|
|
Recent Progress on Nano-heterostructure Photocatalysts for Solar Fuels Generation
HAN Cheng, LEI Yong-Peng, WANG Ying-De
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1121–1130
 Abstract
Abstract(
1867 )
 HTML
HTML(
30)
 PDF
PDF(496KB)(
2417
)
Photocatalytic solar fuels generation, including H2 production from water splitting and hydrocarbon compounds generation from CO2 reduction, is considered as one of the most perspective strategies to solve energy crisis in the future. State-of-the-art photocatalysts yield the highest energy conversion efficiency of 5%, failed to achieve the goal of 10% for the large-scale economic production of solar fuels. Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts have distinct properties which are not observed in bulk heterostructure or in the individual nanoscale components, thus can facilitate the separation of photoinduced charge carries, provide more electrons or stronger redox ability, and consequently improve photocatalytic activity. This review firstly introduces the photocatalytic principles of diverse nano-heterostructures, including type I, type II, p-n, and Z-scheme types. Their applications in solar fuels generation are summarized, and some perspectives on the development are also discussed.
|
|
|
Research Progress of Perovskite Solar Cells
YANG Ying, GAO Jing, CUI Jia-Rui, GUO Xue-Yi
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1131–1138
 Abstract
Abstract(
1987 )
 HTML
HTML(
52)
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
5322
)
Development of perovskite solar cell is very fast in recent years due to its low cost and high photoelectric conversion efficiency. The perovskite solar cell is generally composed by the compact nanocrystalline layer, light absorber CH3NH3PbX3 (X= Cl, Br, I), hole transporting layer, and counter electrode. Among these components, the light absorber species and its preparation techniques, hole transporting material species and the structure design of the device are the most important factors, which directly affect the photovoltaic performances of perovskite solar cells. This paper summarizes the effect of the light-absorbers, hole transport materials, processing parameters, and device structural design on the photovoltaic properties of perovskite solar cells according to recent research progresses in this field. And the development trends of the perovskite solar cells are proposed.
|
|
|
Suspensions Designed for Direct Ink Writing
WANG Xiao-Feng, SUN Yue-Hua, PENG Chao-Qun, WANG Ri-Chu, ZHANG Dou, MA Chao
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1139–1147
 Abstract
Abstract(
1076 )
 HTML
HTML(
24)
 PDF
PDF(428KB)(
1551
)
Direct ink writing is a novel route for three-dimensional complex structures. Research progress of suspensions for direct ink writing is reviewed in this paper. These suspensions are divided to self- and assistant-solidification suspensions according to their solidification feature. Rheological characterizations and design principles of self-solidification suspensions are analyzed, and typical suspensions are concluded. Design principles and solidification mode of assistant-solidification suspensions are also analyzed, including typical assistant-solidification suspensions and solidification mode. Finally, the research tendency of suspensions for direct ink writing is discussed.
|
|
|
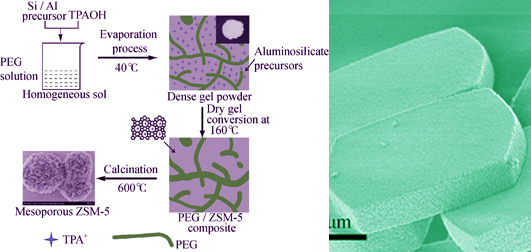
Mesoporous Zeolite ZSM-5 Synthesized via Gel Conversion with Polyethyleneglycol as Template and Its Catalytic Performance
AN Jian-Guo, GAO Xiang, JIN Jun-Jiang, GU Jin-Lou, LI Liang, LI Yong-Sheng, SHI Jian-Lin
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1148–1154
 Abstract
Abstract(
913 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(559KB)(
1675
)
A simple strategy for synthesizing mesoporous zeolite ZSM-5 via gel conversion was successfully developed with polyethyleneglycol as mesopore directing agent. It is revealed that the gel obtained after 9-15 h evaporation of solvents could be transferred into mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite after treatment at 160℃ for 24 h. However, pure ZSM-5 zeolite or mesoporous silica was achieved with too short or too long evaporation periods. The results indicate that the gelation process through solvent evaporation controls the hierarchical structure formation kinetically, which not only provides an appropriate amount of water for zeolite crystallization, but also prevents the phase-separation between zeolite and amorphous phases. Due to the introduction of the mesoporosity of several tens of nanometers in size, this hierarchical micro/mesostructured zeolite exhibits enhanced catalytic activities in the large molecules involved reactions, including aldol condensation of benzaldehyde with n-butyl alcohol and Pechmann reaction of resorcinol with ethylacetoacetate.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Mesoporous Composite Oxides for the Catalysis of NH3-SCR
CHEN Ying, ZHOU Xiao-Xia, WANG Jin, XIE Zhi-Guo, CHEN Hang-Rong
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1155–1160
 Abstract
Abstract(
538 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(390KB)(
1350
)
A novel mesoporous ZrO2-TiO2 (ZT) based multi-component composite oxide catalyst V2O5-WO3-CuO- Al2O3/ZrO2-TiO2 (VWCuAl/ZT) was successfully synthesized by one-pot hydrothermal method using both Brij-35 and P123 as composite template. The results indicated that the active species of V2O5, WO3, CuO and Al2O3 could be homogeneously dispersed into mesoporous ZrO2-TiO2 catalyst carrier. Compared with the reference samples of non-mesoporous I-VWCuAl/ZT and the traditional commercial catalyst V2O5-WO3/TiO2(V-W/Ti), the prepared VWCuAl/ZT showed a superior low-temperature catalytic activity and high stability over the reaction of NH3-SCR of NO, especially high catalytic efficacy for NO reduction within a wide temperature range of between 200℃ to 500℃.
|
|
|
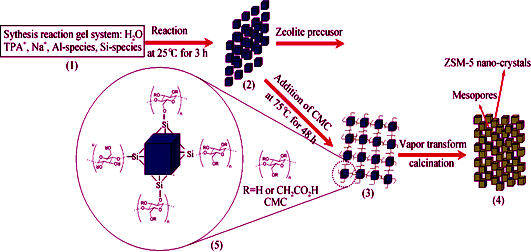
Synthesis of Monolith Hierachical ZSM-5 Zeolite Composed of Nanocrystals by Vapor-phase Transformation Method
ZHENG Jia-Jun, ZHANG Hong-Yan, PAN Meng, LI Biao, ZHANG Qiu, KONG Qing-Lan, LIU Zhi-Ping, LI Rui-Feng
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1161–1166
 Abstract
Abstract(
700 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(459KB)(
1302
)
A monolith ZSM-5 composed of nano-sized MFI crystals was prepared from a dry gel by a vapor-phase transformation method, in which the dry gel was obtained from a mixture of sodium carboxymethylcellulose and a precursor yielding ZSM-5 zeolite crystals. The as-synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), N2 adsorption-desorption, in-situ IR spectra of pyridine and FT-IR. Organic Si- or/and Al-species replace the classic inorganic Si- or/and Al-species to take part in the construction of MFI zeolite frameworks. And the long chain organic groups, which connect with the Si- and Al-species, disturb the normal growth of the zeolites crystals in the manner of the so called “bond block”. The evenly nano-sized zeolite crystals with the sizes of 100-150 nm are therefore formed and then subsequently self-assembly form a monolith ZSM-5. A mesoporous system which centers around 2-20 nm is therefore introduced into the as-synthesized hierachical zeolites samples. As compared with the references catalysts, the monolith ZSM-5 zeolite composed of nano-sized crystals displays an enhanced conversion of isopropylbenzene because of the dramatically increased external surface areas and mesopores volume as tested by the catalytic cracking of isopropylbenzene.
|
|
|
Preparation and Characterization of Water Perm-selectivity ZSM-5 Zeolite Membrane Using Fluoride Route
LI Liang-Qing, ZHANG Wen-Xu, YANG Jian-Hua, LU Jin-Ming, YIN De-Hong, WANG Jin-Qu
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1167–1171
 Abstract
Abstract(
674 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
1442
)
Water perm-selectivity ZSM-5 zeolite membranes were prepared from fluoride media without organic template on the low cost macroporous α-Al2O3 tubular support by secondary growth. A varying temperature hot dip-coating method with different size of crystal was used to form a flat and continuous perfect seed layer. The effects of concentration of the small seed solution on the surface of seed layer, the morphology and pervaporation property of the ZSM-5 membrane were investigated. The results show that when the concentration of the small seed solution is 0.2wt%, the prepared ZSM-5 zeolite membrane displays high water perm-selectivity properties in the pervaporation dehydration of 10wt% H2O/IPA and 10wt% H2O/AcOH mixtures at 75℃, which fluxes are 3.64 kg/(m2·h) and 0.61 kg/(m2·h), separation factor up to 3204 and 1321, respectively.
|
|
|
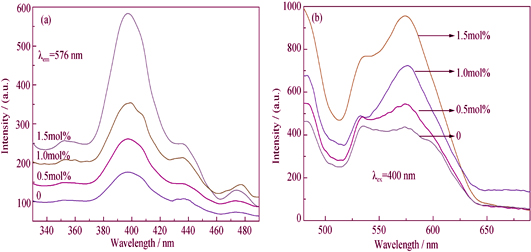
Preparation and Photoluminescence Properties of Pr-doped Mg2SnO4 Nanoparticles
GUO Peng, PENG Lin-Zhi, ZHANG Wei-Hai, LIU Lei, XIONG Juan
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1172–1176
 Abstract
Abstract(
706 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(550KB)(
1249
)
Pr doped Mg2SnO4 in the scope of 0~1.5nm% was synthesized by hydrothermal method and corresponding calcination at low temperature. X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and luminescence/ fluorescence spectrophotometer were applied to characterize Pr doped Mg2SnO4. The relationship between Pr doping contents and the morphologies of Mg2SnO4 particles was studied. The results show that the Mg2SnO4: Pr3+ are confirmed to be the cubic inverse spinel structure and exhibit as cubic particles. An augment of the grain sizes and obvious sharpen edges of the cubic nanoparticles are observed with increasing Pr doping amounts. The emission spectra of Mg2SnO4 nanoparticles with various Pr doping contents indicate two bands centered at 530 nm and 570 nm, respectively. The former emission band is related with the oxygen vacancies in Mg2SnO4 and the latter emission band is attributed to the 3P0-3H5 energy transitions of Pr3+. The increase of luminescence center’s number and Pr-doped Mg2SnO4 particles size result in an obvious enhancement of emission intensity centered at 570 nm with increasing Pr doping contents.
|
|
|
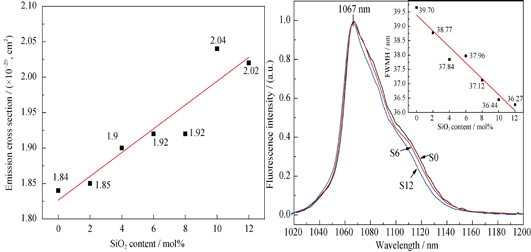
Effects of Silicon Dioxide on Structure and Spectroscopic Properties of Neodymium Doped Calcium Aluminate Glass
KANG Shuai, HE Dong-Bing, GAO Song, HUANG Fei-Fei, DING Ya-Jun, HU Li-Li
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1177–1182
 Abstract
Abstract(
638 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(486KB)(
1489
)
Nd3+-doped calcium-aluminate glasses with different contents of SiO2 were prepared by conventional melting method. The change of glasses structures were studied by Raman spectroscope. The non-bridging oxygens (NBOs) around Si4+ ions increase at higher SiO2 content samples which are transferred from alumina tetrahedron lattices and a more polymerization Al-O network appears in glass structure due to lower NBOs content. From the absorption spectra, J-O strength parameters (Ω), spontaneous transition probabilities (Arad), branching ratios (β), emission cross-sections (σe), and radiative life (τrad) were evaluated by Judd-Ofelt theory. Analysis on the evaluation result and fluorescence spectra reveal that the surrounding structure symmetry of Nd3+ ions is ameliorated and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of emission peak at 1067 nm is narrowed, meanwhile the emission cross-sections is enlarged gradually with the SiO2 content increasing. These results show that Nd3+-doped calcium aluminate glass containing low content of SiO2 has potential applications in ultrashort-pulse laser materials.
|
|
|
Synthesis and Growth of Ce,Pr:YLuAG Crystal for LED Application
NIU Xue-jiao, XU Jia-Yue, ZHOU Ding,WANG Shu-Xian, ZHANG Huai-Jin
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1183–1188
 Abstract
Abstract(
763 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(541KB)(
1524
)
Ce,Pr:YLuAG pure phase powder was synthesized by co-precipitation method and calcined at 1450℃, which had a garnet structure. The feed rod was prepared by press forming and solid state sintering. TEM showed that the sintered rod had good crystallinity and density. Ce,Pr:YLuAG single crystal was grown by the floating zone method. The as-grown crystal was transparent with a pale yellow color, and small cracks were observed in the shoulder. The transmittance of the crystal is 81.8%, which is close to the theoretical value 84.2%. Under 460 nm excitation, Ce,Pr:YLuAG crystal shows the emission band of Ce3+ at 530 nm and peak of Pr3+ at 610 nm, which shows that Ce3+ can transfer the energy to Pr3+. However, only Pr3+ emission peak appears when it is excitated at 487 nm. The color coordinate is located at (0.474, 0.495) which shifts to red zone compared with commercial Ce:YAG yellow phosphor. As a result, Ce,Pr:YLuAG crystal is more suitable to fabricate white LED.
|
|
|
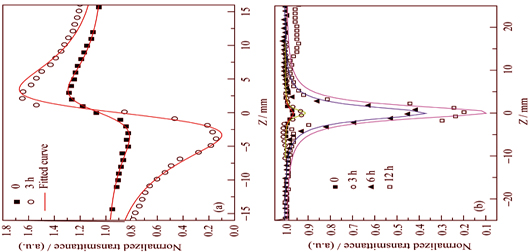
Structure and Third-order Optical Nonlinearity Performance of Ge-Sn-Se Doped TiO2 Glass-ceramics at 1550 nm
QIAO Bei-Jing, CHEN Fei-Fei, NIE Qiu-Hua, DAI Shi-Xun, HUANG Yi-Cong
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1189–1194
 Abstract
Abstract(
602 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(497KB)(
1218
)
TiO2 manifested as nucleating agent was introduced in Ge-Sn-Se ternary chalcogenide glass by heat-melt method. Then the samples were heat-treated for different time. The experiment results indicated that heat treatment process can lead to the precipitation of GeSe2 monoclinic crystals and SnSe2 hexagonal crystals in the TiO2 doped Ge-Sn-Se glass with the heat treatment time increasing. The variety of UV cut-off wavelength, optical band gap and Urbach energy revealed that the number of defect units in glass-ceramic samples increased with the increment of heat treatment time. The third-order optical nonlinearity of all samples was measured by Z-scan technology at 1550 nm. The results showed that the formation of nano-crystals in glass-ceramic samples can improve the third-order nonlinear refraction index significantly due to the strong local field effect. The largest value of nonlinear refraction index reached 5.75×10-16 m2/W, and the sample heat-treated for 3 h was considered as a high-quality nonlinear optical material for its high nonlinear refraction index as well as high figure of merit.
|
|
|
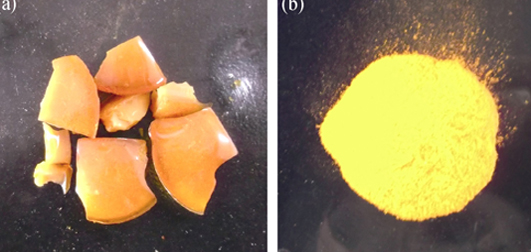
Cationic Iridium(Ⅲ) Complex Doped in SiO2 Micropowder: Preparation and Application in Light-emitting Diodes
MENG Guo-Yun, CHEN Ze-Yu, LIU Yong, WEI Li-Ying, WANG Zheng-Liang, TANG Huai-Jun
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1195–1200
 Abstract
Abstract(
567 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(419KB)(
1206
)
A silica sol was prepared from tetraethyl orthosilicate by hydrolysis method, then 15wt% cationic iridium(III) complex [Ir(ppy)2(o-phen)][PF6] (ppy: 2-phenylpyridine, o-phen: 1-Ethyl-2-(4-(5-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1, 3, 4-oxadiazol- 2-yl)phenyl)-1H-imidazo[4, 5-f][1, 10]phenanthroline) was doped after the sol being aged for 1 d. The sol was turned into xerogel after it was heated at 45 ℃ for 3 d and kept at room temperature for 10 d, then the yellow luminescent micropowder was obtained after the silica xerogel being grounded and dried at 150 ℃ for 8 h. The luminescent micropowder was blended in epoxy resin at concentrations of 6.0wt%, 9.0wt%, 12.0wt%, 15.0wt%, 18.0wt% and 21.0wt%, and the resultant mixtures were coated on 395 nm-emitting InGaN chips as the down-conversion luminescent materials in light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The LED prepared from poxy resin blended with 12wt% cationic iridium(Ⅲ) complex doped SiO2 micropowder exhibited the best luminescent performances, with the maximum efficiency of 51.9 lm/W at 40.0 mA forward current and 5 V reverse voltage, the corresponding CIE color coordinate was (0.42, 0.42).
|
|
|
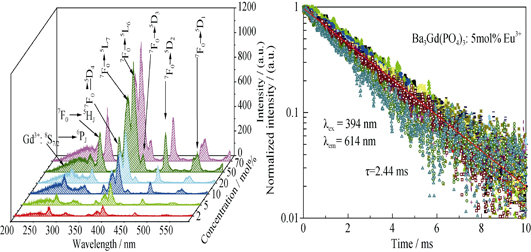
Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Ba3Gd(PO4)3:Eu3+ Phosphors
LI Xue-Ying, CHENG Li-Hong, WU Zhong-Li, CHEN Bao-Jiu
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1201–1207
 Abstract
Abstract(
687 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(482KB)(
1370
)
A series of Ba3Gd(PO4)3 phosphors with different Eu3+ concentrations were synthesized by a high-temperature solid-state method. The crystal structure of the products was examined by means of X-ray diffraction, and it was confirmed that the final products existed in a pure phase and the Eu3+ introduction did not change the crystal structure. The luminescence spectra and decay curves were analyzed as a function of Eu3+ concentration and temperature. It was found that the luminescent color of the phosphor can be adjusted from white to red with the increase of Eu3+ concentration. Concentration quenching for the prepared phosphors was studied based on the Van Uitert model and Dexter theory, which confirmed that the exchange interaction was responsible for energy transfer between Eu3+ ions resulting in the concentration quenching. The temperature dependence of 5D0 fluorescence emissions was analyzed, and it was deduced that the thermal quenching behavior of 5D0 fluorescence followed well the crossover model. The activation energy was obtained from the nonlinear fitting on the temperature quenching of luminescence intensity. Finally, Judd-Ofelt parameters of Eu3+ in the Ba3Gd(PO4)3 phosphors were calculated by a facile method in the framework of the J-O theory, in which the refractive index of Ba3Gd(PO4)3 was deduced to be about 1.55. Meanwhile, the radiative transition rates, fluorescence branching ratios and the J-O parameters were calculated by using the emission spectra and fluorescence decay.
|
|
|
Centimeter Level Monolayer Close-packed of Disk-Shaped Diatomite Particles
ZHANG Wen-Qiang, ZHANG Xin
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1208–1212
 Abstract
Abstract(
627 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(394KB)(
1143
)
Diatomite earth, preferably maintained the morphology and structure of nature diatom, with the characteristic of unique multi-level nanopores and large specific surface area. Diatom is a low-cost at large quantity through repeatable separation from diatomite earth, suitable for industrial application. In this study, the disk-shaped diatom shell particles, size distribution between 40-80 μm, were extracted out by physical settlement method and mechanical screening method. Then, according to the particles self-assembly close-packed principles at air-water interface, the fast close-packed feasibility of hydrophobic diatom shells in a large area was studied. The results showed that by controlling the concentration and forms of diatom shell particles, centimeter level close-packed monolayer can be obtained. The close-packed monolayer area of floating diatom shell particles was over 23.7 cm2, and on drying substrate was about 5.0 cm2.
|
|
|
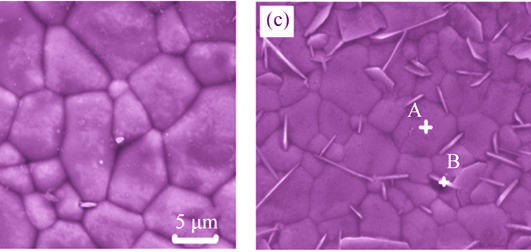
Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Property of (1-x)(Sr0.2Nd0.208Ca0.488)TiO3-xNd(Ti0.5Mg0.5)O3 Ceramics with High Quality Factor
QU Jing-Jing, WEI Xing, JING Ben-Qin, LIU Fei, YUAN Chang-Lai
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1213–1217
 Abstract
Abstract(
822 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(393KB)(
1208
)
(1-x)(Sr0.2Nd0.208Ca0.488)TiO3-xNd(Ti0.5Mg0.5)O3 (0.3≤ x ≤0.4, SNCT-NTMx) ceramics were prepared by solid sate reaction technique. In addition, the crystal structure, microstructures, sintering properties, and microwave dielectric properties of the SNCT-NTMx ceramics were investigated. These results showed that an orthorhombic perovskite structure with a minor amount of unknown secondary phase was formed in the ceramics with the compositions of 0.3≤ x ≤0.35. Additionally, the content of the second phase gradually increased with increasing x value to 0.4. For the SNCT-NTMx ceramics with an increase in NTM content, the dielectric constant (εr) decreased, while the quality factor (Q×f) effectively improved, and the temperature coefficient of resonant frequencies (τf) gradually shifted to negative direction. An optimized microwave dielectric properties with εr ~ 50.1, Q×f ~ 44, 910 GHz and τf ~ -1.7×10-6/℃ could be obtained for the ceramics with x = 0.35 after being sintered at 1520℃ for 4 h.
|
|
|
Preparation and Electrochemical Lithium Insertion of TiO2/Graphene Nanocomposites
CUI Yu, WANG Yan-Zhi, CHEN Zhao-Fan
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1218–1222
 Abstract
Abstract(
608 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(415KB)(
1319
)
TiO2/Graphene nanocomposites was synthesized through solvothermal method with butyl titanate as TiO2 precursor. The character of nanocomposites was measured by scanning electron microscope (SEM), thermogravimetry (TG), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and electrochemical measurements. The result shows that TiO2 nanoparticles are uniformly wrapped in the graphene sheets. The graphene content of TiO2/Graphene nanocomposite is 24.67wt%. When the TiO2/Graphene nanocomposites are used as anode materials for lithium-ion battery, the initial discharge capacity of the nanocomposite electrode is 384.35 mAh/g at a current rate of 2C. It delivers a capacity of 130.26 mAh/g after 100 charge-discharge cycles, 2.93 times as high as that of the pure TiO2 nanoparticles electrode. The charge transfer resistance of the nanocomposites is lower than that of TiO2. The nanocomposite electrode exhibits good rate capability and excellent electrochemical performance as compared with the pure TiO2 electrode.
|
|
|
LaFe1-xMgxO3 Ultrafine Powders Synthesized by Solution Combustion and Its Photocatalytic Performances
LI Jia-Ke, LIU Xin, HUANG LI-Qun, WANG Yan-Xiang
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1223–1227
 Abstract
Abstract(
762 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(292KB)(
1341
)
Mg2+ doped LaFeO3 ultrafine powders were synthesized by solution combustion method. Effects of Mg2+ doping content on phase composition, microstructure and photocatalytic performances of the synthesized powders were investigated by XRD, SEM, BET, and UV-Vis. The results show that Mg2+ substitutes for Fe3+ to form LaFe1-xMgxO3 (0≤x≤0.2) limited solid solution. When Mg2+ doping content is 0.1, LaFe0.9Mg0.1O3 powder has a maximum specific surface area (43.46 m2/g) and smaller particle size (100 nm and 150 nm in diameter and length direction, respectively). It has the best photocatalytic ability with photodegradation efficiency of 75.2% to methyl orange (10 mg/L) under high-pressure mercury lamp irradiation for 180 min. It increases 26.5% than that of the pure LaFeO3 under the same experimental conditions, and the reaction may be described as the pseudo first order kinetics equation.
|
|
|
Sputtering Deposition of VO2 Film Using Plasma Emission Monitor as Reactive Gas Flow Rate Feedback Control
WANG Xiao, YAN Lu, LI Ying, CAO Yun-Zhen
2015 Vol. 30 (11): 1228–1232
 Abstract
Abstract(
836 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(319KB)(
1260
)
Monoclinic VO2 film was deposited on quartz substrate by reactive sputtering using the plasma emission monitor (PEM) system as reactive gas flow rate feedback control. Relationship between oxygen flow rate and plasma emission intensity was studied. It was found that single-phase VO2(M) could be obtained steadily at specific relative emission intensity (REI), which were determined as 0.6-0.65, 0.65 and 0.6 for total deposition pressure of 0.8 Pa, 0.5 Pa and 0.2 Pa, respectively. XRD measurement indicated that the deposited VO2 films were strongly oriented of (011) and the XPS measurements verified stoichiometry of the films as VO2.02. Optical transmission measurement of VO2 film exhibited an abrupt change of transmittance from 81% to 16% as VO2 film switched from semiconductor state to metallic state, at transition temperature of 66℃.
|
|