|
|
Progress of Toughness in Dental Zirconia Ceramics
ZHU Dong-Bin, SONG Yan-Jun, LIANG Jin-Sheng, ZHANG Xiao-Xu, CHU Rui-Qing, WU Min-Qiang
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 363–372
 Abstract
Abstract(
855 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(1109KB)(
1734
)
Zirconia, attributable to high strength, toughness, hardness, and excellent wear resistance, as well as favorable biocompatibility, has been increasingly and widely applied to dental restoration. However, the phase transformation toughness of zirconia ceramics improves at the cost of service life deterioration. And zirconia ceramics may suffer failure and fracture after long-term mastication in the oral surroundings due to frequent changes in temperature and masticatory force, especially in the extremely complex biochemistry surroundings, such as fairly moist oral cavity and saliva. The research progress of zirconia ceramics in the field of dental restoration, toughening theories and their research state of dental ceramics were reviewed. This paper also summarized the issue of toughening degradation which is occurred in clinical application, and elucidated the mechanism and approaches. With the enhancement of comprehensive mechanical properties and the future demand for healthy functionalization, zirconia ceramics will be more widely applied in the biomedical field.
|
|
|
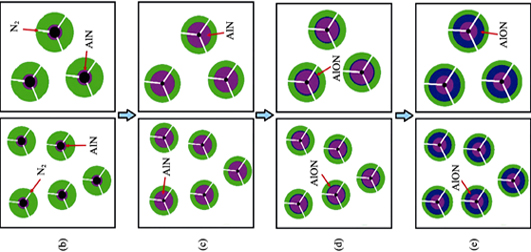
Nucleation Density on the Synthesis of AlON Powder and Preparation of Transparent Ceramics
XU Jian-Xin, SHAN Ying-Chun, WANG Guang, XU Jiu-Jun, WANG Liang, LI Jiang-Tao
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 373–379
 Abstract
Abstract(
850 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1320KB)(
1441
)
Aluminum oxynitride (AlON) powders were synthesized by carbothermal reduction and nitridation process using α-Al2O3 powder as starting material. Activated charcoal powder and submicron carbon powder were mixed with α-Al2O3 respectively to vary nucleation density of AlON. Influence of nucleation density on phase assemblages, morphology of AlON powders and transparence of AlON ceramics were studied. Single phase AlON powders were synthesized after holding at 1750℃ for 60 min with for both mixture powders of different nucleation density. The results show that the synthesized powders exhibit different morphology and milling property. The AlON powder synthesized by α-Al2O3 and activated charcoal mixture show irregular shape, loose structure and small particle size, due to its high nucleation density. Moreover, it is easier to mill the obtained AlON powder into small particle (0.93 μm). However, for the AlON powder synthesized by mixture of α-Al2O3 and submicron carbon powder, their grain grow obviously during the synthesis of the AlON powder, due to its low nucleation density with large near sphere particles close to 2.13 μm in diameter. Therefore, nucleation density plays a key role in controlling morphology, structure characteristics and milling performance of the AlON powders. Using the AlON powder synthesized by high nucleation density powders, high transparent AlON ceramics was fabricated by pressureless sintering at 1880℃ for 150 min, the maximum transmittance was ~76.5% (3 mm in thickness). It is 48.3% higher than that using AlON powder synthesized by low nucleation density powders. Therefore, for using α-Al2O3 as starting material to prepare AlON powder, high nucleation density is beneficial to AlON powder with small particle size and high sintering ability, which contributes to the high transmittance of AlON ceramics.
|
|
|
EBSD Analysis for Orientation Relationship of Textured ZrB2-SiC Ultra-high Temperature Ceramics
ZHENG Hai-Ya, MENG Chen-Xi, HU Dong-Li, GU Hui, LIU Hai-Tao, ZHANG Guo-Jun
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 380–384
 Abstract
Abstract(
921 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(615KB)(
1176
)
Textured ZrB2-ZrC ceramics sintered by spark plasma sintering were analyzed. The results obtained by SEM and EDS demonstrate the formation of an amount of resultant ZrC phase and trace level of ZrO2 and BN phases, due to the various reactions between starting powders and impurities. Compared with conventional methods in which TEM was used to analyze the orientation relationship between the phase and the primary phase, EBSD method in SEM can not only study the orientation relationship, but also study a large number of phase boundaries simultaneously to obtain statistical results, so as to avoid artificial selectivity. By using this method, three orientation relationships that may exist between ZrB2 and ZrC phases, i.e. (011¯0)||(111)&[21¯1¯0]||[101¯], (112¯0)||(2¯02)&[0001]||[111], and (1¯21¯0)|| (2 2¯0)&[0001]||[110] were checked. It is determined that there is no specific orientation relationship between the two phases in this study, inferring that the ZrC phase formed with a homogeneous nucleation mode rather than an epitaxial nucleation.
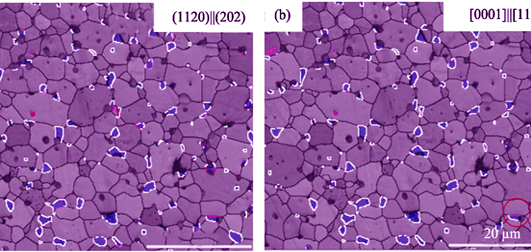
|
|
|
Preparation and Property of β-eucryptite Ceramics Possessing Zero Coefficient of Thermal Expansion with CaO-B2O3 Glass as Sintering Aid
YAO Xiao-Gang, REN Hai-Shen, JIANG Shao-Hu, ZHANG Yi, GU Zhong-Yuan, LIN Hui-Xing
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 385–389
 Abstract
Abstract(
621 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(555KB)(
979
)
β-eucryptite ceramics with zero coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) were prepared via solid state reaction method, adding CaO-B2O3 glass (CB glass) as sintering aid. The thermal property of CB glass and the crystalline phase, micro-structure of β-eucryptite ceramic samples were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), respectively. The results indicate that CB glass is a good sintering aid. It significantly decreased the sintering temperature of β-eucryptite ceramics (from 1300℃ to 1150℃) and increased the relative bulk density (from 93.3% to 97.5%). No micro-cracks were found in β-eucryptite ceramics aided with CB glass. β-eucryptite ceramics added with 4wt%, 6wt% CB glass possessed zero CTE of 0.02×10-6/K and 0.4×10-6/K ranging from room temperature to 200℃, respectively. However, a new phase LiAlO2 with extremely high positive CTE appears in the β-eucryptite ceramics added with 8wt% CB glass which leads to a positive CTE of 3.46×10-6/K.
|
|
|
Structure and Adsorption Property of Magnetic ZnFe2O4-halloysite Composite Material
SUN Qing, QI Qi, ZHANG Jian, PAN Fang-Zhen, SHENG Jia-Wei
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 390–396
 Abstract
Abstract(
597 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(699KB)(
982
)
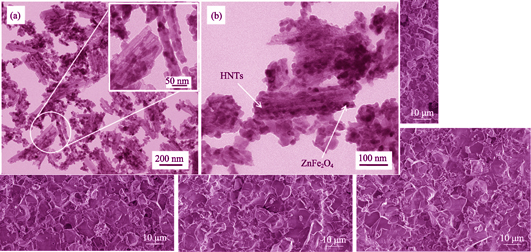
Magnetic ZnFe2O4/halloysite composite (MHNTs) was synthesized by Sol-Gel process and its sorption behavior towards methylene blue (MB) was studied. Structure, morphology and magnetic property of MHNTs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), fourier transfer infrared (FT-IR), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Static batch equilibrium method was used to investigate the adsorption behavior and mechanism of MB on MHNTs. The results show that ZnFe2O4 composites with 10~30 nm spinel type nanoparticles are well loaded on the surface of HNTs. The average grain size of nano-ZnFe2O4 is 19.1 nm calculated by Scherrer equation.MHNTs exhibit good paramagnetic and magnetic recovery properties. MB sorption of MHNTs follows pseudo-second order kinetic model and Langmuir thermodynamics model. MB sorption process is strongly affected by temperature, and higher temperature is beneficial for the adsorption of MB by MHNTs. Furthermore, MHNTs can be recovered effectively by magnetic field and the adsorption properties of MHNTs on 10 mg/L MB solutions hardly decreased after 5 times of repeated use.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Hierarchical Mordenite Zeolite
DAI Guang, XIAO Huan, HAO Wen-Ming, MA Jing-Hong, LI Rui-Feng
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 397–402
 Abstract
Abstract(
920 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(837KB)(
1111
)
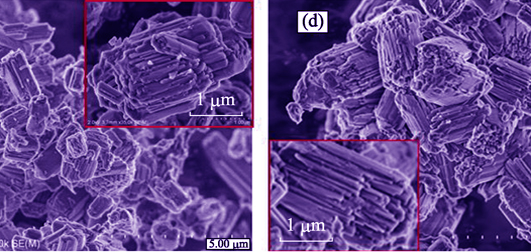
Hierarchical MOR zeolite nanocrystallines with mesoporous architecture composed of 2~4 nm pores were synthesized via a simple hydrothermal route by adding surfactant CTAB as mesoporous template in the absence of organic co-solvent and zeolite seeds, in which the mesoporous volume and external surface area could be adjusted by changing the amount of CTAB. The largest external surface area and mesoporous volume were 191 m2/g and 0.17 cm3/g. Adsorption of mesitylene on the MOR zeolitic samples showed that only a small amount of adsorption could be found in the microporous mordenite, but a large amount of adsorption in hierarchical mordenite which presented the characteristics of typical IV isotherm indicating a mesoporous structure. Catalytic properties of the MOR zeolitic samples were investigated by benzylation reaction of mesitylene and benzyl chloride. Compared with the traditional microporous mordenite, the reaction conversion on the hierarchical mordenite increased ~7 times and the reaction apparent rate constant increased ~19 times. This property is due to the expansive external surface areas and mesopores volume in the hierarchical mordenite zeolite which can effectively improve accessibility of the bulky reactants to acid sites and mass transfer rate of big products, and greatly promote the catalytic efficiency of bulky molecules.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Property of CaSi2O2N2:Ce/Tb, Eu Stacking Luminescence Fibers
CUI Bo, JIA Wei, CHEN Zheng-Hua, LI Yao-Gang, ZHANG Qing-Hong, WANG Hong-Zhi
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 403–408
 Abstract
Abstract(
509 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(1782KB)(
897
)
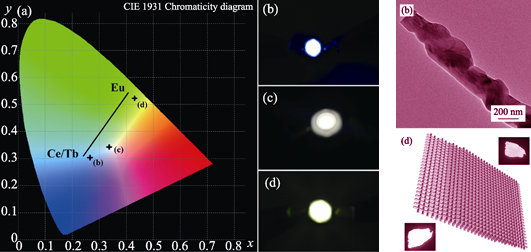
By adjusting composition of spinning solution and spinning time, CaSi2O2N2:Ce/Tb, Eu stacking fluorescent fibers for white LEDs were prepared through multi-step electrospinning and gas-reduction procedures. The obtained samples were characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, and PL. The obtained sample keeps fiber morphology, and assembles as film at macro level. TEM images show that the fluorescent fibers consist of nanocrystalline. XRD patterns demonstrate that CaSi2O2N2 crystal can be prepared through nitridizing at 1300℃ for 1 h, and its phase can be maintained after doping CeTb/Eu ions. Both sides of the CaSi2O2N2:Ce/Tb, Eu stacking fluorescent fiber mats emit different light under the N-UV excitation light. The Eu ion doping side exposed to the exciting light can effectively undercut the emitting light reabsorption process of the fiber-stacking mat. It demonstrates that white light will be emitted when CaSi2O2N2:Ce/Tb, Eu fluorescent fiber stacking mats are applied in a white light emitting diodes with N-UV chip.
|
|
|
Influence of Sulfur Anion Doping on Visible-light Photocatalytic Activity of NaTaO3
LIU Da-Rui
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 409–415
 Abstract
Abstract(
654 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(645KB)(
950
)
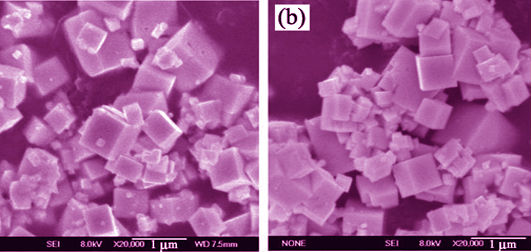
A novel NaTaO3-xSx catalysts were successfully synthesized by one-step hydrothermal method using Ta2O5 as starting material and Na2S2O3 as sulfur source. Its catalytic mechanism and reaction process were tested by degradation experiment. The samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XRS), UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (UV-Vis DRS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results showed that the as-prepared S-doped NaTaO3 did not display obvious variations to the surface charge and micro-morphology of NaTaO3. UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectrum analysis indicated that S2- partially substitute of O2- ions in the lattice to form Ta-S-Ta bonds, and the light response range of the doped NaTaO3-xSx samples extends to the visible region. The results of degradation experiment indicated that NaTaO3-xSx exhibited much higher activity than that of pure NaTaO3. The reason is that in the crystal lattice of NaTaO3-xSx, S2- ions replace part of the O2-ions, which form a mixed valence band energy levels. The results of GC-MS showed that the monohydroxylated species (m/z = 304) results in the production at m/z = 156, 226 and 276, which is further degraded into species of m/z = 212 and 156. Finally, the photogenerated oxidative species forming over S-doped NaTaO3 catalyst surface further decompose these intermediates into the final carbon dioxide and some non-toxic inorganic products (SO42-, NO3- and NH4+). In addition, in a ten-time recycling test, S-doped NaTaO3 displayed reliable recycling photocatalytic performance, whose photocatalytic efficiency kept at a high level and only existed very slight drop, due to the loss of photocatalyst during the reclaiming process.
|
|
|
Gamma-ray Radiation on Magneto-optical Property of Pb-doped Silica Fiber
WEN Jian-Xiang, WANG Wen-Na, GUO Qi, HUANG Yi, DONG Yan-Hua, PANG Fu-Fei, CHEN Zhen-Yi, LIU Yun-Qi, WANG Ting-Yun
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 416–420
 Abstract
Abstract(
643 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(637KB)(
795
)
Effect of gamma-ray radiation on magneto-optical properties of Pb-doped optical silica fiber before and after irradiation were investigated. The experiment results indicated that Verdet constants of the fiber samples at 660, 808, 980, 1310, and 1550 nm were 3.093, 1.676, 1.240, 0.705, and 0.538 rad/(T•m), respectively, larger than these of single mode fiber. Verdet constants decreased with the increase of wavelength. It increased by 20.82% at 660 nm. After the fiber samples being irradiated from 0.8 kGy to 5 kGy, Verdet constants of Pb-doped silica fibers increased with the increase of radiation dose. Especially, Verdet constant of Pb-doped silica fiber irradiated at 5 kGy is 41.94% larger than that of the un-radiation treated fiber, and increased by 33.04% for SMF with the same doses treatment. Verdet constant of the Pb-doped silica fiber can be increased by doping and radiation methods, which is of great significance in the field of current sensing.
|
|
|
In situ Pyrolyzed Carbon on the Property of AlN-based Microwave Attenuation Ceramics
HE Yong-Qin, LI Xiao-Yun, ZHANG Jing-Xian, LI Xiao-Guang
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 421–426
 Abstract
Abstract(
573 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(603KB)(
994
)
Carbon materials exhibit excellent microwave absorbing properties. However, it is difficult to disperse carbon homogeneously in the ceramic substrate. In this study, carbon was introduced into AlN matrix by addition of phenolic resin followed by pyrolysis process. The effects of phenolic resin content on sintering behavior, microstructure, thermal conductivity and dielectric properties of AlN ceramics were investigated. It was found that phenolic resin derived carbon could effectively promote the densification of AlN ceramics and reduce the sintering temperature. Relative density of the AlN ceramics reached 99.26% after sintering at 1700℃ with addition of 3wt% phenolic resin. In addition, it was found that the presence of phenolic resin derived carbon can effectively improve the thermal conductivity of the ceramics. The dielectric properties were also improved due to the carbon films formed in the pores and at AlN grain boundaries. With addition of 6wt% phenolic resin, AlN ceramics showed high thermal conductivity of 135.1 W/(m•K) and excellent microwave attenuation properties (the dielectric loss was 0.3 at X-band), which were perspective candidates for possible applications in high power microwave vacuum electron devices.
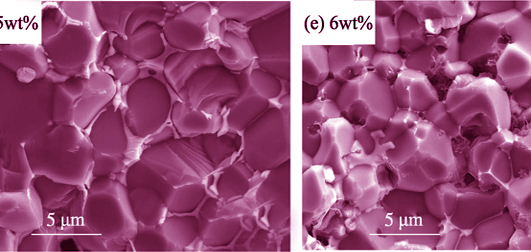
|
|
|
Comparison of High-temperature Dielectric and Microwave Absorbing Property of Two Continuous SiC Fibers
MU Yang, DENG Jia-Xin, LI Hao, ZHOU Wan-Cheng
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 427–433
 Abstract
Abstract(
773 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(1395KB)(
1132
)
Two kinds of SiC fibers with different microstructures were analyzed by XPS, XRD and Raman spectra. The electrical conductivities of the fibers were measured, and their dielectric and microwave absorbing properties at elevated temperatures were investigated. Research results show that KD-I SiC fiber with rich carbon layers possess higher complex permittivities and electrical conductivities than do SLF SiC fiber with Si-C-O phase, resulting in poor impedance match between free space and KD-I fibers. Simultaneously, due to poor dielectric loss of SLF fiber, two fibers display inferior absorbing performance with the reflection loss values of -3.2 dB and -0.3 dB at X band, respectively. With temperatures increasing, ε° and ε? of KD-I fiber sharply increase, while the complex permittivity of SLF fiber display a small increment. Complex permittivities of two fibers are up to 20.9-j25.0 and 5.0-j0.37 at 700℃. Microwave absorbing properties of two fibers degrade at elevated temperatures, mainly ascribed to deterioration of impedance match.
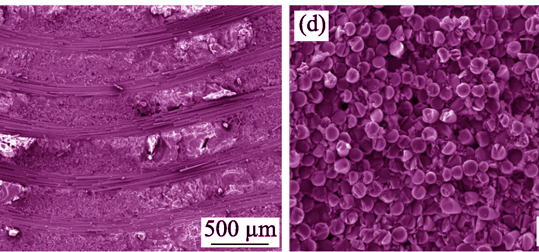
|
|
|
Annealing Temperature on Structural and Electrochemical Property of Mg-free La-Y-Ni Based A2B7-type Hydrogen Storage Alloys
WANG Hao, LUO Yong-Chun, DENG An-Qiang, ZHAO Lei, JIANG Wan-Ting
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 434–440
 Abstract
Abstract(
655 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(1017KB)(
974
)
Effects of annealing temperature on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of A2B7-type La0.33Y0.67Ni3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 hydrogen storage alloys were systematically investigated by XRD, SEM, EDS, and electrochemical measurements. Results showed that the alloy was composed of CaCu5-type, 2H-Ce2Ni7-type, 3R-Gd2Co7 -type and 3R-Ce5Cu19-type phases. Both abundance and unit cell volume of Ce2Ni7-type phase increased gradually with the anneale temperature increase when the annealing temperature was lower than 950℃. CaCu5-type and Gd2Co7-type phases disappeared at 950℃, but both abundance and unit cell volume of the Ce2Ni7-type phase maximized. When annealing temperature was higher than 950℃, Ce2Ni7-type phase decreased while Ce5Co19 type phase increased. The alloy, annealed at 950℃, had the lowest hydrogen desorption platform pressure (0.0192~0.087 atm), maximum hydrogen storage capacity (1.35wt%) and high electrochemical discharge capacity (371 mAh/g) with the maximum capacity retention S100 at 89% after 100 cycle. The high rate discharge ability (HRD) of the annealed alloys were significantly improved, the alloy annealed at 950℃ had the best performance and HRD900 was up to 83.4%. These well performances demonstrated that it is the hydrogen diffusion in the alloys that controls the high rate discharge.
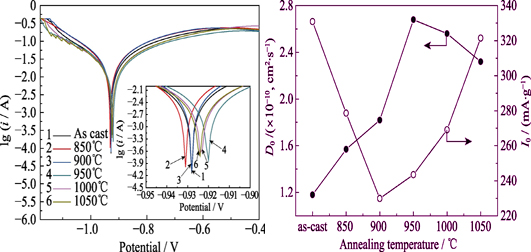
|
|
|
Performance of the Composite Cathode Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ-Ce0.9Gd0.1O2-δ for Medium-low Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
LUO Ling-Hong, HU Jia-Xing, CHENG Liang, XU Xu, WU Ye-Fan, LIN You-Chen
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 441–446
 Abstract
Abstract(
600 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(605KB)(
1065
)
Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ(BSCF) powder was prepared via Sol-Gel method. Porous BSCF-xGDC(x= 30wt%, 40wt%, 50wt%) composite cathodes were prepared via wrapping BSCF powders with Ce0.9Gd0.1O2-δ (GDC) sol. The phase composition of the composite cathodes, the morphology of the cross section of the cell, as well as the BSCF particles coated with GDC were characterized with X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy, respectively. The electrochemical performances of the composite cathodes were studied by impedance spectroscopy. The effects of the amount of GDC on the electrochemical performance of the composite cathode were studied by impedance spectroscopy. All results showed that the electrochemical performance of the composite cathode greatly improved. Electrode polarization resistance of the BSCF-40GDC was the minimum, with the value of 0.397 Ω•cm2 at 650℃. The maximum power density of the single cell was 0.514 W/cm2 with the values of Ohmic resistance at 0.257 Ω•cm2 and the polarization resistance at 0.0588 Ω•cm2, by using H2+3%H2O as fuel and air as oxidizing gas at 650℃.
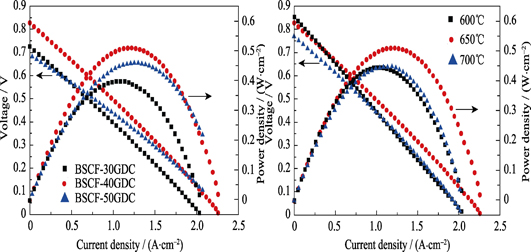
|
|
|
Ge-doping in TiO2-Nb2O5-CaCO3 Varistor Ceramics: Structure and Property
KANG Kun-Yong, XU Kai-Meng, LIU Can, YANG Xiao-Qing, ZHENG Zhi-Feng
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 447–452
 Abstract
Abstract(
497 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(565KB)(
1045
)
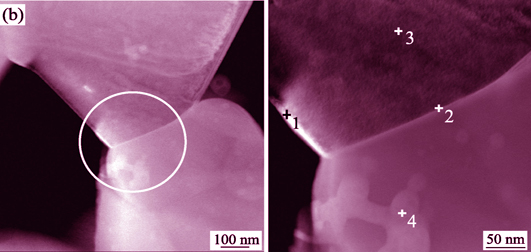
TiO2 varistors are typical electronic devices with nonlinear current-voltage property fabricated from TiO2 ceramics. This study investigated the influence of Ge doping on the nonlinear coefficient α and the breakdown electric field EB of TiO2-Nb2O5-CaCO3 varistor ceramics. TiO2-Nb2O5-CaCO3 varistor ceramics doped with Ge were successfully prepared by using traditional method of ball milling-molding-sintering. The electrical performance, including nonlinear coefficient α, breakdown electric field EB, and leakage current JL, was tested with a varistor-direct current-parameter instrument. Average barrier height ΦB of each sample was calculated by relevant formula. Analysis of X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and scanning transmission electronic microscopy demonstrated that Ge doping notably changed the microstructure of TiO2-Nb2O5-CaCO3 ceramics, thereby increasing α and decreasing EB. When Nb2O5 and CaCO3 doping content were 0.5mol%, the TiO2-Nb2O5-CaCO3 varistor ceramics doping with 1.0 mol% Ge exhibited high α (10.6), low EB (8.7 V/mm), and highest ΦB (1.73 eV), superior to previous published findings. Furthermore, Ge with low melting point as sintering aid could reduce the sintering temperature of the varistor ceramics, with optimal sintering temperature at 1300℃.
|
|
|
Preparation and Gas Sensing Property of SnO2/ZnO Composite Hetero-nanofibers Using Two-step Method
DU Hai-Ying, YAO Peng-Jun, WANG Jing, SUN Yan-Hui, YU Nai-Sen, ZHANG Tao, DONG Liang
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 453–461
 Abstract
Abstract(
786 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(2303KB)(
1325
)
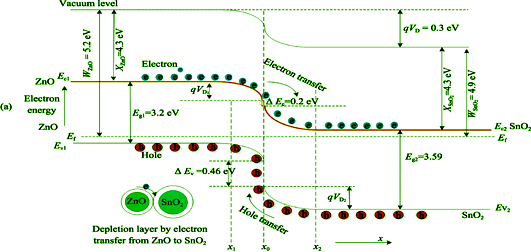
A two-step route was used to prepare SnO2/ZnO composite hetero-nanofibers. In the first step, hierarchical SnO2 nanofibers were synthesized by electrospinning; in the second step, ZnO nanospheres were fabricated in zinc acetate solution using water bath at 90℃. The morphology, structure and composition of SnO2/ZnO composite hetero-nanofibers were characterized and analyzed by XRD, SEM, EDX, and XPS. SnO2 nanofibers in the composite materials keep hollow and hierarchical structure with 300 nm in diameter. The diameters of ZnO nanospheres grown on SnO2 nanofibers are 250-300 nm. Gas sensing properties of SnO2/ZnO composite hetero-nanofibers were tested using a static gas testing system. Gas sensing properties of pure SnO2 nanofibers and ZnO nanospheres were also studied to compare their gas sensing properties. The results show that SnO2/ZnO composite hetero-nanofiber gas sensors exhibit excellent sensing sensitivity, selectivity and long-tern stability for (0.5-100)×10-6 acetone at 350℃. N-N homotype heterojunctions, existed in the joint between ZnO nanospheres and SnO2 particles in the SnO2/ZnO composite materials, change the potential barrier height. The absorption capacity of SnO2/ZnO composite materials increases greatly due to changes of the transport characteristics of electrons and holes, which results in the improvement of acetone sensing properties of SnO2/ZnO composite materials.
|
|
|
Influence of Electronic Conducting Additives on Cycle Performance of Garnet-based Solid Lithium Batteries
DU Fu-Ming, ZHAO Ning, FANG Rui, CUI Zhong-Hui, LI Yi-Qiu, GUO Xiang-Xin
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 462–468
 Abstract
Abstract(
1015 )
 HTML
HTML(
22)
 PDF
PDF(738KB)(
1568
)
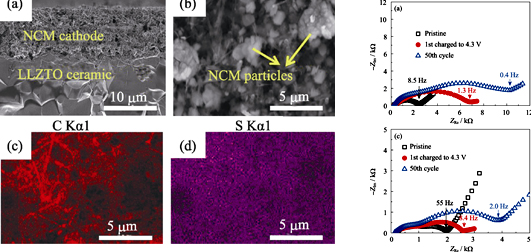
Solid state lithium batteries based on garnet-type solid electrolytes face the problem of contact between the solid electrolytes and the solid cathodes, which deteriorates the cycle performance. Aiming to overcome such problem, the solid state batteries with the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2-based cathodes, the Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12 ceramic electrolytes, and the lithium metal anodes were studied. For constructing the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2-based composite cathodes, three-kind carbons were used as electronic conducting additives. It is found that the batteries with cathodes containing vapor grown carbon fibers (VGCFs) show better cycle performance than those with granular Ketjen Black as well as Super P carbons. Analysis indicates that the VGCFs result in less side reaction at high charge potential than do other two electronic additives, leading to reduced carbonates that cause the increase of the internal cell resistance. These results suggest that stability of electronic additives has important influence on cycle performance of solid state lithium batteries.
|
|
|
Nafion Modified Graphene Aerogel with Hierarchical Porous Structures
WANG Yong, YU Yun, FENG Ai-Hu, JIANG Feng, HU Xue-Bing, SONG Li-Xin
2018 Vol. 33 (4): 469–474
 Abstract
Abstract(
1159 )
 HTML
HTML(
55)
 PDF
PDF(1766KB)(
1617
)
A novel graphene aerogel with pore size less than 1 µm was synthesized by Sol-Gel method, in which Nafion was skillfully introduced as modifiers connecting graphene oxides (GO). Ethylenediamine was used to produce a chemically linked graphene hydrogel during reducing process, which can then be freeze-dried to remove the absorbed water to form graphene aerogel. Nafion in GO solution prohibits the re-stacking of individual graphene sheets during reduction and freeze-drying process. By the above method, the pore size of as-prepared graphene aerogel could be effectively controlled within 1 µm, much less than that of the traditional graphene aerogel (20- 100 µm). The new graphene aerogel with unique structure exhibited excellent properties, such as high specific surface area, high porosity, and better electrochemical properties. All data suggest that this graphene aerogel may have promising application prospect in the field of energy.
|
|