|
|
Research Progress and Prospect of Aqueous Zinc Ion Battery
CHEN Li-Neng, YAN Meng-Yu, MEI Zhi-Wen, MAI Li-Qiang
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 225–234
 Abstract
Abstract(
6620 )
 HTML
HTML(
309)
 PDF
PDF(669KB)(
7140
)
Zinc ion battery, a new type of aqueous secondary batteries proposed in recent years, can deliver high energy and high power density. Meanwhile, safe and efficient discharge processes, cheap and nontoxic electrode materials, and easy fabrication are the advantage of Zinc ion battery, showing great practical value and developmental prospects in the field of scale energy storage. In this paper, the development and exploration of aqueous zinc ion battery are reviewed. Also the advantages and challenges of the zinc anode are summarized. Moreover, this paper analyzed the electrochemical properties and reaction mechanism specifically. In addition, the development of cathode materials is predicted by analyzing the insertion and extraction of multivalent ions.
|
|
|
Improved Performance of Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Redox-reversible Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ Electrodes
YANG Yang, TIAN Dong, DING Yan-Zhi, LU Xiao-Yong, LIN Bin, CHEN Yong-Hong
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 235–240
 Abstract
Abstract(
828 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(575KB)(
1054
)
Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ (PSCF) and Gd0.2Ce0.8O2-δ (GDC) powders were synthesized by a citric acid- nitrates self-propagating combustion method, and La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ (LSGM) electrolyte powder was prepared by conventional solid state reaction process. The LSGM-supported symmetrical solid oxide fuel cell of PSCF│GDC│LSGM│GDC│PSCF with GDC function layer was fabricated. The phase structure, chemical compatibility, polarization resistance, cross-section microstructure and the cell performance were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), electrochemical impedance spectra, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and self-assembly SOFC test system, respectively. The results indicate that PSCF powder exhibits a single perovskite with cubic symmetry and a good redox reversibility. The GDC function layer dramatically improve the chemical compatibility among PSCF, LSGM in hydrogen and the cell performance. The area specific resistance (ASR) of PSCF│GDC decreased from 6.892 Ω·cm2 to 0.314 Ω·cm2 in hydrogen at 800℃ and the maximum power density increased from 269 mW/cm2 to 463 mW/cm2 using humidified hydrogen (3%H2O) as fuel and ambient air as oxidant. The results indicate that PSCF is a promising electrode material for symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells, and GDC function layer is a potential way to enhance the long-term stability.

|
|
|
Ni/YSZ Anode Impregnated La2O3 on Anti-carbon Deposition of SOFC Cell
CHENG Liang, LUO Ling-Hong, SHI Ji-Jun, SUN Liang-Liang, XU Xu, WU Ye-Fan, HU Jia-Xing
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 241–246
 Abstract
Abstract(
781 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(727KB)(
1186
)
For the planar anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell with Ni-YSZ anode, YSZ electrolyte was prepared by aqueous tape casting and La2O3 was impregnated into the Ni-YSZ anode. Traditional composite LSM-YSZ was used as the cathode. Microstructure and composition of the single cell were measured by scanning electron microstrscope(SEM)and energy dispersive spectra(EDS). When using ethanol/steam as fuel, the power density and impedance spectra of the single cell were measured by cyclic voltammetry and AC impedance method at 750℃. The results showed that impregnated La2O3 particles with size of 90 nm were distributed uniformly around the pores of the anode. The single cell with impregnated La2O3 exhibited more stable performance than the cell without impregnated La2O3. With the increase of loading of La2O3, the single cell showed better performance and better anti-carbon deposition ability. The results show that degradation rate of the single cell is 0.09%/h after operating at 7 h with the La2O3 loading of 2.4wt%.

|
|
|
Direct View for the Deformation Evolution of Sulfur Electrode during Li-S Battery Cycling
WANG Yu-Hui, JIN Jun, GUO Zhan-Sheng, WEN Zhao-Yin
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 247–251
 Abstract
Abstract(
755 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(396KB)(
1123
)
An experimental set-up was developed which can observe electrode deformation and electrochemical reaction in-situ during the charge-discharge cycling of lithium-sulfur battery. The positive bending deformation during charge and discharge was monitored at real time. It was found that the positive curvature increased during discharge and reduced during open circuit. The curvature would recover the original state during charge period. As electrochemical reaction proceeds, the electrolyte near positive electrode gradually become yellow and deepened due to polysulfide dissolution of discharge products. Results of surface and section morphology observation on sulfur electrode before and after cycle using scanning electron microscope (SEM) were consistent with curvature changes during cycling and verified the volumetric expansion of sulfur electrode.
|
|
|
Luminescence Properties of Si3N4 Doped Nitride Sr3SiO5: Eu2+ Phosphor
ZHANG Shuang-Shuang, TIAN Wen-Yu, ZHANG Jian-Xin, SONG Kai-Xin, QIN Hui-Bin
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 252–256
 Abstract
Abstract(
605 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(411KB)(
1075
)
Si3N4 doped Sr2.99SiO5-6xN4x:0.01Eu2+ phosphorssampless were prepared by high temperature solid-state reaction method. Testing results of XRD, EDS and CHNS of the phosphor samples demonstrated that the nitrogen atoms could be incorporated into the host lattice of Sr3SiO5 through partial occupation of the oxygen atoms sites to form Sr2.99SiO5-6xN4x:0.01Eu2+solid solution. Under the excitation of 344 nm ultraviolet, the Sr2.99SiO5-6xN4x: 0.01Eu2+ phosphor samples emit orange lights peaked at 580 nm, which originates from 4f65d1→4f7 transitions of Eu2+ ions. With the increase of N3+-ions concentration, the intensities of emission and excitation spectra of Sr2.99SiO5-6xN4x: 0.01Eu2+ phosphor samples are obviously enhanced. The thermal stability testing results of the phosphor samples show that the incorporation of N3- ions significantly improve the thermal stability better than that of undoped samples. The curves analyzed and fitted by the Arrhennius formula model indicate that the quenching temperature is caused by crossover process.

|
|
|
Effect of Sintering Temperature on Luminescence Properties of Color Conversion Glasses in Borosilicate Glasses
LI Yang, HU Li-Li, YANG Bo-Bo, SHI Ming-Ming, ZOU Jun
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 257–262
 Abstract
Abstract(
682 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
1065
)
The color conversion glass is a promising material for light emitting diodes encapsulation due to its high thermal conductivity and good thermal stability. In present study, color conversion glasses were prepared by sintering a mixture of borosilicate glass frits and a YAG phosphor at temperature from 600℃ to 900℃. The effects of sintering temperature on luminescence properties were examined. Characteristics of color conversion glasses, with respect to luminescence intensity, CIE (Commission International de I’Eclairage) chromaticity and CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) were analyzed based on luminescence excitation and emission spectra. These characteristics are dependent on sintering temperature of the color conversion glasses. The CIE coordinates shift with increase of sintering temperature. The glass, sintered at 700℃, shows the best luminescence properties. But for the glasses sintered above 850℃, their luminescence properties may be destroyed. Test results of X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) reveal that degradation of luminescence properties with increase of sintering temperature is ascribed to the lattice disturbance of YAG and oxidation of Ce3+, which is caused by reactions between glass matrix and YAG phosphors. The present study may promote the application of color conversion glasses in light emitting diodes encapsulation.

|
|
|
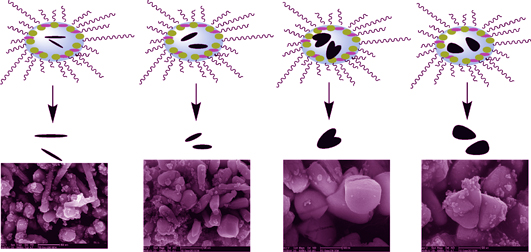
Controlled Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity Evaluation of Nanostructured Ag3PO4
CAI Wei-Wei, LI Jiao, HE Jing, WANG Wei-Wei
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 263–268
 Abstract
Abstract(
730 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(612KB)(
1022
)
Silver phosphate (Ag3PO4) materials with different nanostructures including rod, cambiform and tetrahedron with round edges and corners were synthesized by adjusting the molar ratio (W) of water to surfactant in a reverse microemulsion, which consists of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), isopentyl alcohol, cyclohexane, and aqueous solution, using silver nitrate and potassium dihydrogen phosphate as starting materials. The structure, morphology and visible-light-response of the obtained samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, HRTEM, and UV-Vis-DRS spectra. The formation mechanisms of nanostructured Ag3PO4 were discussed. Moreover, the photocatalytic activity was also evaluated by means of degradation of organic dye methylene blue (MB) in water. The results show that all the samples have body-centred cubic crystal structure, and the W value has an obvious effect on morphologly of nanostructured Ag3PO4. The varied morphologies can be attributed to the change of diameter and interfacial film strength of water nuclear influenced by SDS content. In addition, all the obtained samples exhibit excellent efficient photocatalytic activity for the photo-degradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible light irradiation, and the tetrahedral Ag3PO4 with exposed many {111} facets exhibits the best photocatalytic activity.
|
|
|
Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Bi2WO6 by the Synergistic Action of Ti(IV) and Graphene Bi-cocatalysts
SONG Jia, XU Ying, MO Yan-Ping, LI Yong-An
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 269–274
 Abstract
Abstract(
738 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(535KB)(
1044
)
Cocatalyst modification is an effective way to promote the separation of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. The reduced graphene oxide (rGO) with high electron transfer rate and the amorphous Ti(IV) compounds as hole cocatalyst were loaded on the surface of highly-efficient and flake-like Bi2WO6 nanoparticles by a hydrothermal-impregnation method to prepare Ti(IV)-rGO/Bi2WO6 visible-light-driven photocatalyst. It was found that the Ti(IV) and rGO single-cocatalyst modified Bi2WO6 exhibited an enhanced photocatalytic activity and dual-cocatalyst modified Bi2WO6 photocatalyst showed higher photocatalytic performance than single-cocatalyst modified Bi2WO6. When the amount of Ti(IV) was 5wt%, the photocatalytic rate constant of Ti(IV)-rGO/Bi2WO6 photocatalyst reached 2.2×10-2 min-1, which was 88-fold higher than that of bare Bi2WO6. The enhancement of photocatalytic performance mainly depends on the synergistic effect of novel Ti(IV)-hole cocatalyst and rGO-electron cocatalyst, namely, Ti(IV) compounds rapidly transfer the photogenerated holes, while rGO rapidly capture the photogenerated electrons. The present amorphous Ti(IV) and rGO cocatalysts can be widely applied in the design and development of highly efficient cocatalyst-modified photocatalytic materials.

|
|
|
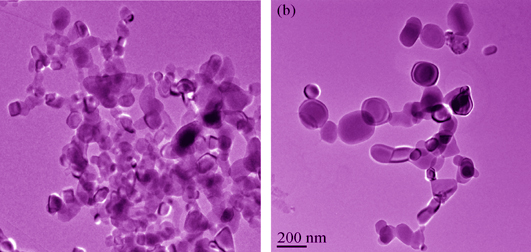
Influence of Explosion Temperature on Structure and Property of Nano-TiO2 Prepared by Gaseous Detonation Method
YAN Hong-Hao, WU Lin-Song, LI Xiao-Jie, ZHAO Tie-Jun
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 275–280
 Abstract
Abstract(
602 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(358KB)(
866
)
TiO2 powders were fabricated by gaseous detonation method, and influences of explosion temperature on phase composition, crystallite size and photocatalytic property of TiO2 were studied. The prepared samples were characterization by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). Photocatalytic performance was determined by degradation of methyl orange dye under UV irradiation. The results show that explosion temperature has a significant effect on mean particle size and weight fraction of rutile in the sampls. The maximum percent content of rutile is 92.2% when explosion temperature is 2524 K. The average particle size has linear relationship with explosion temperature, and the sample particle sizes increase from 87.2 nm to 172.9 nm with explosion temperature increasing from 2399 K to 3114 K. Explosion temperature exerts an indirect influence on photocatalytic performance. Photocatalytic performance decreases with explosion temperature increment. At 2399 K, the sample exerts the highest photocatalytic activity that the degradation rate of methyl orange solution can achieve 90.82% under UV light for 40 min, and the fraction of anatase and mean particle size is 31.7% and 87.24 nm, respectively.
|
|
|
Coupling of Metallurgical Method to Remove Impurities in Solar Grade Polycrystalline Silicon
LI Peng-Ting, WANG Kai, JIANG Da-Chuan, REN Shi-Qiang, TAN-Yi, AN Guang-Ye, ZHANG Lei, GUO Xiao-Liang, WANG Feng
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 281–286
 Abstract
Abstract(
584 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(489KB)(
1215
)
Preparation of 6N grade polycrystalline silicon materials using raw materials of industrial silicon was explored by medium melting, directional solidification and electron beam melting. The contents of impurities B and P in the samples are both lower than 0.20 ppmw, while the total content of metal impurity (TM) is less than 0.23 ppmw. During the process of removing B by medium melting, a large proportion of Al and Ca is simultaneously removed through the redox reaction. During the process of electron beam melting, volatile impurities including P, Al and Ca are further effectively removed by using saturated vapor pressure. Meanwhile, other metal impurities are removed by decreasing beam power, which induces the occurrence of directional solidification. Coupling of metallurgical methods reduces the purification process of polycrystalline silicon, and provides the technical support for continuous and large-scale production.
|
|
|
Structure and Electrochromic Properties of Titanium-doped WO3 Thin Film by Sputtering
PENG Ming-Dong, ZHANG Yu-Zhi, SONG Li-Xin, YIN Xiao-Fu, WANG Pan-Pan, WU Ling-Nan, HU Xing-Fang
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 287–292
 Abstract
Abstract(
1031 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(506KB)(
1532
)
Pure and Ti-doped WO3 thin films prepared by RF (radio-frequency) magnetron at room temperature were determined by XRD, Raman and SEM to analyze the micro-structure and the morphology of the films. In addition, electrochemical workstation and UN-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer were used to measure their cycling stability and optical property. Research results showed that Ti doping had little interference with the surface morphology and optical constants, but the film crystallization temperature could be increased by Ti doping. Electrochemical test results showed that Ti doping could improve reversibility of ion injection and extraction, and improve cycling performance of films. Meanwhile, the switching speed and optical modulation performance of films were enhanced. In detail, the switching time of colored and bleached states were shortened from 9.8 s and 3.5 s to 8.4 s and 2.7 s, respectively. Therefore, Ti doped WO3 thin films has better electrochromic properties.
|
|
|
B-site Substitution by (Mg1/3Ta2/3)4+ on Structures and Dielectric Properties of New Sr-based (Sr, Nd, Ca)TiO3 Microwave Ceramics
QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, SONG Xiao-Hui, YUAN Chang-Lai, LIU Fei
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 293–298
 Abstract
Abstract(
596 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(680KB)(
978
)
(Sr0.2Nd0.208Ca0.488)Ti1-x(Mg1/3Ta2/3)xO3 (0.2≤x≤0.5, SNCTMTx) ceramics were prepared by solid sate reaction technique. Wherein, the relation between phase compositions, microstructures, sintering properties, and microwave dielectric properties of the SNCTMTx (0.2≤x≤0.5) ceramic systems were studied. The XRD results indicated that a single phase with orthorhombic perovskite-like structure was formed in the sample with x = 0.2, and a mixed phase system was formed in the samples with given compositional range x = 0.3 - 0.5 composed of orthorhombic perovskite phase, SrO phase and unknown second phase. Additionally, the εr first increased and then decreased, affected by the appearance and the content of the second phase. Meanwhile, the Q×f value showed down first and then up with the increase of (Mg1/3Ta2/3)4+ content because the increasing degree of 1:2 ordering could suppress the reduction in quality factor. Moreover, the τf gradually shifted to near-zero direction, which resulted from the variation of the oxygen octahedral distortion. The SNCTMTx (x=0.5) ceramic sintered at 1530℃ for 4 h showed better microwave dielectric properties with εr = 55.3, Q×f ≈ 7,400 GHz and τf ≈ 23.6×10-6/℃.

|
|
|
Effect of Sintering Process on Microstructure and Properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 Lead-free Ceramics
LONG Pei-Qing, LIU Xi-Tao, YI Zhi-Guo
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 299–304
 Abstract
Abstract(
787 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(556KB)(
1123
)
The lead-free (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 (BCTZ) piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by conventional solid state reaction combined with a liquid precursor mixing method. The effects of dwelling time on the structural, dielectric, piezoelectric, and ferroelectric properties as well as the temperature dependence electrical properties of BCTZ ceramics were systematically investigated. The results show that dense BCTZ ceramics are obtained with uniform grain size and tetragonal perovskite structure, without any other impure phase. As sintered at 1540℃ with the dwelling time increasing from 2 h to 24 h, the average grain size of the ceramics increases from 10.5 μm to 38.7 μm, which strongly controls the electric properties of the ceramics. With the grain size increasing, the Curies temperature Tc shifts to a higher temperature, the piezoelectric properties increase while the electric-field-induced strain decreases for the ceramics. The ceramics sintered at 1540℃ for 24 h obtain excellent electrical properties of Tc ~90℃, tanδ < 0.05, kp~0.46, d33 ~540 pC/N, and Ps ~17 μC/cm2. Moreover, electrical measurement at different temperature suggests that BCTZ samples have strong temperature dependence, especially in the temperature range below Tc, where the electric properties of the ceramics decrease with increasing temperature.

|
|
|
A New Porous Zirconium Phosphonate Hybride Material and Its Adsorption Properties
ABUBAKER Abutartour, LOTFIA El-Majdoub, SHI Ya-Sai, LI Ni-Li, XU Qing-Hong
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 305–312
 Abstract
Abstract(
735 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(600KB)(
909
)
Synthesis of organic-inorganic hybrid hierarchical porous materials with strong ligand in framework is an important field of current research in adsorption. A new kind of inorganic/organic hierarchical zirconium phosphonate material (ZrPTA) with porous structure was prepared from bis(hexamethylene)triamino-N, N-bisacetyl- phosphonic acid and ZrOCl2·8H2O in water solution by using hydrothermal synthesis technology. The samples were characterized by FT-IR spectroscope, TGA, XRD, XPS, SEM and element analysis. The results show that the material possesses a rod-like morphology, and the rods contain micropores of 1.38 nm and 1.93 nm in diameter, mesopores of 2.99 nm in diameter, and a surface area of ~112.2 m2/g. The as-prepared ZrPTA is more efficient in removing Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ from wastewater. Its maximum adsorption capacities for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ are 742.7, 689.8 and 627.0 mg/g, respectively, which is much higher than the maximum adsorption capacities of the adsorbents reported. The perfect properties make the material good prospects in application as an adsorbent in wastewater processing.

|
|
|
In Situ Preparation and Glucose Sensing Property of Ternary
NiO/Ni/C Microspheres
QIN Dong-Yu, HE Xiao-Long, NIE Qiu-Lin, YIN Hao-Yong, YUAN Qiu-Li
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 313–318
 Abstract
Abstract(
762 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(552KB)(
1055
)
Ternary NiO/Ni/C microspheres was obtained by calcination of the precursor Ni(OH)2/C in pure nitrogen. The precursor was prepared via an one-pot hydrothermal synthesis technology using glucose, nickel chloride and urea. Scanning electron microscope (SEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray energy dispersive (EDS), and Raman were used to characterize the morphology and structure of the sample. Results show that the NiO/Ni/C microspheres have a coral-like structure with diameter of about 1.7 μm, and the crystalline phase of Ni and NiO are cubic. Electrochemical behavior and sensing property of ternary NiO/Ni/C microspheres composites were studied via cyclic voltammetry and amperometric method. When the Ni/NiO molar ratio is 0.19, the ternary NiO/Ni/C microspheres have excellent glucose sensor performance with a sensitivity of 241.09 μA·mmol/(L·cm2) in a range of 10-5.05 mmol/L, and a detecting limit of 10 μmol/L. Furthermore, the sensor has good stability and anti-interference ability.

|
|
|
Surface Microstructure on Hydroxyapatite Spherules and Its Regulation on Stem Cells
ZHI Wei, SHI Feng, LI Jing-Yu, ZHOU Teng, QU Shu-Xin, WANG Jian-Xin, ZHANG Cong, WENG Jie
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 319–325
 Abstract
Abstract(
706 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(513KB)(
948
)
HA spheres with different surface microstructures were prepared by a Sol-Gel route with various hydroxyapatite (HA)/chitin ratios. The surface morphologies, phase compositions, and biomimetic mineralization ability of samples were respectively analyzed with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and biomimetic mineralization test. Furthermore, the influences of the surface microstructure on biological behavior of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells were examined by Alamar blue, SEM, alkaline phosphatase assay and flow cytometry. When the mass ratio of HA/Chitin was increased from 4/1 to 35/1, the surface microstructure of HA spheres changed substantially, as showed by a reduction of micro-porosity from (35%±0.8%) to (10.4%±0.7%), decrease of surface roughness, and gradual disappearance of micro-creases. The result of biomimetic mineralization test showed that the surface microstructure had important influence to the ability of biomimetic mineralization for HA spheres. In vitro culture of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells demonstrated that the rougher sphere surface, with abundant micro-creases and micro-pores, supported cell spreading and proliferation. In comparison, the smoother sphere surface with fewer micro-pores effectively induced cell elongation and up-regulated ALP expression, which suggested stem cells osteogenic differentiation. Meanwhile, the surface microstructure of spherules also modulated the expression of characteristic antigen makers on the surface of stem cells.

|
|
|
Growth, Magnetic and Electrical Transport Properties of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 Thin Films on PLZST Ceramics
XIAO Ling, CHEN Ying, LIU Zhen, WANG Gen-Shui, WEN Zhi-Yu, DONG Xian-Lin
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 326–330
 Abstract
Abstract(
670 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(398KB)(
938
)
La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 (LSMO) thin films with different thicknesses were deposited on (Pb0.97La0.02) (Zr0.58Sn0.3025Ti0.1175)O3 (PLZST) ceramics by RF magnetron sputtering, and their microstructure, magnetic and electrical transport properties were investigated. Microscopy observations show that LSMO thin films are perovskite structure without obvious impurity phase. All the LSMO thin films display smooth surface with uniform, and roughness is as low as 2.93 nm for LSMO thin films at the thickness of 20 nm. Furthermore, large magnetoresistance (MR) effect was observed in LSMO thin films in a broad temperature range of 10-300 K. Particularly the MR of LSMO thin films with 20 nm in thickness exhibits excellent temperature stability. Moreover, the Curie temperature, metal-insulator transition temperature, saturation magnetization and electrical conductivity decrease as the film thickness increases, which is attributed to the diffusion of Pb, Sn, Zr, etc. in the samples, resulting in the distortion of MnO6 octahedron.

|
|
|
Preparation of Ceria-zirconia Mixed Oxides with Improved Thermal Stability for Three-way Catalysts by a Modified Co-precipitation Method
WU Qing-Feng, CUI Ya-Juan, ZHANG Hai-Long, ZHOU Yi, LAN Li, WANG Jian-Li, CHEN Yao-Qiang
2017 Vol. 32 (3): 331–336
 Abstract
Abstract(
807 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(1492KB)(
976
)
A series of ceria-zirconia mixed oxides (CZ-x; x=0, 20, 40 and 80) with Ce/Zr molar ratio of 3/2 were synthesized by co-precipitation method. In order to improve the thermal stability of ceria-zirconia mixed oxides, we extended the time for the primary grain to grow up by a modified synthesis reactor. The resulting samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption-desorption, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results revealed that bigger grain could be obtained by extending time for the primary grain to grow up, which was propitious to enhance the textural properties and structural properties of the materials. Thus, the thermal stability of the materials was improved. In this study, the materials were applied in the field of Pd-only three way catalysts (TWCs). The catalysts exhibited excellent catalytic performance and thermostability, showing better prospect in application.
|
|