|
|
Advances on Low-dimensional Perovskite Manganite Nanostructures
LI Lei, LIANG Li-Zhi, WU Heng, LIANG Shuang, ZHU Ying-Ying, ZHU Xin-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 337–344
 Abstract
Abstract(
792 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(507KB)(
1414
)
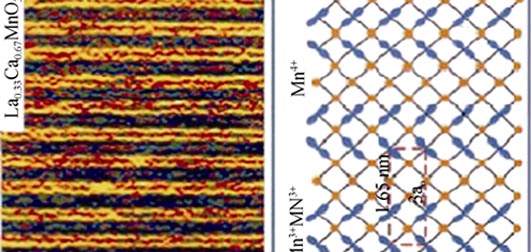
In the perovskite-type manganese oxides, multi-degrees of freedom such as charge, spin, orbital and crystal lattice coexist simultaneously, and the strong completing interactions among them result in a series of novel physical phenomena such as colossal magnetoresistance effect, giant magnetic entropy effect, metal-insulator transition, electronic phase separation and charge/orbital ordering, which make them become attractive issues in condensed matter physics. Advances in integration and miniaturization of the electronic devices have resulted in their feature sizes continued to be decreased, and now the feature sizes of electronic devices based on perovskite-type manganese oxides are down-scaled into nanometered sizes. At nanoscale perovskite-type manganese oxides exhibit apparent size effects and possess the electrical and magnetic transport properties that are different from their bulk and film counterparts, which have important applications in the fields of a new generation of microelectronic devices. In recent years, many advances have been made in fabrication, microstructural characterization electrical and magnetic property measurements of the low-dimensional perovskite manganite nanostructures, and also in the theoretical modelling of the resulting properties. In this paper, an overview of the state of art in the low-dimensional perovskite manganite nanostructures is presented. First, the microstructural characterizations of the low-dimensional perovskite manganite nanostructures are reviewed, and then the electronic phase separation and charge ordering phenomena in the low-dimensional perovskite manganite nanostructures are also introduced. Measurements of the electrical and magnetic transport properties at nanoscale are reviewed. Their potential applications in the fields of spintronics, the next-generation magnetic random access memories and gas sensors, are also discussed. Finally, some key problems in the future researches of the low-dimensional perovskite manganite nanostructures are also outlined.
|
|
|
Sintering Behavior and Electrical Conductivity of Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 with Li2O Additives
YANG Zhi-Bin, ZHU Teng-Long, XIANG Wen-Long, YU Li-An, HAN Min-Fang
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 345–350
 Abstract
Abstract(
848 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(472KB)(
1250
)
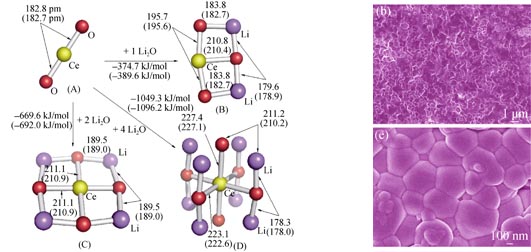
Cerium oxide-based materials are the most widely used electrolyte material for low-intermediate temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC). In this study, the interaction between Li2O and CeO2 was calculated based on density functional theory (DFT). The results showed that the sintering of CeO2 was positively affected by Li2O. Based on this result, the actual sintering process of Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 (GDC) with different concentration (0-5mol%) of Li2O additive was characterized through the sintering behavior and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The electrochemical performance was also being investigated simultaneously. The results show that the initial shrinkage temperature shifted to lower temperature significantly, and the temperature of the highest shrinkage rate also decreased with the increasing of the Li2O additive content. The shrinking of GDC with 2.5mol% Li2O started at 650 ℃, and the GDC electrolyte with higher than 99% relative density was obtained at a low sintering temperature of 900 ℃. The total electrical conductivity of GDC was improved with Li2O additive. Meanwhile, the open circuit voltage of the corresponding single cell maintained nearly the same with pure GDC. These preliminary results indicate that Li2O is a very effective sintering aid for cerium oxide-based electrolyte in SOFC.
|
|
|
Investigation of Porous Silicon/Carbon Composite as Anodes for Lithium Ion Batteries
HUANG Yan-Hua, HAN Xiang, CHEN Hui-Xin, CHEN Song-Yan, YANG Yong
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 351–356
 Abstract
Abstract(
1104 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
1954
)
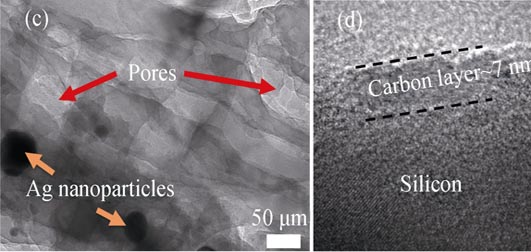
3D porous silicon was synthesized by metal-assisted chemical etching process using commercially available polycrystalline silicon powders. After chemical etching in optimized solution, 3D porous silicon structures with pore size of about 130 nm and specific surface area of about 4.85 m2/g was obtained. Subsequently, the 3D porous silicon powders treated with ball milling and heat carbonization processes were coated with amorphous carbon and utilized as the anode electrode material for lithium ion battery. The combination of the 3D porous structure and a carbon coating layer can accommodate large mechanical strains by providing the empty space of the pores to alleviate the volume change, and by increasing the electrical conductivity with the carbon layer. The electrodes achieve an initial charge capacity of 3345 mAh/g with coulombic efficiency of 85.8% as well as a high reversible capacity of 1645 mAh/g after 55 cycles at 0.4 A/g. And it is capable to retain a capacity of 1174 mAh/g even at 4 A/g. Thus, this work introduces a novel and easy potential industrial method for fabrication Si/C materials for high-performance lithium ion battery.
|
|
|
Dependence of the Texture on the Thermoelectric Properties of C/C Composites
HU Gang, ZENG Xie-Rong, MA Jun, ZOU Ji-Zhao, PENG Biao-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 357–362
 Abstract
Abstract(
597 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(551KB)(
1270
)
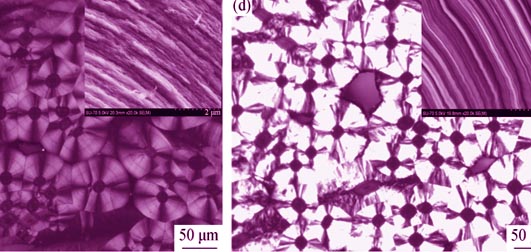
C/C composites with different microstructures were fabricated by microwave chemical vapor infiltration (MCVI) using carbon felt as fiber preform, CH4 as precursor gas and N2 as diluent gas. The different microstructures of C/C composites were characterized by polarizing microscope (PLM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectra. Thermoelectric properties were systematically investigated via thermoelectric performance testing instrument (ZEM-2) and laser thermal conductivity instrument (TC-9000H). The results reveal that positive Seebeck coefficient is obtained from C/C composites with different microstructures and an important relationship is existed between thermoelectric property and orientation of pyrocarbon. Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are increased gradually with the texture of pyrocarbon evolved from isotropy, low texture and middle texture to high texture. With the texture being reinforced, it has a more important influence on carriers than on phonons. As a result, the merit ZT is increased with the reinforce of the texture.
|
|
|
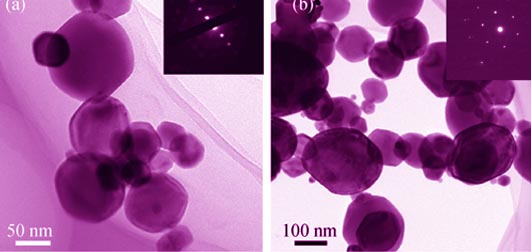
Preparation and Property of La1-xNdxB6 Cathode Material
LIANG Chao-Long, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Jiu-Xing, ZHANG Fan-Xing, WANG Yang
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 363–368
 Abstract
Abstract(
572 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(489KB)(
1251
)
High purity and high density La1-xNdxB6 bulks were prepared by using evaporation condensation combined spark plasma sintering (SPS) with high-purity metal La, Nd bulks and B powder as raw materials. Phase component, the mechanical properties, the resistivity and the thermionic emission properties of La1-xNdxB6 bulks were investigated systematically. The results show that high purity and high density La1-xNdxB6 single-phase bulk material can be prepared by using the above mentioned technology. The sintered samples show high value of Vickers hardness (26.70 GPa) and bending strength (230.48 MPa). According to the thermionic emission results, the bulk of La0.1Nd0.9B6 materials exhibits optimum thermal emission properties, the emission current density is 32.04 A/cm2 and zero field current density reaches 12.72 A/cm2 at the temperature of 1600℃ and the applied voltage of 4 kV, which is better than LaB6 and NdB6 bulk samples under the same conditions. It is shown that proper Nd content is benefit to reducing the work function and improving the thermionic emission properties, the average of effective work function for La0.1Nd0.9B6 at different temperatures is 2.72 eV.
|
|
|
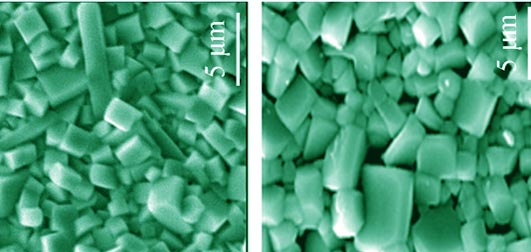
Effect of ZnO-doping on Sinterability and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3 Ceramics
LI Hai-Tao, LI Qian, YAN Yan-Fu, XU Rong-Hui
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 369–373
 Abstract
Abstract(
734 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
1350
)
The Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3 (CLST) ceramic nano-powder was prepared by Sol-Gel method. The influences of ZnO doping content and sintering temperature on sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of CLST ceramics were investigated. A phase transition from orthorhombic to pseudo cubic symmetry was identified by XRD analysis, and a impure phase was found in the x≥1.5 samples. The densification sintering temperature of the CLST+xmol% ZnO ceramics decrease with increasing ZnO doping content, and it reduces from 1300℃ to 1100℃ when the amount of ZnO doping increase from x=0 to x=1.0. The results also reveal that both the dielectric constant εr and the quality factor Qf possess a peak value with increasing ZnO doping content or sintering temperature, whereas the frequency temperature coefficient τf decrease monotonously. The x=1.0 sample sintered at 1100℃ for 2 h has optimal microwave dielectric properties: ρ = 4.85 g/cm3, εr = 102.8, Qf = 5424 GHz, τf =-8.2×10-6/℃, respectively, which indicates that the CLST ceramic doped with 1.0mol% ZnO is a promising microwave dielectric ceramic.
|
|
|
Application of Graphene Oxide in Synthesis of Sc2W3O12 Powder
JU Xiang-Wen, WU Ri-Min, ZHOU Ya-Zhou, MA Shuang-Biao, YANG Juan, CHENG Xiao-Nong
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 374–378
 Abstract
Abstract(
701 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1464
)
Cross-like Sc2W3O12 powder was synthesized via hydrothermal method by using scandium nitrate, ammonium tungstate hydrate as raw materials and graphene oxide as surfactant. XRD, TG-DSC, Raman and SEM were used to study the influence of graphene oxide on structures and morphologies of the as-prepared product, and the negative thermal expansion properties were detected by TMA. Results show that graphene oxide wraps the grain of Sc2W3O12 and inhibits the growth of some of the original crystal faces, which makes the grain grow to nanorods, then the nanorods assemble into cross-like structure. The pure cross-like Sc2W3O12 powder is obtained by hydrothermal method at 200℃ followed by heat treatment at 620℃ for 10 min. The TMA data indicate that the thermal expansion coefficient of Sc2W3O12 is -4.75×10-6 /K from room temperature to 800℃.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Property of Co3O4 and La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ Dual Layer
Coatings on SUS430 Steel
YANG Xiao-Long, TU Heng-Yong, YU Qing-Chun
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 379–384
 Abstract
Abstract(
559 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(515KB)(
1094
)
The cobalt for protective layer on SUS430 steel was firstly deposited by electroplating, and La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ for cathode contact layer was then prepared by screen printing. Co3O4 was used as sintering additives to improve sintering behavior of the contact layer. Dual layer coatings Co3O4 and La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ were formed by subsequent oxidation at 800℃ in air. The phases, morphology and element diffusion of the dual layer coatings were analyzed by XRD, SEM and EDS. The results show that the dual layer coatings achieve good bonding and adhesion, and effectively block chromium diffusion. The interconnect with dual layer coatings exhibits a low ASR value of 23 mΩ·cm2 after isothermal oxidation at 800℃ for 200 h. The dual layer coatings effectively improve the oxidation resistance and electrical properties of SUS430 steel substrate.
|
|
|
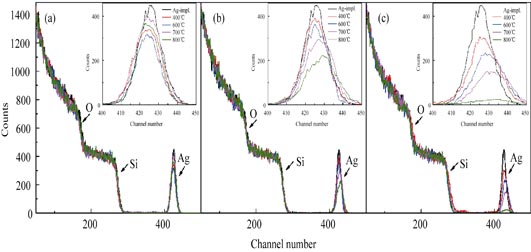
Effect of Annealing Atmosphere on Thermal Evolution of Ag Nanoparticles Embedded in SiO2 Thin Surface Layers
QIAO Yu, JIN Teng, YU Sheng-Wang, HE Zhi-Yong, SHEN Yan-Yan
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 385–390
 Abstract
Abstract(
717 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(523KB)(
1338
)
Silver nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized in thin surface layers of SiO2 glass by 70 keV implantation of Ag ions at a fluence of 5×1016 cm-2, and were then subjected to post thermal annealing in a temperature range of 400-800℃ at different atmospheres, e.g. Ar, N2, air. The evolution of surface morphologies, optical absorption properties, as well as compositions and structures with annealing temperature in different annealing atmospheres were studied by AFM, UV-Vis spectrophotometry and GXRD. The results clearly show that uniformly distributed Ag NPs are observed in Ar ambient samples, which have high particle density and intense optical absorption at 700℃. Similar optical properties are obtained in N2 annealed samples with larger Ag NPs. In contrast, the formation and decomposition of AgO significantly reduce optical absorption of air ambient samples. Moreover, the results of Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy reveal that the evolution of Ag particles should be ascribed to different diffusion behaviors of Ag atoms with variation of annealing temperatures and atmospheres.
|
|
|
Upconversion Luminescence of Er3+/Yb3+ Co-doped La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2 Glasses Prepared by Containerless Processing
ZHU Mei-Juan, YU Jian-Ding, ZHANG Ming-Hui, GU Yan-Jing, LI Qin, FANG Bi-Jun, ZHAO Hong-Yang, SHEN Qing
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 391–396
 Abstract
Abstract(
771 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(439KB)(
1264
)
Sphere transparent titanate glasses (La0.94-xEr0.06Ybx)(Ti0.95Zr0.05)2.25O6 (x=0-0.24, in steps of 0.04) were prepared by containerless processing. The DTA curve shows that the glass(x=0) has high glass transition temperature(Tg=818℃) and onset temperature of crystallization(To=906℃). The thermal stability and the glass forming ability decrease with the Yb3+ concentration increasing. Strong absorption bands at 975 nm are observed, showing effective absorption of Yb3+ at 975 nm. The transmittance is almost 70% in 300-3000 nm except characteristic absorption of Er3+ and Yb3+. Three emission bands centered at 535, 554, 672 nm are obtained at the excitation of 980 nm laser. When the Yb3+ concentration x is 0.16, the glass sample performs the strongest upconversion luminescence, which emission intensity at 672 nm is almost 130 times as high as that of Er3+-doped glass at room temperature.
|
|
|
Syntheses and Photoluminescence Properties of Eu2+/Tb3+ Doped
Sr2Si5N8 Phosphors
PENG Xia, LI Shu-Xing, LIU Xue-Jian, HUANG Yi-Hua, HUANG Zheng-Ren, LI Hui-Li
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 397–400
 Abstract
Abstract(
847 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(675KB)(
1242
)
Eu2+/Tb3+ doped Sr2Si5N8 phosphors were prepared by carbothermal reduction and nitridation method. The luminescence of Tb3+/Eu2+ co-doped Sr2Si5N8 were investigated. The experimental results indicated that owing to spin-allowed f → d transition rule the four emission lines located at 490, 543, 585, and 623 nm which ascribed to the 5D4→7Fj (j = 6, 5, 4, 3) transitions were observed under 330 nm excitation. No obvious changes in spectral line shape were observed for Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+ co-doped with Tb3+. However, the emission intensity was improved by about 20% with Tb3+ doping concentration of x = 0.01 mainly because of the electric multipole energy transfer from Tb3+ to Eu2+.
|
|
|
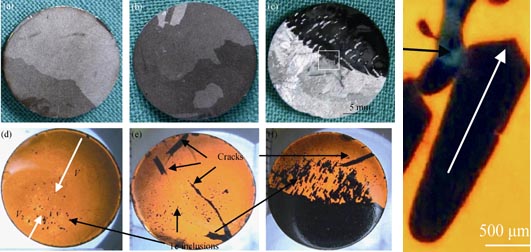
Characterization of Cr-doped ZnTe Crystals Grown by Temperature Gradient Solution Growth (TGSG)
YANG Rui, JIE Wan-Qi, SUN Xiao-Yan, YANG Min, HU Huan, LIN Yun
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 401–407
 Abstract
Abstract(
648 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(541KB)(
1249
)
Cr-doped ZnTe ingot was grown by temperature gradient solution growth (TGSG), using CrTe and Te as dopant source and solvent, respectively. Single crystals in the head of the ingot have larger size of more than 10 mm× 10 mm and less Te inclusions. The size, shape and distribution of Te inclusions well reflect the thermal field distribution of the ingot. Radial asymmetric thermal field of the ingot leads to radial asymmetric distribution of Te inclusions. The thermal migration of Te inclusions under thermal gradient results in their merging, enlargement and enlongation. Defects such as cracks and voids can be introduced into ZnTe matrix by Te inclusions. Some excess amount of CrTe is rejected by the advancing interface, which indicates that the present growth method has self purification effect. The resistivity of Cr-doped ZnTe ( about 1000 Ω·cm ) is slightly higher than that of ZnTe (about 300 Ω·cm). Cr-doped ZnTe exhibits an absorption centered at about 1750 nm, which means Cr2+ ions are successfully incorporated into ZnTe. IR transmittance of Cr-doped ZnTe is lower than that of ZnTe, which can be attributed to defects caused by Cr doping
|
|
|
Synthesis of α-MoO3 Nanobelt and Its Photocatalytic Oxidative Desulfurization(Photo-ODS) Activity of Simulation Fuel
ZHEN Yan-Zhong, LI Jing, WANG Dan-Jun, FU Feng, XUE Gang-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 408–412
 Abstract
Abstract(
892 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(484KB)(
1551
)
1 D α-MoO3 nanobels were prepared by facile hydrothermal synthesis. Phase, morphology, purity and optical adsorption properties of as-synthesized samples were investigated by XRD, SEM, TEM, EDS and UV-Vis-DRS spectra. Furthermore, thiophene was selected as a typical pollutant of simulated fuel to evaluate the photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization (Photo-Cat-ODS) activity of as-prepared 1 D α-MoO3 nanobelt and the mechanism for the photocatalytic oxidation of thiophene was explored. The photocatalysis experimental results indicate that photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization activity of 1 D α-MoO3 nanobelts is better than that of purchased MoO3 and P25 due to their reducing recombination of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. The desulfurization rate of simulated FCC fuel reaches 86.9% under visible light irradiation for 240 min.
|
|
|
Preparation and Property of Oxygen-deficient Bi2WO6-x Photocatalyst Active in Visible Light
LU Qing, HUA Luo-Guang, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen, LIN Bi-Zhou
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 413–419
 Abstract
Abstract(
1054 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(502KB)(
1757
)
Oxygen-deficient Bi2WO6-x catalyst was prepared in situ by a solvothermal method using ethylene glycol as the solvent. The physicochemical properties of the as-prepared catalyst were characterized by XRD, SEM, N2 isothermal, XPS, ESR, UV-Vis DRS, PL and electrochemical analyses. The photocatalytic activity of catalysts was evaluated by the degradation of gaseous benzene under visible-light irradiation (λ > 400 nm). The results indicate that the oxygen-deficient Bi2WO6-x with a larger specific surface area possesses Bi-Ov and W-Ov oxygen vacancies. The formation of oxygen defects narrows optical bandgap of Bi2WO6 and hinders photoinduced electron-hole pairs from recombination, which enhances the photocatalytic activity. The conversion and mineralization rates of benzene on the as-prepared Bi2WO6-x are increased up to 52.5% and 80.6%, respectively, which are correspondingly 1.72 and 1.84 times as high as those on the pristine Bi2WO6.
|
|
|
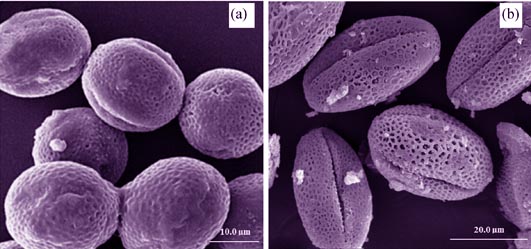
Preparation and Catalytic Property of ZnAlCe Ternary Complex Oxide Porous Materials Based on Rape Pollen Biotemplates
DUAN Sheng-Cong, MENG Zi-Zhen, XIE Jing, CHEN Chun-Xia
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 420–426
 Abstract
Abstract(
585 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(643KB)(
1450
)
Porous ZnAlCe ternary composite oxide was successfully prepared by a simple and mild technology based on microwave-crystallization and co-precipitation through in situ growth and calcination using rape pollen as biotemplate and LDHs as precursors. Morphology and structure of the as-prepared sample were characterized by SEM, FT-IR, XRD, EDX, XPS and N2 adsorption and desorption analysis. The results show that the synthesized ZnAlCe ternary composite oxide can copy micro and nano structure of the rape pollen surface and form hierarchical holes with the pore size within 2-150 nm, between mesoporous and macroporous, and the specific surface area at 112.94 m2/g. Moreover, ZnAlCe ternary complex oxide has good crystallinity and crystal structure. The porous complex oxide ZnAlCe was then applied to catalyze α-pinene oxidation using 30wt% hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. It is showed that the α-pinene conversion rate reaches 61.81%, and the selectivity of 2, 3 epoxypinane, verbenol, verbenone is 40.54%, 27.36% and 32.10%, respectively, under the α-pinene/H2O2 molar ratio of 1∶1.4 using 15.0 mg ZnAlCe as catalyst being dissolved in 2 mL ethyl acetate/H2O (volume ratio was 4∶1) at 30℃ for 4 h.
|
|
|
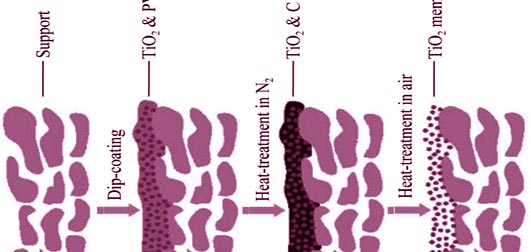
Preparation of Porous TiO2/Stainless-steel Membranes by Carbon Assisted Solid-state Particle Sintering
WEI Lei, HUANG Yan
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 427–431
 Abstract
Abstract(
759 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(442KB)(
1300
)
Porous ceramic membranes on macroporous metal support without any intermediate layer were prepared by a solid-state particle sintering assisted with carbon. Nano-scale TiO2 particle and macroporous stainless-steel tube were employed as membrane material and support, respectively. For surface coating, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was used as adhesive agent, and dip-coating procedure was performed. Effect of different sintering atmosphere (i.e., nitrogen and air) during the preparation of porous ceramic membrane was investigated. For characterization, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry and porometry analyses were conducted, respectively. It was found that serious peeling of the ceramic membrane was occurred when the coated sample was heat-treated in air, but an integrated membrane was achieved when the sintering atmosphere was replaced with nitrogen. Owing to the existence of carbon generated by the carbonization of PVA in nitrogen at high temperature, the mixed structure of TiO2 and carbon can help to weaken the membrane sintering stress which is caused by poor quality of the support surface and by mismatch of the thermal-expansion-coefficients of ceramic and metal. After the sintering of TiO2 particle, the generated carbon can be removed by heat-treatment in air, resulting in a porous TiO2/stainless-steel membrane. The membrane thickness and mean pore size are 10 μm and 0.21μm, respectively, and the corresponding nitrogen flux is 1.72 m3/(m2·h·kPa) at room temperature.
|
|
|
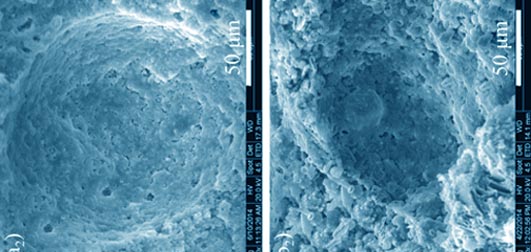
Mechanical Activation Reinforced Porous Calcium Phosphate Cement
HUANG Ping, LI Peng, ZHAO Jun-Sheng, QU Shu-Xin, FENG Bo, WENG Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 432–438
 Abstract
Abstract(
756 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(515KB)(
1238
)
Calcium phosphate cement (CPC) powder was activated by ball milling to improve the mechanical properties of porous CPC scaffolds. The mechanical activation mechanism was investigated by specific surface analyses, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). After ball milling, the average particle sizes of BCPC powder decreased while the specific surface area, apparent density, bulk density, and compact density increased when compared with non-activated CPC powder. The porosity and compressive strength of porous CPC scaffolds prepared from ball-milled powders (BCPC-S) were (77.98 ± 0.58)% and (4.11 ± 0.46) MPa, both significantly higher than those non-activated CPC powders (CPC-S), whose porosity and compressive strength were (64.23 ± 2.32)% and (1.99 ± 0.43) MPa, respectively. SEM revealed that there were two types of pores in the BCPC-S: one ranged a few microns in size and the other ranged several hundred microns. XRD indicated that grain sizes and crystallinities of dicalcium phosphate dehydrate (DCPD), α-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP), calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and hydroxyapatite (HA) in BCPC powder decreased, due to the mechanical activation compared to those of the non-activated CPC powders. In addition, the mechanical activation resulted in the conversion of DCPD to dicalcium phosphate anhydrous (DCPA), which promoted the hydration of CPC and the precipitation of HA, and improved the compressive strength of BCPC-S finally. This study provided a potential approach to improve the mechanical properties of porous CaP based scaffold to meet the clinic requirement.
|
|
|
Preparation of Polyhedral Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Molten-salt
Method and Their Catalytic Performance
ZENG Tao, BAI Yang, LI Hao, YAO Wei-Feng, DONG Xian-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 439–442
 Abstract
Abstract(
828 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(359KB)(
1245
)
Polyhedral copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles were successfully prepared by a molten-salt method without any surfactant or template. Scanning electron microscopy images of the copper oxide samples demonstrated that the as-prepared nanoparticles have a polyhedral structure. The catalytic performances of copper oxide on the degradation of Rhodamine B in the presence of hydrogen peroxide were investigated. The results show that the polyhedral copper oxide nanoparticles exhibited much better catalytic performance in the degradation of Rhodamine B with hydrogen peroxide than commercial nano particles, even with smaller specific surface area. The possible reason can be attributed to the synergistic effect of high crystallinity and the exposed facets formed by polyhedral structure.
|
|
|
Ultra-long VO2(B) Nanobelts : One-step Hydrothermal Synthesis and
Electrochemical Properties
YANG Xue -Mei, LIU Zhong -Ping, LI Xiao -Dong, Zhang Ze -Ming, JI Lan-Xiang, DENG Jian-Guo
2015 Vol. 30 (4): 443–448
 Abstract
Abstract(
727 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(479KB)(
1329
)
Ultra-long VO2(B) nanobelts were fabricated by a facile one-step hydrothermal treatment. It was found that the nanobelts were about ~200 nm in width and dozens of microns in length. Being used as a cathode material, the VO2(B) nanobelts show superior rate capability, with discharge capacities of ca. 425, 175, 125, 90, 75 and 50 mAh/g at 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 and 2000 mA/g, respectively. More importantly, excellent cycling stability without considerable capacity loss (10.41%) for 500 cycles is observed. The present study implied that the unique ultra-long nanobelts morphology and its intrinsic structural features are responsible for their excellent structure stability, and thus resulting in superior electrochemical performance.
|
|