原子层沉积生长速率的控制研究进展
 , 董亚斌
, 董亚斌 , 夏洋
, 夏洋Research Progress on Growth Rate Controlling of Atomic Layer Deposition
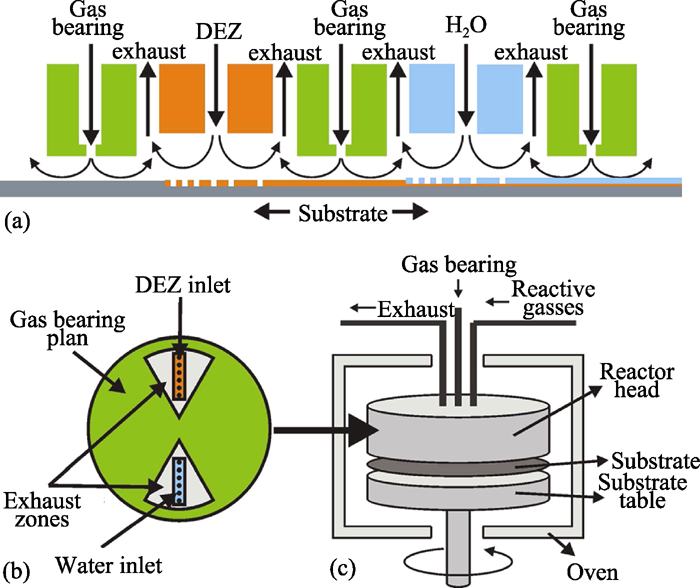
Fig. 10 a Schematic drawing of the spatial ALD reactor [ 38 ] , where the DEZ and water half-reaction zones are separated by gas bearings. By moving the substrate underneath the reactor, the two half-reactions will take place subsequently to form a ZnO monolayer. b Schematic drawing of the bottom side of the spatial ALD reactor head, where the DEZ and water half-reaction zones are integrated into inlets surrounded by exhausts zones and gas bearing planes. c Schematic drawing of the reactor. The reactor head and rotating substrate table with the substrate in between are placed in an oven. The substrate table is rotated by a servo-motor, connected by a drive shaft. The process and waste gas lines are connected to the reactor head through an opening in the top