|
|
Hydrothermal Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Activities of Bi2MoxW1-xO6 Solid Solution
SONG Ji-Mei, HU Hai-Qin, WANG Xiu-Zhi, ZHAO Shao-Juan, SHI Ya-Li, REN Ming-Song
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1275–1280
 Abstract
Abstract(
1036 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(593KB)(
1204
)
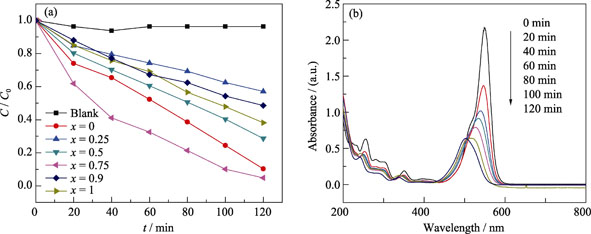
Bi2MoxW1-xO6(x=0~1) solid solutions were successfully synthesized via a facile hydrothermal method. The obtained products were characterized by X-ray diffraction, UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra and FT-IR spectrum. With an increase of Mo content, XRD patterns of the as-synthesized products show that the peaks at 2θ=33°, 47°, 56° gradually split, and the value of I(131)/I(200) gradually increases and then slowly decreases. FT-IR absorb band around 821 cm-1, which refered to the vibration frequency of the metal-oxygen band, is monotonically shifted to 842 cm-1. According to DRS calculations, the band gap of the samples are 2.75, 2.55, 2.50, 2.45, 2.59 and 2.63 eV when x is 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.9 and 1, respectively. This result demonstrates the formation of soluble solid solution. The photocatalytic activities of the products were evaluated by monitoring the degradation of RhB under visible light. It is found that, among solid solutions, the Bi2Mo0.75W0.25O6 exhibites the highest photocatalytic activity which mainly attributes to the special structure of solid solution and the lower energy band gap.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Red Emission of NaY(WO4)2 Phosphor with Lithium and Europium Dopants
LI Meng-Na, LEI Fang, CHEN Hao-Hong, SHI Ying, ZHAO Jing-Tai
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1281–1285
 Abstract
Abstract(
845 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(435KB)(
1219
)
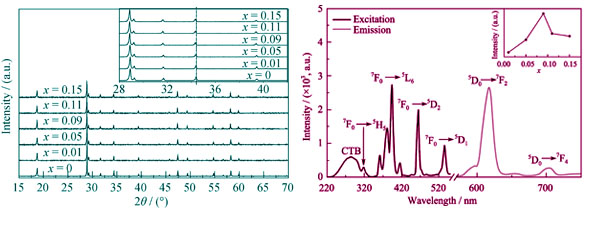
Li and/or Eu doped NaY(WO4)2 phosphors with red emission were synthesized by the solid-state reaction method and characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and ultraviolet-visible luminescence. Pure products were obtained at 1100℃ and maintained only in the range of about 100℃. Different from the reported phosphors obtained by combustion, the luminescence of the Eu3+ doped samples show the concentration quenching with the maximum emission intensity at 9mol%. The electric dipole transition of 5D0→7F2 of Eu3+ under 393 nm excitation dominates the emission spectra, which is good for overcoming the lack of red component in white light LED. Lithium doped does not change the preference but control the intensity of red emission. Appropriate concentration of lithium can improve the red emission but decrease while excess or deficient, and it takes the maximum red intensity at 30mol% Li doped. The tendency can be attributed to the competition between the effects of increasing lattice defect and the enhancement of non-centrosymmetry of Y atom site.
|
|
|
Mesoporous Tungsten Carbide Supported Pt and Their Electro Catalytic Activity for Methanol Electro-oxidation
HU Xian-Chao, HU Jian-Guan, SUN Jie, LI Guo-Hua
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1286–1290
 Abstract
Abstract(
1173 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(514KB)(
1152
)
Mesoporous tungsten carbide supported Pt nanoparticles (Pt/m-WC) with uniform size were prepared using hard template method and H2PtCl6 as the Pt precursor. The crystal phase, structure and morphology of products were characterized with X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), transmission electronic microscope (TEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectrocope (XPS). Results show that the tungsten carbide supporter has pure tungsten carbide phase with pore size of about 10-20 nm. Pt particles (3.4 nm mean size) which are mainly in the metallic form are dispersed on the external walls and pores of m-WC. The electro-catalytic activity of the prepared Pt/m-WC towards the oxidation of methanol was investigated using cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry. In comparison to the common tungsten carbide supported Pt catalyst (Pt/c-WC), the Pt/m-WC catalysts exhibits high electrocatalytic activity, strong anti-poisoning ability and good stability.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Characteristics of the Novel FeS2/VGCF Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries
LIU Ling, YUAN Zhong-Zhi, QIU Cai-Xia, Cheng Si-Jie, LIU Jin-Cheng
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1291–1295
 Abstract
Abstract(
1099 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(488KB)(
1835
)
FeS2/VGCF battery material was prepared by solid-state method using FeC2O4·2H2O, S and Vapor-Grown Carbon Fiber (VGCF) as the starting materials. The synthesized material was characterized by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), cyclic voltammograms (CV) and galvanostatic charge/discharge cycling tests. The result shows that the material of VGCF presents string centers. The discharge specific capacity of the FeS2 and FeS2/VGCF electrodes can reach 692 and 872 mAh/g at 0.1C in the voltage range of 1.0 to 2.6 V (vs Li / Li+), respectively. The FeS2/VGCF electrode can sustain 469, 417 and 254 mAh/g after 50, 100 and 200 cycles at 0.5C (1C = 890 mA/g), much higher than those of FeS2 prepared without VGCF (268, 71 and 28 mAh/g). Compared with FeS2, the cyclic capacity and stability of FeS2/VGCF are improved.
|
|
|
Inorganic Layer Coated Polyolefin Separator with High Performances for Lithium-ion Batteries
ZHAO Li-Li, ZHU Yong-Ping, WANG Xue-Ying
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1296–1300
 Abstract
Abstract(
1092 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(473KB)(
1304
)
Inorganic layer-coated separator was prepared by coating the sides of a porous polyolefin membrane with ZrO2 powder and polyvinylidene fluoride binder. The composite separator exhibits improved thermal stability at high temperatures without significant thermal shrinkage. Moreover, the separator has higher melt temperature. It is expected that the ZrO2-coated separator in this study can be potential candidate as a separator for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries that require thermal safety. Due to the high hydrophilicity of the ZrO2 powder and large surface area of the small particles, the separator shows good wettability in non-aqueous liquid electrolytes. Meanwhile, a higher amount of electrolyte solution is expected to be retained by the separator. By using the ZrO2-coated separator, lithium-ion cell was assembled and its cycling performance is evaluated. The cells are proven to be having better capacity retention than the cells prepared with polyolefin membrane.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Behavior in H2SO4 Electrolyte of Nano-Pb(PbO)/Activated Carbon
GAO Yun-Fang, SONG Yun-Long, REN Dong-Lei, WANG Yan-Ping
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1301–1306
 Abstract
Abstract(
851 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(445KB)(
1318
)
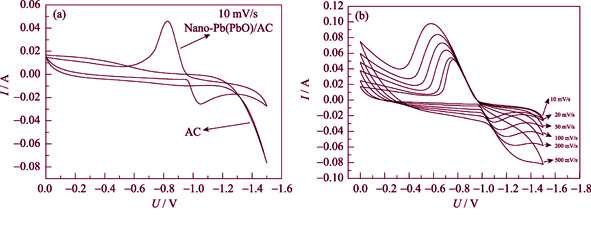
Nano-Pb(PbO)/activated carbon (nano-Pb(PbO)/AC) was prepared by the processes of adsorption of Pb2+, deposition of PbO and further reductive decomposition in the pores of activated carbon. The composite was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The results showed that Pb and PbO nano-crystals were dispersed uniformly on the surface of activated carbon particles. The electrochemical measurements in H2SO4 aqueous solution showed that nano-Pb(PbO)/AC possessed high over-potential of hydrogen evolution, high electrical conductivity, and could provid a certain degree of oxidation-reduction current. Moreover, there was less non-faradic capacitance loss. Ultra-battery was prepared by adding 5wt% of Nano-Pb(PbO)/AC to the negative paste. Initially, the battery was discharged to 60%SOC and then subjected to the test of cycling performance at high rate. The cycle life of the ultra-battery was 4 to 5 times higher than that of traditional lead-acid battery.
|
|
|
Effects of Ag Doping on the Electrical Properties of La2/3A1/3MnO3(A=Ca, Sr, Ba) Composites Materials
LIU Xiang, YAN Yi-Zhi, CHEN Qing-Ming, ZHANG Hui, CAO Ming-Gang, ZHANG Shao-Chun
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1307–1312
 Abstract
Abstract(
646 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(689KB)(
1110
)
La2/3A1/3MnO3:Agx(A=Ca, Sr, Ba, LAMO:Agx, x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, mol%) composites materials were prepared successfully by co-precipitation route. XRD results showed that the pure phase LAMO:Agx samples were obtained. By substitution of A site with Ag ion, the crystal lattice and cell volume were expanded slightly for LCaMO: Agx and LSrMO:Agx, but shrinked slightly for LBaMO:Agx R-T measurement results showed that the maximum temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) of LCaMO:Agx composites reached 28%/K as x=0.4, Tk=271.3 K (Tk: temperature at the maximum TCR value). SEM images showed that for LCaMO composites, the particle size were enlarged. The uniform, homogeneity and crystal quality were improved with increase of Ag doping. The TCR enhancement of LAMO:Agx composites are discussed by the microscopic mechanism with Ag doping.
|
|
|
Controls of Crystal Morphology, Size and Structure in Spontaneous Precipitation of Calcium Carbonate
YANG Ya-Nan, ZHU Xiao-Li, KONG Xiang-Zheng
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1313–1320
 Abstract
Abstract(
1081 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(706KB)(
1963
)
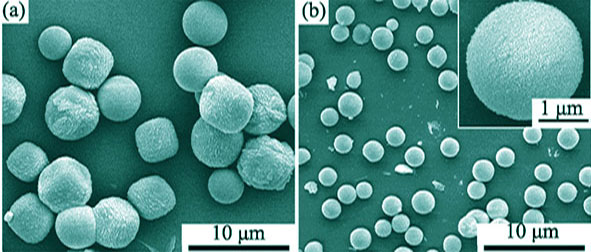
Nano- to micron-meter CaCO3 particles with different shape and crystal structures were prepared by adjusting the experimental conditions, including use of crystal growth inhibitors, concentrations of CaCl2 and Na2CO3, and dispersing methods. CaCO3 particles were characterized using electronic microscope, dynamic light scattering and X-ray diffraction. The results indicated that the nature and concentration of the crystal growth inhibitors had important effects on the morphology and crystal structure of the product. Without inhibitor, the product was of cubic blocks of about 4-5 μm, and cubic crystals were more uniform with ultrasonic dispersion than with mechanical stirring. However, crystal morphology and structures were easily altered by usage of crystal growth inhibitors. Using sodium triphosphate as the inhibitor, amorphous spherulites were usually formed, except at very low amount of the inhibitor where vaterite crystals were detected. With carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC) as the inhibitor, relatively uniform ellipsoidal particles, mostly calcite with small portion of vaterite spherulites of size about 3 μm, were observed, and the size of the spherulites changed with CaCl2 concentration. While using sodium polystyrene sulfonate (PSS) as the inhibitor, uniform crystal spherulites were easily obtained by adjusting concentration of the inhibitors and the reactants. Opposite to the case where CMC was used, the crystalline structure was mostly vaterite with calcite in small portion. Formation mechanism of CaCO3 particles in the presence of the inhibitors was discussed.
|
|
|
Growth of β-Co(OH)2 Nanoflowers on Carbon Nanotube Papers and Its Electrochemical Capacitance Performance
MEN Chun-Yan, SHI Qin, LI Juan, LI Qing-Wen
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1321–1327
 Abstract
Abstract(
1141 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(580KB)(
1160
)
Uniform hierarchical flower-like β-Co(OH)2 anchored on conducting carbon nanotube (CNT) papers were successfully synthesized by hydrothermal method, which could be served as flexible electrode material for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. The structure, morphology and properties of the products were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results indicated that the as-prepared material was pure brucite phase. Three dimensional (3D) loose nano-flowerlike structure with the diameter of about 3 μm were stacked by multilevel β-Co(OH)2 flakes. Electrochemical performances of this flexible paper-like electrode were investigated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge-discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy test in 6 mol/L KOH aqueous electrolyte. Electrochemical data indicated that the interesting β-Co(OH)2/CNT paper composite delivered a considerable specific capacitance of 2764 F/g at current density of 2 A/g. The CNT paper acted as a good conductive and flexible substrate for the composite electrodes in supercapacitors, and the hierarchical flower-like structure of the β-Co(OH)2 could facilitate the contact of the electrolyte. the β-Co(OH)2 nanoflower composite performed an obvious improvement of rate capacity and cycling stability, compared with pure phase β-Co(OH)2.

|
|
|
Preparation by MOCVD and Microwave Absorbing Properties of CF@Fe
LIU Yuan, LIU Xiang-Xuan, CHEN Xin, WANG Xuan-Jun
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1328–1332
 Abstract
Abstract(
667 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(502KB)(
1052
)
The CF@Fe composites were prepared by depositing precusor Fe(CO)5 on carbon fiber (CF) to form continuous α-Fe film through metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) process. The X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and a vector network analyzer were used to characterize the structure and electromagnetic properties of the powder and to study absorbing properties, The results showed that the film layer deposited on the surface of carbon fibers was pure α-Fe phase, at about 0.7 μm in thickness. After being deposited by consecutive α-Fe film, the CF electromagnetic properties changed significantly with the absorbing capacity being improved. By using electromagnetic parameters of the coaxial ring samples, the reflectance curves of the CF and CF@Fe coating at thickness of 2 mm were calculated, The curves showed that absorption peak of the samples deposited by the consecutive α-Fe film moved to the high frequency, the value of the minimum reflection peak reduced, and the bandwidth (less than -10 dB) increased 4.2 GHz.
|
|
|
Preparation and Microwave Absorption Properties of CB/PBO Composite
WANG Li, LUO Fa, LIU Li, ZHOU Wan-Cheng, ZHU Dong-Mei
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1333–1337
 Abstract
Abstract(
731 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(439KB)(
1306
)
TA salt was prepared by the solution of 4,6-diaminon1,3-benzenediol and terephthalic acid, and then copolymerized in PPA to get poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) (PBO) with good thermal resistance. Using as-prepared PBO as matrix, carbon black (CB) as absorber, CB/PBO composites were fabricated by hot pressing. Influences of CB weight concentration on complex permitivity and on thermal properties of CB/PBO composites were investigated. The results show that the real and imaginary parts of permittivity are increased with the increase of carbon black concentration. The reflectivity bandwidth and reflection loss lower than -10 dB are about 2.4 GHz and -32 dB, respectively, when CB weight concentration is 5% and the thickness of composite is 2 mm. The mass loss of PBO and CB/PBO composite are 11.84% and 21.99%, respectively, when kept at 450℃ for 5 h.
|
|
|
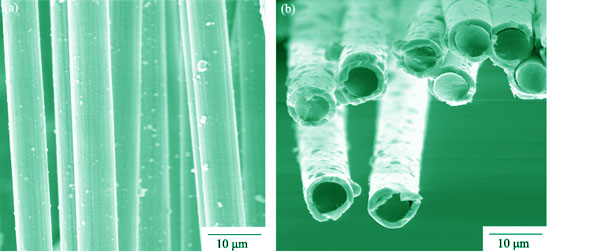
Preparation of 1D C/C Composites with High Thermal Conductivity
LIN Jian-Feng, YUAN Guan-Ming, LI Xuan-Ke, DONG Zhi-Jun, ZHANG Jiang, ZHANG Zhong-Wei, WANG Jun-Shan
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1338–1344
 Abstract
Abstract(
804 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1282KB)(
1226
)
Three kinds of pitches were used as matrix precursors, the self-fabricated mesophase (AR) pitch-based carbon fibers were used as the reinforcing agent, one dimension (1D) carbon/carbon (C/C) composites were prepared by a hot-pressing molding method at about 500℃ and subsequent carbonization as well as graphitization treatments. The influence of precursor pitches and heat-treatment temperatures (HTTs) on the thermal conductive properties of the C/C composites were investigated. The morphology and microstructure of graphitized C/C composites were characterized by scanning electron microscope and polarized-light microscope. The results show that both of the thermal diffusivities and the thermal conductivities of C/C composites along the longitudinal direction of fibers gradually increase with HTT. The C/C composite prepared by using AR pitch as a matrix precursor possesses obvious graphite-like layer structure, exhibiting the highest thermal conductivity. The room-temperature thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of the C/C composite treated at 3000℃ along the longitudinal direction of fibers are 734.4 W/(m·K) and 594.5 mm2/s, respectively.
|
|
|
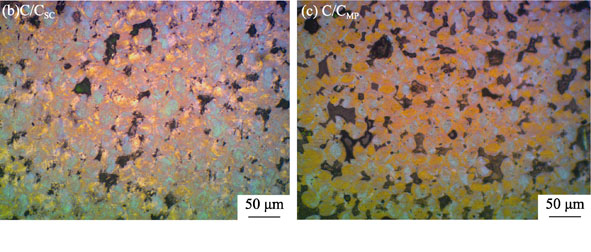
Effect of CeO2 Modified MAS Middle Layer on the Joint of C/C-LAS
ZHU Huan-Xia, LI Ke-Zhi, LU Jin-Hua, LI He-Jun, WANG Jian-Yang
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1345–1348
 Abstract
Abstract(
679 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1139KB)(
1208
)
The joints between C/C composites and lithium aluminosilicate (LAS) glass ceramic were prepared by hot pressing process method using magnesium aluminosilicate glass caremic (MAS) modified by rare earth oxide (CeO2) as an intermediate layer. Morphology and ingredients of the MAS middlelayer and joints were analyzed by SEM and EDS. Shear strength of joints was examined through the INSTRON universal testing tensile machine. The results show that MAS middle layer surface is denser with less defects than with the middle layer without CeO2. The thickness of MAS middlelayer modified by CeO2 is about 150 μm, which of MAS middlelayer without CeO2 is about 50 μm. The average shear strength of joints modified by CeO2 is 25.37 MPa, which is 30% higher than that of the joints without CeO2.
|
|
|
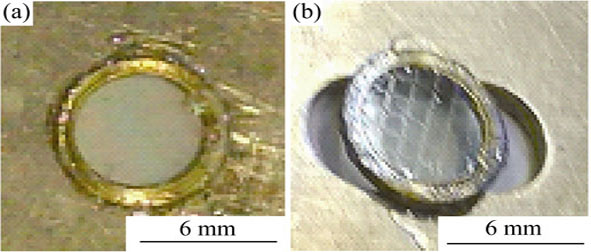
Preparation and Properties of Submicron Free-standing Polyimide Thin Film Using ZnO Demoulding and Laser Ablation
LIU Ren-Chen, WU Yong-Gang, XIA Zi-Huan
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1349–1353
 Abstract
Abstract(
849 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(574KB)(
1062
)
A process for the preparation of free-standing polyimide (PI) thin films of less than 1 μm thickness was proposed and the property of the films was analyzed. In this process, a polyamic acid (PAA) thin film of 1 μm thickness was first prepared on a ZnO coated substrate and then released using diluted hydrochloride acid. The PAA film was reattached to the substrate and treated thermally to create a polyimide thin film. The thickness of the PI film was reduced using excimer laser ablation. The surface morphology and the spectral characteristics of the polyimide film were investigated using atomic force microscope, Fourier transform infrared spectroscope and spectrophotometry. Results showed that ZnO thin films sputtered at room temperature served as a good release agent for preparing free-standing polyimide films with thickness more than 950 nm. The thickness of the PI films could be reduced to as thin as 150 nm by excimer laser ablation. In the wavelength range from 400 nm to 2500 nm, the average transmittance increased from 80.3% to 83.5% when the thickness of the polyimide film decreased from 950 nm to 150 nm.
|
|
|
Influence of Aluminates Composition on Ba-W Cathode Characteristics
WANG Kai-Feng, LIU Wei, WANG Jin-Shu
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1354–1358
 Abstract
Abstract(
988 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(487KB)(
1083
)
Precursor powder of 612 aluminates (n(BaO):n(CaO):n(Al2O3)=6:1:2) was prepared by liquid phase co-precipitation method. In addition, the aluminates were prepared by calcinations of the precursor powder under different atmospheres (H2, CO2, N2) and temperatures (1300℃, 1400℃, 1500℃). The obtained products are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), TG-DTA and so on. Then effects of different aluminates on the emission properties of Ba-W cathode were systematically investigated. The results show that the crystalline phase of aluminates prepared under H2 at 1500℃ is Ba5CaAl4O12, The Ba-W cathodes impregnated with this kind aluminates have the maximum emission current density (12.2 A/cm2) and the minimum rate of evaporation (1.09×10-8 g/(cm2?s)).
|
|
|
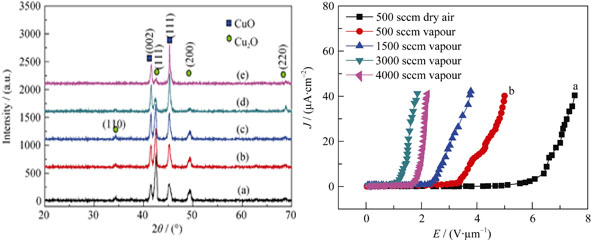
Effects of Different Humidity on the Growth and Field Emission Properties of CuO Nanowires
YE Yun, CHEN Tian-Yuan, CAI Shou-Jin, YAN Min, LIU Yu-Hui, GUO Tai-Liang
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1359–1363
 Abstract
Abstract(
723 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
1048
)
Various kinds of vertical CuO nanowires on the Cu substrate were prepared by thermal oxidation method at 400℃ in 500 sccm air with different flow of water vapour (0, 500, 1500, 3000 and 4000 sccm). The morphology and structure charcateristics of as prepared CuO nanowires were further investigated by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Field Emission Transmission Electron Microscope (FE-TEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD), respectively, and their field emission properties were also explored. The results show that both the density of as-obtained CuO nanowires and their field emission performance including turn-on field are greatly influenced by the water vapour. The CuO nanowires prepared under the water vapour (500 sccm) exibit higher density and better field emission performance than those obtained only in dry air condition (500 sccm). The turn-on field of the former is 3.7 V/μm, obviously lower than those of the latter (6.5 V/μm). Additionally, the field emission performance of as prepared CuO nanowires improves with the increase of water vapour flow in the preparation at first, reaches the extreme value at 3000 sccm, and then turns down. The best field emission performance of CuO nanowires is obtained in 3000 sccm water vapour where the lowest turn-on field is about 1.4 V/μm.
|
|
|
Study on Etching Process and Mechanism of New Phase Change Material Ti0.5Sb2Te3
ZHANG Xu, LIU Bo, SONG San-Nian, YAO Dong-Ning, ZHU Min, RAO Feng, WU Liang-Cai, SONG Zhi-Tang, FENG Song-Lin
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1364–1368
 Abstract
Abstract(
765 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(692KB)(
1117
)
The dry etching characteristic of new Ti0.5Sb2Te3 (TST) phase change material was investigated by using the CF4 and Ar gas mixture. The research mainly focuses on how to optimize the experimental parameters such as gas flow rate within the chamber, CF4/Ar flow ratio, the chamber background pressure and the incident RF power applied to the lower electrode. The results show that CF4 mainly plays a role of chemical etching and Ar plays a role of physical bombardment. The etching rate of TST films increases with the increasing concentration of CF4 in the gas mixture. The etching chamber pressure has less effect on the TST film etching speed, while the etching power has larger effect. The etch rate is up to 126 nm/min with the smooth etched surface (RMS=0.82 nm) and TST film profile is almost vertical (approaching 90°) using optimized etching parameters, including the total flow rate of 50 sccm, CF4 concentration of 26%, power of 400 W and pressure of 13.3 Pa.
|
|
|
Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Si-Al-Y Co-deposition Coatings Prepared on TiAl alloy by Pack Cementation Process
LI Yong-Quan, XIE Fa-Qin, WU Xiang-Qing, LI Xuan
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1369–1375
 Abstract
Abstract(
752 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(1118KB)(
1112
)
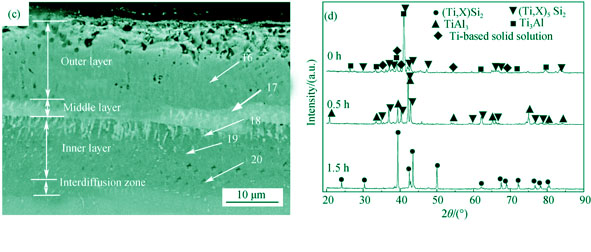
In order to improve the oxidation resistance of TiAl alloy, Al and Y modified silicide coating were prepared by pack cementation process at 1050℃ for 0-4 h. The formative mechanism and oxidation behavior of the coating were studied. The results show that the coating prepared by co-depositing Si-Al-Y at 1050℃ for 4 h has a multiple layer structure: an outer layer composed of TiSi2, a middle layer composed of (Ti,X)5Si4 and (Ti,X)5Si3 (X represents Nb and Cr elements), an inner layer composed of TiAl2, γ-TiAl phases and a Al-rich inter-diffusion zone. Y mainly existed in the outer layer and middle layer of the coating. The coating formation process followed a sequent deposition mechanism, with Al deposited at the initial stage and Si deposited at the later stage. After oxidation at 1000℃ for 20 h, a dense scale composed of a thin TiO2 outer layer and a thick SiO2·Al2O3 inner layer is formed on the co-deposition coating. During the oxidation process, the excessive Y2O3 particles form in the interface of the scale and the substrate, which might promote the adherence of the scale effectively.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoporous Graphitic Nanocages by Sulfur-doping Template Method
SHENG Zhao-Min, WANG-Ying, CHANG Cheng-Kang, LIU Xiao-Rong, ZHANG Dong-Yun, LIU Yan
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1376–1380
 Abstract
Abstract(
1504 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(409KB)(
1467
)
A new sulfur(S)-doping template approach was demonstrated to fabricate highly nanoporous graphitic nanocages (GNCs) by air-oxidizing the template in the graphitic shells to create nanopores. Sulfur was introduced into graphitic shells, when Fe@C core-shell nanoparticles were prepared and then S-doped GNCs were obtained by removing their ferrous cores. Due to removing S-template, both the specific surface area and the mesopore volume of the GNCs have sharply risen from 540 to 850 m2/g, 0.44 to 0.90 cm3/g, resrepectively. Compared with traditional approaches for highly nanoporous graphitic nanomaterials, present S-template approach can sharply increase specific surface area of GNCs without violently destroying their graphitic structure.
|
|
|
Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Residual Stresses in Plasma-sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings
YANG Jia-Sheng, YU Jian-Hua, ZHONG Xing-Hua, ZHAO Hua-Yu, ZHOU Xia-Ming, TAO Shun-Yan, DING Chuan-Xian
2013 Vol. 28 (12): 1381–1386
 Abstract
Abstract(
1753 )
 HTML
HTML
 PDF
PDF(396KB)(
1499
)
Finite element analysis (FEA) was performed to analyze residual stresses development within thermal barrier coatings system consisting vacuum plasma sprayed CoNiCrAlY bondcoat and atmospheric plasma sprayed yttria partially stabilized zirconia topcoat on the GH3128 nickel-based superalloy substrates. The effect of substrate preheating process on the residual stress generated at the bondcoat/topcoat interface was evaluated. The results show that substrate preheating process reduces tensile stresses within the coating. To provide quantitatively comparison to the computational results, hole-drilling method was used to evaluate the residual stresses. The measured residual stresses are in agreement with the numerical simulation results obtained from FEA.
|
|