|
|
Effects of Te-Bi Glass Frit on Performances of Front Silver Contacts for Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells
FU Ming, CHENG Si-Guo, WANG Yue, ZHOU Hong, FAN Lin
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 785–790
 Abstract
Abstract(
1119 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(520KB)(
1272
)
Front silver paste is a key material for metalization of crystalline silicon solar cells. Environmental-friendly paste is one of the main development direction for the front silver contacts. The effects of Te-Bi glass frits with different formulations and components on the performances of front silver contacts were studied by orthogonal experimental method. The heating characteristics of Te-Bi glass frit and front silver pastes were analyzed by TGA-DSC. Size and distribution of the silver microcrystalline on Ag-Si interface were observed by SEM. The influence of glass on the performances of the front silver contacts was analyzed by using tunneling current model. The results show that the transition temperature (Tg) of Z7 glass frit composed of 45wt% TeO2 and 36wt% Bi2O3 is 379.07℃. The endothermic reaction of corresponding paste occurs at 612.8℃ with 0.16% weight loss occurring at the same temperature. The efficiency of polycrystalline silicon solar cells using the corresponding front silver paste is 16.87%, and adhesion of the cell is 4.35 N.
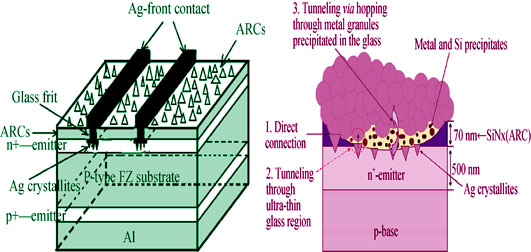
|
|
|
Directional Growth of Bulk Silicon from Si-Al-Sn Melts
Li Ya-Qiong, Li Jia-Yan, Tan Yi, Zhang Li-Feng, Morita Kazuki
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 791–796
 Abstract
Abstract(
661 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(421KB)(
870
)
To separate primary Si from Si-Al-Sn alloy, directional solidification method was applied in this study. The effects and mechanisms of the cooling rate, alloy composition, and G/R ratio on bulk Si growth were investigated for optimizing parameters. By using of the constitutional supercooling criterion for single-phase growth from melts, the effects of Sn addition have been explored as compared with Si-Al and Si-Sn alloys. Finally, with the application of electron probe micro analyzer, the microstructure of Si and the distribution of Al and Sn were analyzed. Based on the obtained results, the directional solidification method is verified to be an effective method to separate Si from Si-Al-Sn alloy without any metal inclusions. The contents of Al and Sn in bulk Si are almost equivalent to the corresponding solid solubility. The obtained results indicate that directional solidification method can be an appropriate and effective technique to separate Si from alloy.
|
|
|
Excellent Thermionic-emission Performances of (Ce1-xGdx)B6 with Ultra-low Work Functions
WANG Yang, ZHANG Xin, ZHANG Jiu-Xing,LIU Hong-Liang, JIANG Hao, LI Lu-Lu
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 797–801
 Abstract
Abstract(
640 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(449KB)(
1017
)
CeB6 with simple cubic CaB6-type structure has attracted much interest owing to its promising scientific and technological characteristics like high brightness, high melting point, low vapor pressure, long service life, and low work function. High-quality Ce1-xGdxB6(x=0~0.3) single crystals with ultra-low work function are successfully synthesized via the spark plasma sintering combining floating zone technique. The quality, chemical composition and thermionic emission properties of the Ce1-xGdxB6 single crystals were systematically investigated by 360° phi scanning X-ray single crystal diffraction, X-ray fluorescence and emission measurements. Based on the testing results, the prepared single crystals exhibit good quality. The emission current density of Ce0.9Gd0.1B6 on (100) crystal surface is up to 82.3 A/cm2 higher than that of CeB6 under 4000 V at 1873 K, while the current density under zero voltage condition is 24.70 A/cm2, about two-fold higher than that of CeB6. The average value of effective work functions at different temperatures is reduced to 2.30 eV lower than 2.93 eV of CeB6. Such excellent performances suggest that the ternary hexaborides can be used as a promising cathode emitter source for exploration and research in the electron emitter field.
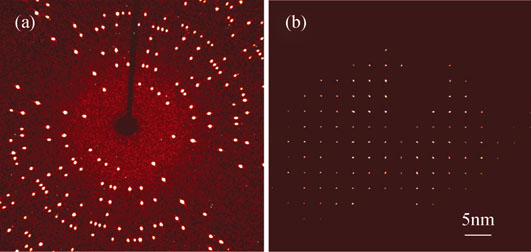
|
|
|
Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of LiFePO4/C Cathode Materials Using Fe Powder
MENG Fang-Li, ZHANG Dong-Yun, CHANG Cheng-Kang, XU Jia-Yue, KAMZIN A S
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 802–806
 Abstract
Abstract(
805 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(409KB)(
1224
)
Using Fe source as starting material, the composite LiFePO4/C material was obtained through a combined method of nano grinding, spray drying and high temperature calcinating. The as-prepared samples were verified by TG/DSC and XRD and characterized by SEM and Mossbauer spectrum. The electrochemical performances were studied by CV and cyclic tests. The results show that the LiFePO4/C composite is successfully synthesized by calcinating the precursor at 500-700℃. The obtained LiFePO4/C materials are spherical porous agglomerates with mean size of 4-5 μm, which are composed of 200 nm particles. According to Mössbauer data, all the iron ions are in +2 valence state. The spherical nano LiFePO4/C composite shows great electrochemical performance as potential cathode material for lithium ion batteries, with a specific capacity of 156 mAh/g at 1C rate and capacity retention of 92.8% after 300 charge/discharge cycles.
|
|
|
Fabrication and Characterization of Lu2O3 Nanowire Arrays by Sol-Gel Template Method Assisted with Ultrasonic Treatment
HU Ya-Hua, GU Mu, ZHANG Zhi-Yuan, LIU Xiao-Lin, HUANG Shi-Ming, LIU Bo, ZHANG Juan-Nan
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 807–811
 Abstract
Abstract(
713 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(370KB)(
840
)
Lu2O3 nanowire arrays were fabricated by a Sol-Gel anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) template method assisted with ultrasonic treatment. The structure and morphology of Lu2O3 nanowire arrays were characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Energy disperse X-ray spectroscope (EDX), and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results indicate that the as-prepared nanowire arrays consist of cubic structure of polycrystalline Lu2O3. The Lu2O3 nanowires are parallel to each other and quite uniform in diameter of about 200 nm. The formation mechanism of nanowires is also explored here. It is found that it is easy to evolve Lu2O3 into bamboo-like nanotubes without ultrasonic treatment. Compared with traditional Sol-Gel template method, a good filling of Lu2O3 nanowires embedded in the AAO template can be obtained by improved ultrasonic- assisted technique. Ultrasonic treatment is useful to prepare for other nanowire arrays of different materials.
|
|
|
Effects of MgO, SrO and La2O3 Co-doping on Structure and Properties of (Zr0.8Sn0.2)TiO4 Ceramics
SUN Qing-Lei, ZHOU Hong-Qing, QIAN-Lei, WANG Ya-Zhou, ZHU Hai-Kui, YUE Zhen-Xing
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 812–818
 Abstract
Abstract(
691 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(476KB)(
982
)
(Zr0.8Sn0.2)TiO4 (ZST) ceramics were fabricated via conventional solid-state reaction method which was promoted by liquid phase. The effects of MgO, SrO and La2O3 co-doping ZST ceramics on phase composition, microstructures, sintering behavior, and high frequency dielectric properties were investigated systematically. The results showed that the main crystalline phase of the ceramics was ZST. The appropriate amount of MgO, SrO and La2O3 additions effectively decreased the sintering temperature of ZST ceramics and improved the microwave dielectric properties. The increment of MgO addition influenced comprehensive properties of ZST ceramics slightly. The decrement in bulk densities, dielectric constants and Q×f values with excessive SrO addition was due to incomplete growth of grains, incompact structures and increasing porosities. Additionally, the additives did not affect obviously the temperature coefficient of resonant frequency (τf) of the ceramics. When added 0.2wt% MgO, 0.6wt% SrO and 1.0wt% La2O3 and sintered at 1300℃ for 5 h, ZST ceramics displayed the optimum comprehensive properties: ρ = 5.14 g/cm3, εr = 40.11, Q×f = 51000 GHz (f = 5.61 GHz), τf = -2.85×10-6℃-1.
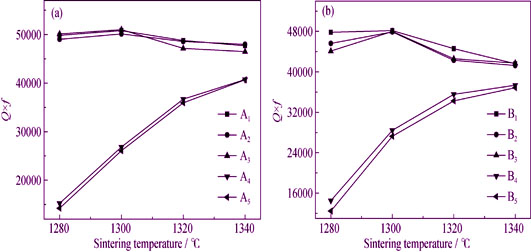
|
|
|
Influence of Eu2+ and Dy3+ Concentrations on Fluorescence and Phosphorescence of Sr2MgSi2O7 Phosphors
MAO Qi-Nan, LI He, JI Zhen-Guo, XI Jun-Hua, ZHANG Jun, KONG Zhe
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 819–826
 Abstract
Abstract(
626 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(636KB)(
951
)
Eu2+-doped Sr2MgSi2O7 and Eu2+ and Dy3+ codoped Sr2MgSi2O7 phosphors were synthesized by conventional solid-state reaction. Eu2+ and Dy3+ concentration effects on the fluorescence and phosphorescence of Sr2MgSi2O7 phosphors were studied. All the samples show a broad emission band centered at about 470 nm, which are ascribed to 4f65d→4f7 transition of Eu2+ ions. Concentration quenching is found to be the dominant factor decreasing emission intensity and afterglow duration time when Eu2+ doping level exceeds the critical concentration. Redshift of the emission bands is also observed as the Eu2+ concentration increasing. In order to explain the redshift of the emission bands, the centroid position of 5d level of Eu2+, crystal-field splitting energy and Stokes shift are estimated from excitation and emission spectra. Based on the calculation, the redshift of the emission bands mainly results from the variations of crystal-field splitting energy and Stokes shift, but is less influenced by the nephelauxetic effect. The Dy3+ ions suppress the fluorescence but enhance the phosphorescence lifetime. When the Dy3+ concentration is over 10mol%, the phosphorescence lifetime is shortened, because of concentration quenching of the Eu2+\Dy3+ ions by the mechanism of tunneling recombination.
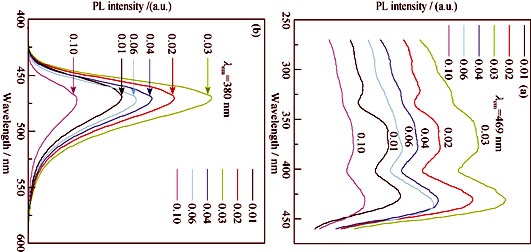
|
|
|
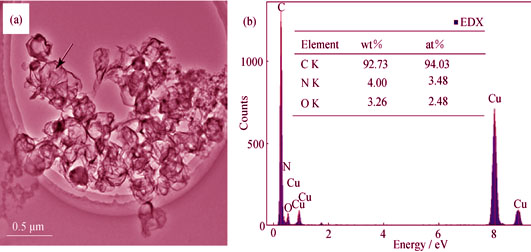
Preparation of N-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres and Investigation of Their Optical Properties
HU Feng-Xiang, LI Ling, LIN Kui, CUI Lan, SHI Cai-Jing, SAYYAR Ali Shah, CUI Shen
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 827–833
 Abstract
Abstract(
698 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(581KB)(
860
)
N-doped hollow carbon spheres (NDHCSs) were prepared by DC arc discharge at 800℃ in nitrogen, using anode prepared by the filling method. The morphology, structure, chemical and phase compositions, and optical properties of the product deposited on the stainless steel sheet were characterized by using FESEM, HRTEM, EDX, EELS, XRD, and UV-Vis, respectively. The results show that the outer diameters of the NDHCSs are in the range of 110-543 nm and their wall thicknesses are in the range of 2-12 nm. The walls consist of two parts, namely, the inner part and the outside part, which are comparatively complete structure of graphite and discontinuously wave-like structure of layer, respectively. The NDHCSs consist of C, N and O elements with comparatively uniform distribution. The phase composition of NDHCSs mainly includes graphitic carbon and another carbon phase. The UV-Vis spectra of the suspensions of the NDHCSs in ethanol show three absorption peaks at 210 nm, 221 nm and 264 nm. Such suspension emits green luminescence under UV light irradiation and can keep stable at least for two months. The NDHCSs may have potential application in the field of optics.
|
|
|
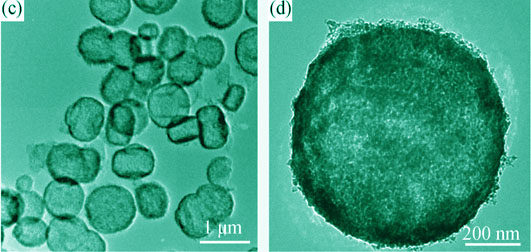
Hollow ZSM-5 Zeolite Microspheres with Improved Adsorption and
Catalytic Properties
SUN Li-Li, YAN Kai, LUO Wen, ZHOU Jian
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 834–840
 Abstract
Abstract(
1159 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(464KB)(
1400
)
A new kind of uniform hollow zeolite spheres were successfully synthesized by non-hard template synthetic method, which involves two key steps: firstly, the conventional hydrothermal synthesis process of zeolite spheres by using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as soft template, and then, the rapid post-alkaline-etching (PAE) technique. Structural features were characterized by XRD, N2 isotherm, SEM, and TEM. The performance in the organic-waste-water treatment and catalytic cracking of bulky molecules were also measured. It was found that crystallinity of the product underwent a reducing tendency after alkaline etching treatment, but the mesoporosity and pore volume were promoted. The diameter and shell thickness of hollow zeolite spheres were about 600 nm and 100 nm, respectively. Moreover, such hollow structure demonstrates remarkably a threefold capability increase in adsorption of benzene molecules in methanol solution if compared with conventional zeolite spheres. Such capability can be basically kept after repeating 6 times, indicating high capability and stability in adsorption. Enhanced catalytic activities were also approved in cracking of isopropyl benzene and triisopropyl benzene.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of TiO2/Co3O4 Nanocomposites and Their Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution
MA Ya-Ting, LI Qiao-Ling
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 841–844
 Abstract
Abstract(
879 )
 HTML
HTML(
33)
 PDF
PDF(363KB)(
1222
)
TiO2/Co3O4 nanocomposites with photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution under visible light were prepared via carbon assistant method and Sol-Gel method. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Transmission Electron Microscope(TEM), High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscope(HRTEM) and UV-Vis spectrophotometer were used to characterize the samples’ crystal structure, morphology and absorptivity of ultraviolet and visible light. The characterization results demonstrate that the prepared nanocomposites have good crystal form, structure and absorptivity of both ultraviolet and visible light. The photocatalytic activity of TiO2/Co3O4 nanocomposites for hydrogen evolution under simulated sunlight was tested and their reusability was also investigated. The results show that the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of pure water over the TiO2/Co3O4 nanocomposites is about 8.25 μmol/(g·h) under simulated sunlight. And the nanocomposites possess ideal reusability.
|
|
|
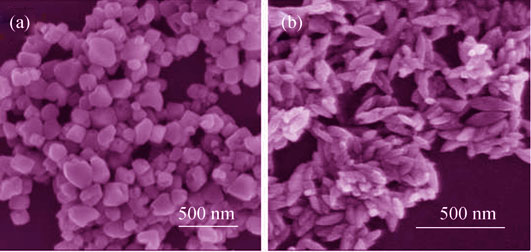
Preparation of Anatase TiO2 Nanocube with Exposed (001) Facet and Its Photocatalytic Properties
WAN Jian-Feng, HU De-Sheng, LU Peng-Hui, LIN Bi-Zhou, CHEN Yi-Lin, GAO Bi-Fen
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 845–849
 Abstract
Abstract(
904 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(399KB)(
1144
)
Anatase TiO2 single crystals with exposed (001) facets were successfully synthesized by a one-step hydrothermal route using TiF4 as raw material. The crystal phase, morphology, microstructure, and photoabsorption of the samples were analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectra (UV-Vis DRS). The influences of hydrothermal temperature and pH of solution on morphology of TiO2 and exposure of (001) facets were also investigated. Photocatalytic catalysts was evaluated by degradation of acid red dye. Experimental results demonstrated that exposure of (001) facets was beneficial for improving photocatalytic performance. Under ultraviolet light irradiation, TiO2 nanocube with exposure of (001) facets ca. 33% exhibited significantly higher activity than the common TiO2 without exposed (001) facets. The photocatalytic efficiency of the former was 1.6 times as high as that of the latter. The sample with the highest exposure of (001) facets was obtained at hydrothermal temperature of 180℃ and pH of solution 4-5. The corrosion of crystal surface would occur at hydrothermal temperature higher than 180℃. In addition, the pH of solution higher than 6 was unfavorable for the adsorption of F- ions on TiO2 crystals and the stabilization of (001) facets, which led to the disappearance of (001) facets.
|
|
|
Physical Properties of Ba(Ti0.96Sn0.04)O3 Ceramics
WU Yan-Qing, ZHANG Jia-Liang, LIU Da-Kang, SUN Dan-Dan
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 850–854
 Abstract
Abstract(
611 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(407KB)(
904
)
The Ba(Ti0.96Sn0.04)O3 ceramics were prepared through solid-state reaction route. Piezoelectric property, dielectric property, ferroelectric property, and microstructure were investigated. It is found that raw material and processing technique can largely affect the piezoelectric property of the Ba(Ti0.96Sn0.04)O3 ceramics. By comparing with the physical property of pure BaTiO3 ceramics, Sn doping significantly increases the transition temperature from orthorhombic phase to tetragonal phase (TO-T) of the Ba(Ti0.96Sn0.04)O3 ceramic to 36.9℃, while the thermal hysteresis at about TO-T is only 1.8℃. Its microstructure shows complicated domain, mainly composed of simple 90° parallel stripes with a few of different 180° configurations. P-E curve shows ideal square-like and saturated form with remanent polarization Pr of 18.9 μC/cm2 and coercive field Ec of 2.5 kV/cm. In addition, it is the non-180°-domain switching that leads large converse piezoelectric constant d33*, (up to 550 pm/V).
|
|
|
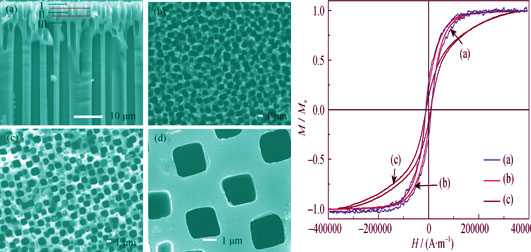
Fabrication and Magnetic Properties of N-type Porous Silicon/Nickel Microtubes Composite
ZHOU Hui, HAN Man-Gui, TANG Zhong-Kai, WU Yan-Hui
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 855–859
 Abstract
Abstract(
700 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(360KB)(
849
)
The highly ordered n-type porous Si template was prepared via electrochemical etching and back side illumination method. Pores of the Si template had squarish shape with side length of about 2 μm and depth of about 50 μm, respectively. Three growth stages, nucleation, self-assembly, and stable growth were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) during the formation process of the porous n-silicon template. Subsequently, nickel microtubes arrays were synthesized by electro-deposition. And the formation mechanism of the microtubes was also investigated. The content and particle size of Ni particles embedded in n-type porous Si templates increase with the increase of deposition time. Ni microtubes are formed by gathering the Ni particles over pore sidewall, which is different from that of insulative AAO template. In addition, the crystal structure of Ni microtubes keeps fcc-Ni in the whole growth process. In particular, due to the fewer defects and grain boundaries of Ni microtubes than that of Ni particles, the coercivity value of Ni microtubes is smaller. Moreover, the magnetic anisotropy of Ni microtubes is mainly contributed to the strong demagnetization energy.
|
|
|
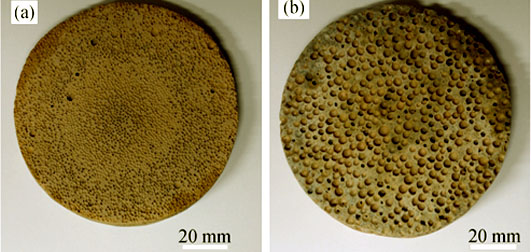
Preparation of Light Weight Porous Ceramics and Sound Absorption Performance Research
SUN Jin-Xing, CHEN Bin, LIU Pei-Sheng
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 860–864
 Abstract
Abstract(
940 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(399KB)(
1073
)
Light weight porous ceramics were successfully prepared by conventional mold. Effects of particle sizes, content of pore-forming agent and sample thickness on sound absorption performance of porous ceramics were studied by means of JTZB absorption coefficient measurement. The results indicate that when pore-forming agent content is 50vol%, sound absorption performance of macroporous ceramics is better than that of microporous ones. As the pore-forming agent content increases, the sound absorption peak moves from low frequency to high frequency, with the peak value increasing from 0.41 to 0.82. Neither high nor low porosity can improve the sound absorption material performance. The first sound absorption peak gradually moves towards the low frequency when sample thickness increasing from 10 mm to 30 mm. The sample obtains super sound absorption performance when pore-forming agent content is 60vol% and sample thickness is 20 mm. By adding cavity layer to the porous ceramics rear one by one, the sound absorption peak moves from high frequency to low frequency and the average sound absorption coefficient gradually increases with the increase of cavity layer number.
|
|
|
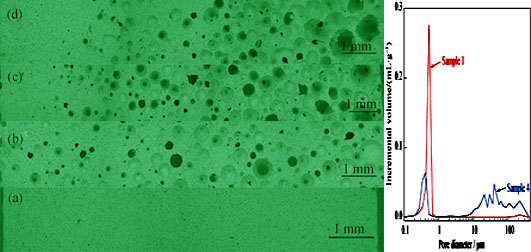
Gradient Porous Silicon Nitride by Slip Casting and Vacuum Foaming
DENG Jian, YAO Dong-Xu, XIA Yong-Feng, ZUO Kai-Hui, YIN Jin-Wei, ZENG Yu-Ping
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 865–868
 Abstract
Abstract(
842 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(370KB)(
1098
)
Gradient porous silicon nitride was fabricated by a combination method of slip casting and vacuum foaming. Firstly, foaming agent was added into Si3N4 aqueous slurry, then the uniformly stirred slurry was poured into the mold with plaster as base. Under low pressure and steady temperature, a green body with gradient pores was formed. Based on our research, the gradient structure and porosity were greatly influenced by the vacuum pressure. With the pressure decrease from 80 kPa to 9 kPa, the porosity increased from 59.01% to 80.85% and the gradient structure became more noticeable. When the pressure was 80 kPa, the sample obtained a uniform pore structure. After the pressure being decreased to 9 kPa, the sample obtained dispersed pore size distribution including values of 0.5, 20, 30, 40, 60, 100 and 200 μm measured through mercury intrusion method. Gradient porous ceramics with adjustable porosity and pore size distribution, as well as achievable complex shape and large scale, may fabricate through this simply and low cost method.
|
|
|
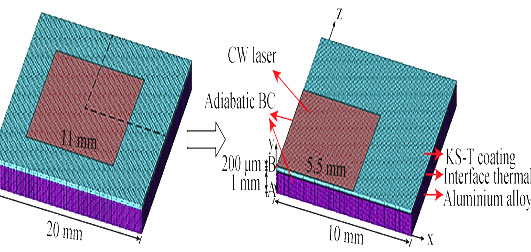
Preparation and Numerical Simulation Investigation of High Reflectance Anti-laser-ablation Coating
ZOU Yang, ZHAO Li-Li, YOU Li-Jun, CHEN Xiao-Ying, SONG Li-Xin
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 869–875
 Abstract
Abstract(
845 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(493KB)(
1126
)
An anti-laser-ablation coating using TiO2 as pigment and potassium silicate as binder (abbreviated as KS-T) was deposited on the aluminum alloy substrate by an air spray process. Factors influencing the reflectance of KS-T coating, including particle size, pigment volume concentration and coating thickness, were investigated. The reflectance of prepared KS-T coating could be up to 96.8% at the laser wavelength of 1064 nm. A three-dimensional finite element model based on the heat-conduction equation was developed to simulate the distribution of transient temperature filed. By monitoring the temperature variation at the backside center of aluminum alloy substrate during laser irradiation and comparing with the simulation results, it is found that KS-T coating could effectively protect the substrate from laser ablation. The simulation results demonstrated reflectance decrease of samples after a period of irradiation. The possible reasons for the reflectance decrease were proposed. The calculation results also showed that an obvious temperature drop emerged at the coating/substrate interface when interface thermal resistance (ITR) was considered. Eventually heat flux was prevented from flowing to the substrate and aluminum alloy kept a low temperature.
|
|
|
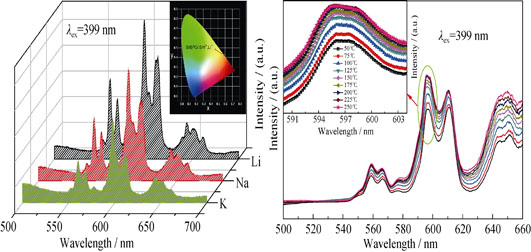
Enhancing Luminescence of SrBPO5: Sm3+ Phosphor by Codoping Alkali Metal for White LEDs
YANG Jing-Wei, LI Xu, JIAO Dian, WU Meng-Ying, WANG Yi-Bing, GUAN Li, GUO Qing-Lin, TENG Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 876–880
 Abstract
Abstract(
674 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(423KB)(
989
)
An orange reddish phosphor SrBPO5:Sm3+ was synthesized by the traditional solid-state method. The phosphor component was characterized by the X-ray powder diffraction (XRD). The photoluminescence excitation (PLE) and emission spectra (PL) were investigated. The influence of the concentration of Sm3+ ions on luminescence properties of samples and concentration quenching mechanism were investigated. The results show that the as-prepared phosphor can be excited by 342 nm, 358 nm, 370 nm and 399 nm UV light and the strongest one at 399 nm. On being excited by 399 nm, the sample emits yellow, orange and red emission at different wavelength. The optimal activator molar fraction in this phosphor is 0.016 and the only sintering temperature is 1000℃. It is meant for enhancing the emission intensity of SrBPO5:Sm3+ phosphor if appropriate Li+ ions are added as charge compensator. The thermal stability was evaluated by emission spectra of phosphor at different measuring temperatures. This research studied the influence of reaction temperature and charge compensator on the luminescence characteristics. The chromaticity coordinates of SrBPO5:Sm3+, R+ phosphor was explored. The results indicate that SrBPO5:Sm3+, Li+ is a potential orange-reddish phosphor in near UV based white LEDs.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Diatomite/g-C3N4 Composite with Enhanced Visible-light-responsive Photocatalytic Activity
WANG Dan-Jun, SHEN Hui-Dong, GUO Li, HE Xiao-Mei, ZHANG Jie, FU Feng
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 881–889
 Abstract
Abstract(
938 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(666KB)(
1094
)
Novel visible-light-responsive diatomite/g-C3N4 composite was successfully synthesized via a facile impregnation-calcination method. The sample was characterized by TG, XRD, FE-SEM, HR-TEM, FT-IR, XPS, UV-Vis-DRS, and PL spectra. The photocatalytic activities of samples were evaluated by degradation of RhB under visible light irradiation. Experimental results indicated that 2.32wt% diatomite/g-C3N4 composite exhibits high efficiency for the degradation of RhB. The photoreaction kinetics constant value is about 1.9 times as high as that of g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation. The radical trap experiments indicate that ·O2- serves as the main active species for the photodegradation of RhB over 2.32wt% diatomite/g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation. The enhanced photoactivity is mainly attributed to the electrostatic interaction between g-C3N4 and negatively charged diatomite, synergistic effect lead to the efficient migration of the photogenerated electrons and holes of g-C3N4.
|
|
|
Luminescent and Cytotoxic Characteristics of an Ellipsoidal and Microsized Europium (Eu)-doped Hydroxyapatite
MA Ming, LU Wei-Peng, CAO Xiao-Feng, MAO Ke-Ya, GUO Yan-Chuan
2016 Vol. 31 (8): 890–896
 Abstract
Abstract(
639 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(412KB)(
783
)
A novel europium (Eu3+)-doped hydroxyapatite microspheres (Eu-HApMs) was successfully prepared via the calcium carbonate template and ion exchange process. The physicochemical, luminescent and cytotoxic properties of the prepared Eu-HApMs powders were investigated by the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP), and MTT assays in vitro. Results showed that Eu-HApMs particles exhibited an ellipsoidal morphology with diameters of about 2.5 μm and lengths of about 7 μm with a hedgehog-like surface. Besides, the pure hexagonal phase of hydroxyapatite with high crystallinity of Eu-HApMs and successful doping of Eu3+ ions into HApMs were revealed. The present study showed that the Eu-HApMs powders actually displayed red fluorescence under ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. It was evident that the 5D0→7F1-4 transitions of Eu (III) ions played a key role in the photoluminescence (PL) activity. Finally, the MTT assay results revealed the continuous proliferation and no morphological change of MC3T3-E1 cells co-cultured with the extracts of Eu-HApMs powders and the calculated relative growth rate (RGR) indicating the cytotoxicity grade at level 1.
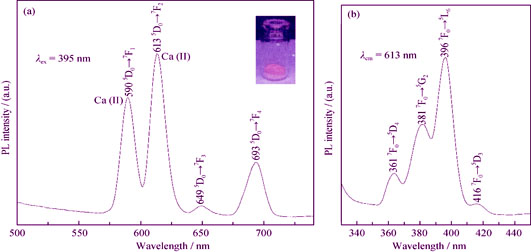
|
|