|
|
Research Progress on Magneto-optical Transparent Ceramics
LI Jiang, DAI Jia-Wei, PAN Yu-Bai
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 1–8
 Abstract
Abstract(
1594 )
 HTML
HTML(
44)
 PDF
PDF(1632KB)(
3034
)
Magneto-optical material is a kind of optical functional material which has the magneto-optical effect from ultraviolet to infrared band. According to the type of material, magneto-optical materials can be classified into magneto-optical glass, magneto-optical crystals, magneto-optical transparent ceramics, etc. As a new type of magneto- optical material which has emerged in recent years, magneto-optical transparent ceramics are considered as one of the most promising candidates for Faraday isolators used in high power lasers due to its high Verdet constant, large size, high thermal conductivity, and high laser-induced-damage threshold. Up to now, the magneto-optical transparent ceramics reported mainly include terbium gallium garnet (Tb3Ga5O12, TGG), terbium aluminum garnet (Tb3Al5O12, TAG) and some sesquioxide ceramics such as terbium oxide (Tb2O3), holmium oxide (Ho2O3), dysprosium oxide (Dy2O3), etc. In this paper, several common magneto-optical effects were briefly introduced, and the basic principles of Faraday effect and Kerr effect were illustrated in detail. In addition, the research progress, all-sides properties and application prospects of magneto-optical transparent ceramics were mainly reviewed. The properties of different kinds of magneto-optical transparent ceramics were compared and analyzed, and the existing problems as well as the research prospects were also proposed.
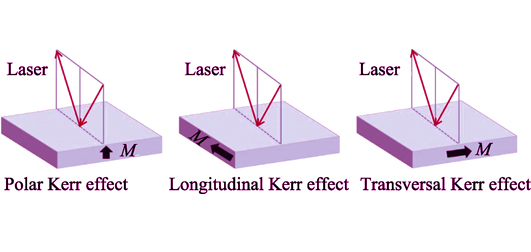
|
|
|
Microstructure Characterization and Luminescent Property of Mixed Spinel Zn6Ga8TiO20:Cr3+ Phosphors
ZHENG Yi-Fan, ZHANG Lu-Lu, WANG Kai, PAN Zai-Fa
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 9–13
 Abstract
Abstract(
750 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(1061KB)(
1357
)
A novel red phosphor Zn6Ga8-xTiO20:xCr3+ was prepared via a high temperature solid-state method. The as-prepared phosphors were examined by means of X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence and transmission electron microscopy. The results showed that the synthesized phosphor had a single mixed spinel structure and Cr3+ could be effectively doped into the host Zn6Ga8TiO20 by occupation of octahedral sites. It was showed that the excitation spectrum was composed of four bands located at 281, 337, 420 and 555 nm, respectively. The band at 281 nm corresponded to the 4A2-4T1 (4P) transition of Cr3+ and that at 337 nm originated from the charge transfer from 2p orbitals of O2- to the 4s4p orbital of Ga3+, while the bands at 420 and 555 nm were related to the transitions of 4A2-4T1 and 4A2-4T2g of Cr3+ ions, respectively. The emission spectrum was composed of the zero-phonon lines corresponding to the 2E-4A2 transition of Cr3+ (689 nm, R sharp line), the N-line (696 nm) of Cr3+ locating at distorted sites, and the phonon-side bands. Therefore, this phosphor can be used as a red phosphor material in white LED.
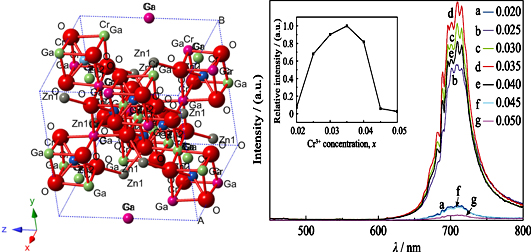
|
|
|
Influence of Impregnated Nano-scale LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3-δ Particles on the Oxygen Permeation Performance of Zr0.84Y0.16O2-δ-La0.8Sr0.2Cr0.5Fe0.5O3-δ Composite Membranes
LIU Xue-Jiao, HE Zhen-Yu, WU Hao, LUO Ting, MENG Xie, CHEN Chu-Sheng, ZHAN Zhong-Liang
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 14–18
 Abstract
Abstract(
482 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(1461KB)(
1133
)
This paper reported on the fabrication of tri-layered oxygen transport membranes, “porous|dense|porous” Zr0.84Y0.16O2-δ-La0.8Sr0.2Cr0.5Fe0.5O3-δ (YSZ-LSCF), by the tape casting, tape lamination and co-firing techniques. Catalytically active nano-scale particles of LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3-δ (LNF) were impregnated into the porous scaffolds. In order to quantatively determine the resistances of the oxygen reduction or evolution reactions against oxygen permeation, an additional dense YSZ layer was introduced inside the dense YSZ-LSCF permeation layer. Electrochemical measurements on the resulting five-layered solid oxide fuel cells showed a large reduction in the interfacial polarization resistances at the presence of these LNF catalysts, with the lowest values observed at the LNF loadings of 12wt%. In particular, the cathodic and anodic polarization resistances were 0.26 and 0.08 Ω·cm2 at 800℃, respectively. The oxygen permeation flux under the air/CH4 gradient was 7.6 mL/(cm2·min), which was 14 times higher than the measured value for the blank YSZ-LSCF membrane. Further impedance analysis indicated that the charge transfer step during oxygen reduction may limit the overall oxygen permeation process.
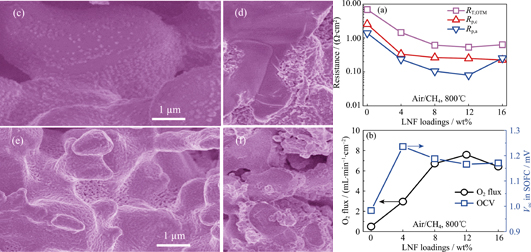
|
|
|
Facile Synthesis of Au/Pd Nano-dumbells for Catalytic Reduction of p-Nitrophenol
YIN Yue-Yue, YANG Yong, ZHANG Liang-Zhu, LI Yong-Sheng, MA Yun-Feng, YANG Li-Li, HUANG Zheng-Ren
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 19–26
 Abstract
Abstract(
857 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(1533KB)(
1356
)
Au nanorods (Au NRs) with good monodispersity and uniform aspect ratio were prepared via seed-meditated method. Au/Pd nano-dumbbells (Au/Pd NDs) were synthesized by using H2PdCl4 as precursor, hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (CTAC) as soft template, Ag+ as structure-directing agent and ascorbic acid as reduction agent to modify Au NRs. Structure and morphology of the samples were characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) and ultraviolet-visible-near infrared spectrophotometry (UV-Vis-NIR). The formation mechanism of Au/Pd NDs were discussed. The results of Au/Pd NDs samples demonstrated that lots of poly-crystalline Pd particles were deposited onto two ends of Au nanorods selectively to form dumbbell-like structure. The dumbbell size can be continuously tuned by adjusting the molar ratio of AA and H2PdCl4. The experiments of reduction of p-nitrophenol by NaBH4 to p-aminophenol indicate that the sample with good dispersibility and large number of total catalytic active sites of Pd nanoparticles has high catalytic performance. Adding 0.04 mg/mL Au/Pd NDs with suitable Pd particles size (20.7 nm) show excellent catalytic activity (rate constant 0.44 min-1), indicating it is useful for reducing p-nitrophenol.
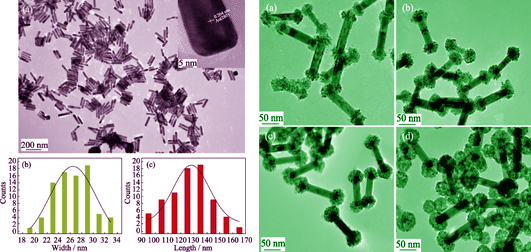
|
|
|
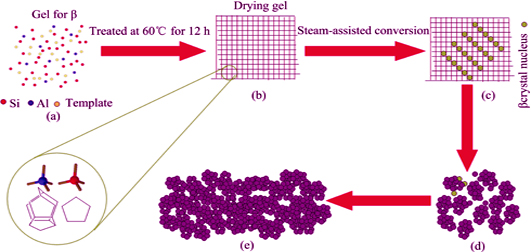
Hierarchical Beta Zeolite Prepared by Steam-assisted Conversion Method
SUN Xiao-Bo, DU Yan-Ze, QIN Bo, KONG Qing-Lan, WU Liang, ZHENG Jia-Jun, PAN Meng, LI Rui-Feng
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 27–34
 Abstract
Abstract(
727 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(1051KB)(
1290
)
Synthesis of hierarchical zeolite with complex micropore-mesopore structures has attracted great attention because of their practical or potential applications. In present study, hierarchical Beta zeolite was synthesized by the “steam-assisted conversion (SAC)” method without secondary template. Factors affecting formation of the hierarchical Beta, such as the added amount of organic template, alkalinity and silica to alumina ratio of the gel precursors yielding the hierarchical Beta zeolite, vapor pressure and crystallization time during the “steam-assisted conversion (SAC)” process, were investigated. The structural, crystalline and textural properties of the as-synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscope, Raman spectrum, N2 adsorption-desorption, and NH3-TPD. The formation mechanism of the hierarchical Beta was explored on the base of the results detected by FT-IR, Raman spectrum, and SEM. Results showed that the as-synthesized Beta zeolite was composed of primary nano-sized crystals with a diameter of 10-40 nm, and a mesoporous structure ranging from 2 to 30 nm was therefore introduced. A tremendous amount of primary and/or subprime building units, which were bred during preparation of dry gel, induced a burst in nucleation rate. Nano-sized zeolite crystals were, therefore, created that subsequently formed polycrystalline Beta zeolite material by aggregating the nanocrsytals with each other.
|
|
|
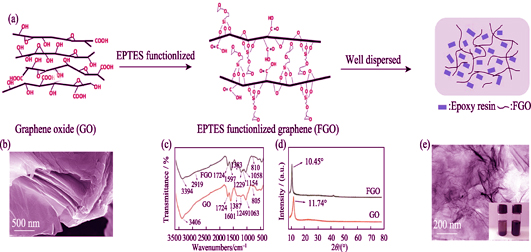
Graphene/Epoxy Composite Coating Damage under γ-ray Irradiation and Corrosion Protection
XIA Wei, WANG Tao, SONG Li, GONG Hao, GUO Hu, FAN Xiao-Li, GAO Bin, ZHAO Jun, HE Jian-Ping
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 35–40
 Abstract
Abstract(
649 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(825KB)(
1271
)
Polymer networks like epoxy resin, as common protection materials, always experience radiolytic oxidation degradation under gamma irradiation environment. To avoid this, we report a scheme to synthesis EPTES modified graphene oxide, and incorporate it into the epoxy resin, followed by thermal polymerization, then obtain a graphene/epoxy composite coating. Electrochemical tests were performed to prove the influence of γ-ray on a anti-corrosion properties of the Graphene/epoxy composite coating. electron spin resonance (ESR) and Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) were used to evaluate the damage degree under the gamma irradiation, as well as to confirm its mechanism of graphene in the epoxy resin matrix during the irradiation. The result of Tafel slope showed that the corrosion current of GEP was 6.140×10-9 A/cm2, smaller than neat epoxy, indicating a better anticorrosion property of the graphene/epoxy composite coating after 280 kGy irradiation. This findings pointed that graphene possesses anti-corrosion property under 280 kGy irradiation. The electron spin resonance and FT-IR detection show that graphene act as radical scavenger, thus decrease damage from gamma irradiation, and slow down ageing process of the coating under the gamma irradiation.
|
|
|
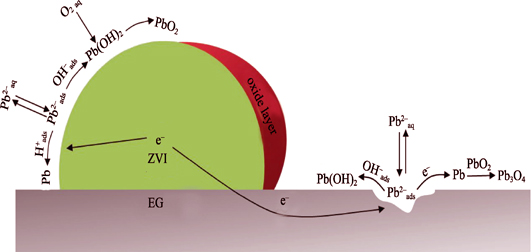
Performance and Mechanism of Pb(II) Removal by Expanded Graphite Loaded with Zero-Valent Iron
XU Cong-Bin, YANG Wen-Jie, SUN Hong-Liang, LIU Wei-Jiang, YANG Yuan-Yu, LIN Ai-Jun
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 41–47
 Abstract
Abstract(
656 )
 HTML
HTML(
10)
 PDF
PDF(3390KB)(
1180
)
Zero-valent iron (ZVI) loaded onto expanded graphite (EG) as a composite material (EG-ZVI) was prepared through chemical deposition method to remove lead ion (Pb(II)). EG-ZVI was characterized by XRD, SEM, FTIR and XPS. Results indicated that the EG was successfully loaded with sub-micron scale zero-valent iron, and showed that the removal rate of Pb(II) by EG-ZVI was 1.43 fold of that by ZVI. Galvanic cell effect and high specific surface area are the main reasons for enhancing removal of Pb(II) by EG-ZVI. The removal process mainly involved chemical reduction and physical adsorption which was well fitted the first-order kinetic model. XPS analyzing showed that the removed Pb(II) was reduced to Pb and then generated its oxides. In addition, EG-ZVI could overcome the shortcomings of forming undesirable precipitation of ferrous hydroxide on the surface when applied ZVI. These data indicate that EG-ZVI has high potential to remove Pb(II) in wastewater due to its high removal capability and stability.
|
|
|
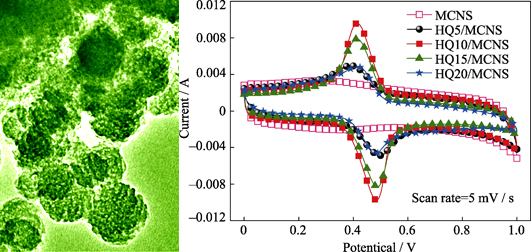
Hydroquinone-modified Mesoporous Carbon Nanospheres with Excellent Capacitive Performance
GAO Xiu-Li, WANG Dan-Dan, LI Shuo, XING Wei, YAN Zi-Feng
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 48–52
 Abstract
Abstract(
618 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(1333KB)(
1109
)
Pure carbon materials store energy mainly by the electric double-layer mechanism, resulting in their low specific capacitance. However, pseudocapacitive materials can store energy through faradaic reactions, leading to drastically improved specific capacitance. Herein, mesoporous carbon nanospheres with 3D ordered pore symmetry were synthesized by soft template method. Then, the hydroquinone (HQ) was used to modify mesoporous carbon nanospheres by hydrothermal method. As demonstrated by cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge-discharge tests, HQ modified carbon nanospheres show both electric double layer capacitance and pseudocapacitance. Carbon nanospheres with 10wt% HQ loading possess the highest specific capacitance of 285 F/g at the current density of 0.5 A/g and 212 F/g at 10 A/g, exhibiting excellent rate performance. This should be ascribed to the HQ molecules adsorbed on carbonaceous mesopore surface by π-π interactions, which not only provide extra pseudocapacitance, but also improve the rate performance of carbons in aqueous electrolyte.
|
|
|
Carbon Nanotubes/Polyaniline Chemically Modified Electrode: Preparation and Ascorbic Acid Detection
DENG Min, JIANG Qi, FANG Yuan, LI Huan, QIU Jia-Xin, LU Xiao-Ying
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 53–59
 Abstract
Abstract(
755 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(2647KB)(
1062
)
Nickel catalyst was deposited on a graphite electrode (GE) surface by constant voltage deposition method. With the nickel catalyst, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were grown in situ on the GE surface to prepare CNTs chemically modified electrode (GSCNTs-CME) by catalytic chemical vapor deposition. After that, polyaniline (PANI) was polymerized in situ on the GSCNTs-CME to obtain GSCNTs/PANI-CME by electrochemical polymerization. Morphology and structure of the obtained electrodes were characterized by scanning electron microscope. Detection performances of the GSCNTs/PANI-CME on ascorbic acid (AA) were evaluated on an electrochemical workstation. Results show that the CNTs grow uniformly on the GE surface and the original tubular structure is remained well. PANI is coated uniformly on the surface of CNTs in the obtained composite with a typical three-dimensional network structure. The GSCNTs/PANI-CMEs show excellent electrochemical response to AA, amongst which the GSCNTs/PANI-CME with small-diameter CNTs shows stronger electrochemical response (wider linear detection range and lower detection limit) to AA. And its linear detection range and detection limit are 1.0×10-6~4.5×10-4 mol/L and 1.0×10-7 mol/L (S/N = 3), respectively. Therefore, the GSCNTs/PANI-CME shows excellent stability, repeatability and reliability.
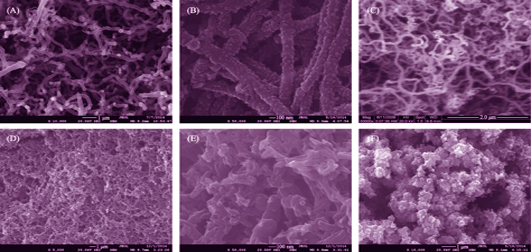
|
|
|
KGM/Gelatin/Nano HAP Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus
CHEN Xi-Liang, CHEN Qing-Hua, ZHUANG Ying, YAN Ting-Ting
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 60–66
 Abstract
Abstract(
681 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(623KB)(
1068
)
Intervertebral disc degenerative disease has become a serious disease which affects people's work and life, and the emergence of tissue engineering technology provides a new way to the treatment of intervertebral disc disease. In this research, Konjac glucomannan (KGM), gelatin, and nano hydroxyapatite (nano HAP) were used to prepare tissue engineering scaffolds for intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus by wet spinning and rolling film method. Composition, structures and morphologies of the scaffolds were analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The compressive strength, water absorption, porosity, in vitro degradation, and cytotoxicity of scaffolds were also measured. The results show that the scaffolds are anisotropic structure, similar to natural annulus fibrosus. The scaffolds are porous, with its strength being improved by adding nano HAP. The strength of scaffolds prepared by wet spinning method are higher than that by rolling film method; the scaffolds cross-linked by glutaraldehyde are stronger than that by ammonia because of better nano HAP combination, and exhibit higher degradation rate. Water absorption and porosity of the scaffolds are over 700%, 66%~75%, respectively. This study provides a theoretical and experimental basis for further development for tissue engineering scaffolds for annulus fibrosus.
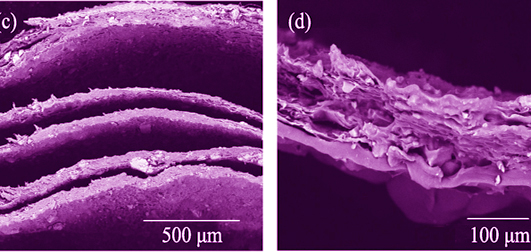
|
|
|
Surface Modification on Property of Mesoporous Calcium Magnesium Silicate/Polyetheretherketone Composites
SHI Zhang-Yu, LI Quan, TANG Song-Chao, QIAN Jun, PAN Yong-Kang, WEI Jie
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 67–74
 Abstract
Abstract(
707 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(6947KB)(
1169
)
Mesoporous calcium magnesium silicate (m-MCS)/polyetheretherketone (PK) bioactive composites for bone repair were prepared, and the surfaces of composites were modified by sanding and sandblasting treatment. The surface roughness of the composites modified by sandblasting was Ra=4.552 while the surface roughness of the composites modified by sanding were 1.727 and 2.103, which were higher than that of the untreated composites (1.359). In addition, the water contact angle of the composites treated by sandblasting was 54.1° while the water contact angles of the composites modified by sanding were 76.3° and 71.6°, which were higher than that of the untreated composites (81.2°). The results indicated that surface roughness and hydrophilicity of composites were significantly enhanced by sandblasting treatment. Porous surface structure and a large number of mesoporous calcium magnesium silicates were exposed on the composites surfaces after sandblasting treatment, resulted in the maximum surface roughness and hydrophilicity. After immersed in simulated body fluid (SBF) solution for 7 d, massive apatites were formed on the composites surfaces, showing a good bioactivity. The in vitro cell experiments indicated that the surface modified composites could significantly promote adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells on the surfaces. Therefore, sandblasting treatment could significantly improve the biological performances of the composites as compared with sanding treatment.
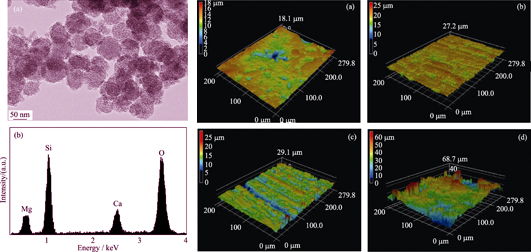
|
|
|
Synthesis and Orientation of Fe-doped Hydroxyapatite in High Magnetic Field
WANG Xiao-Long, REN Zhong-Ming, CHANG Jiang
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 75–80
 Abstract
Abstract(
886 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(782KB)(
1207
)
The surface nanostructure of bioceramics can affect osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, therefore the control of the surface microstructure of bioceramics, especially grain orientation before the ceramic sintering, is one of key to design and develop bioactive ceramics for bone regeneration. This study aimed to investigate the crystal orientation of Fe-doped hydroxyapatite in high magnetic field. Pure hydroxyapatite (HA) and Fe-doped hydroxyapatite (Fe-HA) powders were prepared by co-precipitation method and co-precipitation-hydrothermal method, and their phase composition, microstructure, magnetic property, and elementary composition were analyzed by XRD, SEM, TEM, PPMS, and ICP. The results showed that the phase of Fe-HA is the same as HA with no impurity phase. HA is diamagnetic originally, while Fe-HA becomes paramagnetic. The microstructure of samples prepared by co-precipitation method is needle cluster-like but that prepared by co-precipitation-hydrothermal method is rod-like. It is the rad-like but not the needle cluster-like Fe-HA can be orientated in high magnetic field. Therefore, the orientation of rod-like Fe-HA can be regulated by high magnetic field. Furthermore, pure HA cannot be uniaxial orientated in single-directed high magnetic field. while Fe-HA can be oriented along c axis in certain degree in single- directed high magnetic field.
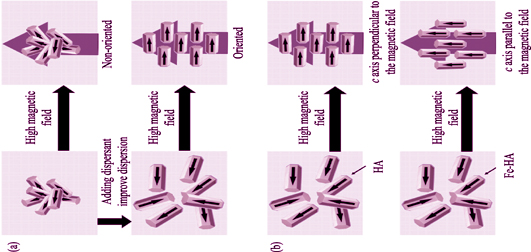
|
|
|
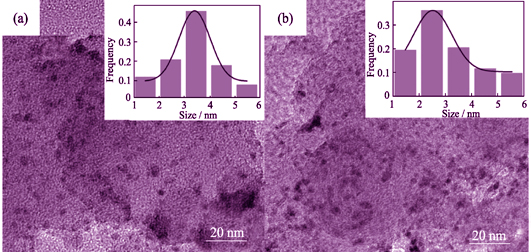
Cathode Performance of Mg-H2O2 Semi-fuel Cell with Pdn-Fe Alloy as Cathode
SUN Li-Mei, SHI Le-Le, ZHANG Shuai-Shuai, ZHANG Yi-Jia, LI Zeng-Hui, HE Wurigamula
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 81–86
 Abstract
Abstract(
567 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(531KB)(
1040
)
Carbon-supported palladium-iron composite electrocatalysts with different Pd to Fe atom ratios (2 : 1, 4 : 1, 8 : 1) were prepared by a chemical reduction method. The morphology and surface state of the Pdn-Fe/C and Pd/C electrocatalysts were characterized by X-ray diffractionanalysis (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results indicated that Fe was added to the Pd/C catalyst and reacted with Pd to form Pdn-Fe alloy, with slightly varied particle size. And the Pdn-Fe catalyst particles were homogeneously distributed on the surface of the C carrier with the average particle size between 2-3 nm. The addition of Fe influenced crystal lattice structure of Pd/C catalysts. Electrochemical (CV, LSV, CA) data showed that the eletrocatalytic activity of the Pd4-Fe/C electrocatalyst for hydrogen peroxide electroreduction was much higher than that of Pd/C. The current density of Pd/C electrode for hydrogen peroxide electroreduction reaction was 17.71 mA/cm2 when E = 0.2 V and the current density of Pd4-Fe/C electrode was up to 19.42 mA/cm2. The Mg-H2O2 semi-fuel cell performance text showed that both the open circuit potential of the two fuel cells were about 1.8 V, of which the power density of Mg-H2O2 semi-fuel cell using Pdn-Fe/C as the cathode was higher 41 mW/cm2 than that using Pd/C as cathode.
|
|
|
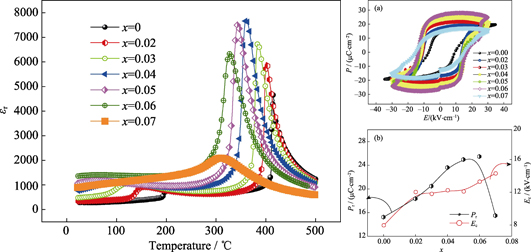
Phase Structure and Piezoelectric Property of (1-x)K0.48Na0.52NbO3-xBi0.45Nd0.05(Na0.92Li0.08)0.5ZrO3 Lead-free Piezoceramics
ZHAO Lin, MA Jian, ZHANG Jun, WU Bo, XIAO Ding-Quan
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 87–92
 Abstract
Abstract(
531 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(972KB)(
1183
)
To enhance the piezoelectric properties and maintain relatively higher Curie temperature (TC), (1-x)K0.48 Na0.52 NbO3-x Bi0.45 Nd0.05 (Na0.92Li0.08)0.5ZrO3 ((1-x) KNN-xBNNLZ) ceramics were prepared by conventional solid-state method. The effects of BNNLZ content on the phase structure and electrical properties of the ceramics were investigated in details. The results show that all ceramic samples exhibit higher TC (>300℃). With the increase of BNNLZ content, both orthorhombic-tetragonal phase transition temperature (TO-T) and rhombohedral-orthorhombic phase transition temperatures (TR-O) shift to room temperature simultaneously, and finally the R-T phase coexistence is constructed near room temperature in the compositions range of 0.05<x<0.07. The phase transitions of the ceramics caused by BNNLZ addition lead to values of d33, εr, Pr, and kp increase firstly and then decrease. The ceramic with x=0.06 exhibits optimal properties: d33=313 pC/N, kp=42%, Pr=25.48 μC/cm2, εr=1353, tanδ=2.5%, together with a higher TC of 327℃.
|
|
|
Porous Cotton-derived Carbon: Synthesis, Microstructure and Supercapacitive Performance
HAO Yan-Xia, QIAN Meng, XU Ji-Jian, BI Hui, HUANG Fu-Qiang
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 93–99
 Abstract
Abstract(
895 )
 HTML
HTML(
20)
 PDF
PDF(868KB)(
1476
)
Biomass materials were widely used to synthesize porous carbon for energy storages considering the simple preparation method and wide availability of raw materials. Herein, we prepared nitrogen doped porous carbon from natural cotton via a simple one-step eco-friendly method. The cotton-derived carbon material delivers a maximum specific surface area of 480 m2/g and a high nitrogen content of 6.84% at the carbonization temperature of 750℃. The obtained material shows excellent performance when used as supercapacitor electrode materials, which exhibits a maximal specific capacitance of 252 F/g at 1 A/g in 1 mol/L H2SO4 electrolyte and retains 94% of the capacitance after 10,000 cycles at 15 A/g. The good performance of the low-cost carbon electrode made from cotton provides a potential application for electrochemical capacitors.
|
|
|
Na1.88Bi1.88S4 and Na1.36Ca1.28Bi1.36S4 Single Crystals: Growth, Structure and Optical Property
WANG Dong, HE Jiao-Qiao, LAI Xiao-Fang, HUANG Rong-Tie, SHI Ying, HUANG Fu-Qiang
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 100–106
 Abstract
Abstract(
604 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(930KB)(
983
)
Na1.88Bi1.88S4 and Na1.36Ca1.28Bi1.36S4 single crystals of high quality were successfully synthesized by solid-state reaction method using NaI as flux. Both compounds crystallize in the rocksalt structure type of a cubic Fm-3m space group. The preferred orientation growth of lattice face (111) were observed in both two compounds. The optical absorption measurements show that the band gap of Na1.88Bi1.88S4 and Na1.36Ca1.28Bi1.36S4 compounds are 1.29 eV and 1.45 eV, respectively. Two compounds were fabricated into devices that exhibit notable photoelectric behavior, suggesting their potential for applications as photoelectric switches.
|
|
|
Solid-state Crystal Growth and Its Application to Fabricate Planar Waveguides
GAN Qi-Jun, JIANG Ben-Xue, ZHANG Pan-De, JIANG Yi-Guang, YANG Chao, ZHANG Wen-Chao, LUO Da-Ping, LI Wen-Xue, ZHANG Long
2018 Vol. 33 (1): 107–112
 Abstract
Abstract(
817 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(1369KB)(
1131
)
The effect of different factors, i.e., annealing temperature, grain size, and dopant ion on the solid-state crystal growth (SSCG), was studied in this work. In the SSCG process induced by heat treatment, a single crystal absorbs grains near the bonding interface, forming a robust bond. Using this method, a planar waveguide (PWG) consisting of a core layer of 12at% Yb:YAG polycrystal (100 μm) was fabricated and cladded by two YAG single crystal layers. No Yb3+ ion diffusion was observed. The CW laser performance of the Yb:YAG PWG was investigated. A maximum power of 1.14 W with a slope efficiency of 16.09% was obtained in the plano-plano resonator, and a maximum power of 1.83 W with a slope efficiency of 9.59% was obtained in the three-mirror resonator. A tunable laser with a continuous output between 1027.5 nm and 1033.5 nm was realized.
|
|