag electrodes were completely exfoliated from the cells by ultrasonic cleaning (40 kHz) for 20 min. Si3N4 film was thoroughly eliminated after the cells were etched with 40wt% HF solution for 10 min, which was proved to be the optimal reaction time. A quantitative experiment was performed in this study with 8. 9068 g cells. The results show that the recycling mass of Al electrodes, Ag electrodes and Si wafers are 1.1102 g, 0.0766 g and 7.7169 g, respectively.
|
|
|
Tuning Electrochemical Performance through Non-stoichiometric Compositions in High-voltage Spinel Cathode Materials
LEE Sai-Xi, WANG Xue-Yin, GU Qing-Wen, XIA Yong-Gao, LIU Zhao-Ping, HE Jie
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 993–1000
 Abstract
Abstract(
802 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(1181KB)(
1315
)
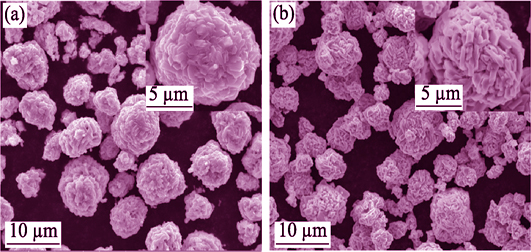
In this study, a simple method to prepare high-voltage spinel cathode materials though controlling stoichiometric ratio in their compositions was reported. Non-stoichiometric and stoichiometric high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials were prepared by solid-state reaction between Li2CO3 and Ni0.25Mn0.75(OH)2 prcursor. Their morphologies, structures and electrochemical performance were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, as well as electrochemical curves. The second particles occupied the similar sizes ~8 μm, which were composed of nanoparticles. Compared to stoichiometric LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4, Ni/Mn cations in non-stoichiometric LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 sample distributed randomly, resulting in structure disorder demonstrated by the analysis of X-ray diffraction, neutron diffration and Raman spectroscopy. Less Mn3+ content in stoichiometric LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 sample was detected though X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It is believed that more Mn3+ content and Ni/Mn cation disorder would benefit rate cpability and cycling performance. As a result, non-stoichiometric LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 sample delivers superior dicharge capacity at higher rates, even though it shows relatively minor discharge capacity at low rates. What’s more, higher capacity retention for the non-stoichiometric LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 sample was found, which was promoted to 91.2% at 1.0C rate after 400 cycles. At the same time, in situ X-ray diffraction measurements revealed that single-step phase transformation for non-stoichiometric LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 sample significantly enhanced structural stability during the electrochemical process. Spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 with non-stoichiometric composition provides a promising solution for their potential application in high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries.
|
|
|
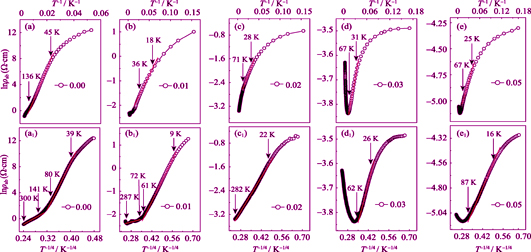
Electrical Transport Property of A-site La Doped of Sr2IrO4
DUAN Tian-Ci, WANG Hao-Wen, WANG Wei, PEI Ling, HU Ni
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 1001–1005
 Abstract
Abstract(
503 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(478KB)(
940
)
The physics of electric transport in iridate Sr2IrO4 has been a long term controversial issue in the field of 5d oxides. A series of single crystal samples (Sr1-xLax)2IrO4 were prepared by flux method, and their electrical transport properties were investigated. The results reveal that the sample shows metallic transport at x≥0.03. A close examination of the transport data reveals drastic modulation for the conduction mechanism upon La-doping. For the non-doped sample, three-dimensional Mott variable range hopping conduction is respectively identified at T>140 K and 40 K<T<80 K, and thermal activation conduction is revealed at 80 K<T<140 K. For the doped sample, the Mott variable range hopping conduction is only found at T<90 K, and the activation energy is revealed to decrease with the La-doping content increasing. In addition, the localization length of the doped samples is found to be much larger than the Ir-O bond length, which may due to delocalization effect of the carriers in the systems.
|
|
|
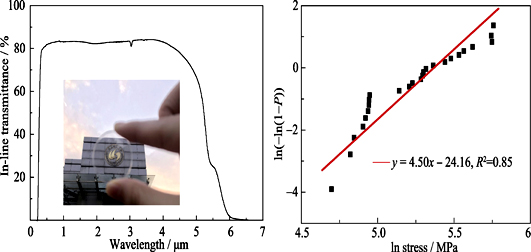
Characterization and Evaluation on Mechanical Property of Mg0.27Al2.58O3.73N0.27 Transparent Ceramic
ZHANG Zhou, WANG Hao, TU Bing-Tian, XU Peng-Yu, WANG Wei-Min, FU Zheng-Yi
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 1006–1010
 Abstract
Abstract(
569 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(1211KB)(
971
)
Owing to excellent optical and mechanical properties, MgAlON transparent ceramic has been considered as a potential candidate for important military and civilian applications in recent years. In this study, several characterizations were conducted to evaluate the hardness, fracture toughness, and flexural strength of Mg0.27Al2.58O3.73N0.27 transparent ceramic. Flexural strength at room temperature of Mg0.27Al2.58O3.73N0.27 were further analyzed using Weibull statistic. The results show that the Vicker’s hardness, flexural strength, fracture toughness, and Young’s modulus of the transparent ceramic were equal to 15.1 GPa, 255 MPa, 2.56 MPa/m1/2, and 288 GPa, respectively, while the flexural strength of samples at 1200℃ was determined to be 125 MPa. The Weibull modulus of specimens was 4.5. Flexural strength and Vicker’s hardness of Mg0.27Al2.58O3.73N0.27 transparent ceramic were also investigated under different loading condition. The work reveals that mechanical properties of MgAlON transparent ceramic are higher than those of MgAl2O4 transparent ceramic, but a slightly lower than those of AlON transparent ceramic.
|
|
|
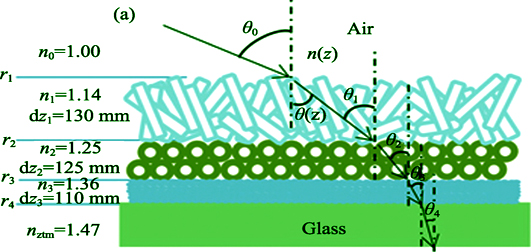
Preparation and Property of Superhydrophobic Antireflective Film with Gradient Refractive Index
JIA Gui-Yu, LI Yi-Wen, WANG Hong-Ning, CHEN Ruo-Yu
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 1011–1016
 Abstract
Abstract(
586 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(3969KB)(
1197
)
Gradient refractive index antireflection film achieves antireflective performance in wider spectrum band at larger incident of angle. In this study, solid silica nanometer particles (SiO2) sol and hollow silica nanometer particles (H-SiO2) sol were synthesized by Sol-Gel method, while hollow rod-shaped magnesium fluoride nanometer particles (MgF2) sol was prepared by solvothermal method. Then, the SiO2/H-SiO2/MgF2 gradient refractive index antireflection film was successfully coated on double sides of borosilicate glass by dip-coating method. The experimental results show that in the wavelength range of 380~1600 nm, when light is incident vertically, the transmittance of the coated glass reaches 99.88%; when the light is at the incident angle of 0°~45°, with the average transmittance higher than 97.85%. And the light is even at the incident angle of 75°, its maximum transmittance is still as high as 95.51%. After modified by hexadecyl trimethoxysilane (HDTMOS) the contact angle of the coated glass is up to 150.6°, showing good hydrophobic self-cleaning performance.
|
|
|
Resistive Switching Effect and Dielectric Property of Epitaxial BiFeO3 Thin Films by Off-axis Magnetron Sputtering
SONG Jian-Min, DAI Xiu-Hong, LIANG Jie-Tong, ZHAO Lei, ZHOU Yang, GE Da-Yong, MENG Xu-Dong, LIU Bao-Ting
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 1017–1021
 Abstract
Abstract(
596 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(750KB)(
1392
)
The Pt/BiFeO3/La0.5Sr0.5CoO3/SrTiO3(Pt/BFO/LSCO/STO) heterostructures were fabricated on (001) SrTiO3 substrate by off-axis RF magnetron sputtering, on which epitaxial BiFeO3 (BFO) thin films were suecessfully grown. The BFO thin film shows good crystal quality with (00l) epitaxial growth as confirmed by the atomic force microscope (AFM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Pt/BFO/LSCO capacitor exhibits a saturated butterfly loop with tuning rate of 14.1% and dielectric loss of 0.19 at 5 V driving voltage. Moreover, the resistance changes from high value to low value with positive voltage 0→5→0 V and negative voltage 0→-5→0 V, which displays switch behavior of ferroelectric diode resistance-change. Based on the I-V fitting curves, the resistance change mechanism fits the space charge limited current trap level when 0→5→0→-5 V and the interface limit F-N tunneling mechanism as -5→0 V, respectively.
|
|
|
Facile Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide In-situ Wrapped MnTiO3 Nanoparticles for Excellent Lithium Storage
LIU Huan-Long, ZHAO Wei, LI Rui-Zhe, HUANG Xie-Yi, TANG Yu-Feng, LI Dong-Mei, HUANG Fu-Qiang
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 1022–1028
 Abstract
Abstract(
986 )
 HTML
HTML(
25)
 PDF
PDF(1172KB)(
1226
)
The stable high-capacity anode has been an urgent demand for high energy density lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). Herein, a simple and effective strategy to synthesize high-performance reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in-situ wrapped MnTiO3 nanoparticles (MnTiO3@rGO) by Sol-Gel method is designed. The MnTiO3 nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed and wrapped by few-layer graphene. Due to high conductivity of rGO, MnTiO3@rGO nanoparticles show excellent rate performance, with a specific capacity of 286 mAh·g-1 being displayed at the higher rate of 5.0 A·g-1. Moreover, benefited from porous structure and flexible rGO shell, the MnTiO3@rGO anode delivers a remarkable long-term cycling stability. The specific capacity maintains 441 mAh·g-1 after 500 cycles at 0.5 A·g-1, only losing 8.4%. Therefore, the results demonstrate that the facile synthetic strategy is highly desirable for improving the conductivity and stability of metal oxide anodes.
|
|
|
Synthesis of α-MnO2 Nanowires via Facile Hydrothermal Method and Their Application in Li-O2 Battery
LU Chang-Jian, ZHU Fa-Quan, Yin Ji-Guang, ZHANG Jian-Bo, YU Ya-Wei, HU Xiu-Lan
2018 Vol. 33 (9): 1029–1034
 Abstract
Abstract(
1048 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(918KB)(
1315
)
Li-O2 batteries are regarded as a promising energy storage system for their extremely high energy density. MnO2-based materials are recognized as efficient and low-cost catalyst for a Li-O2 battery positive electrode material. In this work, α-MnO2 nanowires were successfully synthesized by a hydrothermal method and their electrocatalytic performance were investigated in Li-O2 batteries. X-ray diffraction and field emission scanning electron microscope confirms the formation of α-MnO2. The Li-O2 battery which consists of α-MnO2 nanowires shows a high discharge capacity up to 12000 mAh•g-1 at a restrict voltage of 2.0 V with the current density of 100 mA•g-1. When restricting the discharge capacity at 500 mAh•g-1, it can operate over 40 cycles and exhibit good cycle stability. These results indicate that the α-MnO2 nanowires can be used as positive electrode catalysts for Li-O2 batteries.
|
|