|
|
Progress of Precision Nanomedicine-mediated Gas Therapy
HE Qian-Jun, CHEN Dan-Yang, FAN Ming-Jian
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 811–824
 Abstract
Abstract(
1286 )
 HTML
HTML(
50)
 PDF
PDF(8896KB)(
1840
)
The precision nanomedicine-mediated gas therapy as an emerging and promising therapy strategy has received increasing attention, due to its low toxicity and high efficacy. Recent studies show that the nanomedicine-mediated gas therapy can not only kill cancer cells in specific diseased sites, but also protect normal cells. This review summarizes and reviews the most recent progress of the nanomedicine-mediated gas therapy. We introduce the therapeutic effects and characteristics of the nanomedicine-mediated gas therapy firstly, and then review several main routes to realize the precision nanomedicine-mediated gas therapy, including targeted gas delivery, controlled gas release, biomedical imaging guidance-monitoring of gas therapy, multi-model combined therapy based on therapeutic gases, and so on, and finally summarize the present existing issues and the prospects of further development in the gas therapy field.
|
|
|
Preparation of Ag2S Nanocrystals for NIR Photothermal Therapy Application
DENG Li-Er, LI Yan, GONG Lei, WANG Jia
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 825–831
 Abstract
Abstract(
848 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(2259KB)(
1392
)
Photothermal therapy (PTT) is a promising cancer treatment with both high effectiveness and low side effects. It is very important that the advancement of the NIR photothermal cancer therapy is dependent on the development of photothermal agents. Herein, this study developed hydrophilic DHLA-Ag2S nanocrystals as a new photothermal agent, which were synthesized by combining a thermal decomposition and ligand exchange route. The as-prepared Ag2S nanocrystals appear good water solubility, photo thermal stability and biocompatibility. Under irradiation of 980 nm laser with a power density of 5 W/cm2, HeLa cancer cells in vitro can be efficiently killed by photothermal effects of the Ag2S nanocrystals (40 μg/mL). The photothermal effect of Ag2S nanocrystals and its good fluorescence imaging function can realize the visualization and precision of photothermal therapy.
|
|
|
Application of Transparent Cobalt Sulfide Counter Electrodes in Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
JIANG Qing-Song, CHEN Ruo-Ting, LI Wen-Bo, CHENG Wen-Jie, HUANG Ye-Xiao, HU Guang
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 832–838
 Abstract
Abstract(
764 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1277KB)(
1046
)
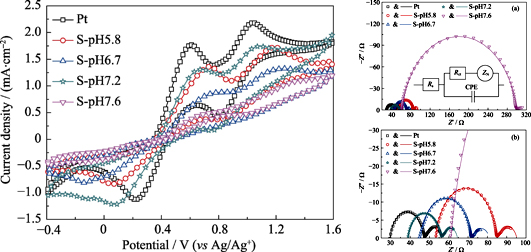
Cobalt sulfide nanomaterials are considered as important counter electrode materials for dye-sensitized solar cells. A potential reversal electrodeposition technique was applied to fabricate transparent cobalt sulfide film with fluorine-doped tin oxide glass as substrate. The experimental results demonstrate that the surface morphology of cobalt sulfide films is mainly dependent on the pH value of plating solution. The thickness of cobalt sulfide films can be effectively controlled by electrodeposition cycles. Then, cobalt sulfide films were used as counter electrodes of dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochemical measurements prove that cobalt sulfide counter electrodes exhibit high electrocatalytic activity. In particular, under electrodeposition condition of pH 7.2 and 12 cycles, cobalt sulfide counter electrode composed of the nanosheet structure exhibits higher electrocatalytic activity than platinum electrode, due to the increase of electrocatalytic active sites. Meanwhile, remarkable photoelectrical conversion efficiency of the dye-sensitized solar cell based on cobalt sulfide counter electrode is up to 7.26% with an average value of 7.18% for ten devices, which is higher than that of the dye-sensitized solar cell equipped with platinum electrode (6.94%).
|
|
|
Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol over N-doped TiO2 Nanofibers under Visible Irradiation
KE Yin-Huan, ZENG Min, JIANG Hong, XIONG Chun-Rong
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 839–844
 Abstract
Abstract(
747 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1384KB)(
1790
)
TiO2 nanofibers with a diameter size of 8-10 nm were prepared on the surface of the mesoporous SiO2 spheres through a vapor-phase growth method. And nitrogen doped TiO2 (N-TiO2) nanofibers were also successfully fabricated in the same way. The N atoms replaced the oxygen sites in the lattices of TiO2. The N-TiO2 nanofibers exhibited a highly catalytic activity under visible irradiation. XPS, UPS, XRD, SEM, TEM, UV-Vis, and PL were used to analyze and characterize the nanofibers. The annealed nanofibers were composed of highly crystalline anatase phase. Nitrogen doping narrowed band gap of the TiO2 nanofibers and enhanced absorption of the visible light. Meanwhile, photo-generated electrons over the N-TiO2 nanofibers exhibited more reductive potential than those over the TiO2 nanofibers. Thus, methanol yield was remarkably improved in CO2 photocatalytic reduction. Upon irradiation of 300 W Xe lamp for 2 h, methanol yield was 493.4 μmol∙g-1∙h-1 over the N-doped TiO2 nanofibers, and the corresponding turnover frequency (TOF) was 0.089 h-1. Comparatively, methanol yield reached 695.1 μmol∙g-1∙h-1 for N-TiO2 with a TOF of 0.125 h-1, which enhanced by 40.1% and 40.4%, respectioely.
|
|
|
Electrocatalytic Activity of Cobalt Doped Ceria Nanoparticles
YANG Zhi-Bin, YUE Tong-Lian, YU Xiang-Nan, WU Miao-Miao
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 845–853
 Abstract
Abstract(
1005 )
 HTML
HTML(
27)
 PDF
PDF(1491KB)(
1496
)
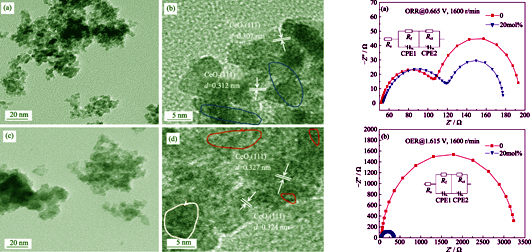
It is very difficult for single ceria to be used as an electrocatalyst because of its relatively poor electron conductivity and rare number of oxygen vacancy. Recently, it has been studied in the field of CO catalysis by doping transition metallic or non-metallic elements to improve the catalytic ability of ceria, while recent research has demonstrated that many oxides containing cobalt display better electrocatalytic activity. In this study cobalt doped ceria nanoparticles were prepared by homogeneous precipitation method. The electrochemical tests show that the optimum doping molar ratio is 20mol% for ORR and OER catalytic effect. After 10 hours of catalysis, the current density of ORR and OER decrease by about 20% and 5%, respectively, far below the corresponding values when noble metal and undoped cerium oxide nanoparticles were used as catalysts, and it indicated that the prepared catalyst owns good catalytic stability. In addition, XPS and other tests show that the decrease of charge transfer impedance (the improvement of electronic conductivity), the increase of active oxygen species, and the increased oxygen vacancies after doping are main reasons for improved catalytic performance. Therefore, doping cobalt greatly enhanced electrocatalytic properties of ceria nanoparticles are greatly enhanced by doping cobalt, providing guidence for other ionic conductors employed as bifunctional electrocatalysts.
|
|
|
A Novel Porous Electronic Conducting Ceramics Loaded with Silver Nano Particles as Cathode for Zinc-Air Batteries
WENG Xiao-Lin, LIU Pei-Pei, ZHANG Ya-Peng, LIU Jiang, LIU Mei-Lin
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 854–860
 Abstract
Abstract(
855 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(4865KB)(
1232
)
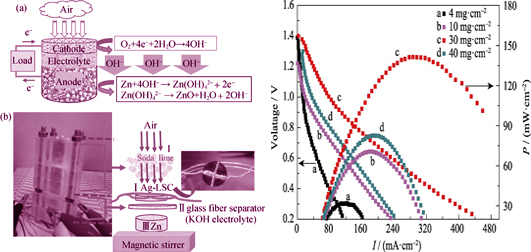
Zinc-air battery has great advantages such as high energy density, low cost and environmentally friendliness. Air electrode plays an important role in electrochemical performance of a zinc-air battery. In this paper, we report our study of a novel air electrode on which a porous perovskite ceramic La0.7Sr0.3CoO3-δ(LSC) with Ag nanoparticles directly grown. The porous LSC is used as substrate while Ag as catalyst. The porous structure of substrate attributes to the amount and dispersion of Ag nanoparticles which affect the electrochemical performance of air electrode. Therefore, the property of the Ag-LSC electrode is optimized by adjusting the mass content of pore-former (starch). Experimental results show that the Ag-LSC electrode, with a porosity of ~32% and a Ag load of ~30 mg/cm2, exhibits the best performance in all tested samples, and a zinc-air battery assembled with such air electrode gives the maximum power density of 141 mW/cm. What’s more, in order to ensure the gas diffusion channels, the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of the cathode is modified with PTFE to prevent flooding. After all that, the life-time of the zinc-air battery, with optimization by coating a PTFE layer as hydrophobic agent on the surface of the selected Ag-LSC electrode, prolongs significantly.
|
|
|
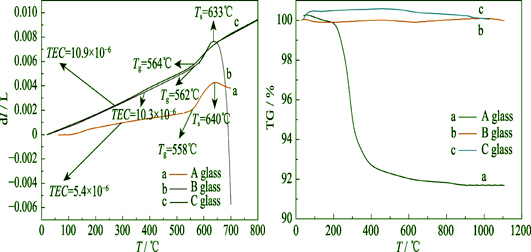
Residual Amount of BaCO3 on Glass Thermal Property Based on BaO-CaO-Al2O3-B2O3-SiO2 System
LIU Liang-Guang, LUO Ling-Hong, WU Ye-Fan, CHEN Liang, XU Xu, WANG Le-Ying
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 861–865
 Abstract
Abstract(
590 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(392KB)(
1094
)
A BaO-CaO-Al2O3-B2O3-SiO2 system for the sealing glass in intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell (IT-SOFC) was prepared. The effects of three fusion processes (heating at 1300℃ for 1 h, heating at 1400℃ for 1 h, and heating at 1400℃ for 3 h) were explored with focus on the residual amount of BaCO3 and the thermal properties of the glasses by thermal-thermogravimetric analysis (DTA-TG). Samples were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and thermal expansion coefficient meter. The results showed that 59wt% BaCO3 retained undecomposed in the glass prepared via heat treatment at 1300℃ for 1 h and its expansion coefficient decreased due to devitrification of monoclinic BaAl2Si2O8. Softening temperature (>800℃) of the glass produced via heating at 1400℃ for 3 h increased obviously owing to the increment of Al2O3 amount. The expansion coefficient of the glass produced via heat treatment at 1400℃ for 1 h was 10.3×10-6 K-1 from room temperature to the glass transition temperature, indiating the process of heat treatment at 1400℃ for 1 h the optimal condition in three candidates for the specific formula, which was found to be eligible for SOFC sealing.
|
|
|
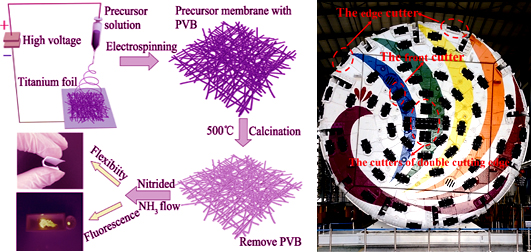
Synthesis, Property and Wear Detection of Disc Cutter for Shield Tunneling Machine of Nanobelt Ca0.68Si9Al3(ON)16 : Eu2+ Luminescence Fibers
ZHAO Hai-Lei, SUN Zhen-Chuan, CHEN Kui, WANG Hong-Zhi, YANG Yan-Dong, ZHOU Jian-Jun, LI Feng-Yuan, ZHANG Bing, SONG Fa-Liang
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 866–872
 Abstract
Abstract(
606 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(2214KB)(
1015
)
Nanobelt Ca0.68Si9Al3(ON)16 : Eu2+ luminescence fibers for wear detection of disc cutter were prepared by a simple process electrospinning combined with gas-reduction method, and then characterized by FE-SEM, XRD, PL, and universal material testing machine. The obtained sample keeps fiber film state in micro and macroscopic level with a certain mechanical strength, temperature, waterproof and chemical stability. XRD patterns of the sample doped with Eu2+ 0.1 nitrided at 1500℃ for 4 h were crystallized well and assigned to Ca0.68Si9Al3(ON)16 in JCPDF card. The fiber film can be effectively excited by blue light, showing a broad emission spectrum in the range from 400 to 700 nm. The luminescent fiber film can be practically assembled onto disc cutters for detection. The wear degree of each cutter can be real-timely monitored in the main control room, which reduces the artificial detection at high pressure and high risk geological section, the investment cost, and the occupational risk of operators.
|
|
|
Structure and Spectral Property of Sc Doped Nd:CaF2 Laser Crystals
PANG Si-Yuan, QIAN Xiao-Bo, WU Qing-Hui, YU Hao, XU Jia-Yue, SU Liang-Bi
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 873–876
 Abstract
Abstract(
573 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(583KB)(
1027
)
0.5at% Nd, xat% Sc:CaF2 single crystals (x=0, 2, 5, 8) were fabricated via the temperature gradient technique in this work. The absorption spectra, fluorescence spectra and fluorescence lifetime of 0.5at% Nd, xat% Sc:CaF2 single crystals were investigated. Both fluorescence intensity and fluorescence lifetime were found to be enhanced with the increase of Sc3+ ion doping concentration. In addition, by optimizing the Sc3+ content, 0.5at% Nd, 5at% Sc:CaF2 yielded the largest absorption cross section of 1.42×10-20 cm2. Moreover, a new peak were observed at 796 nm with the Sc3+ ion doped in 0.5at% Nd:CaF2 crystals. Above all, the concentration of Sc3+ ion can regulate local structure of Nd3+ ion and optimize its crystalline spectral properties.
|
|
|
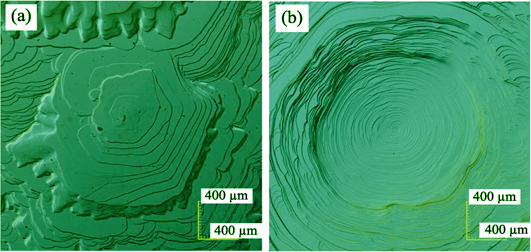
As-grown Surface Morphologies of SiC Single Crystals Grown by PVT Method
CUI Ying-Xin, HU Xiao-Bo, XU Xian-Gang
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 877–882
 Abstract
Abstract(
983 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(6960KB)(
1648
)
As-grown surface of single crystal can reflect abundant information including crystal growth mechanism and defect distribution of the single crystal after growth. The as-grown surface morphologies of 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC single crystals were observed and measured by laser confocal microscope DIC splicing technique and atomic force microscope (AFM). It is found that as-grown 4H-SiC surface tends to appear hexagonal growth steps, while the as-grown 6H-SiC surface tends to appear circular growth steps. Based on Jackson model and thermodynamics theory, Jackson factors of the 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC single crystals are calculated to be 33.15 and 31.87, respectively. Therefore, the surface morphology difference between 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC is caused by the roughness of growth interface and crystal growth temperature. The micropipe on the as-grown surface is the origin of growth steps and multiple micropipes on the as grown surface were measured by AFM. Their diameters are in the range of 760 nm- 6.0 μm, and the corresponding absolute values of Burgers vector are in the range of 5c-14c. Through structure characterization and statistical analysis, the values of micropipe diameters divided by squares of the burgers vectors (D/B2) are in the range of 11.1 nm-1-23.6 nm-1, which means the structure data of these micropipes obtained by AFM cannot strictly obey the Frank theory.
|
|
|
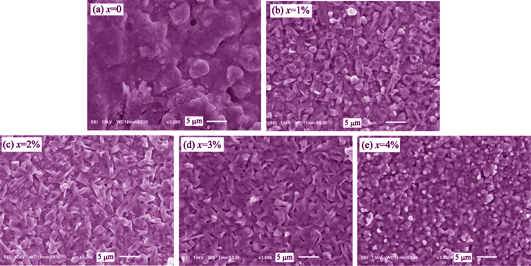
ZBAS on the Structure and Dielectric Property of BaAl2Si2O8
HAN Lin-Cai, DING Shi-Hua, SONG Tian-Xiu, HUANG Long, ZHANG Xiao-Yun, XIONG Zhong
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 883–888
 Abstract
Abstract(
630 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(1809KB)(
955
)
Barium feldspar BaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system materials have been studied widely for satellite communication, microwave substrate and packaging in recent years. BaAl2Si2O8-x(ZnO-Al2O3-SiO2-B2O3) (x=0, 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%) ceramics were prepared by solid state route. The effects of ZBAS glass on the sintering behaviour, phase composition and microwave dielectric properties of BaAl2Si2O8 were investigated. Addition of ZBAS glass can effectirely lower the sintering temperature to 1360℃ without changing phase composition of the sample and greatly propel the transition from hexacelisian to celsian. When x≥2%, the transition from hexacelisian to celsian reaches 100%. Density, dielectric constant and τf of BaAl2Si2O8-ZBAS ceramics increase with the increment of ZBAS glass in the range of 1%≤x≤4%. In addition, the resonant frequency temperature coefficient is negative. The BaAl2Si2O8-ZBAS sintered at 1360℃ obtains a high Q×f of 28058 GHz, εr=6.72 and τf=-29.79×10-6℃-1 at x=3%. Deviations between experimental and theoretical relative permittivity of BaAl2Si2O8-xZBAS is also discussed.
|
|
|
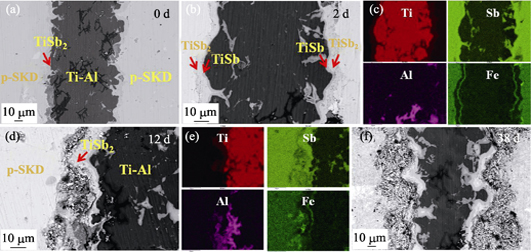
Interface Stability of Skutterudite Thermoelectric Materials/Ti88Al12
ZHANG Qi-Hao, LIAO Jin-Cheng, TANG Yun-Shan, GU Ming, LIU Rui-Heng, BAI Sheng-Qiang, CHEN Li-Dong
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 889–894
 Abstract
Abstract(
949 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(9434KB)(
1288
)
Interface stability is one of the key issues determining the service reliability and life of thermoelectric devices. For skutterudite-based thermoelectric devices, the barrier layer is required in order to restrain the inter-diffusion between the hot-side electrode and skutterudite matrix. In this work, Ti88Al12 was selected as the barrier layer. N-type Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Ti88Al12/Yb0.3Co4Sb12 and p-type CeFe3.85Mn0.15Sb12/Ti88Al12/CeFe3.85Mn0.15Sb12 thermoelectric joints were prepared by one-step hot pressing sintering method. The evolution processes of contact resistivity and microstructure were studied through accelerated aging experiments. The results show that the contact resistivity of n-type joints increases slower than that of p-type joints under the same aging condition. Activation energy for n-type and p-type joints is 84.1 kJ/mol and 68.8 kJ/mol, respectively. Growth of the inter-metallic compound layer and cracking at the AlCo/TiCoSb interface result in rapidly increased contact resistivity of n-type joints. For p-type joints, the difference of coefficient of thermal expansion between CeFe3.85Mn0.15Sb12 and Ti88Al12 becomes the main reason for the cracks.
|
|
|
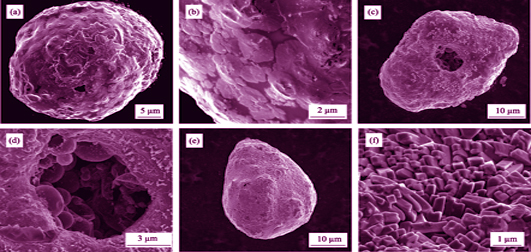
Pore Formation Mechanism of WC-10Co4Cr Coatings Based on Collected In-flight Particles and Individual Splat
CHEN Shu-Ying, MA Guo-Zheng, HE Peng-Fei, LIU Zhe, LIU Ming, XING Zhi-Guo, WANG Hai-Dou, WANG Hai-Jun
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 895–902
 Abstract
Abstract(
531 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(9814KB)(
812
)
The supersonic plasma spray equipment was utilized to fabricate WC-10Co4Cr coatings. Four spraying parameters with different spraying powers were employed to obtain coatings with different porous structure. The liquid nitrogen was used to freezing in-flight particles with different molten status. The individual splat was deposited on mirror polished stainless steel at preheating temperature of about 200℃. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the morphologies of coating, raw spraying powder, freezing particle, and individual splat. The field emission microscopy (FEM) was utilized to observe the microstructure of coating, while the energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) was used to analyze the composition. The results show that with increment of spraying power, the large size pores kept decreasing. With 60 kW spraying power, a few thermal cracks appeared within the coating due to the heat accumulation. Micro hardness of the coatings increased firstly and then decreased with the increment of spraying power. Solidified morphologies of individual splat could be distinguishe as four types, namely, partially melted type, fragmented type, bubble-like type, as well as flower-like type. Pores within the WC-10Co4Cr were mainly formed by shadowing effect of solidified coatings and substrate, gas effect of the micro valley, insufficient wetting of droplet, as well as the pore migration within the liquid phase of the splat.
|
|
|
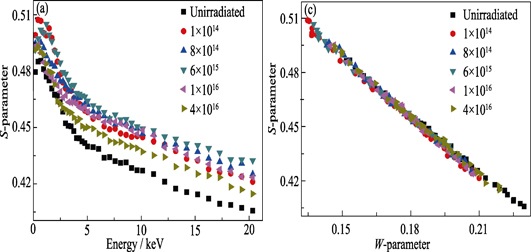
Influence of Proton Irradiation on Defect and Magnetism of Yb-doped ZnO Dluted Magnetic Semiconductor Thin Films
CHEN Wei-Bin, LIU Xue-Chao, ZHUO Shi-Yi, CHAI Jun, SHI Er-Wei
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 903–908
 Abstract
Abstract(
602 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(4739KB)(
865
)
Yb-doped ZnO thin films were prepared by inductively coupled plasma enhanced physical vapor deposition method, the as-deposited Zn0.985Yb0.015O thin films were irradiated by proton with different doses. X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, positron annihilation spectroscopy, and magnetic property measurement were used to study the defect and ferromagnetism. The magnetic property measurement results indicate that the saturation magnetization of Zn0.985Yb0.015O thin films increases with the increment of irradiation doses, and reaches the maximum value at 6×1015 ions/cm2. With the further increase in irradiation doses, the saturation magnetization decreases. The positron annihilation measurement reveals that Zn vacancy-related defects dominate in proton irradiated Zn0.985Yb0.015O thin films. It is found that dependency of saturation magnetization on irradiation doses exhibits the same behavior with the amount of Zn vacancy-related defects on irradiation doses. It is experimentally demonstrated that the ferromagnetism of proton irradiated Yb-doped ZnO thin films is mainly influenced by Zn vacancy- related defects.
|
|
|
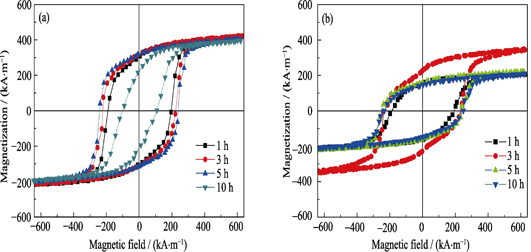
Crystal Structure and Magnetic Property of Si3N4/FePd/Si3N4 Thin Films
ZHOU Xin, MA Lei, LIU Tao, GUO Yong-Bin, WANG Dao, DONG Pei-Lin
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 909–913
 Abstract
Abstract(
548 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(1586KB)(
919
)
Si3N4/FePd/Si3N4 trilayer films were prepared by magnetron sputtering. The effect of Si3N4 insert as a non-magnetic material on structure and magnetic properties of FePd films was investigated. The results show that Si3N4 particles distribute between the FePd nanoparticles after heat treatment, which inhibit the growth of FePd grains. Compared with pure FePd films, the grains of Si3N4/FePd /Si3N4 thin films are obviously refined. By adding Si3N4 insert, the crystallographic parameters c/a of FePd films decrease from 0.960 to 0.946, indicating that Si3N4 content could effectively promote the ordering process of FePd films and improve the coercivity and remanence ratio. The coercivity and remanence ratio are increased to 249 kA/m and 0.86, respectively. With the further increase of the annealing time at 600℃, the magnetic property of the Si3N4-doped FePd thin films does not decrease rapidly, and its relatively high magnetic properties maintain over a wide range of annealing time, which indicate that the thermal resistance of FePd thin films are obviously improved. Si3N4 insert plays a great role in promoting the magnetic properties of FePd thin films, which is significant for the development of magnetic recording film materials.
|
|
|
Preparation of Room Temperature Curable Organic-inorganic Hybrid Thermal Control Coatings
LIU Ding, YU Yang, MI Le, YU Yun, SONG Li-Xin
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 914–918
 Abstract
Abstract(
738 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(403KB)(
954
)
A series of organic-inorganic hybrid thermal control coatings (TCCs) were prepared. The binder was prepared by co-pre-hydrolysis/condensation of tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) and siloxane, subsequently mixing with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) as curing catalyst and ZnO powder as optical pigment. The coatings can be cured at room temperature naturally with low solar absorptance αS and high thermal emittance εH. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) measurements were carried out to understand the structures of the coatings. FT-IR spectra and GPC analysis results showed that the as-prepared hybrid binder carried lots of active hydroxyls with an appropriate polymerization degree. Thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA) test showed that as-prepared coatings have high thermal stability at 200℃. αS/εH value could be further reduced by increasing the coating thickness, and optical absorption of the coatings in the infrared wave band could be further reduced by increasing TEOS content. This work provides an effective way to obtain room temperature cured TCCs with low αS/εH value.
|
|
|
Novel Synthesis Method of Sheet-like Agglomerateβ-Bi2O3 with High Photocatalytic Activity
CHEN Jun, ZHAN Jing, DING Feng-Hua, LI Qi-Hou, TANG Yi-Wei
2018 Vol. 33 (8): 919–922
 Abstract
Abstract(
689 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(928KB)(
931
)
Sheet-like agglomerates β-Bi2O3 were synthesized via an extraction-precipitation stripping-decomposition method using a leaching solution of bismuthinite as raw materials in acidic chloride media. Phase form of as-prepared Bi2O3 was confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and its morphology was observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). Moreover, photocatalytic activity of the β-Bi2O3 was evaluated by measuring the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irradiation. The results showed that the powders consisted of nanoflakes. The β-Bi2O3 exhibited a smaller band gap energy and larger absorbance edge than α-Bi2O3 and reported β-Bi2O3. In addition, 99.23% of the RhB was degraded under 4 h visible light irradiation and β-Bi2O3 was a fairly stable photocatalyst under the experimental conditions.
|
|