|
|
Recent Progress in Research on CsI Thin Film Photocathodes
FAN Long, LI Yu-Kun, CHEN Tao, LI Jin, YANG Zhi-Wen, YUAN Zheng, DENG Bo, CAO Zhu-Rong, HU Xin
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 225–232
 Abstract
Abstract(
929 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(424KB)(
1836
)
Caesium iodide (CsI) thin films have attracted much attention due to good electron transport and emission properties in the soft X-ray and extreme ultraviolet range. With the rapid development of nuclear physics, high energy physics and astrophysics, the requirements for CsI film photocathodes become increasingly severe, and it is therefore of considerable interest to develop CsI photocathodes with high quantum efficiency (QE) and stable performance. However, the internal mechanisms of QE variation and photocathode aging are not entirely clear or certain up to date. In this paper, the recent progress on CsI film photocathodes is reviewed and some controversial issues are introduced. Several perspectives are also proposed in the end.
|
|
|
Electronic Structures and Optoelectronic Properties of
C/Ge-doped Silicon Nanotubes
YU Zhi-Qiang, ZHANG Chang-Hua, LI Shi-Dong, LIAO Hong-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 233–239
 Abstract
Abstract(
671 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(582KB)(
1200
)
The electronic structures and optoelectronic properties of C/Ge-doped single-walled armchair silicon nanotubes were determined by using first-principles calculations in the framework of density-functional theory. In particular, the calculated results indicate that both pure and C/Ge-doped silicon nanotubes display a direct band gap. The band gap is decreased firstly and then increased for the silicon nanotubes doped with C and Ge, respectively. Moreover, the upper of valence band is mainly contributed by the Si-3p states and the lower of conduction band is primarily occupied by the Si-3p states. The state dielectric constant is improved and the optical absorption shows a red-shifted for the C-doped silicon nanotubes, whereas the state dielectric constant is reduced and the optical absorption shows a blue-shifted for the Ge-doped silicon nanotubes. The results provide an useful theoretical guidance for the applications of single-walled armchair silicon nanotubes in optical detectors.
|
|
|
Effect of Iron and Copper Impurity Ions on Laser
Efficiency of Phosphate Laser Glass
XU Yong-Chun, CHEN Dan-Ping, LI Shun-Guang, HU Li-Li, TANG Jing-Ping
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 240–244
 Abstract
Abstract(
459 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(342KB)(
1187
)
The effect of impurity such as Fe and Cu ions on the optical loss and laser performance of N31-type Nd-doped phosphate laser glass was studied. It was found that the laser slope efficiency decreased in accordance with an e exponential function, and the laser threshold increased in quadratic with the increase of Fe concentration. Moreover, the empirical equations between concentration of Fe with laser slope efficiency and laser threshold were obtained. It also showed that laser efficiency was seriously influenced by Cu ion compared with that by Fe ion at the same concentration. The results are useful for improving the gain performance of laser glass and quantitatively control of the impurity in raw materials in the future.
|
|
|
Upconversion Luminescence of Er3+ Doped Chalcohalide Glasses and Its
Potential Application for Si Solar Cell Efficiency Enhancement
ZHANG Ji-Hong, TAO Hai-Zheng, GU Shao-Xuan, ZHANG Gao-Ke, LIU Chao, ZHAO Xiu-Jian
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 245–248
 Abstract
Abstract(
639 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(327KB)(
1120
)
Er3+ doped Ge-Ga-S-CsBr chalcohalide glasses were fabricated by melt-quenching method. The properties of upconversion luminescence under the excitation of 1550 nm laser were investigated. Strong green emissions centered at 525 nm and 545 nm, and weak red emission centered at 660 nm, were observed, along with near infrared emission bands centered at 810 nm and 980 nm. The up-conversion fluorescence was contributed to multi-photon involved process. The Si solar cell efficiency slightly increased from 7.28% (without upconversion layer) to 7.32% (using Er3+ doped 0.9(Ge25Ga10S65)-0.1CsBr glass as upconversion layer). The results show that the investigated Er3+-doped chalcohalide glasses has a potential application for the enhancement of Si solar cell efficiency.
|
|
|
Preparation and Thermoelectric Transport of Polycrystalline In4Se3
with High Figures of Merit
ZHAO Ran, MA Li-Min, GUO Fu, HU Yang-Duan-Rui, SHU Yu-Tian
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 249–255
 Abstract
Abstract(
756 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(553KB)(
1260
)
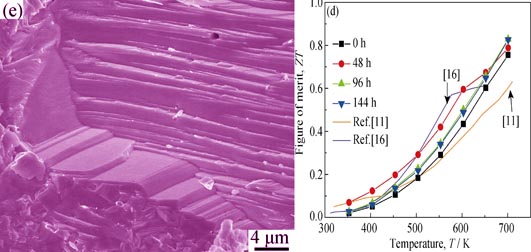
Polycrystalline In4Se3 thermoelectric materials were synthesized in the processing sequence of vacuum melting, annealing and spark plasma sintering. The effect(s) of melting and annealing duration periods on the phase, composition, microstructure, and thermoelectric properties of polycrystalline In4Se3 were investigated. After the melting process, both In and InSe phase were detected in the ingots. With increasing melting duration time, an increase in Se deficiency was observed, leading to an increase of carrier concentration, which contributed to the observed improvement of electrical conductivity. The specimen melted for 48 h showed relatively higher ZT. Thus on the basis of 48 h melting process, the ingots were then annealed for different periods of time, which eliminated the presence of InSe phase. After annealing, scattered large step-like structures were observed in the matrix, which favored the reduction of thermal conductivity but had no significant influence on the electrical conductivity. The ZT was significantly enhanced to 0.83 at 702 K by extending melting and annealing duration time to 48 h and 96 h, respectively, which is 32% higher than that reported in literature. It was concluded that both the extension of melting and annealing duration periods could improve the thermoelectric performance of polycrystalline In4Se3.
|
|
|
Interface Structure and Electrical Property of Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Mo-Cu Element Prepared by Welding Using Ag-Cu-Zn Solder
TANG Yun-Shan, BAI Sheng-Qiang, REN Du-Di, LIAO Jin-Cheng, ZHANG Lan-Ting, CHEN Li-Dong
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 256–260
 Abstract
Abstract(
1038 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(492KB)(
1599
)
The barrier layer of Ti-Al and the contact layer of Ni were joined to Yb0.3Co4Sb12 simultaneously by using spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique. The Mo-Cu electrode was then welded to thermoelectric element Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Ti-Al/Ni by using Ag-Cu-Zn alloy as solder. SEM results show that there are no cracks at the interfaces of Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Ti-Al/Ni/Ag-Cu-Zn/Mo-Cu thermoelectric joints. The EDS analysis shows that intermetallic compounds (IMCs) layer containing AlCo, TiCoSb and TiSb2 phases are formed at the interface between Yb0.3Co4Sb12 and Ti-Al. After thermal aging at 500℃ for 30 d, the inter-diffusions at both Yb0.3Co4Sb12/Ti-Al interface and Ag-Cu-Zn/Ni interface tend to be steady. The contact electrical resistivity of the Yb0.3Co4Sb12/ Ti-Al/Ni/Ag-Cu-Zn/Mo-Cu thermoelectric joints are about 6.1 μΩ·cm2 after welding, and it maintained as low as 10 μΩ·cm2 even after thermal aged for 30 d.
|
|
|
Thermoelectric Properties of Ba8Ga15XSi30 (X= Ga, Zn, Cu)
LIU Li-Hua, SONG Ben-Sheng, LI Feng, WANG Zhen, PAN Hao-Han, LI Yang
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 261–266
 Abstract
Abstract(
627 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(437KB)(
1126
)
A series of Ba8Ga15XSi30 (X=Ga、Zn、Cu) clathrate samples were prepared by combining arc melting, ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) techniques. The crystal structure and thermoelectric properties of all samples were studied. Compared with Ba8Ga16Si30, the lattice constant a decreases as one Ga is replaced by Zn or Cu. What’s more, thermal conductivity decreases and magnitude of Seebeck coefficient increases with Zn or Cu doping. Consequently, thermoelectric figure of merit ZT increases significantly.
|
|
|
Effect of Rare Earth Oxides on Electrical Properties of Spark
Plasma Sintered AlN Ceramics
HUANG Lin-Yun, LI Chen-Hui, KE Wen-Ming, SHI Yu-Sheng, HE Zhi-Yong, ZHANG Qi-Fu
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 267–271
 Abstract
Abstract(
823 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(433KB)(
1211
)
AlN ceramics doped with rare earth oxide (Sm2O3, Y2O3) were prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) in nitrogen atmosphere using AlN powder as raw materials. The effect of rare earth oxide on the phase composition, microstructure and electrical resistivity of AlN ceramics were investigated. The results showed that those sintering additives promoted densification through liquid-phase sintering. AlN ceramics with electrical resistivity values of 1×1010-1×1012 Ω•cm were obtained by precipitating rare earth aluminates as a conducting pathway at the grain boundaries. With the increasing of Sm2O3 doping, the phase of samarium aluminate gradually changed from Sm4Al2O9 to SmAlO3 which had a higher resistivity than Sm4Al2O9. 3wt% Sm2O3 doped AlN ceramics had the minimum resistivity of 1.32×1010 Ω•cm with the relative density of 99.33%. The yttrium aluminate phase gradually changed from Y3Al5O12 to Y4Al2O9 with the increase of Y2O3-doping. The electrical resistivity of different yttrium aluminates were about 1×108 Ω•cm. Y2O3- doped AlN sample with over 3wt% Y2O3 had an electrical resistivity about 1×1010 Ω•cm. 4wt% Y2O3 doped AlN ceramic had the electrical resistivity of 1.60×1010 Ω•cm with the maximum relative density of 99.08%.
|
|
|
Low Temperature Combustion Synthesis of TiC Powder Induced by PTFE
YU Yin-Hu, WANG Tao, ZHANG Hong-Min, ZHANG Du-Bao, PAN Jian-Feng
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 272–276
 Abstract
Abstract(
683 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(364KB)(
1492
)
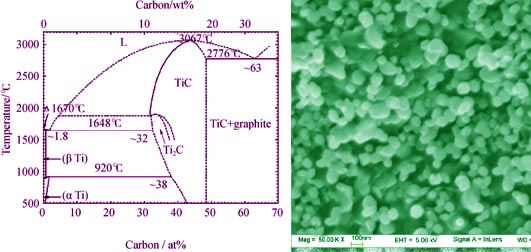
TiC powders were prepared at low temperature from the Ti-C system with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as a chemical activator. The reaction temperature, phase composition and morphology were determined via differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) to explore the reaction mechanism, respectively. The FESEM result shows that TiC powders with average particle size less than 100 nm are synthesized via low-temperature combustion synthesis at 530 ℃ by adding 3wt% PTFE into Ti-C system. Based on the most intensive diffraction peak (200) of the XRD pattern, the crystallite size of prepared TiC powders is calculated to be about 81 nm by the Scherrer formula, which is close to the average particle size observed from the FESEM image. It indicates that TiC particles consist of a single crystal as the result of fast, low-temperature, solid-state synthesis process. According to DSC results, the combustion synthesis mainly includes two reaction processes. Firstly, the initial reaction between titanium and PTFE particles releases a great amount of heat, and subsequently, the heat induced combustion reaction between titanium and carbon particles.
|
|
|
Effects of Heat-treatment Temperature on Properties of Co-continuous β-Si3N4 Reinforced Al Matrix Composites
LU Yuan, LI Jing-Long, YANG Jian-Feng, LI Peng
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 277–281
 Abstract
Abstract(
527 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(391KB)(
1213
)
The co-continuous β-Si3N4 reinforced Al matrix composites were fabricated through squeeze casting of porous β-Si3N4 preforms with porosity of 53.43% which obtained by pressureless sintering. The influences of heat-treatment temperature on the microstructures and mechanical properties of co-continuous β-Si3N4 reinforced Al matrix composites were investigated. With the heat-treatment temperature increase, the degree of interfacial reaction, dislocation density increase, and vickers hardness increases, while fracture toughness decreases, accompanied by flexural strength increasing until 850℃ and then decreasing. The fracture mode of composites changes gradually from ductile intergranular rupture to brittle intergranular rupture. When being heat-treated at 850℃, the composites obtain the optimum mechanical properties with the reaction layer of about 20-50 nm.
|
|
|
Oxidation-resistance of ZrB2-MoSi2 Composite Coatings Prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying
MAO Jin-Yuan, LIU Min, MAO Jie, DENG Chun-Min, ZENG De-Chang, XU Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 282–286
 Abstract
Abstract(
791 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(517KB)(
1479
)
Agglomerated ZrB2-MoSi2 composite powders with different contents of MoSi2 were successfully prepared by spray drying and vacuum sintering. Then ZrB2-MoSi2 composite coatings were deposited on C/C composites by atmospheric plasma spraying (APS) using ZrB2-MoSi2 composite powders with average size of 30 μm as raw material. The microstructure and anti-oxidation performance of coatings were characterized by XRD, SEM, etc. It could be found out that the microstructure of ZrB2-MoSi2 composite coatings was dense with bonding strength up to 7.2 MPa. And oxidation-resistance of composite coating at high temperature could be improved by appropriate addition of MoSi2. The weight loss of C/C composites coated by ZrB2-40wt%MoSi2 coating was only 1.7% after 9 h in air at 1500℃. The coating exhibited good self-sealing performance and excellent anti-oxidation ability.
|
|
|
Deposition and CMAS Corrosion Mechanism of 7YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings Prepared by Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition
ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, SONG Jin-Bing, DENG Chun-Ming, NIU Shao-Peng, DENG Zi-Qian
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 287–293
 Abstract
Abstract(
1293 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(505KB)(
24518
)
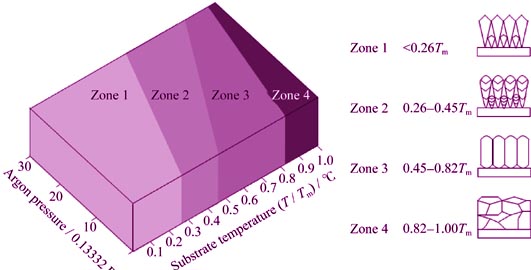
Using agglomerated and sintered ZrO2-7wt%Y2O3 (7YSZ) powders as raw materials, columnar thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) were prepared by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition (PS-PVD) at substrate temperature of 850 ℃. The microstructures of columnar coating were analyzed by field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM). Based on the theory of atoms together, the formation and growth process of 7YSZ nucleus were investigated and the deposition mechanism of columnar coating was also analyzed. Besides, under the temperature of 1200 ℃, the CMAS (CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2) corrosion of columnar 7YSZ coating was examined and its failure mechanism was also discussed. During the deposition process of columnar 7YSZ coating, the 7YSZ gas molecules were firstly absorbed on substrate, then through diffusion and migration, the critical nucleus formed rapidly. Besides, the critical nucleus further grew up forming crystal island by absorbing other molecules. Then after following four steps of island formation, union formation, channel formation and continuation, the columnar coating formed eventually. When above melting temperature, the CMAS could penetrate into porous columnar coating by capillary force and react with the 7YSZ coating. Finally, the cracks appeared in the coating due to thermochemical and thermomechanical interaction.
|
|
|
Synthesis of SAPO-34 Molecular Sieve Membranes by Steam-assisted Conversion Seeding and Their Characterization
ZHOU Liang, YANG Jian-Hua, WANG Jin-Qu, LU Jin-Ming, ZHANG Yan, YIN De-Hong
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 294–298
 Abstract
Abstract(
749 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(576KB)(
1131
)
A new seeding method, the steam-assisted conversion seeding, was used to prepare the high-quality SAPO-34 molecular sieve membranes by secondary growth method on the low cost macroporous α-Al2O3 supports. The seeds with different sizes of 2 μm, 1 μm, 500 nm, and 100 nm were mixed in the synthesis solution to prepare the seeds-containing pastes which was coated on the surface of the support. The effects of the particle size on the paste layers, seed layers and membranes were investigated. A perfect seed layer was formed and effectively modified the defects of the macroporous α-Al2O3 support and then, induced a continuous, compact and unconspicuousl pinholes SAPO-34 membrane. The SAPO-34 membrane displayed high performance in the pervaporation dehydration of 90wt% IPA/water mixtures at 348 K, showing water ?ux up to 1.396 kg/(m2·h) and separation factor at 973.
|
|
|
Tribological Performance of Sol-Gel Derived Superhydrophobic Film
WAN Yong, ZHANG Quan, LI Yang
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 299–304
 Abstract
Abstract(
594 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(519KB)(
1475
)
A simple two-step process was developed in this study to render aluminum with lower friction and superhydrophobicity. Alumina film was firstly fabricated on aluminum by Sol-Gel technology. Fatty acid was then deposited on alumina film to endow superhydrophobicity. The surface morphology of alumina film after treatment using boiling water or hydrazine solution was evaluated. The effect of molecular structure of fatty acid on the wettability of the composite film was investigated. Friction-reducing behavior of the superhydrophobic films on aluminum was determined in a ball-on-plate configuration. It was found that the stearic acid film on alumina film treated by hydrazine solution showed superhydrophobicity and low friction, leading to significantly extending lifespan of the alumina film.
|
|
|
Preparation and Glucose Sensing Property of Core-shelled Nikel
Oxide/Carbon Microspheres
CUI Zhen-Zhen, YIN Hao-Yong, ZHAO Hong-Ting, NIE Qiu-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 305–310
 Abstract
Abstract(
916 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(477KB)(
1411
)
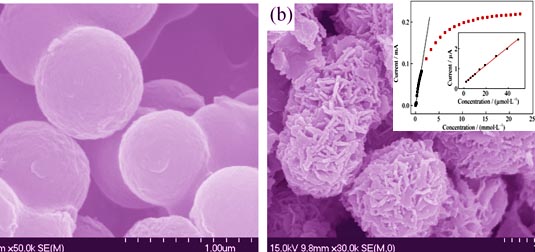
By using carbon spheres as a template, precursor Ni(OH)2/C were prepared by a hydrothermal synthesis technology with the reaction of hexahydrate nickel chloride and urea. And then the precursor was calcinated in pure nitrogen to obtain core-shelled NiO/C microspheres. Scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray energy dispersive (EDX), and the thermo gravimetric analyzer (TGA) were used to characterize morphology and structure of the samples. Results show that the NiO/C microspheres have core-shell structure with diameter around 1.4 μm, carbon sphere as the core, and cubic NiO nanoplates with thickness of 50 nm as the shell. Electrochemical behavior and sensing property of core-shelled NiO/C microspheres were studied via cyclic voltammetry and amperometric method. The results displayed that glucose sensitivity of the NiO/C is 31.37 mA/(mmol·L-1·cm2) better than that of NiO, among the linear range of 2-1279 μmol/L with detecting limit at 2 μmol/L. Furthermore, the core-shelled NiO/C microspheres exhibit good stability and anti-interference ability.
|
|
|
Rapid Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Nanorods at Low Temperature Controlled by Sodium Alginate
MA Li, ZHU Jian-Hua, HUANG Lei
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 311–317
 Abstract
Abstract(
751 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(578KB)(
1219
)
Hydroxyapatite (HA) nanorods with uniform morphology and high aspect ratio were prepared by hydrothermal method using alginate (SA) as controlling agent. The samples were characterized by XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM and TG/DSC to detect the effects of temperature and time on the crystallinity, composition and morphology of the final products. Meanwhile, the growth mechanism of HA nanorods was explored. Experiments showed that uniform HA nanorods with low organic composition could be well synthesized via hydrothermal method at 80°C after 24 h. Investigations on the microstructures of nanorods revealed that their growth could be divided into four stages: initial nucleation, surface regulation, continuous growth and oriented attachment.
|
|
|
Calcium Phosphate Cement Reinforced by Nanocrystalline Cellulose
ZHAO Jun-Sheng, QU Shu-Xin, HUANG Ping, LIU Zong-Guang, WANG Shi-Wen, WENG Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 318–324
 Abstract
Abstract(
771 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(642KB)(
1474
)
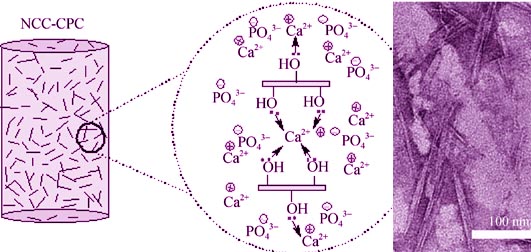
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) with favorable mechanical properties on the compressive strength of calcium phosphate cement (CPC). Compressive test, Gilmore needle test, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to analyze the physicochemical properties of CPC influenced by different contents of NCC. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and fluorescence microscope were used to observe the morphologies of CPC and the dispersity of labeled-NCC in CPC, respectively. NCC significantly increased the compressive strength of CPC up to about 27 MPa when the content of NCC was 2%. Setting times of CPC were prolonged with increased NCC, but still met the clinical requirements when the content of NCC was not more than 2%. XRD and XPS indicated that the combination of NCC with Ca2+ could form unstable coordination compound and NCC promoted the dissolution and conversion of dicalcium phosphate dehydrate (DCPD) and CaCO3. SEM showed that CPC became denser with fewer pores and cracks by addition of NCC. Fluorescence microscope demonstrated the homogeneous dispersion of labeled-NCC in CPC.
|
|
|
An Ionic Liquid-assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of CeO2 Nanorods
CHEN Ting, JIANG Wei-Hui, ZHANG Xiao-Jun, XIE Zhi-Xiang, LIU Jian-Min, JIANG Wan
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 325–329
 Abstract
Abstract(
881 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(394KB)(
1418
)
CeO2 nanorods were synthesized by a hydrothermal method at 160℃ from CeCl6·6H2O and NH3·H2O in the presence of an ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium chloride ([Bmim]Cl). The phase and morphology of the resulting products were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), respectively. The results reveal that morphology of CeO2 prepared in the presence of the ionic liquid is nanorod while it changes to irregular nanoparticle without ionic liquid. The resulting nanorods are about 13-25 nm in diameter and 200-500 nm in length. With the increase of ionic concentration, nanorods were disappeared gradually and nanoparticles were obtained. Moreover, increasing the hydrothermal temperature to 180℃, nanospheres at size of 19-24 nm could be synthesized by aggregation of ~2 nm nanocrystals.
|
|
|
Microwave Assisted Sintering and Photoluminescence Properties of Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+ Green Phosphors
HAN Bin, WANG Yi-Fei, LIU Qian, HUANG Qing
2015 Vol. 30 (3): 330–336
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(669KB)(
1330
)
Eu2+-doped Ba3Si6O12N2 green phosphors were prepared by microwave assisted sintering method at 1275℃ for 4 h, while the counterparts using conventional solid-state reaction method were synthesized at temperature higher than 1300℃ and for to 10 h. Microwave assisted sintering could reduce the activation energy and enhance the diffusion rate, thus greatly improved the sintering. Moreover, the influence of Si3N4 content on phase formation, morphology, absorption, and quantum efficiency, and photoluminescence properties of phosphors were studied. As a result, the Ba3Si6O12N2:Eu2+ samples sintered by microwave assisted sintering method have a higher phase purity and photoluminescence intensity under ultraviolet excitation as compared with samples sintered in the conventional tube furnace. The proposed method is a potential preparation method for the oxynitride phosphors with strong photoluminescence and high phase purity.
|
|