|
|
Recent Progress in Ceramic/Graphene Bulk Composites
LI Jian-Lin, CHEN Bin-Bin, ZHANG Wen, WANG Lian-Jun, JIANG Wan
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 225–236
 Abstract
Abstract(
1625 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(1188KB)(
2194
)
The recent years have witnessed discovery of graphene and related robust research on this new type of two-dimensional carbon nanomaterials. Due to its unique two-dimensional structure and excellent properties, graphene has become a hot topic for materials scientists worldwide. Combined with the authors' related work, this article reviews the recent progress of ceramic-based bulk graphene composites, i.e., carbon nanotubes, SiOC, Al2O3, Si3N4- based bulk graphene composites, focusing on the preparation, toughening mechanisms as well as the excellent performances of them. The key aspects of future research and potential applications of these composites are also discussed.
|
|
|
Research Progress of Oxides Thermoelectric Materials
ZHAN Bin, LAN Jin-Le, LIU Yao-Chun, DING Jing-Xuan, LIN Yuan-Hua, NAN Ce-Wen
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 237–244
 Abstract
Abstract(
2517 )
 HTML
HTML(
17)
 PDF
PDF(495KB)(
3621
)
The oxides-based thermoelectric materials have been attracted widespread concerns due to their high temperature stability, oxidation resistance, safety and long-term durability, but their applications are limited by the thermoelectric properties. In this paper, the research progress on several typical oxides thermoelectric materials, e.g. layered cobalt oxides, perovskite-structured compounds, transparent conductive oxides and novel oxides are thoroughly discussed. In order to achieve the harmonization of thermal and electric properties in thermoelectric materials, the band structure and microstructure are depth regulated. The main issues for developing high performance thermoelectric oxides are analyzed, and some new ideas for further development are proposed.
|
|
|
Effect of Petroleum Coke Expanding by HNO3 on the Performance of Supercapacitor Based on the Activated Carbon
DENG Mei-Gen, WANG Ren-Qing, Feng Yi-Hong
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 245–249
 Abstract
Abstract(
656 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(400KB)(
1236
)
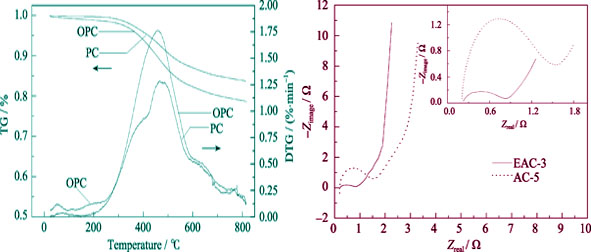
Petroleum coke (PC) was expanded by using KMnO4 as oxidant and HNO3 as intercalator so as to decrease the amount of KOH needed for the successive activation. The expanded PC (EPC) was activated at KOH / coke mass ratio of 3:1, 4:1 and 5:1. The products were denoted as EAC-3, EAC-4 and EAC-5, respectively. As a comparison, PC was also activated at the same KOH / coke mass ratio. The products were denoted as AC-3, AC-4 and AC-5, respectively. Thermogravimetry (TG), XRD, I2 adsorption, N2 adsorption, cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were used to investigate the influence of expanding treatment on the structure and performance of the PCs and ACs. The research revealed that expanding treatment increased the interplanar distance of PC microcrystalline from 0.344 nm to 0.359 nm and decreased the microcrystalline thickness from 2.34 nm to 1.61 nm. The specific surface areas of EAC-3 and AC-5 were 3325 and 3291 m2/g, respectively. The average pore size of EAC-3 was 2.16 nm, which was 0.08 nm larger than that of AC-5. At a scan rate of 0.5 mV/s, EAC-3 and AC-5 achieved a specific gravimetric capacitance of 448 and 429 F/g, respectively. Supercapacitor based on EAC-3 possessed lower resistance and better power performance.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of NiO/AC Asymmetric Capacitor
YE Xiao-Dan, HU Jian-Guan, YANG Qian, ZHENG Yi-Fan, HUANG Wan-Zhen
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 250–256
 Abstract
Abstract(
882 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(584KB)(
1358
)
The nickel oxide nanoparticles were prepared by chemical bath deposition method with NiSO4 as raw materials and NH3?H2O as precipitation agent. The crystal phase, microstructure and morphology of the nickel oxide were characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), thermo gravimetric analyzer (TGA) and physical adsorption instrument. The results show that the product is porous spherical like particles with diameter of about 200 nm. Specific surface area of the nickel oxide heat-treated at 300℃ reaches 132 m2/g, with average diameter of 7.3 nm. The asymmetric capacitor with activated carbon as negative electrode and nickel oxide as positive electrode shows good performance and cycling stability. At the discharge current density of 25 mA/g, the asymmetric capacitor’s specific capacitance can reach 1039 F/g, and its’ charge-discharge efficiency is above 98%.
|
|
|
Preparation of Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2@V2O5 Core-shell Composite and Its Electrochemical Properties
NIE Wen-Bo, XIAO Qi-Chang, WANG Jing-Liang, LEI Gang-Tie, XIAO Qi-Zhen, LI Zhao-Hui
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 257–263
 Abstract
Abstract(
926 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(611KB)(
1428
)
Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2@V2O5 core-shell composite was prepared by coating V2O5 on the surface of the lithium-rich manganese-based solid solution Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 particles through Sol-Gel technology. Its morphology was observed by using scanning electronic microscope (SEM) and transition electronic microscope (TEM) while the crystal structure was calculated from the results of the X-ray diffraction (XRD). It is found that the quasi spherical core-shell composite is coated homogeneously with the crystalline V2O5 nanoparticles. The crystal structure of Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 core is maintained after the surface coating. XPS spectra suggest that Li+ ions intercalate the crystal structure of the V2O5 shell during the first charge. The electrochemical measurements show that the core-shell composite being coated with 15% V2O5 could deliver an initial capacity of 276 mAh/g at the rate of 0.1C accompamied by a coulombic efficiency of 94%. It can remain 89% of the initial capacity after 50 charge/discharge cycles.

|
|
|
Synthesis and Photocatalytic Properties of ZnO/In2O3 Heteronanostructures
HE Xia, LIU Hai-Rui, DONG Hai-Liang, LIANG Jian, ZHANG Hua, XU Bing-She
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 264–268
 Abstract
Abstract(
974 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(460KB)(
1586
)
Homogeneous ZnO/In2O3 heteronanostructure photocatalytic materials were successfully synthesized by a pyrohydrolytic method. The structures and morphologies of ZnO/In2O3 heterostructure were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Results indicate that ZnO/In2O3 heterostructures consist of hexagon nanosheet ZnO with diameter of about 200-300 nm and thickness of 40-60 nm decorated with In2O3 nanoparticles. Compared with the degradation efficiency of RhB by pure ZnO, pure In2O3 and ZnO/In2O3, the results show that ZnO/In2O3 heterostructure photocatalysts possess higher photocatalytic efficiency. The enhanced photocatalytic activity is mainly attributed to the role of narrow-band semiconductor In2O3, which could effectively absorb visible light. Photo-excited electrons of In2O3’senergy band remove to conduction band of ZnO, while photo-excited holes still remain in In2O3’s valence band, which contributes to the separation of photo-generated electrons and holes, decreases recombination probability, and thus improves the photocatalytic efficiency.

|
|
|
Carbonizing Products of the Fe/Co Doped Polypyrrole as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
ZHANG Yu-Hui, YI Qing-Feng, LIU Xiao-Ping, XIANG Bai-Lin
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 269–274
 Abstract
Abstract(
934 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(547KB)(
1379
)
Polymerization reaction of pyrrole in the presence of Fe3+ and Co2+ was carried out to synthesize the metal -doped polypyrrole (PPy). The metal-doped PPy was then calcined at 700℃ to obtain the carbonized products. Finally, the carbonized products were heated to 900℃ to synthesize the catalysts PPY-M(M is Fe or Co). The structure of the catalysts was investigated by SEM and X-ray diffraction techniques. The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activities of the catalysts in acidic and alkaline media were tested by voltammetry. Results show that the catalyst PPY-Co presents the highest electrocatalytic activity for ORR. The ORR current density at rotation rate of 2000 r/min is 7.5 mA/mg@-0.3 V(vs SCE) in acidic solution and 5.7 mA/mg@-0.8 V(vs SCE) in alkaline solution, and the onset potential of ORR is 0.54 V(vs SCE) in acidic solution and -0.11V(vs SCE) in alkaline solution. It is of great significance for the study of carbonizing products of PPY as efficient catalysts for ORR because of their simple preparation and low cost.

|
|
|
Effects of Ba Ratio on Properties of YBCO Film Prepared by MOCVD
LIU Xin, XIONG Jie, ZHANG Fei, ZHAO Xiao-Hui, ZHAO Rui-Peng, TAO Bo-Wan
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 275–278
 Abstract
Abstract(
723 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(498KB)(
1208
)
YBa2Cu3O7-x(YBCO) films were deposited on single crystal LaAlO3(001) substrates by MOCVD with the single source system and flash evaporation mode. The effects of Barium content on the composition, microstructure and current carrying capacity of YBCO superconducting films were systematically investigated. The results demonstrated that CuO grains were inclined to form in YBCO films with lower Ba content. As Ba content increasing, Ba2CuO3 grains began to form and the size of the grain kept increased. The amount and size of the second phase and its lattice match with YBCO played important roles in biaxial epitaxial growth and current carrying capability of YBCO films. When the mole ratio of Ba/Y is 3.9 in precursor, the 300 nm-thickness YBCO superconducting film with good in-plane and out-of-plane texture have been successfully fabricated, showing the critical current density (Jc at self-field, 77 K) of 4.0 MA/cm2 measured by induction method.
|
|
|
Effect of Sn Addition on the Structure and Optical Properties of Ge-Se-Te Chalcogenide Glasses
YIN Dong-Mei, TU De-Yang, CHE Bing-Chen, ZHANG Fang-Fang, LIN Chang-Gui, DAI Shi-Xun
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 279–283
 Abstract
Abstract(
896 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(417KB)(
1147
)
A series of Ge3Se5Te2Snx(x=0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, mol%) chalcogenide glasses were prepared by traditional melt-quenching method. The physiochemical properties and structure changes of glasses were characterized by employing the techniques of X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), visible-near IR spectrum, Fourier transform infrared spectrum (FTIR), and Raman spectroscope. Physiochemical properties of Ge-Se-Te glasses change with the addition of Sn, including glass transition temperature (Tg) decreacing and infrared cut-off wavelength shifting toward long wavelength which effectively inhibits the absorption peaks of impurities in the mid-IR spectral region. In addition, the origination behind these phenomena is discussed by the average coordination number calculated from Philips network-constrained theory and structural evolution of Raman spectra.
|
|
|
Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Microspheres by Hydro-thermal Method under the Control of Sodium Citrate
MA Yi-Juan, HAO Li-Jing, DU Shao-Long, ZHAO Na-Ru
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 284–288
 Abstract
Abstract(
1147 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(365KB)(
1458
)
Hydroxyapatite (HA) microspheres were prepared by using calcium nitrate tetra hydrate (Ca(NO3)2·4H2O) and diammonium phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4) as the resource of calcium and phosphorus, respectively. During the synthesis, propionamide was used as pH adjusting agent to control the supersaturation of the solution, and trisodium citrate was used as the calcium source relievers to control the morphology of HA. The HA microspheres with high crystallinity, regular morphology and good dispersion were synthesized through hydrothermal method. XRD, FTIR and SEM were used to characterize the product. The effects of starting pH value, the amount of trisodium citrate and reaction temperature on the crystallinity, composition and morphology of HA were investigated. The results show that the optimal condition for uniform HA microspheres was as follows, pH=3, molar ratio of sodium citrate to calcium source at about 1:1.5, and reaction temperature of 180℃.
|
|
|
A Novel Technique to Prepare Porous 3D Fluoridated Hydroxyapatite Scaffold Using Pore-forming and Foaming Agents
GONG Meng-An, Rao Qun-Li, WANG Hong-Lie
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 289–293
 Abstract
Abstract(
752 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(527KB)(
1243
)
A novel technology using pore-forming agent and foaming agent was developed to prepare multi-porous fluoridate hydroxyapatite scaffolds. With this technology, scaffolds were produced with uniform and highly interconnected pores in which large pores containing small ones on their walls distributing along 3-dimension. First, the precursor, FHA powder, was prepared by chemical precipitation method. Then it was used to form scaffold through heat treatments by adding ammonium bicarbonate as foaming agent and polymethyl methacrylate as pore-forming agent, and a dense frame of multi-porous structure was obtained. Investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), a dual-phase of FHA/β-TCP in scaffold was confirmed. The uniform morphology in scaffolds and the pore size distribution of large pores (100-400 µm) containing small ones (10~50 µm) were demonstrated by SEM images. HA and β-TCP were also used to prove the universality of this method. Furthermore, the pore formation and its mechanism were discussed in detail.

|
|
|
Erosion Failure Mechanism and Model Establishment of Thermal Barrier Coatings Based on Roughness
ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, ZHANG Ji-Fu, HAN Tao, Song Jin-Bing, LIU-Min
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 294–300
 Abstract
Abstract(
756 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(749KB)(
1398
)
Erosion failure mechanism of atmospheric plasma sprayed (APS) ZrO2-7%Y2O3 (7YSZ) thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) was studied with a san-blasting erosion tester. The failure features of TBCs with laminar and porous structure were investigated using impingement angle 90° at room temperature. Effect of porous and laminar structure on erosion rate was analyzed. Moreover, regarding the failure factors, the relation of ceramic coating roughness and erosion rate was analyzed and their mathematic model was established. The experimental results indicate that the factors of porous and laminar structures play an important role in crack propagation in TBCs. For the TBCs with ununiform, discontinuous pressure-pressure pulsating cyclic load under impact of high velocity particles, the ceramic coatings are loaded with normal stress and shear stress, in which the normal stress leads to appearance of pit in ceramic coating and the shear stress leads to grooves. Meanwhile, the crack propagation in grain boundaries and interfaces of laminar structure will appear based on the net cracks on ceramic coating surface in sprayed TBCs, which will lead to particle exfoliation and flaky debris. So the erosion failures of TBCs follows abrasive wear and low cycle fatigue mode. The relevance between ceramic coating roughness and erosion rate indicates an increased linear relation.

|
|
|
Kinetics Analysis of Cu-Zr Oxygen Carrier for Chemical Looping Oxygen Production
WANG Kun, YU Qing-Bo, QIN Qin, LI Jiu-Chong, WANG Zhi-Mei
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 301–308
 Abstract
Abstract(
525 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(709KB)(
1280
)
2 oxygen carrier was prepared by mechanical mixing. BET, SEM and XRD were used to analyze the specific surface area, surface morphology and phases of oxygen carrier. The phases of oxygen carrier are only CuO and ZrO2. There is no agglomeration in the surface of oxygen carrier. The BET values increase with the increase of weight ratio of binder. The mechanism experiments were carried out in STA409PC thermal analyzer and the temperature programmed thermogravimetry was used to investigate the effects of gas flow, sample mass, heating rate and weight ratio of binder on reduction and oxidation reactions. The results show that the CuO/ZrO2 oxygen carrier has high reactivity of releasing and adsorbing oxygen. When the gases flows are higher than 30 mL/min and sample mass is less than 10 mg, the reaction rates are not controlled by the internal and external diffusion through gas film around the particle. Besides the start and end points, all peaks of DTG curves of reduction-oxidation reactions move forward to high temperature with an increase heating rate. The time for overall conversion decreases with the increase of weight ratio of binder. Based on the experimental data, the kinetics of the CuO/ZrO2 oxygen carrier was determined by the isoconversional model. The differences of distributed activation energy, calculated at different conversion ratios, are all very small. The reduction-oxidation reactions of CuO/ZrO2 oxygen carrier are one-step and the mechanism functions can be explained by nucleation and nuclei growth theory. The kinetics equations of reduction and oxidation reaction are]]>![]() ![]()

|
|
|
First-principles Calculation on Ferroelectricity and Its Coupling Behavior with Mechanical Deformation of Ultrathin PbTiO3 Nanotube
WANG Xiao-Yuan, SHIMADA Takahiro, KITAMURA Takayuki
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 309–314
 Abstract
Abstract(
837 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(528KB)(
1138
)
Ferroelectric properties and its coupling behavior with mechanical strain of ultrathin PbTiO3 nanotubes were investigated by first-principles calculations. The spontaneous polarization still exists in the nanotube despite their sidewalls thinner than the critical thickness at which the thin films lose ferroelectricity, which indicates the absence of an intrinsic critical size of ferroelectricity. Moreover, the total energy of nanotube is lower than that of the thin film. This means that the nanotube structure is energetically more stable than the thin film. In addition, the coupling behavior of ferroelectricity and axial strain is also studied. The axial polarization of nanotube is enhanced by the tensile strain. On the other hand, with the increase of compressive strain, the axial polarization becomes weak and disappears, and the nanotube structure becomes paraelectric state. With the further increase of compressive strain, a vortex type of polarization emerges along the circumferential direction, and the nanotube structure becomes ferroelectric state again. These rich phase transitions in the nanotube structure are induced by the change of covalent Pb-O bond due to the applied strain. Finally, the mechanical strength of PbTiO3 nanotube is evaluated, and the critical stresses under the tension and compression states are obtained.

|
|
|
Fabrication and Gas Sensing Properties of Aligned Vanadium Pentoxide Micro-nano Fiber Membranes by Electrospinning
TANG Yu-Fei, XIE Gao-Wei, ZHAO Kang, JIANG Lei, TENG Le-Tian
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 315–320
 Abstract
Abstract(
664 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(594KB)(
1170
)
Aligned V2O5 micro-nano fiber membrane was fabricated by combination of electrospinning method and separate parallel collector to improve the sensitivity and response time of the micro-nano fiber membrane, a gas sensitive material. The phase composition, morphology and the alignment degree of the fiber membrane were characterized by XRD and SEM. The influences of the alignment degree of fiber membrane on the gas sensitive materials’ sensitivity, response time and response recovery were studied. The results show that micro-nano fiber membrane is composited by V2O5 phase after sintering at 500℃. The distance between the parallel collectors is a key factor of fibers membrane morphology. V2O5 micro-nano fiber membrane with the alignment degree of 66% is obtained when the distance between the parallel collectors is 3 mm. The change of its resistance is about two orders of magnitude at 80-400℃. The V2O5 micro-nano fiber membrane has the higher sensitivity to ethanol gas than to CH4 or NH3 gas at 300℃. The sensitivity of aligned V2O5 micro-nano fiber membrane to ethanol with a concentration of 200 mg/L is 0.9, the fastest response time is 3 s and the response recovery of resistance is only 55% of initial value after 62 s.

|
|
|
Pyrolysis Mechanism of SiBCN Polymer Precursor
LI Ya-Jing, ZHANG Yue
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 321–326
 Abstract
Abstract(
597 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(461KB)(
1368
)
High temperature amorphous materials, mainly in the system of SiBCN, have aroused ever increasing attention. Effective methods should be used to study the structural changes in the process of fabrication. In this paper, the thermal stability of PBSZ and the pyrolysis mechanism of SiBCN polymer precursor were studied by SS-NMR and FT-IR. Polymer-to-ceramic transformation can be divided into three stages as follows. The first stage is the production of initiator in which, the tertiary carbon dehydrogenates to quaternary carbon free radical. The second stage is propagation and termination in which, quaternary carbon free radical attacks methyl group to turn the methyl group into new free radical. With increasing temperature, the free radical attacks Si-CH3 and results in a new free radical. The propagation of the chain occurs when new free radicals are generated, while the termination occurs after the free radicals combination with each other. The third stage is polymer-to-ceramic transformation. Through dehydrogenation, ceramics are produced from the intermediate inorganic products, and amorphous continuous 3D mesh structures are formed. The first and second stages are organic transformations and the third stage is an inorganic transformation. There are four elements in the ceramic, including Si, B, C and N.

|
|
|
Gelcasting of Aluminum Nitride Using a Water-soluble Copolymer
SHU Xia, LI Jun, ZhANG Hai-Long, DONG Man-Jiang, SHUNZO Shi-Mai, WANG Shi-Wei
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 327–330
 Abstract
Abstract(
1444 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(372KB)(
2579
)
AlN ceramic was fabricated via a rapid gelation of AlN slurry and sintering in nitrogen at 1800 ℃ for 4 h. The AlN slurry was made of AlN powder, small amount of Y2O3 powder (sintering aid), deionized water. A new water-soluble copolymer of isobutylene and maleic anhydride (commercial name Isobam) was added into the slurry, and the resultant slurry gelled spontaneously in air at room temperature. The effects of Isobam and polyurethane on rheological properties and gelling behavior were evaluated. Results showed that concentrated AlN slurry (52vol%) with low viscosity (0.2 Pa·s) was obtained with an addition of 0.3wt% Isobam. The final AlN ceramic had a fin-like shape, a density of 3.33 g/cm3 and a thermal conductivity of 204 W/(m·K).
|
|
|
Magnetic Properties of Proton Irradiated Giant Magnetoresistance Multilayers
YIN Cong, XIE Dan, XU Jian-Long, REN Tian-Ling
2014 Vol. 29 (3): 331–336
 Abstract
Abstract(
932 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(412KB)(
2084
)
The magnetic properties of proton irradiated CoFe/(CoFe/Cu)10/CoFe/Ta giant magnetoresistance multilayers (GMR-MLs) were investigated experimentally and theoretically. GMR-MLs were prepared by magnetron sputtering and exposed to 5 MeV proton beam with a series of radiation fluences and fluence rates. X-ray diffraction indicated that the crystal structures of CoFe/Cu were unaffected after irradiation. The saturation magnetization and intrinsic resistance increased monotonically with the increase of the radiation fluence and fluence rate. The value of MR in the irradiated samples decreased slightly with the radiation fluence, which was mainly explained by the two spin- related conductivity channel model.
|
|