|
|
Research Progress on Lithium Titanate as Anode Material in Lithium-ion Battery
TAN Yi, XUE Bing
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 475–482
 Abstract
Abstract(
2265 )
 HTML
HTML(
88)
 PDF
PDF(1862KB)(
2955
)
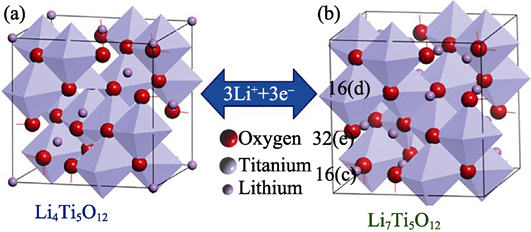
With the increasing demand for light, small, high power rechargeable lithium ion batteries in the application of mobile phones, laptop computers, electric vehicles, hybrid electric vehicles, electrochemical energy storage, and smart grids, the development of anode materials with high safety, environmental benignity, high power density, and long cycle life is in progress in recent years. The spinel lithium titanium oxide (Li4Ti5O12) anode has become more attractive as alternative anode because of its high safety, abundant titanium dioxide raw materials, stable charge/discharge voltage plateau of 1.5 V (vs. Li/Li+), and excellent cycling performance due to its zero-strain volume during charge/discharge process. However, the commercial use of Li4Ti5O12 anode material has been hindered by the low intrinsic electronic conductivity. This review focuses on recent studies of the electronic structure and performance, synthesis methods and strategies for improvement in the lithium storage capacity, charge/discharge characteristics, then on its near future development.
|
|
|
Research Progress on Counter Electrodes of Quantum Dot-sensitized Solar Cells
MENG Xiang-Dong, YIN Mo, SHU Ting, HU Yue, SUN Meng, YU Zhao-Liang, LI Hai-Bo
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 483–493
 Abstract
Abstract(
750 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(1208KB)(
1303
)
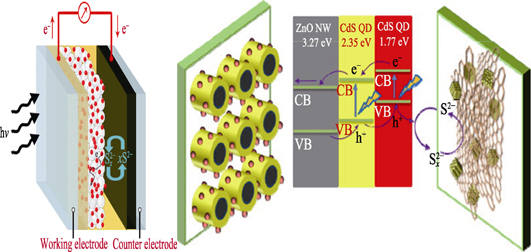
Quantum dots sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) play a key role in the new generation photovoltaic devices due to their low cost and easy fabrication process. The absorption spectrum of quantum dots can be tailored by controlling grain size, and multi-exaction generation. QDSCs using inorganic compound QDs replaces the dye as a sensitizer, which is able to solve the stability of the dye sensitized solar cells. However, further improvement of the conversion efficiency of QDSCs is still a major issue for their application. Recently, tailoring electronic properties of the counter electrode(CE) in QDSCs using different materials has been considered as a promising way to improve photovoltaic performance of QDSCs. This article reviewed the quite recent progress of CE in QDSCs based on synthesis method, surface microtopography and crystal structure. This review gave a panorama of metal chalcogenides, composite materials, hybrid materials, muti-component metal chalcogenides, conductive polymers, and carbon CE materials for QDSCs, while the influence of CE materials on the charge transfer impedance, the electron transport process, catalytic properties, and I-V characteristics was stressed in detail. Finally, an outlook on the future challenges and prospects of novel materials as the CE for QDSCs were also briefly put forward.
|
|
|
Electrochemical Behavior of Sb-Si Nanocomposite Thin Films as Anode Materials for Sodium-ion Batteries
XIAO Na, PANG Yang, SONG Yun, WU Xiao-Jing, FU Zheng-Wen, ZHOU Yong-Ning
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 494–500
 Abstract
Abstract(
721 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(1803KB)(
1536
)
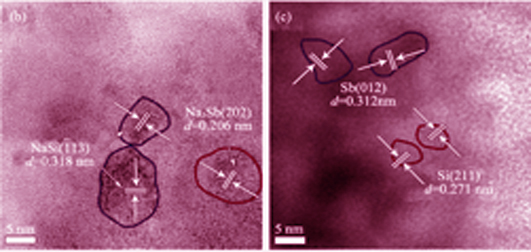
Recent years, alloy attracted significant research interest as anode materials for room temperature sodium-ion batteries, due to its high specific capacity and low cost. Among them, the study of Si-based alloy anodes are very limited, owing to the low electrochemical reactivity of Si with Na ions. In this study, Sb-Si nanocomposite thin films were successfully prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Their electrochemical performance and reaction mechanism were studied as new anode materials for sodium ion batteries. They exhibited a reversible specific capacity of about 0.011 mAh/cm2 (corresponding to 270 mAh/g) over 100 cycles at a rate of 10 μA/cm2, which is much higher than those for pure Si or Sb thin films prepared under the same condition. The investigation of electrochemical reaction mechanism reveals that Na3Sb and NaSi nanocrystallines are formed after discharge, due to the alloying reaction between the Sb-Si films and Na. During the recharge process, Na3Sb and NaSi phases both decompose and form Sb and Si nanocrystallines again, respectively. It is proposed that heterogeneous grain boundaries existing in the Sb-Si nanocomposite thin films are benefical to Na-ion transportation, thus enhance the electrochemical performance of the nanocomposite thin film electrode.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Supercapacitor Property of Ni-doped Co3O4 Nanowire Array
WANG Jun-Xia, ZHAO Jian-Wei, QIN Li-Rong, ZHAO Bing-Ling, JIANG Zheng-Yan
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 501–506
 Abstract
Abstract(
738 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(1027KB)(
1094
)
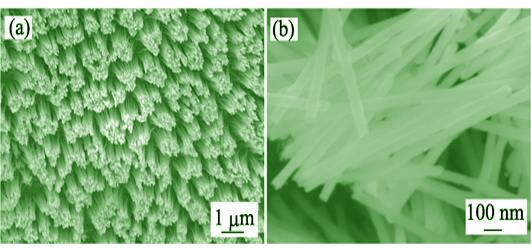
The novel Ni-doped Co3O4 nanowire array was synthesized successfully by electrochemical deposition with the aid of anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) template, followed by oxidation at high temperature. The phase composition and morphology were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope and high resolution transmission electron microscope. The results show that as-prepared Ni-doped Co3O4 nanowire array perpendicular to the substrate displays highly uniform shape and size, with an average diameter of 80 nm and length of 1.4 μm. The nanowire with coarse surface is composed of small crystalline nanoparticles. Average atom ratio of Co to Ni in the nanowire is 20 : 1. Electrochemical characterization was performed using cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge-discharge in a 2 mol/L KOH aqueous solution electrolyte. The test results indicate that the Ni-doped Co3O4 nanowire array exhibits a specific capacitance of 173 mF/cm2 at current density of 10 mA/cm2, and a good cycling stability with 98% capacity retention over 1000 cycles. Excellent electrochemical performance can be attributed to the large specific surface area and the enhanced conductivity achieved by incorporating of Ni.
|
|
|
Preparation of Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cells Based on Hierarchical Structure ZnO Nanosheets
CHENG Hou-Yan, LUO Jun, HUANG Li-Qun, LI Jia-Ke, YANG Zhi-Sheng, GUO Ping-Chun, WANG Yan-Xiang, ZHANG Qi-Feng
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 507–514
 Abstract
Abstract(
624 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(647KB)(
892
)
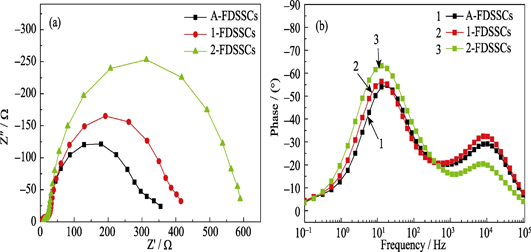
ZnO nanosheets/nanoparticles/microspheres composite photoanodes were synthesized in two steps. ZnO nanosheets photoanodes on Ti foil substrates were first prepared with hydrothermal synthesis method, on which ZnO nanoparticles and microspheres were deposited by using chemical bath deposition method. The corresponding photoanodes were assembled into flexible dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs). Effect of Ti foil substrates pretreatment methods and chemical bath deposition process on the properties of ZnO thin films and devices were mainly studied. Phase composition and morphology of Ti foil substrates and ZnO films were characterized with XRD, SEM and TEM. J-V curves of the FDSSCs were tested by solar simulator and Keithley 2400. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was also carried out to analyze the internal electronic transmission. The results show that when the Ti foil substrates were treated by using acid polishing, and the ZnO nanosheets were modified for 5 h by immersing in 0.15 mol/L methanol solution of zinc acetate after preheat treatment for 24 h, the FDSSCs displayed optimum performance. Its short circuit current density, open circuit voltage, fill factor and photoelectric conversion efficiency were 11.26 mA/cm2, 0.67 V, 0.60 and 4.51%, respectively.
|
|
|
Preparation and Visible Light Photocatalytic Property of g-C3N4/MoS2 Nanosheets/GO Ternary Composite Photocatalyst
YAN Xin, LU Jin-Hua, HUI Xiao-Yan, YAN Cong-Xiang, GAO Qiang, SUN Guo-Dong
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 515–520
 Abstract
Abstract(
983 )
 HTML
HTML(
27)
 PDF
PDF(1344KB)(
1380
)
The g-C3N4/MoS2 nanosheets/graphene oxide (GO) ternary composite photocatalyst was successfully prepared by a ball milling method. Its structure, morphology and optical property were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy (DRS), and photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), respectively. The results indicated that the heterogeneous structure of MoS2 nanosheets and g-C3N4 were formed on the surface of GO. The photocatalytic activity of the photocatalyst was evaluated by degradation of organic Rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irradiation. The ternary composite photocatalyst could degrade 96% of RhB within 120 min, about 3, 2.1 and 2.8 times higher than that of the g-C3N4, g-C3N4/MoS2 composite and g-C3N4/GO composite. Based on the experimental results and the band structure, a possible charge transfer mechanism of ternary composite photocatalyst was proposed.
|
|
|
Multicolor Upconversion Emission Tuning of NaY(WO4)2: Dy3+ via Er3+ Doping
SHI Zhong-Xiang, WANG Jing, GUAN Xin
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 521–527
 Abstract
Abstract(
625 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(844KB)(
1001
)
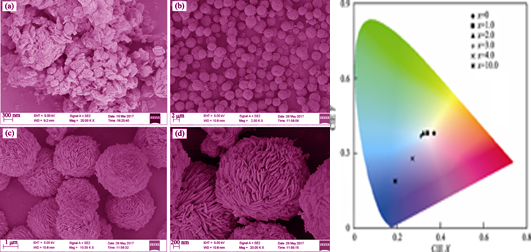
A series of Dy3+ and Er3+ co-doped NaY(WO4)2 phosphors were synthesized by hydrothermal reactions. X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope were used to characterize their crystal structure and morphology. The upconversion luminescent properties and the fluorescence lifetime of 4F9/2→6H13/2 transition of the Dy3+ ion were also investigated. Moreover, the energy transfer from Dy3+ to Er3+ ions in NaY(WO4)2 : Dy3+, Er3+ was analyzed in detail. The results indicated that all the samples had pure tetragonal crystal structure. Furthermore, the micrometer- sized needle spheres and excellent dispersion of the particles were obtained by adding polyethylene glycol (PEG-2000) as surfactant. Under near infrared light excitation at 780 nm, the NaY(WO4)2 : Dy3+, Er3+ samples exhibited blue emission at 480 nm (4F9/2→6H15/2 transition of Dy3+), yellow emission at 576 nm (4F9/2→6H13/2 transition of Dy3+) and green emission at 531 and 554 nm (2H11/2→4I15/2 and 4S3/2→4I15/2 transition of Er3+, respectively). The energy transfer process from Dy3+ to Er3+ is a resonant transfer, in which electric dipole-dipole interaction plays a leading role. By adjusting the doping concentration of Er3+ in NaY(WO4)2 : 1.0mol% Dy3+, xmol% Er3+ phosphors, conversion from quasi white light to blue light can be realized.
|
|
|
Influence of A-site Sm Doping on Structural and Electrical Property of 0.93Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-0.07BaTiO3 Lead Free Ceramics
DOU Run-Pu, LU Xiao-Peng, YANG Ling, WANG Hua, ZHOU Chang-Rong, XU Ji-Wen
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 528–534
 Abstract
Abstract(
671 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(2904KB)(
1426
)
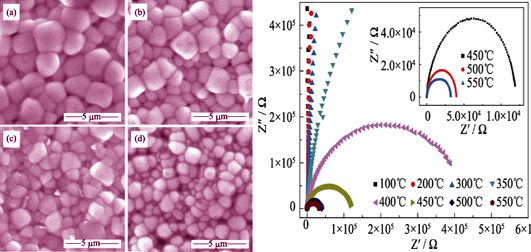
Sm doped [(Na0.5Bi0.5)0.93Ba0.07]1-xSmxTiO3 (BNBST) lead-free dielectric energy storage ceramics were prepared by solid-phase reaction sintering method. Effects of the Sm doping content on phase structure, microstructure, ferroelectric, dielectric, energy storage properties and d.c., and a.c. conductance of BNBST ceramics were systematically investigated. Results indicate that the as-fabricated BNBST ceramics exhibit single-phase perovskite structure, and Sm dopants get into the A-site lattice of (Na0.5Bi0.5)0.93Ba0.07TiO3 matrix. Dense and uniform grains are obtained by grain growth inhibition of Sm dopants with average grain size within 2 μm. The remanent polarization and coercivity of BNBST ceramics sharply decrease after introducing Sm dopants, and the double hysteresis loops are observed with a little decrease of saturation polarization. The energy storage density and efficiency increase firstly and then decrease with increasing Sm doping content, the energy storage density reaches a maximum value of 0.70 J/cm3 at x=0.02 and 70 kV/cm electric field, with corresponding efficiency of 40%. The BNBST ceramics show an obvious relaxation ferroelectric characteristic and its dielectric constant peaks of Tm decrease and planarize with increasing Sm doping content. The electric insulativity of BNBST ceramics has strong temperature dependence, and the excellent electric insulativity can be kept when ambient temperature is below 300℃.
|
|
|
Characterization and Electrical Property of Impurity Concentration in Ge-N Codoped SiC Crystals
LI Tian, CHEN Xiu-Fang, YANG Xiang-Long, XIE Xue-Jian, ZHANG Fu-Sheng, XIAO Long-Fei, WANG Rong-Kun, XU Xian-Gang, HU Xiao-Bo, WANG Rui-Qi, YU Peng
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 535–539
 Abstract
Abstract(
507 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(452KB)(
1013
)
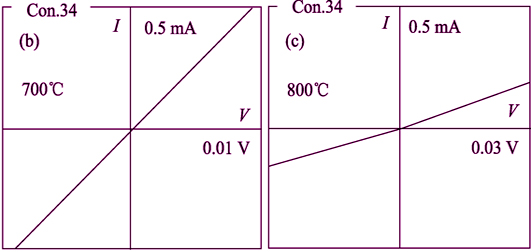
2-inch Ge-N codoped and Ge doped SiC single crystals were grown by physical vapor transport (PVT) method. And the SiC ingots were fabricated into 10 mm×10 mm SiC wafers for characterization. Semiconductor technology was used to fabricate Ti/Pt/Au metal contact on the carbide-terminated face of SiC wafers. Subsequently, all samples were characterized by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) and Hall measurements. The SIMS results showed that Ge-N codoping method could enhance the Ge doping concentration in SiC crystals effectively, which could achieve 1.19×1019 /cm3. According to Hall measurement, ohmic contact could be obtained when samples were annealed at temperature higher than 700℃ and the optimal annealing temperature was 700℃. In addition, the contact resistance of the heavy Ge doped sample was lower than that of the light doped one, indicating that the ohmic contact property could be enhanced by improving the Ge doping concentrations in SiC crystals. Furthermore, as the increase of Ge doping concentration, the mobility gradually decreased. It was ascribed to that the Ge-N atoms matched well with SiC lattice in codoping method leading to higher Ge doping concentration. Under that condition, the impurity scattering effect became evident, which resulted in a lower mobility for Ge-N codoped sample.
|
|
|
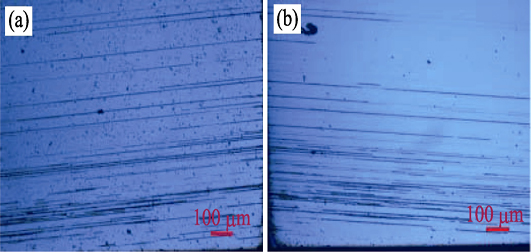
Stacking Faults in 4H-SiC Single Crystal
ZHAO Ning, LIU Chun-Jun, WANG Bo, PENG Tong-Hua
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 540–544
 Abstract
Abstract(
1533 )
 HTML
HTML(
30)
 PDF
PDF(364KB)(
1561
)
Thenitrogen doped and unintentional nitrogen doped 4H-SiC single crystals were grown by PVT method on the C-terminated 4H seeds offcut by 4° from the c-face towards the <11¯20> axis, respectively. Optical microscope was used to investigate the characteristic of stacking fault defects and the effects of nitrogen doped onstacking fault defects in 4H-SiC single crystals etched by molten KOH etching. The result shows that the lines of the basal plane dislocation defect of the 4H-SiC wafer surface are corresponding to stacking fault defects in 4H-SiC single crystals, and the direction of the lines is parallel to <1¯100>. There are more stacking fault defects in 4H-SiC single crystals doped with nitrogen than that of unintentional nitrogen doped 4H-SiC single crystals. This phenomenon is consistent with published literatures in which high concentrations of nitrogen caused the formation of stacking fault defects in 4H-SiC single crystals. However, there is no stacking fault defect in the facet area for nitrogen doped 4H-SiC single crystals, although the nitrogen concentration in the facet area is higher than that in the other area, which is presumably due to specific crystal growth habit in the facet area of 4H-SiC single crystal.
|
|
|
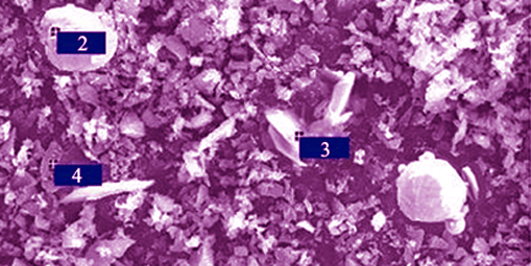
Ballistic Performance of B4C/Al2O3 Composite Ceramic Prepared by Reaction Sintering
SUN Chuan, WAN Chun-Lei, PAN Wei, ZONG Peng-An, LI Yun-Kai, ZHOU Shi-Meng
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 545–549
 Abstract
Abstract(
674 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(1492KB)(
1135
)
Dense B4C ceramic matrix composites were synthesized by reactive hot press sintering at the temperature of 1800℃ and the pressure of 35 MPa using commercial available B2O3, Al, graphite, and B4C as raw materials. Microstructure, phase composition and mechanical properties were observed and tested. The composite ceramics were penetrated by a 7.62 mm calibre armor-piercing bullet at restrained and unrestrained states. Then the protection factor was calculated according to the rules of DOP method. In comparison, the ballistic performances of AZ ceramic and monolithic B4C were also investigated. The results indicated that the main phase of the as-prepared sample was B4C (~70wt%) and the secondary phase was Al2O3. A complex intermediate phase contained Al-B-O was found filled in the holes between the main phase and the secondary phase. Density, hardness, bending strength and fracture toughness of the composite were 2.82 g/cm3, 41.5 GPa, 380 Mpa, and 3.9 MPa•m1/2, respectively. The fracture toughness significantly increased by 85.7s% as compared with that of the pure B4C (2.1 MPa•m1/2). The protection factor of the composite ceramic gets 11% and 70% increase compared to those of AZ ceramic and monolithic B4C, respectively. At restrained states, the protection factors of all the samples are further improved by about 10%. These results suggested that B4C/Al2O3 composite ceramic prepared by reactive hot press sintering method might be a good ceramic armor material.
|
|
|
Preparation of Spherical Alumina Powder by RF Thermal Plasma: Numerical Simulation and Experimentation
CHEN Wen-Bo, CHEN Lun-Jiang, LIU Chuan-Dong, CHENG Chang-Ming, TONG Hong-Hui, ZHU Hai-Long
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 550–556
 Abstract
Abstract(
895 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(2289KB)(
1010
)
Behavior of alumina powder particles in inductively coupled thermal plasma (ICTP) can provide theoretical reference and guidelines for improving preparation process of plasma spheroidization. In this study, the motion trajectories and heating process of alumina powder particles in ICTP were investigated by means of numerical simulation with FLUENT software. Then the plasma spheroidization experiment was carried out on the basis of simulation results, and the effect of input power, powder feeder rate and particle size distribution on alumina powder spheroidization were studied by combination of experimental and the theoretical analyses. The results show that the small particles absorb enough heat from thermal plasma and therefore be heated to completely melt. Furthermore, the particle can get more energy from plasma while the input power of system is increased or the powder feeder rate is decreased, which improve the spheroidization effect of alumina powder particles.
|
|
|
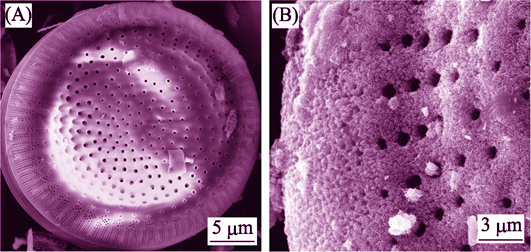
In-situ Growth of Nb2O5 Nanorods on Diatomite and Highly Effective Removal of Cr(VI)
DU Yu-Cheng, WANG Xue-Kai, HOU Rui-Qin, WU Jun-Shu, ZHANG Shi-Hao, QI Chao
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 557–564
 Abstract
Abstract(
640 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(1474KB)(
974
)
Nb2O5 nanorods decorated diatomite were synthesized via a hydrothermal method by using niobic acid, ammonium oxalate and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS). The as-prepared samples were characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, BET, and FT-IR techniques. The Nb2O5 nanorod was obtained with length of 500~700 nm and diameter of 25~35 nm. BET test showed that specific surface area of Nb2O5 nanorods decorated diatomite reached 157 m2/g which show a high adsorbance tendence. Under visible light irradiation, the adsorption capacity for Cr (VI) could be 220 mg/g. With the assistance of UV-light photoreduction, the maximum removal capacity for Cr (VI) could be 340 mg/g, and the absorbed Cr(VI) was transformed to Cr(III). After photodegradation for five times, the degradation rate of Cr(VI) (100 mg/L) were still at about 93%. Nb2O5 nanorods/diatomite could adsorb Cr(VI) from sewage effectively and in the meantime accomplish the toxicity degradation, showing a promising treatment of Cr(VI) containing waste water.
|
|
|
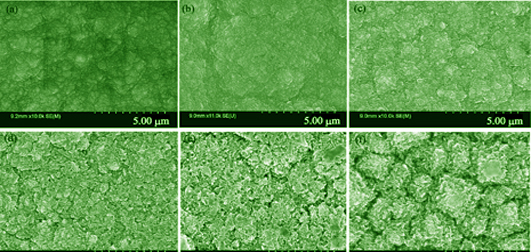
Nitrogen-doped Diamond Electrode Property and Anodic Catalytic Degradation of Nitrobenzene
YAN Shi-Sheng, PENG Hong-Yan, ZHAO Zhi-Bin, PAN Meng-Mei, YANG Da-Li, A Jin-Hua, YE Guo-Lin, WANG Chong-Tai, GUO Xin-Wei
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 565–569
 Abstract
Abstract(
694 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(4921KB)(
995
)
A series of nitrogen-doped diamond (NDD) film electrodes were synthesis by hot cathode direct current plasma chemical vapor deposition (HCDCPCVD) method with varied ratio CH4/H2/N2 gas mixture. Morphologies of diamond films were characterized by SEM. Electrical and electrochemical properties of nitrogen-doped diamond electrodes were characterized by Hall test and cyclic voltammetry. The results show that when the nitrogen flow rate is less than 30 sccm, the conductivity of the film increases slightly with the increase of the nitrogen flow rate. As the nitrogen flow rate continues to increase, the conductivity decreases rapidly, showing the maximum electro- conductibility of 5.091 S/cm. The nitrogen-doped diamond electrode has good voltammetric performance with a wide potential window and a low background current in acidic, neutral and alkaline media. Properties of anodic oxidation degradation of nitrogen-doped diamond electrodes were tested using nitrobenzene as target pollutant. In the supporting electrolyte of 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 solution, 0.5 mmol/L nitrobenzene is decomposed using the nitrogen- doped diamond as anode. After reaction for 300 min, degradation rate of the nitrobenzene reaches 94%, and COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removal rate is about 68%.
|
|
|
Preparation and Property of Nano-Ag/illite Composite Material
WANG Shu-Jiang, YANG Yong-Heng, WEN Chun-Yang, ZHANG Guo-Kui, YUAN Chun-Hui
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 570–576
 Abstract
Abstract(
623 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(546KB)(
956
)
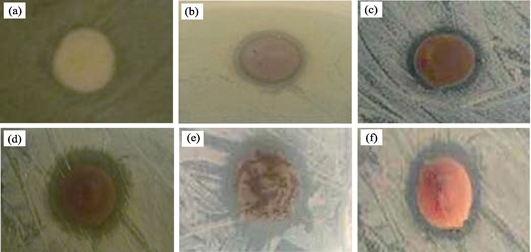
High-content nano-Ag/illite composite was prepared through procedure of hydrothermal modification of illite, microwave-assisted upload and ultraviolet lamp irradiation reduction of Ag. Its structure, morphology, particle size, and affinity of Ag and illite were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), infrared spectra (FT-IR), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and laser particle size distribution analyzer. The results showed that the modified illite became thicker due to the distracted layers, showing flower-like shape. In the meantime, the adsorption performance and ion-exchange capacity of modified illite obviously are enhanced. Through microwave-assisted upload and ultraviolet reduction of Ag, the uniformed Ag nano-particles were dispersed highly on the surface of illite and interacted closely to illite. Ag content in nano-Ag/illite composite is up to 27.66%. The antibacterial activities of nano-Ag/illite composites against Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli were investigated by the inhibition zone test. The results showed that this composite material had excellent antibacterial activity against both Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli, and the maximum antibacterial sizes were up to 5.68 mm and 6.84 mm, respectively. Furthermore, the unique lamellar structure and significant adsorption capacities of illite helped a lot to immobilize more bacteria and improved the antibacterial activity.
|
|
|
Preparation and Application of Water-soluble TiO2-ionic Liquids Hybrid Nanomaterials
ZHANG Jiao-Xia, YI Jing, JIAO Yue-Ting, LI Shi-Yun, SHI Xin-Lan, SUN Kai
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 577–581
 Abstract
Abstract(
738 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(815KB)(
899
)
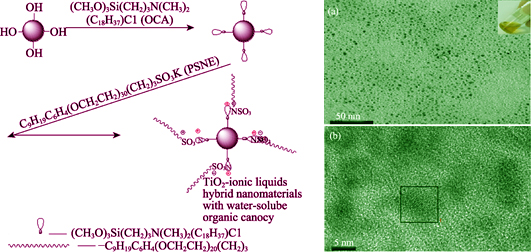
With unique electronic effect, TiO2 nanoparticles can be used as photocatalysts to reduce or eliminate the organic pollutants only under irradiation of sunlight. It is, therefore, highly desirable to improve its dispersion and solubility to broaden its application in different fields especially in environmental conservation. Here provides a case of two-step method to prepare yellow transparent water-soluble TiO2-ionic liquids hybrid nanomaterial. In this hybrid system, organic sulfonate groups as canopy provide “self-solvent” for the dispersion of the TiO2 nanoparticles. This dispersion experiment results indicated that the water-soluble organic canopy in the TiO2-ionic liquids hybrid nanomaterial offered good solubility in water and the TiO2-ionic liquids hybrid nanomaterials used in-home decoration could be easily wiped away on the surface of furniture. Data from photocatalytic degradation efficiency for decomposing formaldehyde demonstrated that the hybrid nanofluids possessed excellent photocatalytic performance. The water-soluble TiO2-ionic liquids hybrid nanomaterials could be a promising candidate for environmental conservation in the future.
|
|
|
Carbon Quantum Dots/BiPO4 Nanocomposites with Enhanced Visible-light Absorption and Charge Separation
ZHANG Zhi-Jie, XU Jia-Yue, ZENG Hai-Bo, ZHANG Na
2018 Vol. 33 (5): 582–586
 Abstract
Abstract(
876 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(542KB)(
1053
)
In this study, a CQDs/BiPO4 nanocomposite with enhanced visible-light absorption and charge separation was fabricated via a one-step hydrothermal reaction. The photocatalytic activity of the CQDs/BiPO4 nanocomposite was evaluated by degradation of rhodamine B (RhB). The result showed that the CQDs/BiPO4 composite exhibited superior photocatalytic performance to pure BiPO4 under simulated solar light, as well as under visible light irradiation. Its enhanced photocatalytic performance could be ascribed to the excellent light harvesting properties, which increased utilization rate of solar energy, electron transfer efficiency and reservoir ability of the nanocompsites, facilitating the charge separation efficiency of the composite.
|
|