|
|
ReX2 (X=S, Se): A New Opportunity for Development of Two-dimensional Anisotropic Materials
WANG Ren-Yan, GAN Lin, ZHAI Tian-You
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 1–16
 Abstract
Abstract(
2241 )
 HTML
HTML(
72)
 PDF
PDF(14375KB)(
2948
)
Two dimensional (2D) materials have attracted wide attention due to their ultrathin atomic structure, large specific surface area and quantum confinement effect which are remarkably different from their bulk counterparts. Anisotropic materials are unique among reported 2D materials. Their orientation-dependent physical and chemical properties make it possible to selectively improve the performance of materials. As representative examples, Re-based transition metal dichalcogenides (Re-TMDs) have tunable bandgaps in visible spectrum, extremely weak interlayer coupling, and anisotropic properties in optics and electronics, which make them attractive in the application areas of electronics and optoelectronics. In this riviev, the unique crystal structures and intrinsic properties of the Re-based TMDs semiconductors are introduced firstly, and then the synthetic method is introduced, followed by discussion on the unique physical characterizations and optimized means. Finally, prospects and suggestions are put forward for the preparation and research of ReX2.
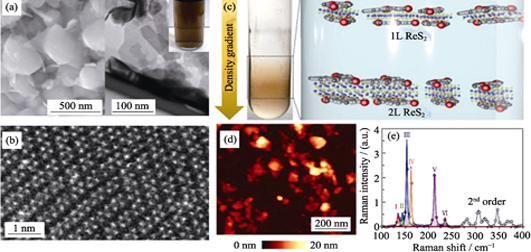
|
|
|
Removal of Radionuclides by Metal-organic Framework-based Materials
WANG Xiang-Xue, YU Shu-Jun, WANG Xiang-Ke
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 17–26
 Abstract
Abstract(
1305 )
 HTML
HTML(
32)
 PDF
PDF(3298KB)(
1823
)
With the development of nuclear energy, the long-lived radionuclides are inevitably released into the natural environment during the mine process, fuel manufacture, nuclear power usable and spent fuel management, which are dangerous to human health and environmental pollution. Thereby the efficient elimination of radionuclides is an important parameter which affects the development of nuclear power. In recent years, the metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted worldwide attention in the adsorption of radionuclides from large volume of aqueous solutions, because of their high chemical stability, abundant functional groups and changeable porous structures. In this review, we mainly summarized the recent works of MOFs in the efficient removal of radionuclides, and to understand the interaction mechanism from batch adsorption experiments, model analysis, advanced spectroscopy analysis, and theoretical calculation. The adsorption capacities of MOFs with other materials were also summarized, and the future research opportunities and challenges are given in the perspective.
|
|
|
Design of the Nature-inspired Algorithms Library and Its Significance for New Materials Research and Development
DU Shi-Yu, ZHANG Yi-Ming, LUO Kan, HUANG Qing
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 27–36
 Abstract
Abstract(
816 )
 HTML
HTML(
19)
 PDF
PDF(1769KB)(
1374
)
The technique for Materials Genetic Initiative (MGI) is the key tool for realizing the demand-oriented design of new materials assisted by the artificial intelligence (AI). Accordingly, the development and application of innovative intelligence algorithms are particularly important. Based on the generalization and analyses of the existing nature-inspired algorithms, this work aims at outlining the suggestion to build the nature-inspired algorithms library (NIAL). The potential route in which inspirations are obtained from varieties of disciplines, was used to produce new algorithms in high-throughput ways is introduced. The general procedure for building algorithm library is elaborated, while its advantages and characteristics are anatomized. Finally, the potential of NIAL in new materials development has been envisioned to enhance the standard for the application of AI including MGI.
|
|
|
Application and Development of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Based Planar Heterojunction LEDs
ZHANG Lou-Wen, SHEN Shao-Li, LI Lu-Ying, ZHANG Zhi, LIU Ni-Shuang, GAO Yi-Hua
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 37–48
 Abstract
Abstract(
1714 )
 HTML
HTML(
82)
 PDF
PDF(6308KB)(
2276
)
All-inorganic cesium lead halide CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) perovskite materials emerged as a rising star in the area of optoelectronics since 2015, due to its excellent photoelectric properties and environmental stability. Substantial progresses were made in the application of many electronic and optoelectronic devices, which attracted wide attention from the scientific community. This paper mainly reviews the latest research progress of cesium lead halide perovskite based planar heterojunction LED, where the structure and working principle of LED devices are briefly introduced. In addition, the classification and summarization of some optimization strategies for improving luminescence performance and working stability of LED devices are emphatically suggested, and the development trend of stable and efficient inorganic perovskite based planar heterojunction LED is finally prospected.
|
|
|
Synthesis, Optimization of Cu Nanowires and Application of Its Transparent Electrodes
WANG Xiao, WANG Ran-Ran, SHI Liang-Jing, SUN Jing
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 49–59
 Abstract
Abstract(
1370 )
 HTML
HTML(
45)
 PDF
PDF(11175KB)(
2255
)
As the continuous development of the photovoltaic industry and the flat panel display devices, the demand for transparent electrodes is increasing rapidly. The most commonly used transparent conductive material, ITO, was criticized for its brittleness, which limited its application in the up-and-coming market. Cu nanowire transparent electrodes acts as promising candidate for the new generation of transparent electrodes due to their superior conductivity, low cost, easy accessibility and high flexibility. The synthesis of Cu nanowires and their application in transparent electrodes has drawn lots of attention. Progresses have been made in recent years. A comprehensive elaboration of the controllable synthesis of Cu nanowires through liquid synthesis methods and the mechanism behind them, the fabrication and post-treatment methods of Cu nanowire electrodes, the application of Cu nanowire electrodes in photovoltaic devices, transparent heaters and flexible devices are given. The trends of Cu nanowire electrodes is proposed.
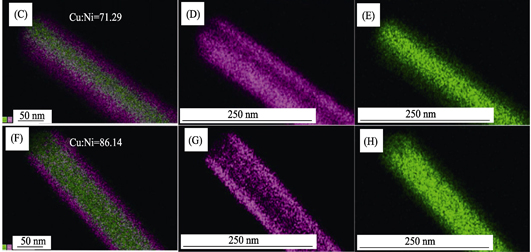
|
|
|
Synthesis of Novel MAX Phase Ti3ZnC2 via A-site-element-substitution Approach
LI Mian, LI You-Bing, LUO Kan, LU Jun, EKLUND Per, PERSSON Per, ROSEN Johanna, HULTMAN Lars, DU Shi-Yu, HUANG Zheng-Ren, HUANG Qing
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 60–64
 Abstract
Abstract(
1595 )
 HTML
HTML(
63)
 PDF
PDF(8397KB)(
2285
)
Using Ti3AlC2 as the precursor, a new MAX phase Ti3ZnC2 was synthesized via an A-elemental substitution reaction in a molten salts bath. Composition and crystal structure of Ti3ZnC2 were confirmed by XRD, SEM and TEM analysis. Its structure stability and lattice parameter of Ti3ZnC2 were further proved by a theoretical calculation based on density function theory (DFT). Moreover, thermodynamics of A-elemental substitution reactions based on Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu were investigated. All results indicated that the similar substitution reactions are feasible to form series of MAX phases whose A sites are Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu elements. The substitution reaction was achieved by diffusion of Zn atoms into A-layers of Ti3AlC2, which requires Al-Zn eutectic formation at high temperatures. The molten salts provided a moderate environment for substitution reaction and accelerated reaction dynamics. The major advantage of this substitution reaction is that MAX phase keeps individual metal carbide layers intact, thus the formation of competitive phases, such as MA alloys, was avoided. The proposed A-elemental substitution reactions approach opens a new door to design and synthesize novel MAX phases which could not be synthesized by the traditional methods.
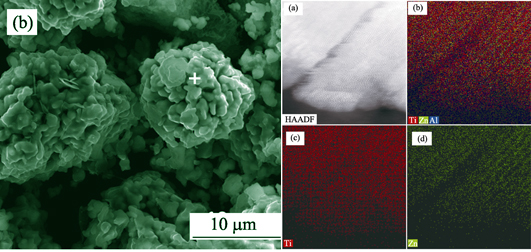
|
|
|
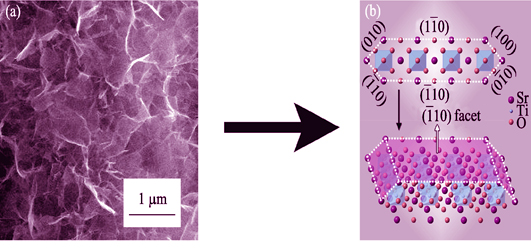
In-situ Synthesis of Perovskite SrTiO3 Nanostructures with Modified Morphology and Tunable Optical Absorption Property
LIU Xiao-Yuan, LIU Bao-Dan, JIANG Ya-Nan, WANG Ke, ZHOU Yang, YANG Bing, ZHANG Xing-Lai, JIANG Xin
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 65–71
 Abstract
Abstract(
858 )
 HTML
HTML(
46)
 PDF
PDF(10640KB)(
1279
)
As a perovskite family member, SrTiO3 shows significant applications in the fields of solar cells, photocatalysis, fuel cells and superconducting as a dependence of its crystallinity, morphology, crystal facet and optical properties. In this work, we reported an in-situ synthetic approach of SrTiO3 nanostructures with modified morphology and tunable optical absorption properties based on conventional plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) associated with hydrothermal method. The morphology of SrTiO3 nanostructures can be selectively modified from microcubes with smooth facets to ultrathin nanosheets by controlling the concentration of Sr source during PEO process. It is found that both SrTiO3 microcubes and Sr1-δTiO3 nanosheets are well-crystallized single crystals. UV-Vis diffuse reactance spectrum (DRS) measurement reveals that Sr1-δTiO3 nanosheets with thin thickness show obvious blue-shift of absorption edge in comparison with SrTiO3 microcubes due to the size effect. Finally, the morphology evolution and nucleation mechanism of SrTiO3 nanostructures in-situ grown on PEO film is discussed.
|
|
|
BN/CsPbX3 Composite Nanocrystals: Synthesis and Applications in White LED
DONG Yu-Hui, ZENG Shu-Yu, HAN Bo-Ning, XUE Jie, SONG Ji-Zhong, ZENG Hai-Bo
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 72–78
 Abstract
Abstract(
829 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(19825KB)(
1449
)
All inorganic perovskite (CsPbX3) nanocrystals has wide applications in the field of optoelectronic devices due to its excellent photoelectric characteristics, however, stability is still the bottleneck restricting its development. Combining with the current research progress, the BN/CsPbX3 composite nanocrystals phosphors was synthesized via all-solid-state reactions. During the process, parameters of ball milling, ratio of reactants and other reaction conditions were optimized, thus the BN/CsPbX3 composite nanocrystals can be stable in the air for more than 60 days. Its luminescence wavelength can cover the range of 417-680 nm with full width at half maximum of 23-47 nm, showing high color purity, and was further used in white LED with high stability and luminance. After placed in the atmosphere for a month, the attenuation of LED luminance is only about 0.7%, and less than 4% deterioration was observed after continuous work of 2 h, showing great working stability.
|
|
|
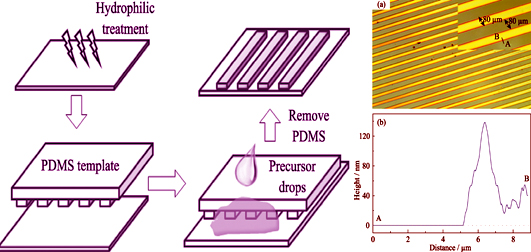
Microfluidic-method-processed p-type NiOx Thin-film Transistors
LIANG Yu, LIANG Ling-Yan, WU Wei-Hua, PEI Yu, YAO Zhi-Qiang, CAO Hong-Tao
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 79–84
 Abstract
Abstract(
852 )
 HTML
HTML(
23)
 PDF
PDF(1925KB)(
1100
)
It’s essential to develop patterning deposition methods to simplify the process of device fabrication and then reduce the production cost. In this work, a new patterning deposition method, i.e. microfluidic method, was demonstrated in details. In this technology, a micro-fluidic channel with a width of 80 μm and a height of 2 μm can be constructed between PDMS modules and substrates, and under capillary force precursor drops will move through the channel to form a patterned liquid film which is then fixed on the substrate via thermal treatments, and finally patterned films are prepared. In addition, the thermal-driven solidification process from NiOx precursor powder to oxide was investigated through thermogravimetric/differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA) measurement. And the evolution of phase structure of the NiOx precursor powder was analyzed with respect to post-annealing temperatures. Finally, thin-film transistors were fabricated applying the patterned NiOx thin films as channels, and the optimized device showed typical p-type transistor features, with a field-effect mobility up to 0.8 cm2·V-1·s-1.
|
|
|
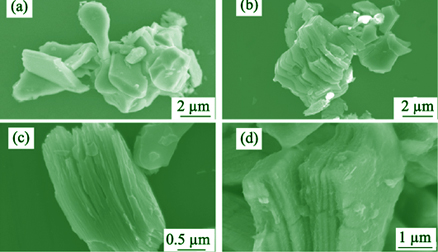
Alkalization Intercalation of MXene for Electrochemical Detection of Uranyl Ion
FAN Mao, WANG Lin, PEI Cheng-Xin, SHI Wei-Qun
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 85–90
 Abstract
Abstract(
1059 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(1290KB)(
1598
)
Given the good electrochemical performance and excellent irradiation stability of two dimensional transition metal carbides (MXenes), the development of MXene-based electrode materials for radionuclide detection is very promising. In this work, Ti3C2Tx MXene was activated via an alkalization strategy to form K+ intercalated Ti3C2Tx (K-Ti3C2Tx). Then the modified electrode of K-Ti3C2Tx/GCE was prepared on glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Ti3C2Tx and K-Ti3C2Tx were characterized by XRD, SEM and XPS techniques, and the electrochemical detection performance of K-Ti3C2Tx/GCE for trace uranyl ion (UO22+) was further investigated. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments showed that the electrochemical response of K-Ti3C2Tx/GCE modified electrode to UO22+ increased significantly. Under the differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) scanning at pH 4.0, the K-Ti3C2Tx/GCE modified electrode presented a good linear detection relationship for UO22+ in the uranium concentration range of 0.5-10mg/L. The detection limit of this method is 0.083 mg/L (S/N = 3), with decent stability and repeatability.
|
|
|
Detection of Cd2+ by Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Using an Activated Bismuth-film Electrodes
YAO Mei-Na, YANG Xian-Jin, CUI Zhen-Duo, ZHU Sheng-Li, LI Zhao-Yang, LIANG Yan-Qin
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 91–95
 Abstract
Abstract(
711 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(1351KB)(
1049
)
The stripping current arising from the oxidation of Cd was related to the concentration of Cd2+ in the sample. This study presents the determination of Cd(II) at low concentration μg/L levels by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV) on an activated bismuth-film electrode (BFE). The electrode was initially modified by an electrochemical method, and then the electrodeposited bismuth-film was prepared again to improve the electrode, thereby enhancing the sensitivity to trace amounts of target Cd2+. The surface of glassy carbon electrode (GCE) before and after modification was characterizad by SEM, CV, EIS, and SWV. The parameters for the determination of the Cd2+ were investigated with the view of its application toward real samples containing low concentrations of Cd2+. Using the selected conditions, the limit of detection is 1 μg/L for Cd2+ at a preconcentration time of 10 min.
|
|
|
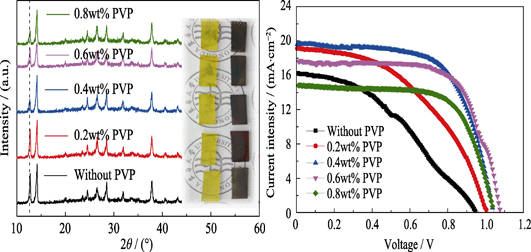
Polymer PVP Additive for Improving Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells
XIONG Hao, ZHANG Bo-Xin, JIA Wei, ZHANG Qing-Hong, XIE Hua-Qing
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 96–102
 Abstract
Abstract(
1406 )
 HTML
HTML(
52)
 PDF
PDF(1726KB)(
1612
)
As a type of novel thin film solar cells, perovskite solar cells develope sharply within a decade, which efficiency has approached to that of the commercial silicon solar cells. However, its poor stability in the air has limited the further practical application. Herein, we achieve uniform sable perovskite films under open environment by adding some poly 4-vinylpyridine (PVP). The morphology, structure and performance test results show that the perovskite films added with PVP were more compact and uniform than the bare one. Moreover, the assembled solar cell with 0.4wt% PVP exhibited highly reproducible efficiencies up to 13.07%, much higher than that of 6.09% for the controlled one. When restored in the air with approximately 50% relative humidity in the absence of encapsulation, its efficiency decay time to a half from 3 d for bare one extended to 3 w. However, high PVP additives result in incomplete reaction between PbI2 and CH3NH3I. If the above mentioned process is further optimized, is expected to be applied to the large-scale preparation of more stable perovskite film.
|
|
|
Fe, N Doped 2D Porous Carbon Bifunctional Catalyst for Zinc-air Battery
MA Long-Tao, ZHI Chun-Yi
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 103–108
 Abstract
Abstract(
1004 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(711KB)(
1772
)
Fe, N doped 2D porous carbon catalyst was synthesized by pyrolysizing the precursor, ZIF-8, on graphene. Meanwhile, Fe-2,2-bipy were coordinated on ZIF-8. The catalyst was analyzed by SEM, XRD, and XPS for morphology, structure and component. The ORR and OER performance of the Fe, N doped 2D porous carbon catalyst were characterized by RDE, CV curves and LSV curves. It was found that the Fe, N doped 2 D porous carbon catalyst shows uniform 2D structure and that the content of Fe element is 1.32%. The catalyst shows 0.83 V half-wave potentials for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in 0.1 mol/L KOH solution and 420 mV over-potential for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) at 10 mA/cm2 in 1 mol/L KOH solution. Then, a zinc-air battery was assembled using as-synthesized catalyst. The power density of zinc-air battery is up to 245 mV/cm2. Furthermore, it shows superior cycling stability.
|
|
|
One-step Synthesis of Black TiO2 Composite Coating on Glass by Pulsed Laser Spraying
ZHANG Li-Xian, LIANG Yan-Qin, WANG Shao-Dan, LU Hong, LIU Ai-Feng, WEI Qiang
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 109–113
 Abstract
Abstract(
676 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(1290KB)(
1054
)
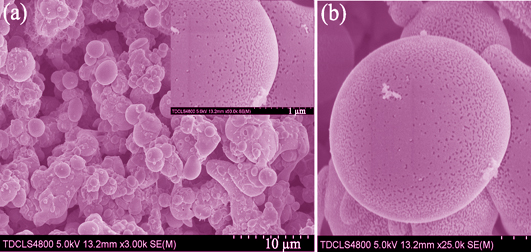
To achieve effective load of black TiO2 nanoparticles and improve the practical application ability, the pulsed laser spraying was proposed. The composite coating was prepared on quartz glass substrate, which consisted of amorphous molecular sieve and rutile TiO2 nanocrystals. The surface morphology of the composite coating was characterized, and a series of test about composite coating powder was conducted including absorption properties, phase structure, chemical valence, and photocatalytic properties. The results show that the coating is porous structure packed with 2-5 μm ball and has strong absorptive capacity in the visible region. In the process of pulsed laser sputtering, the molecular sieve changed to amorphous structure, and TiO2 changed from anatase to rutile type. Ti4+ ion was reduced to Ti3+ ion, which resulted in reduced band-gap. The pulsed laser spraying technology achieves the fast load of the black nano TiO2, which still has good photocatalytic ability under the full spectrum and visible light conditions.
|
|
|
Inkjet-printing and Performance Investigation of Self-powered Flexible Graphene Oxide Humidity Sensors
WANG Gui-Xin, PEI Zhi-Bin, YE Chang-Hui
2019 Vol. 34 (1): 114–120
 Abstract
Abstract(
759 )
 HTML
HTML(
27)
 PDF
PDF(7092KB)(
1302
)
Respiratory frequency and mode could be applied for medical diagnosis and health evaluation. Traditional medical diagnosing devices have bulky size and high cost, and are of inconvenience in use. To fulfill the urgent demand for high-performance, low-cost, and portable electronic devices, this study proposes to fabricate self-powered planar humidity sensors by inkjet-printing method by virtue of the characteristics that graphene oxide self-polarizes and is sensitive to humidity. This sensor linearly responds to the relative humidity, and both responds and recovers rapidly. In addition, this sensor possesses excellent sensitivity and stability after multiple cycling and long-term storage, and has realized monitoring of the respiratory frequency and mode. The humidity sensors in this work is ready to fabricate with low production cost, free from interference by body motion or exterior environment, and suitable for real-time monitoring respiratory frequency and mode.
|
|